TEACHERS’ DIFFICULTIES IN LESSON PLANNING
A Paper
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
MIFTAH FARID
(0809325)
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
INDONESIA UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION
Teachers’ Difficulties in Lesson Planning
Oleh
Miftah Farid
Sebuah skripsi yang diajukan untuk memenuhi salah satu syarat memperoleh gelar Sarjana pada Fakultas Pendidikan Bahasa dan Seni
© Miftah Farid 2014
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia
April 2014
Hak Cipta dilindungi undang-undang.
Skripsi ini tidak boleh diperbanyak seluruhya atau sebagian,
Page of Approval
Teachers’ Difficulties in Lesson Planning
A Research Paper
By
Miftah Farid
0809325
Approved by:
First Supervisor Second Supervisor
Dr. Wachyu Sundayana, M.A. Lulu Laela Amalia, S.S., M.Pd.
195802081986011001 1975040920071022001
The Head of English Education Department
Prof. Dr. H. Didi Suherdi, M.Ed.
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Teachers’ Difficulties in Lesson Planning
Abstract
This study investigated the teachers’ preparation in developing lesson plans, in terms of formulating objectives, developing materials and media, plotting the
teaching procedures and conducting students’ evaluation; also pictured their consideration and difficulties in planning lessons for their classes. As the study employed qualitative data analysis, the data were collected through document analysis on lesson plans, also conducting interview with the teachers. The data then were analyzed using Miles and Huberman’s (1994) interactive model. The findings showed that in developing the lesson plans the teachers applied the systematic planning proposed by Reiser and Dick (1996), in which they started with analyzing the syllabus, followed by formulating objectives and indicators, selecting learning materials, and designing learning activities and assessment procedure. However, the interview result showed that the teachers dealt with some problems during the process, such as formulating indicators, selecting materials, determining learning activities, selecting media and developing assessment procedure. Based on the findings in this study, it is recommended that the teachers improve their competences in lesson planning.
Keywords: lesson plan, lesson planning, teacher’s difficulties
Abstrak
Dibawah bimbingan Dr. Wachyu Sundayana, M.A. dan Lulu Laela Amalia, S.S., M.Pd.,
penelitian berjudul “Teachers’ Difficulties in Lesson planning” menginvestigasi cara guru
mengembangkan RPP dan kesulitan-kesulitan selama proses pengembangannya. Dengan menggunakan pendekatan kualitatif, data diperoleh dari analisis RPP dan wawancara dengan para guru. Data kemudian dianalisis dengan model interaktif Miles dan Huberman (1994:12). Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa para guru mengembangkan RPP sesuai model perencanaan sistematis Reiser dan Dick (1996). Akan tetapi, para guru tersebut menghadapi kesulitan dalam mengembangkan beberapa bagian RPP.
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
TABLE OF CONTENT
1.6. Research Methodology... 4
1.7. Clarification of Terms ... 4
2.1.1. Definition of Lesson Plan and Lesson Planning ... 8
2.1.2. Significance of Lesson Planning in Teaching ... 10
2.1.3. Principles of Lesson Planning ... 12
2.1.4. Elements of Lesson Plan ... 14
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
2.1.4.2. Objectives ... 15
2.1.4.3. Learning Materials ... 16
2.1.4.4. Teaching Methods ... 17
2.1.4.5. Learning Activities ... 18
2.1.4.6. Assessment ... 20
2.1.5. Models/Approaches of Instructional Planning ... 21
2.1.6. Factors Considered in Lesson Planning ... 24
2.2. Problems of EFL Teaching in Indonesia ... 27
2.3. Related Studies on Lesson Planning ... 28
Chapter 3 Research Methodology ... 30
3.1. Research Design ... 30
Chapter 4 Findings and Discussion ... 36
4.1. Lesson Planning Procedure ... 36
4.1.1. Data from Document Analysis ... 36
4.1.1.1. Indicators ... 36
4.1.1.2. Objectives ... 38
4.1.1.3. Learning Materials ... 39
4.1.1.4. Instructional Media ... 40
4.1.1.5. Instructional Activities ... 40
4.1.1.6. Assessment ... 42
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
4.1.2.1. Indicators ... 44
4.1.2.2. Objectives ... 45
4.1.2.3. Learning Materials ... 46
4.1.2.4. Instructional Media ... 46
4.1.2.5. Instructional Activities ... 48
4.1.2.6. Assessment ... 49
4.2. Teachers’ Difficulties in Designing Lesson Plans ... 49
4.2.1. Data from Document Analysis ... 50
4.2.1.1. Lesson Plan 1 ... 50
4.2.1.2. Lesson Plan 2 ... 50
4.2.2. Data from Interview ... 51
4.2.2.1. Interview with the First Participant ... 51
4.2.2.2. Interview with the Second Participant ... 53
Chapter 5 Conclusion ... 55
5.1. Conclusion ... 55
5.2. Recommendation... 57
Bibliography ... 58
Appendices Appendix 1 Questions for Interview ... 66
Appendix 2 Analysis on Lesson Plans ... 68
Appendix 3 Lesson Plans ... 71
Appendix 4 Interview Transcript ... 82
Appendix 5 Interview Transcript (Coded) ... 96
