Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- Maryadi, S.Pd
- Pengajar:
- Drs. H. Mustaghirin Amin, M.BA
- Arie Wibowo Khurniawan, S.Si. M.Ak
- Arfah Laidiah Razik, S.H., M.A.
- Sekolah: Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan
- Mata Pelajaran: Teknik Mekatronika
- Topik: Modul Pneumatik Dengan Aplikasinya
- Tipe: module
- Tahun: 2017
- Kota: Jakarta
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. Introduction
The module on Pneumatics provides a comprehensive overview of the principles and applications of pneumatic systems, essential for students in vocational high schools (SMK) specializing in Mechanical Engineering. It aims to equip learners with the foundational knowledge required to understand and utilize pneumatic systems effectively. The introduction outlines the standard competencies expected from students, the time allocation for learning, and the prerequisites necessary for engaging with the module. By establishing clear educational objectives, the module prepares students for practical applications in the industrial sector.
II. Learning Activities
This section details the structured learning activities designed to reinforce students' understanding of pneumatic principles. It includes three main learning activities: the basics of pneumatics, components of pneumatic systems, and circuit diagram representations. Each activity is allocated specific hours, ensuring a systematic approach to learning. The activities emphasize hands-on experiences and critical thinking, enabling students to apply theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios, thus enhancing their skills in the field of mechatronics.
2.1 Learning Activity 1: Basic Principles of Pneumatics
This subsection covers the fundamental concepts of pneumatics, including the characteristics of compressed air and its applications in various mechanical movements. Students learn about the advantages and limitations of pneumatic systems, fostering a critical understanding of their operational principles.
2.2 Learning Activity 2: Components of Pneumatic Systems
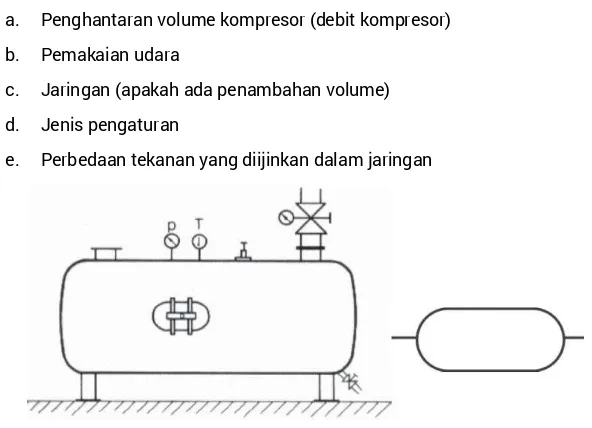
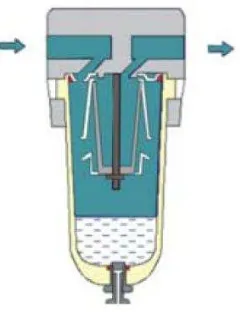
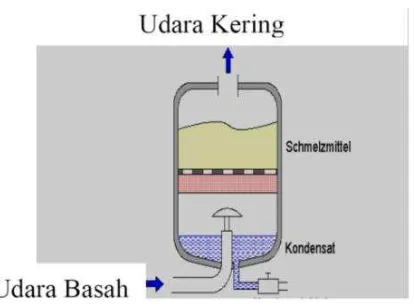
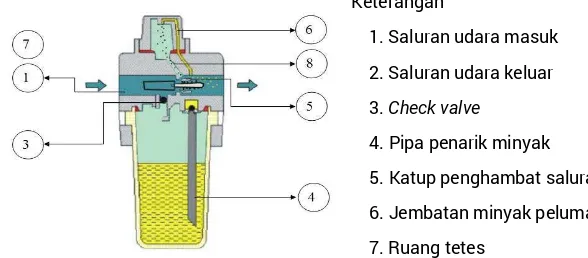
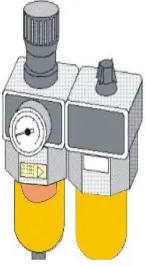
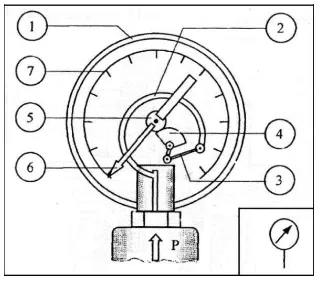
Students explore various pneumatic components such as compressors, valves, and actuators. This section provides detailed descriptions and functions of each component, enabling students to identify and utilize them effectively in real-world applications.
2.3 Learning Activity 3: Circuit Diagram Representation
This activity focuses on the graphical representation of pneumatic circuits. Students practice drawing and interpreting circuit diagrams, which is crucial for troubleshooting and designing pneumatic systems in industrial settings.
III. Evaluation
The evaluation section outlines the assessment methods used to measure students' understanding of pneumatic systems. It includes formative assessments such as quizzes and practical tests, ensuring that students can demonstrate their competencies in both theoretical knowledge and practical applications. The evaluations are designed to align with the learning objectives, providing a clear framework for assessing student performance and ensuring that they meet the required standards.
IV. Conclusion
The module concludes with a summary of the key concepts covered and their relevance to the field of mechatronics. It reinforces the importance of pneumatic systems in modern industrial applications and encourages students to continue exploring advanced topics in this area. The conclusion serves to motivate students by highlighting the practical implications of their learning and the potential career opportunities available in the field.
V. References
This section lists the resources and literature used to compile the module, providing students with additional materials for further study. The references include textbooks, academic journals, and online resources that are pertinent to the study of pneumatics and its applications in engineering.
Referensi Dokumen
- Fundamentals Of Pneumatic Control Engineering - Textbook ( J.P. Hasebrink, R.Kobler )
- Hidrolika dan Pneumatika ( Andrew Parr )
- Pneumatik Basic Level ( Croser, P & Ebel, F )
- Pneumatic System Principles and Maintenance ( Majumdar )
- Pengantar Teknik Pneumatika ( Patient, P., dkk. )