CLIENTS’ PERCEPTION ON SERVICE
PROGRAM DESIGN
STUDENTS’
ENGLISH COURSE AND TEACHING SKILLS
IN SERVICE PROGRAM DESIGN COURSE
A
SARJANA PENDIDIKAN
THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Dian Khenissa Siwiputri Student Number: 071214105
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ART EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work
or parts of the work of other people, except those cited in the quotations and the
references, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, 18 July 2013
The Writer
v
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma:
Nama : Dian Khenissa Siwiputri Nomor Mahasiswa : 071214105
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
CLIENTS’ PERCEPTION ON SERVICE PROGRAM DESIGN STUDENTS’ ENGLISH COURSE AND TEACHING SKILLS
IN SERVICE PROGRAM DESIGN COURSE
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan,
mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di Internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya maupun memberikan royalti kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya.
Dibuat di Yogyakarta Pada tanggal: 18 Juli 2013
Yang Menyatakan
vi ABSTRACT
Siwiputri, Dian Khenissa (2013). Clients’ Perception on Service ProgramDesign Students’ English Course and Teaching Skills in Service Program Design Course. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma
University
Service Program Design (SPD) course requires the students of the English Language Study Program Sanata Dharma University to have their teaching practice as small companies of English courses. Conducting teaching and learning process as designers and teachers to fulfill clients’ needs was students’ tasks. Independent teaching practice requires SPD students to have good teaching skills. Since there was no lecturer involved to give any suggestion and feedback, therefore, this research intended to analyze clients’ perception on SPD students’ teaching skills in the class. The clients were viewed to be the only party who had direct interaction with SPD students. It was concluded that the clients were the only supervisors who were able to have certain perception on SPD students’ teaching skills. The formulated research questions were: (1) What are the clients’ perceptions on the English Course held by PBI Sanata Dharma University
Students for the clients’ needs? (2) What are the clients’ perceptions on the SPD students’ teaching skills in teaching English during the process of learning?
To answer the research questions, the researcher used a survey as the research method. This research was held in five learning groups. The instruments used in this study were closed and open questionnaires and interviews. The questionnaires were aimed to collect data on clients’ perception on the English
course and teachers’ teaching skills. The clients involved in filling the questionnaire were 66 people. Five interviews were conducted to collect supportive statements to be added to the research discussion.
The research findings showed that the clients had good perceptions on the
English course and SPD students’ teaching skills. The clients experienced interesting, exciting and meaningful learning processes. They viewed their teachers as good teachers. It was concluded that the clients were satisfied with the English course as well as the SPD students’ teaching skills.
vii
ABSTRAK
Siwiputri, Dian Khenissa (2013). Clients’ Perception on Service Program Design
Students’ English Course and Teaching Skills in Service Program Design Course.
Yogyakarta: Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Sanata Dharma University
Mata Kuliah Service Program Design (SPD) membutuhkan para mahasiswa untuk melaksanakan praktek mengajar dengan mendirikan sebuah perusahaan bimbingan belajar Bahasa Inggris. Mengadakan proses belajar mengajar sebagai penyusun materi dan sebagai guru untuk memenuhi kebutuhan para klien merupakan tugas para mahasiswa. Praktek mengajar mandiri tersebut menuntut keterampilan mengajar yang baik dari para mahasiswa.
Karena pada pelaksanaan praktek mengajar tersebut tidak ada dosen pembimbing yang dilibatkan untuk memberi saran maupun masukan kepada para mahasiswa, penelitian ini dimaksudkan untuk menganalisa persepsi klien terhadap keterampilan mengaja para mahasiswa SPD di dalam kelas. Para klien dipandang sebagai satu-satunya pihak dan satu-satunya pengamat yang memiliki interaksi langsung dengan para mahasiswa. Dengan demikian dapat disimpulkan bahwa para klien merupakan satu-satunya pengawas yang dapat memberikan persepsinya terhadap ketrampilan mengajar mahasiswa. Rumusan masalah dalam penelitian ini antara lain: (1) Apa saja persepsi klien terhadap bimbingan belajar Bahasa Inggris yang diselenggarakan oleh mahasiswa Sanata Dharma terhadap kebutuhan klien? (2) Apa saja persepsi klien terhadap keterampilan mengajar para mahasiswa SPD dalam mengajar Bahasa Inggris selama proses belajar mengajar?
Untuk menjawab rumusan masalah di atas, metode yang digunakan adalah survey. Penelitian diselenggarakan di lima kelompok belajar (klien). Instrument yang digunakan adalah kuesioner dan wawancara. Kuesioner ditujukan untuk mengumpulkan persepsi klien terhadap keterampilan mengajar mahasiswa. Klien yang di libatkan di dalam penelitian ini adalah 66 klien yang merupakan murid di bimbingan belajar mahasiswa. Wawancara dengan lima klien dilakukan untuk mendapatkan poin pendukung yang nantinya akan ditambahkan di diskusi.
viii
pengalaman belajar yang menarik, menyenangkan dan berharga. Mereka melihat para mahasiswa sebagai sosok guru yang baik. Dengan demikian dapat disimpulkan bahwa para klien puas terhadap bimbingan belajar Bahasa Inggris dan juga terhadap keterampilan mengajar para mahasiswa SPD.
ix
AKNOWLEDGEMENTS
My biggest gratitude goes to Father Almighty, Jesus, and Holy Spirit for
their never ending blessings for me. It would be impossible for me to finish my
long journey of finishing my thesis without Him. Jesus has become by biggest
power to conquer all of the despair and difficulties.
The second gratitude would be for my dearest advisor, Ag. Hardi
Prasetyo, S.Pd., M.A. I thank him for being the most patient advisor for me. He
would have put me in his blacklisted students because of my laziness and my
ignorance, but he saved me once again and helped me finish my thesis. I realize
that I am not a brilliant student and sometimes I drove him crazy because of
countless mistakes I made in writing my thesis. Finally, with his assistance I
could finish this masterpiece of mine, my precious thesis report. I would also like
to thank all the 2008 SPD students who had let me conduct my research on them.
