i
IMPLEMENTING DRILLING TECHNIQUE
TO XI AP CLASS OF SMK BOPKRI 1 YOGYAKARTA
TO IMPROVE THEIR PRONUNCIATION
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Helen Marta Sari
Student Number: 091214133
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work or parts of the work of other people, execpt those cited in the quotations and the references, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, September 30, 2013
The Writer
v
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma:
Nama : Helen Marta Sari
Nomor Mahasiswa : 091214133
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
IMPLEMENTING DRILLING TECHNIQUE
TO XI AP CLASS OF SMK BOPKRI 1 YOGYAKARTA
TO IMPROVE THEIR PRONUNCIATION
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian, saya memberikan kepada Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di Internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu minta ijin dari saya maupun memberikan royalti kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sebenarnya.
Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal: 30 September 2013 Yang menyatakan,
vi ABSTRACT
Sari, Helen Marta. 2013. Implementing Drilling Technique to XI AP Class of SMK
BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta to Improve Their Pronunciation. Yogyakarta: English
Education Department, Sanata Dharma University.
Speaking skill is one of the skills in learning English that should be mastered by students. Having good pronunciation is one of the elements to build a good speaking skill. When the researcher conducted observations, the students of
XI AP class of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta had difficulties in pronouncing
English words. It was because the students were rarely given the examples of how to pronounce some English words. This study is expected to help the students to overcome their problem in pronunciation of English words.
The researcher applied Classroom Action Research (CAR) to help the students practice their pronunciation abilities in the classroom. The researcher tried to make the students be accustomed to saying many English words by implementing drilling technique. The use of drilling technique was adapted as the solution to overcome the students’ problem. This research problem of the study is to what extent drilling technique improves the students of XI AP class of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta to pronounce English words.
There were two cycles in the study.There were plan, action, observation, and reflection in each cycle, in conducting Cycle 1. In the researcher used some research instruments, namely interview, observations, questionnaires, field notes and tests. The researcher conducted the same steps and instruments to be applied in Cycle 2. The researcher provided English words that should be drilled to the students in each cycle. The class who consisted of 21 students practiced to pronounce the words correctly. The students were given more chances to practice their pronunciation through speaking activities in the classroom.
Based on the result of the tests, the researcher found the students’ improvements in pronouncing English words. The students’ pronunciation improvements were different from each other. The improvements were in the elements of phonemes, intonation, stress, and accuracy. Therefore, the use of drilling technique in the classroom improved the students’ pronunciation.
vii ABSTRAK
Sari, Helen Marta. 2013. Implementing Drilling Technique to XI AP Class of SMK
BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta to Improve Their Pronunciation. Yogyakarta: English
Education Department, Sanata Dharma University.
Keterampilan berbicara adalah salah satu keterampilan dalam belajar bahasa Inggris yang harus dikuasai oleh siswa. Memiliki pengucapan yang baik adalah salah satu elemen untuk membangun keterampilan berbicara yang baik. Ketika peneliti melakukan observasi, siswa XI AP kelas SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta mengalami kesulitan dalam mengucapkan kata-kata bahasa Inggris. Itu karena siswa jarang diberi contoh bagaimana untuk mengucapkan beberapa kata dalam bahasa Inggris dengan benar. Penelitian ini diharapkan dapat membantu para siswa untuk menyelesaiakan masalah mereka dalam pengucapan kata-kata bahasa Inggris.
Peneliti menggunakan Penelitian Tindakan Kelas (PTK) untuk membantu siswa melatih kemampuan pengucapan mereka di dalam kelas. Peneliti mencoba untuk membuat siswa terbiasa dengan mengatakan banyak kata bahasa Inggris dengan menerapkan teknik drill. Penggunaan teknik drill diadaptasi sebagai solusi untuk mengatasi masalah siswa. Rumusan masalah dari penelitian ini adalah sejauh mana teknik drill meningkatkan siswa kelas XI AP SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta dalam mengucapkan kata-kata berbahasa Inggris.
Ada dua siklus dalam penelitian ini. Pada siklus pertama, terdapat tahap perencanaan, pelaksanaan, observasi, dan refleksi. Peneliti menggunakan beberapa instrumen penelitian, yaitu wawancara, observasi, kuesioner, catatan lapangan dan tes. Pada siklus kedua, peneliti menerapkan tahap dan instrument yang sama dengan siklus kedua. Peneliti menyediakan banyak kata berbahasa Inggris yang harus didrillkan kepada siswa 21 siswa pada setiap siklus. Para siswa berlatih mengucapkan kata-kata dengan benar. Para siswa diberi lebih banyak kesempatan untuk melatih kemampuan pengucapan kata-kata berbahasa Inggris melalui kegiatan berbicara di dalam kelas.
Berdasarkan hasil tes, peneliti menemukan peningkatan siswa dalam mengucapkan kata-kata berbahasa Inggris. Peningkatan kemampuan pengucapan yeng terjadi pada setiap siswa berbeda satu sama lain. Peningkatan tersebut berada pada unsur fonem, intonasi, stres, dan akurasi. Oleh karena itu, penggunaan teknik drill dalam kegiatan pembelajaran di kelas meningkatkan kemampuan pengucapan siswa dalam kata-kata berbahasa Inggris.
viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, the researcher would like to thank to Allah SWT, for the mercy and the grace that enable the researcher to conduct the research entitled Implementing Drilling Technique to XI AP Class of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta to Improve Their Pronunciation.
This is classroom action research that required some data to help the researcher to conduct the study. The researcher would like to express the great gratitude to the following people.
1. Rohandi, Ph.D. the Dean of the Faculty of Teachers Training and Education.
2. Caecilia Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd. the Chair Person of the English Language Education Study Program.
3. Christina Kristiyani, S.Pd., M.Pd. as the major sponsor who has supported the researcher with patience, guidance, correction, and advice.
4. Selo Hadi Priyanto, S.Pd, Sri Punagi, S.Pd., and my brother Yunarko Hadi Primanto, S.H. for all the prayers and support.
ix
6. Agnes Puji Lestari, S.Pd. as the English teacher of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta.
7. Made Frida Yulia, S.Pd., M.Pd., Drs. Barli Bram, M.Ed., Ph.D., Drs. Pius Nurwidasa Prihatin, M.Ed., Ed.D., and Sister Margareth for the advice given to me.
