STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY ACHIEVEMENT AT CLASS XI OF SMK BUDI KARYA NATAR
LAMPUNG SELATAN
By
ARIFUL HAKIM
A Script
Submitted in a Partial fulfillment of The Requirements for S-1 Degree
In
The Language and Arts Department of Teacher training and Art Education Faculty
LAMPUNG UNIVERSITY BANDAR LAMPUNG
ABSTRACT
THE INFLUENCE OF USING PARLOUR GAMES TOWARDS STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY ACHIEVEMENT AT CLASS XI OF SMK
BUDI KARYA NATAR LAMPUNG SELATAN
By Ariful Hakim
This research was intended to find out whether there was an increase of students’ vocabulary achievement after being taught through parlour games and to know students’ response toward teaching vocabulary through parlour games.
Vocabulary is a component of language containing information about the meaning and the using of word in language. The pretest and the posttest with one group pretest-posttest, pre-experimental design was applied. The subject of the research was class XI of SMK Budi Karya Natar Lampung Selatan in the year 2011/2012. Vocabulary test in the form of multiple choices was used as the instrument of the research and repeated measures t-test was accomplished to analyzed the data. The results show that the students taught through parlour games seemed to be more enjoyable and interested in learning vocabulary since the students could provide a good response during teaching learning process. The teaching learning process challenged and involved all students in the game. It can be seen from the increase of the students’ mean score. The students’ mean score of the pretest was 56.50 while the mean score of the posttest was 63.40. After comparing the result of the pretest and the posttest scores, it was found that there was a significant increase, the mean score of the students had increased 6.9 after the treatments. Based on the data analysis the significant level of 0.05, it was noted that p=0.000. It proves that the students’ scores were significantly different (p<0.05, p=0.000) and the students’ active learning was better. So that the hypothesis (H) proposed in this research was accepted.
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendices page
1. Try Out Test. ... 57
2. Pre Test. ... 60
3. Post Test. ... 62
4. Lesson Plan ... 64
5. Distribution of Try out Test (Upper Students) ... 72
6. Distribution of Try out Test (Lower Students) ... 73
7. Reliability Analysis of Try Out Test ... 74
8. Difficulty Level of Try Out Test ... 75
9. Discrimination Power of Try out Test ... 76
10. Coefficient of the First and the Second Group... 77
11. Students’ Score of Pre Test ... 78
12. Students’ Score of Post Test ... 79
13. Students’ Score of Pre test and Post test ... 80
14. Frequencies of Pre Test ... 81
15. Frequencies of Post Test ... 82
xi
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
1. Table 3.1. Table of Specification of Try Out Test ... 30
2. Table 3.2. Table of Specification of Pre Test... 30
3. Table 3.3. Table of Specification of Post Test ... 31
5. Table 4.1. Distribution of Students’ Score of Pre-test ... 40
6. Table 4.2. Distribution of Students’ Score of Post-test ... 41
I. INTRODUCTION
1.1.Background of the Problem
English is an international language. Almost all countries have adapted English used as a compulsory subject at schools. The national education has decided that English as a foreign language taught in Indonesian schools. It learned started from primary schools up to university. People realize that teaching English at this level becomes very important and need much concern. As an English teacher, he or she demands to explore effective techniques, method, and approaches. The students have to master the four basic language skills. They are listening, speaking, reading and writing. Beside such basic skill, the student has to master some vocabularies as well as possible.
to use words correctly and effectively can help the students make school work easier and more rewarding, and also many tests that they take in school include vocabulary questions. The more vocabularies they know the better their chance to do well on an English test.
Tarigan (1986) states that the quality of language skill depends on the quantity and quality of vocabulary. The more vocabulary we have, the bigger possibility to have a skill to use the language. Mastering vocabulary is the ability to get or to receive a lot of words. By having and mastering vocabulary we will know the meaning of vocabulary in the context. Measuring vocabulary helps to avoid making mistakes in understanding. English vocabulary is needed especially for Indonesian students, started from elementary school up to university level in order to be successful in learning English. As Rivers (1980:14) states that it would be impossible to learn language without words, without vocabulary. It is also stated clearly by Wilkins (1980:11) who says that without grammar very little can be conveyed. We know that vocabulary is one of important factors in understanding and using language. So the mastery of vocabulary is needed in using English.
