SEE 2017 USQ SPRINGFIELD BRISBANE, AUSTRALIA
SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND ENVIRONMENT
PROCEEDINGS OF THIRD INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE – SEE 2017
SCIENCE, ENGINEERING & ENVIRONMENT USQ SPRINGFIELD BRISBANE, AUSTRALIA 13-15 November, 2017
Science, Engineering
and Environment
Edited by
Prof. Dr. Zakaria Hossain
Graduate School of Bioresources Mie University, JapanDr. Jim Shiau
School of Civil Engineering and Surveying University of Southern Queensland, Australia
THE GEOMATE INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY
Copyright @ 2017 by The GEOMATE International Society
All rights reserved. In principle, no part of this publication or the information contained herein may be reproduced in any form or by any means, translated in any language, stored in any data base or retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior permission in writing from the publisher.
Disclaimer: The editors and the publisher have tried their best effort to ensure the integrity and the quality of this publication and information herein. However, they give no warranty of any kind, expressed or implied with regard to the material contained in this book, and will not be liable in any event for the consequences of its use.
Published by:
The GEOMATE International Society Tsu city, Mie, Japan
E-mail: [email protected] http://www.geomate.org/
ISBN Number:978-4-9905958-9-0 C3051
Table of Contents
Preface xi
Organization xii
ID
Keynote Papers
11k
MECHANICS OF GEOSYNTHETICS SUBJECTED TO CHEMICAL EXPOSURE: EXPERIMENTS, CONSTITUTIVE MODELS AND COMPUTATIONS
A.P.S. Selvadurai
2
2k MEETING THE CHALLENGES OF ENGINEERING A SUSTAINABLE FUTURE
David Thorpe 12
3k STATISTICS FOR EVIDENCE-BASED DECISIONS – USE, MISUSE AND ABUSE
Shahjahan Khan and M Ashraf Memon 22
Technical Papers
31ID
Science
323522 SEA LEVEL IN A CHANGING CLIMATE Maria McCrann, Dr John Russell, Dr Daniela Ionescu and Dr Bandita Mainali 33
3534
EBOLA VIRAL PROTEIN 24 (VP24) INHIBITOR DISCOVERY BY IN SILICO FRAGMENT-BASED DESIGN
Syafrida Siregar, Erwin Prasetya Toepak, Usman Sumo Friend Tambunan
39
3535
FRAGMENT-BASED LEAD COMPOUND DESIGN TO INHIBIT EBOLA VP35 THROUGH COMPUTATIONAL STUDIES
Atika Marnolia, Erwin Prasetya Toepak, Usman Sumo Friend Tambunan
45
3547
DEVELOPMENT OF SPECIFIC ELECTROCHEMICAL BIOSENSOR BASED ON CHITOSAN MODIFIED SCREEN PRINTED CARBON ELECTRODE FOR THE MONITORING OF CAPTAN FUNGICIDE Porntip Wongkaew, Buddhapala Wongkaew, Suwita Saepaisan, and Panupong Thanutong
51
3548 A BASIC STUDY ON FLUID PREDICTION OF MORTARYuki takagi, Koji Takasu, Hidehiro Koyamada and Hiroki Suyama WITH VARIOUS POWDERS 57
3549
PHYTOCHEMICALS AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITIES OF THAI RED RICE SEEDS FROM DIFFERENT CULTIVATED AREAS
Muntana Nakornriab, Jiraporn Krasaetep, Maratree Plainsirichai and Sisikka Wannajun
62
3550
A STUDY ON PROPERTIES OF MORTAR WITH FLY ASH REMOVED UNBURNED CARBON BY FLOTATION METHOD
Rika Oie, Koji Takasu, Hidehiro Koyamada and Hiroki Suyama
67 Third International Conference on Science, Engineering & Environment, USQ Springfield Brisbane, Australia, Nov.21-23, 2017, ISBN: 978-4-9905958-9-0 C3051
3551
A STUDY ON PROPERTIES OF WITH FLY ASH REMOVED UNBURNED CARBON BY FLOTATION METHOD
Yuto Murakami, Koji Takasu, Hidehiro Koyamada and Hiroki Suyama
72
3559
CHARACTERIZATION OF CERIUM OXIDE-CHITOSAN NANOCOMPOSITE–MODIFIED SCREEN PRINTED CARBON ELECTRODE AND APPLICATION IN MELATONIN DETERMINATION Pachanuporn Sunon, Porntip Wongkaew, Jeffrey Johns, Nutjaree Johns
77
3564
COMPARISON OF HEART RATE VARIABILITY BETWEEN PATIENTS WITH MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER AND NORMAL SUBJECTS
Warangkana Chompoopan, Sipanut Silaket, Wichai Eungpinichpong, Suwanna Arunpongpaisal and Niramol Patjanasoontorn
83
3566
EFFECT OF ARM SWING EXERCISES ON CARDIOVASCULAR RESPONSE AND BALANCE OF OLDER WOMEN
Worawut Chompoopan, Piyathida Kuhirunyaratn
87
3578 PLASTIC FLOW HETEROGENEITY AND FAILURE OF BIMETAL MATERIAL Svetlana Barannikova, Lev Zuev1and Yulia Li 91
3606
SEARCHING OF NEW ANTIVIRAL COMPOUNDS OF SUDAN EBOLAVIRUS GLYCOPROTEIN BASED ON FLAVONOID COMPOUNDS USING IN SILICO METHODS
Rendy Pramuda Putra, Ahmad Husein Alkaff, Mochammad Arfin Fardiansyah Nasution and Agustinus C. B. Kantale, and Usman Sumo Friend Tambunan
97
3622
NEW ESTIMATION IN AR MODELS WITH EXPONENTIAL WHITE NOISE BY USING REVERSIBLE JUMP MCMC ALGORITHM
Suparman
103
3623
ECOLOGY AND CONSERVATION OF INDIAN HORNBILLS WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO NARCONDAM HORNBILL (ACEROS NARCONDAMI) OCCURRING ON NARCONDAM ISLAND OF ANDAMAN& NICOBAR ISLAND ARCHIPELAGO
Hafiz S.A. Yahya
107
3630
THE IMMEDIATE EFFECTS OF FOOT MASSAGE WITH COCONUT SHELL ON PRESSURE PAIN THRESHOLD AND FOOT GRIP STRENGTH IN HEALTHY SUBJECTS: A PILOT STUDY
Laojeenwong P, Eungpinichpong W
113
3633
MOCAF TEMPEH DATES BISCUIT FOR THE IMPROVEMENT NUTRITIONAL STATUS OF UNDERWEIGHT CHILDREN
Fatmah
117
3637
SPATIAL VARIATION OF WATRBIRDS IN PALLAI AND THADDUVANKODDY IN THE NORTHERN PROVINCE, SRI LANKA
G. Kandasamy, D. K. Weerakoon, and A. Sivaruban
124
3645
FACTORS RELATED TO SELF-CARE ABILITY AMONG ELDERLY WOMEN IN SEMI-URBAN COMMUNITIES, KHON KAEN, THAILAND.
