plSSN 2302-1381
elSSN 2338-4506
dcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
In te rn a tio n a l J o u rn a l
of
In te g ra te d H e a lth S c ie n c e s
Review
Integrating
Basic Sciences into Global Health by Implementing
the
Translational Research
Original Articles
Strategy for the Use of Erythropoetin
Alpha to Maintain Hemoglobin
Level in Breast Cancer Patient Treated with Anthracycline-Base
of
Adjuvant Chemotherapy
Akt-the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Pathways Inhibition
Increases Cervix Cancer Cell Chemosensitivity
to Active
Form of
Irinotecan (SN-38)
Histological Description of Meningeal and Periosteal Dural Layers at
the Porus of Internal Acoustic Canal in the Vestibular Schwannoma
Effect of Overground
Walking and Treadmill
Exercise on Walking
Speed and Walking Ability in Elderly
Preliminary Study: Glycemic Index of Brown and White
Rice Variant
I R64 in Healthy Adult Men
Chlamydial Infection
Prevalence in Human Immunodeficiency
Virus
Patients
Case Report
Nephropathy
and Encephalopathy
in an Indonesian
Patient with
Dengue Viral Infection
p lS S N 2 3 0 2 -1 3 8 1 e lS S N 2 3 3 8 -4 5 0 6
International Journal
of
Integrated Health Sciences
XWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
V o lu m e 1 , N u m b e r 1 , J u ly , 2 0 1 3A d v is o r y B o a r d
tsrqponmlkjihgfedcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
Tri Hanggono Achmad
E d it o r - in - C h ie f
Budi Setiabudiawan
S e c r e t a r y E d it o r s
Irma Ruslina Defi Marissa Tasya
E d it o r s
Ahmad Faried Agung Budi Sutiono Arief Sjamsulaksan Kartasasmita Diba Artsiyanti Ediyana Putri Basar
Dini Norviatin Edhyana Sahiratmadja
Hendra Gunawan Henni Djuhaeni
Herry Garna Herry Herman Sharon Gondodiputro Yanni Melliandari Achmad
R e v ie w e r s
Bachti Alisjahbana (Indonesia) Reinout van Creve I (The Netherlands) Bethy Suryawathy Hernowo (Indonesia) Rovina Ruslami (Indonesia)
Cissy Rachiana Sudjana Prawira (Indonesia) Salequllslam (Bangladesh) Eric Simoes (United States) Shigeru Saito (Japan)
Hugo van Bever (Singapore) Sofie Rifayani Krisnadi (Indonesia) Ida Parwati (Indonesia) Togas Tulandi (Canada)
Makoto Sohmiya (Japan) Wan Arifin Abdullah (Malaysia) Noriyuki Koibuchi (Japan) Wasmen Manalu (Indonesia)
A d m in is t r a t iv e S t a f f
Ati Sulastri Devi Fabiola Syahfitri Erlan Aditya Ardiansyah
Indrianti Ira Andriati
Rahadian
Editorial Address:
Jalan Prof. Dr. Eijkman 38 Bandung 40161, Indonesia Phone (+62-22) 61039773 ext.1401; Fax: (+62-22) 2030776
E-mail: [email protected]
plSSN 2302-1381
elSSN 2338-4506
dcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
In te rn a tio n a l J o u rn a l
of
In te g ra te d H e a lth S c ie n c e s
Volume 1, Number 1, July, 2013
Review
Integrating Basic Sciences into Global Health by Implementing the Translational Research 1 Muhamad Nurhalim Shahib, Diah Dhyanawati, Elrade Rofaani
Original Articles
Strategy for the Use of Erythropoetin Alpha to Maintain Hemoglobin Level in Breast Cancer 8 Patient Treated with Anthracycline-Base of Adjuvant Chemotherapy
Dimyati Achmad, Yusuf Hariady, Benny Isakh, Maman Abdurrahman, Ahmad Faried
kt-the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Pathways Inhibition Increases Cervix . 13 Cancer Cells Chemosensitivity to Active Form of Irinotecan (SN-38)
Leri Septiani, Yudi Mulyana Hidayat, Yusuf Sulaeman Effendi, Tono Djuwantono, Dimas Erlangga Luftimas, Ahmad Faried
Histological Description of Meningeal and Periosteal Dural Layers at the Porus of Internal 22 coustic Canal in the Vestibular Schwan noma
Agung Budi Sutiono, Muhammad Zafrullah Arifin, Ahmad Faried, Takayuki Ohira
Effect of Overground Walking and Treadmill Exercise on Walking Speed and Walking Ability 29 in Elderly
Theresia Chandra Tania Novy, Vitriana, Sunaryo Barki Sastradimaja, Irma Ruslina Defi
Preliminary Study: Glycemic Index of Brown and White Rice Variant IR64 in Healthy Adult 3 7 Men
Nur Irika binti Idril, Aly Diana, Abdullah Firmansyah Wargahadibrata
Chlamydiallnfection Prevalence in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Patients 42 Feilicia Henrica Teja, Rasmia Rowawi, Asmaja Soedarwoto, Diah Puspitosari,
Rini Rasianti, Rahmatdinata, Tony Djajakusumah
Case Report
Original Article
dcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
-e h e
Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Pathway Inhibition
Increases
leal Cancer Cell Chemosensitivity to Active Form of Irinotecan (SN-38)
- Septiani,' Yudi Mulyana Hidavat,' Yusuf Sulaeman Effendi,l Tono Djuwantono,' Dimas Erlangga - as,' Ahmad Faried2
rtment of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Padjadjaran-Or. Hasan Sadikin I Hospital
ogy and Stem Cell Working Group, Health Research Unit, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Padjadjaran-n SadikiPadjadjaran-n GePadjadjaran-neral Hospital
c t Objective: To investigate the molecular pathway of the cytotoxic effect of SN-38 in human cervical cancer cell lines.
