DEVELOPING INTERPRETATION ROUTE AND PROGRAM
OF AGROTOURISM
(Case Study: Malang Regency, East Java Province)
NIKEN DIAS PRASASTI
G051054031
GRADUATE SCHOOL
ABSTRACT
NIKEN DIAS PRASASTI (2008). Developing Interpretation Route and Program of Agrotourism (Case Study: Malang Regency, East Java Province). Under the supervision of YULI SUHARNOTO and SITI NURISYAH.
Agrotourism is the form of tourism which capitalizes on rural culture as a tourist attraction. It is similar to ecotourism except that its primary appeal is not the natural landscape but a cultural landscape. An advantage agrotourism
approach is that rural areas are popular destinations for holidays and excursions, particularly cultural landscapes which still give a review of how previous generations lived and worked. Agrotourism is well known in Malang Regency. Agriculture industries growth well, supporting with the suitable condition such as land condition, weather in these places. The variation of plants and the beauty sceneries are the attractive things beside the visitors allow to get interact with the objects. For example they can pick fruits, learn more about plant or just buy some souvenir.
The objectives in this research are to identify attractive agrotourism tourism objects in Malang Regency, identify agrotourism activities mainly based on farm activities and to develop the agrotourism interpretation route and
programs. Geography Information System (GIS) is used as the main tools to process the analysis.
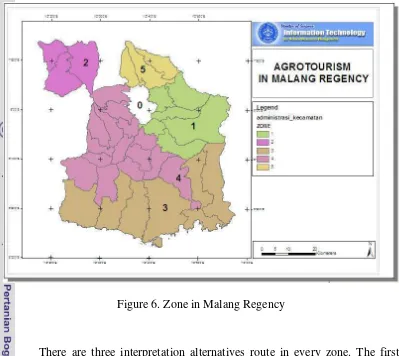
Criteria used for scoring agrotourism objects are the criteria from Dinas Perhubungan dan Pariwisata Kabupaten Malang. Main goal of these methods is for making concept, strategy, plan and program the tourism attraction in Malang Regency by knowing the priority object in every zone. There is 5 Zones in Malang Regency where three interpretation alternatives route are developed in each zone. Determination zoning area is a strategy of tourism object developing in Malang regency.
There are three interpretation alternatives route in every zone. The first alternative is developed by classifying the visited stops based on the object with horticulture and non plant as the agrotourism attraction. Second, is developed by classifying the visited stops based on the object with non horticulture plant and non plant as the agrotourism attraction. The last alternative is developed by visiting all agrotourism objects without classifying the tourism resources. According to the prioritizing analysis using Analysis Hierarchy Process (AHP), alternative 1 has the highest priority for the criteria of educational, recreational and inspirational benefits in zone 1, 2, 3 and 4. For zone 5 alternatives 3 has the highest priority. Those all priority alternatives are expected to be the most preferable alternatives in interpretation route and program of agrotourism in Malang Regency. The output of interpretation program may lead to the
I. INTRODUCTION
1.1. Background
Tourism is a vital industry for many countries, due to the income generated by the consumption of goods and services by visitors, the taxes levied on businesses in the tourism industry, and the opportunity for employment in the service industries associated with tourism.
Tourism in Indonesia still performs as a promising industry, though it has showed deprivation trends because of the economic crisis in the last decades. Its importance is set to grow even more as the economic transforms into a post individual society. With the rapid economic expansion that many countries have experienced, it is highly likely that tourism industry will be the main driver to bring about both economic and social evolution.
World Tourism Organization data showed that Asia Pacific has the biggest tourist growth in 1982 – 1988. In 1992 Asia Pacific get 58 million tourists and increasing until 2000. The growth of tourist in Asia Pacific is a potential market for tourism industries in Indonesia. In 1988, Indonesia tourism industries contribute US $ 1027.8 million and increasing almost US $ 8-9 billion in Pelita IV (Sek. Dirjen Pariwisata , 1993)
In Indonesia, tourism industries has been giving a large contribution to the country’s economic growth, especially in increasing the national income as the third biggest contributor after oil and gas, and textile industry until 1997 (Tim KLH and UNDP in Roslita, 2001)
of Indonesia is become the main basis of tourism development in Indonesia. Indonesia with high biodiversity has a various natural resources that become resources in tourism services.
Agrotourism is the form of tourism which capitalizes on rural culture as a tourist attraction. It is similar to ecotourism except that its primary appeal is not the natural landscape but a cultural landscape. Tourism that based on cultural landscape are divided into primitive, traditional and modern. Primitive means that all activities are done by human resources. In traditional, technology is involved even just in a small part. Third, in modern high technology are involved in the activities. If the attractions on offer to visitors contribute to improving the income of the regional population, agrotourism can promote regional development. To ensure that it also helps to conserve diversity, the rural population itself must have recognized agrobiodiversity as valuable and worthy of protection.
The advantage agrotourism approach is that rural areas are popular destinations for holidays and excursions, particularly cultural landscapes which still give a review of how past generations lived and worked. Typical regional crops and local breeds become a particular attraction for visitors. This generates additional income for farmers and contributes to the conservation and development of the whole region.
(3) the contribution for export (4) a big number of society has depend on this sector as their main living (5) is a main sector in food stock and (6) is a basic for rural growth. (Hanafi et al, 2003).
Unfortunately, Indonesia agricultural nowadays is decrease more than 50%. Many agricultural lands become settlement, industrials area, or business area. The awareness of Indonesian people about agriculture also decreases. For example about job that related to agriculture, they prefer choosing another job that they thought can make more money. If this condition continued, agriculture will be just agriculture for fulfill food requirement without any other benefit on it. Farmers will be the only one who care and interest with it. Agrotourism is one method to support the educational program in agriculture. It is expected to prevent the declining of agriculture and increase people awareness.
The quality of human resources is an importing thing in agriculture sector development. Introduction and appreciation about agriculture sector for society is one way of increasing the quality of human resources. Main idea in developing the interpretation program of agrotourism site is for education. During the program, visitors will learn about something likes how to planting, and how to harvesting. With interpretation program, visitors are expected to more care about agriculture as a one way to take Indonesia becoming the real agricultural country.
Tourism sector can be used as a tool in increasing the autonomy potencies, and for required the society requirement in refreshing. In tourism planning, human or society is the main aspect beside the spatial aspect. Human play a role as a subject and at the same time as an object, it means that required the human requirement is the most important thing in developing tourism planning.
The most important thing in tourism developing program is the tourism object developing that required with tourist desire. In general, tourism object is something that consumed by tourist, start from they move from their places, during the journey, until they come back to their places.