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1. Stages in Designing Instructional Systems ... 7
Table 2.2. Events of Instruction and Their Relations to Process of Learning . 18
Table 3.1. Checklist for Lesson Plan Analysis based on Reiser and Dick’s
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 2.1. Kemp’s Instructional Design Model ... 21 Figure 2.2. PPSI Model ... 22
Figure 2.3. Reiser and Dick’s Systematic Planning ... 23
Figure 3.1. Component of Data Analysis: Interactive Model by Miles and
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
This chapter highlights the background of the study, research questions, purposes
of the study, the scope and significance of the study, research methodology, also
the clarification of terms and organization of the paper.
1.1. Background of the Study
The Decree of Minister of National Education No. 41 Year 2007 which explains
the development of teaching syllabus and lesson plan highlights the importance of
lesson planning stage in teaching. In line with this, Cunningham (2009) states that
having a well-designed lesson contributes to teaching success. As stated by Evans
(2009), good planning can also improve students’ motivation and positive attitude
toward the learning process.
However, during his teaching practice program in a high school in Bandung, the
writer had to prepare a 90-minute instruction within only 15 minutes as he was
suddenly asked to teach in a class by a teacher 15 minutes before it started.
Asking the teacher for the lesson plan, the writer was just told to continue the
previous lesson. Considering the writer’s position at the moment, that
phenomenon reflected that the teacher did not put consideration on the planning
before classroom instruction.
Previously, some research related to lesson planning have been conducted. Fishers
et al’s (1980 cited in Steere, 1988) study concluded that lessons need to be
structured so that the students know why the lesson is occurring, as they tend to
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
(2009) study on lesson plans made by teachers in two elementary schools in
Bandung showed that there was still a gap between each aspect of the lesson
plans, if they should meet the students’ characteristics. In addition, Wijayanto’s
(2010) study on the aspects taken by the elementary school teachers in designing
lesson plans indicated that the teachers were lack of the use of real media.
Moreover, some teachers still delivered their instruction using traditional
grammar-translation method. As mentioned by Emilia (2005), teacher practice
remains the same as it was in the past when the first English curriculum in
Indonesia was created, that is they focused on grammar. In contrary, Lynch (2000
as cited in Reese, 2002) states that most high school students find the traditional
teaching methods involving lecturing, lecturing with overhead or chalkboard, and
working or reading at one's desk are boring.
To picture those phenomena, especially the teachers’ preparation before
conducting an instruction and the difficulties they encounter during the process,
the writer is interested to conduct a study on the teachers’ difficulties in lesson
planning. Taking two English teachers in a vocational school as participants, this
study is focused on the teachers’ consideration in designing learning activities for
the students, as well as the difficulties that the teachers encountered during the
process of lesson planning considering that each teacher has to teach more than a
class, which consists of 24 credit hours in a week, as stipulated in the Decree of
Minister of National Education No. 30 Year 2011.
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
In order to explore how the English teachers prepare their teaching and face their
difficulties in planning a lesson, the writer has formulated the research questions
as follows:
1. How do teachers plan their lessons, in terms of setting indicators and
objectives, selecting materials and media, plotting the teaching procedures
and conducting students’ evaluation?
2. What difficulties do the teachers encounter in planning a lesson?
1.3. Purpose of the Study
This research is conducted to meet the following aims:
1. To picture teachers’ preparation before conducting a lesson in terms of
designing learning activities to conduct in classroom, particularly in setting
indicators and objectives, selecting materials and media, plotting the teaching
procedures and conducting students’ evaluation
2. To investigate the difficulties faced by the teachers in planning lesson
1.4. Scope of the Study
This study focuses on picturing teachers’ preparation before class which includes
the process of designing learning activities, particularly in setting indicators and
objectives, selecting materials and media, plotting the teaching procedures and
conducting students’ evaluation; also investigating their consideration and
difficulties in planning lessons for their classes.