8. The students of XI AP class for their participation in this study.
9. Mbak Niken, Pakdhe-pakdhe, Budhe-budhe and all of my cousins
who have given the researcher support.
10. Kelik Sunaryo, A.Md. for the support and prayer.
11. Pipup Dhanayu, Brigita Itul, Enur Sekar, Ervina Dendot, Friskong Ayu, Niken Hap Hap, Berta Tutik, Bruder Markus, Leo, Dimas Adi, Wanda and Dimas Wek who also had given me advice and support in conducting the thesis.
12. Awang, , Elfri, Dhian, Okta, Ine, Mbokde, Caca, Yudith, Deta,and Vivi for the support.
13. Class D Kosongsanga for the support.
The researcher realizes that this thesis is not perfect. Therefore, the researcher needs suggestions to make the thesis better. The researcher hopes this thesis can be useful for readers.
Yogyakarta, September 30, 2013
x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVALPAGES ... ii
STATEMENT OF WORK’SORIGINALITY ... iv
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ... v
ABSTRACT ... vi
ABSTRAK ... vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... x
LIST OF TABLES ... xiii
LIST OF FIGURES ... xiv
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xv
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Research Background... 1
B. Research Problem... 6
C. Problem Limitation ... 6
D. Research Objectives ... 7
E. Research Benefits ... 7
F. Definition of Terms ... 7
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 10
A. Theoretical Description ... 10
1. English for Teens ... 10
2. Teaching Language ... 11
3. Teaching Speaking ... 12
a. Student-Centered Learning ... 14
xi
c. Teaching Speaking for XI AP Students of SMK BOPKRI 1
Yogyakarta ... 17
d. Elements of Speaking ... 19
e. Oral Communication Skill ... 20
f. Phonetic Transcription ... 24
4. Audio Lingual Method ... 27
a. Repetition Drills ... 28
b. Substitution Drills ... 28
5. Curriculum of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta ... 29
B. Theoretical Framework ... 30
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 33
A. Research Method ... 33
B. Research Setting ... 36
C. Research Participants ... 36
D. Instruments and Data Gathering Technique ... 37
E. Data Analysis Technique ... 41
F. Research Procedure ... 44
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION ... 46
A. Description of the Implementation of Drilling Technique ... 46
1. Cycle 1 ... 48
a. Plan ... 49
b. Action ... 52
c. Observation ... 56
d. Reflection ... 59
2. Cycle 2 ... 61
a. Plan ... 62
b. Action ... 64
c. Observation ... 67
xii
B. The Discussion of the Results ... 71
1. Cycle 1 ... 72
2. Cycle 2 ... 78
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION ... 86
A. Conclusion of the Study ... 86
B. Recommendation of the Study ... 88
xiii
LIST OF TABLES
Tables
Table 2.1 Student-Centered and Teacher-Centered Continuum by Blumberg (2004) ... 14 Table 2.2 The Phonetic Transcription of 30 English words of Cycle 1 by Oxford
Advanced Learner’s Dictionary ... 24 Table 2.3 The Phonetic Transcription of 40 English words of Cycle 2 by Oxford
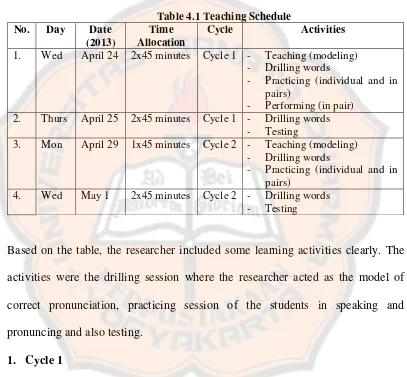
Advanced Learner’s Dictionary ... 25 Table 4.1 Teaching Schedule ... 48 Table 4.2 The Score of the Student’s Speaking Test after Implementing Drilling
Technique (Cycle 1) ... 73 Table 4.3 Students’ Pronunciation Table in Preliminary Study and Cycle 1... 74 Table 4.4 The Students’ Performances in the Elements of Pronunciation in Cycle
1 ... 77 Table 4.5 List of Students who were Observed in the Study.. ... 79 Table 4.6 The Score of the Student’s Speaking after Implementing Drilling
Technique (Cycle 2) ... 79 Table 4.7 Table of Percentages of Students’ Pronunciation Improvements in Cycle 2 ... 80 Table 4.8 Students’Performances in the Elements of Pronunciation in Cycle 1 and
Cycle 2 ... 82 Table 4.9 The Students’ Improvements in the Elements of Pronunciation in Cycle 1 and 2
xiv
LIST OF FIGURES
Figures
Figure 3.1 Action Research by Kemmis and McTaggart (1988) ... 34
Figure 3.2 The Percentages of the Elements in Students’ Pronunciation Abilities to See the Pronunciation improvements ... 43
Figure 4.1 Cued Dialogue of Cycle 1. ... 51
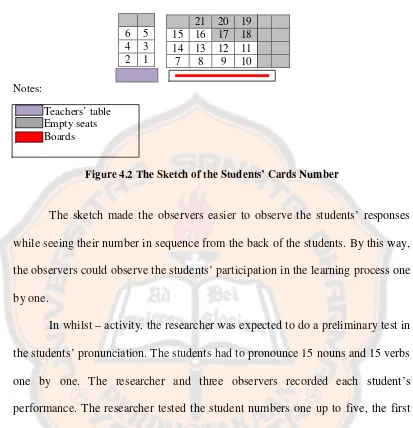
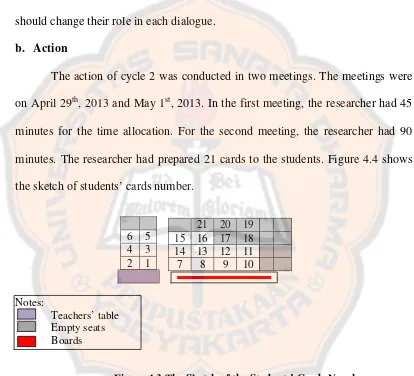
Figure 4.2 The sketch of the students’ cards number. ... 53
xv
LIST OF APENDICES
APENDICES
A. Covering Letter for the Head of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta ... 95
B. Covering Letter for the Governor of DIY ... 97
C. Permission Letter from the Governor ofDIY ... 99
D. Research Official Statement from SMK BOPKRI 1Yogyakarta ... 101
E. Blueprints ... 103
1. Blueprint of Observation Checklists ... 104
2. Students’ Questionnaire ... 106
3. Interview Guideline with English Teacher ... 109
F. Research Instruments ... 110
1. Observation Checklists... 111
2. Questionnaire ... 113
3. Interview Guideline ... 114
G. Lesson Plans and Learning Materials ... 115
1. Lesson Plans for the First Cycle... 116
2. Materials for the First Cycle ... 126
3. Lesson Plans for the Second Cycle ... 134
4. Materials for the Second Cycle ... 144
H. Raw Data ... 147
1. Preliminary Study ... 148
2. Cycle 1 Observation Checklists Result ... 156
3. Field Note of Cycle 1 ... 171
4. Cycle 2 Observation Checklists Result ... 177
5. Field Note of Cycle 2 ... 192
6. Questionnaire Result ... 196
7. Interview Result ... 208
I.