All the potencies from the environment must be concern in developing tourism program. Therefore, is required to conduct more specific study about how big the potencies are. This development will support the development of tourism in Malang Regency, and also expected to increase the income that at least can be used to require their needed. This capability mean that tourism sector not depend on another sector.
object and the entire supporting component to get closer with better tourism that more concern in the tourist satisfaction.
Agrotourism is well known in Malang Regency. Agriculture industries growth well, supporting with the suitable condition such as land condition, weather in these places. The variation of plants and the beauty sceneries are the attractive things beside the visitors allow to get interact with the objects. For example they can pick fruits, learn more about plant or just buy some souvenir.
Attractive tourism objects of agrotourism in Malang Regency can be horticulture (vegetables, flowers, or fruits), fishery or cattle farm. There is not always object that newly develop, not only agricultural object in big scale, but also can be the existing object supported by facilities. The most important thing in agrotourism is about the uniqueness that can be exposed. For example kind of attractive tourism objects, the quality, the beauty scenery of the object, etc.
1.2. Objectives
The objectives in this research are:
• Identify attractive agrotourism tourism objects in Malang Regency • Identify agrotourism activities mainly based on farm activities • Develop the agrotourism interpretation programs.
1.3. Scope
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1. Agrotourism
Tourism is an activity that individuals do and usually enjoy. Tourism is temporary movement of people to destinations outside their normal places of work and residence, the activities undertaken during the stay in those destinations, and the facilities created to cater for their needs (Matthieson and Wall in Sitawati, 2006).
Agrotourism is being developed as a valuable component of a business model to support many agricultural entities when the farm products they produce are no longer economically competitive otherwise. To help promote the single Agrotourism operations, some farms get together to form festivals, tours or other events. People are more interested in how their food is produced and want to meet the producers and talk with them about what goes into food production. Children who visit the farms often have not seen a live duck, or goat, and have not picked an apple right off the tree. This form of expanded agro-tourism has given birth to what are often called "entertainment farms." These farms cater to the pick-your-own crowd, offering not only regular farm products, but also food, mazes, open-pen animals, train rides, picnic facilities and pick-your-own produce *)
gifts, and much more. Each farm generally offers a unique and memorable experience suitable for the entire family (Koeswandono in Suprijanto 2006).
Agrotourism is a mild form of sustainable tourist development and multi-activity in rural areas through which the visitor has the opportunity to get acquainted with agricultural areas, agricultural occupations, local products, traditional cuisine and the daily life of the people, as well as the cultural elements and the authentic features of the area, while showing respect for the environment and tradition. Moreover, this activity brings visitors closer to nature and rural activities in which they can participate, be entertained and feel the pleasure of touring, learning and discovering. At the same time, it mobilizes the productive, cultural and developmental forces of an area, contributing in this way to the sustainable environmental, economic and social development of the rural area *)
Agrotourism is a form in tourism activities that using farming zone as the attractive object. Agrotourism provides beauty scenery of agricultural supporting with the activities related with agricultural. The boundary of agrotourism is the tourism that also using forest and another natural resources besides farming zone. Agrotourims activities are activities that related with rural activities that can increase the economy.
2.2. Tourism Components
Talking about tourism is also talking about everything that sticks on it. Tourism activity are supported by tourism component, there are:
2.2.1 Tourist
Tourist is someone that moving from their places without stay in a long time or making some money from it. Based on Instruksi Presiden RI No. 9 Tahun 1996, tourist can be explaining as:
• Someone that take a journey in order to their own pleasure, or family business
• Someone that moving from their place for a business
• Someone that moving from their place as the delegation for scientific,
sport and excreta
• Someone that comes, and if they stay it will less than 24 hours
Tourist can be classified based on some criteria, there are: • Based on the total of tourist:
a. Individual Tour b. Family Group c. Group Tour
• Based on the arrangement:
a. Pre-arranged Tour b. Package Tour c. Coach Tour
• Based on the goal: a. Holiday Tour
b. Familiarization Tour c. Educational Tour d. Pileimage Tour e. Special Program Tour f. Hunting Tour
• Based on the management : a. Excursion
b. Safari Tour c. Cruise Tour d. Youth Tour e. Marine Tour
People as tourist are doing their tourism activity with motivations. The motivations are:
• Cultural Motivation :
a. Knowing about culture, art, architecture, and history about something b. Knowing the important event (sport, business, national or international
event)
• Individual Motivation
a. Family visiting, friend visiting or looking for a new friend b. For fun
c. Spiritual visiting
• Status and Achievement Motivation a. Hobby
b. Study c. Conference d. Personal meeting
2.2.2 Tourism Object
Tourism Object is the realization of a human creation, life arrangement, art, history and culture, with something unique that make it interesting for tourist (PP No.24, 1979). Tourism Object consists of:
• Natural Tourism Object
Object that using natural component as the attraction. It can be inside or outside the conservation area.
• Cultural Tourism Object
Act and artifact of the society are the main component. • Special Attraction Tourism Object
2.2.3 Facilities
Supporting facilities are divided into: • Main Tourism Facilities
1. Tourism agent 2. Transportation 3. Restaurant
• Supplementing Tourism Facilities
1. Recreation and Sport Facilities, for examples golf court, tennis court, and house riding.
2. Public Facilities, for examples road, bridge, electricity and telecommunication.
• Supporting Tourism Facilities
1. Nightclub and steam bath as the supporting facilities for night entertainment
2. Souvenir shop and mailing service as the supporting facilities.
2.2.3 Promotion
2.3. Interpretation of Tourism Site
The terms of Interpretation are program and activity. The program means a set of objectives for the things that we want our visitor to understand, the activity has to do with the skills and techniques by which that understanding is created. Essentially, how well the visitor or tourist can understand the important meanings and relationship of the site they visit depends on the program and the activity that together make up the interpretation.
Interpretation is a service for visitors to parks, forests, refuges, and similar recreation areas. Though visitors to these areas come for relaxation and inspiration, many also wish to learn about the area’s natural and cultural resources. The resources comprise the geological processes, animal, plants, ecological communities, history and prehistory of humans. Interpretation is the communication link between the visitor and these resources (Sharpe, 1982). Interpretation seeks to achieve three objectives:
• To assist the visitor in developing a keener awareness, appreciation and understanding of the area the visitors are visiting.
• To accomplish management goals. It can be done in two ways. First. Interpretation can encourage thoughtful use of the recreation resource on the part of the visitor, helping reinforce the idea that parks are special places requiring special behavior. Second, interpretation can be used to minimize human impact on the resources in a variety of ways.