3
Furthermore, based on the writer’s experience, when doing his PPL at SMA Negeri 1 Natar, most of students haven’t achieved the target yet. Their vocabulary
was so poor that they felt English was difficult. The lack of studets’ nvocabulary is also caused by many factors, some of which are students’ strategies, students’ motivation, techniques used by the teachers in classroom, limited source material, etc. in relation to the techniques used in classroom, teacher can use various techniques to increase students’ vocabulary achievement.
Therefore, in presenting the material, it is important for the teacher to use a method or technique in teaching learning process. The use of method or technique is a very influential component in the classroom activity because it can create a situation to encourage the students to pay attention to the material presented that is vocabulary. Sometimes the teachers use technique inappropriately. The teacher teach vocabulary the same way as they teach the other aspects. Usually the teachers also stress their teaching too much on grammatical rules rather than on the vocabulary achievement.
Concerning with this, an alternative way of teaching vocabulary is urgently needed. The researcher realize by performing an interesting technique or
presentation the students will be motivated to learn English especially vocabulary. Besides that an interesting technique will avoid students’ laziness and boredom.
have a good experience or something in their life and it is impressed to their mind. It makes the vocabulary that they have learnt stay longer in their mind. As Allen (1983:52) states that the games are helpful because they can make students feel that certain words are important and necessary because without those words, the object of the games can not be achieved. So, it is true that game can be used as a technique to improve students’ English ability.
Hadfield (1995) states that Parlour Games are good exercises to teach vocabulary, grammatical structures and patterns. Parlour Games involve equal participant both slow and fast learners since Parlour Games are interesting, each students get engaged in the task or creativity. He proves that the students who learn vocabulary through parlour games could retain the words longer than the students who learn vocabulary through word list. Davidoff (1986) in his research result, states that parlour games can help the students to enlarge the words effectively.
5
1.2.Formulation of the Problem
In the line with the description above, the research problem is formulated as follows:
1. Is there any increase of using Parlour Games towards students’ vocabulary achievement?
2. What is students’ response of using Parlour Games in teaching vocabulary?
2.1.Objective of the Research
In reference to the problem, the objective of the research as follows: 1. To find out whether there is difference between students’ vocabulary
achievement before and after of using Parlour Games significantly. 2. To find out whether Parlour games can be used to increase students’
vocabulary achievement.
2.2.Uses of the Research
1. Theoretically, it is hoped that the research result can contribute of the teaching English.
2. Practically, it can be used as an alternative consideration in choosing the appropriate technique especially in teaching vocabulary.
2.3.Scope of the Research
would be conducted at class XI students of SMK Budi Karya Natar lampung selatan. It was conducted in five meetings.
2.4.Definition of Terms
1. Parlour Games is a group games played indoors which is played by the
average or intermediate level in Victorian era. It is a game in which the object is to guess some kind of information and instruction such as a word, a phrase, a thing, a title or the location of an object (Hadfield, 1995)
2. Vocabulary is the essential language learning that contains the type of vocabulary that is content words in the form of adjectives, noun, verbs, and adverbs, which will make language meaningful (Fries, 1945:38).
II. FRAME OF THE THEORIES
2.1. Concept of Vocabulary
Vocabulary is one of the four language components, which are spelling, grammar, phonology and vocabulary. It is an important element that cannot be separated from each other in language learning process, Since English as foreign language becomes an international language. No wonder, it becomes so important for foreign language learners to learn and master on it that it is a basic element of a language used before learning more about the foreign language. It happens when one who is learning a language has a great mastery on vocabulary, he will succeed in using the language being studied either in comprehending the meaning of a word in the context of spoken or written language.
Mifflin (2000:1) says “vocabulary as: 1) all of the words of a language; 2) the sum
of words used by, understood by, or at command of a particular person or group; 3) a list of words and often phrase usually arranged alphabetically and defined or translated: a lexicon glossary; 4) a supply of expressive means: a repertoire of communication”. While national institute for literacy defines vocabulary as words
In the line with the theories above, it is clear that learning vocabulary plays an important contribution in learning a language which must be considered by the teacher in order to be careful in selecting the vocabulary that will be taught. Teacher must decide which words should be taught since there are many kinds of words that belong to types of vocabulary.
Mcfayden (2007:1-21) divides content words into some categories: verb, noun, adjective and adverb. Verb is perhaps the most important part of the sentence. A verb assert the most important part of the sentence and expresses actions, events, or state of being. The second category is noun. Heather Macfayden says that a noun is a word used to name a person, animal, place, thing and abstract idea. Noun fall into five categories: proper nouns ( Sunday, Soeharto, Indonesia, etc.), common nouns (boy, chair, description, etc), material nouns (fish, stone, sand, etc),collective nouns (family, people, etc.), abstract nouns (beauty, honesty, kindness, etc).
