THROUGH CONTEXTUAL TEACHING AND LEARNING
(A Classroom Action Research at the Second Grade of MAN Tarumajaya Bekasi)By:
Hadirotusholihah 106014000382
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYA AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
i
Hadirotusholihah. 2013. Improving Students’ Ability in Using Conditional
Sentence Type 2 through Contextual Teaching and Learning (A Classroom Action
Research at the Second Grade of MAN Tarumajaya Bekasi), Skripsi, English Education Department, Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers‟ Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta.
Advisor : Dr. Fahriany, M.Pd.
Keywords : Students’ Ability, Conditional Sentence Type 2, Contextual Teaching and Learning.
.
This research is aimed to know whether Contextual Teaching and Learning can improve students‟ ability in learning Conditional Sentence Type 2 at second grade of Social Class of MAN Tarumajaya Bekasi.
The method of this research is Classroom Action Research (CAR). The writer uses
Kurt Lewin‟s model. It is done in two cycles, and each cycle has four phases: Planning, Acting, Observing and Reflecting. Meanwhile, the data gained from the interview, questionnaire, observation, and test (pretest and posttest).
ii
Hadirotusholihah. 2013. Meningkatkan Kemampuan Siswa dalam Menggunakan Kalimat Pengandaian Tipe 2 melalui Contextual Teaching and Learning (Penelitian Tindakan Kelas pada Tingkat II IPS MAN Tarumajaya Bekasi), Skripsi, Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
Pembimbing : Dr. Fahriany, M.Pd.
Kata Kunci : Kemampuan Siswa, Kalimat Pengandaian Tipe 2, Contextual Teaching and Learning
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui apakah Contextual Teaching and Learning dapat meningkatkan kemampuan siswa dalam mempelajari Conditional Sentence Type 2 pada kelas XI IPS Madrasah Aliyah Negeri Tarumajaya Bekasi.
Metode pada penelitian ini adalah Penelitian Tindakan Kelas (PTK). Penulis menggunakan model Kurt Lewin. Penelitian ini dilaksanakan dalam 2 siklus, dan disetiap siklus mempunya 4 tahap: rencana, tindakan, observasi, dan refleksi. Pada penelitian ini data diperoleh dari wawancara, angket, observasi dan tes (pretest dan posttest).
iii
All praise be to Allah, lord of the world, who has given the writer His
blessing to finish this skripsi. The writer believes without his help, the writer
couldn‟t do anything. Peace and salutation is upon to the prophet Muhammad SAW, his family, his companion, and his followers.
This is a proud of occasion, the writer would like to express her great honor
to her beloved parents, Mr. Mustalab and Mrs. Ayanih who never stop giving their
prayers and greatest efforts for the writer in finishing this skripsi. She also would
like to say thanks a lot to her beloved brothers, Bunyamin, S.Pd.I, Kamaludin,
Abdul Gofur S.Pd.I, Isomulloh, and her lovely sister, Muniroh S.Pd, all of them
always give her support in finishing this skripsi, her beloved husband Ahmad
Zarkasih who always supports her with his love and his smile the writer gets spirit
and gets from her weakness up to finish this skripsi.
The writer also would like to say her sincere gratitude to his advisor, Dr. Fahriany, M.Pd who has patiently given her help, guidance, and corrections to finish this skripsi.
The writer also realizes that she would never finish writing this skripsi
without help of some people around her. Therefore, he would like to say a lot of
thanks to:
1. All lecturers and staffs of English Education Department.
2. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd, the head of English Education Department.
3. Zaharil Anasy, M. Hum, the secretary of English Education Department.
4. Nurlela Rifa‟i, M.A, Ph.D, the Dean of the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers‟
Training Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta.
5. Syarif Hidayat, S.Ag, the school principle of MAN Tarumajaya Bekasi.
6. Drs. Ma‟ali, the English teacher of MAN Tarumajaya Bekasi.
7. All friends in English Department, especially her beloved friends of class “B”
iv weakness of this skripsi.
Jakarta, 15 Mei 2013
v
ABSTRAK ... ii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... iii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... v
LIST OF TABLES ... viii
LIST OF FIGURES ... ix
LIST OF APPENDICES ... x
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION A. The Background of the Research ... 1
B. The Limitation of the Research ... 4
C. The Formulation of the Study ... 4
D. The Objective of the Study ... 4
E. The Significance of the Study ... 5
CHAPTER II : THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK A. Conditional Sentence ... 6
1. The Definitions of Conditional Sentence ... 6
2. The Type of Conditional Sentence ... 7
3. The Form of Conditional Sentence Type 2 ... 8
4. The Use of Conditional Sentence Type 2 ... 10
B. Contextual Teaching and Learning ... 11
1. The Nature of Contextual Teaching and Learning . 11 2. The Components of Contextual Teaching and Learning ... 12
3. The Strategies of Contextual Teaching and Learning ... 13
vi
C.The Place and Time ... 19
D. The Researcher‟s Role on the Study ... 19
E. The Data and Data Sources ... 19
F. The Research Design ... 21
G.The Classroom Action Research (CAR) Procedure ... 23
H.The Technique of Data Analysis ... 24
I. The Trustworthiness of Study ... 26
J. The Criteria of the Action Success ... 29
CHAPTER IV : RESEARCH FINDINGS A. The Description of Data ... 30
1. Findings of the Preliminary Study ... 30
a) The Result of Pre-Observation ... 30
b) The Result of Pre-Interview ... 32
c) The Result of Pre-Questionnaire ... 33
d) The Result of Pre-Test... 36
2.Findings of the Cycle 1 ... 37
a. Planning ... 37
b. Acting ... 37
c. Observing ... 39
d. Reflecting ... 40
3. Findings of the Cycle 2 ... 41
a. Planning ... 41
b. Acting ... 42
c. Observing ... 43
vii
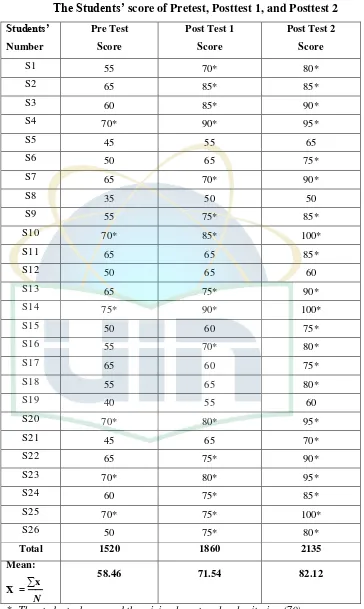
c. The Result of Post-Test ... 48
B. The Analysis of the Data ... 50
C. The Interpretation of the Data ... 55
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion ... 57
B. Suggestion ... 58
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 59
viii
Table 2.1 The Basic Form of Three Types of Conditional Sentence ... 8
Table 2.2 The Form of Conditional Sentence Type 2 ... 9
Table 3.1 Discriminating Power Scale ... 27
[image:12.595.150.460.253.567.2]Table 3.2 Item Difficulty Scale ……….. .. 28
ix
[image:13.595.154.442.271.566.2]Figure 3.1Kurt Lewins‟ Action Research Design ... 21
x
Appendix 1 The Instrument for Pre-test ... 61
Appendix 2 The Instrument for Post-test1 ... 65
Appendix 3 The Instrument for Post-test2 ... 68
Appendix 4 The Answer key of Pre-test, Post test 1, and Post test 2 ... 71