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
The study depicts the lesson planning stage before conducting a classroom
instruction, particularly on the issue of teachers’ selection in developing
classroom activities for the students. Theoretically, the result of the study is
expected to reinforce the importance of lesson planning stage in teaching.
Practically, the result of the study can provide teachers with classroom practice for
their own classes. This study is also expected to help fresh-graduated teachers in
picturing how to develop classroom activities in the future based on the
experiences of the senior teachers.
1.6. Research Methodology
As the purpose of this study is to portray teacher’s preparation before class, which includes their difficulties in planning lessons and their considerations in deciding
classroom activities for the students, the writer conducts the study as a case study,
in which the researcher explores a bounded system (a case) or multiple bounded
systems (cases) over time, through detailed, in-depth data collection involving
multiple sources of information, and report a case description and case-based
themes (Creswell, 2007:73).
Involving two English teachers in a vocational high school as participants, this
study employs document analysis and interviews with the participants as the
means of data collection. First, the teachers’ lesson plans are analyzed using
Reiser and Dick’s (1996) concept of systematic planning. Later, semi-structured stimulated interviews are conducted with the teachers to find out how the teachers
plan their lessons.
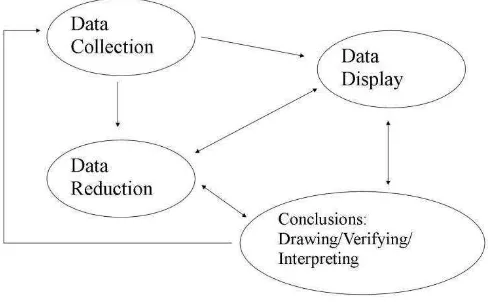
As the data are collected, they are analyzed using Miles and Huberman’s (1994) interactive model which divides the data analysis procedures into three steps; data
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
For details of the procedures, this topic will be elaborated further in Chapter 3.
1.7. Clarification of Terms 1.7.1. Lesson Plan
Lesson plan in this study refers to a series of guidance for teachers in conducting
their classes. Farrell (2002, in Richards and Renandya, 2002) describes lesson
plan as a written description of how students will move toward attaining specific
objectives. In line with this, Milkova (2011) defines a lesson plan as the
instructor’s road map of what students need to learn and how it will be done
effectively during the class time.
1.7.2. Lesson Planning
Lesson planning is defined as considering the students, thinking of the content,
materials, and activities that could go into a lesson to ensure the lesson is good
(Woodward, 2001). Farrell (2002, in Richards and Renandya, 2002) also defines
lesson planning as the daily decisions a teacher makes for the successful outcome
of a lesson. In this study, lesson planning refers to the process in which a teacher
prepares a lesson/instruction before conducting it in the classroom.
1.8. Organization of the Paper
This paper is organized into five chapters: introduction, theoretical foundation,
research methodology, findings and discussion, also conclusion and suggestions.
The first chapter is introduction. It presents the background of the study, which
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
covers the research questions, the purposes of the study, scope of the study,
significance of the study, research methodology, clarification of terms, and the
organization of paper.
The second chapter, theoretical foundation, covers the theories supporting the
issue of lesson planning. The discussion covers some theories of lesson planning
including the definition of lesson plan and lesson planning, its significance in
teaching, the principles of lesson planning, elements of lesson plan,
models/approaches of lesson planning, and factors to consider in lesson planning.
The discussion also covers some problems of EFL teaching in Indonesia, also
related studies on lesson planning.
The third chapter, research methodology, discusses the framework and design
employed in the study.
The fourth chapter, findings and discussion, explores the findings obtained in the
study, as well as the discussion related to the theories used as basis of the study.
The discussion covers lesson planning procedure, teachers’ considerations in
planning a lesson, also elements of lesson plan and the difficulties encountered by
the teachers during the process of planning.
The last chapter, conclusion, concludes the paper with some conclusions obtained
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu CHAPTER 3
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter highlights the methodology employed in the study. The discussion
covers research design, site and participants, data collection method, and data
analysis procedure in the study.