The next category is adjectives. Adjective fall into two categories: descriptive and limiting. Descriptive adjective are those, which describe the colour, size, or quality of person or things (noun or pronoun). For example: beautiful, large, red, interesting, etc. It means that an adjective modifies noun or pronoun by
describing, identifying, or quantifying words. An adjective usually precedes the noun or pronoun, which it modifies.
9
where, how much. Many descriptive adjectives can be changed to adverbs by adding-ly suffix to the adjective base.
According to Burton (1982:98) a large number of vocabularies help the leaners to express idea vividly, precisely, and without repetition of word and with larger vocabulary they can better perform in all aspects of English language work. It means that by having a lot of vocabulary the learner can express their mind, make a sentences, interact and also chat the meaning form the sentences or from
speakers.
From explanation above, it can be summarized that vocabulary is one of the most important elements of the language that make the language meaningful and the total number of vocabulary that students’ master influence toward the ability to comunicate and share the idea. Besides, by mastering vocabulary, people may be able to comprehend what someone say and write. It means that the more words students have learnt, the more ideas students have and the more actively students can communicate.
This research focuses on the vocabulary which is classified into content word (noun, verb, adjective, and adverb) since the researcher assumes that is appropriate with senior high school.
2.2. Concept of Teaching Vocabulary
students. Allen and Vellete (1977:149) state that teaching vocabulary is an
important factor; so that teaching vocabulary should be taken into account and the technique that is used must be considered.
In the line with the statement above, it is true that among many techniques available, which can be applied in teaching language especially vocabulary. Teacher should choose one or more techniques that appropriate to teach vocabulary by considering the students’ condition.
Duke and Moses (2003) state that the effectiveness of raising word
consciousness by playing with words through games, songs and humour, and encouraging students to recognise when they have encountered new words and notice special characteristics of words.
In line with statement above, one way to make the students interested in learning vocabulary is that the teacher can use games as the technique in language
teaching. According to Wallace (1982:105) teaching vocabulary through game has two main reasons; first, to increase an emphasis on the importance of motivation and of positive affective atmosphere in the classroom, Second, to increase an emphasis on the importance of real communication. If a game works properly, it very often supplies a genuine desire to communicate in the target language, even with the artificial confines of room. So by those reasons explained above, it is clear that teaching vocabulary through games can motivate the
11
much, it means that they have a number of vocabulary. The researcher hopes that by applying this technique, the students will be interested in learning English.
2.3. Concept of Game
Teaching should not always be based on one or two strategies, they can be various, where teacher asked to be creative so that the class will not be passive and students will be stimulated to be more interested in learning and the result expected from the process of teaching and learning will be well transferred to students. Game is one of many teaching strategies can be engaged to foreign language learners, it is believed that it can give an elements of fun to learners. It has been the reason why I have been motivated to present a teaching strategy which involves a game as a media for teaching on vocabulary.
compete with each other. By this way, each group tries to be competitive participant in the game.
Nation (1974:19) points out the importance of challenge in attracting the students’ interest in learning vocabulary will give them attention and enthusiasm to the assignment. Further Nation (1990:24) adds the characteristic of good game, as follows:
1. Game should be suitable to the students’ level.
2. Game should motivate the students to enlarge their vocabulary. 3. The materials of the game should be challenging for the students.
Those ideas above, it is clear game can be used in language teaching, in order to make the students interested in learning and make the lesson more enjoyable and interesting. According to Dorry (1966:3) states that games can be introduced in three different stages during the lesson. They can be played at the beginning as the revision of material taught previously or as a kind of warm-up activity preparing for learning new material. Games can also be introduced during the main phase of the lesson. Then are used to practice material being covered. Another option is to introduce games at the end of the class, it is for summary or verification of the material, and make the students remember what they have learn before.