Kanchana Nimsuntorn, Piyathida Kuhirunyaratn and Kanaporn Tansriprapasiri
130
3646
IMMEDIATE EFFECTS OF THAI MASSAGE ON GAIT PARAMETERS IN NORMAL ADULTS: A PILOT STUDY Nutthanun Tatchananusorn, Wichai Eungpinichpong, Uraiwan Chatchawan and Donlaya Promkaew
136
3648
THAI MASSAGE COMBINED WITH MUSCLE ENERGY AND PASSIVE STATIC STRENGTHING TECHNIQUE COULD IMPROVE HEIGHT OF SEPAKTAKRAW SERVES
Apichat Deeminoi, Dr.Wichai Eungpinichpong, Dr.Maitree Pakarasang, Dr.Thanarat Sripongngam
140
3652
A STUDY OF THE CORRELATION BETWEEN FOUR CLINICAL TRIALS FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF HAMSTRING MUSCLE FLEXIBILITY
Apichat Deeminoi, Dr.ThanaratSripongngam
146
3665
EFFECTS OF KAEMPFERIA PARVIFLORA ON PHYSICAL AND PSYCHOLOGICAL STRESSES IN ADULTS
Wichai Eungpinichpong, Uraiwan Chatchawan, Bung-orn Sripanidkulchai Suwanna Arunpongpaisal
150
3673
DEVELOPMENT OF POLY (D, L-LACTIC ACID) WITH POLYBENZOXAZINE VIA SOLUTION BLENDING
Kansiri Pakkethati and Yodthong Baimark
154
3677
BIOCHEMICAL CHANGES IN CHEMICAL INGRADIENTS OF SILK COCOONS UNDER ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
H.N.P. Singh, Sunita Kumari and M.M. Prasad
159
3711
ACUTE EFFECTS OF TRADITONAL THAI MASSAGE ON HEART RATE VARIABILITY, HEART RATE AND SALIVARY ALPHA AMYLASE
Jaruk Keawsod Wichai Eungpinichpong
163
ID
Engineering
1663503 SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL BY USING SHELL HUSKS WASTE AS RECYCLE AGGREGATE Siti Hanggita Rachmawati, Zakaria Hossain 167
3504 ANALYTICAL STUDY ON SINGLE PILE DESIGN FOR SOLAR FOUNDATIONS FOR SLOPING LAND. Alex Otieno Owino, Hossain, M.Z., Ojiro C., Ozumi, S., Harada, H. and Okuyama, S. 172
3510
EXPERIMENTAL BEHAVIORAL INSPECTION OF COMPOSITE CONCRETE-OPEN WEB EXPANDED STEEL BEAMS EXPOSED TO STATIC LOADING
Nazar K. Oukaili and Seezar Sh. Abdullah
178
3512
RESIDENTIAL CUSTOMER DEMAND RESPONSE PROGRAM IN MICROGRID SYSTEM: A SURVEY LITERATURE
Ignatius Rendroyoko, and Ngapuli I Sinisuka
184
3514
CRACKING AND DEFORMABILITY OF BONDED AND UNBONDED PRESTRESSED CONCRETE BEAMS UNDER MONOTONIC STATIC LOADING
Nazar K. Oukaili and Mohammed M. Khattab
190
3515
DISTRIBUTED MODEL OF HYDROLOGICAL AND SEDIMENT TRANSPORT PROCESS IN MEKONG RIVER BASIN
Zuliziana Suif, Chihiro Yoshimura, Nordila Ahmad and Sengheng Hul
196
3516 EVALUATION OF PIER-SCOUR PREDICTIONS FOR WIDE PIERS USING FIELD DATA Nordila Ahmad, Bruce W. Melville, Thamer Mohammad, Zuliziana Suif 202
3521
MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF ARTIFICIAL STONE MADE FROM WASTE OF SILICEOUS TUFF
Hiroaki Shigematsu and Shogo Hashimoto
208
3528
3 DIMENSION REAL TIME IMAGES OF RAINFALL INFILTRATION INTO UNSATURATED SOIL SLOPE
Aniza Ibrahim, Irfana Kabir Ahmad, Hapsa Husen, Jestin Jelani1and Mohd. Raihan Taha
214
3529
STEREO ECHO CANCELLATION USING ADAPTIVE NON-LINEAR NETWORK FILTER FOR HOME THEATRE ROOM
Sunisa Kunarak
219
3530 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF EWECS COLUMNS WITH VARYING SHEAR SPAN RATIO Fauzan, Ruddy Kurniawan and Zev Al Jauhari 224
3538
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION ON BOX-UP COLD-FORMED STEEL COLUMNS IN FIRE Fadhluhartini Muftah, Mohd Syahrul Hisyam Mohd Sani, Ahmad Rasidi Osman, Shahrin Mohammad, Shek Poi Ngian
231
3539 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF COLD-FORMED STEEL CHANNEL SECTION WITH NOTCH Mohd Syahrul Hisyam Mohd Sani, Fadhluhartini Muftah, Muhammad Isha Ismail 237
3542 A REVIEW OF UNEXPECTED LARGE SLOPE FAILURES Marthinus Sonnekus and John Victor Smith 243
3563
THE EFFECT OF STEEL FIBERS EXTRACTED FROM WASTE TYRE ON CONCRETE CONTAINING PALM OIL FUEL ASH
Fauzan, Febrin Anas Ismail and Rio Sandi
249
3574
ACCURACY OF CENTRALIZED AND DECENTRALIZED MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS TOWARDS AN INDUSTRY 4.0’S PERSPECTIVE
Poonpakdee, P. , Koiwanit, J., Yuangyai, C.
254
3576
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF NONLINEAR MODEL OF SFRC SLAB AND NONLINEAR SUBSOIL MODEL IN INTERACTION
Jana VASKOVA, Radim CAJKA
260
3583
AN OVERVIEW OF THE IMPACTS OF SUSTAINABLE HOUSING DESIGN ON ENERGY EFFICIENCY OF THE AUSTRALIAN HOUSING
Javad Asad Poor , David Thorpe, Yong Goh
266
3590 VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENT OF SURIGAO METRO WATER DISTRICT UNDER SEISMIC HAZARD Sheena I. Better and Lessandro Estelito O. Garciano 276
3591
A COMPARISON OF ESTIMATED SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOUTH-EAST QUEENSLAND RESIDUAL SOIL USING FIELD AND LABORATORY TESTING
Darren Newell and Choo Yong
283
3593
STUDY ON LANDSLIDE CATEGORY BASE ON TEMPORAL– SPATIAL CHARACTERISTIC DISTRIBUTION IN NORTHERN VIETNAM USING SATELLITE IMAGES
Thuy Thi Thanh LE and Seiki KAWAGOE
287
3597
THE QUALITY ANALYSIS OF BICYCLE ROUTES FOR SUSTAINABLE URBAN MOBILITY IN THE WESTERN ZONE OF RIO DE JANEIRO
Guilherme Marins Pessanha, Jaime Massaguer Hidalgo Jr
293
3599 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF PAVEMENT FRICTION PREDICTION MODELS
Luciana Omar, Karim Ismail and Abd El Halim O. Abd El Halim 299
3608
APPLICATION OF MEMETIC ALGORITHM FOR SOLVING THE VEHICLE ROUTING PROBLEM WITH TIME WINDOWS
Chaowalit Hamontree , Jiraporn Chuenjai and Nawaporn Chamnanketgorn
305
3614
THE EFFECT OF MODEL DOMAIN SIZE FOR UNSUPPORTED PLAIN STRAIN TUNNEL HEADINGS IN UNDRAINED CLAY
Jim Shiau, Fadhil Al-Asadi
309
3656
APPLICATION OF HEC-RAS AND ARC GIS FOR FLOODPLAIN MAPPING IN SEGAMAT TOWN, MALAYSIA
Noor Suraya Romali, Zulkifli Yusop and Ahmad Zuhdi Ismail
315
3658 EFFECT OF SATURATION ON STRENGTH BEHAVIOR OF SOAPSTONE
Ravikant R Singh, Darga Kumar Nandyala and Faijal Ali 321
3659
MEASUREMENT ACCURACY OF ORIENTATION CODE MATCHING FOR SLOPE DEFORMATION MONITORING
Takeshi YAMAMOTO, Keigo KOIZUMI, Kazuhiro ODA, and Yoshio FUKUDA
327
3670
NANOSTRUCTURAL CHARACTERIZATION OF GLUTATHIONE-S-TRANSFERASE IMMOBILIZING CHITOSAN MODIFIED SCREEN PRINTED CARBON ELECTRODE BY ATOMIC FORCE MICROSCOPY Buddhapala Wongkaew, Porntip Wongkaew, Panupong Thanutong and Chitsanuphong Thanutong
332
3672
COLUMN BASED INFILTRATION EXPERIMENT FOR CONSIDERING INITIAL QUASI-SATURAETED VOLUMETRIC WATER CONTENT DUE TO DEFFERENCES OF WATER SPRAY INTENSITY AND GRAIN SIZE DISTRIBUTION
Hiroshi Kita, Keigo Koizumi and Kazuhiro Oda and Mitsuru Komatsu
338
3683
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF BIOMASS POWER PLANTS FOR SUSTAINABILITY IN THAILAND Manutchanok Jongprasithporn, Adisak Martsri, Supapat Phuangkaew, Wannapong Yeamma,
and Nantakrit Yodpijit
342
3686
THE DESIGN OF AN ALTERNATIVE ENERGY DATABASE IN THAILAND
