i
DESIGNING A SET OF ENGLISH SPEAKING MATERIALS
USING ROLE PLAY FOR GRADE XI STUDENTS OF HOTEL
ACCOMMODATION CLASS SEWON VOCATIONAL SCHOOL I
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements To Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Rinanti Nur Oktapuri Student Number: 051214085
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
iv
“
If you learn from a teacher who still reads,
it is like drinking fresh water from a fountain.
But
if you learn from a teacher who no longer
reads,
it is like drinking polluted water
from a stagnant
pool”
(Anonym, 1954)
I dedicate the thesis to Jesus Christ,
all teachers and academicians, to my beloved parents and family
vi ABSTRACT
Rinanti Nur Oktapuri. 2010. Designing A Set of English Speaking Materials Using Role Play for XI Grade Hotel Accommodation Class of Sewon Vocational School 1. Yogyakarta: English Education Study Program, Departement of Language and Arts Education, Faculty of Teachers Training and Education, Sanata Dharma University.
Role play is one technique used in English lesson, mainly in teaching speaking skill. Role play motivates students to have an eagerness to speak moreover in front of the public. By using role play technique, students are acted to be someone else in a role that the students play. In this context, students should play roles as hotel management workers. Students perform the role play in front of the class. This study was carried out as there is no specific material for hotel accommodation class moreover for preparing students‟ speaking skill.
This study was concerned with two problems: 1) how is a set of English speaking materials using role play for grade XI students of hotel accommodation class Sewon Vocational School 1 designed? And 2) what does the design set of materials look like? In order to answer the first problem of this study, the researcher applied seven stages in designing materials. The seven stages are the adapted steps of instructional design models from Kemp‟s, Banathy‟s, and Yalden‟s and they are in line with the design materials cycle of Borg and Gall‟s Educational Research and Development. This study also employs the theories deal with role play, hotel accommodation class, speaking skill, and communicative teaching in designing speaking materials using role play.
The researcher managed two surveys in this study. The need survey or the first survey was conducted an interview with English teacher of hotel accommodation class and by distributing questionnaires to thirty one students grade XI of hotel accommodation class. The result of the first survey indicated that students needed interesting speaking materials to be done and practiced the real hotel management jobs. The second survey was done to get the evaluation and opinion on the designed materials. One of English teachers of hotel accommodation class and two lecturers of English Language Education Study Program Sanata Dharma University were the participants of the second survey. The result of the second survey was used as the basis for the revision and improvement of the designed materials and it was found out that the designed materials were acceptable although there were some revision needed.
vii ABSTRAK
Rinanti Nur Oktapuri. 2010. Designing A Set of English Speaking Materials Using Role Play for Grade XI Students of Hotel Accommodation Class Sewon Vocational School 1. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa dan Seni, Fakultas Keguruan dan Ilmu Pendidikan, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Role play merupakan salah satu teknik yang digunakan dalam pengajaran Bahasa Inggris terutama dalam mengajarkan aspek berbicara. Role play memotivasi siswa untuk lebih berani lagi berbicara terlebih lagi di depan umum. Dengan metode role play siswa dilatih untuk memerankan seseorang yang bukan dirinya sendiri dalam suatu peran yang mereka mainkan. Penyusunan skipsi ini ditunjang pula dengan tidak adanya materi khusus yang memang diperuntukkan bagi siswa kelas perhotelan apalagi untuk melatih kemampuan berbicara mereka.
Terdapat dua permasalahan untuk dipecahkan dalam studi ini: 1) bagaimana seperangkat materi pembelajaran bebicara bahasa inggris dengan menggunakan teknik role play bagi siswa akomodasi perhotelan dirancang? dan 2) seperti apakah seperangkat materi tersebut? Untuk menjawab pertanyaan pertama, peneliti menggunakan tujuh tahap merancang materi pembelajaran. Ketujuh tahap tersebut diperoleh dengan mengadaptasi Model Rancangan Kemp, Banathy dan Yalden dan tahapan tersebut sejalan dengan siklus penelitian dan pengembangan (R & D) dari Borg dan Gall. Studi ini juga menggunakan teori-teori yang berkaitan dengan role play, kegiatan pembelajaran di sekolah menengah kejuruan, ketrampilan berbicara, dan pengajaran yang komunikatif dalam mendesain kegiatan pembelajaran berbicara menggunakan metode role play.
Peneliti malaksanakan dua survey dalam studi ini. Survei kebutuhan yang menjadi survei pertama dilaksanakan kepada seorang guru bahasa Inggris hotel akomodasi kelas XI SMKN 1 Sewon dan menyebarkan kuesioner kepada 31 siswa hotel akomodasi kelas 2. Hasil survey pertama menunjukkan bahwa siswa membutuhkan materi pelajaran bebicara yang menarik untuk dilaksanakan, mempelajari peran yang nyata dan yang membantu mereka untuk berani berbicara di depan umum. Survey yang kedua dilaksanakan untuk memperolah evaluasi dan opini mengenai materi pembelajaran yang dirancang. Seorang guru kelas perhotelan dan tiga dosen Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Univeristas Sanata Dharma Yogyakarta menjadi peserta dalam survei kedua ini. Hasil survei kedua digunakan untuk revisi dan perbaikan materi pembelajaran yang telah dirancang, hasil menunjukkan bahwa materi yang telah dirancang baik dan diterima walaupun masih diperlukan beberapa revisi.
viii
ix
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswi Universitas Sanata Dharma: Nama : Rinanti Nur Oktapuri
Nomor Mahasiswi : 051214085
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
DESIGNING A SET OF ENGLISH SPEAKING MATERIALS USING
ROLE PLAY FOR GRADE XI STUDENTS OF HOTEL
ACCOMMODATION CLASS OF SEWON VOCATIONAL SCHOOL 1
Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya maupun memberikan royalty kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya. Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal : 23 April 2010
Yang menyatakan,
x
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
It will be a beautiful opportunity for me to express my deepest gratefulness to all of those who have supported and facilitated me in accomplishing this thesis. First and foremost, my greatest gratitude is addressed to Gusti Yesus Kristus who has given me this beautiful experience and His eternal blessing so I can finish my thesis and my study.
I would like to express my heartfelt thanks to my sponsor, Dr. Retno Muljani, M.Pd., who is willing to spend her precious time for the sake of guiding me in writing this thesis. My deepest thanks also go to all my lecturers in PBI who have guided me and taught me very well, especially to Christina Lhaksmita Anandari, S.Pd., M.Ed., and Drs. YB Gunawan, M.A. for their time to evaluate my speaking materials.