Even though I did not know them at the beginning, they still cooperated and
helped me willingly.
My mother is my biggest motivation ever. I dedicate this work to my
dearest mom Lucia Andri Susintowati, A. Md., for her never ending support,
prayers and motivation. She is the best mom in the world. She struggles her life
for her children and this is one of the gifts from a daughter for her mother. I thank
my mom for being there for me every day, for not complaining, for not doubting
x
Witono, S.E,. Even though he has passed away since a long time ago, I believe
that he is watching me and praying for me every day. I would also like to thank
my sisters, Dewi Ratna Suhita, S.Pd., Vinny Deviana and all my family for all the
support and motivation for me.
I also dedicate this work to my beloved boyfriend, Nicolas Ivan Evani, S.T.,
for his love, support and presence in my every night and day. I thank him for
being my funny and humorous boyfriend who can light up my darkest day. I am
so grateful that he has become my motivation in finishing my thesis as one of the
paths of reaching our future.
My best friends are my mood booster. I thank my best friends, Krengstiko
gang: Wendy, Midhud, Coro, Rarangs, and Trek; Fendi and Gwen for every thing
they have given to me. I am proud to have friends like them, especially for Triana
Sari who has walked with me in laughs and tears together. She accompanied me
everywhere I need her to be, she helped me with everything she could do and
cheer me up with all her ridiculous behavior. She is my best buddy ever.
Last but not least, I would like to thank all of the people who have given
their contribution to me to finish my thesis. I would like to thank Mbak Tata Fendi, Gwen, Lindsay Little, and Wendy for being my proof readers and gave me
their feedback. May God bless them all.
xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... iv
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ... v
ABSTRACT ... vi
ABSTRAK ... vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... xi
LIST OF TABLES ... xiii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xiv
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION A. Research Background... 1
B. Problem Formulation ... 5
C. Problem Limitation ... 5
D. Objectives of the Study ... 5
E. Benefits of the Study ... 6
F. Definition of Terms ... 7
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Theoretical Description ... 10
1. Perception ... 10
2. Factors Affecting Perception ... 12
3. Teaching ... 14
a. Teacher ... 15
xii
4. Teaching Skills ... 18
5. The Overview of Service Program Design (SPD) Course ... 22
B. Theoretical Framework ... 23
CHAPTER III. METHODOLOGY A. Research Method ... 25
B. Research Participants ... 26
C. Research Setting ... 26
D. Research Instruments and Data Gathering Technique ... 27
E. Data Analysis Techniques ... 31
F. Research Procedure... 32
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION A. Perceptions on the Service Program Design Students’ English Course ... 33
B. Clients’ Perception on the SPD Students’ Teaching Skills in Teaching English During the Process of Learning ... 39
1. Teaching Skills ... 39
2. Teachers’ Characteristics ... 58
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS A. Conclusions ... 60
B. Recommendations ... 61
xiii
LIST OF TABLES
Table. 3.1. Research Setting ... 27
Table. 3.2. Sample of the Questionnaires ... 28
Table. 3.3. Questionnaire Blueprint ... 29
Table. 3.4. A List of Interview Questions ... 30
Table. 3.5. Table of Closed Type Questionnaire Analysis ... 32
Table. 4.1. Clients’ Perceptions on the English course ... 34
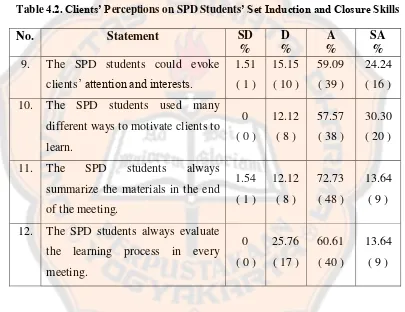
Table. 4.2. Clients’ Perceptions on SPD Students’ Set Induction and Closure Skills ... 40
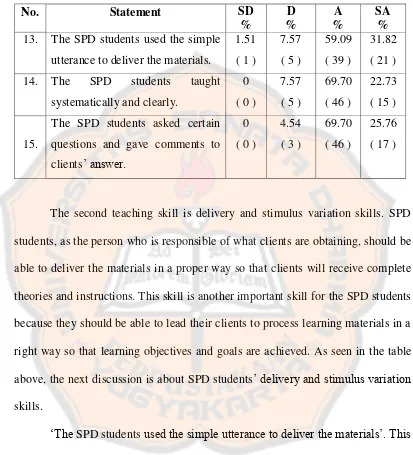
Table. 4.3. Clients’ Perceptions on SPD Students’ Delivery Skills and Stimulus Variation Skills... 44
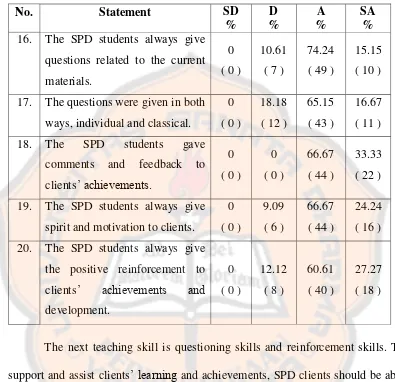
Table. 4.4. Clients’ Perceptions on SPD Students’ Questioning Skills and Reinforcement Skills ... 47
Table. 4.5. Clients’ Perceptions on SPD Students’ Ability of Conducting Integrated Teaching Skills... 52
Table. 4.6. Clients’ Perceptions on SPD Students’ Characteristics ... 59
xiv
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1: Questionnaire ... 66
Appendix 2: Questionnaire Result ... 73
Appendix 3: The Result of Open-ended Questions... 77
1
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This research investigates clients‟ perception of the Service Program
Design students‟ teaching skills in the classroom. To make the information more
detailed, there were six sections, namely, the research background, problem
formulation, problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits and
definition of terms.
A. Research Background
Teaching is a noble profession for those who want to dedicate their life to
the educational world and educate people. Being a teacher requires devotion of
knowledge, heart, and passion. It is said that in recently teaching as a profession
was increasingly discussed (Labaree, 2005; Neville, Sherman, & Cohen, 2005).
