ASSESSMENT OF AUTHENTIC LEARNING SOCIAL STUDIES
THROUGH PROJECT BASED LEARNING STUDENTS
ELEMENTARY SCHOOL TEACHER EDUCATION
Naniek Sulistya Wardani, S.PD., M.Si.
Study Program Elementary School Teacher Education Faculty of Teacher Training and Education
Satya Wacana Christian University [email protected]
Abstract
This study aims to determine how to assess authentic learning social studies through project-based learning (PBL) approach students Elementary School Teacher Education (PGSD).
This research is descriptive research. The data collection technique was an observation and focus group discussion (FGD). Data are analyzed qualitative and quantitave. Subjects of this research were student PGSD in Salatiga year to 3 as many as 33 students.
The research result showed that: one of the most important thing for improving competency student, spesialy students of PGSD is innovation in teaching. PBL can improve the competency of PGSD, because for PBL steps include (1) Starts With the Essential Question; (2) Design a Plan for the Project; (3) Creates a schedule teachers and learners collaboratively; (4) Monitor the students and the progress of the project; (5) Assess the outcome and (6) Evaluate the Experiences. As for the competency owned by students is good.
Asses authentic learning using the balance assessment consisting of traditional assessment using tests (fokus cognitif), assessment using the portfolio teamwork and opinions (focus process) and reports (focus product), as well as performance appraisal using the assessment rubric skill to read, write, presentations, and literacy. The test results of social studies, the lowest score is 69.95 the highest score is 96.45, with an average of 83.04. While social studies assessment results with the assessment rubric with pretty good category is writing and literacy which has mean of 3,23 and 2,7, good categories are reading, report and presentation which has mean score of 3,83; 3,97 and 4,15; and teamwork and opinions which has mean score of 4,56 and 4,55 is included in the very good category. Mean score assessment which has a total average value of 3,85 is included in the good category, it means that students of PGSD have assess is good.
Keywords: assessment of authentic learning, social studies, project based learning.
1. Introduction
In the classroom, each student has a different learning character from one another, because of
to change their teaching and assessment practices by varying the content they teach, the process students use to learn the content, and the products the require students to produce to prove they have met the standards.
According to UNESCO, education should be built with the four pillars, namely learning to know, learning to do, learning to be and learning to live together. Education is not only oriented towards purely academic, but also put it into practice to solve the problems of everyday life.
Real problems in life are studied in social studies. Social studies or Ilmu Pengetahuan Sosial (IPS) is one of the lessons which are started from SD/MI/SDLB to SMP/MTs/SMPLB. The IPS learning discusses a lists of events, facts, concepts, and generalizations those related with social issues so that the IPS learning scope is so wide those consists of place, time, social system, and behavior. Hence, one of the IPS learning goal formulations is to have a basic skill on logical and critical thinking, curiosity, inquiry, problem solving, and skill in the social life (Government Regulation Number 22 Year 2006 about Standard Contents).
The consequence of the learning implementation is the teacher should involve the students to be active. It is in line with shifting and changing in the education paradigm, from the old paradigm that emphasize on behavioristic in the teaching-testing form into the new paradigm that emphasize on the constructivistic process in the form of learning-continuous- improvement.
Learning process is directed on the learning experience to arrange and make a work or to create a new idea through the application of a set of events, facts, concepts, and generalizations on the social issues in the social environment, so the basic competence can work effectively. This learning experience provides an essential meaning. Therefore, the need to design appropriate learning using PBL approach.
PBL involves students to learn actively. The entire learning activity starts from the learning process and the learning outcomes required appropriate assessment, which can measure all good student activity which includes cognitive, affective and skills.
Assessments to become an integral part of the instructional process. Teachers need to change their approach in three important ways. They must (1) use assessments as sources of information for both students and teacher, (2) follow assessments with high-quality corrective instruction, and (3) give students second changes to demonstrate success. Teachers must think about and use assessments differently than their teachers did. (Guskey, 2007, pp. 16-17).
Traditional assessments do not measure the entire ability of learners. Traditional assessments
do not test many skills and abilities students need to be successful. Students must be prepared to do more than memorize information and use algorithms to solve simple problems. In lessons, students are expected to be able to practice higher-order thinking skills, and and think critically
Early theories of learning indicated that educators needed to use a "building blocks of knowledge” approach whereby students acquired complex higher order skills by breaking learning down into a series of skills (Kay Burke, 2009, 5).
