EIGHTH GRADE STUDENTS’ PERCEPTIONS ON THE USE
OF MIND MAPPING TO DEVELOP THEIR ORGANIZATION
OF IDEAS IN SPEAKING AT SMPN 2 SEDAYU
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Agnes Mira Damayanti Student Number: 09 1214 010
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
OF MIND MAPPING TO DEVELOP THEIR ORGANIZATION
OF IDEAS IN SPEAKING AT SMPN 2 SEDAYU
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Agnes Mira Damayanti Student Number: 09 1214 010
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
DEDICATION PAGE
I dedicate this thesis to:
1. Jesus Christ, my Almighty God
2. My beloved parents, Antonius Lamija and Agustina Rahayu
3. My brother, Felix Novaldy Zulham 4. My love, R. Dimas Adhi Ratmoko
Damayanti, Agnes Mira. 2013. Eighth Grade Students’ Perceptions on the Use
of Mind Mapping to Develop their Organization of Ideas in Speaking at SMP N 2 Sedayu. Yogyakarta: Sanata Dharma University.
Speaking can be one of the language skills that is not easy to learn. Many students are reluctant to speak in English because they are worried about making mistakes in grammar, pronunciation, and they are lack of confidence. Besides, the students are worried if they cannot deliver the content of the speech well. To solve the problems in speaking, there are many techniques that can be used, one of the techniques is mind mapping. Mind mapping can be an interesting technique to help the students preparing and delivering their speaking. It is then interesting to investigate the students’ perceptions on the use of mind mapping.
There are two research problems of this study, namely: (1) What are the students’ perceptions on the use of mind mapping to develop their organization of ideas in speaking, and (2) What are the implications of the findings?
This research belongs to survey research which uses qualitative and quantitative analysis. The participants of this research were 47 students of class VIII at SMP N 2 Sedayu. Furthermore, the researcher used a questionnaire and an interview as instruments. To analyze the results of the questionnaire, the researcher used numerical form. There were 30 statements of the questionnaire using likert scale type. The data analysis of the questionnaire was in form of percentage. Thus, the results of the interview were collected after the results of the questionnaire were obtained. The results were analyzed by summarizing each number of the interview questions based on the classification of the questions.
The results of the research showed that the students had positive perceptions on the use of mind mapping to develop their organization of ideas in speaking. From the study, the researcher concluded that mind mapping was really helpful for the students to use in speaking, especially to develop their organization of ideas. Students also had perceptions that mind mapping could improve their speaking ability and it was easily implemented in speaking. Moreover, from the findings, it implied that the students’ perceptions on the use of mind mapping in speaking were good. Mind mapping was effective and very beneficial for the students to use. In addition, mind mapping could be implemented in junior high school as the technique to help them learning speaking English. Mind mapping made the students’ ability to develop their organization of ideas was improved.
ABSTRAK
Damayanti, Agnes Mira. 2013. Eighth Grade Students’ Perceptions on the Use
of Mind – Mapping to Develop their Organization of Ideas in Speaking at SMP N 2 Sedayu. Yogyakarta: Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Berbicara dapat menjadi salah satu keterampilan bahasa yang tidak mudah untuk dipelajari. Para siswa cenderung takut untuk berbicara dalam bahasa Inggris karena mereka khawatir untuk membuat kesalahan dalam tata bahasa, pengucapan, dan juga mereka kurang percaya diri. Untuk mengatasi masalah dalam berbicara, ada banyak teknik yang dapat digunakan, salah satunya adalah mind mapping. Mind mapping dapat menjadi salah satu teknik yang menarik untuk membantu siswa dalam menyiapkan mereka berbicara bahasa Inggris di depan kelas. Hal ini kemudian menarik untuk diselidiki mengenai persepsi siswa tentang penggunaan mind mapping.
Penelitian ini terdiri dari dua rumusan masalah, yaitu: (1) Apa persepsi siswa tentang penggunaan mind mapping untuk mengembangkan organisasi ide-ide mereka dalam berbicara? dan (2) Apa implikasi dari hasil tersebut?
Penelitian ini menggunakan metode survei yang dalam menganalisanya mengunakan analisis kuantitatif dan kualitatif. Partisipan dalam penelitian ini adalah 47 siswa kelas VIII SMP N 2 Sedayu. Selanjutnya, untuk mengumpulkan data, peneliti menggunakan kuesioner dan wawancara. Untuk menganalisa hasil kuesioner, peneliti menggunakan bentuk numerik. Ada 30 pernyataan dari kuesioner dan menggunakan jenis skala Likert. Analisis data dari kuesioner adalah dalam bentuk persentase. Dengan demikian, hasil wawancara dapat dikumpulkan setelah didapat hasil kuisioner. Wawancara ini dianalisis dengan merangkum setiap pertanyaan berdasarkan klasifikasi pertanyaan.
Berdasarkan hasil penelitian, peneliti dapat menyimpulkan bahwa para siswa memiliki persepsi positif terhadap penggunaan mind mapping untuk mengembangkan ide mereka dalam berbicara bahasa Inggris. Hal ini juga dapat disimpulkan bahwa menurut persepsi siswa, mind mapping benar-benar membantu mereka dalam berbicara, terutama dalam mengembangkan organisasi ide-ide. Siswa juga memiliki persepsi bahwa mind mapping dapat meningkatkan kemampuan berbicara mereka dan itu mudah untuk diimplementasikan. Selain itu, hasil penelitian mengimplikasikan persepsi siswa terhadap penggunaan mind mapping dalam berbicara sangatlah baik. Mind mapping sangat efektif dan sangat bermanfaat untuk digunakan para siswa. Selain itu, mind mapping dapat diimplementasikan di sekolah menengah pertama sebagai teknik untuk membantu mereka belajar berbahasa Inggris. Mind mapping meningkatkan kemampuan siswa dalam mengembangkan ide untuk berbicara bahasa Inggris.
First of all, I would like to express my greatest praise to Jesus Christ for His blessing and amazing grace for me during the process of finishing my thesis. I believe that without His amazing grace and blessing, I could not finish this thesis.
I would like to express my highest gratitude to my major sponsor
Veronica Triprihatmini, S.Pd., M.Hum., M.A. for her suggestions, kindness,
and patience in helping me to finish this thesis. My appreciation also goes to all of the lecturers, the secretariat staff in PBI and all the librarians in Sanata Dharma University.
I also express my gratitude to the headmaster of SMP N 2 Sedayu, Drs.
Ponidi, M.M, for allowing me to conduct the research there and the English
teacher of grade eight, Ekwarnadi, S.Pd., for the time and for the guidance during the research. I would like to thank all students of VIII C and VIII D academic year 2012/2013 for helping me completing the research.