3.1. Research Design
This study is conducted as a case study, in which the design focuses on a particular
unit or set of units – institutions, programs, events, etc – and the aim is providing a
detailed description of the units (Richards, 2003:20). Similarly, Creswell (2007:73)
mentions that this design enables the researcher to understand an issue or problem
using the case as a specific illustration.
As the study is trying to explore how the teachers prepare the lessons to be conducted
in the classroom, including their considerations in selecting materials, learning
activities and assessment procedures for the students; this design is well suited for the
study for its specific-illustrated nature.
3.2. Site and Participants
The data are taken in a vocational school (Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan – SMK) in Bandung, West Java. The school is chosen as site of the study as it is accessible for
conducting the study, which fits one of the considerations in conducting a research
proposed by Cohen et al. (2007:100).
As this study is conducted in the context of school based curriculum (Kurikulum
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
research questions in this study; which are to do with lesson planning procedure in
the school, especially in the context of KTSP. In addition, those teachers are available
and willing to participate in this study. Those criteria match the considerations in
conducting a research proposed by Gay et al (2006), also Hancock and Algozzine
(2006).
3.3. Data Collection Method
The data used in this study are obtained from documents and interviews with the
participants. As mentioned by Richards (2003:20), qualitative study usually involves
multiple sources of information in order to generate rich description of the case. Thus,
those procedures are conducted to get the clear information regarding the teachers’
difficulties in planning lessons. The details of each instrument can be seen in the
following subsections:
3.3.1. Documents
The documents used in this study refer to lesson plans which are collected from the
participants in the beginning of the study. As mentioned by Gay et al (2006:421),
qualitative researchers examine various types of records or documents to gain
valuable insights, identify potential trends and explain a phenomenon (See also
Hancock and Algozzine, 2006 for similar discussion).
The two lesson plans apply the standard format of the school, i.e. written in Bahasa
Indonesia and consisted of several elements such as title, number of lesson plan,
identity (school name, lesson, grade and semester), basic competence, competence
code, competence standard, indicators, allotted time, lesson objectives, materials,
teaching method, learning activities, teaching media, reference, and assessment
procedures. However, this format is still in line with the elements of lesson plan
mentioned in Decree of Minister of National Education No. 41/2007 regarding the
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Related to the aims of this study which focus on the teachers’ decisions in setting
indicators and objectives, selecting materials and media, plotting the teaching
procedures and conducting students’ evaluation, some elements of the lesson plans
such as title, number of lesson plan, identity (school name, lesson, grade and
semester), basic competence, competence code, competence standard, allotted time,
and the reference will not be elaborated in the following chapters.
3.3.2. Interview
Another method of collecting data in this study is interview with the participants.
Hancock and Algozzine (2006:39) mention that interviews are frequently used in case
study research. The interviews in this study are conducted as non directive interviews,
which mean that the interviewer has a number of key issues which s/he raises in
conversational style instead of having a set questionnaire (Cohen et al, 2007:356).
In this study, the interviews are conducted with the teachers to find out how the
teachers plan their lessons. The questions are developed based on the Process
Standard in Decree of Minister of National Education No. 41/2007 regarding the
development of lesson plan and principles of lesson planning, supported by Gagne
and Briggs’ (1979) theory about principle of instructional design (See Appendix 1 for the detailed list of the questions).
The interviews are conducted in Bahasa Indonesia in order to keep the conversation
communicative and natural. Audio-taping is required in this study to avoid losing
important information provided by the participants, as suggested by Creswell
(2007:134).
3.4. Data Analysis
As the interviews have been conducted and audio-taped, the next step to do is
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
with teachers are analyzed using qualitative method in order to identify teacher’s
difficulties in planning lessons and their considerations in deciding classroom
activities.
In analyzing the data, the writer employs the interactive model by Miles and
Huberman (1994:12) which divides the data analysis procedures into three steps; data
reduction, data display and drawing conclusion and interpretation. The data analysis
begins as the observation conducted, and keeps on going during the whole study. The
process can be seen in the following figure:
Figure 3.1. Components of Data Analysis: Interactive Model (Miles and Huberman, 1994:12)
After the data are collected, the first step of data analysis is data reduction, which
refers to the process of selecting, focusing, simplifying, abstracting, and transforming
the data that appear in written-up field notes or transcriptions (Miles and Huberman,
1994:10).
The second process involved in the study is data display. Miles and Huberman
(1994:11) define data display as “an organized, compressed assembly of information
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
analysis and interviews are classified and analyzed to get clear description from the
data. Regarding this, Hancock and Algozzine (2006:57) mention that summarizing
and interpreting information are key aspects of doing case study research. In this step,
the researcher is writing the research report, including the researcher’s interpretation of the data (Lodico et al., 2010).