This leads to the possibility that being a professional teacher is highly demanded.
There are higher standards and expectations for a teacher as the result of better
preparation and bigger trusts for teachers. As the seventh semester students in the
English Language Education Study Program, students are required to have
sufficient teaching skills. They have been learning in the English Language
Education Study Program for more than six semesters, and that was time for
students to prove they are qualified enough to be professional teachers. English
the learning in such a way in order to well train students during the process of
gaining knowledge of becoming teachers.
The teacher-training courses are offered to students since they are in the
sixth semester when they take Micro Teaching. In the Micro Teaching course
students are trained and prepared how to teach and how to be a good teacher. The
subject is where they could integrate what they have received in previous
semesters to be a proper set of teaching approach. In this Micro Teaching course,
the students were practicing their teaching skills for the first time. They were
given some indicators of being a good teacher by learning the several points of
basic teaching skills. For example, they are introduced with the teacher basic
teaching skills of opening and closing the learning process, delivering learning
materials, behave properly, and many other things. The learning and training
process in Micro Teaching class gives students a good base of becoming teachers.
After students took the Micro Teaching subject, they had to be ready to face the
real class and the real teaching situation through Program Pengalaman Lapangan (PPL) where they have to be in a real official school to teach real students. This is also the place where they are able to apply their experience and knowledge
obtained from Micro Teaching class.
Concerning the teaching system, a higher step in the teacher training
process is through the Service Program Design course. In this course, students are
required to be more independent. Students are treated professionally as if they are
working in a real company; as a result, the students finally will be involved in the
Students are required to create an independent mini company which
provides English Course service for the clients. They have to find at least one
client; the company that will use their English Course service to learn English.
The next thing is the students as the English instructors have to teach the clients
appropriate English based on the client‟s need.
The teaching practice is a big step for the students because they will face
the real working world by themselves. There will be no assistance from the
university like what they had in PPL. There are no supervising teachers or lecturers to guide them like what they had in Micro Teaching and PPL. There is no feedback from lecturers, no material or lesson plan consultation. They have to
prepare everything and have to be professional because they are expected to be
professional. There will be more complicated things such as preparing the
modules, materials, class management, and so forth. A set of teaching materials
and teaching approaches for the clients are created by Service Program Design
students as the company service for the clients.
Being a teacher and material designer at one time is the first real teaching
experience for most of the students in the real company with their own efforts.
They have to sell their set of materials to the clients and teach the materials. That
is why this course is difficult for them to accomplish. Because teaching some
companies‟ employees is a relatively new experience for the students, there will
be a lot of things to be considered carefully, including: the materials they will
teach, whether the materials are suitable for the learners‟ needs or not, the class
on. That is why SPDstudents have to study and comprehend the client‟s needs on
the language for clients will learn.
In academic year of 2011/2012, the SPD students were given the
opportunity to have the cooperation with Sanata Dharma University especially
with some students from different study programs and faculties. Since there was a
new regulation for student of non-English departments to follow English
proficiency tests of TKBI (Tes Kemampuan Bahasa Inggris) as the prerequisite test of graduation requirements. Therefore, the SPD students were encouraged to
recommend themselves to assist students from different study programs to learn
English.
As the new experience for SPD students to teach the real clients, their
performance will also be important for the clients. Are the clients satisfied? Do
the teachers teach well? Do the teachers explain well? Do the clients get the
advantage of learning English? Those questions will be the guidance for the SPD
students on their achievements after they have taught their clients. Whether or not
they need more preparation or more teaching improvements will depend on the
clients‟ opinion.
It can be seen that clients‟ feeling about the SPD students‟ skills in the
class will be the biggest consideration of how successfully their duty is. That is
why the researcher will conduct a study of the clients‟ perception on SPD students‟ skills in teaching English in teaching English as the requirement of
B. Problem Formulation
In this study, the researcher would like to address two questions related to
the clients‟ perception on SPD students‟ skills in teaching English. The research
questions are as follows.
1. What are the clients‟ perceptions on the English Course held by PBI Sanata Dharma University Students for the clients‟ needs?
2. What are the clients‟ perceptions on the SPD students‟ teaching skills in
teaching English during the process of learning?
C. Problem Limitation
The study was limited to clients‟ perceptions on the SPD students‟ skills in
teaching English during the process of learning. Related to the second research
questions, there are so many characteristics proposed by the experts and some of
them cannot be seen by the clients. The characteristics of a good teacher in this
study are limited to the characteristics which are visible to the clients.
D. Objectives of the Study
The study will find out the answers to the problems stated on the problem
formulation. The objectives of the study are as follows.
1. To find out the clients‟ perceptions onthe SPD students‟ English Course.
2. To find out the clients‟ perception on the SPD students‟ teaching skills in
E. Benefits of the Study
The researcher expects that this research will be for the students and study
program.
1. The Students of the Study Program
The students will also gain the benefits. They will get feedback in their
own teaching skills. They can also know whether they have already been good
teachers or not. They also can be motivated by knowing how successful their
performance is and more, they can develop their teaching skills by the time they
know their weaknesses.
2. The Researcher
The researcher will also receive the advantages by conducting this study.
When the researcher succeeds in answering the research problems, the researcher
can also find out how good teachers should be and apply the knowledge to their
future experiences especially in teaching. The researcher could attempt to reflect a
F. Definition of Terms
The following terms are need clarifying to assist readers to understand this
study.
1. Perception
The definitions of perception are gathered from some experts. According
to Huffman and Vernoy (1997), perception is a process of selecting, organizing,
and interpreting sensory data into usable mental representation of the world.
While according to Worchel and Shebilske (1998), perception is like the process
of interpreting something. From the definitions above it can be concluded that
perception is an activity which a person do to interpret some information or
something that they get from the outside world. The information that they get is
processed in their mind and become meaningful information.
In this study, the perception refers to the clients‟ perception on the
students‟ teaching skills in the class room. The clients will also give the opinions
and impressions to the students‟ teaching skills as well.