I am truly grateful to Dra. H. Sudaryati, the principal of SMKN 1 Sewon Bantul, who has permitted me to conduct my research. I would also like to address my thanks to Yunita, S.Pd., and F.A Susilarto, S.Pd., as the English teachers, who have helped me during the research. I also thank all the students of Hotel Accommodation Class grade XI for being my research participant and for the cooperation during my research.
xi
big family, Mbah Ibuk and Eyang Edi for their encouragement to finish my thesis. I thank them all for giving me great affection.
My sincerest thanks go to my bestfriends Mgee Wulandari, Dinar Ratnasari, Abe Sano, Yebe Agung, Ruma, Andre Ha-ha, Indro, Krishna Murti, Aditya “Djumbo”, my Sampan‟s friends, my ex 4B „02 friends, my De Djogdja‟s and PT Muntiplus Sepakat‟s friends, they always keep my fire on in finishing my thesis.
I would like to give my deepest love to someone who always tells me the meaning of this life. I thank him for his never ending love and support. He never gave me motivation to finish my thesis but his weird and wonderful utterances force me much to do my best in finishing my thesis.
With love,
xii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
PAGE OF DEDICATION ... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK‟S ORIGINALITY ... v
ABSTRACT ... vi
ABSTRAK ... vii
PUBLICATION PAGE ... ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... x
TABLE OF CONTENT ... xii
LIST OF TABLES ... xvi
LIST OF FIGURES ... xvii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xviii
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION ... 1
1.1 Research Background... 1
1.2 Problem Formulation ... 3
1.3 Problem Limitation ... 4
1.4. Research Objectives ... 4
1.5 Research Benefits ... 4
xiii
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 8
2.1 Theoretical Description ... 8
2.1.1 Speaking ... 9
2.1.1.1 The nature of speaking ... 9
2.1.1.2 Teaching speaking ... 10
2.1.2 Role play ... 12
2.1.2.1 The nature of role play ... 12
2.1.2.2 The procedure of using role play ... 13
2.1.2.3 The reason of using role play ... 14
2.1.3 Communicative Language Teaching... 15
2.1.4 Vocational School ... 18
2.1.4.1 The outcomes of vocational school ... 19
2.1.5 Instructional Design Model ... 20
2.1.5.1 Kemp‟s Instructional Design Model ... 21
2.1.5.2 Banathy‟s Instructional Design Model... 22
2.1.5.3 Yalden‟s Instructional Design Model ... 24
2.1.6 Material Development ... 26
xiv
CHAPTER III. METHODOLOGY ... 31
3.1 Research Method ... 31
3.2 Research Participant ... 32
3.3 Research Instrument ... 33
3.4. Data Gathering Technique ... 35
3.5 Data Analysis Technique ... 37
3.6 Research Procedure ... 38
CHAPTER VI. RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS ... 44
4.1 The Steps of the Development of the Designed Materials ... 44
4.1.1 Conducting Needs Analysis ... 45
4.1.1.1 The Result of the Interview with English Teachers of Sewon Vocational School 1 ... 45
4.1.1.2 The Result of Questionnaires Distributed to Grade XI Students of Sewon Vocational School 1 ... 47
4.1.2 Considering Goals, The List Topics, Stating the General Purposes for Teaching Each Topic ... 50
4.1.3 Selecting Teaching and Learning Activities ... 52
4.1.4 Developing the Materials ... 54
4.1.5 Evaluating the Design Materials ... 54
4.1.6 Implementing the Designed Materials ... 54
4.1.6.1 The Teachers‟ Roles ... 55
xv
4.1.7 Revising ... 56
4.2 The Findings and Discussions on the Designed Materials Evaluation and Implementations ... 56
4.2.1 Preliminary Field Testing ... 57
4.2.1.1 The Result of Respondent Opinions on the Designed Materials ... 57
4.2.1.2 The Respondents‟ Comments and Suggestions on the Designed Materials ... 58
4.2.2 Main Product Revision ... 61
4.2.3 Main Field Testing ... 62
4.2.4 Operational Product Revision ... 62
4.3 The Presentation of the Designed Materials ... 65
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 69
5.1 Conclusions ... 69
5.2 Suggestions ... 70
xvi
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1: The Data Needed by the Researcher ... 36 Table 2: Points of Agreement ... 38 Table 3: Specification of a Set of English Speaking Materials for Grade XI
Students of Hotel Accommodation Class of Sewon Vocational School 1 38 Table 4: The Result of Need Analysis‟ Questionnaire... 47 Table 5: The Description of Competence Standard, Basic Competence,
Topic and Indicators of Each Unit ... 51 Table 6: The Description of the Evaluation of the Material Design Respondents 55 Table 7: Points of Agreement of Preliminary Field Testing Questionnaire... 58 Table 8: The Result of Respondents‟ Opinion ... 58 Table 9: The Result of Respondents‟ Opinion of the Implementation
Process (closed questions) ... 62 Table 9: The Result of Respondents‟ Opinion of the Implementation
xvii
LIST OF FIGURES
xviii
LIST OF APPENDICES
APPENDICES ... 75
Appendix 1: Letter of Permission ... 75
Appendix 2: Questionnaire for Need Analysis... 78
Appendix 3: Questionnaire for Expert Validation ... 82
Appendix 4: Questionnaire for Evaluation ... 88
Appendix 5: Field Notes and Lists of the Students ... 90
Appendix 6: General Description of the Designed Materials ... 97
Appendix 7: Syllabus and Lesson Plans of the Designed Materials ... 101
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, the researcher would like to discuss the introduction of the study by elaborating the research background, problem formulations, problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits, and definition of terms.
1.1 Research Background
Yogyakarta is rich for its tourism aspect and most of economic incomes come from tourism aspect. DIRECTORATE GENERAL TOURISM UNESCO / UNDP (1992: 10-11) states that Jogjakarta is a region in which tourism becomes more important to support the local economy of the region.
Tnunay (1991: xii) states that “Jogjakarta adalah kota pariwisata,
tinggal bagaimana masing-masing komponen dalam rangkaian itu berfungsi secara baik dan maksimal”. It can be implied that Jogjakarta is a tourism city, and the development of the tourism depends on how each component is functioning well and maximal.
Many people take the benefits by working in tourism sector. People not only turn out to be the provider of tourism but most of them turn into tourism lovers. This is important to increase the ability of people who work inside the tourism aspect especially for those who work inside the hotel management, as written by Mistiani (1997: 1). This is necessary for the
component of tourism (the people who work in tourism) especially for those who work at hotel to be able to speak English, because most of the international tourist (foreigners) are using English for their communication.