Finally, the last step in Miles and Huberman’s (1994:11) interactive model is
conclusion drawing. In this study, the conclusion is drawn to get a description of
teacher’s difficulties in planning lessons and their considerations in deciding classroom activities.
The detailed procedure of data analysis can be seen in the following subsections:
3.4.1. Document Analysis
In this study, lesson plans are analyzed to get a broad picture of the instruction before
it is conducted in the classroom, in relation to the first research question. Later, the
lesson plans are analyzed using several categories in Reiser and Dick’s (1996)
Systematic Planning, as mentioned previously in Chapter II. The checklist can be
seen as follow:
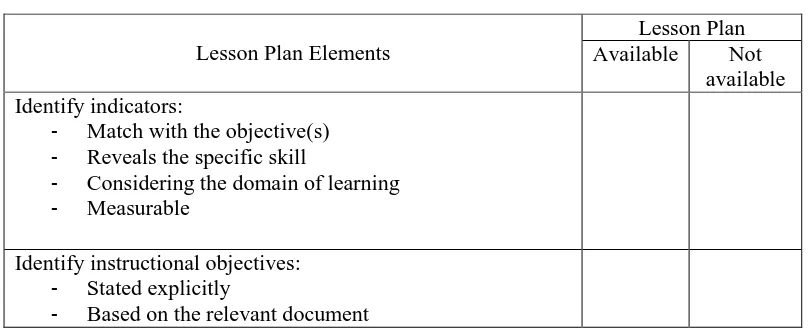
Table 3.1. Checklist for lesson plan analysis based on Reiser and Dick’s (1996)
Systematic Planning (Adapted from Jannah, 2008)
Lesson Plan Elements
- Considering the domain of learning
- Measurable
Identify instructional objectives:
- Stated explicitly
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu - Translated on the instruction
- Measured on the assessment tools
Choose the material:
- Appropriate with the goals and objectives
- Appropriate with student’s level
- Relevant with the condition & students’ characteristics
Plan instructional activities:
- Reflecting students-centered instruction
- Reflecting communicative method
- Motivate students to learn and to expose foreign language
- Helping students to recall prerequisite
- Presenting information and examples
- Integrating the four skills (reading, listening, speaking & reading
The results of interviews with participants are coded to get the information regarding
the procedures of lesson planning and the difficulties faced by the teachers during the
process. Miles and Huberman (1994:56) define codes as “tags or labels for assigning
units of meaning to the descriptive or inferential information during a study”. Further,
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
data s/he has retrieved and the reflections s/he makes about the information (Miles
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
CHAPTER 5
CONCLUSION
This chapter presents the conclusion drawn from the study, as well as some
recommendations for future research.
5.1. Conclusion
Based on the findings that have been presented in the previous chapter, some
conclusions can be drawn. They are:
1. Each Lesson plan collected from the participants contains specific elements
mentioned in Decree of Minister of National Education No. 41/2007, which
consist of course identity, competence standard and basic competence, objectives
and indicators, learning materials, learning activities, instructional media, and
assessment tools.
2. The indicators mentioned in all lesson plans cover three learning domains, i.e.
cognitive, affective and psychomotor domains. From the interview with the
participants, it was found that in formulating the indicators, the teachers
considered the syllabus, characteristics of the students and the school facilities.
This is in line with Muslich’s (2007:33) theory. However, a participant claimed to have difficulties in formulating the indicators that meet the students’ needs and
condition.
3. Each lesson plan included objectives of the lesson. In formulating the objectives,
the participants claimed to follow the guidelines in the syllabus and the Decrees
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
objectives with the other elements of the lesson plan. However, only one lesson
plan reflected the criteria of good objectives mentioned by Haynes (2007:14).
4. All lesson plans contained learning materials to deliver in the instruction. In the
interview, both participants claimed to develop the materials from authentic
materials such as magazine, recordings, videos, also newspaper and internet
articles. This practice is in line with the Decree of Minister of National Education
No. 41/2007. However, it was found that the materials in both of the lesson plans
mismatched the instructional objectives. The interviews with participants
revealed that the teachers encountered difficulties in finding suitable materials
for the students due to the lack of resource books for vocational school.