I would also like thank my parents, my beloved father, Antonius Lamija, and my dearest mother, Agustina Rahayu for their endless love, prayers, sacrifices, support, and love to me. I also thank my brother, Felix, my aunt Peni¸ and my grandparents for their love, support, and prayers for me.
for the time availability when I share my difficulties during writing this thesis. I also thank Maris, Septi, Romo Anton, and Lia for helping me checking my thesis. My enormous acknowledgement goes to everybody who has contributed their thoughts and energy whose names I cannot mention one by one.
Last, this thesis could not have been accomplished without a marvelous person who always stands by my side when I was down, R. Dimas Adhi
Ratmoko. I thank him for his love, care, support, patience, and prayers for me. He
is the man who has been sent by God for accompanying me in my life.
TITLE PAGE……… i
APPROVAL PAGES………... ii
DEDICATION PAGE………. iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY……… v
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS………. vi
ABSTRACT……… vii
ABSTRAK……… viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS……… ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS………... xi
LIST OF TABLES……….. xv
LIST OF FIGURES……… xvi
LIST OF APPENDICES……… xvii
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION………. 1
1.1Background of the Study………... 1
1.2Research Problems………. 5
1.3Problem Limitation………... 6
1.5Research Benefits………. 7
1.6Definition of Terms……….. 8
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE………. 11
2.1 Theoretical Description……… 11
2.1.1 Perception ………. 11
2.1.1.1 Definition of Perception………. 12
2.1.1.2 Factors Influencing Perception……….. 13
2.1.2 Speaking……… 14
2.1.2.1 The Nature of Speaking………. 15
2.1.2.2 Determining the Purpose and the Ideas in Speaking……… 18
2.1.2.3 Organizing Speech………. 19
2.1.2.4 Teaching Speaking Skill……….. 20
2.1.3 Mind Mapping Technique……… 21
2.1.3.1 Mind Mapping Concept……… 22
2.1.3.2 Mind Mapping for Organizing Idea……….. 23
2.1.3.3 Benefits of Mind Mapping……… 27
2.1.3.4 Mind Mapping and Language Teaching………... 27
2.2 Theoretical Framework………... 28
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY………... 31
3.3 Research Participants………. 32
3.4 Instruments and Data Gathering Technique………... 33
3.4.1 Questionnaire……….. 34
3.4.2 Interview………. 37
3.5 Data Analysis Technique……… 39
3.6 Research Procedure……… 40
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION………... 44
4.1 Research Results……… 44
4.1.1 The Results of the Questionnaire……… 44
4.1.1.1 The Students’ Previous Experience of Using Mind Mapping……… 47
4.1.1.2 The Problems Faced by the Students in Speak- ing………. 47
4.1.1.3 The Process of Using Mind Mapping in Speak- ing……… 49
4.1.1.4 Students’ Perceptions on the Use of Mind Map- ing in Speaking………. 50
4.1.2 The Results of Interviews………... 52
ping in Speaking………. 54
4.2.2 The Implications of Students’ Perceptions on the Use of Mind Mapping in Speaking………... …. 57
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS……… 61
5.1 Conclusions……… 61
5.2 Suggestions……… 62
Table
3.1 Blueprint of Questionnaire………. 35
3.2 Blueprint of Interview……… 37
3.3 Data Analysis Technique………... 39
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure
Appendix A. Letter of Permission……… 66
Appendix B. Research Instruments……… 71
Questionnaire’s Blueprint……….. 72
Interview’s Blueprint……… 74
Questionnaire in English version……….. 75
Questionnaire in Indonesian version………... 77
Interview ……… 80
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
In this study, the researcher would like to investigate the perceptions on the use of mind mapping to develop the students’ organization of ideas in speaking skill at SMP N 2 Sedayu Bantul grade eight. This chapter presents six parts, namely background of the study, research problem, problem limitation, objectives of the study, benefits of the study, and the definition of terms.
1.1 Background of the Study
In the 21st century, English plays a role as an international language. As an international language, English is learnt by millions of people around the world. The language is important to be mastered by people because there are many official activities and formal activities use English as the main language in communication. In many countries, English is learnt by people mostly for the fact that having good English proficiency is compulsory for getting jobs and studies.
While as a foreign language, English is learnt as an obligation for students. Barbara (2001) defines that English is used primarily as an international language, especially in the business, scientific, legal, political and academic communities In Indonesia, English is used as a foreign language and it is learnt by elementary level students. Even though English is a foreign language, English plays a role in many field of studies, namely, education, technology, science, economics, politics, and international relationship. English plays a role as an important language to be mastered by students in order to help them acquiring knowledge.
In the education field of Indonesia, government has set English as a compulsory subject to be learnt in junior high schools and senior high schools. Moreover, English has been taught to students in pre-school and elementary school in order to prepare the students to have a basic concept of learning English. When the students are in junior high school or senior high school level, they are supposed to have good ability in learning English as they have learnt English since they are in preschool and elementary school.
3
The mastery of speaking skills in English is a priority for many second-language or foreign-second-language learners. Consequently, learners often evaluate their success in language learning as well as the effectiveness of their English course on the basis of how much they feel they have improved in their spoken language proficiency. (p.19)
From all of the skills mentioned before, based on the observation to the students, speaking could be one of the skills which worry students to learn. The students could be reluctant to speak in English because they were worried about making mistakes in grammar, pronunciation, and they were lack of confidence. Besides, the students were worried if they could not deliver the content of the speech well. Those problems usually came up in many levels of schools, including junior high school, senior high school, and university level.
In SMP N 2 Sedayu, English was one of the compulsory subjects which had to be learnt by all of the grades. The students of grade eight learnt English four hours a week. The students of grade eight had to learn English in all skills. Although there was no particular schedule for each skill, the teachers set their own time to cover all of the skills in the materials. Through observing the students and interviewing the teachers, the researcher found that the students of grade eight found problems in speaking. Speaking skill was lack to be developed compared to other skills in this school.
to deliver their speech in front of the class, most of them tended to repeat the same ideas they had said before. The second problem was about the matter of confidence in speaking. Most of the students of grade eight were lack of self-confidence, especially when they were asked to deliver their speech or to speak in front of the class. They were shy and they did not want to come in front to deliver their speech even if their teacher asked them to do that. They were afraid to make mistakes if they delivered their speech in front of the class.
Based on the problems found by the researcher in observing the students of grade eight at SMP N 2 Sedayu, the researcher chose to focus on the first problem. The researcher thought that the problem of the confusion in developing organization of idea is necessary to be solved. Developing the organization of ideas is the main thing to be mastered by the students in order to have well-organized ideas in their speaking. In addition, the second problem could also be solved if the students have solved the first problem.
To solve the problems, there are many techniques that can be used to prepare and deliver speech well; one of them is mind mapping technique. Buzan (2005) mentions that:
5
Mind mapping will be one of the interesting techniques that will be very useful for the students of grade eight to prepare and deliver their speech. Mind mapping can help the students to develop their organization of ideas because mind mapping is specially designed to help the students make and develop ideas. Mind mapping is also designed to enhance the creativity of the students.