Methods: Two human cervical cancer cell lines were treated with various concentrations of irinotecan for 24-72 hours and the sensitivity was analysed using the MTI assay. Apoptosis was further observed through microscopic examinations. The protein expression was determined using Western blot analysis.
Results: CaSki cells demonstrated the highest sensitivity to SN-38, whereas HeLa cells showed the lowest. In cervical cancer cells, SN-38 induced apoptosis through an intrinsic- and extrinsic-pathways. In addition, we showed that SN-38 down regulated the phosphorylation of Akt-mTOR pathways in CaSkicells, but not in HeLacells. Interestingly, in HeLacells, which were more suggestive of a resistant phenotype, pre-treatment with LY294002and rapamycin inhibited activation of Akt-mTOR signaling and significantly enhanced the sensitivity of HeLacells to SN-38.
- ed: r3 1 ,2 0 1 2
Conclusions: Irinotecan exerts its anti-neoplastic effects on cervical cancer cells by inducing apoptosis through caspase-cascade. Inhibition of Akt-mTOR, LY294002and rapamycin, which is targeted to Akt-mTOR pathways, may sensitize irinotecan-resistant cervical cancer cells.
d :
ary 1 , 2 0 1 3 Keywords: Akt-mTOR pathways anti-neoplastic drugs, cervix cancer cells,
LY294002,rapamycin ed:
ary 2 4 ,2 0 1 3 IJIHS.2 0 1 3 ;1 ( 1 ) :1 3 - 2 1
o d u c tio n cervical cancer is generally treated with radical
operations but up to now there is no fixed standard therapy for FIGO stadium Ib-lIa of cervical cancer. Cancer within these stadiums can be treated with radical operation, radiotherapy, surgery-radiotherapy combination, surgery-anticancer drug combination, or chemotherapy although these combination therapy protocols may vary. The administration of the combination therapy for each patient is based on many factors including age, general condition, and patient's preference to achieve maximum therapy target with minimum complications.
The standard surgery for cervical cancer in stadium Ib and lIa is radical hysterectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy. The benefit of surgical therapy is the ability to extract primary tumor and apply staging accurately which leads to the inorna of the cervix is the second most
on neoplasm in Indonesian women and second most common neoplasm leading emale cancer rnortalitv.' Furthermore, it is
he second most frequently found cancer g women in reproductive age between 1 5 -ears 01d.2It constitutes almost 1 5 ,0 0 0 new
sand 7 ,5 0 0 deaths per annum."
Cervical cancer treatment depends on the
eration
BA
I n t e r n a t i o n a l e d e G y n e c o l o q i e e tstetrique
(FIGOl staging. Early stadium ofpondence:
- Septiani,Departmentof Obstetricsand Gynecology, of Medicine,UniversitasPadjadjaran-Dr.Hasan - GeneralHospital
::IasteurNo.3 8 ,Bandung,Indonesia
=--a :
[email protected]Akt-the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Pathways Inhibition Increases Cervix Cancer Cell Chemosensitivity to Active form of Irinotecan (SN-38)
selection of the most appropriate type of adjuvant therapy for the patient. For stadium Ib2 and lIa, neoadjuvant chemotherapy is one of several adjuvant therapy alternatives applied. The goal ofthis neoadjuvant chemotherapy is to eradicate micrometastasis and reduce primary tumor volume so the next treatment effectiveness can be improved both for surgery and radiotherapy. In addition to radiotherapy, chemotherapy is the standard treatment for advanced cervical cancers. However, the systemic therapy protocol for this kind of cervical cancer keeps changing. In the past, chemotherapy was used for recurrent and persistent cervical cancer, or cervical cancers with metastasis. Currently, chemotherapy is the primary treatment for cervical cancers with a high risk of reccurrency.
The best possible treatment of locally advanced cervical cancer is a combination of radiation and cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Cisplatin-based chemotherapy as the main regimen is still the primary choice for advanced, metastatic, and recurrent cervical cancers. Even with this regimen, the response rate of advanced stadium patients was only 23% with limited response time." From this data, it is suggested that conventional treatment methods have reached a plateau and, therefore, to overcome this problem, finding a good prognostic factor and predictor response to chemotherapy might be useful.