• To promote public understanding of an agency’s goals and objectives, that
image of the agency that supplies it. If it is overdone, the message is labeled propaganda rather than interpretation or public information. Interpretation is a communication process designed to reveal meanings and relationship of our cultural and natural resources to the public, through first hand experiences with objects, artifacts, landscapes or site. Interpretation is not only talk about information that only a present answers to questions that visitors are not asking. Interpretive communication takes the information by transforming and translating the information into the language of the visitor. To be truly “interpretive”, the message (interpretive panel, brochure, etc.) must be follow the following criteria:
• The communication must first provoke the attention or curiosity of the audience
• Relate to everyday life of the visitor; tell them why they need to know this information.
• Reveal the key concepts of the message or story through a unique viewpoint save the surprise ending or answer for last.
• Address the whole; illustrate to the visitor how each individual stop along concept of the total byway experience or story.
2.4. The Interpretation Program
The overall interpretation effort is known as the interpretation program. It includes the personnel, facilities and all interpretation activities of an organization, agency or individual area. The interpretation program relates the natural or cultural phenomena of the object to the visitors and utilizes a wide variety of methods to present this subject matter (Sharpe, 1982).
Interpretation provide many benefits, there are:
• Contribute directly to the enrichment of visitor experiences.
• Makes visitors aware of the place in total environment and give them a better understanding of the complexities coexisting with that environment. • May broaden the visitor’s horizon beyond the park or forest boundary,
giving a greater understanding of the total natural resources picture.
• Informs the public and an informed public may make wiser decision on matters related to natural resources management,
• May reduce the unnecessary destruction of tourism property, resulting in
lower maintenance and replacement costs.
• Provides a means of moving people subtly from sensitive areas to sites that
can better sustain heavy human impact, thus protecting the environment. • A way to improve public image and establish public support.
• May inspire in visitor sense of pride in their country or in the region’s culture and heritage.
• May be effective in preserving a significant historic site or natural area by arousing citizen concern.
• May motivate the public to take action to protect their environment in a sensible and logical way.
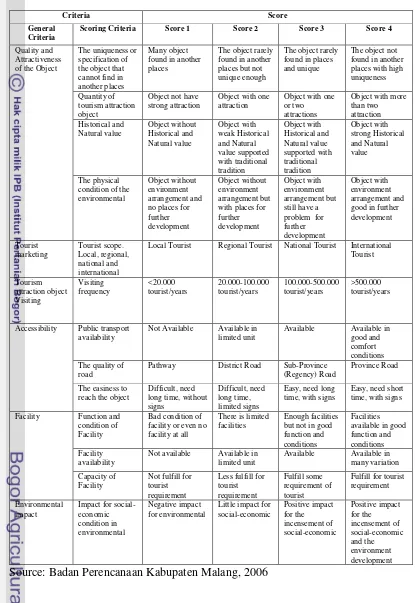
2.5. Criteria in Scoring for Tourism Attraction
Tourism object and attraction are the main component for developing any tourism program, include the developing the interpretation program. These two factors are the one of the main factors for tourism satisfaction (Gunn, 1994).
Attractions are everything that can be seeing, hearing, feeling and enjoying. Tourism attractions are important things in developing the interpretation program. Tourism attractive analysis using for knowing the attraction index in tourism objects through the potential attractions of the object, scoring and weighting are used to make the analysis easily. Scoring and weighting system for tourism attributes with expertise judgment can generally explain the importance of tourism developing program. Smith (1989) categorized the attractive factors in a tourism site in five main categories, there are:
• Natural Factor
• Cultural and social factor • Historical factor
• Recreational factor
Attractive attraction is the attractiveness of environment that includes beautiful senses in tourism object, and tourism component and supply. Beautiful senses are:
• Vision
The natural beauty of landscape. Examples: farming zone, lakes, and settlement areas.
• Smell
Natural smell coming from the environment (smell of grass, forest, etc).
• Sound
Natural sounds likes water, birds singing, wind, etc. • Taste
Unique taste comes from the attractive objects. Tourism Component & Supply are :
• Natural Resources
Consist of use and the enjoyment of visitors, air and climate, land form, terrain, flora, fauna, water bodies, beaches, and natural beauty scenery.
• Infra Structure
• Transportation and Transportation Equipment 1. Air
2. Motor coach 3. Ship and Boat 4. Rail
5. Taxis
• Hospitality and Culture Resources 1. Activities
2. Shopping
3. Entertainment, Recreation and other 4. Museums
Score is something that stick in object in order to satisfy the needed of people in their life including their needed of beauty. In general, score is an abstract thing depends on logical factors, esthetic, physical and cultural. Gunn (1994) noted that there are many ways for choosing criteria in tourism object. For natural tourism the important things in scoring and choosing criteria are:
• The variety: object with higher variety of biota and ecosystem has important rules in keeping the balancing of environment.
• The delegation: biota formation can be used as the parameter for another special biota’s in another place.
• The originality: the originality of biota and physical • The effectiveness: management aspect
World Heritage Committee criteria can be used for scoring in cultural object in tourism. In this method the criteria for cultural tourism object are:
• Religions system • Social factors • Economic factor • Art
• Language • Tools and
• Education system.
2.6. Geographic Information System
Geographic Information System (GIS) is a particularly horizon technology in the sense that it has wide ranging applications across the industrial and intellectual landscape. For this reason, it tends to resist simplistic definition. GIS stores spatial data with logically linked attribute information in a GIS storage database where analytical function is controlled interactively by a human operator to generate the needed information products (Tomlinson, 2003).
Geographic Information System (GIS) is a set of tools that are used for compiling, storing, manipulating, updating, analyze, and present is all data to be spatial information (ESRI, 1990). GIS has four main capabilities to handle geographic reference data, they are: data entry, data management, data manipulate and analyze, and data output (Arronoff, 1989).
GIS is one information system used to working with spatial reference data or geographic coordinate (Star and Ester 1990). Other word, GIS is a system of database with specific capability for spatial reference data with a set of working operation. The capability of GIS if compared with another database processing system is its capability to display spatial and non-spatial information at the same time. For example; land-use data will be able to be presented within polygons boundary (spatial information) and attributes that contain information of polygon (non-spatial information). Information with different themes is represented into different layer coverage. GIS tries to make simple real earth phenomenon, and it is expected to represent real condition for one particular application. (Chrisman, 1996).
In GIS, data storage is divided into 2 parts, they are: spatial and attribute data. For analysis need, spatial and attribute data will be stored separately, and then the both will be integrated (Macguire and Goodchild, 1991). Occasionally, some data derive from remote sensing image will be combined with GIS data storage for implementation particularly goal.
processing, and data output, (4) three components above are functioned based on high technology (Arronoff, 1989).
Figure 2. Stucture of GIS (Malczewski 1999).