Based on the previous consideration, the researcher decided to investigate the students’ perceptions on the use of mind mapping to develop their organization of ideas in speaking at SMP N 2 Sedayu. This study gains the students’ perception of mind mapping technique in speaking skill since the teachers need to know whether the technique is useful and meaningful. Then, this study emphasizes the eighth grade students of SMPN 2 Sedayu as the subject of the study because they have had enough basic knowledge in learning English from elementary school.
1.2. Research Problems
There are two problems which are going to be discussed on this study. They are: 1. What are the eighth grade students’ perceptions on the use of mind
mapping to develop their organization of ideas in speaking at SMP N 2 Sedayu?
1.3 Problem Limitation
The scope of this study is the use of mind mapping in speaking section. The study will focus on the use of mind mapping for the eighth grade students of SMPN 2 Sedayu. As stated before, the focus of the study is to investigate the
students’ perceptions on the use of mind mapping to develop their organization of ideas in speaking and the implications of the students’ perceptions on the use of mind mapping to develop their organization of ideas in speaking. This study chooses narrative text as the material of the study. Narrative text is chosen for the reason that is closely related to the students’ real life and it is also interesting to learn. Besides, narrative text is compulsory to be learnt and to be mastered by the eighth grade students.
The treatment which is chosen by the researcher to help the students of SMPN 2 Sedayu grade eight is mind mapping technique. The students are
7
1.4 Research Objectives
Related to the previous research problems, the objectives of this study are: 1. to investigate the students’ perceptions on the use of mind mapping to
develop their organization of ideas at SMPN 2 Sedayu grade eight. 2. to find out the implications of the findings.
1.5 Research Benefits
This study is expected to give essential contribution for the following related parties. They are:
1.5.1 English Teachers
This study is expected to give contribution to English teachers who teach eighth grade students of junior high schools. They can obtain some information related to mind mapping from this study. By obtain some information related to mind mapping for developing students’ ability to organize the ideas for speaking, teachers can help the students to develop their ideas in speaking through mind mapping.The information is valuable since students sometimes encounter difficulties in organizing ideas of speaking. The teachers can use mind mapping as one of the alternative techniques to teach speaking.
1.5.2 Eighth Grade Students of Junior High School
speaking. They can explore and organize their ideas through mind mapping. As the result, students are expected to have a good organization of ideas when they speak or deliver their speech
1.5.3 For Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris / English Language Education Study
Program ( PBI )
This research is expected to give contribution to PBI study program. The results of this research can be used as the reference for PBI in using the mind mapping technique in any classes. The results can give any enlightenment for the lecturers to implement the use of mind mapping in their classes.
1.5.4 Further Researchers
For the further researchers, it is expected that the result of this study can be used as the reference for other researchers. Mind mapping is a simple technique that can be used not only in speaking, but it can also be used in reading, writing, and listening. Therefore, this study can encourage other researchers to revise, reconstruct, and modify this study as the attempts to conduct further study in other levels/ objectives.
1.6 Definition of Terms
9
1.6.1 Perception
Altman, Valenzi, and Hodgetts (1985) mention that perception is the way how the stimuli is selected and grouped by a person so that it can be meaningfully interpreted. Perception reflects a person’s view on reality. Perception’s process helps us to understand the enviroment in which we live (p.85). In addition to the definition, Huffman, Mark, and Vernoy (1997) say that “Perception is the process of selecting, organizing, and interpreting sensory data into usable mental representation of the world” (p.79). In this study, perception refers to the mental representation of the eighth grade students’ at SMP N 2 Sedayu in selecting, organizing, and interpreting any point of view on reality. It will see on how the students’ perceive the use of mind mapping to develop their organization of ideas in speaking.
1.6.2 Mind mapping
Buzan (2003) mentions that mind mapping is a powerful technique that provides a universal key to unlock the potency of the brain. Mind mapping technique can be applied for any aspects of life in order to improve learning and clear thinking of human performance (p.55). In this study, mind-mapping is the technique used for developing the eighth grade students’ organization of ideas at SMP N 2 Sedayu. Mind mapping is a powerful graphic technique which provides
1.6.3 Speaking
Speaking skill is the basic element in having communication and it is the common measurement on how people master the language. Bygate (1987) mentions speaking as a skill which deserves attention every bit as much as literary skills, in both the first and second languages. The learners may need to be able to speak with confidence in order to carry out many of the most basic transactions (p.1). Besides, Bygate (1987) also mentions that speaking is the skill which can be traced to the processing conditions of communication and the words are being spoken as they are being decided and as they are being understood (p. 11). This means that the speaking skill itself is the skill which needs more attention in order to carry out the transactions of communication and the learners need the confidence to carry out the transactions of communication itself. Besides, speaking also needs the good idea on what they will decide and understand on a certain idea. In this study, speaking is the skill which has function for producing speech in a good order of organization of ideas, fluency, and accuracy.
1.6.4 Eighth Grade Students of SMP N 2 Sedayu
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In this chapter, the researcher will talk about the review of some related literature of the study. This chapter will be divided into two parts, namely theoritical description and theoritical framework. In theoritical description, the researcher will discuss some related literature of the research. In theoritical framework, the researcher will discuss the summary of the related literature which will be used to answer the problem formulations.
2.1 Theoritical Description
There are three major points that will be reviewed in this part. They are: perception, the nature of speaking, and mind mapping technique.
2.1.1 Perception
2.1.1.1Definition of Perception
A person’s perception in facing phenomena and things will be different one to another. In this study, the researcher investigates the students’ perceptions on the use of mind mapping to develop their organization of ideas in speaking. Perception from a student will be different from other students. Perception in this study means the students’ point of view in facing phenomena and things. Szilagyi and Wallace (1980: 70) define that perception is the process which individuals attend to incoming stimuli, organize, and then interpret such stimuli into a message that in turn indicates an appropriate action and behavior.Perception represents the human mind and it has some stages of process. According to Huffman et al. (1997: 89) perception is the process of chosing, organizing, and interpreting the sensory data into the mental representation of the real situation or object. While Gibson, Ivancevich, and Donnely (1985) mention that “perception is the cognitive process from an individual in giving meaning to the enviroment” (p. 60).
In accordance of a stimuli to be a perception, there are some steps in the process of perception. According to Huffman et al. (1997: 89), perception has three steps. The steps are:
a. Selection : A person selects the stimuli which we will pay attention. b. Organization: After he has selected the stimuli, he must arrange and
13 c. Interpretation: This is the final stage of perception. This stage can be influenced by some factors, such as early life experiences, perceptual expectancy, cultural factors, needs and interests, and frames of reference. Thus, Gibson et al. (1985: 61) mentions that the intepretation of perception includes objects, symbols, and people in the light of pertinent experiences.