APPENDIX I
... 210xvi
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, the researcher focuses on teaching technique to the students of XI AP class of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta. The study discusses the implementation of drilling technique to improve the students’ pronunciation in English learning. This introduction presents the research background, research problem, problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits and definition of terms.
A. Research Background
To be able to communicate with people from different cultural backgrounds and states, English has become a main language that is used to communicate. English is an international language. Many people in the world speak English as a language to communicate in business, tourism, education, science, technology, media, and the Internet. English dominates all of the functions (Crystal, 1997).
important. English has become a subject that needs to be learned for Indonesian, especially for students in school.
There are four skills in learning English, namely speaking, listening, reading and writing skills. In this study, the researcher focuses on the students’ pronunciation in speaking skill. According to Robertson (2009), speaking is one of the important skills in learning English. When the students speak English, the students will be able to chat online, write and travel the world using English to communicate with others.
Based on Florez (1999), there are three competences to support the students in building their speaking skill, namely grammar, vocabulary and pronunciation. To build a good speaking skill, the students must practice those three competences. Florez adds that grammar is the sentence structure, vocabulary is the students’ knowledge in knowing some English vocabulary, and pronunciation is the way that the students pronounce English words.
The researcher chose the students of XI AP class in SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta as the subject of this study. The students of XI AP class is the second grade students of Akuntansi Perkantoran class. The researcher chose SMK
BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta as the object of the study because the researcher did the
teaching practice in the school. The session was called PPL or Praktek Pengalaman Lapangan session. In that session, the researcher taught and
observed students of XI AP class.
students, and interviewed the English teacher. The observations were done when the researcher had the PPL session. The researcher observed the English teacher’s activities and the students’ activities twice. The researcher made field notes about the observations.
In the observations, the researcher found that the students of XI AP class had low abilities in pronouncing English words. First, the students could not pronounce the English words correctly. Then, the students rarely got the example of how to pronounce some English words correctly and the correction of the students’ mispronunciation. Next, the students had difficulties in memorizing the meaning of some words. The last aspect was that the students seldom spoke in English. The students were not accustomed to pronouncing many English words. Therefore, the students did not know how to pronounce many English words correctly.
There will be an oral test, which requires the students to speak in English in the final exam. In this case, the students’ of XI AP class had low abilities in pronouncing English words. The researcher tried to help the students to solve the problem. Therefore, the researcher focused on the pronunciation because almost all the students had low abilities in pronouncing many English words.
By conducting the observations, the researcher checked the students’ pronunciation by giving four words such as extension, receive, tough and company to the students. The researcher took the four words from the students’ worksheet that they had learned before. All of the students had wrong pronunciation when they were asked to pronounce the four words. For example, the word ‘extension’ should be pronounced /ɪk’sten.tʃən/. However, they pronounced /ekstention/. Another example was the word company /’kʌm.pə.ni/, which they pronounced /`kom`pani/. They did not know how to pronounce each word correctly. The complete fact can be seen in appendix H. The result was none of the students could pronounce the words correctly.
To reinforce the finding, the researcher gave questionnaire (the first questionnaire) to check the students’ difficulties in learning English. Based on 15 students who answered the questions in the questionnaire, 11 students stated that they had difficulties in pronouncing English words.
or she had to pronounce English words. However, they wanted to pronounce some English words correctly.
To make sure about the problem faced by the students, the researcher conducted an interview with the English teacher of XI AP class. The result of the interview was that the students of XI AP class had difficulties in learning English, especially in speaking skill. The students always responded to the English teacher’s instruction using Indonesian language in the class. Based on the English teacher’s experience, there were some factors that caused the students not to use English in the English learning. One of the factors was the students had difficulty to pronounce some English words because the students were not motivated and accustomed to speaking in English.
The researcher tried to find the appropriate learning technique based on the students’ characteristics. Later, the technique would require the students to speak actively. The students’ problems were that the students could not pronounce English words correctly. Then, the students rarely got the example of how to pronounce some English words correctly and the correction of the students’ mispronunciation that should be given by the teacher. Therefore, the students need to practice in pronouncing some English words.
drills. By implementing drilling technique, the students would do many practices to get used to pronouncing the English words correctly and appropriately. Then, they would have a good speaking skill later. Based on Russel (2008), drilling is a good method. it was because the students were given excellent model of pronunciation immediately before they are asked to respond. In drilling activity, the researcher will be an excellent model for the students to practice correct pronunciation before they are asked to repeat. Drilling technique would also make the students familiar with English words.
B. Research Problem
Based on the problem of the students, the researcher comes up with a research problem as follows:
“To what extent does drilling technique improve students of XI AP class of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta to pronounce English words?”
C. Problem Limitation
D. Research Objective
This study has an objective to help the students to improve their pronunciation by implementing drilling technique in the classroom. The aim of the implementation is to know to what extent drilling technique improves the students of XI AP class of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta to pronounce English words.
E. Research Benefits
There are some benefits of the study for the readers.
1. The researcher will be able to be more creative in teaching the students. The researcher will also be able to answer the problem formulation of the study. 2. The teacher will be able to know the problems faced by students in speaking
activities and uses drilling technique with more intensive practices to improve students' speaking. The teacher will get the idea of teaching English by asking the students to be more active to speak English.
3. The students will know what their problems are in learning English. By drilling technique, the students were expected to master in speaking. With the application of drilling technique, the students should practise the pronunciation of many English words to support their speaking skill.
4. For future researcher who is going to conduct a similar research, this study will be beneficial. The report in the study can be used as a reference.