Appendix 5a The English Teacher‟s Interview and its Result before CAR ... 72
Appendix 5b The English Teacher‟s Interview and its Result after CAR ... 74
Appendix 6a The Interview Guideline for Students before CAR ... 76
Appendix 6b The Interview Guideline for Students after CAR ... 77
Appendix 7a The Result of Students‟ Interview before CAR ... 78
Appendix 7b The Result of Students‟ Interview after CAR ... 80
Appendix 8a The Questionnaire for Students before CAR ... 83
Appendix 8b The Questionnaire for Students after CAR ... 84
Appendix 9a Recapitulation of Students‟ Questionnaire before CAR ... 85
Appendix 9b Recapitulation of Students‟ Questionnaire after CAR ... 86
Appendix 10a Field Notes in the First Cycle (First Meeting) ... 87
Appendix 10b Field Notes in the First Cycle (Second Meeting) ... 88
Appendix 11a Field Notes in the Second Cycle (First Meeting) ... 89
Appendix 11b Field Notes in the Second Cycle (Second Meeting) ... 90
Appendix 12 Observational Checklist for Teacher‟s Activity ... 91
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents the introduction, which is consisting of the
background of the research, the limitation of the problem, the formulation of the
problem, the objective of the study, and the significance of the study.
A.
The Background of The Research
All people in this world need to communicate with each other. When they
communicate, they use a language absolutely. It can be spoken or written
form. “Language is a system for the expression of meaning”.1 By using
language, people can convey what they need, they want, and they mean.
According to Steven E. Weisler and Slavko Milekic, “language is an amazing
flexible tool that allows us a vast range of expressiveness”. 2 So that, for
expressing and communicating what they mean, they absolutely need a
language.
Today, English has an important role in education curriculum, and one of
the most influential languages in the world. English is not only used in
education, but also in many sectors of life such as politics, science and
technology, trading, and so on. Nowadays we had been facing a great
challenge in this global era. Anna Pakir states on her book that “one of the
greatest challenges facing language teachers in the classroom today is the
rapid development of English as a lingua franca for an inter-connected
world”.3 The teachers should be ready for great challenge above because
English is developed rapidly as a lingua franca for inter-connected world.
In mastering English, the students need to understand the English skill,
because gaining a new language necessarily involves developing four
1
Jack C. Richards and Theodore S. Rodgers, Approaches and Methods in Language Teaching, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 1986), p. 71
2
Steven E. Welster and Slavko Milekic, Theory of Language, (London: Massachussets Institute of Technology Press, 2000), p. 9
3
Ho Wah Kam and Christoper Ward, Language in the Global Context, (Singapore: SEAMEO Regional Language Centre, 2000), p. iii
modalities in varying degrees and combinations; listening, reading, speaking,
and writing.4 They are supported by English components, such as grammar,
vocabulary and pronunciation. If they master all above, they may be able to
use English in spoken or written communication.
Meanwhile, students who learn English will find a number of problems,
especially with grammar as a component of English. “Grammar is the correct
usage of the English language”.5 When they want to communicate either
spoken or written, it should be correct. So, what they want to convey will be
understood by others. The students sometimes find the difficulties in learning
English at this component. They think of grammar is a difficult subject and it
is confusing and hard to understand.
Grammar need to be taught appropriately because it is the basic element of
a language. Without the proper knowledge of grammar, the learners will find
many problems to express their ideas and built up sentences for
communication.
There are many aspects discussed in English grammar. One of them is
Conditional sentence. It is usually discussed after the basic verb forms.
“Conditional sentence is the sentence contains two clauses: a dependent clause beginning with if (or another conjunction performing the same general
function) and a main clause”.6 Conditional sentence as a part of grammar
rules sometimes makes the students confused moreover on conditional
sentence type 2 (unreal conditional sentence). Unlike conditional sentence
type I that may be easier to understand because it has not a change in the verb.
“Unreal conditional sentences are difficult for foreign students to understand because it seems that the truth value of a sentence is the opposite of the way
4
Rebecca L. Oxford, Language Learning Strategies: What Every Teacher Should Know, (New York: Heinle and Heinle Publishers, 1990), p. 5
5
Kathryn Riley and Frank Parker, English Grammar (New York: Chestnut Hill Enterprises, inc, 1998), p.1
6
the sentence appears”.7 Therefore students will find some difficulties in
learning conditional sentence because the value of a sentence is the opposite
of the way the sentence appears, so that they often misunderstand the
meaning.
Besides, the students‟ problem in learning conditional sentence is related
to their previous knowledge in English. They have not mastered the simple
past and also they have not mastered the irregular verb, so they face the
difficulties in the verb change in conditional sentence type 2. “Ron Cowan
stated on his book that the students have difficulties in mastering appropriate
tense sequences across clauses”.8
Teaching and learning can be successful when the students can directly
feel the advantages of learning materials by experiencing and learning it.
There are many other factors supporting teaching and learning process, such
as the using of appropriate media, learning materials which support teaching
learning process, class management, and teacher's method in conveying the
subjects, it means the teachers‟ ability and creativity in developing and conveying the materials in learning process optimally. The teachers must
apply the appropriate method in teaching and learning process.
To improve students‟ ability in using conditional sentence type 2, the teachers need to have the appropriate method to present the material in
teaching and learning process. Because “method is an overall plan for the
orderly presentation of language material, no contradicts, and all of which is
based upon, the selected approach”.9 If the teachers use an appropriate
method, the students will understand well and get high motivation to learn
English.