Before choosing the game, the teacher should consider some factors of good game in english teaching, it is supported by Tyson in Mei and Jang (2000:4) who states that there are some factors that should be considered before choosing the game as follows:
13
2. A game should involve “friendly competition”.
3. A game should keep all of the students involve and interested.
4. A game should encourage students to focus on the use of language rather than on the language itself.
5. A game should give students a chance to learn, practice, or review a specific language material.
Five factors above are so important in the selecting game, because there are so many kinds of game that are sometimes overlap. According Hadfield and Jill (1999:4) state that classifying game into categories can be difficult, because categories often overlap. She classifies language games into two types: linguistic games and communicative games. Linguistic games focused on accuracy, such as supplying the correct antonym. On the other hand, communicative games focused on successful exchange of information ideas, such as two people identifying the differences between their two pictures which are similar to one another but not exactly alike. Correct language usage, though still important, is secondary to achieving the communicative goal.
Concerning with the explanation above, the researcher conclude that game is activity that can be used in the language learning process. Besides that, it can create students’ creativity, motivating, a competitive, challenging circumstances.
2.4. Concept of Parlour Games
kinds of fun activities are needed to attract them and increase their attention in learning English.
They need activities which are exciting and stimulating their curiosity: They need to
be involved in something active (They will usually not sit and listen). One of the fun
activities which can be used in teaching English to the young learners is by using parlour games.
According to Hadfield and Jill (1995), Parlour Games are games played indoors which is played by the average or intermediate level of Victorian era. These games were played to amuse themselves at that time. It is a game in which the object is to guess some kinds of information and instruction such as a word, a phrase, a thing, a title, or the location of an object. By using these games, the researcher assumes that it can make the students interested in learning vocabulary, besides make the learning process more enjoyable and interesting.
Teaching vocabulary through Parlour games is possible to be applied in English teaching since this game can be used individually or in groups. There are many kinds of parlour games that can be applying in English teaching, but the
researcher choose two games, they are:
1. Sentence in the cup (charades)
Charades means something that is acted out, something pretend. In the game one person uses gestures to o act out the name of things, song, etc. They must not speak. They act out the tittle word by word. One word at a time.
15
Example: “Mechanic”
So the player must act like a “Mechanic”. Then use gesture to describe a “Mechanic”
When the other players guess “Mechanic” nod yes and they will get the point. Player 1 : act like “Mechanic”
Players : “guess”
Player 1 : does another act or gestures of Mechanic Players : Mechanic!
Player 1 : nods yes Etc.
2. Who am I (Botticelli)
In this game the player Pick a Chooser from the group; everybody else will be Guessers. The Chooser picks a title, a thing, and a famous person (or a non-famous one all of the players are familiar with) known as an Identity. It's important that the Chooser be familiar with the details of this person's life. The Chooser then tells the Guessers the first letter of the Identity.
Decide which Guesser will go first and let them ask a yes/no question relating to any famous person that has the same first letter in their last name. If the Chooser is able to answer the question, play goes to the next Guesser. If the Chooser can't answer it then the Guesser can ask a specific yes/no question about the subject. Play continues in this manner until the person is guessed or the Guessers give up.
Example:
thinking of Laszlo Biro" and asks their specific question about the Identity, such as "Is the person male?" Play then goes to the next Guesser. If a guesser thinks he knows who the person is, he will say "Is the person Tony Blair?" If he is correct then he becomes the next Chooser; if not, then play moves to the next Guesser.
Answer the Guessers with any person that you can think of when you are the Chooser, even if it isn't what they are thinking of. As long as your answer fits the question then play can continue, the Guesser can always ask the question again, forcing you to come up with a new name.
From the explanations above, the researcher assumes that parlour games can be applied for teaching English, especially English vocabulary.
2.5. Teaching Vocabulary through Parlour Games
Learning a foreign language is a complex task that teacher should be aware of good classes are the outcome of careful planning. Planning is closely related to motivational concerns. As far as possible, we must encourage students to feel positive about language learning. Whatever takes place in the classroom may provide this encouragement and good planning can ensure that it does, without adequate preparation, even the advanced skill class will fall flat on its face. However many teachers still consider game for teaching language as a frivolous activity and they think that games are used only for a short time. They do not realize that in using games, the real learning takes place when students in relaxed atmosphere, participate in activities that require them to use what they have drilled on.
17
should be taken into account by the English teacher in applying this game they are:
1. The learners’ age
The learners age should be noticed by the teacher in applying this game since the students who can join this game is in the average or in
intermediate level especially in the age of up to 14th. Hopefully by knowing this the teacher can select the material that suitable for the students.
2. The number of the students in the class
This term is used as the consideration for the teacher to decide whether the students in the class are divided individually or in groups. If the number of students in the class is more the teacher can group them.