F. Definition of Terms
1. Drilling Technique
According to Harmer (2000), drilling is a technique in repeating structural pattern through oral practice. In this way, the researcher focuses on the repeating and practising until the students are familiar with many English words.
2. The students of XI AP class of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta
According to Evans and Herr (1978), Vocational High School is a vocational education which is a part of education system that prepares someone to have better skill in working in a certain job than other common jobs. Then, Vocational High School is one of the levels of education which becomes the next level of Junior High School. In this level, students are expected to have a certain skill related to Administrasi Perkantoran or Official Administration, and then they can use the skill in their working world after graduating from the school. Speaking skill can be beneficial for them to communicate with other people later.
The students of XI AP class of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta are the second grade of Akuntansi Perkantoran or Official Administration class in SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta. There are 21 students in the class. They have different characteristics. Some of them are good in English lesson. However, some of them are low in English lesson. Their pronunciation abilities were low. The researcher is going to conduct research in the class to help them improve their pronunciation. 3. Pronunciation
10 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter consists of two parts, namely the theoretical description and the theoretical framework. In the theoretical description, there are sources used to support and to guide the research. The theoretical description covers theories of English for teens, theory of teaching speaking, theory of Audio Lingual Method, and the Curriculum of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta. In theoretical framework, the researcher explains the benefit of the theories and how the theories used in the study.
A. Theoretical Description
In the theoretical description, the study presents some theories in order to broaden the topic. The theoretical description consists of English for teens, teaching speaking, teaching language, the audio lingual method and the curriculum of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta.
1. English for Teens
Based on the research of youth’s characteristics conducted by American Academy of Pediatrics (1991), teens are the people whose ages are between 15 up to 19 years old. Teens cannot control their development of adolescence successfully. Teens’ characteristics are different from children’s and adults’. The students of XI AP class are categorized as teens whose ages are between 15-19 years old.
according to the research of American Academy of Pediatrics (1991). American Academy of Pediatrics (1991) reported that the intellectual characteristics of teens are that they can solve problems better, think about their future, appreciate opinions of others, and understand the long and short-term memory. The students have the long terms and short-term memory in the case of learning English. In the long-term, the students will remember some memories that happened some years ago. Then, the short-term memory is that the teens can remember some memories in short time ago.
There are some social charcteristics teens had based on Amarican Academy of Pediatrics (1991). The social charcteristics are teens prefer having more experiences with their friends rather than with their family. When teens feel more comfort to have activities with their close friends who they meet in their particular group, they will build a group of close friends. For their emotional characteristic, teens get depressed-sadness, lasting more than two weeks, and it is not normal. Nevertheless, when teens have problems, they will become more emotional than adults.
2. Teaching Language
Nunan (2003) states that English has four basic skills which must be learned in school. Those are listening and reading as the receptive skills, and writing and speaking as the productive skills. The students can find those skills during their study in school. Speaking is one of the skills that must be mastered in communication through English language. English is a tool of communication between countries, cultural groups, various companies and organizations, communities and friends (Kilgour, 1999).
3. Teaching Speaking
There are four skills in learning English, namely speaking, listening, reading and writing skills. The focus of the study is in the pronunciation in speaking skill. According to Robertson (2009), speaking is one of the important skills in learning English. The students will understand what they are saying through listening to someone who is speaking. When the students try to understand what is being said, they have to be able to speak. Thus, speaking is an important skill to be learned in school in order to communicate with others internationally.
According to Omagio (1986), in order to make the speaking skill optimal, the students need to determine some aspects such as what range of level is likely to be attainable (p. 176). The teacher should use the appropriate language based on the students’ ages and characteristics. For example, based on the observation sessions, the researcher determined what level of English used in the XI AP class. The teacher of XI AP used very simple English. Even sometimes the teacher used the Indonesian language in the whole session. The teacher said that it was difficult for the students to grasp points of the materials if the teacher spoke English all the time. The students needed the teacher to use bilingual.
The level of difficulty of the materials must be appropriate for students’ ages. The teacher should teach the understandable or simple English to the students and the teacher does not teach the vocational high school’ students with complicated language. The teacher needs to use simple English language in order that the students can fully understand the materials. Therefore, knowing the students’ ages is important.
Speaking is used for many purposes, and each purpose involves different skills (Richards & Renandya, 2002). For example, when a teacher needs to give instruction, the teacher will use instructional language to the students. Then, when a teacher needs his or her student’s help to close the door, the teacher must use the appropriate language to ask for help. Consequently, speaking has to have purposes inside.
classroom, the teacher uses the English to have interaction with the students. English must be introduced to make the students become familiar with the English language.
a. Students-Centered Learning
In teaching speaking especially when the teacher wants to focus on the students’ pronunciation, the learning process needs the students to be more active to be the decision-maker. Blumberg (2004) says, “students-centered learning is an approach to teach that is increasingly being encouraged in higher education”. Students-centered learning does not employ a single teaching method (pp. 68-80). So, in teaching speaking, the students also have to participate themselves. In traditional teaching, the center of learning process is the teacher. However, in teaching speaking, the center of the learning should be in the students. The students have to be given more chances to participate actively in the class.
Table 2.1 Student-Centered and Teacher-Centered Continuum by Blumberg (2004)
Teacher-centered learning Student-centered learning
Low level of students’ choices High level of students’ choices Passive students Active students
Power is primarily in the teacher Power is primarily in the students
what he or she does, and does not about what the students learn. This learning process emphasizes what the instructors do often leads to the students who are passive learners and who do not take responsibility for their own learning. Educators call this traditional method, “instructor-centered teaching.” In contrast, “learner-centered teaching” occurs when instructors focus on student learning (Blumberg, 2004).
Besides, in the student-centered learning, the students have high level of choices to be active because they can have some chances to choose or determine what they want to do in the learning process. For example, when the teacher asks the students to make a conversation based on a situation, the students can decide what character they want to be, and it can build the students’ creativity. So, the power is primarily in the students with the teacher’s assistance.
In this study, the researcher combines those learning processes. In giving the materials and the drilling session, the researcher uses teacher-centered learning because the researcher needs to guide the students to pronounce English words correctly. In practicing and performing the dialogues, the researcher employs students-centered learning. It is because the researcher wants to give more chances to the students to determine what the students want to be in the dialogues. b. Speaking for Communication
and also have the ability to speak English – “needs English becomes an important factor as well as a benchmark in the world of work”. English is a good factor to determine the quality of a person in the working world.