The writer use Contextual Teaching Learning as a suitable method in
teaching conditional sentence to improve students‟ ability in using Conditional
7
Michael A. Pyle and Mary Ellen Munoz Page, Test of English as a Foreign Language Preparation Guide, (New Delhi: Wiley Dreamlech, 2002), p. 115
8
Ron Cowan, The Teachers’ Grammar of English, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2008), p. 461
9
Sentence Type 2. Students will get higher ability and get the materials
optimally when the material is related to their daily life. “Contextual Teaching
Learning is a conception that helps teacher relate subject matter content to real
world situation and motivates students to make members, citizens, and
others”.10 It means that when teaching learning process, the materials should
be connected to the real life so the students will have critical and creative
thinking. By using CTL, the students may be able to make connections
between what they are learning and how that knowledge will be used.
Based on the background above, the writer is interested to choose the title
of her research that is Improving Students’ Ability in Using Conditional Sentence Type 2 through Contextual Teaching Learning.
B.
The Limitation of the Problem
To clarify the problem, the writer limits this research in using ccontextual
teaching learning to improve students‟ ability in using conditional sentence
type 2 at the second grade students of MAN Tarumajaya, Bekasi.
C.
The Formulation of the Problem
The writer formulates the problem as follows:
“Can Contextual Teaching and Learning improve students‟ ability in using conditional sentence type 2?”
D.
The Objective of the Study
The objective of the study in this Classroom Action Research is the writer
would like to find out whether contextual teaching and learning can improve
students‟ ability in using conditional sentence type 2 or not?
10
E.
The Significance of the Study
This study is expected to give the contribution to the English teachers, the
students, the school principal, and exclussively to the writer to try contextual
teaching learning method to relate students‟ real world situation and materials
they get. Furthermore, the English teachers are hoped to explore their English
teaching technique, especially in teaching conditional sentence type 2. The
writer hopes that this technique will help the teacher and the student in
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
This chapter discusses about the theoretical framework which is consisting
of conditional sentence and contextual teaching and learning. Conditional
sentence consists of definition, type of conditional sentence, form, and the use of
conditional sentence type 2, whereas contextual teaching and learning consists of
the nature of contextual teaching and learning, components, strategies, and the
benefits of contextual teaching and learning.
A.
Conditional Sentence
1.
The Definitions of Conditional Sentence
Conditional sentence is almost appears in every English textbook.
It usually comes after the chapters that present some of basic verb form
or somewhere in more advanced section of the book.
There are a lot of definitions of conditional sentence from the
language experts. According to Marianne Celce-Murcia and Dianne
Larsen-Freeman “conditional sentence is the sentences consisting of two
clauses, a subordinate clause, and a main clause”.1
George E. Wishon stated that “conditional sentence is the sentence
contains two clauses: a dependent clause beginning with if (or another
conjunction performing the same general function) and a main clause”.2
In another definition of conditional sentence from Martin Parott
“conditional sentences consist of two clausesa main („conditional‟) clause containing a verb with a form with will or would, and a
subordinated clause that is introduced by if.”3
1
Marianne Celce Murcia and Diane Larsen-Freeman, The Grammar Book: An ESL/EFL
Teacher’s Course, (Newbury: Heinle & Heinle Publisher, 1999), p. 545
2
George E. Wishon and Julia M. Burks, Lets Write English, (New York: Litton Educational Publishing, 1980), p. 249
3
Martin Parott, Grammar for English Language Teacher, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2000), p. 231
Based on the definitions above, the writer concludes that
conditional sentence is a sentence which consists of two clauses; a main
clause which containing modal auxiliary and a subordinated clause which
begins with if, unless or adverb clauses.
2.
The Types of Conditional Sentence
There are three different types of conditional sentences. Each type is
composed of a different combination of tenses. According to Marianne
C. Murcia and Larsen Freeman “conditional sentence is divided into
three types”, they are:
a. Future conditional : If I have money, I will take a vacation
b. Present conditional : If I had money, I would take a vacation
c. Past conditional :If I had had money, I would have taken a
vacation.4
George E. Wishon also stated that there are three types of
conditional sentences:
a. Future-Possible Condition
b. Present-Unreal Condition
c. Past-Unreal Condition.5
In the first type, the sentence expresses a future-possible condition
refers to an action that may or not may take place in the future. The
present tense of the verb is used in the if clause, and the future tense is
used in the main clause.
In present-unreal condition, the sentence describes a situation which
does not exist or unreal. We do not expect the condition in the if clause to
become a fact. The past tense of the verb is used in the if clause, and the
modal would, should, could, and might are used in the main clause.
4
Murcia. loc. cit. 5
In this type, the subjunctives were in the if clause is used for all persons: if
I were, if he were, if we were, if you were, etc.
The third type of conditional sentence is past-unreal condition. This
conditional sentence indicates past time and indicates an unreal and
unfulfilled situation. In this conditional sentence, the past perfect is used in
the if clause, and would have, should have, could have, and might have are
used in the main clause.
3.
The Form of Conditional sentence
As stated in chapter I, the writer has limited the discussion only at
conditional sentence type 2, but it is necessary to know the basic forms of
each types of conditional sentence.
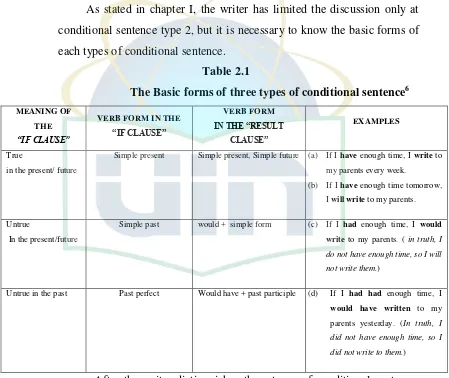
[image:22.595.91.540.292.670.2]Table 2.1
The Basic forms of three types of conditional sentence6
MEANING OF THE
“IF CLAUSE”
VERB FORM IN THE
“IF CLAUSE”
VERB FORM
IN THE “RESULT CLAUSE”
EXAMPLES
True
in the present/ future
Simple present Simple present, Simple future (a) If I have enough time, I write to my parents every week.
(b) If I have enough time tomorrow, I will write to my parents.
Untrue
In the present/future
Simple past would + simple form (c) If I had enough time, I would write to my parents. ( in truth, I do not have enough time, so I will not write them.)
Untrue in the past Past perfect Would have + past participle (d) If I had had enough time, I
would have written to my parents yesterday. (In truth, I
did not have enough time, so I did not write to them.)
After the writer distinguishes three types of conditional sentence,
the writer presents the form of conditional sentence type 2 further.