Manutchanok Jongprasithporn,Supapat Phuangkaew, Siravitch Atipatha, and Nantakrit Yodpijit
348
3691 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF 2D TRAPDOOR STABILITY
Jim Shiau, Mohammad Mirza Hassan 354
3695
INSTALLATION CONSTRAINTS OF SUCTION ASSISTED FOUNDATIONS AND ANCHORS FOR OFFSHORE ENERGY DEVELOPMENT
Kingsley Osezua Akeme, Alireza Rezagholilou and Meysam Banimahd
360
3706
DIFFERNTIAL THERMAL ANALYSIS OF PMMA (POLY METHYL METHACRYLATE) - EXPERIMENTAL CONCERNS
Sam M Dakka
368
3717
INVESTIGATION OF CURING PERIOD OF CEMENTITIOUS ADHESIVE AND PERFORMANCE OF RUST PREVENTION
YoichiMimura, Vanissorn Vimonsatit and Isamu Yoshitake
373
3721 REGIONAL DEPOSITION CHARACTERISTICS OF NANOPARTICLES IN A RAT NASAL CAVITY Yidan Shang, Jingliang Dong, Kiao Inthavong and Jiyuan Tu 379
3733 SEGMENTATION OF PAP SMEAR IMAGES TO IDENTIFY AND DETECT CERVICAL CANCER Vasundhara Acharya, Preetham Kumar 383
ID
Environment
3903506
NUTRIENT LOADS AND SELF-REMEDIATION ASSESSMENT IN KHLONG RUNGSIT TAI, PATHUM THANI PROVINCE, THAILAND
Boontarika Thongdonphum, Kittima Vanichkul, Saming Champasri and Jirapon Kulkham
391
3517 INFLUENCE OF ABIOTIC STRESS FACTORS ON BLACKCURRANT RESISTANCE TO PESTS I.V. Mashkova, T.G. Krupnova, A.M. Kostryukova 395
3518 USING BIRCH LEAVES TO INDICATE AIR POLLUTION
T.G. Krupnova, I.V. Mashkova and A.M. Kostryukova 399
3519 STUDY OF SYNANTHROPIC PLANTS OF THE SOUTH URAL A.M. Kostryukova, I.V. Mashkova, T.G. Krupnova and E.E. Shchelkanova 405
3531
A STUDY ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF LIQUID SMOKE PRODUCED FROM PALM KERNEL SHELLS IN INHIBITING BLACK POD DISEASE IN CACAO FRUIT IN VITRO
M. Faisal, Tjut Chamzurni, Hiroyuki Daimon
411
3543
HEAVY METALS IN MICROALGAE BIOMASS ADDED WITH DIFFERENT CONCENTRATION OF WET MARKET WASTEWATER
Radin Maya Saphira Radin Mohamed, Najeeha Apandi, Siti Nor Hidayah Arifin, A.A.S. Al-Gheethi and Amir Hashim Mohd Kassim
417
3546
INFLUENCING PARAMETER OF SELF PURIFICATION PROCESS IN THE URBAN AREA OF CIKAPUNDUNG RIVER, INDONESIA
Yonik Meilawati Yustiani, Mia Nurkanti, Neneng Suliasih and Annisa Novantri
422
3562
THE PHYSICAL MICROHABITAT REQUIREMENTS OF FRESHWATER MUSSEL, WESTRALUNIO CARTERI, (BIVALVIA: HYRIIDAE) IN SOUTH-WESTERN AUSTRALIA
Le Ma1, Alan Lymbery, Stephen Beatty and David Morgan
426
3567
EVALUATING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF VIRGINIA BUTTONWEED FOR EROSION CONTROL OF DAM RESERVOIR SLOPES IN JAPAN.
Taizo Uchida, Yuya Imamura, Yoshifumi Kochi, Mamoru Yamada, Kunihiko Fukaura, Aki Matsumoto, William T. Haller and Lyn A. Gettys
432
3577
NANOCOMPOSITE WITH DUAL FUNCTIONALITY IN SIMULTANEOUS REMOVAL OF HEAVY METALS, DYE AND ANIONIC SURFACTANT FROM MULTICOMPONENT WASTEWATER Maria Visa, Nicoleta Popa, Andreea Maria Chelaru
437
3600
EFFECT OF WATER ACTIVITY ON ENZYMES ADSORBED ON BIOMASS CHARCOAL IN ORGANIC MEDIA
Hidetaka Noritomi, Jumpei Nishigami, Nobuyuki Endo, Satoru Kato and Katsumi Uchiyama
443
3602
EVALUATION OF ENERGY EFFICIENCY AND ENVIRONMENTAL PERFORMANCE IN LOBLAW COMPANIES LIMITED IN CANADA
Koiwanit, J., Chan, V. K., Piewkhow, L., Katipelly, N. D.
449
3611 AN EVALUATION FOR EFFECTIVE PUBLIC PARTICIPATION IN EIA IN THAILAND Chutarat Chompunth 455
3649
ACHIEVING WATER SENSITIVE CITY CONCEPT THROUGH MUSRENBANG MECHANISM IN SURABAYA CITY, INDONESIA
Eddy Setiadi Soedjono, Nurina Fitriani, Rifda Rahman, I Made Wahyu Wijaya
462
3651 THE STUDY ON MITIGATION METHOD OF BEACH EROSION USING THE CORAL CELLS
Sang Kil Park, Hong Bum Park, Kyeong Mo Lim 467
3662 THE DESCRIPTION OF LIGHTING ENVIRONMENTAL ON THE URBAN STREET Shuto Takeuchi, Kazunari Tanaka and Shin Yoshikawa 473
3684
SOCIAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL RESPONSIBILITY IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES: A THEORETICAL APPROACH OF REGULATION
Lindrianasari, Mahatma Kufepaksi, Yuztitya Asmaranti, and Agrianti Komalasari
477
3688 ASSESSMENT OF URBAN CLIMATE CHANGE IN IPOH CITY, PERAK, MALAYSIA Mohd Hairy Ibrahim, Mazlini Adnan, Nor Kalsum Mohd Isa & Kamarul Ismail, 482
3707
TREND OF DAILY RAINFALL AND TEMPERATURE IN PENINSULAR MALAYSIA BASED ON GRIDDED DATA SET
Chee-Loong Wong, Zulkifli Yusop, Tarmizi Ismail
488
3708
SPATIO-TEMPORAL ANALYSIS OF LAND USE AND LAND COVER CHANGES IN ARID REGION OF SAUDI ARABIA
Eman Albalawi, Ashraf Dewan and Robert Corner
496
3718
COMPARISON OF LUNG DAMAGES DUE TO PETROL AND DIESEL CAR SMOKE EXPOSURES: HISTOLOGICAL STUDY
Wardoyo, Arinto Y.P.a, Juswono, Unggul P., Noor, Johan A. E.
502
3723
SPATIAL VARIATIONS OF SURFACE WATER QUALITY AND POLLUTION SOURCES IN KHLONG U-TAPAO RIVER BASIN
Saudee Maprasit, Chaisri Suksaroj, Vichit Rangpan, and Rotchanatch Darnsawasdi
508
3724
DIVESIRY AND POLLEN MORPHOLGY OF IMPORTANT TREE SPECIES OF RANIKOT FORT, SINDH, PAKISTAN.
Nabila Shah Jilani, S.S Hassney, Muhammad Tahir Rajput and Feroza shar Baloch
514
3727 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PAVEMENT TEXTURE AND MOVEMENTYuki OGIMOTO,Kazunari TANAKA and shin YOSHIKAWA 517
3728 REMOVAL AMMONIA FROM LANDFILL LEACHATE USING ULTRASONIC IRRADIATION PROCESS
Sartaj M., Tobalt A., and Kennedy K. 521
3729 THE IMPLEMENTATION OF WATER SENSITIVE CITY AT DEPOK -MIDDLE CITY IN INDONESIA
Firdaus Ali, Irene Sondang, Esty Suyanti and Ahmad Zubair 524
3730 RISK MAPPING STUDIES OF HYDRO-METEOROLOGICAL HAZARD IN DEPOK MIDDLE CITYR. Jachrizal Soemabrata, Ahmad Zubair, Irene Sondang and Esty Suyanti 528
3698
ROLE OF GOVERNMENT AND PRIVATE SECTOR IN MARINE ECOTOURISM RELATED TO CONSERVATION OF BIODIVERSITY IN SERIBU ISLANDS
Lily Surayya Eka Putri and Kristiyanto
534
3689
SEISMIC MICROZONATION FOR URBAN PLANNING AND VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENT OF NON-ENGINEERED STRUTURE IN EARTHQUAKE PRONE AREA, PADANG, INDONESIA Rusnardi Rahmat Putra, Junji Kiyono, Ganefri Fahmi Rijal and Syahril
540
Authors Index
x
3545 RAINWATER HARVESTING STUDY AT MASJID JAMEK RIYAHDUS SOLIHIN, PINTAS PUDING, BATU PAHAT JOHOR MALAYSIA Amir Hashim Mohd Kassim, Siti Mariam Sulaiman, Radin Maya Saphira Radin Mohamed and Adel Ali Saeed Al Gheethi
Preface
On behalf of the SEE 2017 Organizing Committee, it is our great pleasure to welcome you to the Third International Conference on Science, Engineering & Environment, held at the USQ Springfield Brisbane Australia organized in conjunction with University of Southern Queensland, Mie University Research Center for Environmental Load Reduction, The GEOMATE International Society, Useful Plant Spread Society, Glorious International, AOI Engineering, HOJUN, JCK, CosmoWinds and Beppu Construction, Japan.