5. Both participants determined the teaching media in the process of lesson
planning. The lesson plans showed that all participants used various media in
teaching. From the interviews, it was revealed that they did this to gain students’
interests and participation during the instruction. This practice is in line with the
Decree of the Minister of National Education No. 41/2007. However, the
participants claimed to encounter some difficulties in determining media of
instruction, such as finding appropriate medium for teaching and using the school
facilities.
6. All lesson plans contain learning activities to conduct in the classroom. In
determining the activities, a participant claimed to always use PPP
(Presentation-Practice-Production) technique while another one claimed to make her decision
based on the learning materials. The analysis on all lesson plans revealed that the
activities reflected student-centered instruction as mentioned by Burden and
Williams (1998), as they involve students’ active roles in the activities. However, both of the lesson plans are not specific in depicting the procedure to conduct in
the classroom.
7. All lesson plans contain assessment tools. This is in line with the assessment
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
The assessment procedures in all lesson plans include written and oral test.
However, a test item in one of the lesson plans mismatched the objectives of the
instruction. In setting assessment procedure, a participant stated that the
assessment was based on three domains of learning, also the materials that she
taught in the lesson. However, interview with a participant revealed that she
sometimes had issues in developing the assessment procedure.
5.2. Recommendation
This section presents some recommendations offered based on the findings in this
study. The recommendations are as follow:
1. Even though the participants showed positive attitude toward the procedure of
lesson planning and have implemented the procedure of lesson planning in the
process standard mentioned in Decree of Minister of National Education No.
41/2007, the teachers still need to improve their competences. As the findings
previously presented in Chapter 4 revealed that there were some mismatches
between some elements of the lesson plans, it is suggested that the teachers pay
more attention to the details in developing their lesson plans in the future.
2. The study involved a small number of participants, only three EFL teachers in a
vocational school. It is recommended that a future study will involve a large
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Ahmadian, M. J. (2011). The Effects of Simultaneous Use of Careful Online
Planning and Task Repetition on Accuracy, Complexity, and Fluency in
EFL Learners’ Oral Production. [online]. Available at: http://ltr.sagepub.com/content/15/1/35 [4 January 2013]
Ali, M. (2009). Education for Indonesian National Development. Bandung:
IMTIMA.
Arends, R. I. (2012). Learning to Teach (9th eds.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Berliner, D. C. and Rosenshine, B. V. (Eds) (1987). Talks to Teachers. New York:
Random House.
Brown, G. (1975). Microteaching: A Programme of Teaching Skill. London:
Methuen & Co.ltd.
Brown, H. D. (2001). Teaching by Principles: An Interactive Approach to
Language Pedagogy, Second Edition. New York: Pearson Education.
Bungin, M. B. (2007). Penelitian Kualitatif. Jakarta: Kencana Prenada Media
Group.
Burden, R. and Williams, M. (1998). Thinking through the Curriculum. London:
Routledge.
Burns, A. and Hood, S. (Eds) (1995). Teachers’ Voices: Exploring Course Design in a Changing Curriculum. Sydney: Macquarie University.
Cameron, L. (2001). Teaching Languages to Young Learners. Cambridge:
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Celce-Murcia, M. (Eds) (2001). Teaching English as a Second or Foreign
Language (3rd Edition). Boston: Heinle & Heinle.
Choate, J.S. et al. (1995). Curriculum-Based Assessment and Programming (3rd
ed.). Needham Heights: Allyn & Bacon.
Cohen, L. et al. (2007). Research Methods in Education. New York: Routledge.
Creswell, J.W. (2007). Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing
Among Five Approaches. California: Sage Publication.
Creswell, J.W. (2008). Educational research: Planning, conducting, and
evaluating quantitative and qualitative research (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle
River, NJ: Pearson Education Inc.
Cunningham, G. (2009). The New Teacher’s Companion: Practical Wisdom for Succeeding in The Classroom. [online]. Available at:
http://www.ascd.org/publications/books/109051.aspx [3 January 2013]
Darling-Hammond, L. et al. (1999). A Lisence to Teach: Raising Standards for
Teaching. San Fransisco: Jossey-Bass Publishers.
Davies, I. K. (1981). Instructional Technique. New York: McGraw-Hill Inc.
Depdiknas. (2003). Standar Kompetensi Mata Pelajaran Bahasa Inggris: Sekolah
Menengah Atas dan Madrasah Aliyah. Jakarta: Pusat Kurikulum Balitbang
Depdiknas.
