THE ABILITY OF USING CONDITIONAL SENTENCES BY THE STUDENTS OF SMA CAHAYA MEDAN
A THESIS
BY :
HANNA M PANGGABEAN REG. NO. : 110705046
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH
Approved by the Department of English, Faculty of Cultural Studies of University of Sumatera Utara (USU) Medan as thesis for The Sarjana Sastra Examination.
Head, Secretary,
Dr. H. Muhizar Muchtar, M. S.
NIP. 195411171980031002 NIP. 197502092008121002
v
AUTHOR’S DECLARATION
I, HANNA M PANGGABEAN, DECLARE THAT I AM THE SOLE AUTHOR OF THIS THESIS EXCEPT WHERE REFERENCE IS MADE IN THE TEXT OF THIS THESIS. THIS THESIS CONTAINS NO MATERIAL PUBLISHED ELSEWHERE OR EXTRACTED IN WHOLE OR IN PART FROM A THESIS BY WHICH I HAVE QUALIFIED FOR OR AWARDED ANOTHER DEGREE. NO OTHER PERSON’S WORK HAS BEEN USED WITHOUT DUE ACKNOWLEDGMENTS IN THE MAIN TEXT OF THIS THESIS. THIS THESIS HAS NOT BEEN SUBMITTED FOR THE AWARD OF ANOTHER DEGREE IN ANY TERTIARY EDUCATION.
Signed :
vi
COPYRIGHT DECLARATION
NAME : HANNA M PANGGABEAN
TITLE OF THESIS : THE ABILITY OF USING CONDITIONAL
SENTENCES BY THE STUDENTS OF SMA CAHAYA MEDAN
QUALIFICATION : S-1/SARJANA SASTRA
DEPARTMENT : ENGLISH
I AM WILLING THAT MY THESIS SHOULD BE AVAILABLE FOR REPRODUCTION AT THE DISCRETION OF THE LIBRARIAN OF DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH, FACULTY OF CULTURAL STUDIES, UNIVERSITY OF SUMATERA UTARA ON THE UNDERSTANDING THAT USERS ARE MADE AWARE OF THEIR OBLIGATION UNDER THE LAW OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA.
Signed :
vii ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, the researcher thank all who in one way or another contributed in
the completion of this thesis. The researcher give thanks to Jesus Christ for
protection and ability in finishing this thesis as requirement to finish her study in
Deparment of English, Faculty of Cultural Studies, University of Sumatera Utara.
Special and heartily thanks to her supervisor, Dr. Roswita Silalahi, Dip.
TESOL M. Hum and her co-supervisor Drs. Yulianus Harefa, M. Ed. TESOL who given time, guidance and help this thesis towards a completion. The researcher
is also thankful to Dr. Syahron Lubis, M. A., the Dean of Faculty of Cultural
Studies, Dr. H. Muhizar Muchtar, M. S., the chief of Department of English,
Rahmadsyah Rangkuti, M. A., Ph. D as secretary of Department of English, University of Sumatera Utara. The researcher also thankful to all lecturers and staffs
who had given their useful and valuable knowledge during her academic years. The
researcher wishes to thank Sr. Ludovika Situmorang, S. Psi, the headmaster of
SMA Cahaya Medan for having allowed the students in grade XI as respondents of
her study and entire teacher.
Deep gratitude to her parents, Manat M. Panggabean and Anita R. Siahaan
and her brother, Todo Lukas Panggabean who encouraged me and prayed for me
throughout the time of my research. This research is heartily dedicated to her parents
who took the lead to heaven before the completion of this work. May the Almighty
viii The researcher would like to acknowledge her fellows Sheila, Mariaty and
Atika who giving ideas, comments and productive critics. Sweet thanks for her bestfriend Dj, Irna and Septalia for treating the friendship during the past 4 years
and I hope it never be the end of the story. Specially thanks for Maya and also
thanks for all her friends and classmates for supporting her in finishing this research.
Finally, I do appreciate any recommendations and suggestions to make this
research better. Therefore, I cordially welcome any critics and comments. I do hope
this research will be useful for those who want to enhance and expand his/her
knowledge on the concept of ability.
Medan, July 2nd, 2015
ix ABSTRAK
Skripsi yang berjudul “The Ability of Using Conditional Sentences by The Students of SMA Cahaya Medan” merupakan skripsi yang menganalisa kemampuan penggunaan kalimat conditional dalam mengisi pertanyaan-pertanyaan yang diberikan kepada siswa kelas XI SMA Cahaya Medan.
Tujuan dari skripsi adalah untuk mengamati bagaimana kemampuan siswa kelas XI SMA Cahaya Medan dalam menggunakan kalimat conditional dengan mengklasifikasikan kemampuan tersebut ke dalam beberapa tipe berdasarkan standar kelulusan dari SMA Cahaya Medan yaitu ‘Very Good’ (90-100), ‘Good’ (80-89), ‘Average’ (70-79), ‘Poor’ (60-69) dan ‘Very Poor’ (0-59) dan masalah apa yang dialami oleh siswa kelas XI SMA Cahaya Medan dalam menggunakan kalimat conditional.
Metode yang digunakan dalam penulisan skripsi adalah deskriptif kualitatif dan kuantitatif dengan melakukan riset lapangan di SMA Cahaya, memberikan pertanyaan yang sudah dipelajari dan mencari referensi yang berhubungan dengan judul skripsi.
x ABSTRACT
The thesis entitled “The Ability of Using Conditional Sentences by The
Students of SMA Cahaya Medan” is a thesis that analyzed the ability of using
conditional sentences by completing the test which is given to the students of grade XI SMA Cahaya Medan.
The objective of this research is to find out the ability of students in grade XI of SMA Cahaya Medan in using conditional sentences by classifying them into score range based on KKM (Minimum Standart Scores) of SMA Cahaya Medan is 'Very Good' (90-100), 'Good' (80- 89), 'Average' (70-79), 'Poor' (60-69) and 'Very Poor' (0-59) and to find out the problems of students in grade XI of SMA Cahaya Medan in using conditional sentences.
The method which is used in the thesis is a qualitative and quantitative descriptive by conducting field research in SMA Cahaya Medan, giving them a test that have been learned and find references that relate to the title of the thesis.
Based on the research, it can be concluded that most students of SMA Cahaya Medan are in 'Very Poor' ability (68.3%) and there are no students in 'Good' ability (0%). 1 students are in 'Very Good' ability (1.7%), 5 students are in 'Average' ability (8.35) and 41 students are in 'Poor' ability (21.7%). It means the process of teaching and learning English in SMA Cahaya Medan is not optimum.
xi
CHAPTER II REVIEW OF LITERATURE... 6
2.1 Ability... 7
2.1.1 Factors of Ability... 8
2.2 Grade XI... 11
2.3 Conditional Sentences ... 12
2.3.1 Future Conditional (Conditional Sentence Type 1)... 13
2.3.2 Present Conditional (Conditional Sentence Type 2)... 17
2.3.3 Past Conditional (Conditional Sentence Type 3)... 20
2.4 Test... 23
2.4.1 Kinds of Test... ... 24
2.4.2 Criteria of Test... 29
2.5 A Case Study... ... 31
CHAPTER III METHOD OF RESEARCH... 32
3.1 Research Design... 32
3.2 Location and Time... 33
3.3 Population and Sample... 34
3.4 Data Collection Procedures... 35
3.5 Technique of Data Analysis... 36
CHAPTER IV ANALYSIS AND FINDINGS... 40
4.1 Data Analysis…... 40
xii
CHAPTER VI CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS... 55
5.1 Conclusions... 55
5.2 Suggestions... 56
xiii LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1 The number of students in grade XI SMA Cahaya Medan... 12
Table 2.2 Form of future conditional and the examples... 14
Table 2.3 Form of present conditional and the examples... 18
Table 2.4 Form of past conditional and the example in sentence... 21
Table 3.1 Distribution of Research Population... 35
Table 3.2 Students’ score range in SMA Cahaya Medan... 39
Table 4.1 Conditional Sentences function and each item... 41
Table 4.2 The Highest to The Smallest Scores... 42
Table 4.3 The Students’ Score in Using Conditional Sentences... 47
Table 4.4 The Percentage of Students’ Score in Using Conditional Sentences... 48
Table 4.5 The Students’ Ability in Using Conditional Sentences... 49
ix ABSTRAK
Skripsi yang berjudul “The Ability of Using Conditional Sentences by The Students of SMA Cahaya Medan” merupakan skripsi yang menganalisa kemampuan penggunaan kalimat conditional dalam mengisi pertanyaan-pertanyaan yang diberikan kepada siswa kelas XI SMA Cahaya Medan.