There are several facts which state that English language is crucial. According to Keith (2003), over 80% of the information stored in the world's computers is in English. More than half of the world's scientific journals are in English and English is the main language on the Internet, films, and songs. Those statements show that English is very important as a language of instruction to communicate with others. Some companies currently require the human resources who are capable in speaking English and also have good pronunciation, because a lot of information is provided in English.
On the other hand, Canale and Swain (1980) and Canale (1983) state that communicative competence as a synthesis of a knowledge system and skill needed for communication. Canale and Swain (1980) and Canale (1983) add that “in the concept of communicative competence, knowledge refers to the (conscious or unconscious) knowledge of an individual about language and about other aspects of language use” (p. 13). Based on their explanations, there are three types of knowledge, those are knowledge of grammar in a language, knowledge of the use of the language in context to communicate, and knowledge of how the combination with communicative utterances. Those types of knowledge proposed to communice with others.
Communicative competence related to the goal of the learning that must be achieved by the students in learning language. After the students have done the process of not knowing to knowing, the students need the communicative competence to be applied in their life. In this way, communicative competence is the goal which should be built to the students’ speaking skill.
c. Teaching Speaking for XI AP Students of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta Teaching speaking for XI AP class of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta is important because in the future, the students will deal with their working world that needs the employees to master English for communication. In the school, the students must practice more in pronunciation in order to be able to speak English correctly. Based on Brown (2004), there are four kinds of speaking assessments that can be implemented in the classroom. Those are interview, dialogues or conversation, role play, and games.
1) Interview
McNamara (1999) states that interviews are particularly useful for getting the story behind a participant’s experiences and views. The interviewer can pursue in-depth information around the topic. Interviews may be useful as follow-up to certain respondents to further investigate their responses. In interview session, the teacher has an interaction with students of XI AP directly to dig some information about the students understanding on the materials given.
2) Dialogue or Conversation
communication. In common sense, “dialogue is defined as a process of conversation between two or more persons for exchanging opinions or ideas” (Passi & Passi (n.d)).
Dialogues for social awareness mean that dialogues will happen in the society when people need to ask and answer someone’s questions. In this case, the students are aware that they have to make a dialogue with others. Dialogues for education mean that dialogues are needed when students are learning something. For example in a learning process in classroom, the researcher will have dialogue or conversation with the students when they are discussing materials. The researcher will make a dialogue to give questions to the students. Dialogues will happen between the researcher and students or between the student and student. Dialogue is very important to be applied in the teaching process in XI AP class. The researcher and the students need to communicate with each other using dialogue so there will be a communication that exists in the classroom.
3) Role Play
4) Games
In doing games, the students are expected to get themselves actively in the learning activities. Brown (2004) states that the students follow the rule of the game while learning English, especially in speaking (p. 175). Game is almost similar with role play which requires the students to have communication with others. The researcher does not apply any kinds of games in the learning process of the study. It was because the researcher will employ role-play to the students’ speaking activity.
d. Elements of speaking
There are some elements in speaking to build a good speaking skill that should be mastered by the students. Following are the elements of speaking skill according to Harmer (2001), “a language features are the connected speech, expressive devices, grammar, and negotiation language. He says that connected speech is to modify the pronunciation. Then, an expressive device is the alteration of the speed, volume, and stress of utterances to show the feeling”. Harmer also says that the use of this device contributes the ability to convey meaning (pp. 269-271). Those elements make the students produce a various words to make interaction or connection with others correctly.
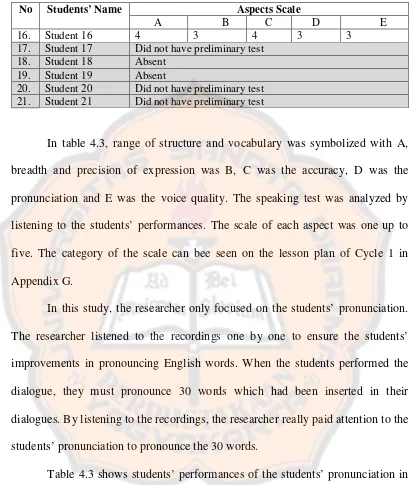
correct vocabulary in the dialogues. Then, breadth and precision is to what extent is the expression exact and specific to the topic of dialogues. Accuracy is the accuracy of the students’ articulation that is spoken clearly. Pronunciation is the sound produced by the students and voice of quality is how loud the students’ voices in performing the dialogues.
e. Oral Communication Skill
Based on Brown (2007), there are some aspects of oral communication skill that can synergize together in speaking process (p. 322). The aspects are conversational discourse, teaching pronunciation, accuracy and fluency, interaction effect, active factors, growth of speaking corpora, and genres of spoken language.
1) Conversational Discourse
Conversational discourse is one part of speaking processes where there is a conversation happened in the process. Richards (1990) notes that “a class with a conversation inside will be the stimuli to the students”. Therefore, the teacher should have a conversational discourse with the students in order to build a relationship among them.
2) Teaching Pronunciation
communication will be successful or be materialized well. Pronunciation is the important aspect in doing the communication.
Pronunciation makes the English speaking sounds good and also delivers the clear information with correct syllables, intonations and spellings. Students will have a good speaking skill if they know how to pronounce the English words correctly. At school, the teacher teaches how to pronounce words. There are some general elements in pronunciation according to Paultson and Bruder (1967, pp. 93-126):
a) Teaching Phonemes
Based on Paultson and Bruder (1967) a phoneme is a speech sound (p. 93). Phoneme is the smallest unit of language and phoneme does not have meaning. So, phoneme is a single unit of a word which cannot stand alone to build a language or meaning, even sentence. For example, the word “sun” has three phonemes. Those are /s/, /u/ and /n/.
b) Intonation
Based on Paultson and Bruder (1967), “intonation is the rising and the falling of the voices when people is speaking” (p.93). In a conversation, intonations are heard when the students as the speakers speak the words with rising or falling voice. There are two patterns of intonations, those are pattern 1. / 2 3 1 / and pattern 2. / 2 3 3 /.
Pattern 1. / 2 3 1 / Example:
2 3 1 I am going downtown.
2 3 1
I am going downtown tomorrow.
Pattern 2. / 2 3 3 / Example:
233
Are you Going? 233
Note:
: Falling Intonation : Raising Intonation c) Stress
Stress is a syllable which is uttered with more force or intensity than the others. So, stress will give a stress on a word when the speaker is speaking.