The conference covers three major themes with many specific themes including:
Engineering Science Environment
•Environmental Engineering
•Chemical Engineering
•Civil and Structural Engineering
•Computer Software Web Engineering
•Electrical and Electronic Engineering
•Energy and Thermal Engineering
•Aerospace Engineering
•Agricultural Engineering
•Biological Engineering and Sciences
•Biological Systems Engineering
•Biomedical and Genetic Engineering
•Bioprocess and Food Engineering
•Geotechnical Engineering
•Industrial and Process Engineering
•Manufacturing Engineering
•Mechanical and Vehicle Engineering
•Materials and Nano Engineering
•Nuclear Engineering
•Petroleum and Power Engineering
•Forest Industry Engineering
•Environmental Sciences
•Chemistry and Chemical Sciences
•Fisheries and Aquaculture Sciences
•Astronomy and Space Sciences
•Atmospheric Sciences
•Botany and Biological Sciences
•Genetics and Bacteriology
•Forestry Sciences
•Geological Sciences
•Materials Science and Mineralogy
•Statistics and Mathematics
•Microbiology and Medical Sciences
•Meteorology and Palaeo Ecology
•Pharmacology
•Physics and Physical Sciences
•Plant Sciences and Systems Biology
•Psychology and Systems Biology
•Zoology and Veterinary Sciences
•Environmental Technology
•Recycle Solid Wastes
•Environmental dynamics
•Meteorology and Hydrology
•Atmospheric and Geophysics
•Physical oceanography
•Bio-engineering
•Environmental sustainability
•Resource management
•Modelling and decision support tools
•Institutional development
•Suspended and biological processes
•Anaerobic and Process modelling
•Modelling and numerical prediction
•Interaction between pollutants
•Water treatment residuals
•Quality of drinking water
•Distribution systems on potable water
•Reuse of reclaimed waters
This year we have received many submissions over 50 universities of different countries all over the world including Australia, Brazil, Canada, Czech Republic, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Iraq, Japan, Malaysia, Philippines Romania, Russia, South Korea, Sri Lanka and Thailand. The technical papers were selected from the vast number of contributions submitted after a review of the abstracts. The final papers in the proceedings have been peer reviewed rigorously and revised as necessary by the authors. It relies on the solid cooperation of numerous people to organize a conference of this size. Hence, we appreciate everyone who support as well as participate in the joint conferences.
Last but not least, we would like to express our gratitude to all the authors, session chairs, reviewers, participants, institutions and companies for their contribution to SEE 2017. We hope you enjoy the conference and find this experience inspiring and helpful in your professional field. We look forward to seeing you at our upcoming conference next year.
Best regards,
Prof. Dr. Zakaria Hossain, Conference Chairman (General)
Dr. Jim Shiau, Conference Chairman (Program)
Third International Conference on Science, Engineering & Environment, USQ Springfield Brisbane, Australia, Nov.13-15, 2017, ISBN: 978-4-9905958-9-0
Organization
Scientific Committees:
Conference Honorary Chairmen:
Dr. John Yeaman, Professor, Univ. of the S/Coast, Australia Dr. Sohji Inoue, Emeritus Professor, Mie University, Japan
Conference Chairmen:
Dr. Jim Shiau, Senior Lecturer, USQ, Australia (Program Chair) Dr. Zakaria Hossain, Prof. Mie Univ., Japan (General Chair)
Conference Organizing Committee:
Dr. Jim Shiau, S./Lec. Univ. of Southern Queensland, Australia Dr. Stephen Buttling, Principal, National Geo. Cons., Australia Dr. Karu Karunasena, Prof. USQ, Australia
Dr. David Thorpe, A/Prof., USQ, Australia Dr. Toshinori Sakai, Prof. Mie University, Japan Dr. Zakaria Hossain, Prof. Mie University, Japan National & International Advisory Committee: Dr. Allan Manalo, Senior Lecturer, USQ, Australia Dr. Soma Somasundaraswaran, Lecturer, USQ, Australia Dr. John Smith, A/Prof. RMIT University, Australia
Dr. Arul Arulrajah, Prof. Swinburne Univ. of Tech., Australia Dr. Robert Evans, A/Prof., Swinburne Univ. of Tech., Australia Dr. Chaminda Gallage, A/Prof, Queensland Uni. of Tec, Australia Dr. Iyad Alkroosh, A/Prof., Curtin University, Australia
Dr. Sammy Kwok, Geo. Eng. Cardno Bowler, Australia Dr. Jun Sugawara, S/Eng. Golder Associates Pty Ltd, Australia Dr. N. Sivakugan, A/Prof. James Cook Univ., Australia Dr. Erwin Oh, Senior Lecturer, Griffith University, Australia Dr. Fumio Tatsuoka, Prof. Tokyo University of Science, Japan Dr. Jing-Cai Jiang, Prof. University of Tokushima, Japan Dr. Toshihiro Morii, Prof. Niigata University, Japan
Dr. Kimitoshi Hayano, Prof. Yokohama National Univ., Japan Dr. Sai Vanapalli, Prof. University of Ottawa, Canada Dr. Musharraf Zaman, Prof. Univ. of Oklahama, USA Dr. Rafiqul Tarefder, Prof. University of New Mexico, USA Dr. M. Bouassida, Prof. National Sch. of Engg. of Tunis Dr. L.R. Austriaco, Prof. Angles Univ. Found., Philippines Dr. A.S.M. Abdul Awal, Prof., UTHM, Malaysia
Dr. Bujang B.K. Huat, Prof. Univ. Putra Malaysia Dr. Nemy Banthia, Prof. UBC, Canada
Dr. Ian Jefferson, Prof. Univ. of Birmingham, UK Dr. John Bolander, Prof. Univ. of California, USA Dr. Shamsul Chowdhury, Prof. Roosevelt Univ., USA Dr. Isabel Pinto, Prof. University of Coimbra, Portugal Dr. Hj. Ramli Bin Hj. Nazir, A/Prof.. UTM, Malaysia Dr. Aly Ahmed, A/Prof.. Beni-Suef University, Egypt
Dr. Chang-Yu Ou, Prof. National Taiwan Univ. of Sci. &Tech.
International Technical Program Committee:
Prof. Adolf Heinrich Horn, Geological Institute - Federa University of Minas Gerais, Brazil Prof. Bang-Fuh Chen, National Sun Yat-sen University, Taiwan
Prof. Bindeshwar Singh, Kamla Nehru Institute of Technology, India
Third International Conference on Science, Engineering & Environment, USQ Springfield Brisbane, Australia, Nov.13-15, 2017, ISBN: 978-4-9905958-9-0
Prof. Catherine Mulligan, Concordia Institute of Water, Energy and Sustainable Systems, Canada Prof. Chi-Min Liu Chienkuo Technology University, Taiwan
Prof. Daffalla Rabih, Kenana Sugar Company, Sudan
Prof. Essaid Bilal, Ecole Nationale Superieure Des Mines De Saint Etienne, France Prof. Hakan Caliskan, Usak University, Faculty of Engineering, Turkey
Prof. Ibrahim Maiyza, National Institute of Oceanography & Fisheries, Egypt Prof. Loc Nguyen, Sunflower Soft Company, Vietnam
Prof. Marilia Hagen, Indiana University, United States
Prof. Md Najib bin Ibrahim, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Malaysia Prof. Md. Abdul Baset Mia, BSMR Agri. Univ., Bangladesh Prof. Mihaela Popescu, University of Craiova, Romania
Prof. Mohamed Abdou, Faculty of Education Department of Mathematics, Egypt Prof. Mohamed Tahiri, Présidnce de l'Université Hassan II de Casablanca, Morocco Prof. Nazar Oukaili, University of Baghdad, Iraq
Prof. Radim Cajka, Technical University Ostrava, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Czech Republic Prof. Rajaraman Jambunathan, AMET University, India
Prof. Saad Farhan Ibrahim Alabdullah, University of Almustansiriyah, Iraq Prof. Salem Alsanusi, Benghazi, Libya
Prof. Sudhir Kumar Das, Retired Senior Project Manager of Indian Railways, India Prof. Zachary Senwo, Alabama A&M University, United States
Prof. Imed Jabri, University of Tunis, Tunisia
A/Prof. Bindeshwar Singh Kamla Nehru Institute of Technology, India A/Prof. Hasi Rani Barai, Yeungnam University, South Korea
A/Prof. Jamaluddin Mahmud, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Malaysia A/Prof. Mohamed Ramadan, University of Hail, Saudi Arabia A/Prof. Najam Hasan, Dhofar University, Oman
A/Prof. Nosina Krishna Chaitanya, Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, India A/Prof. Nurbek Saparkhojayev, Almaty Management University, Kazakhstan A/Prof. Pandian Vasant, Universiti Teknologi Petronas, Malaysia