6
Here are the forms of conditional sentence type 2:
[image:23.595.144.507.150.557.2]Table 2.2
Form of Conditional Sentence Type 2 7 Affirmative statements
If Clause: Simple Past Result Clause: Would + Base Form of Verb
If I knew his telephone number I would call him
Negative Statements
If I did not know his telephone number I would not call him
Yes/No Question
Result Clause If Clause
Would I call him If I knew his telephone number?
Wh-Questions
What Would you do If you knew his telephone number
Short Answer
Affirmative Negative
Yes, I would No, I would not
General variants of conditional sentence type 2
The followings are possible variants of conditional sentence type 2:8
1. Using progressive verb form
If it were not raining, I would go for a walk
2. Using could, might, and should
If I were a bird, I could fly
7
Marjorie, Fuchs and Margaret Boner, Grammar Express for Self Study or the Classroom, (England: Pearson Education Limited, 2003), p.280
8
If you were a better student, you might get better grades
I shouldn’t get to sleep at all if I lived next the noise 3. Omitting If
Were Iyou, I wouldn’t do that
4. Verb form following wish
I wish I could speak Japanese
5. Using asif
She talked to him as if he were a child
4.
The Use of Conditional Sentence Type 2
Every type of conditional sentence has a specific form and usage.
The writer will try to describe the use of conditional sentence of type
2.
a. It can describe improbable future event or situation. The condition
is unlikely to be fulfilled because the future event is unlikely to
happen.
If the result of the test were positive, we would call you within two
days.
b. It can also describe a hypothetical current situation or event, i.e.
one which is contrary to known facts. It is therefore impossible to
fulfill the condition:
If the police were confident of their case against Sykes, surely they wouldn’t hasitate to take him into custody? (The police aren‟t confident of their case.)9
Beside, the second conditional is used to express a variety
functions:
Giving advice
If I were you, I would take her out of that school.
Polite request
9
If you could dealwith this matter, I’d be very grateful.
Desire/regrets
If we didn’t have to work so hard, we could spend more time together.
B.
Contextual Teaching and Learning
1.
The Nature of Contextual Teaching and Learning
In teaching and learning process the students need to get interesting
method. They want to get the teaching method which is more fun and easy
to be understood. Unlike the conventional point of view that knowledge
which is given from the teacher should be memorized by the students.
They have to memorize the concepts what the teachers gave. While,
students will understand the materials if they connect the subject with their
real life and it will be saved in long-term memory, and they do not need to
memorize compulsory. Contextual teaching and learning will improve
students‟ ability because it relates the students‟ real life to the subject
matter.
“Contextual Teaching Learning system is an academic material they are studying by connecting academic subjects with the context of
their daily lives, that is, with the context of their personal, social, and
cultural circumstances”.10
Susan Sears stated in her book that “contextual teaching learning is
a concept that helps teachers relates subject matter to real-world
situation”.11
By using Contextual Teaching Learning, students connect the
subject to their context in real life situation. Making these connections,
students see meaning in schoolwork. When students formulate projects or
identify interesting problems, when they make choices and accept
10
Elain B. Johnson , Contextual Teaching and Learning (Thousand Oaks: Corwin Press, 2002), p. 25
11
responsibility, search out information and reach conclusion, when they
actively choose, organize, touch, plan, investigate, questions, and make
decisions to reach objectives, they connect academic content to the context
of life‟s situation, and through those way the student will discover meaning. It means that students can get high understanding in their
learning.
From the definitions above, the writer concludes that contextual
teaching and learning is a concept that helps teacher and students to relate
academic material in teaching and learning process to the real word
situations.
2. The Components of Contextual Teaching and Learning
Here are seven components of contextual teaching learning:12
1. Constructivism
Constructivism is a process to motivate or to organize new
experience in students‟ cognitive structure based on their
experience. In constructivism, knowledge can be formed by two importance factors; they are the object which is the source of the observing, and the ability of the subject to interpret the object itself.13
2. Inquiry
Inquiry is the core of CTL process. While designing the tasks of activities in class, teachers should refer to an inquiry activity both in reading and speaking. Knowledge and skill that achieved by the students expected not from remembering the facts, but from self inquiry. The cycles of inquiry are observation, questioning, hypothesis data and gathering and conclusion.
3. Questioning
Questioning is not new strategy. In teaching and learning process, teachers have already applied this strategy. What is new is that questioning is not only monopolized by the teacher but also is asked by the students. It is natural to say that curiosity means questioning. If someone in curious about something, she/he will ask questions concerning the things she/he is observing. Good
questions can raise students‟ interest, motivate them and lead to
attract their attention to the phenomena observed.
12
Johnson, op. cit., p. 24
13
4. Learning community
Learning community suggests that the result of teaching and learning is resulted from doing tasks with other student in group. In other word sharing is needed among friends, other groups, and between make out person and not.
5. Modeling
Basically, modeling is verbalization of ideas, teacher demonstrates students to study and acting what the teacher need to be implemented by students. Modeling activity can be summarized
into demonstrates the teacher‟s opinion and demonstrates how does
the teacher wants the students learn. 6. Reflection
Reflection is the ways of thinking about what the students have learned and thinking about what the students have done in the past. Reflection is a figuration of activity and knowledge that just have received. Teacher need to do the reflections in the end of teaching learning process. In the end of teaching learning process, teacher spends a little time and ask student to do the reflection.
7. Authentic Assessment
Authentic assessment is the process of collecting the data that can give the description of student learning development. In the process of learning not only the teacher that can be placed to
provide accurate assessments of students‟ performance, but also
students can be extremely effective at monitoring and judging their own language production.
3. The Strategies of Contextual Teaching and Learning
The following are the strategies of CTL:14
a. Problem-based
Contextual Teaching Learning (CTL) can begin with a simulation or real problem. Students use critical-thinking and systematic approach to inquiry the problem or issue. Students may also draw upon multiple content areas to solve their problems. Worthwhile
problems that are relevant to students‟ families, school experience,
workplace, and communities hold greater personal meaning for students.
b. Using multiple context
Theories of situated cognition suggest that knowledge cannot be the physical and social context in which it develops. How and where a person acquires and creates knowledge is very important. CTL experiences are enriched when students learn skills in multiple contexts, such as school, community, workplace, and family.