Data sources requirement for GIS analysis process generally can be divided into 3 categories (Laurini, 1992),they are: (1). Field data, (2). Map data, which its information has recorded on paper or film that are converted into digital format and (3). Remote sensing involves airborne photo and satellite imagery.
The process from data input become data output is a connecting structure that is started from real world and recorded on image and airborne photo, then by GIS facility, data are stored and processed to generate output that will be used for decision-making in the real world. Procedure of GIS working system is organizing hardware, software, and geographic data to optimize the system of storing, manipulating, analysis and displaying all geographic information. Attribute and
Data Storage and Management
User Interface
Data Output Data Manipulation
and Analysis User
spatial data have relationship with space aspect-location that is presented as database on a map. To acquire spatial analysis result use overlaying technical from some thematic maps (vector or raster). New spatial information is acquired based on new digital value that constitutes an integration of old digital value.
2.7. Multi Criteria Decision Making (MCDM)
Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) is the study of methods and procedures by which concerns about multiple conflicting criteria can be formally incorporated into the management planning process. Decision analysis looks at the paradigm in which an individual decision maker (or decision group) contemplates a choice of action in an uncertain environment. The decision theory helps identify the alternative with the highest expected value (probability of obtaining a possible value). The theory of decision analysis is designed to help the individual make a choice among a set of pre-specified alternatives. The decision making process relies on information about the alternatives. The quality of information in any decision situation can run the whole gamut from scientifically-derived hard data to subjective interpretations, from certainty about decision outcomes (deterministic information) to uncertain outcomes represented by probabilities and fuzzy numbers. This diversity in type and quality of information about a decision problem calls for methods and techniques that can assist in information processing. Ultimately, these methods and techniques (MCDA, MCDM) may lead to better decisions (Malczewski 1999).
measurement. This process is called Standardization, a basic operation in MCE. Criteria should be standardized keeping in mind the goal and alternatives that are under evaluation. Standardization can change the outputs entirely if proper attention is not paid. For environmental criteria, there is a lack of valid and reliable standardization processes (Bunn, 1982).
Decision-making is a subjective process, as the perception regarding a problem can diverge from person to person. One cannot expect a decision maker or an expert to be highly consistent while dealing with such a subjective process. The real world problems are influenced by many natural factors and processes that are difficult to measure and model precisely. After the problem is evaluated for optimum conditions, sensitivity analysis assesses different conditions near the optimum values to check for the sensitivity of the criteria. Many decision-making methods lack a valid approach towards sensitivity analysis. Sensitivity analysis also aids in understanding the interaction between the criteria, dominant criterion and its effect, i.e. the variation in the final results when the weight of that criterion is varied (Keeney and H. Raiffa, 1976).
A decision involves making a selection from a set of alternative choices. Broadly speaking, a decision-support system (DSS) is simply a computer system that helps to make a decision by leveraging the multi-criteria decision-making model. DSS provide a means for decision-makers to make decisions on the basis of more complete information and analysis (Szidarovszky et al, 1986). Among the main advantages of the use of DSS are the following:
• Increased number of alternatives examined • Better understanding of the business • Fast response to unexpected situations • Improved communication
• Cost savings • Better decisions
• More effective teamwork • Time savings
• Better use of data resources • When Theory Meets Practice
2.8. Analytical Hierarchy Process
The Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) is one of Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) that developed by Saaty, it aims at quantifying relatives priorities for a given set of alternatives on a ratio scales based on the judgment of the decision makers, and stresses the importance of the intuitive judgment of a decision makers as well as the consistency of the comparison of alternatives in the decision making process (Saaty., 1980).
Since a decision maker bases judgment on knowledge and experience, then makers decision accordingly, the AHP approach agrees well with the behavior of the decision maker. The strength of this approach is that it organizes tangible and intangible factors in a systematic way and provides simple solution for the decision makers. In addition, by breaking a problem down in a logical fashion from the large, descending in gradual steps, to the smaller and smaller, one is able to connect, through simple paired comparison judgments, the small to the large.
AHP is a systematic method for comparing a list of objectives or alternatives. It is a comprehensive, logical and structured framework that allows improving understanding of complex decisions by decomposing the problems in a hierarchical structure. The method will be performed based on the three principles of AHP, there are:
comparisons of decision criteria, rather than utility and weighting functions. Table above explains of a preference for one criterion versus another using a nine-point scale:
1: if the two elements are equally important
3: if one element is weakly/moderately more important than the other element 5: if one element is strongly more important than the other element
7: if one element is very strongly more important than the other element
III. METHODOLOGY
3.1. Time and Location
This research was conducted from September 2007 until Desember 2007, at Malang Regency, East Java.
Figure 4. East Java
3.2. Study Area Profile
Malang Regency is located between 112° 17' 10,90° to 112° 57' 0,00° East and between 7° 44' 55,11° to 8° 26' 35,45° South. Malang is one of regency in East Java Province.
The boundaries of Malang regency are:
• North : Jombang, Mojokerto and Pasuruan Regencies • South :Indian Ocean
• West : Blitar and Kediri Regencies East : Probolinggo and Lumajang Regencies
Malang regency is located between 0-2000 m above the sea level, that showing various kind of topography from low until highland areas. Lowland areas are located in Bululawang, Gondanglegi, Tajinan, Turen, Kepajen, Pagelaran, Pakisaji, Singosari, Lawang, Karangploso, Dau, Pakis, Dampit, Sumberpucung, Kromengan, Pagak, Kalipare, Donomulyo, Bantur, Nganjun, and Gedangan district.
Middle land areas are located in Sumbermanjing Wetan, Wagir, and Wonosari district. Highland areas are located in Pujon, Ngantang, Kasembon, Poncokusumo, Jabung, Wajak, Ampelgading and Tirtoyudo district.
Soil types in Malang Regency are andosol, latosol, mediteran, litosol, alluvial, regosol and brown forest. The total areas for each type are shown in Table 4.
Table 4. Soil Type in Malang Regency
No Soil Type Area (ha)
1 Andosol 43.782,42
2 Latosol 86.260,36
3 Mediteran 55.811,30
4 Litosol 69.133,25
5 Alluvial 28.003,25
6 Regosol 45.654,17
7 Brown Forest 6.142,25
3.4. Data Source
Data collection are taken in several methods which are field surveys and document or literature study. Source of data are collected from government institutions there are Dinas Perhubungan dan Pariwisata, Pengelolaan Data Elektronik, Dinas Pertanian, Dinas Bina Marga, Badan Pertanahan, Badan Pusat Statistik, Badan Perencanaan, and Dinas Permukiman of Malang Regency.