A/Prof. Teodor Lucian Grigorie, University of Craiova, Romania A/Prof. Zawawi Daud, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia A/Prof. Abdull Halim Abdul, OIl and Gas department, Malaysia A/Prof. Baoping Cai, China University of Petroleum, China
A/Prof. Dariusz Jakóbczak, Koszalin University of Technology, Poland A/Prof. Edgar Allan Mendoza, University of the Philippines
A/Prof. Lakhveer Singh, Universiti Malaysia Pahang (UMP) Malaysia, Malaysia A/Prof. Lidia Sas Paszt, Research Institute of Pomology, Poland
A/Prof. Mahmood Barbooti, University of Yechnology, Iraq A/Prof. Majid Mirzaei, Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman, Malaysia A/Prof. Najeh Lakhoua, University of Carthage, Tunisia
A/Prof. Ryan Joseph Calinao, Lyceum of the Philippines University-Laguna A/Prof. Sarawut Thepanondh, Mahidol University, Thailand
A/Prof. Yasir Al Hussein, Jerash University, Faculty of Engineering, Jordan A/Prof. Grigorie Teodor Lucian, University of Craiova, Romania
A/Prof. Hêriş Golpîra, Islamic Azad University, Sanandaj, Iran A/Prof. Muhammad Aslam, King Abdulaziz University, Saudi Arabia A/Prof. Tomasz Plech, Medical University of Lublin, Poland
A/Prof. Fellah Mamoun, Abbes laghrour University, Algeria A/Prof. R. S. Ajin, GeoVin Solutions Pvt. Ltd., India
A/Prof. Roman Szewczyk, Industrial Research Institute for Automation and Measurements, Poland Dr. Abolghasem Akbari, University Malaysia Pahang, Malaysia
Dr. Ahmad Safuan A Rashid, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia
Dr. Akinola Johnson Olarewaju, Federal Polytechnic Ilaro, Ogun State, Nigeria
Dr. Alexandre Costa, Federal University of the valleys of Jequitinhonha and Mucuri, Brazil Dr. Angelo Gallone, Scotland’s Rural College (SRUC), United Kingdom
Dr. Azizul Azhar Ramli, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Dr. Bashir Dar, University of kashmir Delina Baramulla J&K India, India
Dr. Bassam Abdellatif, National Authority for Remote Sensing and Space Sciences, Egypt
Dr. Binh Phu Nguyen, National University of Singapore, Singapore Dr. Cazacu Gabriela, S.C. Geotech Dobrogea, Romania
Dr. Chengen Yang, Intel Corporation, United States
Dr. Dayang Norulfairuz Abang Zaidel, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
Dr. Evgeni Starikov, KIT, Karlsruhe, Germany; Chalmers, Gothenburg Sweden, Germany Dr. Fatma Khanchel, University of Tunis El Manar, Tunisia
Dr. Hamidreza Khataee, Griffith University, Australia Dr. Hêriş Golpîra, Islamic Azad University, Iran
Dr. Iskhaq Iskandar, Dept. Physics, University of Sriwijaya, Indonesia Dr. Jingwei Zhao, University of Wollongong, Australia
Dr. Jitendra Agrawal, Rajiv Gandhi Proudyogiki Vishwavidyalaya, India Dr. Liza Patacsil, Malayan Colleges Laguna, Philippines
Dr. Mohamed Amine, Ferrag Guelma University, Algeria Dr. Mohd Afendi Rojan, Universiti Malaysia Perlis, Malaysia
Dr. Mohd Altaf, University of kashmir Delina Baramulla J&K India, India Dr. Mohd Hairy Ibrahim , Sultan Idris Education University, Malaysia Dr. Mostafa Khater, Egypt - El sharqia - Zagazig, Egypt
Dr. Najam Hasan, Dhofar University, Oman
Dr. Namir Alkawaaz, University of Almustansiriyah, Iraq
Dr. Nashrul Fazli Mohd Nasir, Universiti Malaysia Perlis, Malaysia
Dr. NaufaL Mansor Kampus Uniciti Alam, Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP), Malaysia Dr. Obed Majeed Ali, Northern Technical University, Iraq
Dr. Piyapong Janmaimool, King Mongkhut' University of Technology, Thailand Dr. Po-Sheng Chiu, National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan
Dr. Prabu Mohandas, Adhiyamaan College of Engineering, India Dr. Raman Kumar, D A V Institute of Engineering and Technology, India Dr. Riccardo Colella, University of Salento, Italy
Dr. Rolando Javellonar, Romblon State University, Philippines Dr. Shikha Agrawal, Rajeev Gandhi Technical University, India Dr. Stefania Tomasiello CORISA, University of Salerno, Italy Dr. Sumiyyah Sabar, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Malaysia Dr. Suphaphat Kwonpongsagoon, Mahidol University, Thailand Dr. Wei Hong Tan, Universiti Malaysia Perlis, Malaysia Dr. Yoshiro Fujii, Shin Kobe Dental Clinic, Japan
Dr. Yuk Feng Huang, Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman (UTAR), Malaysia Dr. Zongyan Zhou, Monsh University, Australia
Dr. Purnanand Savoikar, Goa Engineering College, India
Dr. Ahmed Toaha Mobashsher, University of Queensland, Australia Dr. Chupong Pakpum, Maejo University
Dr. Emanuele Quaranta, Politecnico di Torino, Italy Dr. Jiangling Yin, Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA, United States Dr. Khor Shing Fhan, Universiti Malaysia Perlis, Malaysia Dr. Mario Chauca, Ricardo Palma University, Peru Dr. Santosh Gaikwad, Model College, Ghansawangi, India Dr. Tse Guan Tan, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan
Dr. Vikas Panthi, National Institute of Technology, India Dr. Watoo Phrompittayarat, Naresuan University, Thailand
Dr. Hamidreza Namazi, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Dr. Parichat Phumkhachorn, Ubon Ratchathani University, Thailand Dr. Subhasis Roy, University of Calcutta, India
Conference Correspondence:
Dr. Jim Shiau, Senior Lecturer, USQ, Australia, Program Chair Dr. Zakaria Hossain, General Chair,
Prof. Graduate School of Bioresources,
Mie University 1577 Kurima Machiya-cho, Tsu-city,
Mie 514-8507 Japan, E-mail: [email protected] Tel & Fax: +81-59-231-9578
Conference History:
SEE-Mie, Japan, Nov. 19-21, 2015
Chairman: Prof. Dr. Satoshi Kaneco, Mie University, Japan SEE-Osaka, Japan, Nov. 21-23, 2016
Chairman: Prof. Dr. Zakaria Hossain, Mie University, Japan
Editorial and Executive Committee:
Prof. Dr. Zakaria Hossain Dr. Jim Shiau
Ms. Siti Hanggita Rachmawati Mr. Md. Aminul Islam Mr. Alex Otieno Owino
Note- A: Associate, E-Emeritus
SEE -USQ, Brisbane, Australia, Nov.13-16, 2017
1
540
SEISMIC MICROZONATION FOR URBAN PLANNING AND
VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENT OF NON-ENGINEERED
STRUTURE IN EARTHQUAKE PRONE AREA, PADANG,
INDONESIA
*Rusnardi Rahmat Putra1,, Junji Kiyono2, Ganefri3 Fahmi Rijal4 and Syahril5
1,4Civil Engineering, Engineering Faculty, Universitas Negeri Padang, Indonesia, 3Graduate School of
Engineering, Kyoto University, Japan, Elect4Mechanicall Engineering, Engineering Faculty, Universitas
Negeri Padang, Indonesia
Abstract: Padang city is located at earthquake prone area, several powerful earthquakes have struck Padang during recent years, one of the largest of which was an M 7.6 event that occurred on September 30, 2009 and caused more than 1000 casualties. The basic purpose of seismic microzonation is to produce input for urban planning and to supply site specific ground motion data to be used for the assessment of the vulnerability of the non-structure houses stock. A very detailed geological and geotechnical studies were conducted to evaluate the variation of site characterization within the city of Padang. We performed single observations of microtremors at 110 sites in Padang. The results enabled us to estimate the site-dependent amplification characteristics of earthquake ground-motion. We also conducted a 12-site microtremor array investigation to gain a representative determination of the soil condition of subsurface structures in Padang. Based on soil characteristic in whole Padang, We simulated the recorded ground motion of earthquake 2009 to obtain ground motion whole Padang. This seismic microzonation is a parameter for vulnerability assessment to non-engineered houses. We conducted vulnerability assessment to non-engineered structure of houses stock to estimate current structure condition to face predicted earthquake event in near future. About 1400 non-engineered structure were assessed and interviewed. The residents received explanations for each item on the questionnaire from the interviewers, and answers were filled in directly on the answer
sheets. This survey produced a map of the shaking intensity and houses’ vulnerability distribution in Padang.
