Majalah Kedokteran Nusantara Volume 41 y No. 1 y Maret 2008 1
Histopathology Types of Polyposis in Adam Malik Hospital
Delfitri Munir
Ear Nose Throat, head and Neck Surgery Department Faculty of Medicine, Sumatera Utara University
Abstract: The treatment of polyposis until now unsatisfied. Recurrent rate are still high by medicine or surgery, and this problem need to know the type of polyp. The aim of this research are detect nasal and sinus paranasal polyp type in Adam Malik Hospital Medan. The conclusion are allergic type (type I) is the most common (62%).
Keywords: allergic, polyposis
Abstrak: Cara pengobatan terhadap polypolis sampai saat ini belum memuaskan. Tingkat kambuhnya masih tinggi melalui medis atau pembedahan, dan jenis polyp dari masalah ini harus diketahui. Tujuan dari penelitian ini untuk mendeteksi jenis nasal dan sinus paranasal di Rumah Sakit Haji Adam Malik Medan. Kesimpulannya adalah jenis alergi (Tipe 1) adalah yang paling banyak (62%)
Kata kunci: alergi, polypolis
INTRODUCTION
Polyposis management unsatisfied until now. Its recurrence still high in patient who under gone medicine or surgery management.
1,2,3
Dhaeng (1996) found 51 cases (25,49 %), who have undergone more than once operation and 76,92 % are allergic polyposis (tipe I).4
Soetjipto (2005) found recurrence 13 from 73 cases (17,8 %).5
Recurrence of polyposis influence by allergy, so it have to detect the polyp type. 6,7
Nasal polyposis is chronic inflamation of nasal mucous has been known since 3000 years ago.8,9,10
It is 1,3 % populations in East Europe and 1-4 % in North America. 11
Data from allergic – immunology Department Indonesian University reveal that nasal polyposis 2,7 % from 110 alergic rhinitis.12
Hellquist (1996) define 4 polyposis histopathology are alergic polyp (type I), fibro inflamatory polyp (type II), seromucin glandula hyperplasia polyp (type III) and polyp with atipical stroma (type IV).13
Several researches prove that type I is the most common cases. Vogels (2001) found type I 94,8 % from 39 cases and Bucholtz (1999) found 69 % from 16 cases.9,14
While
Mangunkusumo (2004) found most common type II (74,2 %).12
Definite etiologi still unknown. There are many theory has been presented but it is not satisfied yet. The theory are allergic, infection and Bernaulli theory.15,16
MATERIAL AND METHOD
This research is cross section method was done in ENT Department Medicine Faculty North Sumatera University/Adam Malik Hospital. Sample is patient come to the Hospital with diagnosis nasal and sinuses paranasal polyposis from Maret 2004 to February 2005. Polyposis mass that take durante operation send to Pathology Anatomi Department, Faculty of Medicine North Sumatera University.
RESULT
We found 26 patients polyposis nasal and sinus paranasal
Table 1. Sex distribution
Sex Amount %
Male 17 65
Female 9 35
Total 26 100
KARANGAN ASLI
Karangan Asli
Majalah Kedokteran Nusantara Volume 41 y No. 1 y Maret 2008 2
This table show that male 17 cases (65 %) and female 9 cases (35 %) with ratio 1,8 : 1.
Table 2.
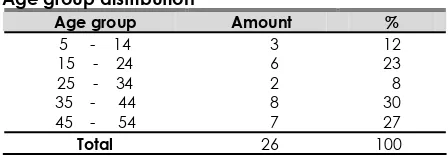
Age group distribution
Age group Amount %
The most age group is 34–35 years old (30 %) and the rare is 25-34 years old (8 %).
Table 3.
Histopathologic type distribution according Hellquist criteria
Histopathology type Amount %
Type I 16 62
Type II 6 23
Type III 3 12
Type IV 1 3
Total 26 100
The commonest histopathologic type is type I are 16 cases (62 %).
DISCUSION
We have sample 26 consist of male 17 (65 %) and female 9 (35 %) with ratio 1,8 : 1. Appropriate with another researches that male more than female. Voegels (2001) and Soetjipto (2005) found ratio male and female 1,8 : 1.5,9
Suheryanto (1999) found 3 : 1.17
Dowel (1992) and Wang (2005) found 2,5 : 1. 6,15
Mangunkusumo (2004) found 2 : 1 and Dhaeng (1996) 1,5 : 1.4,12
While Siregar (1995) found similar sex ratio 1 : 1.18
Presence difference sex ratio may be because difference sample each research.