Vocational schools of tourism and hotel accommodation provide graduate students who are ready to work in tourism world. The students in those schools were accustomed to acquire good teaching and learning related to tourism materials in sequence to prepare toward the factual work world. Based on the interview on the 20th of September 2008 with Yunita, S.Pd, the English teacher of hotel accommodation class Sewon Vocational School I, and on the 3rd April of 2008 with Mr. Oni Gamayanto the Human Resource Development of De Djogja Karaoke in Ina Garuda Hotel Site, the researcher concluded that the significant thing for the students of hotel accommodation class is the preparation on English conversation. Speaking is one of the main needs for those who would like to work in tourism world especially for hotel accommodation’s students and who will serve and meet the guests directly.
SMA/SMK Students by Dachar Dadang (2007), there are no specific textbooks that refer to hotel accommodation class students of vocational school.
Therefore, the researcher designs the speaking materials for hotel accommodation class of vocational school in order to make the students who will work in a hotel to be accustomed to the conversation that is used in the real hotel management. The hotel itself will be able to get the best students who can work and cooperate. So that when there are foreigner guests, the students are able to speak fluently to the guests.
1.2 Problem Formulation
From the previous research background, the research problem can be formulated as follows.
a. How is a set of speaking materials using role play for grade XI students of hotel accommodation class of Sewon Vocational School 1 designed?
1.3 Problem Limitation
In order to make a clear boundary to this research the researcher makes one limitation focuses on designing. The researcher limits this research to design a set of speaking materials using role play for grade XI students of hotel accommodation class of Sewon Vocational School 1.
1.4 Research Objectives
From the previous problem formulation, the research objectives can be formulated as follows.
a. To design a set of speaking materials using role play for grade XI students of hotel accommodation class Sewon Vocational School 1. b. To provide the appropriate speaking materials using role play for
grade XI students of hotel accommodation class Sewon Vocational School 1.
1.5 Research Benefits
This research will primarily benefit the teachers and the students.
For teachers
For students
The study provides the students of hotel accommodation class some examples of conversation that is used in the real work of hotel management to facilitate the students to be accustomed to real work situation.
1.6 Definition of Terms
This part will elaborate the definitions that will be used in the study. They are as follow:
1. Speaking
Widdowson (1979: 58) stated that speaking skill is kind of active and productive interactions that make us use aural mediums. Aural mediums include mouth, lips, tongue and other activities. Louma (2004) stated that speakers also need to know words, phrases and strategies for creating time to speak. Related to this study, designing a set of speaking materials is meant to develop speaking materials (an activity which uses aural mediums) that are used by the hotel accommodation class of Sewon Vocational School 1.
2. Material
activities which engage the learner thinking capacities; opportunities for learners to use their existing knowledge or skills; content which both learner and teacher can cope with.
3. Vocational School
According to Peraturan Pemerintah on chapter 2 the purposes of vocational education are to improve intelligence, personality, moral and personal skills of students to become independent, to enter the workforce in accordance with previously studied education and is able to communicate in accordance with the field work. In line with that, Rakestraw (1947, 2) stated that vocational education is preparing persons of employable age for advantageous entrance into skilled trades and occupations.
4. Hotel Accommodation School
5. Role play
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter presents a discussion of the theories as the foundation of this research. This discussion is divided into two major areas; theoretical description and theoretical framework.
The theoretical description discusses basic theories of speaking, role play, communicative language teaching, vocational school in general and instructional design.
The theoretical framework discusses the relation among the concepts stated previously as the basis of designing a set of speaking materials using role play for grade XI students of hotel accommodation class of Sewon Vocational School 1.
2.1 Theoretical Description
In this section, the researcher would like to discuss five parts. The first part is speaking skill since the materials designing in this research emphasizes is on the speaking skill. The second part is role play since this research uses role play as the main technique. The third part is communicative language teaching theory. The fourth is vocational school since the designed materials will be used in vocational school. The fifth part, the researcher would discuss the instructional design model which will be
used in this research. Those previous theories will be used to establish the framework of the designed materials in this research.
2.1.1 Speaking
The researcher attempts to design a set of speaking materials using role play for grade XI students of hotel accommodation class of Sewon Vocational School 1. Therefore, this section will discuss the basic theory of speaking skill.
2.1.1.1 The Nature of Speaking
Brown and Yale as quoted by Nunan (1989: 26-27) begin their discussion of the nature of speaking by distinguishing spoken and written language. Written language is characterized by well form sentences which are integrated into highly structured paragraphs. Spoken language, on the other hand, consists of short, often fragmentary utterances, in range of pronunciation. It is a skill that generally has to be learned and practised.
Louma (2004) states the variation within spoken language use:
information-related talk refers to speech aimed at transferring information on a particular topic.
- Talking in different social status: Hymes as quoted by Luoma (2004) has summarized the framework of talking in different social status that forms the acronym of SPEAKING: Situation (the physical setting and the nature of the event), Participant (speaker, hearer, audience, etc), Ends (conventional outcomes of the event, the ends also include the individual participants’ goal), Act
sequence (the form and content of speech acts), Key (tone, manner, or spirit of act), Instrumentalities (channel or mode and form of speech), Norms (norms of interpretation and norms of interaction), and Genre (categories).
- Roles, role relations/ships and politeness: Grice’s as quoted by Luoma (2004) gives four conversational maxims: quantity (give sufficient information but not too much), quality (say only what you know to be true), relation (be relevant) and manner (be brief, clear and orderly).
2.1.1.2 Teaching Speaking
learners many opportunities to practice speaking skill. When the teacher provides more complicated matter of the foreign speech to be answered, the learners ability will be greater developed also. Rivers (1968: 16) stated teacher will need to use his imagination in devising situations which provoke the students to the use of the language in the expression of his own meaning.
Speaking comes naturally to humans, but it is not as simple as it seems. Sometimes people feel afraid to speak in front of a large group. According to Davies (2000: 82), there are some implications for teaching:
Try to create relaxed atmosphere in your classes so that most learners are not frightened of speaking in front of the rest of the class. And do as many speaking activities as possible in pairs and groups, so that the learners can speak English without the rest of the class listening.
Expose the learners as much as possible to naturally pronounce speech, and also integrate some pronunciation work into your lessons. They will not learn to pronounce intelligibly, or to develop speaking skill in general, if they do not hear enough natural speech.
2.1.2 Role Play
In this research, the researcher emphasizes the use of role play, which is one of communicative activities in speaking skill. It consists of 4 parts: the nature of role play, the use of role play in teaching speaking, and the procedures of using role play, role play and the approach. By discussing these parts, the researcher would like to give an overall view of role play.
2.1.2.1 The Nature of Role Play
Hawley (1975: 10) states that role playing is one teaching method that involves student actively in the learning process, both in simulated interactions and in determining what path to take in the discussions that follow the role play and it is a common and natural human activity, not just another artificial structure limited in the classroom.