Irinotecan (CPT-ll) and its analog have given promising results on many clinical trials. SN-38, which is a semi-synthetic derivative of camptothecin, is the active metabolite of Irinotecan. Like other camptothecin-derivatives, SN-38 inhibits topoisornerase. I (Topo I), a nuclear enzyme needed for replication and transcription by unwinding supercoiled DNA.4 SN-38 interferes with Topo I activity by trapping Topo I-DNA cleavage complexes, leading to lethal replication-mediated double strand breaks and ended with cell death." Currently, irinotecan is used as a standard therapy for colon cancer but not for cervical cancer. lrinotecan specificity against cervical cancer needs to be studied.
Chemotherapeutic agents kill cancer cells through interaction with several distinct intra-cellular targets, including factors affecting cells cycles, apoptosis cell death, and survival pathways. Class I phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and its downstream effectors, such as Akt and mTOR, have emerged as a prominent proliferation and survival pathway. Activation of the PI3KjAkt-mTOR pathway has been implicated in many human cancers and shown to be associated with chemoresistance.' We have previously shown that advanced cervical cancer
expressed Akt and mTOR and the expression of p-mTOR could predict the response to neoadjuvants and the survival of the patients treated with cisplatin-based neoadjuvant chernotherapv.v' A therapeutic strategy for selectively modulating the expression of a gene of interest is the use of inhibitor agents of Akt such as LY294002 and inhibitor agents of mTOR such as rapamycin. We assessed whether the active form of irinotecan treatment enhanced the inhibition of proliferation signals, in this case the Akt-mTOR pathway, which led to increase of cell death.
XWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
M e t h o d s
Cell lines and culture conditions
Two human cervical cancer cell lines, the HeLa cell line which is an adenoma cell carcinoma with human papilloma virus or HPV-18 (+) and CaSki cell line which is a squamous cell carcinoma with HPV-16 (+l, were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) (Manassas, VA). HeLa cells were maintained in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium (EM EM) obtained from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MOl, supplemented with 2 mM L-glutamine, 1.0 mM sodium pyruvate, and 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) obtained from Gibco (BRL, Grand Island, NY). The CaSki cells were maintained in Rosewell Park Memorial Institute-1640 (RPMI-1640) medium (Gibco) supplemented with HEPES (Sigma) and 10% heat-inactivated FBS. .
Drugs and cell treatment
Irinotecan was purchased from Wako Pure Chemicals (Osaka, Japan) and received as sterile lyophilized powder. A stock solution of 5
BA
m g jmL was made in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) and stored at 4
dcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
" C . Further dilutions were made in culture media to reach the desired concentrations when the cells obtained approximately 80% confluency. The final concentration of DMSO did not exceed 0.08%, a concentration that does not alter the growth or survival properties of any cell type. We used CPT-ll and SN-38 stock of 3 ~M peak plasma concentration (ppc) with a range of 9.8 ng/rnl.-S ~M. LY294002 and rapamycin were purchased from Calbiochem (San Diego, CA). For LY294002 (25 ~M) or rapamycin (100 nm), cells were pre-incubated with these inhibitors for 6 hours (h) prior to irinotecan treatment.Drug sensitivity assay
Cell proliferation analysis was performed on human cervical cancer cell lines in the presence of various concentrations of drugs by a colorimetric
L e ri S e p tia n i, Y u d i M u ly a n a H id a y a t,
et al.
tsrqponmlkjihgfedcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
mM EDTA, 140 mM NaCI, 1% Nonidet P-40, 1% aprotinin, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonylfluoride, and 1 mM sodium vanadate). The concentration of the sample protein was determined by bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay (Pierce, Rockford, IL). Equal amounts of protein (40
us)
were subjected to a 5-20% Tris-tricine Ready Gel (Bio-Rad, Tokyo, Japan) and then transferred to nitrocellulose membrane (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Buckinghamshire, UK). Membrane was blocked with Tris-buffered saline/O.l% Tween 20 with 5% nonfat dry milk and incubated in primary antibodies against caspase-3, caspase-8, caspase-9 and PARP(Santa Cruz); phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt, Ser473), phosphorylated mTOR (p-mTOR, ser2448) and phosphorylated p70 S6 Kinase (pS6Kl,Thr389) from Cell Signaling at 4 "C overnight. The bands were visualised by a chemiluminescence system (Amersham). The expression of beta-actin (Sigma) served as a loading control. The density of the bands was quantified using Ouantitv.One (BioRad).methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium (MTI) assay. Briefly, exponentially growing cells (2xl04 cells/well) were plated in 96-well plates. After an overnight culture, the medium was substituted by a fresh medium with different concentrations of drugs. At the end of various treatments, 10 ul, of a cell-counting solution (WST-8, Dojindo Labs, Tokyo, Japan) was added. After dissolving the crystals with 1 N HCI-isopropanol, the absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 450 nm using a microtiter plate reader (Beckton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ). A value of 100% was assigned to untreated control and the concentration of drug that reduced the number of viable cells to 50% after 24 h of exposure (CPlso) was derived from cell survival plots. All experiments were performed in triplicate.