3. Their ability to cooperate in a team
In this case the teacher has to evaluate or observe whether the students can work in a team or not since in the team work the students try to share their idea to other students. If the students can not work in a team (they just keep silent) the teacher may ask them to work in individually.
5. Their interest to take part in the activity
Students’ interest also plays an important role because if the students do
not interested in the game activity the learning process cannot be achieved.
Hadfield (1995) states that the teacher should consider the things such as; the learners’ age, the number of students in the class, their ability to cooperate in a
team, their language ability and their interest to take part in the activity in order to come to the teacher’s goal. He assumes that if parlour games applied in a good
way, it can help the students to improve their vocabularies. It is proved in his research result that the students who learn vocabulary through parlour games (Who Am I) could retain the words longer than the students who learn vocabulary through word list. Vocabulary learning is done through the information given by the players in the game. From those information students should guess the intended vocabulary. For example, one player has a word “mechanic” she/he should give information that lead other players to the correct guess. If the other players can guess the word correctly, it means that the purpose of the game to increase the students’ vocabulary can be achieved.
19
adds, students like acting by doing so they will easy to get knowledge of a language.
Concerning with the explanation above, the researcher conclude that there is a difference assumption both of them about rule in playing parlour game. Therefore in this researcher, the researcher would like to combine two assumptions (game) in order to give more variation in the class. The students learn the vocabulary not only through guessing from information but also from the instruction or action given in the game. Hopefully, by doing so, the students will find it easy to learn the language.
2.6. Advantages and Disadvantages of Parlour Games
the researcher believes that there are some advantages and disadvantages of Parlour Games.
2.6.1 Advantages of Parlour Games
- Parlour Games could make the students more interested in learning the material. When the students were interested in learning the material, they would give more attention to the lesson given. That condition gave a good chance for both the teacher and the students. On the occasion the teacher could deliver the material very well and the students could understand what they had learned on that day.
- Teacher didn’t need to explain too many materials to the students. The teacher just explained the materials needed by the students because they can
give the students more chance to understand the materials given because through playing they can learned something without realize that.
- Parlour games increase students’ talking time. Using parlour games quite simply substantially increases the opportunities the students get to speak english
- Parlour games more secure and positive classroom atmosphere. For the most students, being called n by the teacher to answer a question in front of their peers can be a frightening experience. Even if they think they have an idea about the answer, they are often not sure if it is correct. If they do not know the answer. Panic can occur and usually dead silence is the talking risk and making errors is all part of effective language learning. However, bu using parlour games there is a sense of security because they are working with their classmates to come up with an answer or accomplish a task.
21
2.6.2 Disadvantages of Parlour Games
- the teacher may feel like they are losing control of the class. Applying this game in teaching learning process was by attracting student’s interest to games, all of them were active and made noisy. Sometimes they too much moved and spoke. That condition made the teacher difficult to control them. - Students would speak only in their L1. The workshop participants came up
with several reasons why this may occur. These included the activity may be too difficult, it may be too easy or it may be just plain boring for the students. So the solution the participants offered was to choose actvities that are
relevant, interesting and fun for the students. Another occassion when students may use too much L1 when the do not understand the instructions. So the instructions must be very clear to the students, so they know exactly how to complete the task successfully. Some participants felt that giving instructions in the L1 was appropriate, especially for their level of the lower students.
2.7. Procedure of Teaching Vocabulary through Parlour Games
There are many types of Parlour Games that can be applied in language learning. According to Hadfield (1995) Parlour Games material and the Procedures as follows:
1. Who Am I (Botticeli) Game
players may ask a question. The first player should answer the other players’
question.
The procedures are as follows: a. The teacher greets the students.
b. The teacher encourages their attention by asking some questions related to the topic. For example by asking “ who wants to be a doctor”.
c. The teacher introduces “Who Am I” game to the students.
d. The teacher asks them to play the game. It will be started from the first group. A representative of the first group should answer the question given by the other groups. For example, they may ask a question “ Am I a person who work in the hospital?”or “Am I a person who work to repair a
machine?” then the first group should answer yes or no based on the right
or wrong guess or answer by the other groups. Each groups has the same chance to give their question.
e. The teacher allows the groups who give a right question to guess what word the first group thinks of. But if they get the wrong guess they have no chance to give more questions. If other groups can not guess the right question the first group should give clues. And if other groups still can not answer, the first group should tell the word. The right answer will be given 10 score and 0 for the wrong answer.
f. At the end of the game, the scores are tallied. The group with the most points is the winner.