2. Service Program Design (SPD)
According to Buku Panduan Akademik (2006), SPD or Service Program Design Course (KPE 477) is a course where the students are trained to have the
ability to understand how to have a good habit in the working world, how to
design a proposal, and how to market the program proposed. When its main
assignment is to apply the real English course service program to authorized
organizations or company and after that they have to apply the materials they have
In this study, SPD (Service Program Design) course is the course followed
by the 7th semester students of PBI in the academic year 2011-2012.
3. Teaching
“Teaching in the Foundation Stage is based upon the premise that positive,
respectful relationships between children and adults are essential for children‟s
well being now and success in the future” (Pascal, 2011). On the other hand,
according to Hough and Duncan (1970), teaching is an activity, a unique
professional, rational, and humane activity where he is creatively using himself
and his knowledge to promote learning and welfare of others. Hough and Duncan
also define teaching as the activity of four phases those are planning phase,
instructing phase, measuring phase and evaluating phase. From the experts‟
definitions toward teaching, it is apparent that teaching is the activity which
relates to parties; the teacher and the students. Teaching requires relationship
between humans to create the learning process which is essential for students and
their future.
This study defines teaching as the learning activity which involves
teachers and students in positive interactions and beneficial relationships to
promote the effective learning in mastering English. The teachers were using
themselves as the learning media and supporting students learning.
Teaching skills is viewed as teacher‟s abilities of „knowing and doing‟ in
the classroom which involve three main elements of knowledge, decision
making and action to support and foster students‟ learning (Kyriacou, 2007, p.
1). The similar definition of teaching skills is stated by Uppsala University,
saying that teaching skills are teacher activity during teaching and leaning
process to promote student achievements. In this study, teaching skills is
defined as teachers‟ ability to conduct teaching and learning process to
10
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter discusses all theories related to the study. Those theories will
be divided into two parts. The first discussion deals with the theoretical
description. In this section the researcher will present the theories related to the
study. The theory description covers the concepts of (1) perceptions (2) factors
affecting perception (3) teaching (4) teaching skills and (5) the overview on SPD
course. In this section, the researcher would discuss the explanation on how those
theories will be used to solve the research problems.
A. Theoretical Description 1. Perception
Conducting research on perception, some related theories were compiled
to present a complete view on perception itself. Some theories on perception were
taken from some experts. Perception is defined as organisms’ awareness of certain
objects brought by their sense organs stimulation (Bootzin, Loftus & Zajonc
1983). Bootzin et al. claimed perception is different from sensation. From the
definition above, perception defined as ‘someone’s awareness’ of certain objects
in his/her environment which is processed into a meaningful interpretation.
Perception is said as the result of having a more complex process compared to
sensation which occurred without any awareness of the organisms’ sense.
perception where they described the sensation as the raw data before it is
processed in someone’s brain to produce perception. Aiken (1969) mentioned
when someone perceived some objects in his interactions, the influence of
organismic states and his learned background is affecting the process of making
the perception. This means that perception involves all brain sensors activity to
process the stimuli in organisms’ environment.
Another description on perception brought by Huffman and Vernoy (2000)
stated that the perception is the process of selecting, organizing and interpreting
raw sensory data (sensation) into complex and useful representation of the
environment. It is apparent that perception is the way people interpret something
which is received by people’s sensory organs. When people see, feel, hear, taste
and smell something from their environment and then they select, organize and
interpret the stimuli it is called perception.
Perception is also related to organisms’ experience. Bootzin et al. (1979)
claim that experience and expectation shaping someone’s perception on his
sensory events. People who experience the same sensory events at the same time
might have different perceptions since they might have different experience and
expectation. As what Mouly (1973) has stated that people might have different
perceptions of the same thing even they have experienced the same event. In line
with Bootzin et al. and Mouly, Wick and Pick (1978) also had the same idea that
2. Factors Affecting Perception
Since perceptions are diverse, some factors affecting someone’s
perception are described in this study. Some experts suggested some factors that
could affect someone’s perception. This research addressed six factors that could
affect someone’s perception on a certain thing or object in his environment. Those
factors are as follows.
a. Stereotype
According to Gibson, Ivanovich and Donnely (1985), stereotype was a
way of thinking of particular people or group on something which was
generalized. It means that someone or some people will already have a thought on
something about a certain object or people, and they will directly judge it even
without knowing the truth.
This factor might have influenced the process of perceiving SPD student
teachers’ teaching skills by the clients. The clients might have pre-judgment of the
SPD student teachers’ teaching ability. It could be positive judgment or even the
negative one. Clients’ pre-judgment brought some influence to their perceptions.
b. Selectivity
The next factor is selectivity. Selectivity refers to the stimuli processed in
our brain. It is impossible to accept all the stimuli from our environment, only
some of them which are enable to be processed in our brain. It is because our
interest to those stimuli. Perception is gained based on something that we select or
to select the stimuli which are interesting for them. The similar idea was presented
by Huffman and Vernoy (1997). They stated that in the process of selection,
people’s interests and needs will affect the selection. People choose and select
certain objects because they give a positive impact for them. People also tend to
ignore the stimuli which make them feel uncomfortable. As people have various
interests in life, they may select stimuli which are able to fulfill their needs. This
factor makes people perceive something differently.
c. Object Frame and Context
Huffman and Vernoy (1997) mentioned people’s perception was affected
by the frame and context of the stimuli. People will perceive differently with their
previous perceptions when they are brought into a different context. Huffman and
Vernoy illustrated the phenomena by giving a slight description on how a man
will have a different perception than he had before after the object is put into a
broader context.
d. Self-concept
The way someone see him or her self will affect his way of seeing the
environment. How a person sees himself or herself can influence the process of
perceiving something that he faces. Gibson et al. (1985) stated that someone’s
self-concepts are often reflected in their attitudes based on the stimuli which are
e. Motivation and Needs
People’s perception is affected by their self-motivation and needs for
certain thing. This theory was suggested by Huffman and Vernoy (1997). They
claimed that people tended to notice stimuli which have given them a state of
satisfaction in certain ways. If the stimuli bring the positive impacts in their early
experiences and when the stimuli are in line with their needs, they tend to
recognize and select the stimuli.