Tujuan dari skripsi adalah untuk mengamati bagaimana kemampuan siswa kelas XI SMA Cahaya Medan dalam menggunakan kalimat conditional dengan mengklasifikasikan kemampuan tersebut ke dalam beberapa tipe berdasarkan standar kelulusan dari SMA Cahaya Medan yaitu ‘Very Good’ (90-100), ‘Good’ (80-89), ‘Average’ (70-79), ‘Poor’ (60-69) dan ‘Very Poor’ (0-59) dan masalah apa yang dialami oleh siswa kelas XI SMA Cahaya Medan dalam menggunakan kalimat conditional.
Metode yang digunakan dalam penulisan skripsi adalah deskriptif kualitatif dan kuantitatif dengan melakukan riset lapangan di SMA Cahaya, memberikan pertanyaan yang sudah dipelajari dan mencari referensi yang berhubungan dengan judul skripsi.
x ABSTRACT
The thesis entitled “The Ability of Using Conditional Sentences by The
Students of SMA Cahaya Medan” is a thesis that analyzed the ability of using
conditional sentences by completing the test which is given to the students of grade XI SMA Cahaya Medan.
The objective of this research is to find out the ability of students in grade XI of SMA Cahaya Medan in using conditional sentences by classifying them into score range based on KKM (Minimum Standart Scores) of SMA Cahaya Medan is 'Very Good' (90-100), 'Good' (80- 89), 'Average' (70-79), 'Poor' (60-69) and 'Very Poor' (0-59) and to find out the problems of students in grade XI of SMA Cahaya Medan in using conditional sentences.
The method which is used in the thesis is a qualitative and quantitative descriptive by conducting field research in SMA Cahaya Medan, giving them a test that have been learned and find references that relate to the title of the thesis.
Based on the research, it can be concluded that most students of SMA Cahaya Medan are in 'Very Poor' ability (68.3%) and there are no students in 'Good' ability (0%). 1 students are in 'Very Good' ability (1.7%), 5 students are in 'Average' ability (8.35) and 41 students are in 'Poor' ability (21.7%). It means the process of teaching and learning English in SMA Cahaya Medan is not optimum.
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background of the Study
In Indonesia, English is used as a foreign language or second language while
people in the country itself use Indonesian or ethnic language as their first language.
In term of first language acquisition, Indonesian or ethnic language is used as their
mother tongue which is obtained naturally from mother and environment around
them while second language acquisition like English is the language which is
obtained by learning after acquire first language. Ortega (2009:2) says, “Second
Language Acquisition is the scholarly field of inquiry that investigates the human
capacity to learn languages other than first, during late childhood, adolescence, or
adulthood, and once the first language or languages have been required.”
Nowadays, English language is not a strange matter for everybody because
using English can be perceived all over the world. Due to those reasons, Indonesian
government applies English as a core subject from elementary up to university.
People also join English course (informal education) to improve language skills or
language ability. In globalization era, language users force to learn English. It needs
ability for Indonesia people in using another language other than their native
language for making them ready to deal with competition in the global era. English is
2 In learning English, language ability needs to know to prove whether the
individual has been able to understand the language lessons he/she learned or not. As
it has been known that language ability has a great influence in increasing motivation
to learn English. As Allison (1999:43) says, “Language users with the modest scores
on tests of system knowledge were sometimes perceived to be more effective and
accomplished than other language users who still scored higher on these test.” In
addition, Allison (1999:42) says, “Language was taken to consist of a number of
levels, including the levels of phonology, morphology, syntax and lexis. In language
testing, efforts were made to sample language items for each level: for example, to
test command of phonemic contrast, or grammatical structures, or vocabulary items.
Demonstrating knowledge of these items, and of distinction between them, was taken
as sufficient evidence of language ability on the part of test taker.” Then, language
testing is needed to know how the language ability of students is as Lado (1961:20)
says, “The same basic understanding of the facts of language learning applies to
language testing. What the student has to learn constitutes the corpus of what we
have to test. Since the student has to learn the language, it is the language that we
must test.”
The important thing in learning English which it cannot be forgotten is using
grammar as well as structure to make sentences. Folsom et al. (1838:1) says that
“Grammar is the art of rightly expressing our thoughts by words” and Graham
(1996:3,4) says that “Grammar includes two aspects: (1) the arrangement of words
and (2) the internal structure of words.” Although grammar is not actually used in
everyday life but it is often used in English test such as TOEFL, IELTS, employee
3 One of the topics in an English test is conditional sentences. Conditional
sentences or if clause is modality sentence which is used to express that the action in
the main clause (without if) can only take place if a certain condition (in the clause
with if) is fulfilled. Therefore, it can be concluded that conditional sentences consist
of if clause as the requirement and main clause as the purpose.
As the researcher has observed some students at SMA Cahaya Medan, the
researcher found that they are confused to discriminate tenses which are found in
three types of conditional sentences. Then, the researcher wants to describe and
analyze students’ ability in using conditional sentences at SMA Cahaya Medan.
Based on syllabus of SMA Cahaya Medan, conditional sentences are studied
in grade XI. Conditional sentences divide into three; they are future conditional
(conditional sentence type 1), present conditional (conditional sentence type 2) and
past conditional (conditional sentence type 3). Future conditional is used to express
events that have not happened so it is likely to occur if the conditions are fulfilled.
Present conditional is used to declare that events may not occur because the
condition may not be fulfilled. Past conditional is used to express events that may not
be fulfilled because it happened in the past so that the event could not have happened.
The example of Conditional Sentences in sentence:
Future conditional (Conditional Sentence Type I)
If he invites me, I will go to the party.
4 Present conditional (Conditional Sentence Type II)
If he were in Jakarta today, he would come to my house.
I would send him the letter if I knew his address.
Past conditional (Conditional Sentence Type III)
If you had gone by car, you would have arrived in Bandung.
You would have spoken English well if you had studied English seriously.
This research analyze student’s English ability of using conditional sentences
in grade XI at SMA Cahaya Medan that located on Jl. Hayam Wuruk No. 11, Medan
which has 3 classes of Natural Science and 3 classes of Social Science. It tests 60
students at random. The location is chosen as object of research because the terms of
accessibility and the same research are never conducted in this school. Students of
grade XI SMA Cahaya Medan is chosen because conditional sentences are learned at
grade XI.
1.2 Problems of the Study
In analysing student’s ability of using conditional sentences, there are two
questions that are needed to lead the researcher to explain and solve the problems.
The questions that are relevant to the problems are:
1. What is the ability of SMA Cahaya Medan students in using conditional
sentences?