Light microscopy examination
All cells were cultured in a 6-cm plate and treated with drugs as described previously. Morphological changes were examined at the times indicated and photographed using a regular phase contrast microscope.
Western blot analysis
Western blot analysis was applied as described." Cells were harvested at the time indicated and prepared in a buffer (20 mM Tris-HCI, pH 7.6, 1
BA
( A ) Control 2 h o u rs
Statistical analysis
Quantitative experiments were analyzed using Student's t test. The P value was gained from the two-sided tests and were considered significant when p<0.05.
2 4 h o u rs 3 6 h o u rs
(B)
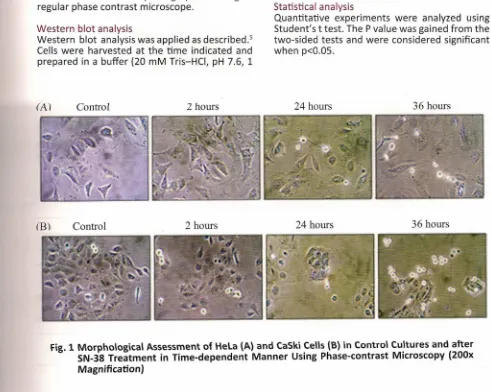
C o n tro l 2 h o u rs 2 4 h o u rs 3 6 h o u rsF ig . 1 M o rp h o lo g ic a l A s s e s s m e n t o f H e la { A }a n d C a S k i ~ e lls (B ) in C o n tro l C U .ltu re s a n d a fte r SN-38 Treatment in Time-dependent Manner USing Phase-contrast Microscopy (200x Magnification)
Akt-the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Pathways Inhibition Increases Cervix Cancer Cell Chemosensitivity to Active form of Irinotecan (SN-38)
""'BA
l 70
I:
dcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
.S 6 0
••
...
. f ) 50
~
"" 4 0
a
o
'.G 30
e
r2
~ O..•
e
10c..
~ 0
H eL a (C P I5 0 = 6 8 7 ,5 n M - 7 2 W
""'
C aS k i(C P I5 0 =
1 8 ,6 2 n M -7 2 h l
l 1 0 0g
9 0 .~ 8 0~ .t:: 70 ~ 60
§ 5 0
.~ 4 0
'"
~ 3 0
~ so
e
c..
10::=
0'---'----'----'-"""----'---'--'--"""----'---'
t3
- + - 2 4 h - + - 4 8 h
-b-m
9 B 1 9 5 3 9 .1 7 8 .1 1 5 6 3 3 1 2 5 m m o 2 5 0 0 5 0 0 0
S N '3 8 C o n cen tratio n ( n W
9 .8 1 9 5 3 9 .1 1 8 .1 1 5 6 .3
ms
m n so 2 5 0 0 5 0 0 0S N '3 8 C o n cen tratio n (n M )
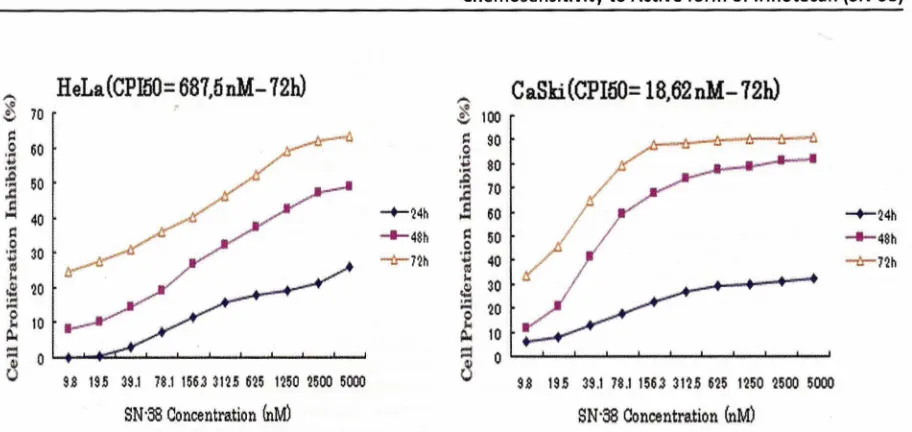
Fig. 2 The Effect of SN-38 on the Growth Inhibition of HeLa (Left) and CaSki (Right) Cells Using MTT Assay. Concentration-and Time-related Inhibition of Cells Growth at 24, 48 and 72 Hours were Shown
Results
Sensitivity of human cervical cancer cells to CPT-11 and SN-38
To investigate the sensitivity of human cervical cancer cells to CPT-11 and SN-38, the cells were treated for 24-72 h in a medium containing various concentrations of drugs. The exposure to drugs (9,8 ng/ml-5 ~M) produced a dose and time dependent cell growth reduction in Hela and CaSki cells (Fig. 1-2). CaSki cells demonstrated a higher sensitivity compared to Hela. The cell proliferation inhibition SO (CPls.Q)values for 72 h treated Hela were 320 ~M, 1.~1 ~M and 687.5
nM for CPT-11, SN-38 disolved with medium, and SN-38 disolved with pure water (Hpj, respectively. On the other hand, for 72 h treated CaSki, the results were 224 ~M, 50.8 nM and 18.6 nM for CPT-11, SN-38 disolved with medium, and SN-38 disolved with pure water, respectively (Table 1). Based on these results, both Hela and CaSki cells treated in SN-38 disolved with pure water were used for further experiments.