2.1.1.2. Factors Influencing Perception
The difference of everyone’s perception can be influenced by some
factors. Altman et al. (1985: 86) defines some factors influencing perception. Those factors are:
a. Selection of stimuli
There are many stimuli that come up in our surrounding. From all of the stimuli, the focus is only on a small number. People select certain stimuli and filter out others. The selection of stimuli from one person to another person can be different.
b. Organization of stimuli
c. The situation
The third factor influencing perception is the situation. A person familiarity, expectations, and experiences in her past affect what the person perceives about a certain thing. Perceiving a situation also has a close relation with the way how a person adjusts her or his behavior to situations. For example, a teacher who is not from teaching training program in his or her college will find difficulty to manage the classroom, or to understand the norms and values in the field of teaching.
d. The person’ self-concept
Self-concept is the way how people feel and perceive about themselves. The way people see themselves affects their perception of the world around them. The person’ self-concept is important because the mental picture of the person will influence much on how they perceive and do in their life.
In the study, those factors of perception are important to be used. Those factors can be used as the basis information of the implementation on how the students’ perceive the use of mind mapping.
2.1.2 Speaking
15 language and it is one of the language skills (Harmer, 2005,p. 275). The following part will talk further about the nature of speaking, determining purpose and idea in speaking, organizing speech, and teaching speaking skill.
2.1.2.1The Nature of Speaking
Speaking is the skill which cannot be separated from other skills namely reading, writing, and listening. Those skills are divided into written and spoken skills. Reading and writing belong to written skill while listening and speaking belong to spoken skill. Meanwhile, speaking is productive skill and it has a close relation with listening skill. Speaking in this study is the major skill which will be researched. Speaking is able to deliver speech with a certain idea to other people and it may be planned or unplanned. According to Luoma (2004), there are some features of spoken discourse:
- Arranged in the central idea
- May be planned (e.g., a lecture) or unplanned (e.g., aconversation) - Employs more vague or generic words than written language - Employs fixed phrases, fillers, and hesitation markers
- Contains slips and errors reflecting online processing
- Involves reciprocity (i.e., interactions are jointly constructed) - Shows variation (e.g., between formal and casual speech),
While Harmer (2005: 269) add some language features of speaking. Those language features of speaking are:
1. Connected speech: speakers of English should be able to produce fluent connected speech. For example: in speaking, people might say I’d’ve gone rather than I would have gone.
2. Expressive devices: native speakers of English make variations in speaking, namely changing the pitch and stress of particular parts of utterances, varying volume and speeed, and showing by other phsyical and non-verbal means how they feel.
3. Lexis and grammar: Spontaneous speech is signed by the use of a certain number of common lexical phrases in the performance of certain language functions.
4. Negotiation language: effective speaking has advantages from the negotiatory language that people use to get the clarification and show the structure of what people are saying.
17 Besides the language features, speaking has some basic types. (Brown, 2004, p. 141) mentions that there are five basic types of speaking. The basic types of speaking are:
1. Imitative: The focus of this type is that students are able to repeat a word or a phrase or possibly a sentence that is read by the teacher. This type is usually used in “pronunciation” class.
2. Intensive: The focus of this type is the production of short stretches of oral form of language. The examples are directed response tasks, reading aloud, sentence and dialogue completion, translation up to the simple sentence level.
3. Responsive: This type includes the interaction and test comprehension in the basic level of short conversations, namely, greetings, simple requests, giving and asking something.
4. Interactive: This type is similar to responsive type. The difference is only on the length and the complexity of the interaction. In this type, the interaction is longer and more complex than responsive. The interaction includes transactional conversations.
the organization of idea in speaking. The extensive (monologue) type is the type which is used as the speaking activity. The students use monologue type as the speaking activity through the help of mind mapping.
2.1.2.2Determining the Purpose and the Ideas in Speaking
Everyone speaks or delivers speech with a certain purpose. The expectation of speaking is that people who are listening to others will understand of what they are going to convey. According to Koch (1995: 15) there are some major purposes in speaking:
a. To entertain – to obtain pleasurable response, to evoke curiousity, to provide interesting response, or to amuse the listeners.
b. To inform – to enrich or to add information to the listeners. c. To persuade – to convince, to reassure, or to encourage
19 the ideas in speaking is important since the purpose and the ideas are the main things which the students should have before they speak or deliver their speech. In this study, determining the purpose and the ideas of speaking should be possessed by the students before they practice a monologue speaking. Determining the purpose and the ideas can be done through the use of the mind mapping technique.
2.1.2.3Organizing Speech
In order to have a good organization of speech, the speaker should arrange and organize their speech in a clear way. A good speech organization will help the listeners to understand the content systematically. As stated by Koch (1995: 57), there are three parts of speech organization, namely:
a. Introduction : This part is the beginning of the speech organization. An introduction part should get the attention of the audience. In this part, the speaker should express the clear of the central idea and the reason for listening.
c. Conclusion: In this part, the speaker states the summary, the main points, and the follow up of the speech to the listeners. A conclusion should be short and to the point. It should comprise from 5 to 10 percent of the total speech.
2.1.2.4Teaching Speaking Skill
Teaching speaking skill should be done by the teachers in various activites. Teaching speaking can be done in some activities since there are some different types of speaking. As has been discussed above, there are five basic types of speaking according to Brown (2004), namely imitative, intensive, responsive, interactive, and extensive. In this study, the type which will be used is
the extensive type since the focus of this study is speaking activity which will be done individually by the students. This activity can be called as prepared talks. According to Harmer (2005: 274) prepared talks can be defined as a popular activity that is used in speaking classroom. The students prepare their presentation on a certain topic based on their own choice. The students also have to speak based on their own notes rather than from a script. Prepared talks are a useful speaking genre because the students can develop their ideas in their speaking based on the notes. If this activity can be properly organised, it can be very interesting for both the speaker and the listeners.
21 speaking. As stated by Koch (1995: 15), the purposes of speech or speaking are to entertain, to inform, and to persuade. The topic or the ideas of the speech or speaking is based on the purposes of the speech. The development of the speech can be made in some parts of the speech. As stated by Koch (1995), the parts of speech organization are introduction, body, and closing. By having a good order of speech, the students are supposed to have a systematic order of the speech content.
In the prepared talks, the teacher also plays a role. The teacher should be participate in the teaching learning activities and monitor the students. In this kind of activity, the teachers’ role is as a feedback provider. According to Harmer (2005: 274), as a feedback provider, the teacher should be able to give feedback, correct the students’ speech by carefully considering the effects of different approaches. If the teacher gives feedback to the students in the middle of their speech, it will disturb them in continuing the speech or the communication. It is better to let them finish their speech and allow them to assess what they have done. Then, the teacher gives the feedback to the students.