Example:
Extension: /ɪk’sten.tʃən/
d) Correcting Pronunciation Mistakes
Students will often make errors when they speak. The mistakes in speaking should be corrected by the students directly. Pautson and Bruder (1967) say that the corrections in pronunciation mistakes are similar to those in grammar correction (p. 115). In correcting pronunciation mistakes, the students will know immediately why they wrongly pronounce the English words and where their mistakes are.
3) Accuracy and Fluency
4) Interaction Effect
In a speaking process, there should be an interaction among the speakers (Paultson & Bruder, 1967). The interaction will raise a conversation in the speaking process. For example, when a student is having conversation with the teacher, they will have interaction with each other. They have to think what to say and how to say the statements.
5) Affective Factors
The teacher has an important role in the interaction with the students. The teacher has to know what should be given to the students in order that the students are brave enough to speak. Sometimes, the students keep their mouths closed when they should say something. In this situation, the teacher’s role is needed. The teacher has to motivate the students to be brave to speak (Paultson & Bruder, 1967).
6) The Growth of Speaking
Based on Brown (2007), “the growth of speaking is the terminology of words that is stated”. It means that the termnology or vocabulary in English has growth. The English evolves over time. Therefore, the students as the speakers must be able to follow and learn the terminology presented to complete or renew the language to communicate.
7) Genres of Spoken Language
genres of spoken language to the students. The genre can be found when the teacher is doing observation. If the students are not able to understand the teacher who spoke a complecated language, the teacher needs to simplify the language so that students can understand the conversation.
f. Phonetic Transcription
According to Ball and Rahilly (1996), phonetic transcription provides an easily accessible tool for examining articulator aspects of speech sounds (p. 140). English phonetic transcription helps the researcher to pronounce English words correctly. The researcher provides the phonetic transcription of the words that would be pronounced in implementing drilling session in the classroom. The researcher used Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary by Hornby (1995). The researcher uses the phonetic transcription to make the researcher easier to check the students’ pronunciation when they pronounce the English words provided. Table 2.2 shows the phonetic transcription of 30 English words in Cycle 1.
Table. 2.2 The Phonetic Transcription of 30 English words in Cycle 1 by Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary
No Words of Cycle 1 Phonetic Transcription
1. happen /ˈhæp. ə n/
2. look /lʊk/
3. go /gəʊ/
4. can /kæn/
5. ask /ɑːsk/
6. try traɪ/
7. need /niːd/
8. make /meɪk/
9. busy /ˈbɪz.i/
10. type /taɪp/
No Words of cycle 1 Phonetic Transcription
To enrich the students’ ability in having correct pronunciation, the researcher adds the English words that must be pronounced by the students of XI AP class. The students had to pronounce 40 English words based on their worksheets that will be inserted in the students’ exercises in Cycle 2. The researcher employs Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary by Hornby (1995). The researcher uses
the phonetic transcription to make the researcher easier to check the students’ pronunciation when they pronounce the English words provided.
Table. 2.3 The Phonetic Transcription of 40 English words in Cycle 2 by Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary
No Words of Cycle 2 Phonetic Transcription
No Words of cycle 2 Phonetic Transcription
15. glasses /glɑːses/
16. clean /kliːn/
17. folder /ˈfəʊl.də r /
18. keep /kiːp/
19. repair /rɪˈpeə r /
20. breakfast /ˈbrek.fəst/
21. search /sɜːtʃ/
22. use /juːz/
23. want /wɒnt/
24. know /nəʊ/
25. work /wɜːk/
26. tell /tel/
27. way /weɪ/
28. machine /məˈʃiːn/
29. worker /ˈwɜː.kə r /
30. do /du/
31. remember /rɪˈmem.bə r /
32. forget /fəˈget/
33. suggestion /səˈdʒes.tʃə n/ 34. office boy /ˈɒf.ɪs/ /bɔɪ/
35. person /ˈpɜː.s ə n/
36. room /ruːm/
37. move /muːv/
38. people /ˈpiː.pl ̩/
39. last /lɑːst/
40. queue /kjuː/
The researcher states some words in Cycle 1 that still should be pronounced in cycle 2. The researcher determines to state those words again by considering for the spelling and pronunciation of the words. Based on O’Neil (1988), it is unfortunate that the English orthography bears so little relation to Indonesian phonology. What is meant that the spelling does not directly reflect the way in a word is pronounced (p. 35). There are many English words, which are not pronounced as the spelling stated.
word suggestion should be pronounced by /sugestion/. However, in English language, the students should pronounce it by /səˈdʒes.tʃən/. Therefore, the students need to practice more in pronouncing many English words according to the English phonetic transcription.
4. Audio Lingual Method
Brown (2001) says that audio lingual method is a method which has a great deal with oral activity-pronunciation and pattern drills and conversation practice-with virtually none of grammar and translation found (pp. 22-23). In audio lingual method, the teacher does not use any translation of the sentences in the classroom. The teacher teaches grammar through their spelling and pronunciation to practice them to be accustomed to pronouncing English words by drilling technique. Using audio lingual method, the students are invited to have oral drills so that they can participate actively in the learning process.
One of techniques in audio-lingual method is drilling technique or oral drills. According to Harmer (2000) drilling technique is a technique in repeating structural pattern through oral practice. In this study, the students should repeat the structural pattern that is given by the teacher. Nunan (1999) says that dialogues are used for repetition and memorization . The correct pronunciation and stress are emphasized. After the students repeat the dialogues, specific grammatical in the dialogue will be the focus of the drilling technique.
Mechanical drill is a drill which there is a response which is complete from the students. In this situation, the students will have drill completely in pronouncing the English words, such as repeating from the teacher. Two kinds of mechanical drills are repetition drill and subtitution drill.
a. Repetition Drill
Repetitio drill is known as listen and repeat. Repetition drill is mainly used for modeling target language. The teacher says a word or a sentence loudly and students repeat it with correct pronunciation, stress and intonation. It is a good method because it means that students are given excellent of model pronunciation immediately before they were asked to respond (Russell, 2008). So, the teacher as the model of pronunciation gives some examples to the students and the students have to repeat it.
b. Substitution Drill
Substitution drill is when the teacher gives an example of sentence, then the researcher asks the students to change one or more words in it (Russell, 2008). By this method, students can check their sentences each other. They also have visual proof of how well they performed afterwards.