2.1.2.2 The Procedures of Using Role Play
Schmuck (1980:146) states that the sequences in using role play involve: (1) selecting the problem; (2) warming up; (3) setting the stage by explaining the situation, describing participant roles and explaining audience role; (4) enactment; (5) analyzing and discussion; (6) evaluation; (7) re-enactment of the role play; and (8) generalizing to the daily life of the classroom.
Further, Hawley (1975:108-112) states that there are seven-part sequences of teaching concerns as clarified below:
1. Orientation
It is concerning in giving an outline of the activity to the students in order not to make them confused in what should they do.
2. Community building
It is the extension of orientation, where the students should be able to find in common with each other and with the teacher.
3. Achievement motivation
It is relating to motivate the students by explaining the goals, procedures and rules of the class clearly to the students.
4. Fostering open communication
It is in relation to the preparation of the place where the role play will be done.
6. Value exploration
It is concerning to the gathering information to determine which parts are significant, which trivial.
7. Planning for change
It is relating to the exploration of students’ value and determines what
things are important to them, and then the final concern is to help the students’ plan for change.
2.1.2.3 The Reason of Using Role play
By using role play method, the teacher is able to design the theme of the situation and some clues for the students. According to Hawley (1975:126) the benefits that can be derived from role playing can be viewed in terms of five general and overlapping categories: problem solving, rehearsing, reporting, developing empathy and managing the class.
Harmer (19xx, 352-353) states that role play has some advantages: encourage general oral fluency or to train students for specific situations, while the distinct advantages: they can be good fun and are thus motivating, they allow hesitant students to be more forthright in their opinions and behaviour without having to take responsibility for what they say in the way that they do when they are speaking for themselves, and allow students to use a much wider range of language.
2008, the researcher concluded that to teach using role play is an appropriate method in teaching speaking. The teacher supposed that by using role play, expectantly the students enjoy the activity and they can learn English deliberately in order to improve the speaking fluency of the students.
2.1.3 Communicative Language Teaching (CLT)
One of approaches in language teaching which is going to be implemented by the researcher to develop a set of speaking materials for Grade XI students of Hotel Accommodation Class Sewon Vocational School 1 is CLT. Richard and Rodgers (2001: 172) stated that CLT refers to a varied set of principles which reflect a communicative view of language and language learning and which can be used to support a wide var iety of classroom procedures. This includes some principles of CLT, they are:
1. Through using the language, the learners learn to communicate.
2. The goal of classroom activities is at authentic and meaningful communication.
3. Fluency is an important aspect of communication.
4. The integration of different language skill is involved in the communication.
Brown (2001:87) offers four interconnected characteristic as a definition of CLT, namely:
a. Classroom goals are focused on the entire component of communication competence and not restricted to grammatical/linguistic competence. b. Language techniques are designed to engage learners in the pragmatic,
authentic and functional use of the language for meaningful purposes. Organizational language terms are not the central focus but rather aspects of language that enable the learner to accomplish those purposes.
c. Fluency and accuracy are seen complementary principles underlying communicative techniques. At times fluency may have to take on more importance than accuracy in order to keep learners meaningfully engaged in linguistic use.
d. In communicative classroom, students ultimately have to use the language productively, in unrehearsed context.
There are three kinds of materials considered in CLT: a. Text-based materials
Text-based materials are materials that based on the texts that help the teacher to initiate conversation. The examples of these materials are visual cues, pictures, and sentence fragments.
b. Task-based materials
In order to support CLT classes, a variety of games, role play, and task-based communication activities have been prepared. These are usually in the form of one-of-a-kind items: exercise handbooks, cues cards, pair communication practice, and learners-interaction practice. c. Realia
Realia might be included as proponents of CLT. This might include language based realia such as sign, magazines, newspaper, or visual sources around which communicative activities can be built (maps, pictures, etc)
Hence, in this research the researcher would like to design a set of speaking materials by using role play technique and through the CLT approach.
2.1.4 Vocational School
2.1.4.1 The Outcomes of Vocational School
Vocational school prepares the students into the job world. Outcome of the vocational education, based on Wenrich, (1974:21)
1. Children and youth acquire knowledge of the materials of our culture and develop the ability to use them effectively.
2. Children and youth develop an understanding of the world of work and gain insight as to how they can relate to it.
3. Children and youth acquire an understanding of the meaning of work in their lives and develop a wholesome attitude toward work.
4. Children and youth develop a respect for the dignity of work and appreciate the value of work to society.
5. Children and youth experience and learn to appreciate good workmanship.
6. Children and youth develop good work habits.
7. Children and youth discover and develop their special aptitudes and talents and relate them to productive activity.
2.1.5 Instructional Design Model
In designing the instructional material, Hutchinson and Waters (1987:55-65) suggest some importance considerations to be taken into account as presented below:
a. Instructional Materials design must be based on the target need that is what the learners have to know in order to function effectively in the target situation, the learner’ wants and the
learning needs.
b. Instructional materials design should pay attention to the significant potentialities and constraints such as experience, finance, facilities, competence, background knowledge, and time, which exist in the learning situation in order to adjust what is possible and what is impossible to be done in the system.
c. Instructional design is supposed to develop either language-centered approach, the skill approach, or learning language-centered approach.
The brief discussion of each instructional design models are presented below:
2.1.5.1 Kemp’s Instructional Design Model
Kemp (1977) states eight steps of the instructional design plan, the steps are as follow:
1. Considering goals, the list topics, stating the general purposes for teaching each topic.
2. Enumerate the important characteristics of the learner for whom the instruction is to be designed.
3. Specify the learning objectives to be achieved in terms of measurable students’ behavioural outcomes.
4. List the subject content that supports each objective.
5. Develop pre-assessments to determine the student’s background and present level of knowledge about the topic.
6. Select teaching/ learning activities and instructional resources that will treat the subject content so the students will accomplish the objectives.
7. Coordinate such support services as budget, personnel, facilities, equipment, and schedules to carry out the instructional plan.
The stages of Kemp’s instructional materials design model can be
clarified in the following figure:
(Figure 1) The Instructional Design from Kemp
2.1.5.2 Banathy’s Instructional Materials Design Model
Banathy (1968:3) stated that educational is a system. System has three components, namely purpose, process, and content. Purpose gives direction to the system that is what should be done. Then, purpose determines the processes that have to be carried out in order to accomplish the purpose. And in order that there will be a good process, there will be contents.
The stages of Banathy’s instructional materials design model can be clarified in the following figure:
(Figure 2) The Instructional Design from Banathy
The following is explanation of the system: I. Formulate objective
The initial step is to formulate a statement about what we expect the learners to do, know, and feel as a result of learning experience.