Dick, W. and Carey, L. (1990). The Systematic Design of Instruction (3rd ed.).
Florida: HarperCollinsPublishers.
Djojonegoro, W. (1996). Lima Puluh Tahun Perkembangan Pendidikan
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Dudeney, G. and Hockly, N. (2007). How to Teach English with Technology.
Edinburgh Gate: Pearson Education Ltd.
Duncan, G., & Met, M. (2010). STARTALK: From Paper to Practice. College
Park, MD: National Foreign Language Center at the University of
Maryland. [online]. Available at:
http://www.startalk.umd.edu/lesson_planning [4 January 2013]
Emilia, E. (2005). A Critical Genre-based Approach to Teaching Academic
Writing in a Tertiary EFL Context in Indonesia. University of Melbourne:
Unpublished Paper.
Emilia, E. (2011). Pendekatan Genre-Based dalam Pengajaran Bahasa Inggris:
Petunjuk untuk Guru. Bandung: Rizqi Press.
Evans, C. et al. (2009). Teaching English: Developing as a Reflective Secondary
Teacher. London: SAGE Publications Ltd.
Feez, S. and Joyce, H. (1998). Text-based Syllabus Design. Sydney: Macquarie
University.
Forsyth, I. et al. (1995). Planning A Course: Practical Strategies for Teachers,
Lecturers and Trainers. London: Kogan Page.
Gagne, R. M. and Briggs, L.J. (1979). Principles of Instructional Design. New
York: Holt, Rineheart and Winston.
Gay, I. R. et al. (2006). Educational Research: Competencies for Analysis and
Applications. New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc.
Graves, K. (2000). Designing Language Courses: A Guide for Teachers. Canada:
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Green, D. (Eds) (2003). “From Theory to Practice: Gagné’s Theory of Instruction”. The Office for Teaching and Learning Newsletter [online], Vol 7 (5), 4 pages. Available at: http://www.otl.wayne.edu [29 December 2013]
Greenwood, G. G. and Parkay, F. W. (1989). Case Studies for Teacher Decision
Making. Toronto: Random House, Inc.
Griffiths, C. (Eds) (2008). Lesson from Good Language Learners. New York:
Cambridge University Press.
Halliwell, S. (1992). Teaching English in the Primary Classroom. New York:
Longman Publishing.
Hancock, D.R. and Algozzine, B. (2006). Doing Case Study Research: A
Practical Guide for Beginning Researchers. New York: Teachers College
Press.
Harmer, J. (2007). How to Teach English: New Edition. Cambridge: Pearson
Education Ltd.
Haynes, A. (2007). 100 Ideas for Lesson Planning. New York: Continuum
International Publishing Group.
Ibrahim, R. and Syaodih, N. (1996). Perencanaan Pengajaran. Jakarta:
Depdikbud.
Imperiani, E. D. A. (2012). English Language Teaching in Indonesia and Its
Relation to the Role of English as an International Language. [online].
Available at: http://ejournal.upi.edu/index.php/psg/article/view/43/13 [21
January 2013]
Ivone, F. M. (2005). “Teaching English as a Foreign Language in Indonesia: The
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Jalal et al. (2009). Teacher Certification in Indonesia: A Strategy for Teacher
Quality Improvement. Jakarta: Depdiknas.
Jannah, M. (2008). The Difficulties Encountered by English Teachers in
Designing Instructional Plan towards the Implementation of Kurikulum
Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP). UPI Bandung: Unpublished Paper.
Kauchak, D. et al. (2002). Introduction to Teaching: Becoming a Professional.
New Jersey: Merril Prentice Hall.
Kemp, J.E. (1977). Instructional Design: Plan for Unit and Course Development
(2nd ed.). Belmont: David S. Lake Publishers.
Kizlik, B. (2012). Lesson Planning, Lesson Plan Formats and Lesson Plan Ideas.
[online]. Available at: http://www.adprima.com [13 August 2012]
Lestari, L. A. (1999). “English Classroom Culture Reformation: How Can It be
Done?”. TEFLIN Journal. 10, (1).
Lie, A. (2007). “Education Policy and EFL Curriculum in Indonesia: Between the Commitment to Competence and the Quest for Higher Test Scores”. TEFLIN Journal. 18, (1), 1-14.
Lodico, M. G. et al. (2010). Methods in Educational Research: From Theory to
Practice (2nd ed.). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Loughran, J. (2010). What Expert Teachers Do. Australia: Allen Unwin.