2. What are the problems of SMA Cahaya Medan students in using conditional
5 1.3 Objectives of the Study
The objectives of this research are:
1. To find out the ability of SMA Cahaya Medan students in using conditional
sentences.
2. To find out the problem of SMA Cahaya Medan students in using conditional
sentences.
1.4 Scopes of the Study
In writing this thesis, limitation of study should be made due to time
limitation. It focus on the analysis of tenses which is found in conditional sentences;
future conditional, present conditional and past conditional. This research chooses 60
students of grade XI who are studying English as one of their core subject at SMA
Cahaya Medan as the baseline data.
1.5 Significances of the Study
This significance of this study is expected be useful for the researcher to
understand the concept of language ability as evidence of learning outcomes, the
students who want to increase knowledge about conditional sentences and for those
who are interested in analysing the same kind of study. Another significance of this
study, it is expected that this thesis be useful for the English teacher who want to
evaluate the ability of the students in grade XI SMA Cahaya Medan especially in
6 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
This research is based on some linguistic theories proposed by some
prominent linguists. As the researcher have researched, there has not been any
previous analysis about conditional sentences before. In relation to review of the
related literature, the following books and websites are consulted as the secondary
sources to find out some supportive data and information :
Understanding Second Language Acquisition (1985) by Rod Ellis. Rod Ellis
book contains how to understand second language acquisition in describing theory of
SLA and giving some examples of research. In this book, it is found that SLA also
means acquiring L2 grammar, as a result learners should be able to develop their
grammatical knowledge. This basic explanation helps me in conducting this research.
Language Testing (1961) by Robert Lado is also useful for giving the concept
of testing the language.
English for SMA (2012) by MGMP Bahasa Inggris SMA Kota Medan is a
handbook used by student of SMA Cahaya Medan in grade XI. This book can be
used as reference in describing conditional sentences.
Bimbingan Pemantapan BAHASA INGGRIS (2002) by Otong Setiawan
Djuharie describes about the kind of grammar with the explanation and also
exercises to help students in understanding gramar. It is used to construct a
7 There are also some researches which had analysed the same studies in
language acquisition and language testing such as : An Analysis of Year IX
Primagama Student’s Ability in Mastering Elliptical Construction (a thesis) by Dona
Marlina P. (2010). The research has given me much help. This research contains how
to test learners in order to know how better the learner is in mastering elliptical
construction.
An Analysis on Primary School Students’ Ability to Use Personal Pronouns:
A Case Study on The Sixth Year Students of SDN No. 101878 Tg. Morawa by
Prambandari (2008), is another research that describes about the students’ ability to
use personal pronouns. The writer assumed that in general there are still many
language problems especially grammatical problems.
An Error Analysis of the Use of Using Present Tense Made by Students of
Second Year Junior High School of Madrasah Tsanawiyah Al Wasliyah 16
Perbaungan (a thesis) by Achirani (2011) describes about testing learner to find out
errors in grammar. This research has been one of my references to make a more
comprehensive analysis for my research.
2.1 Ability
According the Hornby (2000:2), “Ability is the fact that somebody/something
is able to do something.” If someone has ability then he/she is considered to be doing
something effectively or it is contrary. The ability can be obtained by the way of
8 According to Robbin (2007:58) capability consists of two factors, namely:
1. Intellectual ability that the skills needed to perform a variety of mental
activity-thinking, reasoning and problem solving.
2. Physical ability is the ability to perform tasks that require stamina, skill,
strength, and similar characteristics.
Carrol (1993) an influential psychologist in the field of educational linguistics
divided the four ability components as follows:
1. Phonetic coding ability is ability to perceive distinct sounds, associate a
symbol with that sound and retain that association.
2. Grammatical memory is ability to recognize the grammatical function of a
lexical element (word, phrase, etc.) in a sentence without explicit training in
grammar.
3. Associative memory is ability to learn associations between words in foreign
language and their meanings and retain that association.
4. Inductive learning ability is ability to infer or induce rules governing the
structure of a language.
2.1.1 Factors of Ability
According to Ellis (1985), there are several factors which may affect a
9 1. Personal Factors are divide into three headings as follows:
a) Group dynamics
Differences level of ability of different students in understanding a foreign
language can make a competition among students. This competition encourages
students to learn a foreign language actively in the classroom or it repress the
students so that the students have a sense of mistrust in studying a foreign language.
b) Attitudes to the teacher and course material
The role of the teacher in the class and teaching materials which is used by
students also influence students' ability to learn a foreign language. Generally, most
students prefer use their own learning paths such as student-student interaction in the
class or democratic teaching style. Students also prefer use a variety of materials than
a course book.
c) Individual learning techniques
Some students motivate themselves to be able to use a foreign language by
using their own learning techniques, for example, students prepare and memorize
vocabulary lists like dictionary, students pick up some vocabulary from paragraph
that usually used in context, and they practice to use vocabulary in a sentence,
10 2. General Factors divide into :
a) Age
Ellis (1985) says, “...children are better language learners than adults.” It
means that the ability of language acquisition at childhood is better than adulthood.
Because the more we older, the more we lack of ability to acquire a foreign language.
Although there are adults who are able to learn the language, and they who has the
reach higher levels of proficiency.
b) Intelligence and aptitude
Intelligence and aptitude influence the ability in learning L2. Learner who has
high level in intelligence and aptitude is able to understand the using of L2 rapidly.
In formal teaching method, it usually used for some skills such as reading
comprehension, dictation, and free writing but much less in naturalistic SLA.
c) Cognitive style
Cognitive style is a term to use the manner in which people perceive,
conceptualize, organize, and recall information. It talks about the process in
receiving the information (understanding of SLA).
d) Attitude and Motivation
Gardner and Lambert (1972) in Ellis (1985) define ‘motivation’ in terms of
the L2 learner’s overall goal or orientation, and ‘attitude’ as the persistence shown by
the learner in striving for a goal. If the learners have more or less motivation in
11 divide motivation into integrative and instrumental. Integrative motivation occurs for
learners who want to maintain their mother tongue when they learn a L2. It means
they naturally learn L2 for having knowledge. Instrumental motivation occurs for
learners who want to learn L2 for functional such as passing an examination,
furthering career opportunities or facilitating study of other subject.
e) Personality
Personality refers to personal traits. In psychology, personalities divide into:
- Extroversion and Introversion: Extrovert learns L2 rapidly than introvert
because they have more contacts with each other. The more we have contacts
with others, the more we can use language practically and become habitual.
- Social skills : According to Strong (1983) in Ellis (1985) there are seven
social styles but only ‘talkativeness’ and responsiveness’ which more easy in
learning L2 rapidly because they have interact with each other in using L2
practically.
- Inhibition: Inhibition is negative factor stated by Guiora (1972a:1972b) in
Ellis (1985). It determine the way of the learners in taking risk while learning
L2 and turn leads to increased self-consciousness of learners in learning L2.
2.2 Grade XI
In Indonesia, grade XI is the second grade in the senior high school. Students
12 and Social Science. Both of them have learned grammar about conditional sentences.