II. Develop criterion test
The development is based on the stated objectives and uses it to test terminal proficiency. The criterion test is used to measure the degree in which the learners have attained the objectives.
I Formulate objectives
VI Change to
Improve V Implement and
Test Output IV Design System III
Analyze Learning Task
II Develop
III. The analysis of the learning task
It is used to find out what has to be learned by the learners so that they can behave in the way described by the objectives’ specifications. The input
of the learners’ abilities must be assessed too. IV. The design of the system
This system is aimed to determine alternatives and to identify what has to be done and how (functional analysis), to determine what or who has the best potential to accomplish these functions (component analysis), and to determine here and when the functions are to be carried out (design the system).
V. Implementation and quality control
The designed system is to be tried out, implemented, and installed. Finally the performance of the learners as the product of the system is to be evaluated in order to measure the learners’ degree assessment to which they
behave in the way initially described. VI. Change to improve
The performance data is used as a feedback to adjust the system.
2.1.5.3 Yalden’s Instructional Materials Design Model
The process of constructing the type of syllabus is as follows:
1. Needs survey, the teacher should make surveys of needs before stating the purposes in order to find the importance of the community/ local needs.
2. Description of purpose, the description of purpose is prepared in term of: (1) the characteristic of the students, and (2) the skill of the students on entry to and on exit from the program.
3. Selection and development of syllabus type.
4. The proto-syllabus production, describes the language itself and language use to be covered in the program.
5. The pedagogical production that develops the teaching materials, learning and testing approaches which consist of testing sequence and decisions on testing instruments.
6. Development and implementation of classroom procedures. It can be describe as follows:
a. Development of classroom procedures, in terms of selecting of exercise types and teaching techniques, preparing of lesson plan and of weekly schedules.
b. Teacher training, in terms of briefing and workshops in principles and desired outcomes and exploitation or creation of teaching materials.
8. Stage recycling. It can be describe as:
a. Congruence/ fit between goal set and student performance is determined.
b. Content is reassessed.
c. Materials and methodological procedures are revised.
(Figure 3) The Language Program Development from Yalden
2.1.6 Material Development
This part the writer discussess a model for developing mater ials. In developing materials, the writer does materials adaption as well. Materials adaption is used to make the materials suitable for specific learners, teachers or situations. The writer adapts the Hutchinson and Waters’ model which is consisted of four elements Hutchinson and Waters, 1987: 108-109). The elements are:
1. Input
Input provides stimulus material for activities, new language items, correct models of language use, a topic for communication. It also provides the opportunities for learners to use their existing knowledge both of the
Needs
survey Description of Purpose
Selection/ Development of syllabus
language and the subject matter. It may be by reading a text, listening to an audio cassette, answering questions, etc.
2. Content focus
Language is not an end in itself, but a means of conveying information and feeling about something. The writer focuses the materials on the specific skill which is to be taught and the teaching and learning activities will be more effective when the content is related to daily hotel management activities.
3. Language focus
Language focus provides the learners to use language. The writer gives the opportunity to the learners to identify the vocabulary and the expressions deal with the discussed topic.
4. Task
Task provides the learners to use the content and language knowledge they have built up through the unit. Task makes learners practice and use their knowledge both of language and content.
2.2 Theoretical Framework
described in the theoretical description section. The theories are put under t he umbrella of R&D as the main framework for this research.
There are seven major adapted steps of the Kemp’s, Banathy’s and Yalden’s model to develop the materials as follows:
1. Conducting Need Analysis (taken from Yalden)
This step included review of literature, classroom observations and survey. The survey was conducted by observation, interview and questionnaires. This step is supported by the theories that have been collected such as the theory of role play and the theory of instructional design. The collected data is to discover the target needs and the learning needs.
2. Considering goals, the list topic, stating the general purposes for teaching each topic (taken from Kemp)
This step included defining skills, stating objectives based on the curriculum and the syllabus that is used in the school. The researcher prepared the materials and developed the product in this step.
3. Selecting teaching and learning activities (taken from Kemp)
This step included preparation of instructional materials and evaluation devices. After collecting the data from the two previous steps, the researcher was making the form of product based on the gathered data.
4. Developing the materials (addition)
the materials. The materials consist of four elements: input, content focus, language focus and task.
5. Evaluating the designed materials (taken from Yalden)
Expert verification was required in this step. This step was conducted to gain feedback from evaluators towards the designed materials. To evaluate the designed materials, the researcher distributed questionnaires.
6. Implementing the design (taken from Banathy)
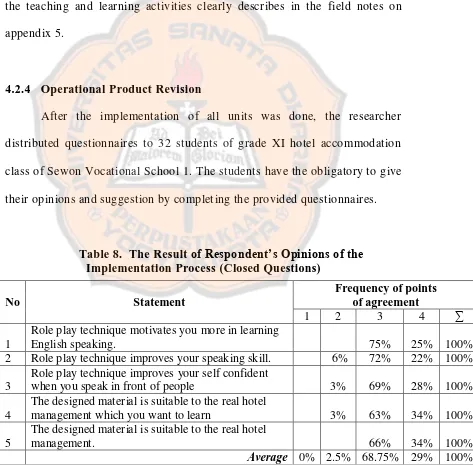
The researcher held the implementation in XI grade students of Hotel Accommodation Class Sewon Vocational School 1 for six times. As the implementation has finished, the researcher distributed questionnaire to the students and teacher of grade XI students of hotel accommodation class Sewon Vocational School 1.
7. Revising (taken from Kemp)
The researcher revised and improved the product after getting feedback from the students’ questionnaires based on the implementation of
To obtain a clearer idea on the theoretical framework which is applied in this study, the researcher’s theoretical framework is presented below:
(Figure 4) The Steps of Designing Materials Adapted from Kemp’s, Banathy’s and Yalden’s Model
Considering goals, the list topics, stating the general purposes for teaching each
topic
Selecting teaching and learning activities
Developing the materials (addition)
Evaluating the designed materials
Implementing the design Conducting need analysis
CHAPTER 3
METHODOLOGY
In this chapter the researcher will discuss about the research method, research participant, research instrument, data gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
3.1 Research Method
This research is dealing with two major problems to be solved. First problem is how a set of speaking material using role play for grade XI students of hotel accommodation class of Sewon Vocational School 1 is designed. The second problem is what a set of speaking material using role play for grade XI students of hotel accommodation class of Sewon Vocational School 1 looks like.