Magos, K. and Politi, F. (2008). The Creative Second Language Lesson: The
Contribution of the Role-play Technique to the Teaching of a Second
Language in Immigrant Classes. [online]. Available at:
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
McDonald, E. S. and Hershman, D. M. (2010). Classrooms that Spark! Recharge
and Revive Your Teaching (2nd ed.). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Miles, M. B. and Huberman, A.M. (1994). Qualitative Data Analysis (2nd ed.).
California: SAGE Publications, Inc.
Mulyasa. (2008). Implementasi Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan:
Kemandirian Guru dan Kepala Sekolah. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
Muslich, M. (2007). KTSP: Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan. Jakarta: Bumi
Aksara.
Patton, Q. (2002). Analyzing Qualitative Data. [online]. Available at:
http://sperkins.org/wk5slides.pdf [11 June 2012]
Reese, S. (2002). Contextual Teaching and Learning. Texas: ProQuest Education
Journals.
Reiser, R. A. and Dick, W. (1996). Instructional Planning: A Guide for Teachers
(2nd ed.). Massachusetts: Allyn & Bacon.
Rejeki, A. (2009). Lesson Plans for Teaching English to Young Learners: A Case
Study of Lesson Plans of Two Elementary Schools In Bandung Kulon, West
Java. UPI Bandung: Unpublished paper.
Richards, J. C. and Bohlke, D. (2011). Creating Effective Language Lessons. New
York: Cambridge University Press.
Richards, J. C. and Farrell, T. S. C. (2011). Practice Teaching: A Reflective
Approach. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Richards, J. C. and Renandya, W. A. (Eds) (2002). Methodology in Language
Teaching: An Anthology of Current Practice. Cambridge: Cambridge
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Richards, J. C. and Rodgers, T. S. (2001). Approaches and Methods in Language
Teaching (2nd ed.). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Richards, K. (2003). Qualitative Inquiry in TESOL. London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Rifkin, B. (2003). “Guidelines for Foreign Language Lesson Planning”. Foreign Language Annals. 36, (2), 167-179.
Ritchie, J and Lewis, J. (2003). Qualitative Research Practice: A Guide for Social
Science Students and Researchers. London: SAGE Publication.
Sambaugh, N. and Magliaro, S. G. (2006). Instructional Design. Boston: Pearson
Education.
Saville-Troike, M. (2006). Introducing Second Language Acquisition. New York:
Cambridge University Press.
Steere, B. F. (1988). Becoming an Effective Classroom Manager: A Resource for
Teachers. New York: State University of New York Press.
Sundayana, W. (2009). “Persepsi dan Kesulitan Guru Bahasa Inggris SMP/MTs di Jawa Barat dalam Pengembangan Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan”. Paper presented at Seminar Nasional Himpunan Pengembang Kurikulum
Indonesia (HIPKIN), Bandung.
Suparlan. (2011). Tanya Jawab Pengembangan Kurikulum dan Materi
Pembelajaran. Jakarta: PT Bumi Aksara.
Suskie, L. (2009). Assessing Student Learning: A Common Sense Guide. San
Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Tanni, M. (2012). “Teacher Trainees’ Information Acquisition in Lesson
Planning”. Information Research, 17, (03), paper 530.
Taylor-Powell, E. (1998). Questionnaire Design: Asking questions with a
Miftah Farid, 2014
Teachers difficulties in lesson planning
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
http://learningstore.uwex.edu/Questionnaire-Design-Asking-Questions-with-a-Purpose-P1028C0.aspx [8 April 2013]
TEFLIN. (2013). Pokok Pikiran dan Rekomendasi tentang Kurikulum Mata
Pelajaran Bahasa Inggris Tahun 2013. [online]. Available at: http://upi.edu
[17 October 2013]
Thomas, R. M. (2003). Blending Qualitative & Quantitative Research Methods in
Theses and Dissertations. California: Corwin Press, Inc.
Wijayanto, M. D. (2010). Lesson Planning in Young Learner: A Descriptive Study
towards Teachers’ Lesson Plan of Elementary School. UPI Bandung: Unpublished paper.
Woodward, T. (2001). Planning Lessons and Courses: Designing Sequences of
Work for the Language Classroom. Cambridge: Cambridge University
Press.
Yuwono, G. (2005). “English Language Teaching in Decentralised Indonesia:
Voices from the Less Privileged Schools”. Paper presented at AARE 2005