From the dispersion curve of microtremor array observations, the central business district of Padang corresponds to relatively soft soil condition with Vs30 less than 400 m/s, the predominant periods due to
horizontal vertical ratios (HVSRs) are in the range of 2.0 to 4.0 s, and 98% of houses in high risk due to predicted earthquake. These results enable produce clear information to Padang people including local government of Padang how to create a mitigation system to reduce earthquake risk.
Keywords: array observation, vulnerability assessment, non-engineered structure, seismic microzonation
1. INTRODUCTION
The city of Padang is located on the west coast of Sumatra in western Indonesia, lies close to the Sumatran subduction zone that is formed by the subduction of the Indo-Australian Plate beneath the Eurasian Plate. Relative motion of the plates occurs at a rate of about 50 to 70 mm/year and this is the main source of subduction-related seismicity in the area [1]. Based on our catalog, several giant earthquakes have occurred in this region since records began: 1779 (Mw 8.4), 1833 (Mw 9.2), 1861 (Mw 8.3), 2004 (Mw 9.2), 2007 (Mw 7.9 and 8.4), 2009 (Mw 7.6), and 2017 (6.4). The hypocenter of the Padang earthquake that occurred on September 30, 2009 was located in the ocean slab of the Indo-Australian Plate at -0.81°S, 99.65°E and at a depth of 80 km. It produced a high degree of shaking and the tremor was felt in the
Indonesian capital, Jakarta, about 923 km from the epicenter. The tremors also were felt in neighboring countries such as Malaysia and Singapore [2]. The earthquake caused landslides and collateral debris flows in the hills surrounding Lake Maninjau. A major landslide in Gunung NanTigo, Padang Pariaman completely destroyed some villages and forced road closures.
This 1900-km-long active strike-slip fault zone that runs along the backbone of Sumatra poses seismic and fault hazards to a dense population distributed on and around the fault zones [3]. The Sumatran Fault is highly segmented. It consists of 20 major geometrically defined segments and the slip rate along the fault increase to the northwest, from about 5 mm/yr [3].
This fault also has generated large destructive earthquakes, e.g., 1892 (Mw 7.1), 1943 (Mw 7.6) and 2007 (Mw 6.4). These faults are
SEE - USQ, Brisbane, Australia, Nov.13-16, 2017
541
capable of generating strong ground motion in the future that would greatly affect vulnerable structures. Based on the latest earthquake events catalogs from USGS (2017) showed the number of earthquake events with magnitude from 3 to 6 is creasing within one month for each month in 2017. It shows how the activity of plate currently is.
Fig.1 Seismicity of Sumatra Island from 2005 to 2010, Mw>6.5, <100km depth of hypocenter, and Padang City
Regional Geology and Recent Earthquake
The city of Padang, with a population of 914,968 people as of 2016, is the capital of West Sumatra province. The location of the city center is at 100.38°E, 0.95°S. The main part of Padang is situated on an alluvial plain between the Indian Ocean and the mountains. For the most part, the countainous area is formed of Tertiary sedimentary rocks with outcrops of metamorphic rocks seen in some places. The alluvial plain spreads along the base of the mountains and is roughly 10 km wide in the east-west direction and 20 km wide in the north-south direction.
The topography of the Padang region is very similar to the tsunami-damaged area of Miyagi Prefecture in Japan, that was inundated by as much as 4-5 km from the coast after the March 11, 2011 Mw 9.0 Tohoku earthquake off the east coast of Honshu. In Padang, about 650,000 people live in the coastal area (covering about 60 km2). The
population density is very high, about 10,833 people/km2. The city is located on the coast of the
Indian Ocean between the Sumatran Fault and the Sunda Trench Fault. Both faults are active with slip rate ranging from 10 to 27 mm/year [3]. According to our catalog, 3,174 events with a magnitude greater than 4 occurred in this region from AD 1779 to 2017 [4]. The several giant earthquakes mentioned previously have all been strongly felt here. For example, the source of the 2009 Padang earthquake was located in the ocean slab of the
Indo-Australian Plate. It produced extensive shaking and severe damage to houses and buildings in Padang and Padang Pariaman, because its epicenter was about 60 km offshore from Padang. As the Padang earthquake was an intra-slab earthquake at intermediate depth with a comparable magnitude, the event did not generate a tsunami of significance [5]. Due to this earthquake, 1117 people were reported killed, 1214 severely injured, 1688 slightly injured, and 3 were left missing in West Sumatra. The earthquake also destroyed many houses, buildings and infrastructure (heavily damaged houses numbered 114,797, with 67,198 moderately damaged and 67,837 slightly damaged). In Padang, 5458 buildings sustained damage [6]. This event occurred at the end of the working day, just 15 minutes after offices and schools closed; if it had struck earlier, the number of causalities would definitely have been higher as a result of building collapses. Several hours after Padang earthquake, 1st October 2009, Sumatran fault line generated
Mw7.1 and 10km depth. Due to this earthquake destroyed many houses and building (heavily damaged houses numbered 600, with 550 moderately damaged). Since Padang has high potential to great earthquake shaking in near future with great acceleration too compare with previous earthquake in 2009 [7]. With great potential shaking occur in Padang for several return period of earthquake events, Padang has highest vulnerability to non engineered structure in Indonesia [8]. Based on observation in Palu city, Palu its self has the same soil characteristic as Padang city [9],[10].
There are four accelerometers in Padang. Three were donated by Engineers Without Borders Japan (EWBJ) and installed in 2008, and the other
was installed by the Indonesian Government’s
Bureau of Meteorology, Climatology and Geophysics (BMKG). However, only one ground motion record is available for the Padang earthquake. Due to an electric power cut during the earthquake, only the BMKG device recorded the time history of the earthquake. The observed record shows about 20 s of strong shaking with a peak ground acceleration (PGA) of 0.3 g and a predominant period of 0.5 s [11]. Response spectra at law period is greater then Indonesia code for rock condition (0.83g).The location of this station is a mountainous suburb about 12 km in from the coast. The subsurface condition at this station is rocky; the average shear wave velocity for the upper 30 m of the subsurface here, Vs30, is 1200 m/s [10].
DAMAGE FROM THE 2009 PADANG EARTHQUAKE
The city of Padang covers an area of about 695 km2 and is divided into 11 districts:
SEE - USQ, Brisbane, Australia, Nov.13-16, 2017
542
P. Utara, and Pauh. 51.0% of the land is forested, 28.52% is used for farming, 9.54% for housing and 7.1% for rice fields [12]. The population of more than 914.968 is increasing by 1%-2% per year. The K. Tangah district has the highest population and most extensive area compared with the other districts in the city.
The central business area of Padang is close to the coast and consist of several district: P. Barat, P. Utara, P. Selatan and P. Timur, B.T. Kabung, K. Tangah. The downtown area is utilized as a center of political and commercial activities. Although the Padang earthquake affected all districts of the city, the major damage occurred downtown, because about 80% of population lives near the coast. The majority of houses in the city are one- and two-storey non-engineered structures. These structures are typically built of confined masonry, with reinforced-concrete (RC) frames acting as confinement for the brick masonry walls. There are three general categories of houses in Padang: permanent houses (RC), semi-permanent houses (mix of RC and wood) and traditional houses (wood). Unfortunately, no detailed damage statistics are available for each type of building, so we cannot classify the category of the house. This earthquake also affected lifelines in Padang. The strong ground shaking destroyed public water distribution pipes leading to 2,906 reported leakage points in total [13]. Damage to pipelines forced the cessation of water delivery to consumers for several weeks.
2. SITE CHARACTERIZATION BY MICROTREMOR OBSERVATION
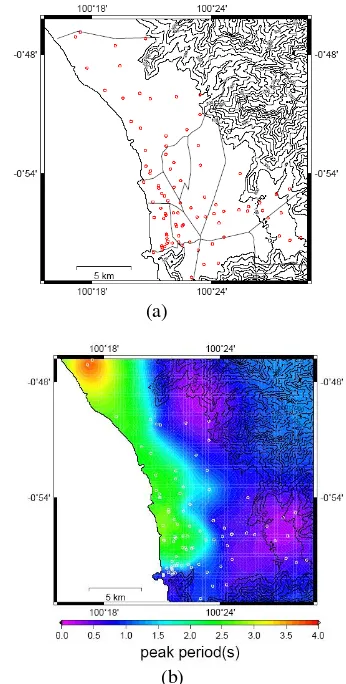
Single Microtremor Observation
A microtremor is a very small ground motion that can be recorded on the ground surface. It can be produced by a variety of excitations (e.g., wind, traffic, breaking sea waves). A full microtremor record can be described by one vertical and two horizontal components. Our analysis was conducted using the recorded microtremor. First, the horizontal and vertical spectrum ratios (HVSR) were computed for all sites (Fig. 2). HVSR (Horizontal-Vertical Spectra Ratio) is consists in estimating the ratio between the Fourier amplitude spectra of the horizontal (H) to vertical (V) components of ambient noise vibrations recorded at one single station.
