Brain Research 888 (2001) 326–329
www.elsevier.com / locate / bres
Short communication
Preconditioning by motor activity protects rat hippocampal CA1
neurons against prolonged ischemia
*
V.D. Gerasimov, D.P. Artemenko, O.A. Krishtal
Bogomoletz Institute of Physiology, Department of Cellular Membranology, 4 Bogomoletz Street, Kyiv, 01024, Ukraine
Received 8 May 2000; accepted 10 October 2000
Abstract
Recovery of orthodromic and antidromic population spikes in CA1 hippocampal slices of 30-day-old Wistar rats has been studied in the reperfusion period after prolonged (90 min) decapitation ischemia with and without preceding 15 min long non-voluntary motor activity of intact animals. The preconditioning motor activity significantly enhances the resistance of pyramidal neurons to ischemia at a temperature of 308C. The period of protection lasts for up to 40 min after the end of motor activity. In case the ischemia was started within 5–10 min after the preconditioning, complete restoration of the field potentials to preischemic control level could be achieved. These data are the first indication of the neuroprotective effect of preconditioning motor activity in CA1 damage after prolonged global ischemia. 2001 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved.
Theme: Disorders of the nervous system
Topic: Ischemia
Keywords: Global ischemia; Hippocampal slice; Population spike; Motor activity; Neuroprotection
Preischemic functional state and the level of metabolism in in vitro experiments that increased excitability promotes are among the factors determining the susceptibility of tolerance against anoxia in hippocampal slices [11]. Based central neurons to ischemic insults. It has been shown that on this data we decided to investigate how the post-short, sublethal cerebral ischemia (ischemic precondition- ischemic survival of central neurons depend on their ing) induces the tolerance of the neurons to subsequent preischemic functional state caused by the non-voluntary more prolonged, lethal ischemia [2,8,13]. Similar results motor activity of the animal. Hippocampal slices were were obtained in the experiments with preconditioning by used as the model neuronal tissue to study the effects of anoxia / hypoxia both in vivo and in vitro [3,4,12,14]. The global ischemia. Our results demonstrate a surprisingly exitotoxic hypothesis of ischemic neuronal death is based strong protective effect of preconditioning motor activity on the neurotoxic effects of high extracellular concen- in hippocampal pyramidal neurons subjected to the is-tration of glutamate released as the result of enhanced chemia.
excitatory synaptic activity. This toxicity is largely related Wistar rats (30-day-old) were used for investigation. To
21
to the Ca influx into the nerve cell [1,6]. Brief non-lethal induce global ischemia, the animal was decapitated and its ischemia does not reach the critical level for initiation of head, with intact non-perfused cerebral brain was kept in a neuronal death but produces, on the contrary, the acquired thermostatically controlled moist chamber for a certain tolerance to lethal ischemia [13,15]. In such ‘ischemia- period of time (ranging between 30 and 120 min) at 308C. tolerant’ neurons, intracellular calcium elevation is mark- Then the brain was rapidly removed and the slices of edly inhibited after an anoxic–aglycemic episode, as hippocampus (500 mm thick) were prepared with a vib-compared to the neurons in control [15]. It has been shown ratome in the usual way. The slices prepared immediately after decapitation were taken as a preischemic control value. The slices were placed in the chamber and
super-*Corresponding author. Tel.:1380-44-293-2466; fax: 1
380-44-256-fused at the rate of 1–2 ml / min with artificial
cerebrospi-2590.