In SMA Cahaya Medan, there are six classes of grade XI that has been divided into 3
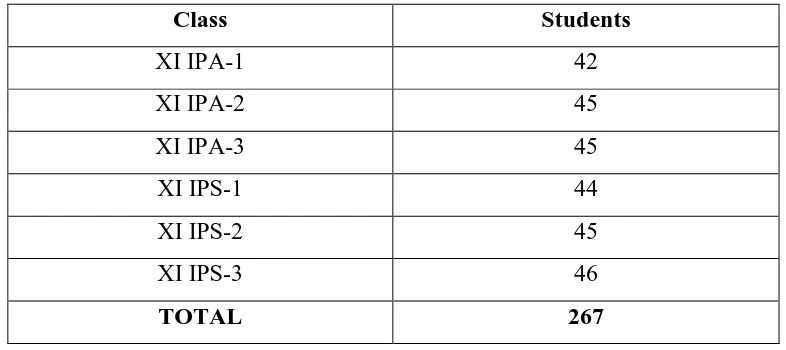
Natural Science classes and 3 Social Science classes. The total students of grade XI
is 267 that can be described in the following table.
TABLE 2.1 The number of students in grade XI SMA Cahaya Medan
Class Students
XI IPA-1 42
XI IPA-2 45
XI IPA-3 45
XI IPS-1 44
XI IPS-2 45
XI IPS-3 46
TOTAL 267
2.3 Conditional Sentences
According to Berry (2012:246), “Conditional sentences are generally equated
with sentences with ‘if’, i.e. multiple complex sentences with a subordinate,
adverbial clause introduced by ‘if’”. According to Greenbaum (1999), conditional
sentences tells about a direct condition that indicate the truth of host clause is
dependent on the condition of conditional clause is fulfilled or not.
Based on the handbook of students in grade XI of SMA Cahaya Medan,
13 2.3.1 Future conditional (Conditional Sentence Type 1)
Future conditional or conditional sentence type 1 expresses the activity that
might happen in the future if the condition is fulfilled.
Example:
a. I will go if he gives me money.
b. If he has a lot of money, he will build a house.
Here further explanation about future conditional:
According to Azar (1989:114), future conditional expresses the true and
factual idea in the present or in the future (real or possible).
Djuharie (2007:73) said that conditional type 1 explains something probably
occurs in the future or now if certain conditions are fulfilled.
Future conditional consist of two clauses; if clause and main clause. Here the
basic form of future conditional by Djuharie (2007:73):
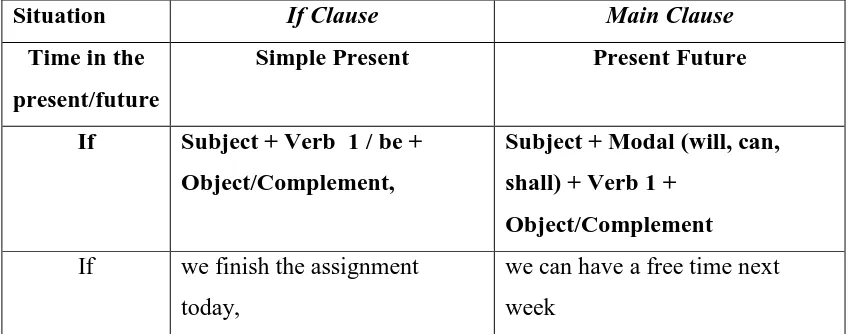
IF CLAUSE (SIMPLE PRESENT) + MAIN CLAUSE (PRESENT FUTURE)
NOTE: We use ‘comma’ if the if clause is in the beginning of the sentence.
OR
MAIN CLAUSE (PRESENT FUTURE) + IF CLAUSE (SIMPLE PRESENT)
14 In the future conditional, the modal ‘will’ appears in the main clause and
‘V1’ appears in the if clause. Here are some examples:
• If you come with me for a joyride tonight, you will have a great fun.
• If you don’t have any money, you may borrow from me.
• You must study hard if you want to enter favorite university.
• If we finish the assignment today, we can have a free time next week.
• If you leave now, you’ll be able to catch the 5 o’clock train.
• We will need more chairs if we are going to invite so many people to the
performance.
Table 2.2 Form of future conditional and the examples
Situation If Clause Main Clause
Time in the present/future
Simple Present Present Future
If Subject + Verb 1 / be + Object/Complement,
Subject + Modal (will, can, shall) + Verb 1 +
Object/Complement
If we finish the assignment
today,
we can have a free time next
week
According to Surayin (2009:328), there are variant forms of future
15 Variant of main clause.
A. IF + PRESENT + MAY/MIGHT
If the rain gets heavier the rice, fields may/might be flooded.
If the dry season becomes longer, the famine may/might happen
B. IF + PRESENT + MAY / CAN
.
If your documents are in order, you may/can leave at once.
If it stops raining, we can go out
C. IF + PRESENT + MUST, SHOULD
.
If you want to lose weight, you must/should eat less bread.
If you want to lose weight, you had better eat less bread.
If you want to lose weight, eat less bread
D. IF + PRESENT + ANOTHER PRESENT TENSE
.
If you heat ice, it turns to water.
If there is a shortage of any product, prices of that product go up
A. IF + PRESENT CONTINUOUS
.
Variant of If clause.
If you are waiting for a bus, you’d better join the queue.
16 If you are staying for another night
B. IF + PRESENT PERFECT
, I’ll ask the manager to give you a better
room.
If you have finished dinner, I’ll ask the waiter for the bill.
If he has written the letter
a. To express aspects of persuasion, giving warning and making threats. , I’ll post it.
According to Martin Parrot (2006:232), there are some functions of future
conditional which is explained as follows:
Persuasion: I’ll take the children to the party if you collect them from school.
Warning: If you try to take a short cut, you’ll get lost.
Threat: If you poke your brother again, I’ll thrash you.
b. To give advice or instruction.
IF + PRESENT, IMPERATIVE
If you go to the supermarket, bring back a carton of milk please.
c. To arranged future.
IF + PRESENT CONTINUOUS
17 d. To plan future events.
IF + GOING TO
They’re going to take their mother to the old house if she remembers where it
is.
IF + PRESENT PERFECT
If it hasn’t rained by the weekend, we’ll have to water the garden.
IF + PRESENT CONTINUOUS
If they’re watching TV, they won’t hear you.
2.3.1 Present Conditional (Conditional Sentence Type 2)
A present conditional or conditional sentence type 2 expresses the activity
which is contrary to the fact in the present time.
Example:
a. I would go if he gave me money.
b. If he had a lot of money, he would build a house.
Here further explanation about present conditional:
According to Parrot (2006:233), present conditional refer to something that is
18 According to Djuharie (2007:74), present conditional explains something that
is contrary to what is / is happening now or later.
Here the basic form of present conditional by Djuharie (2007:74):
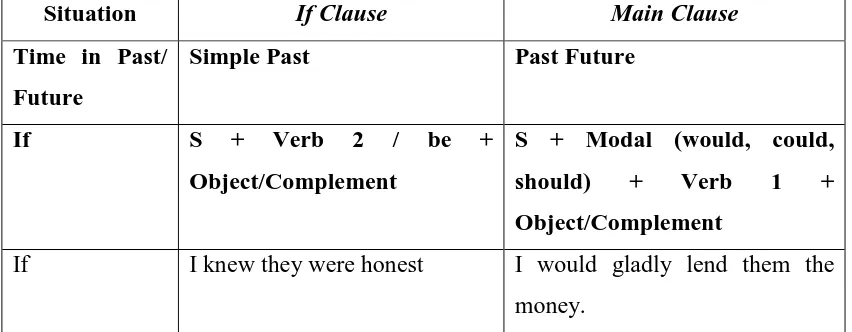
IF CLAUSE (SIMPLE PAST) + MAIN CLAUSE (PAST FUTURE)
OR
MAIN CLAUSE (PAST FUTURE) + IF CLAUSE (SIMPLE PAST)
NOTE: We only use ‘were’ to all subject.
In present conditional, the modal ‘would’ appears in the main clause and
‘V2’ appears in the if clause. Here are some examples:
• If I had time, I would go to the beach with you this weekend.