2.1.3 Mind Mapping Technique
2.1.3.1Mind Mapping Concept
Mind mapping is the technique used to develop ideas of a certain content. In this study, mind mapping refers to help the students to develop their organization of ideas in speaking skill. Mind mapping is the technique used to develop ideas by writing the key of the idea in the central and it uses powerful graphic technique. It uses the ability from the brain and it also helps the students to use both left and right brain skills. It is proven by the theory of Buzan. Buzan (2003) states that “Mind Map is a natural function of the human mind. It is a powerful graphic technique which provides a universal key to unlocking the potential of the brain” (p.55). According to Hofland (2007: 12), mind mapping is a friendly technique of the brain to study, memorize, and take notes. It also uses the skills of left and right brain in the purpose of the best use of the brains.
Mind mapping has its own characteristics. It is the special characteristics of mind mapping that are not possessed by other techniques. According to Buzan (2003: 55), there are four essential characteristics of mind mapping, they are:
a. The subject or the central idea is put in the central image.
b. The sub topic of the subject radiates from the central image as branches.
c. Branches consist of a key image or key word that is written on an associated line. The sub topic of lesser importance are also represented as branches attached to higher level branches.
23
2.1.3.2Making Mind Mapping to Organize Ideas
In making mind mapping, the students need to be able to undersand the concept of mind mapping and the laws of mind mapping. According to Buzan (2003: 87), there are two laws of mind mapping; the laws of technique and the laws of layout. In the following part is stated the summary of the Mind Map laws.
Figure 2.1: The Summary of the Mind Map Laws
Summary of the Mind Map Laws
Techniques
1. Use emphasis
• Always use a central image.
• Use images throughout your Mind Map.
• Use three or more colours per central image.
• Use dimension in images and around words.
• Use synaesthesia (the blending of the physical senses).
• Use variations of size of printing, line and image.
• Use organized spacing.
• Use appropriate spacing. 2. Use Association
• Use arrows when you want to make connections within and across the branch pattern.
Continued from page 23
While according to Hofland (2007: 20), the steps to make mind mapping to develop ideas are:
a. Use blank paper to start making mind mapping. Place your paper sideways so that it will not be bumped into the margins quickly.
b. Draw a picture in the middle of the page. It represents the main topic of your thought.
c. Draw some thick, curved, connected lines from the picture in the middle of the page and make the branches from the picture. These branches represent the main sub-topics.
d. Always start to write the idea from the same point and work in the Summary of the Mind Map Laws
• Make major branches connect to central image.
• Connect lines to other lines.
• Make the central lines thicker
• Make your boundaries ‘embrace’ your branch outline
• Make your images as clear as possible
• Keep your paper placed horizontally in front of you.
• Keep your printing as upright as possible 4. Develop a Personal Style
Layout
1. Use Hierarchy 2. Use Numerical Order
25 e. Give name for each of these ideas and if possible add a little picture of
each idea. Use only keywords for giving the name of each idea.
f. From each of these ideas you can draw other connected lines, spreading like the branches of a tree. Connected lines create associations and structure. Add your thoughts on each of these ideas. These additional branches represent the details.
After the students’ mind mapping has been made, there will be many colors and pictures in the students’ mind mapping. The theories of how to make mind mapping based on the theories of Buzan (2003: 87) and Hofland (2007: 20) can be combined with the theory of Koch (1995: 15-20) in order to make a mind mapping which is related to develop the students’ organization of ideas in speaking. The form of the speaking will be on extensive (monologue) type. The steps on how to make the mind mapping are:
a. First, determine the purpose of your speaking, whether your purpose is to entertain, to inform, or to persuade the audiences.
b. Determine your central or main idea on what you are going to say in front of the class. Put your central idea by writing or drawing a picture in the middle of the page.
d. Always start to write the idea from the same point and work in the same direction.
e. Use arrows when you want to make connections within and across the branch pattern.
f. Try to write the keywords only at any branches of the main sub – topics or sub – sub topics.
g. You can add any colors based on your creativity.
On the following page, the writer will show an example of mind mapping. After knowing the theory about how to make mind mapping, the principal and the laws of mind-mapping, the researcher can get enough basic knowledge to conduct the research. The researcher uses those theories to teach the students in implementing mind mapping in the speaking activity.
Figure 2.2: The Example of Mind Mapping
27
2.1.3.3Benefits of Mind Mapping
Using mind mapping technique can give some benefits. In this study, students can reap a lot of benefits from using mind mapping to develop their organization of ideas in speaking. The students can save their time to prepare their speech, they can get a systematic organization of idea, and they can add or improve their idea easily by using mind mapping. According to Hofland (2007: 30), the benefits of mind mapping are:
a. Mind mapping can save time.
b. Make revision become faster and easier because they are compact and brain-friendly.
c. It is possible to look over and think over the different relations between key topics.
d. It is easy to add the new information to the mind map.
While according to Buzan (2008: 6) that “Mind Map dapat membantu kita untuk merencana, berkomunikasi, menjadi lebih kreatif, menghemat waktu, dan
memusatkan perhatian.” It means that mind mapping can help the students to
plan, communicate, be more creative, save time, and centralize the concentration.
2.1.3.4Mind Mapping and Language Learning
use personal associations to make and is easy to remember the new information obtained by the students and also to visualize in the thinking process. It is proven that mind mapping is a useful technique to master a foreign language, especially English.
In this study, the focus of mind mapping is the use of speaking skill. In the speaking skill, mind mapping can be used in order to develop students’ organization of ideas. Mind mapping is usually used in the preparation to make and develop the students’ speaking. Moreover, in the speaking performance, mind mapping is used for reminder of their content. As stated by Hofland (2007: 38), students can use mind mapping to prepare a topic of a speech. In addition, during the task, mind mapping can only be used for reminder for them. In mind mapping there is no sentence, it should be only keywords and symbols.
2.2 Theoritical Framework
29 Furthermore, knowing about the students’ perceptions on the implementation of teaching learning activities is necessary. It should be known whether the activities can be useful, meaningful, or helpful for the students in the teaching learning process or not. It will be meaningless if the technique is great but it is not appropriate with the students’ need. Considering the students’ needs, the theory of the nature of perception proposed by Huffman et al. (1997) and the theory of the factors influencing perception proposed by Altman et al. (1985) will be used as the basic foundation for the teachers to analyze how students think and respond the use of mind mapping. The data of the students’ perceptions are obtained based on the experiences of the students in using mind mapping to develop their organization of ideas in speaking. Moreover, knowing the specific technique that can be used in teaching speaking skill based on the types of speaking is also necessary. As stated by Brown (2004) there are five basic types of speaking namely imitative, intensive, responsive, interactive, and extensive (monologue). Mind mapping which will be used as the technique in speaking skill in this study belongs to extensive (monologue).
benefits of mind mapping and from Luoma (2004) about the features of spoken discourse.