E-mail address: [email protected] (O.A. Krishtal). nal fluid (308C) of the following composition (mM / l):
V.D. Gerasimov et al. / Brain Research 888 (2001) 326 –329 327
NaCl (124); KCl (3); KH PO (1.25); MgSO (2); CaCl2 4 4 2
(2); NaHCO3 (26); glucose (10), saturated with a gas mixture of 95% O215% CO at pH 7.4. Orthodromic and2
antidromic field potentials were recorded from dorsal and ventral CA1 stratum pyramidale with glass micropipettes filled with 130 mM NaCl (resistance 2–3 MV)). Bipolar metal (Ni / Cr) electrodes (0.05 mm thick) were used to stimulate either the Schaffer collateral–commissural path-way in stratum radiatum (orthodromic stimulus) or nerve fibers in the alveus (antidromic stimulus). The stimulus intensity evoking maximal responses was chosen. The survival of the number of excitable units was estimated by measuring the mean amplitude of the population spike. Before the start of the 90 min ischemia, the rats were preconditioned by swimming in a tank filled with warm (308C) water or by running in a free-rotating wheel. The duration of the motor activity was limited to 15 min. Unpreconditioned rats subjected to 90 min decapitation
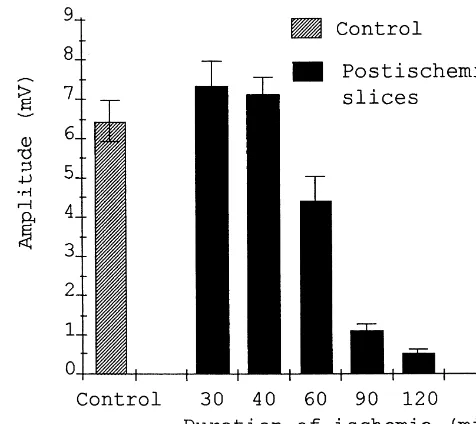
ischemia were used for postischemic control. Between 10 Fig. 1. Amplitude of the orthodromic population spike in CA1 hippocam-and 15 slices obtained from each animal were tested. pal slices measured during reperfusion period after decapitation ischemia of different durations indicated on abscissa. Each bar is a mean value of
About 30 measurements along the entire CA1 cell body
the maximum population spike6S.E.M. measured between 3rd and 7th
layer were made in each slice. The highest maximum
hour of the reperfusion (the data for each bar are from five rats). Here and
population spike value was taken from each slice to
below the ischemia was induced at 308C.
calculate a mean value for one animal. Mean amplitudes of both orthodromic and antidromic population spikes for
each animal were used for statistical analysis. All the data We have found no difference between protective effects are expressed as the mean6standard error of the mean. induced either by swimming or running. Therefore, the The unpaired Student’s t-test was used for statistical results are not discriminated depending on the type of
analysis. motor activity employed.
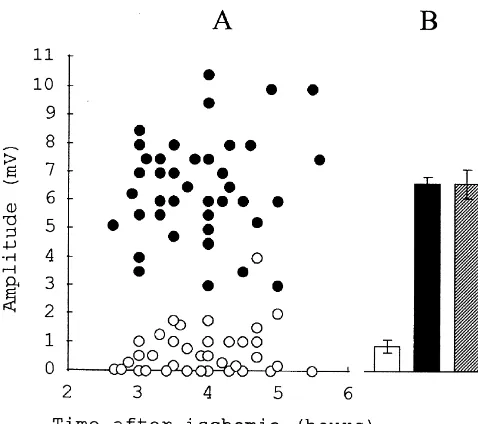
In the hippocampal slices prepared after a certain period Fig. 2 demonstrates the striking differences in the degree of cerebral ischemia, the gradual recovery of the electrical of the orthodromic population spikes recovery in the slices responses was usually observed. After the ischemia, lasting subjected to 90 min long decapitation ischemia for the rats up to 30–40 min, the amplitude of the population re- with and without preconditioning motor activity. In the sponses completely recovered in the course of 4–6 h of majority of preconditioned rats, the recovery of population reperfusion and often exceeded preischemic control level spikes started earlier in comparison with unconditioned (Fig. 1). This process started with the appearance of a ones and the time of restoration to the steady-state was small antidromic population spike, then the population about two times reduced. The motor activity before EPSPs could be observed in stratum radiatum and, at last, ischemia resulted in a dramatic increase in the mean orthodromic population spikes appeared in stratum amplitude of the restored orthodromic population spikes in pyramidale. After more prolonged ischemia, the amplitude comparison with postischemic tissue from the non-con-of electrical responses did not restore completely even ditioned animals (about 700%). The population EPSPs during 7–8 h of reperfusion (Fig. 1). Some slices lost the were increased as well. In many cases additional popula-ability to generate any electrical response. Thus, after 90 tion spikes could be recorded in the preconditioned tissue min of decapitation ischemia, the mean maximal amplitude in the reperfusion period: after the first orthodromic of the orthodromic and antidromic population spikes was population spike smaller and more prolonged second and respectively 1.1160.17 mV (27 rats, about 20% of the third delayed orthodromic spikes were recorded. These