14
c. Drawing upon student diversity
Diversity is a valuable resource for the learning all of participants in the classroom community. From the diversity, the students can work together to achieve real goals with others who are quite different from themselves, they learn to understand and value different viewpoints and abilities and to collaborate effectively with students tend to retain higher-level knowledge and skills longer when their learning experience by contexts that are close to real life as possible. d. Supported self-regulated learning
Ultimately, students must become lifelong learners. Lifelong learners are able to seek out, analyze, and use information with little to no supervision. To do so, students must become more aware how they process information, employ problem-solving strategies, and use background knowledge. CTL experiences should allow for trial and error; provide time and structure for reflection; and provide adequate support to assist students to move from dependent to independent learning.
e. Using interdependent learning groups
Learning groups, or learning communities, are established in workplaces and schools in an effort to share knowledge, focus on goals, and allow all to teach and learn from each other. When learning communities are established in schools, educators act as coaches, facilitators, and mentors.
f. Employing authentic assessment
CTL is intended to build knowledge and skills in meaningful ways by engaging students in real life, or "authentic" contexts. Assessment of learning should align with the methods and purposes of instruction. Authentic assessments show (among other things) that learning has occurred; are blended into the teaching/learning process; and provide students with opportunities and direction for improvement. Authentic assessment is used to monitor student progress and inform teaching practices.
4. The Benefits of Contextual Teaching Learning
The followings are the benefits of contextual teaching learning:15
Students are the subject of study (active)
Students learned by grouping activities, discussion, and sharing
knowledge
Learning process is connected to the real world situation
Students‟ abilities are achieved through their experiences
15
Students have responsibilities to organize and to develop the
learning process
The ‘setting’ of learning process is contextually.
C.
The Previous Related Studies of Conditional Sentence Type
2.
Many researchers have taken conditional sentence type 2 for their
research to get the students‟ problems in learning it. The previous
researchers used various methods in solving students‟ problems.
Widji Widjayanti stated that “the students who learn conditional
sentence may understand the syntactic change of each type, but they may
have difficulties in understanding the semantic all types”.16 Conditional
sentence type 1 may be easier to understand since it has same meaning in
Indonesian, but both conditional sentence type 2 and conditional sentences
type 3 may cause problems since according to the students these types do
not exist in Indonesian language. Indonesian students do not realize that
unlike conditional sentence type 1, both conditional sentence type 2 and
conditional sentence type 3 cannot be translated as jika, but seandainya. As
in If I had wings, I would fly to the moon, which should be translated as
seandainya (not jika) saya punya sayap, saya akan terbang ke bulan.
Students‟ awareness of differences in the meaning of the three conditional sentences can be seen through the way they translate the conditional
sentence.
From the stated above the writer concluded that the students still
have difficulties in the form and usage of conditional sentence type2, and
they often make the mistakes that conditional sentence type 2 refers to
present not past time.
16 Widji Widjayanti “
In another studies, Lia Nurshohifah stated that “conditional sentence
type 2 is difficult for the students to understand since the grammatical rule
in terms the verb form of English and Indonesian language is totally
different”. 17 It can be said that Indonesian language has no change in verb
form between present and past time, although in English it has a change of
verb form between present and past time.
In this research the writer tries to apply Contextual Teaching and
Learning to improve students‟ ability in using conditional sentence type 2.
The way of writer‟s teaching is totally different from the previous
researcher. She related the subject material with the students‟ real life.
By using contextual teaching and learning the writer connects the
students‟ materials with their real life, such as what they were facing in their
life, what they knew about the current issues around them, the most popular
figure they knew, their experience and so on. It would make them creative
and critical thinking to relate the subject matter.
The writer begins the lesson by reminding the students about the
irregular verb, because this was related to the material would be explained,
that is Conditional Sentence Type 2. Besides, she wants to increase their
vocabularies. She presents a slide within a picture of popular singer. The
aim is to connect students‟ real life with the subject material. Then she gives
them a question related to Conditional Sentence Type 2. Then she begins to
explain the pattern and the use of conditional sentence type 2. She also
explains the changes of the verb.
The students are divided into some groups. One student of each
group becomes a model to presents what they had got in group work.
Because of modeling is one of Contextual Teaching and Learning
components. She also gives some questions related to the conditional
sentence type 2. Its aim is to get the respond from the students with the
17Lia Nurshohifah, “ Improving Students’ Ability in
Learning Conditional Sentence Type
correct answer by grammatical pattern of the conditional sentence type 2.
And also they are more active in teaching and learning process.
The writer also applies fun learning. She uses a song lyric to
motivate the students in getting higher understanding in using conditional
sentence type 2. Then she gives assessment or evaluation to the students
about conditional sentence type 2.
All above is the writer‟s way of teaching which involved all of the
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter describes about The Method of Research, The Participants of
the Research, Time and Place of the Research, The Researcher‟s Role of the
Research, The Research Design, The Classroom Action Research (CAR)
Procedures, The Technique of Collecting Data, The Technique of the Data
Analysis, The Trustworthiness of the study and Criteria of the Action Success.
A.
The Method of Research
The method which is used by the writer in this research is Classroom
Action Research (CAR). Some experts have definitions of classroom action
research based on their opinions.
According to Suharsimi Arikunto, “classroom action research is an
action research which is carried out in the classroom aimed to improve
learning practice quality”.1
Michael J. Wallace stated that “classroom action research is a type of
classroom research carried out by the teacher in order to solve problems or
to find answers toward context-specific issues”.2
In another definition from James H. Mc. Millan and Sally
Schumacher, “action research is the process of using research principles to
provide information that educational professional use to improve aspects of
day-to-day practice”.3
From definitions above, the writer concludes that classroom action
research is an action research carried out by the teacher to improve learning
practice quality of day to day practice.
1
Suharsimi Arikunto, Penelitian Tindakan Kelas, (Jakarta: Bumi Aksara, 2008), p. 5
2
Michael J. Wallace, Action Research for Language Teachers, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006), p. 5
3
James H. Mc. Millan and Sally Schumacher, Research in Education, (Boston: Pearson Education, Inc, 2006), p. 414.
B.
The Participant of the Research
The participant of this research was students of Social Class at second
grade of State Islamic Senior High School, Tarumajaya Bekasi, and
academic year 2011/2012. The number of students is 26 (twenty six). In the
first meeting with the English teacher who teach them, he suggests her to
take the research at Social Class because he said that the students in social
class has low motivation in learning English and their scores are very low,
almost they could not achieve the minimal mastery level criterion (KKM) of
that school. So the writer accepted the suggestion of the English teacher to
hold the research in Social Class.
C.
The Place and Time
The place of this Classroom Action Research (CAR) is at MAN
Tarumajaya Bekasi. The research started from May up to the middle of June,
it held is about one half months.
D.
The Researcher’s Role on the Study
The writer held the research collaborates with the English teacher.
The writer‟s role is as a teacher who makes the lesson plan, prepares the
teaching media, and makes the pre-test before conducting Classroom Action
Research (CAR) and post-test after implementing the actions. Whereas, the
English teacher as a collaborator. Then, the writer and the English teacher
observe and analyze students‟ activities and their abilities in teaching and learning process.