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
In this chapter, the researcher will discuss how the study will be conducted. It provides deeper information how to gather the data and analyze the data to answer the research problems. This chapter consists of six parts namely research method, research setting, research participants, instruments and data gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
3.1 Research Method
This study belongs to survey research in which the researcher uses it to answer the research problems. According to Frankel and Wallen (1998: 389), survey research is a study which enables the researcher to collect the information from a group of people to describe abilities, opinions, attitudes, beliefs, and/ or knowledge. Survey research collects the information through asking questions which can be presented in the questionnaires and interviews. The advantage of survey research is that the data can be collected in short time. Besides, survey research is conducted for problem solving rather than hypothesis testing.
research was conducted to find out the students’ perceptions on the use of mind mapping to develop their organization of ideas in speaking and the implications of the findings. The questionnaires and interviews were employed in order to obtain the students’ perceptions.
3.2 Research Setting
To conduct the research, the writer collected the data at SMP Negeri 2 Sedayu. This school is a junior high school and it is a public school. This school is
located in Sedayu, Bantul, Yogyakarta. The research was conducted during May 1, 2013 till May 18, 2013 in which the students were in the second semester of academic year 2012/2013.
3.3 Research Participants
The research participants of this study were the eighth grade students of SMP Negeri 2 Sedayu. In this school, eighth grade students were divided into five
33 elements and the nature of his research (Babbie, 1973, p. 106). The researcher chose class VIII C and VIII D as the representative classes for the reason that VIII C had the higher average achievement in English subject and VIII D had the lowest average achievement in English subject. The researcher wanted to compare the results of the research from those classes. Besides, the researcher also wanted to helped the students of class VIII D to improve their average achievement in English subject through this research.
3.4 Instruments and Data Gathering Technique
based on the questionnaire.. The information of the instruments will be explained as follows:
3.4.1 Questionnaire
According to Backstrom and Cesar (1981: 187), a questionnaire is one of the instruments which represent the physical form of all theories, hypotheses, and hunches that have gone into the survey planning. In this research, the researcher used questionnaire in order to gain the students’ perceptions. In addition, this study focused only on the students as the respondents. The questionnaire represented all of the theories and hypotheses of the study. In the questionnaire, the researcher used two types of questionnaire, namely open-ended and close-ended questionnaires.
1. Close-Ended Questionnaire
Close-Ended questionnaire forms the questions in the multiple-choice questions. The respondents should choose the answer based on a number of opinions (Wiersma, 1995,p. 181). According to Frankel and Wallen (2008: 397) this type can be used to measure opinions, attitudes, and knowledge. Close-ended questionnaire enhances consistency of response across respondents and it is easier and faster to tabulate.
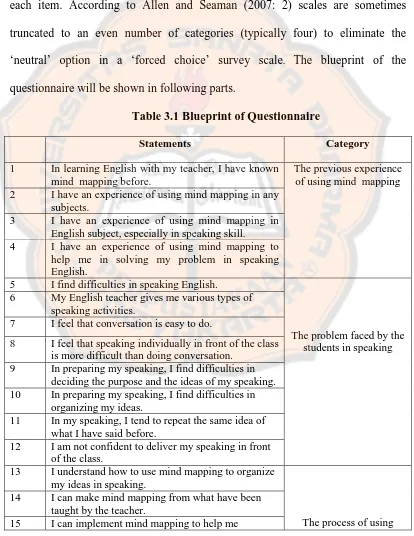
35 seven levels. The questionnaire of the research consisted of thirty items which had to be answered by the students. The questionnaire used statements and there were four options of ‘strongly agree’, ‘agree’, ‘disagree’, and ‘strongly disagree’ for each item. According to Allen and Seaman (2007: 2) scales are sometimes truncated to an even number of categories (typically four) to eliminate the ‘neutral’ option in a ‘forced choice’ survey scale. The blueprint of the questionnaire will be shown in following parts.
Table 3.1 Blueprint of Questionnaire
Statements Category
1 In learning English with my teacher, I have known
mind mapping before.
The previous experience of using mind mapping
2 I have an experience of using mind mapping in any
subjects.
3 I have an experience of using mind mapping in
English subject, especially in speaking skill.
4 I have an experience of using mind mapping to
help me in solving my problem in speaking English.
5 I find difficulties in speaking English.
The problem faced by the students in speaking
6 My English teacher gives me various types of
speaking activities.
7 I feel that conversation is easy to do.
8 I feel that speaking individually in front of the class is more difficult than doing conversation.
9 In preparing my speaking, I find difficulties in deciding the purpose and the ideas of my speaking. 10 In preparing my speaking, I find difficulties in
organizing my ideas.
11 In my speaking, I tend to repeat the same idea of what I have said before.
12 I am not confident to deliver my speaking in front of the class.
13 I understand how to use mind mapping to organize my ideas in speaking.
The process of using
14 I can make mind mapping from what have been
taught by the teacher.
Continued from page 35
organize ideas for my speaking. mind mapping in
speaking 16 Before making mind mapping, I decide the purpose
and the ideas of my speaking.
17 I put the central idea of my speaking on the center of my mind mapping.
18 I develop my ideas of speaking by putting the sub idea on the branches of the mind mapping.
19 I use arrows to make connections within and across the branch pattern.
20 I use only key word on each branch.
21 I make mind mapping creative and interesting. 22 I use my mind mapping to help me speak in front 23 Mind mapping helps me to prepare my speaking
well.
24 Mind mapping really helps me to develop the organization of ideas in speaking.
25 I become confident and motivated to speak in front of class when I use mind mapping.
26 By using mind mapping, I can save much time to prepare and develop my ideas.
27 By using mind mapping, I can add new information related to my speech easily.
28 I can improve my speaking well when I use mind mapping.
29 Mind mapping is easily implemented to prepare and develop my organization of ideas of speaking. 30 Overall, I like to use mind mapping to develop the
organization of ideas in speaking.
2. Open-Ended Questionnaire
37
3.4.2 Interview
According to Babbie (1990: 20), interview is an instrument which is commonly done in face-to-face encounter. It enables the interviewer to ask the questions verbally and record the respondents’ answers. In this research, the researcher used interview as one of the instruments because the researcher could obtain the further information by having face-to-face interaction with the respondents.
Interview has two forms of questions, namely unstructured questions and structured questions. According to Backstrom and Cesar (1981: 128), unstructured questions invite the respondents to answer freely and at length. It gives respondents to have free-response in answering the questions. While structured questions gives fixed-response alternatives to the respondents. In this form, the respondents should choose one of the alternative answers. In this research, the researcher used unstructured questions to the students of class VIII C and VIII D who mostly answer ‘disagree’ or ‘strongly disagree’ on the questionnaire of the classes. The interview questions consisted of six questions. The blueprint of the interview is presented in the following table.