The similar thing will occur in this study since each client has a different
motivation and needs; it is possible for clients to have different perceptions of
SPD students on their teaching skills among each other.
f. Situation
Another factor which influences someone’s perception is situation.
According to Aftman, Valenzi and Hodgetts (1985) situation may refer to the
whole situation of someone’s condition, meaning that someone’s background,
experience, and habit can influence his perception on certain things. The concept
also supported by the idea originated from Huffman and Vernoy (2000) where
they said that early experience could significantly affect someone’s perceptual
responsiveness to the stimuli. While according to Gibson et al. (1985), situation
refers to someone’s condition in doing his or her activities which can influence
3. Teaching
According to Hamachek (1990, p. 394), a good teaching is both an art and
science. In other words, good teaching is done by an artist who is able to utilize to
the fullest in a classroom the best scientific research to the human resources and
technological advances. While according to Hough and Duncan (1970), teaching
is an activity, a unique professional, rational, and humane activity of creatively
using himself and his knowledge to promote learning and welfare of others. Both
statements from the two experts have the same idea about the activity in the class
as process of learning, and also from the statements we can see that both experts
see it is the activity of learning that needs creativity, knowledge and facilities to
promote the best teaching and learning activity.
a. Teacher
According to Hough and Duncan (1970), teacher is a professional who is
capable of making rational, humane, and creative decisions regarding the teaching
act. It is clear that a teacher is someone who is in charge in the classroom to teach
the students something they are expected to learn. Teachers are the ones who are
responsible for the whole class, the whole teaching-learning process, the whole
students and even the classroom environment. According to Danielson’s
Framework of teaching (2007), classroom environment is the second important
domain which the teachers should pay attention to.
b. The Characteristics of Good and an Effective Teacher
We often hear about these two words, a good teacher and an effective
characteristics of being a good teacher. Berliner (1987) made a distinction
between a good teacher and an effective teacher. He stated that being a good
teacher deals with how good the teaching skills of the teacher is, how good the
teacher behave in the classroom and about the standard of a good practice of a
teacher in the classroom without considering whether the students really learn
something or not. While being an effective teacher is always related to the
instructional outcomes or the students’ achievements on the materials they have
learned. Once again, the good teacher always deals with the teacher’s behavior in
the classroom, while an effective teacher always deals with the students’ academic
performance. Based on Berliner’s distinction on a good teacher and an effective
teacher we can see that it is just a matter of point of view. As Hamachek (1990, p.
395) stated that it is important to distinguish between a good teacher and an
effective teacher in the research, he prefers to use the terms interchangeably; the
researcher has the same idea that in this study, the terms are used interchangeably
because it can be more complete if the researcher uses these terms all together.
Hamachek (1990, p. 396) stated that it is not possible to define exactly
what an effective teacher is at least not in a very specific way. While Berliner
(1987, p. 94) stated that the effective teacher is someone who is able to get most
of his students to learn what they are supposed to learn and the teacher can have
all the knowledge to fit with some particular different type of students.
Being a good and effective teacher is important for future teachers. The
description on being a good and effective teacher gives apparent points that the
Hamachek also stated that there is no exact definition of what a good
teacher is. It is supported by Getzel and Jackson (1963, p. 574); they stated that
after summarizing the fifty years of research on teachers’ personality and
characteristics, they conclude that after all of the research efforts finding the
meaning of an effective teacher, very little is known to ensure about the
measurement of teacher personality and the connection with teachers’
effectiveness. Hamachek (1990, p. 396) suggested three dimensions of effective
teachers’ behavior. Those are: personality traits, intellectual characteristics, and
instructional approaches.
Teachers’ personality traits are the personality performed by the teacher in
the class. Teachers, as a fully human being, must be able to perform the
personality of being warm, caring and friendly. Teachers should also be able to be
enthusiastic and proactive in guiding the students to promote more effective
learning.
Good teachers’ intellectual behaviors are the behaviors of having a balance
between their knowledge with the implementation of the knowledge itself. The
teachers should have a balance between knowing and doing. Teachers are also
required to have thorough preparation in the class so that they will have fully
organized and clear materials to be delivered. Placing a high value on the
academic achievements and students’ learning are the other intelligent behaviors
of good teachers.
The last dimension of effective teachers’ behaviors is the instructional
learning through effective approaches, such as giving specific feedback, giving
positive rapport, giving sufficient time for learning and giving flexible instruction
and interaction.
Those are the characteristics of effective teachers suggested by Hamachek. He also stated that good teachers are good for many reasons, and one of the
reasons is that they are good people to begin with. In other words, the
characteristics of effective teacher that suggested by Hamachek is the most
characteristics found after some research on the characteristics.
4. Teaching Skills
In order to meet the requirements of being a good and effective teacher,
future teachers should consider some teaching skills that need to be trained and
mastered. In this study, the researcher addressed some teaching skills by
Purnomo, Rismiati, Domi and Rohandi in Buku Pedoman Pengajaran Mikro
(2008) integrated with the theories of teaching skills by Brown (1975).
Purnomo et al. (2008) suggests some teaching skills which are categorized
into four sections as follows.
a. Set induction skills and closure skills
Set induction and closure are teaching activities which are conducted at the
beginning and at the end of the learning process. Set induction skills related to
teacher’s ability to open the learning process by emerging students’ learning
motivation and interest. Set induction is also aimed to give students the learning
beginning of the learning process with students’ attention-grabbing which is a
very effective way to increase both learning and motivation (Kauchak & Eggen,
2011). Set closure is conducted in the end of every learning process. A teacher
should be able to summarize and review all of the learning process in order to
give more meaningful learning for students. Kauchak and Eggen (2011) in their
book also stated that summarizing the whole learning materials in the end of the
meeting is able to help students to organize what they have learned into a
meaningful idea. Set closure is also a moment for a teacher to evaluate the
learning and give students feedback on their achievements.
b. Delivery Skills and Stimulus Variation Skills
Delivery skills and stimulus variation skills are conducted in the middle of
students’ learning process. In delivering the materials, a teacher should be able to
use a simple language in explaining the materials and interacting with students.