Expression and modulation of other apoptosis-related proteins by SN-38
In this study, it is also observed that SN-38 treatment had significantly upregulated the
Table 1 Concentration Proliferation Inhibition 50 (CPlso) of HeLa and CaSki Cells to Rinotecan, SN-38 Disolved with Medium, and SN-38 with Pure Water (HP)
Cell type Irinotecan SN-38 (med) SN-38 (H20)
H e L a 3 2 0 11M(7 2 h ) 1 .9 1 11M(7 2 h )
C a S k i 2 2 4 11M(7 2 h ) 5 0 .8 nM (7 2 h )
6 8 7 .5 nM (7 2 h)
1 8 .6 2 nM (7 2 h)
Table 2 Concentration Proliferation Inhibition (CPlso) of HeLa and CaSki Cells to SN-38 Alone, with Pre-treatment LV294002 (LV), and Rapamycin (Rap)
Cell type SN-38 lY-SN-38 Rap-SN-38
H e L a 6 8 7 .5 nM
C a S k i 1 8 .6 2 nM
2 6 5 .6 3 nM
1 5 .6 8 nM
1 8 1 .6 nM
4 .9 nM
LY,LY294002; Rap, rapamycin
~ -actin
tsrqponmlkjihgfedcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
I.· ....
L e ri S e p tia n i, Y u d i M u ly a n a H id a y a t,
et
BA
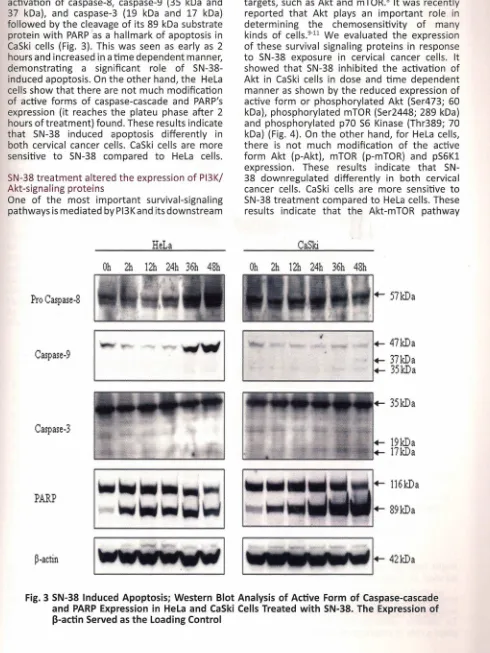
0 1 .activation of caspase-8, caspase-9 (35 kDa and 37 kDa), and caspase-3 (19 kDa and 17 kDa) followed by the cleavage of its 89 kDa substrate protein with PARP as a hallmark of apoptosis in CaSki cells (Fig. 3). This was seen as early as 2 hours and increased in a time dependent manner, demonstrating a significant role of SN-38-induced apoptosis. On the other hand, the HeLa cells show that there are not much modification of active forms of caspase-cascade and PARP's expression (it reaches the plateu phase after 2 hours of treatment) found. These results indicate that SN-38 induced apoptosis differently in both cervical cancer cells. CaSki cells are more sensitive to SN-38 compared to HeLa cells.