Table 3.2 Blueprint of Interview
No Questions Category
1 Do you find any difficulties in speaking skill? If
there any, please tell me what are they? Problems in speaking
2 What are the strategies that use to solve your
difficulties in speaking?
Continued from page 37
4 Is determining the purpose and the ideas for speaking English easy to do? Why/ why not?
5 Is developing the organization of ideas for
speaking easy to do? Why/ why not?
6 Do you understand how to make mind mapping
well? Why/ why not?
The process of using mind mapping in speaking
7 Can you make and implement how to use mind
mapping to develop the organization of ideas? Why/ why not?
8 Is mind mapping interesting to develop your
organization of ideas in speaking? Why/ why not?
9 Does mind mapping help you to develop your
organization of ideas in speaking? How can it help you?
Perception and implications of using mind mapping in speaking
Students’ perception of using mind mapping in speaking
10 Does mind mapping help you to develop your
organization of idea in speaking? Why/ why not?
11 Does your speech become in good order by the
use of mind mapping? Why/ why not?
12 Are you motivated to speak in front of the class by the use of mind mapping? Why/ why not?
13 Do you like to use mind mapping to develop your organization of ideas in speaking?
14 What are your suggestions on the use of mind
mapping in speaking?
While the data gathering technique in this research was done in some steps.
1) The researcher gave preliminary action of applying mind mapping as one of the technique to develop their organization of idea in speaking. (including giving example of mind mapping and how to make a good mind mapping)
2) The students practiced to construct mind mapping to develop idea of speaking and practiced speaking using mind mapping. (3 meetings)
39
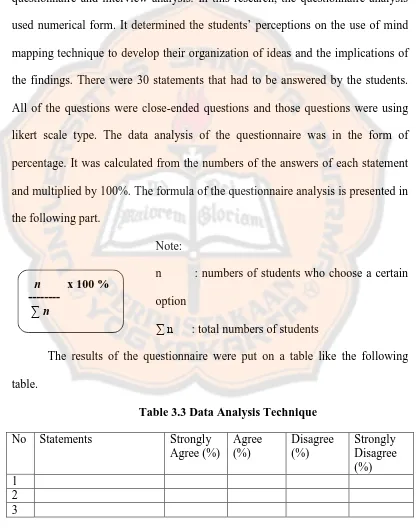
3.5 Data Analysis Technique
In this part, there are 2 main parts of the data analysis. They are questionnaire and interview analysis. In this research, the questionnaire analysis used numerical form. It determined the students’ perceptions on the use of mind mapping technique to develop their organization of ideas and the implications of the findings. There were 30 statements that had to be answered by the students. All of the questions were close-ended questions and those questions were using likert scale type. The data analysis of the questionnaire was in the form of percentage. It was calculated from the numbers of the answers of each statement and multiplied by 100%. The formula of the questionnaire analysis is presented in the following part.
Note:
n : numbers of students who choose a certain option
∑ n : total numbers of students
The results of the questionnaire were put on a table like the following table.
Table 3.3 Data Analysis Technique
After the researcher finished the data calculation of the questionnaire, the researcher drew conclusions of each statement and combined it at each category of the questionnaire. The researcher drew conclusion of the students’ perceptions on the use of mind mapping to develop their organization of ideas in speaking and the implications of the findings.
The interview analysis was obtained by having all of the results of the interviews. The interview results were about further information of the data questionnaire on why they chose the answers. The samples of the interviewees were the students of class VIII C and VIII D who mostly answered ‘disagree’ or ‘strongly disagree’ from the questionnaire. They were selected as the interviewees because they were asked further information about problems in speaking, the process of using mind mapping, and the students’ perceptions on the use of mind mapping in speaking. Besides, it was also about clarification of the ambiguous answers. The interview results were analyzed by summarizing each number of the interview questions. The researcher drew conclusion based on the results of the answers each number. Afterwards, the researcher rechecked all of the answers from the data analysis in order to get applicable conclusion.
3.6 Research Procedure
41 used by the researcher to facilitate in the research process. The steps of the research were:
1. Finding the Problem
Firstly, the researcher conducted observation to the students of SMP N 2 Sedayu and had an informal conversation to the English teachers of SMP N 2
Sedayu. Through the observation and the informal conversation, the researcher
found that the students were difficult in practicing speaking skill. The researcher decided to conduct a study on the technique for helping the students in learning speaking. Mind-mapping was proposed by the researcher as the technique which would be used to help the students develop their organization of ideas in speaking. The researcher focused the study on the students’ perceptions on the use mind mapping in speaking skill.
2. Review of Related Literature
In order to get a complete understanding of the study, the researcher tried to attain some information related to the study by collecting some theories. The researcher collected the theories, synthesized the theories and used those theories as the background knowledge in conducting the research.
3. Preparing the Research (asking permission)
to the headmaster of SMP N 2 Sedayu in order to get the permission of conducting research in that school.
4. Planning the Research
After having the letter of permission, the researcher prepared the instruments to conduct the research. The instruments were included interview and questionnaire. The researcher made the questionnaire and interview to collect the data of the research.
5. Conducting the Research
The researcher conducted the research after the instruments were fixed to be distributed to the respondents (eighth grade students and English teachers). At the first time, the researcher taught the mind mapping technique to the students and it was used to implement the technique in teaching learning process. The students had to use mind mapping to develop their organization of idea in speaking. The process of using mind mapping took 3 meetings. The researcher implemented mind mapping technique to class VIII C and VIII D.
6. Evaluating
RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter will elaborate the research results and the discussion part. The results of the research are about the students’ perceptions on the use of mind mapping to develop their organization of ideas in speaking. The research results will talk about the results of questionnaire and interview. To answer the first problem formulation, in the discussion part, the researcher will present the discussion of students’ perceptions on the use of mind mapping to develop their organization of ideas in speaking. Meanwhile, to answer the second problem formulation, the researcher will elaborate the implications of the findings.
4.1. Research Results
This part consists of two sections, namely the results of the questionnaire and the results of the interview. Those sections will show the results of the research based on the instruments used in this research.