23
2. Sentence in the Cup (Charades)
To play the game in which the students take one paper in the cup; then he or she must act like what he or she reads on the paper. Then, the member of the group should guess what she or he is doing.
The procedure as follows:
a. The teacher greets to the students.
b. The teacher encourages their attention by asking some questions related to the topic.
c. The teacher introduces “Sentence in the Cup” game to the students. d. The teacher divides the students into several groups and each group
consists of 4-6 students.
e. The teacher tells the rules and gives the example. The representative of the groups will take one paper in the cup and he or she must pantomime like what they read on the paper. After that the member of the group should guess what he or she is doing. If the group has correct answer the group will be given 10 points. And the other groups chance to take and act. But if the group has wrong answer other groups have a chance to answer it. f. At the end of the game, the scores are tallied. The group with the most
points is the winner.
2.8. Theoretical Assumption
Vocabulary is important element of the language; it consist of total number of word to make a language. Therefore to master a language students should master the element of the language that is vocabulary. In teaching vocabulary the teacher should choose the appropriate materials that will be taught for students and it should be based on the need of the students. Beside that the teacher should also select the appropriate technique that can make students interest in learning vocabulary.
There is the technique that can be used in teaching vocabulary; there is Parlour games. By using Parlour games the students will do the learning activities through such rules. They have a good experience or something happen to their life and it is impressed to their mind. It makes the vocabulary what they have learnt will stay longer in their mind.
25
2.9. Hypothesis
III. RESEARCH METHOD
3.1. Research Design
This is a quantitative research, which has one group pretest-posttest design. Researcher selected one class as the experimental group using simple random probability sampling.
The design can be presented as follows: T1 X T2
T1 is pretest X is treatment T2 is posttest
(Hatch and Farhady, 1982:20)
27
3.2. Population and Sample
The population of this research was the students at class XI of SMK Budi Karya Natar Lampung Selatan. There were six classes of class XI. Each class consisted 30-35 students. The researcher was choose one class as experimental class. In determining samples, the researcher uses simple random probability sampling, by using lottery.
3.3. Steps in Collecting the Data
In collecting the data, the researcher uses the following steps: 3.3.1. Conducting Try Out
Try out is to make sure that the test is appropriate to be used as a research instrument. This test was multiple choices tests which consist of 40 items with allocation time in 60 minutes. The 40 items of try out test was
reduced become 35 items to be used in pretest and posttest. The aim of try out test is to know the quality of the test which would be used as the instrument of the research and to determine which item should be revised for the pretest and posttest. This research used the result of try out test to measure the level of difficulty and discrimination power, to find out the validity and the reliability of the test.
3.3.2. Conducting pretest
Pretest was conducted before treatments. It used to know how far the students’ achievement of vocabulary before treatments is given. Pretest
3.3.3. Giving treatment
There are two treatments conducted in this research. Each treatment was held for 90 minutes consisting of procedure of teaching vocabulary through Parlour Games.
3.3.4. Conducting posttest
Posttest was conducted after treatments. They were 30 items of multiple choices in 60 minutes to find out whether there is any influence of using parlour games towards students’ vocabulary achievement after giving the treatments.
3.3.5. Analyzing the Data
In analyzing the data, the researcher was arranged the data systematically into a score table based on the pretest and posttest to see whether there is any influence of the students’ vocabulary achievement significantly.
3.4. Instrument Used for Collecting the Data
This research instrument is vocabulary test in the form of pretest and posttest. Pretest was given to check the students’ basic vocabulary achievement. It is done before the treatments. Posttest was used to get the data of the students’ vocabulary achievement after the treatment was given. Then, the researcher found out
29
3.4.1. Validity
A test is valid if the test measures the object to be measured and suitable with the criteria. To measure whether the test has a good validity, the researcher analyzes from construct and content validity.
a. Construct validity is concerned with whether the test is actually in line with the theory of what it means to know certain language knowledge skill. Knowing vocabulary means knowing; meaning, form, and pronunciation (Nation 1991). This is requires the students to show their knowledge on the meaning, form, and pronunciation of the words.
Table 3.1. Table of Specification (Try out test)
Word Class Items Total Percentage
(%) Verb 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,10, 11,
12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, and 20.
20 50
Noun 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, and 32.