Giving illustration and examples of related materials is also required since the
students need clearer views on the learning materials. Delivery skills also cover
teacher’s ability to have clear and systematic explanation on the material itself so
that students will not be confused or even lost in the middle of the learning
process. Some former studies on teachers organization and clarity revealed the
similar and consistent results that teachers with good qualities of organization and
clarity in delivering the materials were viewed to be more effective in supporting
more learning among students (Cruickshank 1985; Good & Grouws 1977; Land &
Stimulus variation skills are teacher liveliness. A good teacher should be
able to reflect positive behaviors in front of his/her students. It is said that teacher
liveliness supports student involvement in learning. Teachers with enthusiastic
liveliness is said to be able to encourage students to respond positively to their
learning (Rosenshine, 1970).
c. Questioning Skills and Reinforcement Skills
Questioning skills are teacher abilities to give questions to students related
to the learning materials. This questioning section is aimed to help student’s
understanding on the materials given by the teacher. Good and Brophy (2008)
stated that many research addressed the similar thoughts that guiding students
through questioning is more effective that just explaining the materials. By
addressing some different questions, students will prepare themselves to answer
the teacher’s questions. Another objective of questioning is to check student
progress.
Brown (1975) stated that positive reinforcements encourages students to
contribute something to the discussion as well as encouraging them to struggle to
achieve. Reinforcement skill is another teaching skill which is related to teacher’s
ability in giving positive response to student achievements and behaviors. Good
teachers should be able to support students to learn meaningfully. Teachers should
be able to give positive view of what students have experience. It is supproted by
some studies which have revealed that giving praise and corrective feedback to
students deliver positive influence to students’ achievements and attitudes toward
d. Conducting integrated teaching skills
Integrating every teaching skill to produce more effective learning is
another skill which needs to be considered by teachers. This teaching skill covers
every basic aspect of teaching which supports students’ learning process.
Hough and Duncan (1970) proposed some requirements of being a good
teacher. They stated that teachers should be capable of creating rationale, humane
and creative decisions in the process of teaching the students. Facilitating students
learning is another requirement of being good teachers. Teachers as educated,
trained and experienced person who is in charge in the class are expected to be
able to give beneficial knowledge to the students to reach the learning goals.
Teachers also have to be able to help students to gain knowledge, skills and
abilities that students need to work effectively. Measuring students learning is
where teachers are required to check whether the students have reached learning
objectives or not. Lastly, as good teachers they have to be able to evaluate their
own teaching and improve their teaching as well.
While Ryan and Cooper (1984) stated teachers must be able to integrate
between what they know and what they do. Teachers should be able to apply their
knowledge to their profession as teachers. Ryan and Cooper also administer some
figures of being effective teachers; they stated that teachers should have the ability
to, (1) Ask many different questions to the students which require students’
responses, (2) Reinforce any kinds certain student behaviors, (3) Determine
involving the students, (5) Recognize student behavior/ responses during the
learning process, and (6) Use certain media to support learning.
5. The overview of Service Program Design (SPD) course
As stated before that according to Buku Panduan Akademik (2006, p. 99), SPD or Service Program Design Course (KPE 477) is a course where the students
are trained to have the ability to understand how to have a good habit in the
working world, how to design a proposal, and how to market the program
proposed. The main activity of the course in every week is lecturing on the value
of how to be a good person in the working world. There are many other activities
in the classroom including the assignments, and the final project or the final
assignment is to have the clients for students to sell their service program.
In the very beginning step, the students must make a proposal of their own
company; they have to explain what program they want to offer. Students must
advertise or propose their program in the form of proposals to some clients in the
real companies after making the proposals. The next step is they will have their
own deal on everything related to the course including the fee. After they have the
deal, they will have to make a Memorandum of Understanding as the formal
agreement between two parties. Finally, they will begin their service program in
English course to teach the clients. And if all the teaching-learning process has
done, they have to make a report on what they have done in the teaching practice
to the lecturer. It has been clear that this is where the students are required to be
with the law. This could discourage students because they are on their own and
they will have to manage and undergo their own policies. Even though the SPD
students generally have the clients from many different companies, in the
academic year of 2011/2012 they had the opportunity to teach students from
English department study programs. Regarding the fact that students from
non-English department study programs must follow the non-English proficiency test of
TKBI (Tes Kemampuan Bahasa Inggris); those students need to learn English as the preparation before doing the TKBI test.
B. Theoretical Framework
After having the theoretical description, the researcher gives further
explanation of the theoretical framework on how the problems of the study will be
solved. Since this study is aimed to investigate clients’ perceptions on SPD
students teaching skills, the researcher used the term perception as Bootzin et al.
(1983) has claimed that experience and expectation shaping someone’s perception
on his sensory events. This research emphasizes clients’ experience in following
the English course as their sensory events which creating their perceptions. Based
on the clients’ experience, the researcher is able to have the concrete sight of how
the clients’ perceived their teachers (SPD students). The research also uses the
statement from Mouly (1973); saying that people might have different perceptions
toward the same thing even they have experienced the same event, as the
consideration of having diverse data. In obtaining clients’ perceptions on SPD
clients’ perceptions as stated by Gibson et al. (1985), Huffman and Vernoy
(2000), Atman, Valenzy and Hodgetts (1985) namely: stereotype, selectivity,
object frame and context, self-concept, motivation and needs, and situation.
In answering research questions about clients’ perception on SPD
students’ teaching skills, the researcher mostly used the theories of teaching skills
by Purnomo et al. (2008) which was adapting the theories of teaching skills by
Brown (1975), while the theories of teaching skills by Hough and Duncan (1970)
and by Ryan and Cooper (1984) were also used as the additional points since their
theories are relatively similar to each other. Every basic teaching skill is divided
into some indicators where the clients will stated their perceptions in the Likert
Scale provided in the questionnaire. Besides the use of teaching skills theories, the
researcher used the theory of teacher characteristics by Hamachek (1990). The
researcher will take the points of each teaching skill and teacher characteristic that
is visible for the clients. It means that not all of the teaching skills and teacher
characteristics can be seen by the students because some of the characteristics deal
with the preparation of the performance. The limited visible indicators for the
clients result in the limited teaching skills indicators which were used in this
25
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY
This chapter discusses the method used in the study and divide it into six
parts namely research method, research participants, setting, research instrument,
data gathering technique and research procedure.