SN-38 treatment altered the expression of PI3Kj Akt-signaling proteins
One of the most important survival-signaling pathways is med iated by PI3 K a nd its downstrea m
H eL a
O h 2 h 1 2 h 2 4 h 3 6 h 4 8 h
P ro C aspase-B
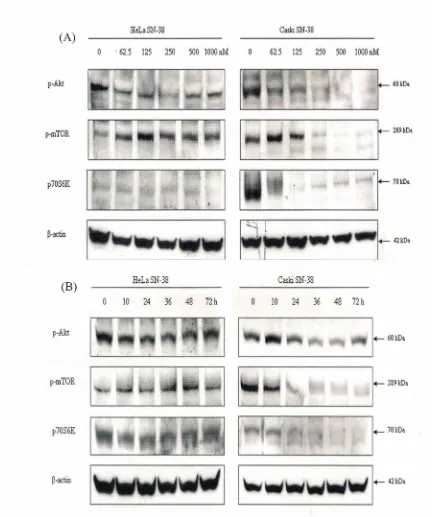
targets, such as Akt and mTOR.8 It was recently reported that Akt plays an important role in determining the chemosensitivity of many kinds of cells."!' We evaluated the expression of these survival signaling proteins in response to 5N-38 exposure in cervical cancer cells. It showed that 5N-38 inhibited the activation of Akt in Ca5ki cells in dose and time dependent
manner as shown by the reduced expression of active form or phosphorylated Akt (5er473; 60 kDa), phosphorylated mTOR (5er2448; 289 kDa) and phosphorylated p70 56 Kinase (Thr389; 70 kDa) (Fig. 4). On the other hand, for HeLa cells, there is not much modification of the active form Akt (p-Akt), mTOR (p-mTOR) and pS6K1 expression. These results indicate that 5N-38 downregulated differently in both cervical cancer cells. Ca5ki cells are more sensitive to 5N-38 treatment compared to HeLa cells. These results indicate that the Akt-mTOR pathway
C aS k i
O h 2 h 1 2 h 2 4 h 3 6 h 4 8 h
C asp ase-9
'--__ ll__ i_l:~~:
_ . .+ - 3 5 k D a
Fig. 3 SN-38 Induced Apoptosis; Western Blot Analysis of Active Form of Caspase-cascade and PARP Expression in HeLa and CaSki Cells Treated with SN-38. The Expression of (3-actin Served as the Loading Control
International Journal of Integrated Health Sciences. 2013;1(1):13-21
C asp ase-3
P A R P
I
+ - 1 1 6 k D a
+ - 8 9 k D a
~---~
__________ ~~_._.~~42illa
A k t - t h e M a m m a lia n T a r g e t o f R a p a m y c in ( m T O R ) P a t h w a y s In h ib it io n In c r e a s e s C e r v ix C a n c e r C e ll
C h e m o s e n s it iv it y t o A c t iv e f o r m o f Ir in o t e c a n ( S N - 3 8 )
dcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
H eL aS N -3 8 C aslciS N -3 8
(A )
a
62.5 125 250 500 1000 nM 0 62.5 125 250 500 lO O O nMp -A k t
roo'~
tsrqponmlkjihgfedcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
p-mTOR
1'-
Im ~
p70S 6K
I"
7 0 k D a
~ -a c tin
1
4 2 k D a
(B ) H eL aS N · 38 C aski S N · 38
0 10 24 36 48 72h 0 10 24 36 48 72h
p-A kt
I
~oo.~
p-m T O R
I
r~'~'
p70S 6K
I
r"".
~ -a c tin
I I
1__ 4 J ~
F ig . 4 S N - 3 8 E f f e c t o n p - A k t , p - m T O R a n d p - 7 0 S 6 K l W e s t e r n B lo t A n a ly s is o f A c t iv e F o r m A k t - m T O R P a t h w a y s in H e L a a n d C a S k i C e lls H a r v e s t e d f o r t h e T im e In d ic a t e d ( A ) a n d D if f e r e n t D o s e ( B ) . j3 - a c t in S e r v e d a s C o n t r o l
might have an important role to maintain the survival of CaSki cells in response to SN-38. Inhibition of Akt-mTOR pathway increases the sensitivity of SN-38 induced apoptosis
To confirm whether the Akt-mTOR pathway plays a role in response to SN-38, the LY294002
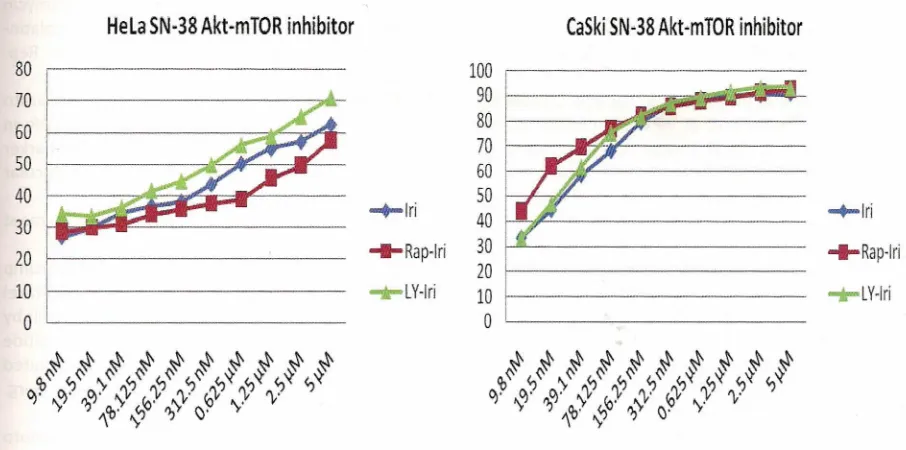
and rapamycin as pretreatment to irinotecan were used. Pre-treatment with LY294002 and rapamycin significantly enhance the cell proliferation inhibition in HeLa cells (p<O.05, Table 2, Fig. 5). As in CaSki cells, pre-treatment with LY294002 did not significantly enhance the cell proliferation inhibition. On the other hand,
L e ri S e p tia n i, Y u d i M u ly a n a H id a y a t,
et al.
tsrqponmlkjihgfedcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
highest sensitivity, whereas HeLa cells was the most resistant. Furthermore, an examination on whether CPT-ll and SN-38 induced apoptosis in human cervical cancer cells was also performed. To determine the molecular mechanism that
mediates the cytotoxic effect of SN-38 in human cervical cancer cells, we performed Western blot analysis. In this study, it is demonstrated that SN-38 activated caspase-8, caspase-9, caspase-3 and PARP in CaSki cells. These results indicate that in sensitive CaSki cells the induction of apoptosis by SN-38 might take place through intrinsic and extrinsic pathways.
It was recently reported that CPT-ll and SN-38 activate a serinefthreonin protein kinase Akt, which is the downstream target of PI3K.1 0
,1 2 Our
results demonstrated that SN-38 inhibits the activation of Akt in CaSki cells, which were more suggestive of a sensitive phenotype, which is shown by the downregulation of phosphorylated Akt at serine 473, phosphorylated mTOR at Ser2448, and phosphorylated p70 S6 Kinase at Thr389. Akt-mTOR pathwavs'have the main role in promoting cell survival and are frequently associated with chemoresistance to cytotoxic drugs. The elevation level of phosphorylated Akt-mTOR pathways was reported to be involved in the mechanism ofc h e m o re s is ta n c e ." Surprisingly, however, in the HeLa cells, which were more suggestive of a resistance phenotype, pre-treatment with rapamycin significantly
enhanced the chemosensitivity of CaSki cells to SN-38 (p<O.OS, Table 2). To further evaluate the effect of pre-treatment with these inhibitor agents on apoptosis, an analysis on the morphological changes were performed using phase contrast microscopy. The results show that pre-treatment with rapamycin induced apoptosis in most of CaSki cells, which appeared as bright, rounded, and detached cells from the dish.
Discussion
Irinotecan, which is one of the anti-neoplastic agents with the broadest spectrum, is currently used in the treatment of many types of advanced cancers, but not in the cervical carcinoma. Until now, the prognosis of patients with advanced, persistent, or recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix has been pOOr.1
,2 Resistance to chemotherapy is the most frequent obstacle to effective treatment. Although the molecular mechanisms of paclitaxel in the mediation of cell death are well characterised, its effects on survival signaling remain unclear. This study determined the sensitivity of human cervical cancer cells to irinotecan (CPT-ll) as well as its active form (SN-38) and the results from the MTI assay showed that CaSki cells had the
Hela SN-38 Akt-mTOR inhibitor
8 0
7 0
60
5 0
40
3 0
20
1 0
o
-+-Iri
••••• Rap-lri
••••• LY·lri
CaSkiSN·38 Akt·mTOR inhibitor
1 0 0
;---90
~---==~~~L
8 0
I----__...,.,..;[F-=---7 060
5 0
40
3 0
20
1 0o
••••• Iri
+Rap·lri
••••• LY·lri
Fig. 5 Akt-Mtor Inhibitor Enhances Chemosensitivity of Hela (Left) and Caski (Right) Cells to 5n-38; Cells Treated with 5n-38 Alone, with or without 25 11M Ly294002 or 100 11M Rapamycin Pre-Treatment. The Cells Proliferation Inhibition was Determined by MTT Assay
A k t - t h e M a m m a lia n T a r g e t o f R a p a m y c in ( m T O R ) P a t h w a y s In h ib it io n In c r e a s e s C e r v ix C a n c e r C e ll
C h e m o s e n s it iv it y t o A c t iv e f o r m o f Ir in o t e c a n ( S N - 3 8 )
tsrqponmlkjihgfedcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
there was no altered activation of Akt-mTOR pathways to SN-38 treatment. It is tempting to speculate that the Akt-mTOR inhibitor might have an important role in promoting the cell death of HeLa cells. To elucidate this
phenomenon, we have conducted experiments using LY294002 or rapamycin as the Akt-mTOR inhibitor. We observed that the inhibition of Akt activation using LY294002 significantly enhance the sensitivity to SN-38 in HeLa cells (p<O.05). Furthermore, the inhibition of mTOR activation using rapamycin more significantly enhance the sensitivity to SN-38 in HeLa cells (p<O.Ol).