12 30
Adverb 33,34, and 35. 3 7.5
Adjective 36,37,38,39, and 40. 5 12.5
Total 40 40 100
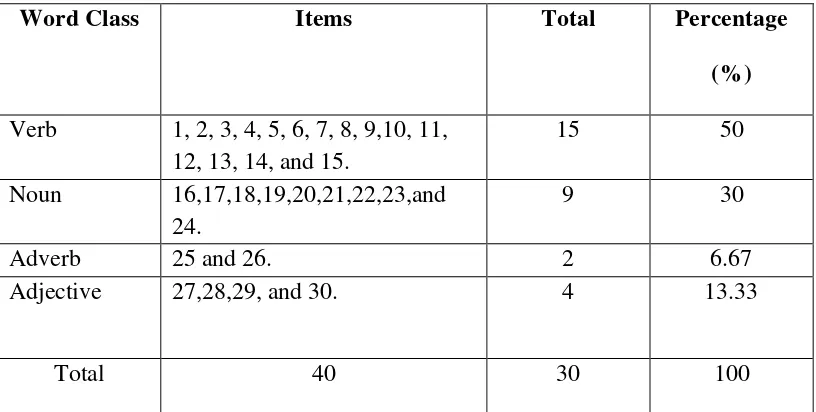
Table 3.2. Table of Specification (Pre test)
Word Class Items Total Percentage
(%) Verb 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,10, 11,
12, 13, 14, and 15.
15 50
Noun 16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,and 24.
9 30
Adverb 25 and 26. 2 6.67
Adjective 27,28,29, and 30. 4 13.33
31
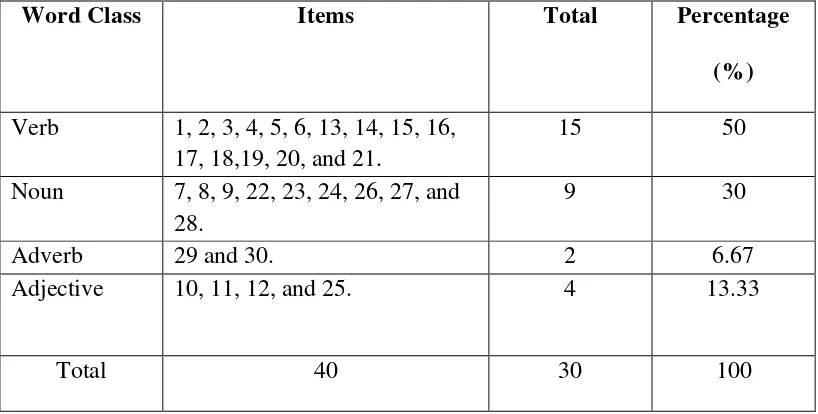
Table 3.3. Table of Specification (Post_test)
Word Class Items Total Percentage
(%)
Hatch and Farhady (1982:243) state that reliability of a test can be define as the extent to which a test produces consistent result when administered under similar conditions. In order to estimate the reliability of the test, this research used spilt-half technique and to measure the cofficient of the reliability between odd group and even group, this research uses “the
Pearson Product Moment Formula” as follows:
)
y = even number
2X = total score of odd number items
Y = total score of even number items
XY = total number of odd and even numberTo know the coefficient correlation of whole items “Spearmen Brown’s”
prophecy formula” (Hatch and Farhady, 1982:286) is used. The formula is as follows:
The criteria of reliability are: 0.80 – 1.00 : very high
33
U : the proportion of upper group students L : the proportion of lower group students
N : the total number of students following the test
The criteria are:
< 0.30 : difficult 0.30 – 0.70 : average > 0.70 : easy (Shohamy, 1985:79)
3.4.4. Discrimination Power
Discrimination power is used to indicate the discrimination of the failed and the success of the students. To see the discrimination power, the researcher will use the following formula:
N
DP : discrimination power
L : the proportion of lower group students N : total number of students
The criteria are:
1. If the value is positive, it has positive discrimination because a larger number or more knowledgeable students than poor students get the item correct. If the value is zero, it means no discrimination.
2. If the value is negative, it has negative discrimination because more low-level students than high-level students get the item correct
3. In general, the higher discrimination index, the better, in classroom situation most items should be higher than 0.20 index.
(Shohamy, 1985: 82)
3.4.5. Scoring System
In scoring the students’ result of the test, this research employed Arikunto’s
formula. The ideal highest score is 100. The score of pretest and posttest was calculated by using the formula as follows:
S=
� x 100%
Where,
S : The score of test
R : total of the right answer N : total items
35
3.6. Data Analysis
After conducting the pretest and posttest, the researcher analyzed the data. It is used to know whether there is an influence of using parlour games towards students’ vocabulary achievement.