The most common age group is 35–44 years old (30 %). The youngest age is 10 years old and the oldest is 54 years old. Appropriate with another research that more than 30 and rare under 20 years old.19
Dowel (1992) found the youngest is 14 years old and oldest 78 years old. 15
Siregar (1995) found the youngest 17 years old and the oldest 50 years old.18
Soetjipto found the youngest 12 years old and
the oldest 65 years old.5
While Mangunkusumo (2004) found the youngest is 8 years old and the oldest 74 years old.12
Be base on histopathology type and Hellquist criteria, we found the most common
is type I (62 %). This result similar with Voegels (2001) that the most common is type I (94,8 %) from 39 sample.9
Like wise Bucholtz (1999) found the most common type is type I (69 %) from 16 sample. 14
While Mangunkusumo (2004) found the most common is type II (74,2 %).12
Some researcher believe that allergy is the importance factor for polyposis formation. 9,20
The evidence allergic factor in polyposis is similar histopathology polyposis and allergic tissue such as edema, eosiniphilia in blood and nasal secret. There any close relation between polyposis and astma, hay fever, urticaria and eczema. The another evidence that more case polyposis cure after avoidance allergent and hyposensitization.4,8
Some researchers found that eosinophil is predominant in nasal polyposis. Be base on this fact polyposis research tend to eosinophil accumulation in tissue. In allergic tissue, mucosal iritation make edema and polyp formation. 20
CONCLUSION
The conclusion are allergic type (type I) is the most common (62%).
REFERENCES
1. Collman BH. Disease of the Nose, Throat and Ear, Head and Neck. Longman Singapore Publishers. 14 th
ed. Singapore 1993: 29-34.
2. Wang H, Zhang L, Zhou B, Zhang W, Liu HC, Liu M. Relationship between allergic factors and chronic sinusitis with or without nasal polips, Zhonghuo Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2005, Vol. 40 (3): 168-71.
3. Rifki N. Surgical Treatment for Ear, Nose and Throat Allergic Diseases in Indonesia. Journal of Oto Rhino Laryngology Indonesia. Vol XXV. January-April 1994: 277-82.
4. Dhaeng S, Mulyadi U, Saroso S. Rekurensi Poilp hidung Di Bagian THT RSUP DR. Sardjito Yogyakarta Periode Januari 1993 – Desember 1995. Kumpulan Naskah Ilmiah PIT. PERHATI. Batu-Malang. Oktober 1996: 736-42.
Delfitri Munir Histopathology Types of Polyposis…
Majalah Kedokteran Nusantara Volume 41 y No. 1 y Maret 2008 3
5. Soetjipto. D, Nasal Poliposis: The Importance of Post – Operative Care. Indonesian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. 35(2) April-Juni. 2005: 46-50.
6. Wynn R, Har-El G. Recurrence rates after endoscopic sinus surgery for massive sinus polyposis. Laryngoscope 2004, Vol. 114 (5): 811-3.
7. Kirtsreekul V. Nasal polyps: the relationship to allergy, sinonasal infection and histopathological type. J Med Assoc Thai, 2004, Vol. 87 (3): 277-82.
8. Mabry RL. King HC. Allergic Management of Nasal Polyps. Rhynology and Sinuse Diseases A problem-Oriented Approach. Schaefer Mosby Inc.London 1998: 51-4.
9. Voegels RL, Santoro P, Butugan O. Nasal Polyposis and Allergy: Is There a Correlation ?. American Journal of Rhinology 2001.15 (1): 9-13.
10. Tripathi A, Conley DB, Grammer LC, Ditto AM, Lowerry MM, Seiberling KA.
Immunoglobulin E to staphilococcal and streptococcal toxins in patiens with chronic sinusitis/ nasal polyposis. Laryngoscope 2004, Vol. 114 (10):1822-6.
11. Bert van der Baan. Epidemiology and natural history, in: Nasal Polyposis an inflamatory disease and its treatment, 1st
ed, Munksgaard. Copenhagen. 1997: 13-15.
12. Mangunkusumo E. Hamadi F. Kurniawan.
Histopathologic Characteristics of Nasal Polyps in Jakarta, Indonesia. The Medical Journal of Malaysia 2004, Vol. 99: 224.
13. Hellquist HB, Nasal polyps update. Histopathology, Allergy Asthma Proc. 1997. Vol. 17 (5): 237-42.
14. Bucholtz GA, Ejercito VS, Burmester JK.
The Cystic Fibrosis Conductance Regulator Gene Exon Sequence is Normal in Patient With Edematous Eosinophilic Nasal Polyps. American Journal of Rhinology. 1999. Vol. 13(4): 221-3.
15. Dowell M. Ahmess L.Nasal Polypectomy: Should Antral Washout be a Routine? The Journal Of Laryngology and Otology 1992, Vol. 106: 695-6.
16. Kennedy DW, Bolger WE, Zinrelch SJ. Polyps. In: Disease of the Sinuses Diagnosis and Treatment. BC Decker, Inc. London 2001. 39-40.
17. Suheryanto R. Efektifitas Pengobatan Poilp hidung dengan Menggunakan Kortikosteroid. Kumpulan Naskah Ilmiah KONAS XII PERHATI, Semarang, Oktober 1999: 578-90
18. Siregar.A. Hubungan total Ig E Dengan Histopatologi Polip Hidung Di Bagian THT FK. USU/RSUP H. Adam Malik Medan. Tesis. 1995.
19. Paparella MM, Shumrick DA, Gluckman JS. Nasal Polyposis The Aspirin Triad And Non Allergic Rhinitis. In: Otolaryngology Head and Neck. Vol.III.3rd
Ed. WB Saunders Company. USA 1892.
20. Scavuzzo MC, Fattori B, Rocchi V, Carpi A, Berni R. Inflammatory mediator and eosinophilia in atopic and non atopic patiens with nasal polyposis. Biomed Pharmacother 2005, Vol. 59 (6): 323-9.