For example:
5. Curriculum in SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta
Hamalik (2008) states that curriculum is a set of lessons that must be taken by the students, so they can get a diploma (p. 3). It means that curriculum is a set of systems or lessons in school that must be learned by the students in order to get a certificate as a sign of graduation from the school. There is a set of lessons or subjects that must be undertaken by the students during their school.
Romine (1954) says that “curriculum is interpreted to mean all of the organized courses, activities, and experiences which have under direction of the school, whether in the classroom or not”. It means that in a curriculum, there is not only a set of subjects, but also covers the larger thing behind it. In the curriculum applied by the school, there are the activities called extra-curricular which can accommodate aspirations, inspiration and creativities of students, such as OSIS and scout. In the implementation of the curriculum, all activities must be done well indoor or outdoor that require the students to participate actively.
Based on the PPL (Praktek Pengalaman Lapangan) reports, the curriculum in Vocational High School is different from the curriculum in Senior High School because the lessons of materials in vocational high school focus more on vocational materials such as Accounting and Book keeping. In the senior high school, it contains materials and lessons which are more common as follows: Pancasila Education, Literature, Biology, Physics, Chemistry, Economics,
Sociology, Anthropology, Geography and History.
on Romine (1954), SBC, a development of the 2004 Curriculum, is Competency-Based Curriculum (CBC) and an operational curriculum conceived and developed in each unit of Education and the School Committee, which contains: Destination Education Unit, Structure and Content Curriculum Education Unit, Education Calendar, and Syllabus.
B. Theoretical Framework
In the theoretical framework, the researcher summarizes the theories and the benefits of the theories. The object observed in the study is the students of XI AP class of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta. The students are categorized as teens whose ages are between 15 up to 19 years old. The study uses theory of English for teens in order to know what kinds of assessments, stimulus, and the difficulty level of the tests which appropriate to the students. If the researcher knows the characteristics of students in their ages, the researcher will easily determine the appropriate inducement for the students.
Language is important to build a communication among people in the world. Students have to master in pronunciation of English words to communicate with the others because English is used internationally. The researcher states theory of teaching language to make sure that teaching language is important to be taught to the students. Theory of teaching guide the researcher to choose the appropiate level of language to communicate with the students.
have the ability to speak intelligibly to the others (p. 1). By having a good ability to speak such as mastering the pronunciation, the students will improve their skill in English speaking. Therefore, the researcher tries to help the students’ to improve their pronunciation.
In considering what kinds of speaking activities used in the classroom, the researcher needs to state the way of teaching in the classroom. The researcher mixes the teacher-centered learning and the students-centered learning to become the way of teaching. When the researcher determines the activities in drilling sessions, the researcher needs to use teacher-centered learning. It is because the researcher will be a model for the students to get the example of the correct pronunciation of English words. In the speaking activities, the researcher employs students-centered learning. It is aimed that the students will have choices to choose what they want to be in a role-play context.
The researcher uses theories of speaking to guide the researcher to check the students’ improvements in pronunciation. The speaking theories are also used to find the appropriate aspects to be scored in the students’ speaking test. Then, pronunciation point is stated to know the improvements of the students’ pronunciation. In this way, the aspects of pronunciation become the basic assessment of the study.
the words correctly. The phonetic transcription is the researcher’ guideline to drill the English words correctly to the students.
In finding the technique, the researcher uses the theory of Audio Lingual Method. By this method, the students are expected to be familiar with English words. The researcher chooses drilling technique in the Audio-Lingual Method. In drilling technique, the students should participate themselves actively in the learning process. Thus, the reason why the researcher uses the theory of drilling technique is to make the students participate actively in the classroom.
33 CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
In the Chapter 3, the researcher discusses the methodology used. The methodology is aimed to complete the data of the study in SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta. This chapter presents the research method, the research setting, the research participants, the instruments and data gathering technique, the data analysis technique, and the research procedure.
A. Research Method
The researcher focused on the implementation of drilling technique to the
XI AP students of SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta to improve their pronunciation.
The researcher applied classroom action research (CAR) as the methodology of the study. Classroom action research (CAR) is systematic inquiry with the goal of informing practice in a particular situation. “CAR is the way for researcher to discover what works best in the classroom situation. Thus, it allows decision about the best teaching method applied in the classroom.” (Mettetal, 2003).
There was a preliminary study conducted by the researcher. The preliminary study was done by observing the students twice, giving questionnaires to the students twice, and interviewing the English teacher of XI AP class once. The researcher conducted the first and the second observations on September 3rd and 5th, 2012, when the researcher had PPL (Praktek Pengalaman Lapangan) session. The researcher distributed the first questionnaire on October 24th, 2012 and the second questionnaire was on March 20th, 2013. Then, the interview session was also conducted on March 20th, 2013.
This study used the integration of two organizational schemes for the stage-by-stage process of action research by Kemmis and McTaggart (1988).
Figure 3.1 Action Research by Kemmis and McTaggart (1988)
four stages in each cycle of the stud, namely planning, acting, observing, and reflecting.
1. Plan Stage
Planning stage was the first stage in doing the study where the researcher started to identify the problem faced by the students of XI AP class. After having found the problem, that was the students had low pronunciation of English words, the researcher limited the topic. The limited topic was the students’ pronunciation which should be increased by technique. Next, in the study, the researcher chose drilling technique to be applied in the classroom to improve the students’ pronunciation. Then, the researcher provided the lesson plan for conducting the study.
2. Action Stage
After formulating the plan, the researcher continued to make the the learning scenarios or lesson plan to be applied in the class. In acting stage, the data were collected by conducting teaching learning process included observing, giving questionnaires, recording, and testing. The researcher collected the data while implementing the teaching learning process in the class.
3. Observation Stage
4. Reflection Stage
The researcher made reflection based on the data. The researcher checked whether the students’ pronunciation increased. Next, the researcher made the reflection on what had been going on and what part should be improved in the Cycle 1 as the basic facts to make some changes in the Cycle 2. The researcher made some changes and modifications to be applied in Cycle 2 optimally.
By implementing drilling technique, the researcher helped the students improve their pronunciation. The researcher used choral repetition drill in the study. Choral repetition drill is known as listen and repeat, or choral drills, are mainly used for modeling target language.
B. Research Setting
The study took place in SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta which is located in Jl. Cik Di Tiro No.37 Yogyakarta. The school is included into a vocational high school in Yogyakarta. SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta prepares the students to have a better skill to prepare the students for a certain job. The time allocation to conduct the study were April 24th, 25th, 29th and May 1st, 2013.