Data from field surveys are conducted as the main point in interpretation program. Agrotourism point will get score from field survey data, and it will be continued to interpretation program development. Literature study is also important in comparing the data on the field with the theory.
3.5. Criteria in Scoring for Agrotourism Attraction in Malang Regency
Figure 6. Zone in Malang Regency
3.7. Analytical Hierarchy Process
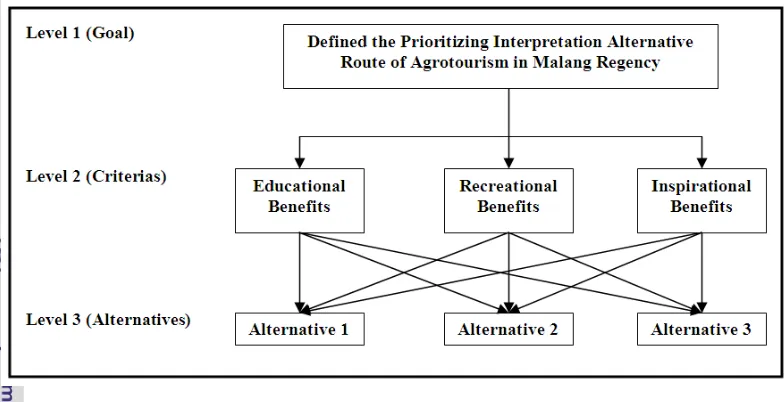
A comparative judgment is needed to select the prioritizing interpretation alternatives route in every zone. Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) is used in this research by setting some required criteria in weighting the priority factors of defined alternatives in pair wise comparisons. These priority weights are obtained by capturing expert perception towards the most preferable alternatives of interpretation route based on certain considerations.
Defined the prioritizing interpretation alternatives route among those three alternatives is become the first level and the goal in this stage. The second level, that contribute to the goal are educational benefits, recreational benefits, and inspirational benefits. In the last or third level are the three alternatives of interpretation routes.
3.8. Flowchart of Study
!
" # $ %!&
'
(
IV. RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Agrotourism Objects in Malang Regency
Agrotourism is tourism with agriculture as an attractive objects, where visitors can do some “farm” activities. It is not always the agriculture object that already became tourism area, but agriculture lands with strong object attractive also called agrotourism site. In Malang Regency there are many agriculture lands with various objects (Table 7). Complete information about the Agrotourism Object in Malang Regency can be seen in Apendix 1.
Table 7. Agrotourism object in Malang Regency
No Agrotourism Object Organizer Location (Subdistrict)
1 Pakis - Sweet Potatoes Local People Pakis
2 Jabung - Sweet Potatoes Local People Jabung
3 Tumpang - Honey Local People Tumpang
16 Air terjun Coban Rondo Perum Perhutani KPH Unit Jawa Timur Pujon
17 Donomulyo - Melinjo Local People Donomulyo
18 Bantur – Paddy Local People Bantur
19 Gedangan – Cengkeh Local People Gedangan
21 Sbrmanjing Wetan – Chocolate Local People Sumbermanjing Wetan
22 Tirtoyudo - Kesemek Local People Tirtoyudo
23 Ampelgading - Argo Semeru Local People Ampelgading
24 Kalipare – Soybean Local People Kalipare
25 Pagak – Banana Local People Pagak
26 Pagelaran - Salak Suwaru Agribusiness Salaca Group Pagelaran
27 Turen – Corn Local People Turen
28 Dampit – Peanut Local People Dampit
29 Bululawang - Durian Local People Bululawang
30 Gondanglegi – Corn Local People Gondanglegi
31 Kepanjen - Papaya Local People Kepanjen
32 Bendungan KarangKates Perum Jasa Tirta Sumber Pucung
33 Bendungan Sutami Perum Jasa Tirta Sumber Pucung
34 Kromengan – Salak Jambuwer Local People Kromengan
35 Kromengan – Bagelan Coffee PTP. XII Kec Kromengan Kromengan
36 Pakisaji - Sugarcane Local People Pakisaji
37 Wagir – Banana Local People Wagir
38 Ngajum – Cassava Local People Ngajum
39 Wonosari – Coffee Local People Wonosari
40 Dau - Orange Local People Dau
41 Karang Ploso – Vegetables Local People Karangploso
42 Karang Ploso – Corn Local People Karangploso
43 Singosari – Tea Wonosari PTP. XII Kec Wonosari Lawang Singosari
44 Singosari - Avocado Local People Singosari
45 Lawang - Avocado Local People Lawang
These all agrotourism objects are spread in 33 subdisctrict of Malang Regency with various kind of attraction in horticulture plant, non horticulture plant (mainly paddy and second crops) or non plant. Most of them are organized by local people or society around the agrotourism object and also become their living income.
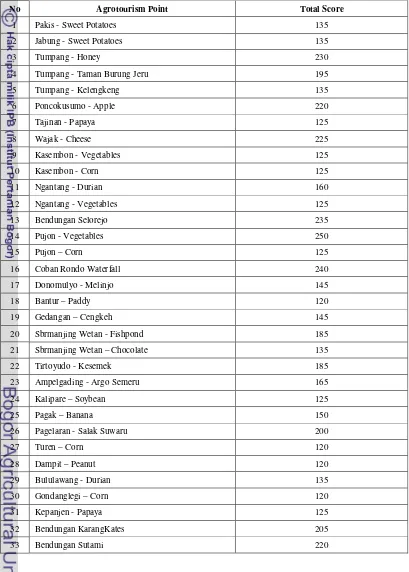
zone. Table 8 shown the calculation of assessment for all zones. The complete calculation for each object can be seen in Appendix 2.
Table 9. Score of Agrotourism object in Malang Regency Zone I
No Agrotourism Point Total Score
Priority agrotourism object in zone I is subdistrict Tumpang with honey as the attractive object, and the other objects are Wajak – Cheese, Poncokusumo – Apple, Tumpang – Taman Burung Jeru, Pakis – Sweet Potatoes, Jabung – Sweet
Potatoes, Tumpang – Kelengkeng, and Tajinan – Papaya as the supporting objects.
4.1.2. Zone II
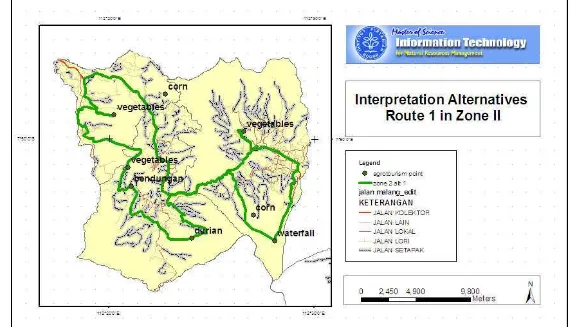
Priority Agrotourism object in Zone II ( Kasembon, Pujon and Ngantang subdistrict) is Pujon with vegetables, and the other objects are Bendungan Selorejo, Ngantang – Durian, Air Terjun Coban Rondo, Kasembon – Vegetables, Ngantang – Vegetables and Pujon - Corn as the supporting objects.