E.
The Data and Data Sources
In this Classroom Action Research (CAR), the researcher used
qualitative data and quantitative data.
The following are the research instruments of collecting data used by
a. Questionnaire
“Questionnaire is a tool of collecting written data which consists of questions or statements and it arranged especially and used to get the
information to be analyzed”.4 In this research, the researcher gave the
questionnaire to the students of MAN Tarumajaya Bekasi grade eleventh
to reveal students‟ opinion of grammar class especially at conditional
sentence type 2 had been conducted both before and after implementing
CAR.
b. Interview
“Interview is a technique of collecting the data through directly communication (face to face) between interviewer (questions giver) and
interviewee (questions receiver)”.5 In this classroom action research,
researcher as an interviewer used interview guide to get the information
from the students and English teacher. In this case students and English
teacher are the interviewees. Interview activity involves 4 (four)
components; questions, interviewer, respondent, and the situation during
interview.
Before implementing contextual teaching and learning in the
classroom, the researcher asks to the English teacher to know about
students‟ ability, their motivations, and their scores in learning grammar especially in conditional sentence type 2. Then, after implementing the
actions, the researcher also asks to the English teacher to give the
feedback about the use contextual teaching and learning in teaching
conditional sentence type 2.
c. Observation
Observation is used to observe the writer and students‟ activities
generally during the process of teaching learning in the classroom.
4
Djudju Sudjana, Evaluasi Program Pendidikan Luar Sekolah, (Bandung: PT Remaja Rosdakarya, 2006)p. 177
5
d.Test
“A test is a formal, systematic, usually paper-and-pencil procedure for gathering information”.6 The Researcher used the test to know the
students‟ score improvement before and after implementing the Classroom Action Research. In this CAR, the researcher used three kinds
of test; pretest, posttest 1 and posttest 2.
F.
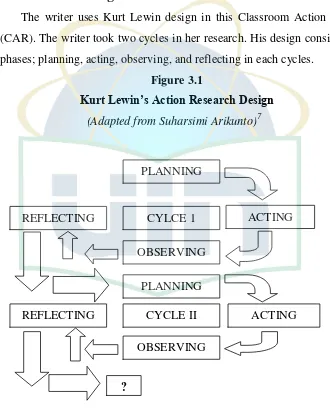
The Research DesignThe writer uses Kurt Lewin design in this Classroom Action Research
(CAR). The writer took two cycles in her research. His design consist of four
phases; planning, acting, observing, and reflecting in each cycles.
[image:35.595.135.465.272.681.2]Figure 3.1
Kurt Lewin’s Action Research Design
(Adapted from Suharsimi Arikunto)7
6
Peter W. Airasian, Classroom Assessment, (New York: Mc Graw Hill, 2008) p. 9 7
Arikunto, op. cit., p.16
PLANNING
ACTING CYLCE 1
REFLECTING
OBSERVING
PLANNING
REFLECTING CYCLE II ACTING
OBSERVING
From the figure above, we can see that CAR consists of four phases within
one cycle. They are planning, acting, observing and reflecting. If the students
cannot reach the criteria, so it is necessary to continue to the second cycle with the
same concepts of the first cycle which uses identical phases.
Based on the Kurt Lewins' Action Research Design above, the writer
described the detailed steps in this following figure.
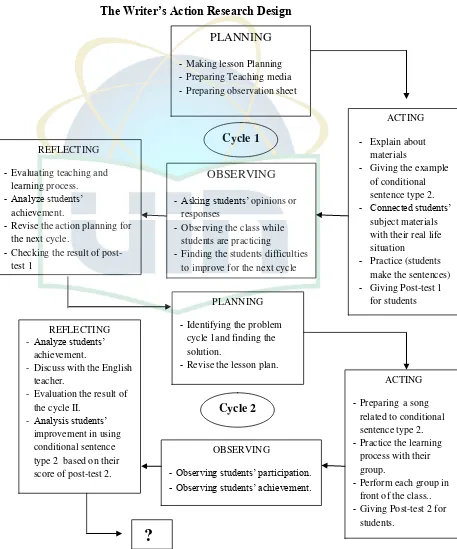
[image:36.595.116.573.254.803.2]Figure 3.2
The Writer’s Action Research Design
PLANNING
-Making lesson Planning -Preparing Teaching media -Preparing observation sheet
ACTING
- Explain about materials
- Giving the example of conditional sentence type 2. - Connected students‟
subject materials with their real life situation
- Practice (students make the sentences) - Giving Post-test 1
for students OBSERVING
-Asking students‟ opinions or responses
-Observing the class while students are practicing
-Finding the students difficulties to improve for the next cycle
PLANNING
- Identifying the problem cycle 1and finding the solution.
- Revise the lesson plan. REFLECTING
-Analyze students‟ achievement.
-Discuss with the English teacher.
-Evaluation the result of the cycle II.
-Analysis students‟ improvement in using conditional sentence type 2 based on their score of post-test 2.
REFLECTING
- Evaluating teaching and learning process. - Analyze students‟
achievement.
- Revise the action planning for the next cycle.
- Checking the result of post-test 1
ACTING
- Preparing a song related to conditional sentence type 2. - Practice the learning
process with their group.
- Perform each group in front of the class.. - Giving Post-test 2 for
students. OBSERVING
-Observing students‟ participation.
-Observing students‟ achievement.
Cycle 1
Cycle 2
G.
The Classroom Action Research (CAR) Procedures
The writer uses classroom Action Research which consists of four
phases within one cycle. They are planning, acting, observing and
reflecting. This research will be done on two cycles. If the first cycle has not
been achieved, it will be continued to the next cycle with the identical
phases of the first cycle.
The following are the explanations about four phases:
1. Planning phase
The first phase in this research is making a planning before
implementing the action in the class. In this phase, the writer prepares
what she needs to take the research, or what she uses in teaching and
learning process. She prepares the materials, makes lesson plan based on
the syllabus which is used at that school, prepares the teaching aids to
facilitate the research and also she prepares research instrument such as:
observation sheet, and the tests which are going to use in this Classroom
Action Research.
2. Acting Phase
Acting performed by the researcher to solve or answer the problem by
analyzing classroom organization, or who needs to be a collaborator, and
who will take the test. In this phase, both the researcher and the teacher
collaborate to carry out the planned action.
The researcher hold teaching learning process based on lesson
planning which has been arranged, with the material has been planned
based on the result of decision with observer.