C. Research Participants
The researcher chose SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta as the object of this research because Sanata Dharma University had an agreement to send the researcher to teach and to observe the school. The session was called PPL or Praktek Pengalaman Lapangan session. Then, there were problems faced by the
The subject of the study was the Second Grade Students of Akuntansi Perkantoran (XI AP) class in SMK BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta. The students were not
accustomed to pronouncing English words because they seldom experienced pronouncing some English words. The researcher focused on the XI AP class for three reasons. First, the XI AP class was the first class observed. Second, when the researcher distributed questionnaires, the students said that they had difficulties in pronouncing English words. The last, the students of AP class are going to have a speaking test in their final exam. Therefore, the students needed help to speak in English with correct pronunciation.
There were some types of sampling in research. One kind of the samplings was purposive sampling. Based on Coyne (1997), purposive sampling is when the researcher selects the participants according to the needs of the students. The subjects were selected because of some characteristics. The characteristics of XI AP students were they had low pronunciation in English words. The researcher had also a purpose in conducting the research. The purpose was that the researcher would help the students solve their problems in pronouncing English words.
D. Instruments and Data Gathering Technique
1. Observations
Observation is data collection in which the situation of interest is watched and the relevant facts, actions and behaviors are checked (Rusell, 2008). The researcher used observation sheets to gather data of the beginning of the study to find students’ problems and needs. The researcher used observation to see the students’ activities until the end of the study to prove the improvement of the students’ pronunciation in the classroom. Through the observations stage, the researcher had the data about the class situations and the observations were conducted directly in the learning process.
There were two kinds of observation checklists in the learning process. The first was observation checklist for teacher’s activities and the second was observation checklist for the students’ activities. Those observation checklists were filled by three observers who helped the researcher to conduct the research. The observation checklist for teacher focused on the activities of the researcher in the teaching learning process. The observation checklist for students focused on the students’ responses to the activities.
2. Questionnaire
open-ended questions. In the close open-ended questions, the researcher would like to see the students’ difficulties in learning English. The researcher presented open-ended questions to see the students’ opinions about the difficulties. The third questionnaire was distributed to know the students’ opinions after they experienced drilling technique in the classroom after finishing the action stage in Cycle 2. The form of the third questionnaire was close-ended question. It made it easier for the researcher to check the result.
3. Interview
The researcher interviewed the English teacher of XI AP class. The interview was particularly useful for getting the information from a participant’s experience. According to Mcniff and Withhead (2002), the researcher could pursue in-depth information around the topic. Interview is a source of data that captures response of people to a certain situation (p. 96). The researcher used the interview session to get some data about the students’ characteristic to the English teacher before the researcher conducted the study. The researcher asked to the English teacher’s opinion about the students’ needs and difficulties in learning English.
4. Field Note
reflection on the study. The researcher wrote what was going on, what parts should be improved, what kinds of difficulties were found and how the students’ participation in the learning process were.
5. Speaking Test
In assessing the students’ improvements, the researcher used test to assess the students’ pronunciation improvements. Based on Carroll (1980), “speech is part of interactive chain and it is unreal to expect to be able to test it as in isolated language activities”. Actually, speaking was difficult to be assessed in the form of test. However, the researcher used oral tests to test the students’ pronunciation in each cycle. The tests were done orally and face to face with the researcher in the form of partnership.
In this study, the researcher used speaking test. So, the students had to perform two dialogues in pairs. The researcher recorded the performances. Later, the recordings would be played back to listen to the students’ pronunciation of certain words provided from the dialogues.
E. Data Analysis Technique
The researcher analyzed the data based on instruments provided. The instruments were interview, observations, questionnaires, field notes, and tests. 1. Interview
The researcher conducted an interview with the English teacher before the researcher implemented drilling technique in the classroom. The researcher used
Bahasa Indonesia in the interview session and the teacher answered it using
Bahasa Indonesia, too. The forms of the questions were opened-ended questions.
It was intended for the English teacher to explain the answers free. Based on the teacher’s explanation, the researcher got some information about the students’ difficulties in speaking and the students’ characteristics.
2. Observation Checklist
The observation checklist for the teacher and the students were filled by the researcher in the learning process. The three observers observed the researcher’s and the students’ activities in classroom. Later, the observation checklists showed whether the researcher and the students had done the interrelationships in the class completely. The researcher discussed the points in observation checklist one by one and gave some notes related to the statements. When the students joined all the activities, it meant that the students had already achieved the indicators of the lesson plan.
3. Questionnaire
difficulties in learning English. Then, the researcher distributed the third questionnaire to the students in the last session of the study in Cycle 2. The third questionnaire was distributed to know the students’ opinions to the classroom activities. Later, the researcher analyzed each point of the questions.
4. Field Note
There were two field notes which in Cycle 1 and Cycle 2. The field notes were filled by the researcher to reflect what had happened in the class, what had been going on and what part should be improved. The field notes supported the data in observation checklist. The field notes added some information about the implementation of drilling technique in classroom and also the students’ participation in the learning process.
5. Speaking Test
There were three tests in the study. The first test was the preliminary test which was conducted before implementing drilling technique to the students. The researcher used the test to check the students’ pronunciation. The second test was speaking test in Cycle 1 which contained 30 words which should be inserted in dialogue. The last test was the speaking test which contained 40 words which should be inserted in dialogue in Cycle 2.
researcher listened to the recording to analyze the students’ speaking performances.
The researcher focuses on the students’ pronunciation. To check the students’ pronunciation improvements, the researcher listens to their phonemes, intonation, stress, and accuracy when they are pronouncing the English words provided. The researcher checks the students’ pronunciation when they are doing their performances one by one for each word provided. Based on the data, the researcher makes the percentages of each student’s pronunciation in the element of pronunciation in Cycle 1 and Cycle 2. Then, the percentages of each element in Cycle 1 are compared to the percentages of each element in Cycle 2 to see the students’ pronunciation improvements in each element.
Figure 3.2 shows how to find the percentages of the elements in students’ pronunciation to see the pronunciation improvements.
∑
P = --- X100% S
Figure 3.2 The Percentage of the Elements in Students’ Pronunciation Abilities to See the Pronunciation Improvements
Notes:
P : The percentage of each element of pronunciation ∑ : The number of the correct word of each element S : The number of the words provided