Figure 9. Agrotourism objects in Zone II Ngantang -
Vegetables
Coban Rondo Waterfall Pujon -
Vegetables Pujon – Corn
Kasembon - Vegetables
Ngantang - Durian
Kasembon - Corn
Table 10. Score of Agrotourism object in Malang Regency Zone II
No Agrotourism Point Total Score
1 Kasembon - Vegetables 125
2 Kasembon - Corn 125
3 Ngantang - Durian 160
4 Ngantang - Vegetables 125
5 Bendungan Selorejo 235
6 Pujon - Vegetables 250
7 Pujon – Corn 125
8 Coban Rondo Waterfall 240
4.1.3. Zone III
Zone III consist of Donomulyo, Bantur, Gedangan, Sumbermanjing Wetan, Tirtoyudo and Ampelgading subdistric. Sumber Manjing Wetan with fishpond is the priority object for this zone. This object has a highest score in all criteria for scoring agrotourism object.
Figure 10. Agrotourism objects in Zone III
Table 11. Score of Agrotourism object in Malang Regency Zone III
No Agrotourism Point Total Score
government center in Malang regency. Priority Agrotourism object in Zone VI is Kromengan –Bagelan Coffee, and the other objects are the supporting objects. Table 12. Score of Agrotourism object in Malang Regency Zone IV
4.1.5. Zone V
Priority Agrotourism object in Zone V is Singosari with Wonosari tea. This object is well known inside or outside Malang Regency. Various activities in this object are the most attractive things for agrotourism. Singosari and lawang with avocado, Karang Ploso with vegetables, and Karang Ploso with corn are the supporting objects in zone V.
Figure 12. Agrotourism in Zone V
Table 13. Score of Agrotourism object in Malang Regency Zone V
No Agrotourism Point Total Score
1 Karang Ploso – Vegetables 125
2 Karang Ploso – Corn 125
3 Singosari – Tea Wonosari 330
4 Singosari – Avocado 135
5 Lawang - Avocado 130
Singosari – Avocado
Lawang - Avocado
Singosari – Tea Wonosari Karang Ploso –
Corn
The potential objects together with the supporting areas are then considered in developing Interpretation Program of Agrotourism in Malang Regency. The areas that are being considered are especially the area with high until low potential quality of tourism. They are especially considered as the stops that will linked by tracks and sequencing the visitor movement.
Tourism Activities based on farm activities
Something special that visitors can do in agrotourism objects is farm activities. Visitor not only visiting the objects but also can directly involving in this objects. Through agrotourism, visitors are expected to get some benefit in educational, recreational and inspirational. They can pick fruit, doing some maintenance in field, and others.
Table 14. Tourism activity in Agrotourism objects
No Agrotourism Object Tourism Attractions
1 Pakis - Sweet Potatoes Enjoying and learn about sweet potatoes
2 Jabung - Sweet Potatoes Enjoying and learn about sweet potatoes
3 Tumpang - Honey Honey production process
4 Tumpang - Taman Burung
Jeru Camping, fishing, enjoying and learn about bird and unique plants 5 Tumpang - Kelengkeng Enjoying and learn about kelengkeng
6 Poncokusumo - Apple Enjoying and learn about apple and it products
7 Tajinan - Papaya Enjoying and learn about papaya
8 Wajak - Cheese Chess production process
9 Kasembon - Vegetables Enjoying and learn about vegetables
10 Kasembon - Corn Enjoying and learn about corn
11 Ngantang - Durian Enjoying and learn about durian
12 Ngantang - Vegetables Enjoying and learn about vegetables
14 Pujon - Vegetables Enjoying and learn about vegetables and apple, paralayang, milk production process
15 Pujon – Corn Enjoying and learn about corn
16 Coban Rondo Waterfall Water fall, zoo, medicine plant garden and the laboratories
17 Donomulyo - Melinjo Enjoying and learn about melinjo
18 Bantur – Paddy Enjoying and learn about paddy
19 Gedangan – Cengkeh Enjoying and learn about cengkeh
20 Sbrmanjing Wetan - Fishpond Fishing
21 Sbrmanjing Wetan –
Chocolate Enjoying and learn about chocolate 22 Tirtoyudo - Kesemek Enjoying and learn about kesemek
23 Ampelgading - Argo Semeru Enjoying and learn about vegetables, paralayang
24 Kalipare – Soybean Enjoying and learn about soybean
25 Pagak – Banana Enjoying and learn about banana
26 Pagelaran - Salak Suwaru Enjoying and learn about salak
27 Turen – Corn Enjoying and learn about corn
28 Dampit – Peanut Enjoying and learn about peanut
29 Bululawang - Durian Enjoying and learn about durian
30 Gondanglegi – Corn Enjoying and learn about corn
31 Kepanjen - Papaya Enjoying and learn about papaya
32 Bendungan KarangKates Usually used for PON (Pekan Olahraga nasional) event , sport facilities
33 Bendungan Sutami sport facilities, water ski, parasailing, canoe, etc
34 Kromengan – Salak Jambuwer Enjoying and learn about salak
35 Kromengan - Kopi Bagelan Enjoying and learn about coffee
36 Pakisaji - Sugarcane Enjoying and learn about sugarcane
37 Wagir – Banana Enjoying and learn about banana
38 Ngajum – Cassava Enjoying and learn about cassava
39 Wonosari – Coffee Enjoying and learn about coffee
40 Dau - Orange Enjoying and learn about orange
41 Karang Ploso – Vegetables Enjoying and learn about vegetables
42 Karang Ploso – Corn Enjoying and learn about corn
43 Singosari – Tea Wonosari Tea harvesting, tea production process, hiking, jogging, cycling
44 Singosari – Avocado Enjoying and learn about avocado
Interpretation Program of Agrotourism Site
The tourism gateway and tourism center service are two important things in interpretation program development. It will make tourists or visitors are easier in doing their movement. The linkage of one object with others is also need to be considered in developing the alternatives route.
Tourist or visitors movement usually have certain patterns. These patterns are starting in one point that becomes the concentration point because has easier access than other as well as most complete facilities. This point called tourism gateway and center service at the same time. There are some conditions that make some place become a tourism gateway and center service, such as must have an accommodation facilities at least class a motel, restaurant in good condition, and have a post office as telecommunication facilities (Dinas Perhubungan dan Pariwisata Kabupaten Malang, 2006). In interpretation program, scoring method for determined priority object is used to choose starting point each alternative.