A. Research Method
The study conducted by the researcher was survey research where the
researcher intended to find out the perceptions of the research participants.
Pinsonneault and Kraemer (1993 p. 77) stated that a survey is a method of
obtaining information about the characteristics, actions, or opinions of a large
group of people. This research was aimed to find out the perceptions of the clients
on the Service Program Design course student teachers’ teaching skills. This
research will focus on the number of data collected from the clients. To be more
specific, this survey study used questionnaires and interviews to obtain deeper
perceptions on Service Program Design (SPD) students’ teaching skills including
their strengths and weaknesses. The reason to select this method is the researcher
could collect the big number of data just in a relatively short time. Regarding the
fact that this study had relatively big number of participants, survey research was
B. Research Participants
SPD students in the academic year of 2008 had the opportunity to have
cooperation with other non-English faculties in Sanata Dharma Universty. The
research participants of this study were the clients of the seventh semester SPD
students groups in year of 2012. There were five groups or teams in SPD class, each group had at least more than ten clients. This study gathered data from all
clients of five different learning groups. Each learning group consisted of 10 to 20
clients, providing the researcher with 66 clients in the study. The clients were
Sanata Dharma university students who came from different faculties and study
programs. The clients had a similar range of age from 22 to 35 years old because
they came from relatively the same year. The purpose of collecting data from all
SPD groups was to have the thorough result of the clients’ perceptions.
C. Research Setting
The study was conducted in the second last meeting of each group. The
time of collecting the data depended on the schedule in each group because every
group had a different teaching schedule. The following, table. 3.1., shows the
Table.3.1. Research Setting
Group Date Place Clients 1 February 7, 2012 YOUTH, Kota Baru 10
2 March 12, 2012 P.FIS faculty laboratory
Paingan 16
3 March 20, 2012 P.FIS faculty laboratory
Paingan 17
4 March 22, 2012 P.MAT faculty Paingan 12 5 March 28, 2012 IPPAK faculty 11
D. Research Instruments and Data Gathering Technique
The study used two kinds of instruments, namely, the questionnaire and
interview.
1. Questionnaire
Questionnaire was the main instrument in the study because it gathered
clients’ perceptions on the SPD students’ teaching skills. Ary, Jacobs, & Azghar,
(1979, p. 178) stated that questionnaire has two forms; the first one is open form
or unstructured and closed form or structured. The research used two types of
questionnaire, those were closed form questionnaires consists of 30simple
closed-ended statements where the students just need to give check marks in the provided
spaces. In each statement, the researcher provided four columns to be filled. First
column indicated strongly disagree (SD), the second column indicated disagree
(D) the third column indicated agree (A) and the fourth column indicated strongly
agree (SA). The closed-type questionnaires were also divided into six categories.
The first one contained seven statements related to the English course, the second
skills, the third one contained three statements related to teachers’ delivery and
stimulus variation skills, the fourth one contained five statements related to
teachers’ questioning skills and reinforcement skill, the fifth one contained seven
statements related to the teachers’ ability of conducting integrated teaching skills
in the class, and the last one contained three statements related to teachers’
characteristics. The complete description of the questionnaire is available in
following table 3.2 of questionnaire blueprint.
The second type was the open form questionnaires which consisted of five
open-ended questions related to the SPD student teachers’ teaching skills. The
clients had to answer the questions in the provided space with their own words.
This type of questionnaire gave the complete and clear overview of how the
clients perceived on the SPD student teachers’ teaching skills.
Table 3.2. Sample of the Questionnaires Name:
Age :
No. Statements SD D A SA
1. English language mastery is a very
Table 3.3. Questionnaire Blueprint
Statement/ Question Indicator
No. 1-7 Clients’ perceptions on the English course.
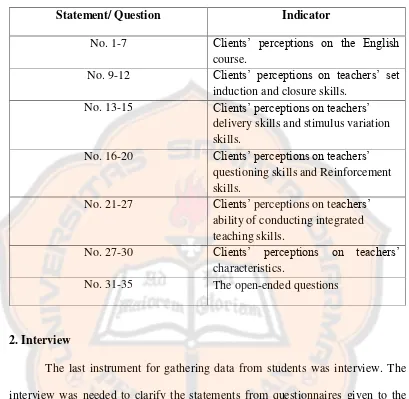
No. 9-12 Clients’ perceptions on teachers’ set induction and closure skills.
No. 13-15 Clients’ perceptions on teachers’ delivery skills and stimulus variation skills.
No. 16-20 Clients’ perceptions on teachers’ questioning skills and Reinforcement skills.
No. 21-27 Clients’ perceptions on teachers’ ability of conducting integrated teaching skills.
No. 27-30 Clients’ perceptions on teachers’ characteristics.
No. 31-35 The open-ended questions
2. Interview
The last instrument for gathering data from students was interview. The
interview was needed to clarify the statements from questionnaires given to the
clients. Because of the clients’ limited time, the researcher took one person from
each learning group to be interviewed. The interview questions were five
questions related to the questionnaire statements. The questions were open-ended
questions. The clients had to answer all the questions based on their questionnaire.
During the interview, the researcher used a hand phone which has a recording
Table.3.4. A List of Interview Questions
No. Questions
1. How did you feel after following English training course with the teachers?
2. How does your English skills after attending the training course?
3. In your opinion, how were teacher teaching skills?
4. Do you think they've taught you well?
5.
What are the deficiencies of the students that you think need to be
improved? And is there any strength possessed by teachers which
need to be maintained?