This research in particular is focused on making a set of speaking material. The researcher developed this research using the model from Kemp (1985), Banathy (1976), Yalden (1987) and Research and Development cycle (1983). Research and Development cycle aimed to discover new knowledge, where evaluation techniques play a major role in this cycle. Borg and Gall’s
The researcher adopts seven steps of the R&D cycle for the materials design, they are (1) research and information collecting, (2) planning, (3) develop preliminary form of product (4) preliminary field testing (5) main product revision (6) main field testing (7) operational product revision.
3.2 Research Participants
The participants of this research were divided into three; those were research and information collecting participants, preliminary field testing participants, and implementation participants.
1. Participants in Research and Information Collecting
The research participants were the English teachers and the students of grade XI students of hotel accommodation class Sewon Vocational School 1, who were closely related to the curriculum and the syllabus of that is used in Hotel Accommodation Class. In order to get the learners’ need, the researcher conducted classroom observations, interview with the English teacher and distributed questionnaire to the students.
2. Participants in Preliminary Field Testing
language learning assessment, and instructional design. They evaluated the designed materials and gave suggestion to the researcher or so-called expert validation.
3. Participants in Main Field Testing
The participants were the students of grade XI students of hotel accommodation class Sewon Vocational School 1. The students gave feedback after the product was implemented.
3.3 Research Instruments
In order to collect valid and reliable data, the researcher used the questionnaire and interview as the instruments as clarified below.
1. Instruments for Research and Information Collecting Step
The instruments used in research and information collecting were observation, questionnaire and interview. The researcher conducted the observation started in September 2008. During the observation, the researcher observed the school condition both physically and pedagogically. The English teachers also gave the researcher an opportunity to teach the students before designing and implementing the design. The aim was to gather information about the students’ needs, interest, and characteristics.
The second instrument was questionnaire. By using questionnaires, all grade XI students of Hotel Accommodation Class Sewon Vocational School 1 will be involved. The questions were written in Indonesian so that the learners find no difficulties in answering all the questions. The questionnaires were using closed and open questions. This questionnaire’s purpose was aimed to get the guideline for the design. Informal interview with two English teachers of Hotel Accommodation Class Sewon Vocational School 1 was also conducted. In this study, the researcher conducted interview to gather the data needed before designing the product.
2. Instruments for Preliminary Field Testing Step
University. It is used to get opinions and evaluations of the designed materials. The opinions and evaluations were used as the source of revising the designing materials. The questions were written in English and using closed and opened questions. Informal interview to the teacher and lectures were also conducted in this step in order to gain a comprehensible data as the guideline in revising the product.
3. Instruments for Main Field Testing Step
The instruments for main field testing were questionnaire and interview. The questionnaire contained evaluation and feedback from the grade XI students of Hotel Accommodation Class 1 Sewon Vocational School 1, after the researcher conducted the research. The purpose of distributing the questionnaires was to acquire some reliable feedbacks as the revision and improvements for the design. The researcher conducted the informal interview after the implementation was done to gain information about students’ response and influence toward students’ speaking skill after the implementation of the product was done.
3.4 Data Gathering Technique
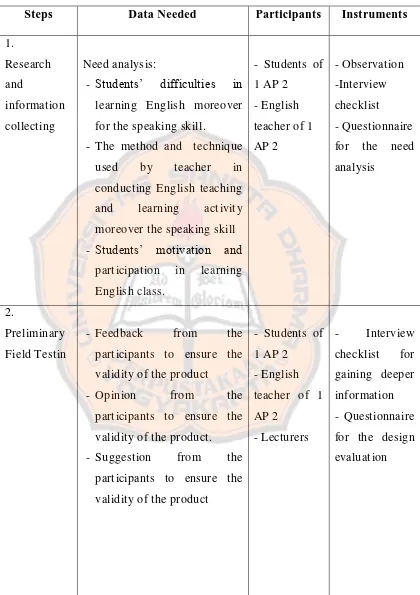
Table 1. The Data Needed by the Researcher
Steps Data Needed Participants Instruments
1. Research and information collecting Need analysis:
- Students’ difficulties in learning English moreover for the speaking skill.
- The method and technique used by teacher in conducting English teaching and learning activity moreover the speaking skill - Students’ motivation and
participation in learning English class.
- Students of 1 AP 2 - English teacher of 1 AP 2
- Observation -Interview checklist - Questionnaire for the need analysis
2.
Preliminary Field Testin
- Feedback from the participants to ensure the validity of the product
- Opinion from the participants to ensure the validity of the product. - Suggestion from the
participants to ensure the validity of the product
- Students of 1 AP 2 - English teacher of 1 AP 2
- Lecturers
Steps Data Needed Participants Instruments
3.
Main Field Testing
- Feedback from the participants deal with the final version of the materials, the implementation itself and the
influence of the
implementation toward students’ speaking skill
- Students of 1 AP 2 - English teacher of 1 AP 2
- Interview checklist for gaining the influence of the implementation - Questionnaire for gaining the feedback from the students
after the
implementation
3.6 Data Analysis Technique
The researcher analyzed the data as the data needed have been gathered. The participants’ opinions in the form of closed questions were shown statistically. The participants’ opinions in the form of open questions
were shown in sentences.
In analyzing the questionnaires, the data collected would be calculated using percentage as follow:
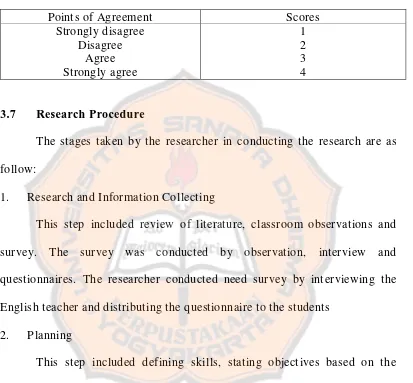
Note:
The data obtained trough questionnaires is in the form of scores. There are four agreements are applied as follows:
Table 2. Points of Agreements
Points of Agreement Scores
Strongly disagree Disagree
Agree Strongly agree
1 2 3 4
3.7 Research Procedure
The stages taken by the researcher in conducting the research are as follow:
1. Research and Information Collecting
This step included review of literature, classroom observations and survey. The survey was conducted by observation, interview and questionnaires. The researcher conducted need survey by interviewing the English teacher and distributing the questionnaire to the students
2. Planning
This step included defining skills, stating objectives based on the curriculum that is used in the school. The researcher prepared the material for the module and developed the product and also determined the instructional goals, topic, and general purposes.
3. Develop Preliminary Form of Product
previous steps, the researcher was making the form of product based on the gathered data.
4. Preliminary Field Testing
Expert verification was required in this step. The researcher distributed questionnaires to the English teacher and two lecturers from English Language Education Study Program at Sanata Dharma University. The purpose of this step is to gain opinion, comments, suggestion and criticism as an evaluation.