There are three alternatives each zone that is developed in this study by using the concept of developing interpretation program. The first alternative is developed by classifying the visited stops based on the object with horticulture and non plant as the agrotourism attraction. Second, is developed by classifying the visited stops based on the object with non horticulture plant and non plant as the agrotourism attraction. The last alternative is developed by visiting all agrotourism objects without classifying the tourism resources.
along the track. Those three alternatives are developed based on the same vision of interpretation that is try to explore and communicate the resources with scoring and weighting qualities within agrotourism object in Malang regency.
4.3.1. Interpretation Alternatives Route in Zone I
Interpretation alternatives route are developed based on zone I, which consists of Pakis, Tumpang, Jabung, Tajinan, Wajak and Poncokusumo subdistric. In this zone, subdistric Tumpang is the center of tourism services. The objective of this method is that the visitors can obtain the information from various agrotourism resources and all the attraction, as well as the knowledge besides their recreational experience during their movement.
The potential stops are determined with considering the potential area result from previous analysis together with the existing agrotourism objects. The highest score are prioritized to be potential stop along the track, and also linked to the other objects that have a lower score. There always be specific objective in every object stop, based on the value of the resources that era being interpreted.
At the end visitor will learn more about honey. How honey is formed, and honey home industry.
2 Wajak - Cheese
At the end visitor will learn more about cheese. Knowing the dairy cattle farm, how to take care of them in case to get good quality of cheese, learn about cheese production process.
3 Poncokusumo - Apple
At the end visitor will learn more about apple (Malus
domestica) field. How exactly apple plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it and learn about various product made from apple and also buy it.
4 Tumpang - Taman Burung Jeru
At the end visitor will learn more about bird especially Cucak Ijo bird that well known as the fauna mascot for Malang Regency. Visitor also offered by unique plants, camping and playing ground.
5 Tumpang - Kelengkeng
At the end visitor will learn more about kelengkeng (Nephelium longan Camb.) field. How exactly kelengkeng plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
6 Tajinan - Papaya
At the end visitor will learn more about papaya (Carica papaya Gaerth) field. How exactly papaya plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
Alternative 2 is developing with connection agrotourim objects that concern in non horticulture plant (sweet potatoes) and non plant attractions (honey, cheese, and taman burung Jeru).
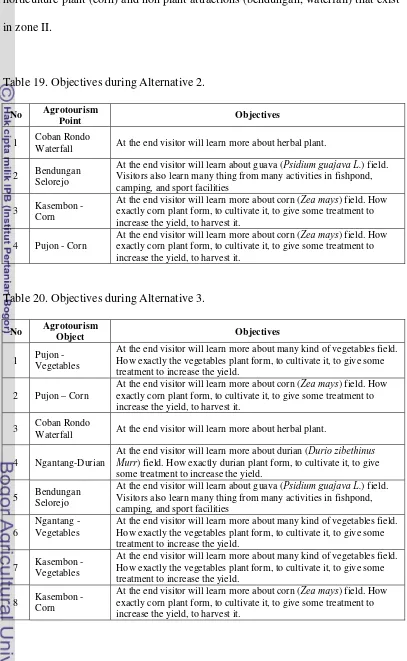
Table 16. Objectives during Alternative 2
No Agrotourism Point Objectives
1 Tumpang - Honey At the end visitor will learn more about honey. How honey is formed, and honey home industry.
2 Wajak - Cheese
At the end visitor will learn more about cheese.
Knowing the dairy cattle farm, how to take care of them in case to get good quality of cheese, learn about cheese production process.
3 Tumpang - Taman Burung Jeru
Alternative 3 is developing with visiting all agrotourim objects in zone I. With various objects automatically visitors also get various objectives that can enrich their experience in agrotourism.
Table 17. Objectives during Alternative 3.
No Agrotourism Object Objectives
1 Tumpang - Honey At the end visitor will learn more about honey. How honey is formed, and honey home industry.
2 Tajinan - Papaya
At the end visitor will learn more about papaya (Carica papaya Gaerth) field. How exactly papaya plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
3 Wajak - Cheese
At the end visitor will learn more about cheese. Knowing the dairy cattle farm, how to take care of them in case to get good quality of cheese, learn about cheese production process.
4 Poncokusumo - Apple
At the end visitor will learn more about apple (Malus
domestica) field. How exactly apple plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it and learn about various product made from apple and also buy it.
5 Tumpang - Kelengkeng
At the end visitor will learn more about kelengkeng (Nephelium longan Camb.) field. How exactly kelengkeng plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
6 Tumpang - Taman Burung Jeru
At the end visitor will learn more about bird especially Cucak Ijo bird that well known as the fauna mascot for Malang Regency. Visitor also offered by unique plants, camping and (Ipomoea batatas L.) field. How exactly sweet potatoes plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it and enjoy the various products from sweet potatoes and also buy it.
8 Pakis – Sweet Potatoes
4.3.2. Interpretation Alternatives Route in Zone II
Interpretation alternatives route are developed based on zone II, which consists of Kasembon, Pujon and Ngantang subdistric. In this zone, Pujon is the center of tourism services. In alternative 1, visitor will visit agrotourism objects with vegetables, durian, honey, cheese and guava as the attractions.
Table 18. Objectives during Alternative 1.
No Agrotourism
Point Objectives
1 Pujon - Vegetables
At the end visitor will learn more about many kind of vegetables field. How exactly the vegetables plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
2 Coban Rondo
Waterfall At the end visitor will learn more about herbal plant.
3
Ngantang - Durian
At the end visitor will learn more about durian (Durio zibethinus Murr) field. How exactly durian plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
4 Bendungan Selorejo
At the end visitor will learn about guava (Psidium guajava L.) field. Visitors also learn many thing from many activities in fishpond, camping, and sport facilities
5 Ngantang - Vegetables
At the end visitor will learn more about many kind of vegetables field. How exactly the vegetables plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
6 Kasembon - Vegetables
In alternative 2, visitor will visit agrotourism objects that concern in non horticulture plant (corn) and non plant attractions (bendungan, waterfall) that exist in zone II.
Table 19. Objectives during Alternative 2.
No Agrotourism
Point Objectives
1 Coban Rondo
Waterfall At the end visitor will learn more about herbal plant.
2 Bendungan Selorejo
At the end visitor will learn about guava (Psidium guajava L.) field. Visitors also learn many thing from many activities in fishpond, camping, and sport facilities
3 Kasembon - Corn
At the end visitor will learn more about corn (Zea mays) field. How exactly corn plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it.