After making the planning, the researcher begins to implement the
technique in the classroom and it is done in two meetings within each
cycle. Before implementing the first meeting, she gives the students
pre-test in order to know their ability in conditional sentence type 2.
3. Observing Phase
In this step, the researcher writes what all happened to know, and
either is appeared by planning or not in the class during acting. Collecting
the data needs observation or assessment format which is arranged to
accurate of performing scenario acting from time to time and the impact
toward the process of teaching and learning activity in the class.
4. Reflecting Phase
Reflecting is the last phase of classroom action research. It is a step
for processing the data which the researcher finds when acting
observation. It is necessary to hold evaluation for completing the next
cycle. The data are interpreted and analyzed by the writer. She works
collaboratively with the English teacher. His participation in this phase is
to help the researcher holds reflecting and evaluation accurately.
However, if the students have not reached the KKM, the writer will continue to the next cycle with the same concepts which uses identical
phases, they are; planning, acting, observing, and reflecting.
H.
The Technique of Data Analysis
In this research, the writer analyzes two kinds of data which have been
collected during the Classroom Action Research, there are: qualitative and
quantitative data. The qualitative data covers the observation of students‟
activities during teaching learning process, the interview before and after
Classroom Action Research and questionnaire. Besides, quantitative data is
gained from the students‟ score of pretest, posttest1 and posttest2. It is used to measure students‟ ability in understanding the material given and also to
know their improvement after learning the material by using the writer‟s
technique. To analyze this data, the writer uses formulas as follows:
First, the writer calculate the average of students‟ score each actions
wit one cycle. It is used to know whether the students can reach the KKM or
not. Here is the formula:8
8
X : mean
x : individual score
n : number of students
Then, the writer tries to get the class percentage which passes the
minimal mastery level criterion (KKM) of that school which is 70 (seventy). It
uses the formula:9
P : the class percentage
F : total percentage score
N : number of students
The last, after getting the mean of students‟ score per actions, the
writer identifies whether the students get improvement score in
understanding Conditional Sentence Type 2 from pre-test up to post-test in
cycle 1 and cycle 2. And to analyze it, he uses the formula:10
9
Anas Sudijono, Pengantar Statistik Pendidikan, (Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada, 2006), p. 43.
10
Ibid., p.46.
F
P = ── X 100% N
y1 - y
P = ───X 100% y
P : percentage of students‟ improvement
y : pre-test result
y1 : post-test 1
P : percentage of students‟ improvement
y : pre-test result
y2 : post-test 2
I.
The Trustworthiness of Study
To analyze the examined test items, the writer implements the
trustworthiness of the test; they are discriminating power and difficulty
items. It is aimed to identify the quality of test items which will be used in
this research.
Besides, the writer also examines the tests which are used as the
instrument of the study to get its validity. To analyze the examined test
items, the writer implements the trustworthiness of the test. It is used as the
evidence of the truth of this research. Furthermore, there are some phases
including:
1) Discriminating Power
The analysis of discriminating power of test items is to know the
performance of the test through distinguishing students who have high
achievement and low achievement.
y2 - y
And to calculate the discriminating power the writer uses formula as
follow:11
D = Ba – Bb Ja Jb
In which,
D : The index of discriminating power
Ba : The number of pupils in the upper group who answered the item
correctly
Bb : The number of pupils in the lower group who answered the item
correctly
Ja : Number of pupils in the upper group
Jb : Number of pupils in the lower group
[image:41.595.146.493.129.628.2]Furthermore, it uses the discriminating power scale as follow:
Table 3.1
Discriminating Power Scale
(Adapted from Suharsimi Arikunto)12
DP REMARK
0.70 - 1.00 Excellent
0.40 - 0.70 Good
0.20 - 0.40 Satisfactory
0.00 - 0.20 Poor
Negative Discarded
11
Suharsimi Arikunto, Dasar-Dasar Evaluasi Pendidikan, (Jakarta: Bumi Aksara, 1993), p. 218.
12
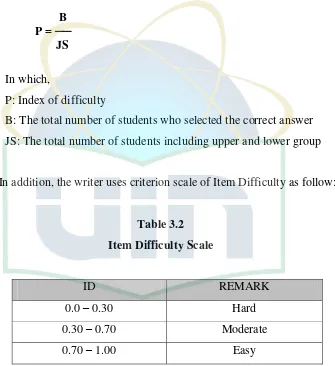
2) Item Difficulty
The difficulty item analysis concerns with the proportion of
comparing students who answer correctly with all of students who follow
the test. Item difficulty is how easy or difficult an item is form the
viewpoint of the group of students or examinees taking the test of which
that item is a part.13 The formula used as follow:14
B P = ── JS
In which,
P: Index of difficulty
B: The total number of students who selected the correct answer
JS: The total number of students including upper and lower group
[image:42.595.151.486.269.635.2]In addition, the writer uses criterion scale of Item Difficulty as follow:
Table 3.2 Item Difficulty Scale
ID REMARK
0.0 – 0.30 Hard
0.30 – 0.70 Moderate
0.70 – 1.00 Easy
13
John W. Oller, Language Test at School, (London: Longman Group Limited, 1979), p. 246.
14
J.
The Criteria of the Action Success
Classroom Action Research can be called successful when it fulfills
the criteria which have been determined, on the other hand it will be called
failed when the result cannot achieve the determined criteria.
In this study, the research will be success when there are 75% number
of students can improve their achievements from the pre-test until the
second post-test in cycle two and/or they can pass the target score of the
minimal mastery level criterion, which is seventy (70).
If the criteria mentioned above are achieved, the researcher will stop
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS
This chapter presents the result and discussion based on the data collected
from the implementation of Contextual Teaching and Learning to improve
students‟ ability in using Conditional Sentence Type 2 at second grade of Social class MAN Tarumajaya, Bekasi academic year 2011/2012. The discussion
presented The Description of Data and Analysis of Data. The Description of Data
consists of Finding of the Preliminary Study, Finding of Cycle 1, Finding of Cycle
2, and Finding after Implementing the Action. While Analysis of Data consists of
data analysis based on the data has been collected and the data interpretation.
A.
The Description of Data
1.
Findings of the Preliminary Study
The writer did the survey before implementing this research, and the
aim is to know the detail information about the class condition which
would be taken for this research. The further explanation will be explained
as follow:
a. The Result of Observation
Pre observation was done in order to observe the teaching and
learning activity of English grammar, especially in Conditional
Sentence Type 2 before implementing the action. It was conducted at
the second grade of social class of MAN Tarumajaya Bekasi academic
year 2011/2012. There consisted of 26 students. The researcher did
pre-observation on Wednesday, April 25th 2012.