5. Main Product Revision
This step was the final product which was edited based on the result o f the preliminary field testing. The researcher revised the material based on the evaluation result.
6. Main Field Testing
The researcher held the implementation in grade XI of Hotel Accommodation Class 1 Sewon Vocational School 1 for six times. As the implementation has finished, the researcher distributed questionnaire to the students and teacher of grade XI of Hotel Accommodation Class 1 Sewon Vocational School 1.
7. Operational Product Revision
The researcher made a figure showing the stages of R&D cycle which match with the instructional design models of Kemp’s, Banathy’s and
Yalden’s, as follow:
R&D cycles Instructional Design
(Figure 5) The Researcher’s R & D Cycle Completed with Kemp’s, Banathy’s and Yalden’s Adapted Model
Research and information collecting
Considering goals, the list topics, stating the general purposes for teaching each
topic
Main Field Testing Preliminary form of product
developing
Selecting teaching and learning activities
Developing the material (addition)
Evaluating the designed materials
Implementing the design Preliminary field testing
Conducting need analysis
Main Product revision
Operational Product Revision Revising
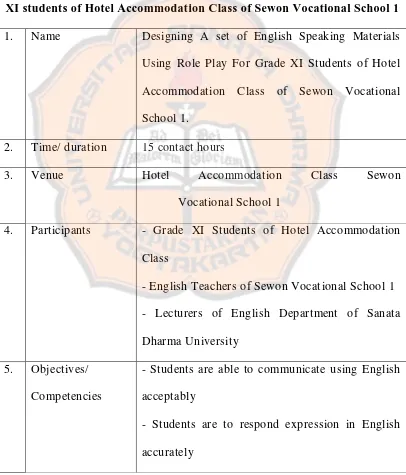
Based on the Educational Seminar held by the Department of National Education in 2008, a research and development should construct a specification product of the designed materials. Specification Product was used to distinguish the product with other products. The specification of the result of the product was presented on table 3.
Table 3. Specification of a Set of English speaking Materials for Grade
XI students of Hotel Accommodation Class of Sewon Vocational School 1
1. Name Designing A set of English Speaking Materials Using Role Play For Grade XI Students of Hotel Accommodation Class of Sewon Vocational School 1.
2. Time/ duration 15 contact hours
3. Venue Hotel Accommodation Class Sewon
Vocational School 1
4. Participants - Grade XI Students of Hotel Accommodation Class
- English Teachers of Sewon Vocational School 1 - Lecturers of English Department of Sanata Dharma University
5. Objectives/ Competencies
- Students are able to communicate using English acceptably
- Students are able to use spoken English to support their professional qualifications as a hotel attendant accurately.
6. Materials Printed materials
7. Technique Role play
8. Approach CLT
9. Syllabus Type Content Based Syllabus
(English For Elementary Level)
10. Sources English for Vocational School, 1B, written by Yiyis Kristiani, Kalam Offset Jogjakarta
English For Vocational School, 1A, written by Yiyis Kristiani, Kalam Offset Jogjakarta
Be Our Guess, written by Donald Adamson, Prentice Hall
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS
In this chapter, the researcher would like to describe the result and discussion of the findings of the study, and the presentation of the designed materials. This chapter is divided into three parts. The first part is the stages of the materials design development. This part provides the answer to the first formulated problem. The second part is the findings of the study. The third part is the presentation of speaking material design using role play for the grade XI students of hotel accommo dation class of Sewon Vocational School 1. This part provides the answer to the second formulated problem.
4.1 The Steps of the Development of the Designed Materials
With the intention of answering the first problem formulation of this research, the researcher combined the steps of Kemp’s, Banathy’s and Yalden’s models. The Instructional Design Models are in line with Borg and Gall’s Educational Research and Development (R&D) cycle to design the
materials. Those steps are (1) conducting need analysis, (2) cons idering goals, the list of the topics, stating the general purposes for teaching each topic, (3) selecting teaching and learning activities, (4) developing the material (addition), (5) evaluating the designed materials, (6) implementing the design, (7) revising.
4.1.1 Conducting Needs Analysis
In conducting needs analysis, one of the English teachers of Sewon Vocational School 1 was interviewed. Questionnaire sheets were also distributed for thirty two students of grade XI hotel accommodation class. Here is the discussion of the result of interview and the questionnaire.
4.1.1.1 The Result of the Interview with English Teachers of Sewon
Vocational School 1
Before designing the speaking materials, the researcher had an opportunity to have an interview with the English teachers of Sewon Vocational School 1 who taught hotel accommodation class grade XI.
Based on the interview, the researcher found out that there was no scheduled time to deliver speaking skill in English lesson. Because of there were no specific book designed for hotel accommodation class moreover for speaking skill, that is why the teacher put the speaking session in the middle of teaching and learning activity without any reference’s book. The teacher
having no interesting references for English lesson moreover for speaking skill.
Another finding in this interview was the fact that the teacher has no specific technique to deliver English speaking lesson. They ever tried to hold an English day by asking the students to go to Malioboro Street and to find a foreigner and interviewed them. The activity was intended to motivate the students to be able to speak English. The result of this activity was good, students were able to note some information from the foreigner. Because of consuming much time and much money for students’ transportation, the activity was only done once. The teacher realized that English speaking skill is important for hotel accommodation class students due to students’ future
job.
4.1.1.2 The Result of Questionnaires Distributed to Grade XI Students
of Sewon Vocational School 1
[image:65.595.113.547.274.746.2]The researcher distributed questionnaires to the hotel accommodation class grade XI students of Sewon Vocational School 1. The number of the participants was 31 students. The explanation of the questionnaire result is presented below:
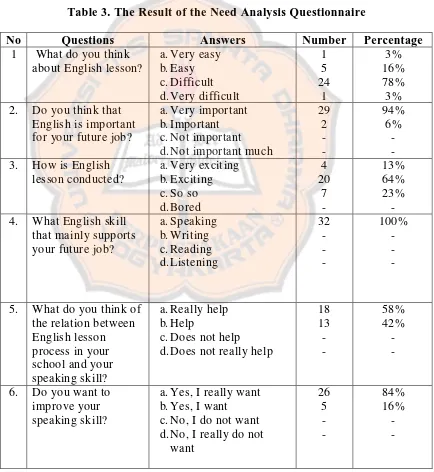
Table 3. The Result of the Need Analysis Questionnaire
No Questions Answers Number Percentage
1 What do you think about English lesson?
a. Very easy b. Easy c. Difficult d. Very difficult
1 5 24 1 3% 16% 78% 3% 2. Do you think that
English is important for your future job?
a. Very important b. Important c. Not important d. Not important much
29 2 - - 94% 6% - - 3. How is English
lesson conducted?
a. Very exciting b. Exciting c. So so d. Bored
4 20 7 - 13% 64% 23% - 4. What English skill
that mainly supports your future job?
a. Speaking b. Writing c. Reading d. Listening
32 - - - 100% - - -
5. What do you think of the relation between English lesson process in your school and your speaking skill?
a. Really help b. Help
c. Does not help d. Does not really help
18 13 - - 58% 42% - -
6. Do you want to improve your speaking skill?
a. Yes, I really want b. Yes, I want c. No, I do not want d. No, I really do not
No Questions Answers Number Percentage 7. Do you ever use role
play technique in English lesson?
a. Yes b. No
24 7
77% 23% 8. *only for the student
who answered “No” in the question above.