6. Are you satisfied with the service of English course?
After asking permission to conduct research in each learning group, the
first technique was distributing the questionnaires. The research was conducted
inside the classroom and outside the classroom. First, the researcher distributed
the questionnaires to the clients. The researcher gave the clients around 15
minutes to fill the questionnaires. The questionnaire distribution was conducted in
the second last meeting to each learning group. After researcher distributed the
questionnaires, then the researcher used the second technique; interview. The re
searcher conducted five interviews to one participant in each learning
group/client. The researcher obtained the data that she needed through those two
instruments and after the raw data had been collected, the researcher then
E. Data Analysis Technique
After gaining the data from 66 questionnaires and interviews, the
researcher analyzed the data to answer problems. The data from closed type would
be shown in the form of percentage. Firstly, the researcher presented the
percentage result of clients’ perceptions by dividing it into six different tables.
The researcher categorized the perceptions into one table of the clients’
perceptions on the English course, five tables of basic teaching skills and one
table of teachers’ characteristics. By dividing the data percentages in six different
tables according to its category, it made the researcher feel easier to discuss the
research findings. After the data had been presented, the researcher then directly
discussed the research results without making the new sub title.
In the discussions of answering the problem formulations, the researcher
not only used data from questionnaire percentage but also used data from
open-type questionnaire and interviews results. Even though the researcher used the
questionnaires percentage as the main source of answering the research questions,
the researcher also added some supporting information from clients’ answers in
the open-typed items and the interviews so that the research results will be more
convincing for the readers.
In this study, the researcher only used the result of data percentage only.
Using data percentage to analyze the result, the researcher perceived that it is clear
enough to see and conclude the clients’ perceptions on SPD student teachers’
Table.3.5. Table of Closed Type Questionnaire Analysis
No. Statements
Strongly Disagree
(%)
Disagree
(%)
Agree
(%)
Strongly Agree
(%)
F. Research Procedure
The research began with questionnaire distribution on the day that had
been scheduled with the group. The researcher went to five SPD groups to
distribute the questionnaires to all clients. Questionnaires distributed to the clients
aimed to obtain clients’ perception on the SPD students’ teaching skills. The
clients did the questionnaire directly and submitted it on the same day to the
researcher. The researcher gave around 15 minutes for the clients to do the
questionnaires. After data from the questionnaires had been collected, the
researcher conducted five interviews to one participant in each learning group
some minutes after the data collection from questionnaires. The interviews took
approximately 10 to 15 minutes each participant. After all the data needed by the
researcher had been collected using all the instruments, the researcher analyzed
the data using the data analysis technique to sum up all the data gained from the
students to find the percentage of each point. The researcher used data percentage
to answer research problems. After the data had been analyzed, the next task for
the researcher was to interpret the result and give clear description to answer the
33
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents the data and the analysis based on clients’
perceptions on the SPD students’ teaching skills in the classroom. There are 66
questionnaires and five interviews were used to obtain the data from the clients.
The compiled raw data then were analyzed and interpreted to answer two research
questions. In discussing research findings, the terms of teacher for SPD students
and students for clients are used interchangebly since the researcher is willing to
discuss teachers and students in general together with the phenomena hapenning
to the SPD students and their clients.
A. Perceptions on the Service Program Design Students’ English Course
The first problem formulation is aimed to find out how the clients
perceived the English Course. The perceptions on the course for clients’ needs
were a very significant thing to examine. The first research problem was intended
to enquire whether the English course is still needed or not. The researcher also
discovered whether the clients could obtain any advantages from the English
course or not. The answers to all those questions were presented in the
Table 4.1. Clients’ perceptions on the English course
abilities after following the English
course program.
environment and climate. According to Danielson’s framework of teaching
(2007), classroom environment is the second important domain which the teachers
should pay attention to. Danielson stated that classroom environment is not only a
physical place for students to learn, it is also a place for teachers and students to
interact and communicate with each other. SPD students should be able to create a
positive classroom environment and prepare clients to reach the learning goals. In
this study, there were 60.61% of the clients who agreed that the classroom
situations were fun for them to learn. While there were 30.30% of the clients who
strongly agreed. Most of them agreed that the SPD student teacher could build
such an interesting and fun situation in the classroom. Classroom situation is able
to help students’ learning process. If the classroom situation is different from the
student expectations, it will affect student motivation and enthusiasm in following
fun; clients will learn more productively in the class. Considering the fact that
students require good classroom climate, the teachers should possess the ability to
create the environment where students can live and learn (Emmer, Evertson, &
Worsham, 2009)
The sixth statement is about the clients’ progress after following the
course process. The data percentage shows 60.61% of the clients agreed and
30.30% strongly agreed that they could improve their English skills after
following the course. The learning outcomes from the long process of learning are
the important thing to consider since it indicates how effective the learning
process is. Learning results could be seen by clients’ progress. This study
investigated clients’ self reflection on their English language progress after
following the learning process. It is pictured in the data presentation that over
90% of the total clients felt their English skills were improved after following the
course.
The last statement of the first category is the advantages of following the
course. There were 77.27% of the clients who agreed with the statement and
19.70% who strongly agreed that they could obtain many things to support their
English ability. Clients’ perceptions on the advantages of following the course
showed that the the English Course held by SPD students is important and
beneficial for them.
By looking at the result from the close-ended typed questionnaire
statement one to seven, it can be concluded that most of the clients had good
English today are important. It leads to the needs for learning English through
English Courses. Almost all of the clients needed to learn English because they
needed to master English. Aside from awareness to learn English, the clients also
had good perceptions on the course they had. They felt the classroom situations
were fun and interesting; they were enthusiastic to follow the course not only
because of the duty. Finally, they also could have the advantages from following
the course. Through some interviews , the first interview question questioning
about clients’ feelings after following the course, it is found that all of the
interviewees had the similar feelings. They felt satisfied, happy, proud of
themselves, more confident, and motivated. They felt that the learning process
brought many positive things in their lives. They received many advantages,
benefits and gained new experiences through the course they were following. The
only issue was that they only got very short time to learn English while they
thought they need more than what they had experienced. Even though the research
traced that most of the clients had good perceptions on the English Course, there
were still few of them who had bad perceptions on the English Course. This
means there are some things that still need to be fixed and improved by the SPD
students.
B. Perceptions on the SPD Students’ Teaching Skills in Teaching English During the Process of Learning
After discussing the clients’ perceptions on the English Course, this part