While writer observed on teaching and learning process, she also
observed the way of the English teacher‟s teaching and the condition
of the students in grammar class especially in Conditional Sentence
Type 2. The English teacher gave the explanation of the material
without connecting simple past tense and irregular verb, although in
Conditional Sentence is very related to those materials (simple past
tense and irregular). Then he gave the formula of conditional sentence
type 2 and he asked to the students to memorize it. He did not connect
the subject matter with their life or what they had been facing in their
real life. This teacher-oriented technique was less effective because
the students were expected to remember the formula, consequently if
they did not remember it they would not be able to make the sentences
of the material was being taught. The teacher gave the example of
conditional sentence type 2 was too far from the real situation or their
real life so that they were difficult to understand the lesson. If he made
the example using hot issues or the event which had been facing in
their life, it would be easy to understand the lesson. Besides, the
teacher also told too much during teaching learning process, therefore
the students as good listeners without giving opportunities for the
students to give ideas or opinions, comments, even to ask the
questions. Finally, they got low scores in doing exercise.
While observing, she also absolutely paid attention to the
students during teaching and learning process. The students were lack
of vocabulary. The writer stated this statement because while she was
observing, many students asked the vocabularies they used in doing
exercises to another student. Moreover they didn‟t know the change of
the verbs. They haven‟t mastered either simple past tense or irregular
verb. As the result, they still made much mistakes in completing the
verb in conditional sentence type 2. It meant that the students got low
achievement.
Besides, the writer also observed the students‟ motivation while
teaching and learning process. She found that many students were not
serious in learning. They did not pay full attention to the English
teacher‟s explanation. Some of students made a joke with their friends, some of students looked so bored and they were not care
the students need the best method in their learning process in the
classroom. They need a method which can relate the subject matter
with their real experience, their real situation in their life, with the
realities they are facing in their life. So that they will understand the
subject matter easily, they will be more fun in learning, and they will
get higher motivation. As the result they will achieve the minimal
mastery level criterion (KKM) of the school.
b. The Result of Pre-Interview
Pre-interview in this research was done on Wednesday, May
2nd 2012. It was started from 10.30 a.m until 11.30 a.m. In this part,
the writer asked the English teacher some questions and she divided
the questions into three categories. They were students‟ general
condition in grammar class especially at conditional sentence type 2
and their performance, the difficulty faced by students and their
participation, and the last is about the method used by the teacher in
teaching and learning process.
First category discussed about students‟ general condition in
grammar class especially at conditional sentence type 2, their
performance and motivation. The teacher said that most of students at
social science second class of MAN Tarumajaya still got low
achievement in English grammar especially in Conditional Sentence
Type 2. They also were not serious and enthusiastic in teaching and
learning process. It could be seen from their attention in teacher‟s explanation, their response to the teacher‟s question, moreover in the
result of their tasks were given by the teacher, it was far from KKM of
the school, which was seventy (70).
The second category was about the difficulty faced by students
in learning conditional sentence type 2. Based on the English teacher‟s
answer, the students had difficulties in understanding conditional
sentence type 2, they could not make right sentence based on the
pattern of conditional sentence type 2, they did not know the use of
conditional sentence type 2, and also they did not understand the
change of the verb. It meant that they also had low understanding in
simple past tense and irregular verb.
At the last category was about the teacher‟s method. At the result of teacher‟s interview that he used speech and giving tasks.
Based on the teacher‟s answer of those questions above, writer
concludes that the students need an appropriate and interesting way in
teaching and learning process in order to get higher understanding in
using conditional sentence type 2.
Then, in interviewing the students the writer asked about their
feeling or interest in learning conditional sentence type 2, their
difficulty in understanding conditional sentence type 2, and their
response to the learning method of their English teacher. Based on the
result of pre interview with the students, the writer concluded that they
had low interest in learning conditional sentence type 2. Then they had
difficulties in the change of the verb in conditional sentence type 2,
most of them did not know the structure and the use of conditional
sentence type 2. Besides, the way of their English teacher made them
confused, and they wanted to get more interesting method to get
higher understanding in using conditional sentence type 2.
c. The Result of Pre-Questionnaire
Questionnaire is a tool of collecting written data which consists
of questions or statements and it arranged especially and used to get
the information to be analyzed.1 In this research pre-questionnaire was
taken on Thursday, May 3rd 2012. The result of pre-questionnaire
would be described as follow:
1
1. The students’ interest in learning grammar, especially in
conditional sentence type 2 by using their English teacher’s
method.
The result of questionnaire showed that 34.62% or 9 students like
studying English, especially in conditional sentence type 2 through
their English teacher method, and the rest of them 65.38% or 17
students did not like studying English, especially in conditional
sentence type 2 through their English teacher method. It can be
concluded that most of the students of social science second grade
of MAN Tarumajaya did not like learning grammar with their
English teacher‟s method.
2. The students’ enthusiasm in teaching and learning process
There were only 6 or 23.08% students felt enthusiast in teaching
and learning process, and majority 20 students or 76.92% students
did not feel enthusiast in teaching and learning process. The
researcher concluded that most of students did not feel enthusiast
in teaching and learning process.
3. The student knew the structure of conditional sentence type 2
The result of questionnaire showed that 73.08% or 19 students did
not know the structure of conditional sentence type 2, and there
were only 26.92% or 7 students who knew it. It could be concluded
that most of them did not know the structure of conditional
sentence type 2.
4. The students understood conditional sentence type 2 through their English teacher’s method.
There were only 4 or 15.38% students understood the conditional
sentence type 2, and the rest 22 or 84.62% students did not
understand conditional sentence type 2. It could be concluded that
most of students did not understand conditional sentence type 2
5. Feeling satisfied with their English score which had been achieved.
The result of questionnaire showed that 11.53% or only 4 students
felt satisfy with their English Score, and 88.54% or 23 students did
not feel satisfy with their score. The writer concluded that they did
not feel satisfy with their English score.
6. The students wanted to get a higher score
The result of questionnaire showed that 100% or 26 students
wanted to get a higher score. They did not want to get low score
because most of them had not passed the minimum mastery level
(KKM).
7. The students could answer or response the teacher’s question
about conditional sentence type 2.
The researcher concluded based on the result of questionnaire that
only15.38% or 4 students could answer the teacher‟s question, and
84.62% or 22 students could not answer it. It meant that most of
them did not have ability to answer or response the teacher‟s
question.
8. The students always did the task given by the teacher
The result of questionnaire showed that 26.92% or there were only
7 students who did the task given by the teacher, and 73.08% or 19