4.1.1. The Results of the Questionnaire
45
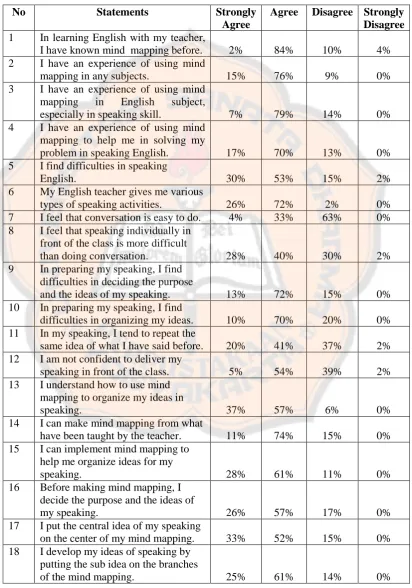
Table 4.1 The Percentage of Each Statement of the Questionnaire Results
No Statements Strongly
Agree
Agree Disagree Strongly
Disagree 1 In learning English with my teacher,
I have known mind mapping before. 2% 84% 10% 4%
mapping to help me in solving my
problem in speaking English. 17% 70% 13% 0%
5 I find difficulties in speaking
English. 30% 53% 15% 2%
6 My English teacher gives me various
types of speaking activities. 26% 72% 2% 0%
7 I feel that conversation is easy to do. 4% 33% 63% 0%
8 I feel that speaking individually in front of the class is more difficult
than doing conversation. 28% 40% 30% 2%
9 In preparing my speaking, I find difficulties in deciding the purpose
and the ideas of my speaking. 13% 72% 15% 0%
10 In preparing my speaking, I find
difficulties in organizing my ideas. 10% 70% 20% 0% mapping to organize my ideas in
speaking. 37% 57% 6% 0%
14 I can make mind mapping from what
have been taught by the teacher. 11% 74% 15% 0%
15 I can implement mind mapping to help me organize ideas for my
speaking. 28% 61% 11% 0%
16 Before making mind mapping, I decide the purpose and the ideas of
my speaking. 26% 57% 17% 0%
17 I put the central idea of my speaking
on the center of my mind mapping. 33% 52% 15% 0%
18 I develop my ideas of speaking by putting the sub idea on the branches
Continued from page 45
No Statements Strongly
Agree
Agree Disagree Strongly
Disagree 19 I use arrows to make connections
within and across the branch pattern. 43% 48% 9% 0%
20 I use only key word on each branch. 15% 74% 11% 0%
21 I make mind mapping creative and
interesting. 30% 67% 3% 0%
22 I use my mind mapping to help me speak in front of the class.
22% 67% 11% 0%
23 Mind mapping helps me to prepare
my speaking well. 30% 61% 7% 2%
24 Mind mapping really helps me to develop the organization of ideas in
speaking. 20% 63% 17% 0%
25 I become confident and motivated to speak in front of class when I use
mind mapping. 24% 67% 9% 0%
26 By using mind mapping, I can save much time to prepare and develop
my ideas. 15% 68% 15% 2%
27 By using mind mapping, I can add new information related to my
speech easily. 26% 63% 11% 0%
28 I can improve my speaking well
when I use mind mapping. 15% 76% 9% 0%
29 Mind mapping is easily implemented to prepare and develop my
organization of ideas of speaking. 22% 63% 17% 0%
30 Overall, I like to use mind mapping to develop the organization of ideas
in speaking. 20% 65% 15% 0%
47
4.1.1.1The Students’ Previous Experience in Using Mind Mapping
There were four statements related to the previous experience of using mind mapping. There were 2% of respondents who strongly agreed, 84% of respondents who agreed, 10% of respondents who disagreed, and 4% of respondents who strongly disagreed that in learning English with teacher they had known mind mapping before the research was conducted. The next results of the statement were 15% of respondents who strongly agreed, 76% respondents who agreed, 10% of respondents who disagreed, and 0% of respondents who strongly disagreed that they had an experience of using mind mapping in any subject. Related to the experience of using mind mapping in a subject, there were 7% of respondents who strongly agreed, 79% of respondents who agreed, 14% of respondents who disagreed, and 0% of respondents who strongly disagreed that they had any experience of using mind mapping in English subject, especially in speaking skill. For the next statement, there were 17% of respondents who strongly agreed, 70% of respondents who agreed, 13% of respondents who disagreed, and 0% of respondents who strongly disagreed that they had an experience of using mind mapping to help them solve their problem in speaking English.
4.1.1.2 The Problems Faced by the Students in Speaking
strongly agreed, 53% of respondents who agreed, 15% of respondents who disagreed, and 2% of respondents who strongly disagreed that they found difficulties in speaking English. The next statement, there were 28% of respondents who strongly agreed, 40% of respondents who agreed, 30% of respondents who disagreed, and 2% of respondents who strongly disagreed about the opinion that speaking individually in front of the class was more difficult than doing conversation.
Related to the activity of speaking in front of the class, there were 13% of respondents who strongly agreed, 72% of respondents who agreed, 15% of respondents who disagreed, and 0% of respondents who strongly disagreed that in preparing their speaking, they found difficulties in deciding the purpose and the ideas of the speech and also in organizing and developing their ideas. Furthermore, there were 20% of respondents who strongly agreed, 41% of respondents who agreed, 37% of respondents who disagreed, and 2% of respondents who strongly disagreed that in delivering their speaking, they tended to repeat the same idea of what they had said before. For the last statement, there were 5% of respondents who strongly agreed, 54% of respondents who agreed, 39% of respondents who disagreed, and 2% of respondents who strongly disagreed that they were not confident to deliver their speaking in front of the class.
49 students mostly found difficulties in deciding the purpose and ideas of their speaking. Besides, they encountered difficulties in organizing their ideas. Furthermore, most of the students tended to repeat the same ideas they had said before. They were also not confident to speak in front of the class when delivering their speaking.
4.1.1.3 The Process of Using Mind Mapping in Speaking
There are six statements from the results of the questionnaire that will be elaborated in this part. For the first statement, there were 37% of respondents who strongly agreed, 57% of respondents who agreed, 6% of respondents who disagreed, and 0% of respondents who strongly disagreed that they understood how to use mind mapping to develop their organization of ideas in speaking. Next, there were 11% of respondents who strongly agreed, 74% of respondents who agreed, 15% of respondents who disagreed, and 0% of respondents who strongly disagreed that they could make mind mapping through using the explanation given by the teacher. Furthermore, there were 28% of respondents who strongly agreed, 61% of respondents who agreed, 11% of respondents who disagreed, and 0% of respondents who strongly disagreed that they could implement mind mapping to help them organizing their ideas for their speaking.
0% of respondents who strongly disagreed that they made mind mapping to guide them to speak properly by following the steps of making mind mapping, namely deciding the purpose and the ideas of speaking, putting the central idea of their speaking on the center of their mind mapping, developing their ideas of speaking by putting the sub ideas on the branches of the mind mapping, using arrows to make connections within and across the branch patterns, and using key words only on each branch.
The last statement is related to the creativity in making mind mapping. There were 30% of respondents who strongly agreed, 67% of respondents who agreed, 2% of respondents who disagreed, and 0% of respondents who strongly disagreed that they made their mind mapping creatively and interestingly. The results showed that the students mostly created their mind mapping as creative as possible and as interesting as possible to make them to more easily speak in front of the class.
4.1.1.4 Students’ Perceptions on the Use of Mind Mapping in Speaking