preischemic control) and 2.1360.18 mV (29 rats, about postischemic additional population responses may be due 30% of the control). However, when such period of to the attenuation of inhibitory processes as a result of ischemia was preceded with 15 min long intensive motor greater susceptibility of inhibitory interneurons to pro-activity of the animal, the mean maximal amplitude of longed ischemia and their incomplete recovery after re-orthodromic and antidromic population spikes reached perfusion [7]. Our preliminary observations indicate that 5.3260.46 mV (11 rats) and 6.1260.43 mV (11 rats) the late component of the orthodromic responses is sup-respectively (about 100% of the preischemic control pressed by small concentrations (bath application) of MK-value). The maximum amplitude of the population spikes 801, a noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist. in the preischemic control slices did not depend on the The protective effect of preconditioning motor activity
precondition-328 V.D. Gerasimov et al. / Brain Research 888 (2001) 326 –329
Fig. 3. Electrical responses of the hippocampal neurons subjected to 90 min of decapitation ischemia which was started at different time intervals (abscissa) after the end of motor activity. Bars represent the mean amplitudes of ortodromic (filled) and antidromic (open) population Fig. 2. Effect of preconditioning motor activity on the recovery of
spikes. The data are from 5–11 preconditioned rats for each interval and electrical responses in the rat hippocampal slices after prolonged
decapi-27 unconditioned rats for the control. tation ischemia. (A). Each point represents the maximum amplitude of the
orthodromic population spike recorded from one slice. Altogether the data were obtained from five control (empty circles) and five preconditioned
tioning remain unknown. The resistance of nerve and
(filled circles) rats during the reperfusion period after 90 min decapitation
myocardial cells to ischemia / hypoxia (which is quickly
ischemia. (B). Bars represent the averaged values of the population spike
manifested after the ischemic / hypoxic preconditioning)
amplitude. Open bar: unconditioned postischemic tissue (control). Filled
bar: preconditioned postischemic tissue. Shaded bar: non-ischemic tissue. lasts for up to 1–2 h. Some authors connect the changes in
Preconditioning motor activity lasted for 15 min. Immediately after the cell metabolism (reduction of O consumption, enhanced 2
period of motor activity 90 min decapitation ischemia was started.
glycolysis, depression of ATP consumption) with protec-tive effects of endogenously released adenosine, which ing motor activity, the mean maximum amplitude of the activates Al receptors as well as certain types of potassium recovered orthodromic population spikes were 2.3960.39 channels [5,9,10,12,17]. These factors may also be respon-mV and 5.3260.46 mV respectively. The protective effect sible, in part, for the tolerance induced in hippocampal of motor activity lasting over 15 min was not studied. neurons by preconditioning motor activity. Such tolerance In another series of experiments, we investigated how may depend on the reduction of nerve cell metabolism and long the protection against ischemia can last after cessation energy demand. Further experiments are needed to de-of the motor activity (the period between the end de-of motor termine the actual neuroprotective mechanisms of pre-activity and decapitation). Fig. 3 represents the mean conditioning motor activity. The effect itself may help to maximum amplitude of orthodromic and antidromic popu- understand basic mechanisms of ischemic damage. In lation spikes recorded after 90 min ischemia which started connection with this, it is interesting to note that sponta-either immediately after the end of the preconditioning neous locomotor activity of gerbils for 2 weeks preceding motor activity or 5, 10, 15 and 30 min later. Most 15–20 min forebrain ischemia reduces mortality of the significant protective effects corresponded to the minimal animal and attenuates delayed cerebral histological damage interval. Then the protective effect gradually declined and (except the CA1 area) [16].
in the case of 30 min interval there was no significant difference with control.