• He would tell you about it if he were here.
Table 2.3 Form of present conditional and the examples
Situation If Clause Main Clause
Time in Past/ Future
Simple Past Past Future
If S + Verb 2 / be +
Object/Complement
S + Modal (would, could, should) + Verb 1 + Object/Complement
If I knew they were honest I would gladly lend them the
19 According to Surayin (2009:331), there are variant forms of if clause in
present conditional as follows:
A. IF + PAST CONTINUOUS
If we were going by boat, I would feel much happier.
If my car was working
B. IF + PAST PERFECT
, I would/could drive you to the station.
If he had taken my advice
a. To an unlikely or hypothetical condition and its probable result. , he would be a rich man now.
Here some functions of present conditional as follows:
If the weather wasn't so bad, we would go to the park. (But the weather is bad
so we can't go.)
If I was the Queen of England, I would give everyone a chicken. (But I am
not the Queen.)
b. To expresses an unfinished or continuing action or situation.
I would be working in Italy if I spoke Italian. (But I don't speak Italian, so I
am not working in Italy)
She wouldn't be living with Jack if she lived with her parents. (But she is
20 2.3.2 Past Conditional (Conditional sentence type 3)
A past conditional or conditional sentence type 3 expresses the activity which
is contrary to the fact in the past time.
a. I would have gone if he had given me a lot of money.
b. If he had had a lot of money, he would have built a house.
Here further explanation about past conditional:
According to Parrot (2006:235), past conditional sentence is to speculate past
events, and about how things that happened or didn’t happen might have affected
other things.
According to Djuharie (2007:75), past conditional sentence explain
something that is contrary to what has happened / something that has passed.
Past conditional consist of two clauses; if clause and main clause. Here the
basic form of present conditional by Djuharie (2007:75):
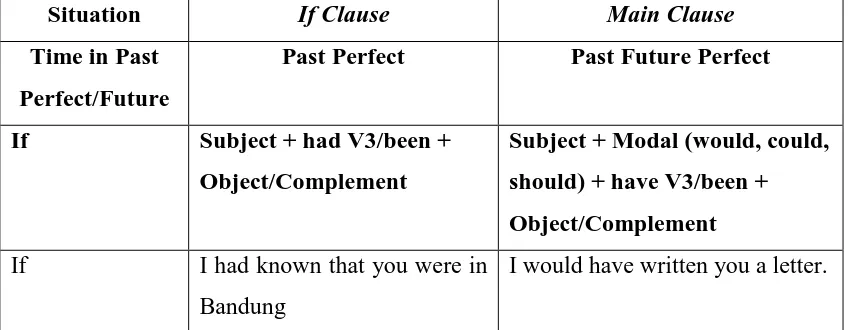
IF CLAUSE (PAST PERFECT) + MAIN CLAUSE (PAST FUTURE
PERFECT)
OR
MAIN CLAUSE (PAST FUTURE PERFECT) + IF CLAUSE (PAST
PERFECT)
In past conditional, the modal ‘would’ appears in the main clause and ‘V3’
21 • If I had known you were there, I would have written you a letter.
• If you had asked me, I would have told you the whole story.
Table 2.4 Form of past conditional and the examples
Situation If Clause Main Clause
Time in Past Perfect/Future
Past Perfect Past Future Perfect
If Subject + had V3/been +
Object/Complement
Subject + Modal (would, could, should) + have V3/been + Object/Complement
If I had known that you were in
Bandung
I would have written you a letter.
According to Surayin (2009:332), there are the possible variations of basic
form that can be seen below:
A. Could or might be used instead of would.
If we had found him earlier, we could have saved his life. (Ability)
If we had found him earlier, we might have saved his life. (Possibility)
If our document had been in order, we could have left at once. (Ability or
22 B. The continuous form of the perfect conditional may be used.
At the time of the accident I was sitting in the back of the car, because Tom’s
little boy was sitting beside him in front. “If Tom’s boy had not been there I
would have been sitting in front.”
C. We can use the past perfect continuous in the if clause.
I was wearing a seat belt. “If I hadn’t been wearing one, I would have been
seriously injured.”
D. A combination of type 2 and 3 is possible.
The plane I intended to catch crashed and everyone was killed. “If I had
caught that plane, I would be dead now or I would have been killed.”
If I had worked harder at school, I would be sitting in a comfortable office
now; I wouldn’t be sweeping the streets.
E. ‘Had’ can be placed first and the if omitted.
If you had obeyed orders, this disaster would not have happened.
Here some functions of Past Conditional:
a. To express the impossible condition in the past and its probable result in the
past.
If I had worked harder I would have passed the exam. (But I didn't work hard,
23 If I had known you were coming I would have baked a cake. (But I didn't
know and I didn't bake a cake.)
b. To express criticism or regret.
Criticism: If you had driven more carefully, you would not have had an
accident. (You had an accident because you didn’t drive carefully)
Regret: If we had played a little better, we could have won the game. (We
didn’t play well, so we lost the game.)
2.4 Test
According to Ellis (1985:112), the purpose of test is to measure the abilities
of learners, to discriminate the meaningful sounds of language, to associate sounds
with written symbols, and to identify the grammatical regularities of a language.
Through the test, students can know how good their ability in learning foreign
languages, especially in understanding grammar of conditional sentences in order to
students can improve their performance to become expert.
According to U.S Congress (1992:5), “A test is an estimate. It is based on
sampling what the test taker knows or can do. For example, by asking a sample of
questions (drawn from all the material that has been taught), a biology test is used to
estimate how much biology that student has learned. Tests can provide valuable
24 As stated by Depdikbud, Dirjen Dikti, 1983/1994, PPS, & 15 with its
guidelines “To determine whether students are regarded successful, at least 75%
must get score 60 or more if less than 75% students get this score, they are
considered to have failed”. Then the results of the test compared to the Department
of Education standardization.
2.4.1 Kinds of Test
According to Lado (1961:32), there are 5 types of tests as follows:
1. Translation
Translation test a test to test the skill of transfer meaning from one language
to another language. Examiner will give a text in the form of paragraphs and then
examinees should translate the source language into the target language or the target
language into the source language. Translation test are used to measure general
achievement in foreign language courses, as a measure of proficiency to determine
entrance in school that require a foreign language. A translation test is a valid test of
ability to translate. In scoring a translation can be made objective if those people trust
the translation test as the best testing device.
2. Essay
Essay or composition test is a test that require students to answer a question
in the form of describing, explaining, discussing, comparing, giving reasons, and
other similar forms by using words and language itself. Examinees will be given a
25 Characteristic of the test is the answer not provided by the people who construct the
items, but supplied by the examinees. Examinees are free to construct the answer.
Each participant tests can select, connect, or convey their ideas by using their own
words. Essay is used as a test of the ability to write essays.
3. Dictation
Dictation is a test which the examiner dictates a text and examinees rewrite
the text which is read out. Examiner will read out sentence by sentence slowly then
he/she gives a break while the examinees rewrite a text which is heard. The reading
material is usually used in the form of a narrative text. In this test, participants
practice listening and writing skill such as letter formation to spelling, punctuation
and lay-out, vocabulary, syntax, and grammar.