The peak period of the HVSR is known to correspond to the resonant period of the site. This method postulates the shape of the Fourier spectrum . Equation. (1) shows the method used to calculate HVSR using the observed records.
𝑯𝑽𝑹𝒔 = √𝑭𝑵𝑺𝒊(𝝎)𝟐+𝑭𝑭𝑾𝒊(𝝎)𝟐
𝑭𝑼𝑫𝒊(𝝎)𝟐 (𝟏)
where 𝑭𝑵𝑺𝒊(𝝎) and 𝑭𝑼𝑫𝒊(𝝎) denote the Fourier amplitude of the NS, EW and UD components of each interval, respectively, and 𝝎 is the frequency.
We performed 140 single site surveys that sampled every district of the city of Padang. These observations were carried out in November 2008, September, November, and December 2009 and January 2010. The locations of observations are plotted in Fig.3. Microtremor was measured using a GPL- 6A3P sensor. The two horizontal (NS and EW) and the vertical (UD) components were
(a)
(b)
Fig. 2 Observation sites and results of HVSR.(a) Microtremor single observation sites at every district in Padang, (b) Distributed HVSR ratio.
SEE - USQ, Brisbane, Australia, Nov.13-16, 2017
543
mountainous areas. These results indicate an affect related to the thickness of alluvium in the coastal
The velocity of surface waves is well known to vary as a function of frequency (or period) due to dispersion. Since dispersion is a function of subsurface structure, the substructure can be estimated from a Rayleigh wave dispersion curve. We carried out microtremor array investigations using 12 sites at several districts in Padang (Fig.3). Dispersion curves were calculated using the SPAC method [13] to obtain a velocity structure from the microtremor recordings. An outline of the procedure follows. It is necessary to simultaneously record microtremors with an instrument array of at least three stations. The dispersion of a measured surface wave is a response to the subsurface structure directly below the array, and the estimation of the subsurface structure causing the dispersion is determined by means of inversion of Rayleigh waves. The basic principles of the SPAC method assume that the complex wave motions of microtremors are stochastic processes in time and space. A spatial autocorrelation coefficient for a circular array can then be defined when the waves composing the microtremor (i.e., the surface waves) are dispersive. Hence, the spatial autocorrelation is a function of phase velocity and frequency. Rayleigh wave records were measured for the 12-array observation sites using the SPAC method and inversion analysis was undertaken on the observed dispersion curves to estimate the soil profiles. In the inversion analysis, the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm was adopted to solve the non-linear optimization problem [14]. The basic procedures of PSO are outlined below. he particle swarm concept originated as a simulation of simplified social system. The original intent was to graphically simulate the choreography of bird of a bird block or fish school. However, it was found searched. All the birds do not know where the food is. But they know how far the food is in each iteration. So what's the best strategy to find the food? The effective one is to follow the bird which is nearest to the food. PSO learned from the scenario and used it to solve the optimization problems. In PSO, each single solution is a "bird" in
Fig.3 Array observation sites
the search space. We call it "particle". All of particles have fitness values which are evaluated by the fitness function to be optimized, and have updating generations. In every iteration, each particle is updated by following two "best" values. The first one is the best solution (fitness) it has achieved so far. (The fitness value is also stored.) This value is called pbest. Another "best" value that is tracked by the particle swarm optimizer is the best value, obtained so far by any particle in the population. This best value is a global best and called gbest. When a particle takes part of the population as its topological neighbors, the best value is a local best and is called lbest.
We estimate the subsurface structure of the model by solving a nonlinear minimization problem with the fitness function below.
𝒗𝒊𝒅𝒕+𝟏= 𝝎 𝒗𝒊𝒅𝒕 + 𝒄𝟏𝒓𝟏(𝒑𝒕𝒊𝒅− 𝒙𝒊𝒅𝒕 ) + 𝒄𝟐𝒓𝟐(𝒑𝒈𝒅𝒕 −
𝒙𝒈𝒅𝒕 ) (1)
𝒙𝒊𝒅𝒕+𝟏 = 𝒙𝒊𝒅𝒕 + 𝒗𝒊𝒅𝒕+𝟏 (2)
where 𝑣𝑖𝑑𝑡 is particle velocity of the
SEE - USQ, Brisbane, Australia, Nov.13-16, 2017
544 shallow subsurface structures (Ono et al., 2010). The outline of the SPAC method for the phase velocity calculation of Rayleigh waves follows.
𝑨
𝒇(𝝎)
,
𝑨
𝒈(𝝎)
and
∅
𝒇(𝝎)
,
are difference
between the amplitude of
∅
𝒈(𝝎), 𝑭(𝝎)
,
𝑮(𝝎)
respectively. Futher cross correlation in
the frequency region of the two waveforms will
be as follows.
𝑪𝑪𝒇𝒈= 𝑭(𝝎) ∙ 𝑮(𝝎)̅̅̅̅̅̅̅ = 𝑨𝒇(𝝎) ∙ 𝑨𝒈(𝝎) ∙
𝒆𝒙𝒑( 𝒊∆∅(𝝎)) (𝟓) Type equation here.
It shows the phase difference of∆∅(𝝎)
∆∅(𝝎) =𝒄(𝝎)𝝎𝒓 (6)
𝒄(𝝎) is the phase velocity from the phase difference.
𝑪𝑪𝒇𝒈= 𝑨𝒇(𝝎) ∙ 𝑨𝒈(𝝎) ∙
𝒆𝒙𝒑 (𝒊𝒄(𝝎)𝝎𝒓) (𝟕)
The complex coherence of two waveforms is defined by the following equation.
𝑪𝑶𝑯𝒇𝒈(𝝎) =𝑨 𝑪𝑪𝒇𝒈(𝝎) transform of the observed microtremors.
From the SPAC coefficient ρ(r,ω), the phase velocity is calculated for every frequency from the Bessel function argument of equation. 15 and the velocity model can be invert. The layer thickness and the average S-wave velocity in Figure 6 each array site. For the average S wave velocity model obtained by averaging the estimated ground structure of the array site was to be calculated by a weighted average using a S-wave velocity structure is estimated as a weighted layer thickness.
𝑹𝒆(𝑺𝑷𝑨𝑪(𝝎, 𝒓)) = 𝑱 (𝒄(𝝎)𝝎𝒓 ) (𝟏𝟒)
From the SPAC coefficient𝝆(𝒓, 𝝎), the phase velocity is calculated for every frequency from the Bessel function argument of equation. 15 and the velocity model can be invert. The layer thickness and the average S-wave velocity in Figure 6 each array site. For the average S wave velocity model obtained by averaging the estimated ground structure of the array site was to be calculated by a weighted average using a S-wave velocity structure is estimated as a weighted layer thickness.
𝑽𝒔
̅̅̅̅ = ∑ 𝑽𝒔𝒊∙𝑯𝒊𝑯 (15)
From the dispersion curve, we can produce an interpretation Vs30 (average shear wave velocity
for the upper 30 m) as show in Table 4, shows the contours of Vs30 for every 200 m/s increment and
soil characteristic every layer.
SEE - USQ, Brisbane, Australia, Nov.13-16, 2017
545
(b)
(c)
(d)
Fig.4 Observation sites, soil profile and distribution of average shear wave velocity, (a) Array observation sites, (b) layer 1 (Vs < 400m/s) and (c) layer 2 (Vs >400m/s), (d) Distribution of Vs30 (m/sec).
4. VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENT
Vulnerability can simply be defined as the sensitivity of the exposure to seismic hazard(s).
The vulnerability of an element is usually expressed as a percentage loss (or as a value between zero and one) for a given hazard severity level [16]. In a large number of elements, like building stocks, vulnerability may be defined in terms of the damage potential to a class of similar structures subjected to a given seismic hazard.
Vulnerability analysis reveals the damageability of the structure(s) under varying intensity or magnitudes of ground motion. Multiple damage states are typically considered in the analysis. Based on the data of damaged houses by ground shaking of Padang earthquake in 2009.
5. ASSESSMENT TO RESIDENTIAL HOUSES
Survey Outline
The main purpose of assessment of housing has been used to quantify the structural condition after giant earthquake based on observed or interviewed to the owner its self. Since Padang has been conducted for seismic intensity in 2011 [11]. The method was originally developed by Japan architecture disaster prevention association earthquake. This method widely applied to assess houses for preventing future ground shaking due to predicted earthquake. It has been useful for estimating house condition such as the earthquake resistant performance and earthquake resistant repair to improve earthquake-resistant performance the observed houses by knowing the weak point at the structural. The original questionnaire sheet was written in Japanese (juutaku day taishinnshinndan); however, it was translated into Indonesian language for its application to Padang city. The questionnaire has 10 items that cover recognition of structural condition in general, had experience past giant earthquake and strengthened after struck by earthquake. Some sentences were modified to make
SEE - USQ, Brisbane, Australia, Nov.13-16, 2017
546
it more relevant to local people while not changing
the original topics covered by questionnaire. People living near the observation points were interviewed using the questionnaire [17][18]. The questionnaire survey was conducted from October 2nd to
November 23rd ,2016. The survey was carried out
in all districts of Padang by distributing and completing 1235 the questionnaire. People living near the observation points were interviewed using the questionnaire. The questionnaire survey was conducted from October 2nd to November 23rd,2016.