4 Pujon - Corn
At the end visitor will learn more about corn (Zea mays) field. How exactly corn plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it.
At the end visitor will learn more about many kind of vegetables field. How exactly the vegetables plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
2 Pujon – Corn
At the end visitor will learn more about corn (Zea mays) field. How exactly corn plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it.
3 Coban Rondo
Waterfall At the end visitor will learn more about herbal plant.
4 Ngantang-Durian
At the end visitor will learn more about durian (Durio zibethinus Murr) field. How exactly durian plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
5 Bendungan Selorejo
At the end visitor will learn about guava (Psidium guajava L.) field. Visitors also learn many thing from many activities in fishpond, camping, and sport facilities
6
Ngantang - Vegetables
At the end visitor will learn more about many kind of vegetables field. How exactly the vegetables plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
7 Kasembon - Vegetables
At the end visitor will learn more about many kind of vegetables field. How exactly the vegetables plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
8 Kasembon - Corn
4.3.3. Interpretation Alternatives Route in Zone III
Interpretation alternatives route are developed in Donomulyo, Bantur, Gedangan, Sumbermanjing Wetan, Tirtoyudo, and Ampelgading subdistric that merged as zone III. Sumbermanjing Wetan is the center of tourism services.
Similar with another zone, alternative 1 is developing with concerning in horticulture plant and non plant as attractions, alternative 2 concerning in non horticulture plant and non plant, and alternatives concerning in all agrotourism objets. Route alternatives developed in zone III starts and ends at different point because the limitation of the accessibility that impossible to start and end at the
At the end visitor will learn about many thing from activities in fishpond
2 Donomulyo – Melinjo
At the end visitor will learn more about melinjo (Gnetum gnemon L.) field. How exactly melinjo plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
3 Tirtoyudo - Kesemek
At the end visitor will learn more about kesemek (Diospyros kaki L.f.) field. How exactly kesemek plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
4 Ampelgading - Argo Semeru
At the end visitor will learn about many thing from activities in fishpond
2 Gedangan - Cengkeh
At the end visitor will learn more about cengkeh (Syzigium aromaticum) field. How exactly cengkeh plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
3 Bantur – Paddy
At the end visitor will learn more about paddy (Oryza sativa) field. How exactly corn plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it.
4 Ampelgading - Argo Semeru
At the end visitor will learn more about many kind of vegetables field. How exactly the vegetables plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield. Visitors also learn many thing from activities paralayang sport facilities.
At the end visitor will learn about many thing from activities in fishpond
2 Gedangan - Cengkeh
At the end visitor will learn more about cengkeh (Syzigium aromaticum) field. How exactly cengkeh plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
3 Bantur – Paddy
At the end visitor will learn more about paddy (Oryza sativa) field. How exactly corn plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it.
4 Donomulyo – Melinjo
At the end visitor will learn more about melinjo (Gnetum gnemon L.) field. How exactly melinjo plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
5 Sbrmanjing Wetan - Chocolate
At the end visitor will learn more about chocolate (Theobroma cacao) field. How exactly corn plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it.
6 Tirtoyudo - Kesemek
At the end visitor will learn more about kesemek (Diospyros kaki L.f.) field. How exactly kesemek plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
7 Ampelgading - Argo Semeru
4.3.4. Interpretation Alternatives Route in Zone IV
Interpretation alternatives route are developed in zone IV, which consists of Wonosari, Wagir, Dau, Kepanjen, Sumber Pucung, Pagak, Dampit, Bululawang, Gondanglegi, Kalipare, Kromengan, Pagelaran, Pakisaji, Turen and Ngajum subdistric with Kepanjen as the center of tourism services. Three route alternatives are developing with same object for start and end point.
Table 24. Objectives during Alternative 1.
No Agrotourism Point Objectives
1 Bendungan Sutami At the end visitor will learn about guava field. Visitors also learn many thing from many activities in fishpond
2 Bendungan KarangKates At the end visitor will learn about guava field. Visitors also learn many thing from many activities in fishpond
3 Pagak - Banana
At the end visitor will learn more about banana (Musa paradisiaca) field. How exactly banana plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
4 Kepanjen - Papaya
At the end visitor will learn more about papaya (Carica papaya Gaerth) field. How exactly papaya plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
5 Pagelaran - Salak Suwaru
At the end visitor will learn more about salak (Salacca adulis Reinw.) field. How exactly salak plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
6 Bululawang - Durian
At the end visitor will learn more about durian (Durio zibethinus Murr) field. How exactly durian plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
7 Wagir- Banana
At the end visitor will learn more about banana (Musa paradisiaca) field. How exactly banana plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
8 Dau- Orange
At the end visitor will learn more about orange (Citrus sp.) field. How exactly orange plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
9 Kromengan – Salak Jambuwer
At the end visitor will learn more about coffee (Coffea sp.) field. How exactly the coffee plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
2 Bendungan Sutami At the end visitor will learn about guava field. Visitors also learn many thing from many activities in fishpond
3 Kalipare - Soybean
At the end visitor will learn more about soybean (Glycine max.) field. How exactly corn plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it.
4 Bendungan KarangKates
At the end visitor will learn about guava field. Visitors also learn many thing from many activities in fishpond
5 Turen - Corn
At the end visitor will learn more about corn (Zea mays) field. How exactly corn plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it.
6 Dampit - Peanut
At the end visitor will learn more about peanut (Arachis hypogea L.) field. How exactly peanut plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it.
7 Gondanglegi - Corn
At the end visitor will learn more about corn (Zea mays) field. How exactly corn plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it.
8 Pakisaji – Sugarcane
At the end visitor will learn more about sugarcane field. How exactly corn plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it.
9 Wonosari - Coffee
At the end visitor will learn more about coffee (Coffea sp.) field. How exactly coffee plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
10 Ngajum - Cassava
At the end visitor will learn more about cassava field. How exactly corn plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it.
Table 26. Objectives during Alternative 3.
No Agrotourism Object Objectives
1 Kromengan – Bagelan Coffee
At the end visitor will learn more about coffee (Coffea sp.) field. How exactly the coffee plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
2 Pagelaran - Salak Suwaru
At the end visitor will learn more about salak (Salacca adulis Reinw.) field. How exactly salak plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield.
3 Bendungan Sutami At the end visitor will learn about guava field. Visitors also learn many thing from many activities in fishpond
4 Kalipare - Soybean
At the end visitor will learn more about soybean (Glycine max.) field. How exactly corn plant form, to cultivate it, to give some treatment to increase the yield, to harvest it.
5 Pagak - Banana
At the end visitor will learn more about banana (Musa