4. Objective Tests
Objective tests is a test that consist of questions that can be answered by the
examinees by selecting one or more of several possible answers that have been
attached to the each items or by the way of writing the answer in a space that has
been provided. Objective test is also known as short answer test, yes-no test and new
type test. Objective test examine the entire range of the sound system of a language,
or the major grammatical patterns, or representative sample of the vocabulary for
short in time which is taught during a whole year or several year. They can score
26 Generally, the objective tests can be divided into six kinds namely:
a. Completion test: Completion test is a test which ask student to complete/fill the test. Completion test consists of sentences that some parts had been
removed (already eliminated). It was replaced by space (....). The space
should be filled or completed or perfected by examinees.
b. Short answer: The short answer test is kind of test which the items can be answered by statements with a single word, a phrase, a number or a formula.
c. True-false: True-false test is a test which the items is given in a statement; there is a true statement and false statement. Then examinees will be asked to
determine which statements is true or false.
d. Multiple choice: Multiple choice test is a test that consists of possible answers or alternatives which is sorted by a, b, c, d. Examinees will be asked
to choose which one is the right answer.
e. Matching: Matching test is a test which consist of a series of items and a series of answers. Examinees ask to find the right answer and match to the
right item.
f. Rearrangement exercise: Rearrangement test is a test which consist of some sentences are not arranged coherently, so that the original form
unrecognizable. Examinees are asked to rearrange the sentence in accordance
27 5. Auditory Comprehension Tests
Auditory comprehension test is a test to practice listening skill. Examinees
are required to listen paragraphs or sentences or an essay which is read out loudly by
the examiner then examinees choose the right answer of multiple choice responses.
In testing student's ability, there are two ways that can be used to obtain the
the baseline data. In this research, the researcher uses two kind of test that consist of
multiple choice and completion test.
The examples of conditional sentences on multiple choice:
Future conditional
“What if your father asks you about the scratch on his new car?”
“I_____that it’s my fault.”
(A) simply told him
(B) am simply telling him
(C) will simply tell him
(D) would simply told him
(E) would simply have told him
The correct answer is (C).
Present conditional
If you were going to participate in a big athletic contest or give an important business
presentation, you _____ the same way.
(A) will feel
(B) had felt
(C) would feel
(D) feel
28 The correct answer is (C)
Past conditional
If he _____ more confident during the interview, he might have got the job he
wanted.
(A) were
(B) would be
(C) could have been
(D) had been
(E) was being
The correct answer is (D)
The examples of conditional sentences in completion test:
Future conditional
If they _____ (come) on time, I will talk to them.
The correct answer: If they come, I will talk to them.
Present conditional
If I _____ (fail) in my present job, I would think about another career.
The correct answer: If I failed in my present job, I would think about another career.
Past conditional
If I _____ (know) that she was in the hospital, I would have visit her.
The correct answer: If I had known that she was in the hospital, I would have visited
29 2.4.2 Criteria of Test
According to Lado (1961:30), criteria to evaluate language tests describe as
follows:
a. Validity
According to Lado (1961:30), “Validity in language tests depends on the
linguistic content of the test and on the situation or technique used to test this
content.” and “Validity can be achieved and verified indirectly by correlating the
scores on a test with those of another test or criterion which is valid.” It means that
the items which is formulated should be suitable with the level of examinees' ability.
Due to the reason, the items should have components that can be answered by
examinees who have studied the material. In addition, tests is valid, if all examinees
have the opportunity to demonstrate the knowledges, skills, and attitudes which they
have understood.
b. Reliability
Reliability is one of the characteristics of good test. It refers to the
consistency of the measurement. Lado (1961:31) says, “Reliability is measured by a
correlation between the scores of the same set of students on two consecutive
administrations of the test.” It means that if the scores of the students which are
applied are stable by different people or on different occasions then it can be
concluded that the test is reliable. But, if the score tends to fluctuate too much, the
30 c. Scorability
Scorability is the most basic thing to determine which evaluation is valid. It
means that which a test can be score accurately so that the results which are obtained
are valid. In the evaluation test, examiner should be careful in giving score.
According to Lado (1961:31), “Objective tests are easy to score.” Evaluation can be
made objectively by eliminating the personal opinion of the examiner. If a test gets
evaluation results steadily, with the same result, does not change even if the
evaluation was to be performed by different examiners, the test is valid.
d. Economy
Lado (1961:31) said that it will be practical and economical if the test
measures what is needed in a reasonable time with consider the situation. In giving a
test, the researcher should have consider a reasonable time; it is not too fast and not
too long. The test should provide sufficient information in accordance with the time
which is given in order to obtain the result which is expected.
e. Administrability
Lado (1961:32) states, “Can the test be given under the condition that prevail
and by the personnel that is available? That is, if we do not have a record player, a
test on record cannot be administered.” It means that the test should have the
31 2.5 A Case Study
Hasan (2002:15) says, “A case study is a research on the status of the study
subjects related to a specific phase or typical of the whole personality.” It means that case study aims to describe the subject which is examined as a 'case'.
Case study focuses on one particular subject as a case to be studied deeply to
answer the reality of phenomenon. In this case the subject can be individuals, groups,
organizations and communities. Case study concern on certain cases specifically
such as certain phenomena in a certain place and a certain time. The advantage of the
case studies can be used as a reference to develop investigation of subject’s
background, emphasizing the studied approach in understanding the subjects or can
be useful to solve problems or it could be used to define the kind of difficulties or
32 CHAPTER III
METHOD OF RESEARCH
3.1 Research Design
In this thesis, two methods of research that consist of descriptive qualitative
and quantitative is applied.
Calderon and Gonzales (2007:61) states, “Descriptive research describes and
interprets what is. It is concerned with conditions of relationships that exist; practices
that prevail; beliefs; processes that are going on; effects that are being felt, or trends
that are developing. The process of descriptive research goes beyond mere gathering
and tabulation of data. It involves the elements or interpretation of the meaning or
significance of what is described. Thus description is often combined with
comparison and contrast involving measurements, classifications, interpretation and
evaluation.”
Douglas (2000:255) states, “There are numeruous statistical, quantitative
techniques for analyzing the test performance of groups of test taker. Which ones are
appropriate for any given test will be determined by whether it contains objectively
scored tasks, such as multiple-choice, true-false, error-recognition, or subjectively
scored tasks, as in writing and speaking tests. Typical techniques of quantitative
analysis which might be employed include... a technique useful for matching the
difficulty of multiple-choice items with varying ability levels among the test takers;
33 error of measurement; ... for the purpose of determining what abilities are being
measured.”
Douglas (2000:256) also states, “Qualitative methods generally focus more
on the individual than on groups, and on verbal rather than numerical data.
Techniques such as observations, questionnaires, interviews, verbal report, and
think-aloud studies can be used with the trial candidates to gain information about the
quality of the test rubric, the instructions, time allotment, and the prompt, the
appropriateness and level of the content, the process of responding to tasks, and
general satisfaction with the format of the test.”
Descriptive qualitative method is used to do evaluation about the students’
ability in using conditional sentences. The resesarcher do collecting the data by
giving the test of multiple choice and completion test. Descriptive quantitative
method is used to do measurement about the data of students’ ability in using
conditional sentences. The researcher do analysing the data with some formulation to
find the result of the test.
Library research was done to find the data of theory and to help in analysing
the research with reading some books related to the subject of analysis (about
conditional sentences and ability) and field research was done when collecting the
data from the school.
3.2 Location and Time
This research was held at SMA Cahaya Medan which is located on Jl. Hayam
34 3.3 Population and Sample
Arikunto (1993:102) says, “Population is the whole number of the subject or
people under observation in research.”
In this research, the population is the grade XI students of SMA Cahaya
Medan that consist of 42 students in grade XI IPA 1, 45 students in grade XI IPA 2,
45 students in grade XI IPA 3, 44 students in grade XI IPS 1, 45 students in grade XI
IPS 2, and 46 students in grade XI IPS 3. The total of population in grade XI of SMA
Cahaya are 267 students.