Rapamycin has been found to inhibit serine/threonin kinase mTOR by binding to the immunophilin FK506-binding protein 12 (FKBP12). The inhibition of mTOR kinase leads to dephosphorylation of its two major downstream signaling components, p70 S6 kinase (S6K1) and
4E-BPl.
dcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
1 4 Furthermore, we used rapamycin toinhibit Akt-mTOR activation in both HeLa and CaSki cells. As expected, we found that the inhibition of Akt-mTOR significantly enhanced the sensitivity of HeLa cells to irinotecan. Analysis of the morphology of cells under light-microscopy strengthened our findings that the inhibition of Akt-mTOR effectively increased
R e f e r e n c e s
1. Ferlay J, Bray F, Pisani P, Parkin D. GLOBOCAN
2002. Cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence
worldwide. IARC Cancer Base No.5, version 2.0.
Lyon: IARC Press; 2004.
2. Castellague X, de 5anjose 5, Aguado T, Louie K5,
Bruni L, Munoz J, etBA0 1 . HPV and cervical cancer in the world: 2007 report. Vaccine [serial on
the internet]. 2007 Nov [cited 2012 April 5]:
2007;25(5upp 3):[about 230]. Available from:
www.who.int/hpvcentre.
3. Thigpen T, Vance RB, Khansur T. The platinum
compounds and paclitaxel in the management
of carcinomas of the endometrium and uterine
cervix. 5emin Oncol, 1995;22(5 5uppI12):67-75.
4. Fiorica J v . The role of topotecan in the treatment of advanced cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol,
2003;90(3 Pt 2):516-21.
5. Faried L5, Faried A, Kanuma T, Nakazato T, Tamura
T, Kuwano H, et 0 1 . Inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) by rapamycin
increases chemosensitivity of Ca5ki cells to
paclitaxel, EurJ Cancer. 2006;42(7):934-47.
6. Faried L5, Faried A, Kanuma T, Sano T, Nakazato
T, Tamamura T, et 0 1 . Predictive and prognostic
20
irinotecan-induced apoptosis. Taken together, our results suggest that Akt-mTOR and its downstream effectors, S6K1, playa role in the survival of HeLa cells and that the inhibition of mTOR signaling may substantially potentiate apoptosis.
In summary, the study presented here is
the first to directly address the potential of targeting Akt-mTOR protein in the enhancement of therapeutic efficacy of a Topoisomerase I agent, irinotecan, in human cervical cancer cell lines. This information may increase our understanding to apply molecular targeting therapies that may improve the management of cancer with chemotherapy.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Post Doctoral Research (PHK-PKPD SK No. 853/ UN6.C/Kep/HK/2011) from the Indonesian Directorate General of Higher Education. (DIKTI)-Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Padjadjaran, Bandung (FK Unpad) for Led Septiani.
Author Disclosure Statement
Authors have no conflict of interests.
role of activated mammalian target of rapamycin
in cervical cancer treated with
cisplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Oncol Rep.
2006;16(1):57-63.
7. Faried LS, Faried A, Kanuma T, Sano T, Nakazato
T, Tamura T, et 0 1 . Expression of p-mTOR in adenocarcinoma of cervix: a potential biomarker
. and molecular target therapy. Molecular
Carcinogenesis. 2008;47(6):446-57.
8. McCormick F. Cancer: survival pathways meet
their end. Nature. 2004;428(6980):267-9.
9. Nguyen DM, Chen GA, Reddy R, Tsai W, Schrump
WD, Cole G Jr, et 0 1 . Potentiation of paclitaxel cytotoxicity in lung and esophageal cancer cells by
pharmacologic inhibition of the phosphoinositide
3-kinase/protein kinase B (Akt)-mediated
signaling pathway. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
2004;127(2):365-75.
10. Mabuchi S, Ohmichi M, Kimura A, Hisamoto
K, Hayakawa J, Nishio V, et 0 1 . Inhibition of phosphorylation of BAD and Raf-l by Akt sensitizes
human ovarian cancer cells to paclltaxel. J Bioi
Chem. 2002;277(36):33490-500.
11. Fahy BN, Schlieman MG, Virudachalam S, Bold
L e r i S e p t ia n i, Y u d i M u ly a n a H id a y a t ,
et
01.tsrqponmlkjihgfedcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
RJ. Inhibition of AKT abrogates
chemotherapy-induced NFkB survival mechanisms: implications
for therapy in pancreatic cancer. J Am Coli Surg.
2004;198:591-9.
12. un HL, Lui WY, Liu TY,
dcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
C h i C W o \\e.\Jexsa\ o~ ta'Y-o\resistance in hepatoma by cyclosporin A:
involvement of the P/-3 kinase-AKTl pathway. Br
J
BA
C a n c e r . 2 0 0 3 ; 8 8 ( 6 ) : 9 7 3 - 8 0 .13. Page C, Un HJ, Jin Y, Castle VP, Nunez G, Huang M,
et al.
Overexpression of Akt/AKT can modulate chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. AnticancerRes.2000;20(lA):407-16.
1 .1 \.
M ~ T \C .t,
~un't
¥... \'('an 5 \au an \n \u o .u an \n c.o n c.~ T · .
a novel target for therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2002;1(11):971-9.