Do you want to learn speaking English using role play?
a. Yes b. No
7 -
100% -
9. What is your purpose to learn speaking in English using role play?
a. To have a lively class b. To see the real
situation
c. To have a work in group
d. To be brave speak in front of other
e. To be listened directly by the teacher and friends
f. To get a direct
comment from teacher and friends
g. Other
5 14 1 11 - - - 16% 46% 3% 35% - - - 10 .
What kind of situation that you want in the role play?
a. Hotel Accommodation b. Office
c. School d. Other
22 1 3 5 71% 3% 10% 16% 11 .
What kind of roles that you want in the role play?
a. Hotel Accommodation Staff
b. Officer c. School’s Staff d. Other
26 - 4 1 84% - 13% 3%
difficult. There were only (16%) said that English lesson is easy and another (3%) said that English is very easy.
Related to students’ motivation in learning English, most of the students (94%) stated that English is very important for their future job and the other (6%) said that English is important. All of the students (100%) stated that the most important English skill that supports their future job is speaking skill. (58%) students stated that the teaching and learning activity process really help them improving their speaking skill and the rest (42%) stated that the teaching and learning activity help them improving the speaking skill.
Knowing that English is significant for their future, (84%) students really want to improve their speaking skill and (16%) students want to improve their speaking skill.
management situation as their role play performance, (10%) want to have school activity as the situation and (3%) want to act as officer staff and the rest or (16%) choose other situations. Dealing with students’ preferable in
acting as someone else, (84%) students prefer to be hotel management staff, (13%) prefer to be school’s staff and the rest (3%) choose other roles.
From the gathered data of the distributed questionnaire, the researcher draws a conclusion of students’ need in learning speaking, as follows:
1. Students need a speaking material which makes them interested in learning English.
2. Students need a speaking material which makes a livelier English lesson class.
3. Students need a speaking material which imitated the real situation as a hotel management.
4. Students need a speaking material which makes them to be more confidence to speak in front of people or in public.
4.1.2 Considering Goals, The List Topics, Stating The General
Purposes for Teaching Each Topic
determining the goal, the researcher listed topics that were used in the designed materials. Then the researcher specified the indicators of each topic.
[image:69.595.107.517.278.747.2]The goal, the list of the topic, the general purposes, and the indicators of the design material for grade XI hotel accommodation class students of Sewon Vocational School 1 are presented below:
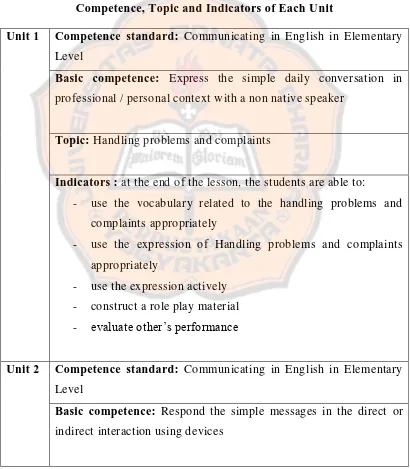
Table 4. The Description of Competence Standard, Basic
Competence, Topic and Indicators of Each Unit
Unit 1 Competence standard: Communicating in English in Elementary Level
Basic competence: Express the simple daily conversation in professional / personal context with a non native speaker
Topic: Handling problems and complaints
Indicators : at the end of the lesson, the students are able to:
- use the vocabulary related to the handling problems and complaints appropriately
- use the expression of Handling proble ms and complaints appropriately
- use the expression actively - construct a role play material - evaluate other’s performance
Unit 2 Competence standard: Communicating in English in Elementary Level
Topic: Phone Conversation
Indicators : at the end of the lesson, the students are able to:
- use the vocabulary related to the Phone Conversation appropriately
- use the expression of phone conversation appropriately - use the expression actively
- construct a role play material - evaluate other’s performance
Unit 3 Competence standard: Communicating in English in Elementary Level
Basic competence: Specify the duties and education background spoken or written
Topic: My Duties as A Hotel Staff
Indicators : at the end of the lesson, the students are able to
- use the vocabulary related to the my duties as a hotel staff appropriately
- use the expression of phone conversation appropriately - use the expression actively
- construct a role play material - evaluate other’s performance
4.1.3 Selecting Teaching and Learning Activities
The detailed information is explained in the following description.
1. Appetizer
The role of the teacher in this section is important. The teacher should be able to make the students to get closer to the topic discussed. The teacher presents pictures and let the students guess the meaning of the picture. Appetizer gives a chance the students to brainstorm their idea of the pictures which are related to the topic of each unit.
2. Main Menu
This section is divided into four parts. The first is reading the examples of dialogue related to the discussed topic. This part the teacher and the students take turn in reading the dialogue. The second is the lists of expression related to the discussed topic. The third is the lists of vocabulary related to the discussed topic. Both of part two and part three, students have to read the expression and the vocabulary one by one. The last part is dare to speak out, make a draft of the role play by choosing which situation would they play in the performance (the role play is done in group of 2-3 students).
3. Dessert
4.1.4 Developing the Material (addition)
The researcher added developing material steps into the combination of Kemp’s, Banathy’s, and Yalden’s materials design models. The researcher
added some activities, some exercises and some picture, and reduced the difficulty of the materials. These were carried out to facilitate the learners with interesting materials which could help the students developing their speaking skill and to obtain the appropriate speaking materials for the learners. The researcher developed the materials based on the syllabus and the needs of the students.
4.1.5 Evaluating the Designed Materials
Having done designing the designed materials, the researcher distributed evaluation questionnaire to the respondents. The respondents were an English teacher of Hotel Accommodation Class of Sewon Vocational School 1, and two lecturers of English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. Based on the result of the materials evaluation questionnaires, the researcher found that the designed materials were acceptable and good for hotel accommodation class grade XI students of Sewon Vocational School 1.
4.1.6 Implementing the Design Materials
in 25th, 29th of August, 3rd, 5th, 10th and 12th of September 2009. The rese