For limited the time, the data of all population can not be analyzed but some
of them can be taken as a sample which has represented the student’s ability.
Arikunto (1993:109) says, “A sample is a limited number of elements selected from
a population to be representative of that population”. Random sampling is used to
gives students a chance of being selected as the sample. As Gay (1987:104) states,
“Random sampling is the best single way to obtain a representative sample. This
procedure guarantees a higher probably than any other way.” and Lado (1961:20)
says, “The sample should ordinarily be randomly selected.” Then it is decided to take
them in random sampling by lottre.
In this study, there are 6 classes of SMA Cahaya Medan students in grade XI
and it was choosen 60 students as sample (about 25% of population). It is considered
representative enough and relevant as Arikunto (1993:107) said that the size of
sample is 10%-15% or 20%-25% the population is relative large. It was choosen 30
students from XI IPA 3 and 30 students from XI IPS 1 at random. Here are the
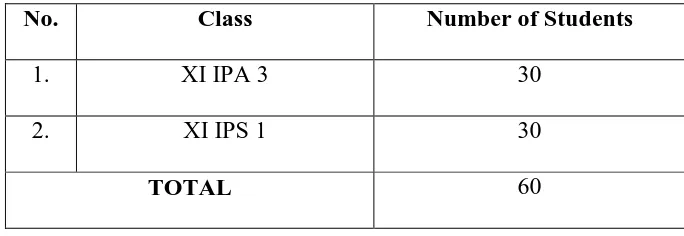
35 Table 3.1 Distribution of Research Population
No. Class Number of Students
1. XI IPA 3 30
2. XI IPS 1 30
TOTAL 60
3.4 Data Collection Procedure
According to Wikipedia, “Data is a set of values of qualitative or quantitative
variables; restated, pieces of data are individual pieces of information. Data is
measured, collected and reported, and analyzed, where upon it can be visualized
using graphs or images.” It means that the data is instrument for researcher to
measure, reported and analyzed the problems to be information to solve the problems.
Based on the explanation, it is needed some baseline data that represent
student’s ability with giving them a test about conditional sentences. It was done by
the grade XI students of SMA Cahaya Medan by giving them 15 items of multiple
choice and 15 items of completion test. In scoring the test, it was given one point for
one item. So, there are 30 items which was conducted in 60 minutes. It is enough
because Lado (1961:20) says, “We must test in one hour what has been learned in a
month or a year or five years”.
Then, the researcher arranged the instrument of research as follows :
1. Test on the use of Future Conditional, number 1,2,3,4,5 in multiple choice and
36 2. Test on the use of Present Conditional, number 6,7,8,9,10 in multiple choice and
completion test.
3. Test on the use of Past Conditional, number 11,12,13,14,15 in multiple choice and
completion test.
In this research, the test was given to them which should be filled by sixty
students who are selected at random. After doing the test, the answer-sheets were
collected.
3.5 Technique of Data Analysis
After collecting the baseline data, it was used several steps to analyze the data
as follows :
1. First, scoring the test with use the formula of Nurkancana and Sumartana (1986)
as follows:
X = R x 100 N
In which:
X = the individual score
R = the number of correct answers
N = the number of questions
37 3. To make sure that the test is good, find out the reliability of the test with some
formulation as follows:
First, find out standard deviation with following formula:
SD = 1 }
N
Where,
SD = standard deviation
∑X = the total of correct answer
N = the number of respondents
∑X2 = the quadrate of the total score
Second, find out the mean of the total of correct answer:
= ∑X
N
Then, calculate coeffisient of reliability :
38 In which:
r = the reliability of the instrument
k = the number questions
M = the mean of the test score
S2 = the standard deviation
3. Then, it is needed to find out the percentage of the number of students get score ≥
60, the number of students get score <60 and also to find out the percentage of the
students’ ability in answering the test which is calculated by using the formula of
Sudijono (1991:41) as follows:
P= f x 100% n
In which:
P = the percentage
f = the number of frequency
n = the total numbers of respondents
4. To categorize the level of the students’ ability of using conditional sentences, the
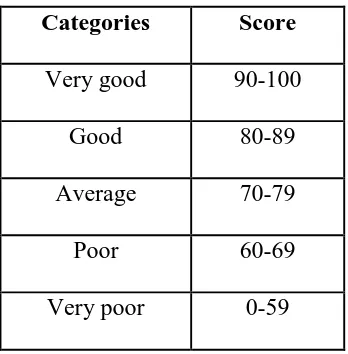
39 Table 3.2 Students’ score range in SMA Cahaya Medan
(Adapted from KKM (Minimum Standard Scores) of English subject) Categories Score
Very good 90-100
Good 80-89
Average 70-79
Poor 60-69
40 CHAPTER IV
ANALYSIS AND FINDINGS
4.1 Data Analysis
The researcher gave a multiple choice test and completion test, which was
focused on conditional sentences. This test consists of 30 items, each of conditional
sentences type has certain items; future conditional or conditional sentence type I, it
has five items of multiple choice and five items of completion test, present
conditional or conditional sentence type II has five items of multiple choice and five
items of completion test and past conditional or conditional sentence type III has five
items of multiple choice and five items of completion test. The researcher put the
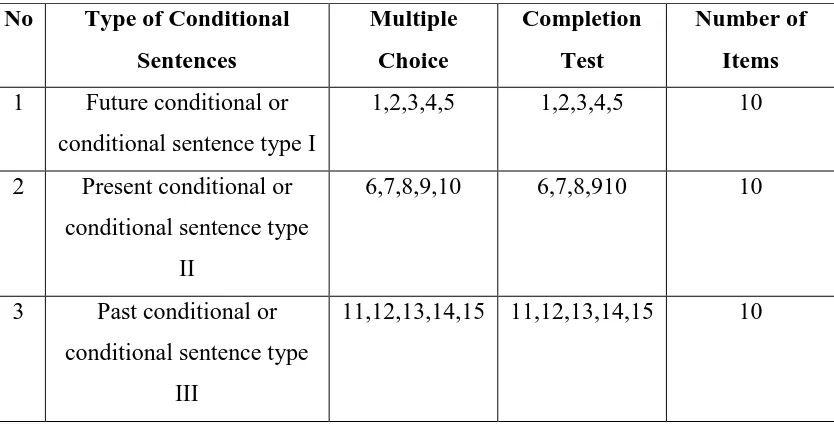
41 Table 4.1 Conditional Sentences function and each item
No Type of Conditional Sentences
1 Future conditional or
conditional sentence type I
1,2,3,4,5 1,2,3,4,5 10
2 Present conditional or
conditional sentence type
II
6,7,8,9,10 6,7,8,910 10
3 Past conditional or
conditional sentence type
III
11,12,13,14,15 11,12,13,14,15 10
First, it is needed to tabulate the scores of each student. In scoring the test, the
researcher used the formula of Nurkancana and Sumartana (1986) as follows:
X = R x 100 N
In which:
X = the individual score
R = the number of correct answers
N = the umber of questions
Table 4.2 are arranged based on the result of scoring the test and it is
arranged on the highest to the lowest to distribute students’ scores in sequence as
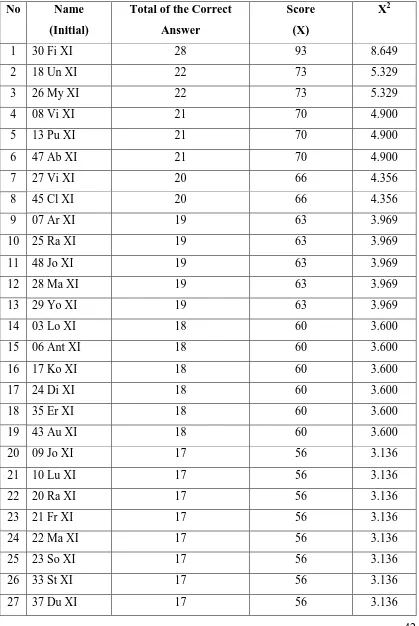
42 Table 4.2 The Highest to The Smallest Scores
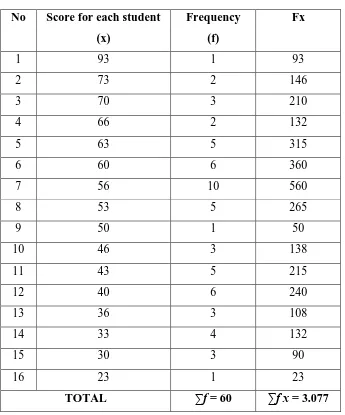
44 After being ranked, the highest score of the students’ test result in using
conditional sentences is 93 and the lowest score is 23. It is also found that there are
922 the correct answers of 60 students which describe the correct answer on average
15 and the total of score is 3.077 which describe students on average 51,2 and the
quadrate of total score is 170.370.