Our data indicate that preconditioning by motor activity Acknowledgements induces a significant, though short-lasting protection of
hippocampal neurons against ischemia. It markedly im- The work was supported by the grant from INTAS proves the ability of pyramidal neurons to recover somatic (96-1493, 97-0382) and from the Wellcome Trust. excitability and synaptic transmission following prolonged
global (decapitation) ischemia. Such protection is dramatic
even after 90 min decapitation ischemia at 308C. Similar References protective effects have been previously reported for
is-chemic and anoxic / hypoxic preconditioning both in vivo [1] D.W. Choi, M. Maulucci-Gedde, A.R. Kriegstein, Glutamate neuro-and in vitro [3,8,12–14]. The exact mechanisms for these toxicity in cortical cell culture, J. Neurosci. 7 (1987) 357–368.
20-month-V.D. Gerasimov et al. / Brain Research 888 (2001) 326 –329 329
´ ´
old gerbils long-term survival with functional outcome measures, [11] M.A. Perez-Pinzon, J.G. Born, I.M. Centeno, Calcium and increase Stroke 30 (1999) 1240–1246. excitability promote tolerance against anoxia in hippocampal slices, [3] J.M. Gidday, J.C. Fitzgibbons, A.R. Shah, T.S. Park, Neuroprotec- Brain Res. 833 (1999) 20–26.
´ ´
tion from ischemic brain injury by hypoxic preconditioning in the [12] M.A. Perez-Pinzon, P.L. Mumford, M. Rosenthal, T.J. Sick, Anoxic neonatal rat, Neurosci. Lett. 168 (1994) 221–224. preconditioning in hippocampal slices: role of adenosine, Neurosci. [4] N. Gordias, P. Maidatsi, M. Tsolaki, A. Alvanou, G. Kiriazis, K. 75 (1996) 687–694.
´ ´
Kaidoglou, M. Giala, Hypoxic pretreatment protects against neuro- [13] M.A. Perez-Pinzon, G.P. Xu, W.D. Dietrich, M. Rosenthal, T.J. Sick, nal damage of the rat hippocampus induced by severe hypoxia, Rapid preconditioning protects rats against ischemic neuronal Brain Res. 714 (1996) 215–225. damage after 3 but not 7 days of reperfusion following global [5] C. Heurteaux, I. Lauritzen, C. Widmann, M. Lazdunski, Essential cerebral ischemia, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 17 (1977) 175–182.
1
role of adenosine, adenosine Al receptors, and ATP-sensitive K [14] A. Schurr, K.H. Reid, M.T. Tseng, C. West, B.M. Rigor, Adaptation channels in cerebral ischemic preconditioning, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. of adult brain to anoxia and hypoxia in vitro, Brain Res. 374 (1986)
USA 92 (1995) 4666–4670. 244–348.
¨
[6] T. Kristian, B.K. Siesjo, Calcium in ischemic cell death, Stroke 29 [15] K. Shimazaki, T. Nakamura, K. Nakamura, K. Oguro, T. Masuzawa, (1998) 705–718. Y. Kudo, N. Kawai, Reduced calcium elevation in hippocampal CA1 [7] K. Krnjevic, Y.Z. Xu, L. Zhang, Anoxic block of GABA ergic neurons of ischemia tolerant gerbils, Neuroreport 9 (1998) 1875–
IPSPs, Neurochem. Res. 16 (1991) 279–284. 1878.
[8] Y. Liu, H. Kata, N. Nakate, K. Kogure, Protection of rat hippocam- [16] W. Stummer, K. Weber, B. Tranmer, A. Baethmann, O. Kempski, pus against ischemic neuronal damage by pretreatment with subleth- Reduced mortality and brain damage after locomotor activity in al ischemia, Brain Res. 586 (1992) 121–124. gerbil forebrain ischemia, Stroke 25 (1994) 1862–1869.
[9] G. Losano, D. Gattullo, P. Pagliaro, Myocardial, neuronal and [17] Z.L. Xu, H. Endon, A. Ishihate, E. Takahashi, K. Doi, Effect of vascular aspects of ischemic preconditioning, Life Sci. 59 (1996) ischemia preconditioning on myocardial oxygen consumption during
1185–1192. ischemia, J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 30 (1998) 2165–2174.