The survey was carried out in all districts of Padang by distributing and completing 1235 questionnaires through a direct interview process with residents of
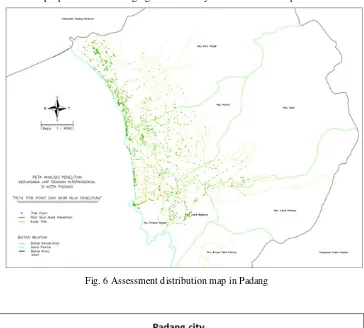
the city The interviewers explained each item of the
questionnaire to residents, discussed the responses given, and documented the answers on the standard answer sheets. The results of the questionnaire survey conducted to estimate the houses condition distribution in Padang after earthquake in Padang 2009. The interview distribution showed in figure 11 and its result showed in figure 12, the interview result is indicated 98% of houses in Padang with score < 8 (Japan architecture disaster prevention association), its means the houses need to consult and discuss with experts directly soon as possible. Fig. 6 Assessment distribution map in Padang
SEE - USQ, Brisbane, Australia, Nov.13-16, 2017
547
6. CONCLUSION
According to microtremor observations, downtown Padang is underlain by soft soil conditions (Vs30<400 m/s). Consistent results
concerning the soil condition were found based on predominant period observations.
In both cases, the coastal area was determined to have a soft soil conditions (Vs30<400 m/s), a
longer predominant period, and a greater seismic intensity.
Padang has a thick alluvial layer in the coastal area (with a predominant period between 2.0 and 4.2 s) that thins toward the mountains (with a predominant period less than 2.0 s). The subsurface geology also changes slowly from soft soil in the coastal area to rocky conditions in the mountains. The results show clear information on soil condition especially at the downtown and residential houses current condition with 98% of houses need to consult to expert as soon as possible as a way to mitigate future earthquake event.
7. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author would like to thank to Professor Junji Kiyono from Kyoto University who provided strong support throughout the period. Thanks also go to Professor Yusuke Ono and Professor Noguchi from Tottori University, Japan for their great assistance during the field survey. Thanks to Dr. Safriani from Universitas Negeri Padang as research partner. Finally would like to thanks Indonesian government DIKTI who provided financial support on research schema Penelitian Unggulan Perguruan Tinggi year 2016.
8. REFERENCES
[1] Prawirodirjo, L., Y. Bock, J.F. 2000, “One century of tectonic deformation along the Sumatran fault from triangulation and global
positioning system surveys”, J. of Geophysical
research, 105, 28, 343-28,363.
[2] Aislinn Laing, 2009, “More than 1000 feared
dead in Sumatra earthquake’,
www.telegraph.co.id.
[3] Natawidjaja and WahyuTriyoso 2007. “The
Sumatran fault Zone-from Source to Hazard”, J. of Earthquake and Tsunami, Vol. 1 No. 1, 21-47. [4] Rusnardi Rahmat Putra, J. Kiyono, Y. Ono, H
Parajuli, “Seismic Hazard Analysis For Indonesia”. Journal of Natural Disaster Science,
Vol. 33, No.3 pp.59-70, June 2012.
[5] EERI 2009. “The Mw 7.6 Western Sumatra Earthquake of September 30, 2009”, Special
report.
[6] BNPB 2009 (National Disaster Management
Agency of Indonesian Government). “Total
damage report and verification for West
Sumatra due to Padang earthquake”,
www.bnpb.go.id.
[7] Rusnardi Rahmat Putra, J. Kiyono, Y. Ono, H Parajuli. 2012, Seismic Hazard Analysis for Indonesia,Journal of Natural Disaster Science, Vol. 33, No.3 pp.59-70, June 2012.
[8] Rusnardi Rahmat Putra, Junji Kioyono, Aiko Furukawa,VulnerabilityAssessment of Non Engineering Houses Based on Ddamage Data of the 2009 Padang Earthquake in Padang City,International Journal of Geomate, Vol 7, No.2 (SI.No.14) pp.1076-1083,2014
[9] Rusnardi Rahmat Putra, Junji Kiyono, Yusuke Ono, Yasuo Yoshimoto, Syharil, Determined Soil Characteristic of Palu in Indonesia by
Using Microtremor Observation, International
Journal of Geomate, Vol. 10, No.2 (SI. No. 20) 1737-1742, 2016.
[10] Rusnardi Rahmat Putra, Estimation of Vs30
Based on Soil Investigation by Using
Microtremor Observation in Padang,
Indonesia, International Journal of Geomate, Oct., 2017, Vol.13, Issue 38, pp.135-140, 2017
[11] Rusnardi Rahmat Putra, J. Kiyono, Y. Ono, Estimation of Earthquake Ground Motion in Padang City, Indonesia. International Journal of GEOMATE, Vol..1 (S1.No.1), pp.71-77, October, 2011.
[12] Padang City Statistic Center Agency of Local Government, www.padangkota.bps.go.id. 2017.
.[13] Aki, K. 1957.”Space and time spectra of stationary stochastic waves, with special
reference to microtremor”, Bull. Earth. Res.
Inst., Vol. 35, No. 3, 415-456.
[14] Keneddy, J. and Eberhart, R. C. Particle swarm optimization, Proc. Of IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks,
Vol.4,pp.1942-1948, 1995
[15] Ono, Y., Kiyono, J., Rusnardi, P. R. and Noguchi, T. 2010. Microtremor Observation in Padang City, Indonesia to Estimate Site Amplification of Seismic Ground Motion, Proc. of International Symposium on a Robust and Resilient Society against Natural Hazards and Environmental Disasters and the third AUN/SEED-Net Regional Conference on Geodisaster Mitigation, pp.386-391.
[16] Baker, Jack W. 2008. “Introduction
Probabilistic Hazard Analysis”, handbook. Version 1.3 Oct 1st 2008.
[17] Fallahi. A, P. Teymourzadeh, M. Miyajima, T. Tobita and R. Alaghebandian (2008). Statistical Study to Determine JMA Earthquake Intensity by QuestionnaireSurvey
in 2003 Bam (Iran) Earthquake, The 14 World
SEE - USQ, Brisbane, Australia, Nov.13-16, 2017
548
October 12-17, Beijing, China.
[18] Sutrisno, Rusnardi, Ganefri, A Comparative Study on Structure in Building Using Different Partition receiving expense earthquake,
Authors Index
G
G. Kandasamy 124
Guilherme Marins Pessanha 293
Authors Index
Mahatma Kufepaksi 477
Mamoru Yamada 432
Manutchanok Jongprasithporn 348 Maratree Plainsirichai 62
Maria McCrann 33
Maria Visa 437 Marthinus Sonnekus 243
Mazlini Adnan 482 Meysam Banimahd 360 Mia Nurkanti 422 Mitsuru Komatsu 338 Mochammad Fardiansyah 97
Mohammad Mirza Hassan 354 Mohammed M. Khattab 190 Mohd Hairy Ibrahim 482 MohdSyahrul Hisyam Sani 231,237 Mohd. Raihan Taha 214 Muhammad Isha Ismail 237 Muhammad Tahir Rajput 514
Muntana Nakornriab 62 N Nabila Shah Jilani 514 Najeeha Apandi 417
Authors Index
Rotchanatch Darnsawasdi 508
Ruddy Kurniawan 224
Seezar Sh. Abdullah 178 Seiki KAWAGOE 287
Sengheng Hul 196 Shahjahan Khan 22
Shahrin Mohammad 231 Sheena I. Better 276
Siravitch Atipatha 348 Sisikka Wannajun 62 Siti Hanggita Rachmawati 167 Siti Nor Hidayah Arifin 417 Stephen Beatty 426 Svetlana Barannikova 91 Syafrida Siregar 39
T T.G. Krupnova 395,399,405 Taizo Uchida 432
Takeshi YAMAMOTO 327 Tarmizi Ismail 488
Authors Index
Yuangyai, C. 254
Yuki OGIMOTO 517
Yuki takagi 57
Yuto Murakami 72
Yuya Imamura 432
Yuztitya Asmaranti 477
Z
Zakaria Hossain 167
Zev Al Jauhari 224
Zuliziana Suif 196,202