After finishing the tabulation of the raw scores, the standard deviation of the
test result is found out in following formulation:
SD = 1 }
N
Where,
SD = standard deviation
45 So,
SD = 1 }
N
= 1 √ {60 x 170.370) – (3.077)2} 60
= 1 √ 10.222.200 – 9.467.929 60
= 1 √ 754.271 60
= 1 (868,49) 6
= 14,47
= 14 (rounded)
The calculation of mean is:
= ∑X
N
= 922
60
= 15,36
= 15 (rounded)
After knowing the mean and the standard Deviation, then the coefficient of
46
(KR)r =
]
=
]
=
]
=
]
=
1,034 ( 1 – 0,038 )= 1,034 x 0,962
= 0,99
The calculation above shows that the reliability of the test is 0,99. So, the
reliability of the test is very high. It is based on Arikunto (1986:93), the standard of
reliability is:
0,00 – 0,40 = The reliability is low
0,41 – 0,70 = The reliability is significant
0,71 – 0,90 = The reliability is high
47 4.2 Findings
After analysing the data, table 4.3 describe the ability of grade XI students of
SMA Cahaya Medan to use conditional sentences in the multiple choice and
completion test with tabulating their grade and the percentage.
Table 4.3 The Students’ Score in Using Conditional Sentences No Score for each student
(x)
Based on the table 4.3, it is found that the frequency is 60 and total score is
3.077. Then, to find out the mean score of the students’ ability in using conditional
48
Then, the researcher tabulates the percentage of students’ score based on
KKM (Minimum Standard Scores of English subject) that can be seen at table 4.4.
Table 4.4 The Percentage of Students’ Score in using Conditional Sentences
Frequency Percentage
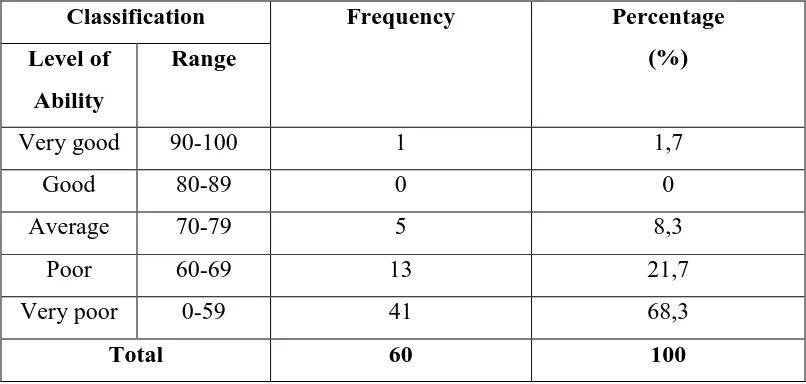
From the table 4.5, it shows that 1 student (1,7% of the respondents) have
very good ability, 0 students (0% of the respondents) has good ability, 5 students
49
respondents) have poor ability and 41 students (68,3% of the respondents) have
very poor ability.
Based on classification criteria (Table 4.4) above, then it is reconstituted
the student's ability as in table 4.5 as follows.
Table 4.5 The Students’ Ability in Using Conditional Sentences
51
No Name
(Initial)
Total of the Correct Answer
Score (X)
Level of Ability
50 50 Vi XI 17 56 Very poor
51 51 Mi XI 13 43 Very poor
52 52 Ke XI 13 43 Very poor
53 53 Fe XI 9 30 Very poor
54 54 El XI 9 30 Very poor
55 55 Eg XI 12 40 Very poor
56 56 Gr XI 12 40 Very poor
57 57 Ri XI 10 33 Very poor
58 58 Me XI 10 33 Very poor
59 59 Ch XI 9 30 Very poor
60 60 Ma XI 16 53 Very poor
Total 3077
Mean Score 51,2
From Table 4.6, it can be reviewed distribution of students' ability as the
following chart.
52 According to the chart above, the ability of the grades XI students of SMA
Cahaya Medan, it is stated that:
• 1 student (1,7% of the respondents) has very good ability in using conditional
sentences.
• 0 students (0% of the respondents) have good ability in using conditional
sentences.
• 5 students (8,3% of the respondents) have average ability in using conditional
sentences.
• 13 students (21,7% of the respondents) have poor ability in using conditional
sentences.
• 41 students (68,3% of the respondents) have very poor ability in using
conditional sentences.
Based on the data analysis, it is found that the ability of using conditional
sentences by students of SMA Cahaya Medan is mostly very poor. Then, the
researcher find out the problems of students of SMA Cahaya Medan in using
conditional sentences by distributing questionnaire which some items as follows:
1. Did you learn the conditional sentences?
a. Yes
b. No
c. I did know
2. Is the conditional sentences studied with exercises?
a. Yes
b. No
53 3. Do you think the conditional sentences is difficult to understand?
a. Difficult to understand
b. Easy to understand
c. I do not know
4. Can you understand when the conditional sentences given in one
meeting?
a. Yes
b. No
c. I do not know
Table 4.6 the Percentage of Questionnaire Items
No Items Answers
(Percentage)
Explanation
A B C
1 Did you learn the conditional sentences?
66,6 25 8,4 Choosing A
greater than B and C 2 Is the conditional sentences studied
with exercises?
8,3 66,6 25 Choosing B
greater than A and C 3 Do you think the conditional
sentences is difficult to understand?
83,3 6,7 10 Choosing A
greater than B and C
4 Can you understand when the
conditional sentences given in one meeting?
5 83,3 11,7 Choosing B
greater than A and C
Processed from Questionnaire
Based on Table 4.6, there are 40 students (66,6% of respondents) who choose
A, 15 students (25% of respondents) who choose B, and 5 students (8,4% of
respondents) who choose C in the first item. In the second item, there are 5 students
(8,3% of respondents) who choose A, 40 students (66,6% of respondents) who
54 students (83,3% of respondents) who choose A, 4 students (6,7% of respondents)
who choose B, and 6 students (10% of respondents) who choose C. In the fourth
item, 3 students (5% of respondents) who choose B, 50 students (83,3% of
respondents) who choose A, and 7 students (11,7% of respondents) who choose C.
In addition, the researcher also conducted interviews with English teachers.
Answers were obtained generally equal to the results of the questionnaire submitted
by the students. It is found that the teaching of conditional sentences is delivered in
one meeting and the teacher didn’t give the exercises as much as possible so that the