The following steps are used to examine the students’ score: 1. Scoring the pretest and posttest
2. Tabulating the score of teaching English vocabulary test result using repeated measures t-test. The formula as follows:
3. Drawing conclusion from the tabulated result of the pretest and posttest administering, that is statistically analyzed using SPSS (Statistical Package For Social Sciences) in order to test whether the influence of stdents’ gain is significant or not.
3.7. Hypothesis Testing
After collecting the data, the reearcher recorded and analyzed them in order to find out wheter there is an influence of the students’ vocabulary achievement or not after the treatment. The researcher used matched T-test to know the level of significance of the treatment effect.
� 1 : Mean from pre-test
� 2 : Mean from post- test
� : Standard error of differences between means n : Subjects on sample
(Hatch and Farhady, 1982:114)
The criteria are:
V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
This chapter is intended to elaborate the conclusion and suggestion. It includes the explanation of the influence of using parlour games towards students’ vocabulary achievement, the obstacles faced by them and some suggestions for further research.
5.1. Conclusions
Having finished conducting the research and analyzing the data, the researcher draws the conclusions as follows:
1. Based on the research result, there was a significant difference of students’ vocabulary achievement who are taught through parlour games. it could be seen from the result of the hypothesis which showed that value two tail significance was smaller than (sign 0.00 < 0.05). it also supported by the data mean score of experimental class. The mean score of the pretest was 56.50 and the post test was 63.40. meaning that the experimental class gained 6.9 score. It means that parlour games was influence the students’
53 5.2. Suggestions
1. Since there is an influence of vocabulary achievement taught through parlour games, English teachers are suggested to use this game as the variation in teaching English vocabulary.
2. During the teaching learning process, the researcher saw that there were some students busy with themselves. To overcome this situation, the English teacher should arrange the students’ chair position and give time limitation in doing the game. It can make them focus their attention to the representative of a group coming in front of class.
3. It was found that there were some students did not know the meaning of some English words used as vocabulary target. Therefore, the English teacher should observe whether all the students in the class give
appropriate response or comprehend the vocabulary meaning which has been learned. It is needed to avoid the students’ misconception of the
REFERENCES
Allen, B Harold and Russel N Compbel. 1983. teaching English as Second Language.
Arikunto, S.1997. Dasar-Dasar Evaluasi Pendidikan. Jakarta: Bina Aksara
Dorry, G.N. 1966. Games for Language Learning. London and N. York: McGraw. Hill.
Duke,N. and Moses, A. (2003) 10 research tested ways to build children’s vocabulary. New York,NY: Scholastic Inc.
Fries, Charles. C. 1970. Teaching and Learning as Foreign Language. Ann Arbor: The university of Michigan Press.
Hatch, Evelyn and Farhady. 1982. Research Design and Statistic for Applied Linguistic. London: New Burry House, Inc.
Hadfield and Jill, C.1995. Reading Games. London. Longman. Mei, Yin Yong and Jang Yu-jing. Using Games in an EFL Class for
Children. DaejinUniversity ELT Research paper Fall, 2000. May 27, 2007. http://www.Teflgame.com/index/html
Mifflin, H. 2000. The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition. London. Houghton Mifflin Company.
Nation, I.S.P, 1990. Teaching and learning Vocabulary. Heinle and Heinle Publishers. United States of America.
Nation, I.S.P, 1974. Technique for Teaching Vocabulary. English teaching forum XIII. United States of America.
Rodger, Theodore. 1980. A Framework for Making and Using Language, Guidelines for Language Games. (i) Singapore; SEAMEO
Regional Language Center.
Setiyadi, Ag. Bambang.2006. Metode Penelitian untuk Penagajaran Bahasa Asing: Pendekatan Kualitatif dan Kuantitatif. Graha Ilmu Publish. Yogyakarta
Shohamy, E. 1985. A Practical Handbook in Language Testing for the Second Language Teacher. Tel Aviv. Tel Aviv University Press.
Sutardjo, Sukirah. 1985. Reading Technique for College Students. Jakarta. Depdikbud.Dikti.
Tata Mc Graw-Hill Publishing Company, Ltd.New Delhi.
Wallace, M.J. 1998. Teaching Vocabulary. New York: Haineman Educational.