Results of the lessons, students who scored poorly on standardized tests usually be assigned to the remedial or basic skills classes to master those essential basic skills before being exposed to the more challenging and motivation complex thinking skills. In other words, learning approach used could not handle the rigor and they went to the "time out" programs, or grades until students showed they could "merge" back into the regular classes.
Popham (2001, 20) believes that incessant "skill and drill" often turns into "drill and kill". He believes that repetitious instructional activities tend to deaden students genuine interest in learning. Chen and Mc Namee (2007) say, “For classroom teachers, assessment is the process of listening, observing, and gathering evidence to evaluate the learning and development of children in the classroom context”. Archbald and Newmann (1988, 1) describe the term authentic assessment as follows, A valid assessment system (that) provides information about the particular tasks on which students succed or fail, but more important, it also presents tasks that are worthwhile, significant, and meaningful in short authentic”.
Social studies is the science that studies the relationship between human integrated approach. Thus, assessment authentic is done through a learning process that involves the student directly using PBL.
The problem is how to assess authentic learning social studies through PBL approach students PGSD.
2 References
2.1 Authentic assessment
A commonly advocated best practice for classroom assessment is to make the assessments authentic (Bruce B. Frey., Vicki L. Schmitt, and Justin P. Allen. 2012). Authentic is often used as meaning the mirroring of real-world tasks or expectations.
presents tasks that are worthwhile, significant, and meaningful in short authentic”.
Shulman (1988) said, teachers need to combine various methods of assessment so that the strengths of one offset the limitations of the other.
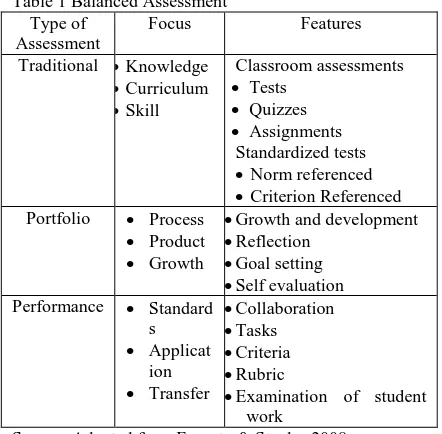
Each single measurement by itself is insufficient to provide a true portrait of the student or learner. If educators combine standardized and teacher made tests measuring knowledge and content with portfolios measuring process and growth, and performances measuring application, they will provide a more accurate portrait of the individual learner. Fogarty and Stoehr (2008) discuss the balanced assessments, and performance assessments and subsequently meet the needs of all students. See table 1.
Table 1 Balanced Assessment Type of
Assessment
Focus Features
Traditional Knowledge Curriculum Skill
Classroom assessments Tests
Quizzes Assignments
Standardized tests Norm referenced Criterion Referenced Portfolio Process
Product Growth
Growth and development Reflection
Goal setting Self evaluation Performance Standard
s Applicat
ion Transfer
Collaboration Tasks Criteria Rubric
Examination of student work
Source: Adapted from Fogarty & Stoehr. 2008.
Authentic assessment aims to evaluate students' abilities in 'real-world' contexts. In other words, students learn how to apply their skills to authentic tasks and projects. Authentic assessment does not encourage rote learning and passive test-taking. Instead, it focuses on students' analytical skills; ability to integrate what they learn; creativity; ability to work collaboratively; and written and oral expression skills. It values the learning process as much as the finished product.
Authentic assessment in the classroom
Authentic assessment utilizes performances samples-learning activities that encourage students to use higher-order thinking skills. There are five major types of performance samples:
a. Performance Assessment
Performance assessments test students' ability to use skills in a variety of authentic contexts. They frequently require students to work collaboratively and to apply skills and concepts to solve complex problems. Short- and long-term tasks include such activities as:
writing, revising, and presenting a report to the class
conducting a week-long science experi ment and analyzing the results
working with a team to prepare a position in a classroom debate.
b. Short Investigations
Many teachers use short investigations to assess how well students have mastered basic concepts and skills. Most short investigations begin with a stimulus, like a math problem, political cartoon, map, or excerpt from a primary source. The teacher may ask students to interpret, describe, calculate, explain, or predict. These investigations may use enhanced multiple-choice questions. Or they may use concept mapping, a technique that assesses how well students understand relationships among concepts.
c. Open-Response Questions
Open-response questions, like short investigations, present students with a stimulus and ask them to respond. Responses include:
a brief written or oral answer a mathematical solution a drawing
a diagram, chart or graph
d. Portfolios
A portfolio documents learning over time. This long-term perspective accounts for student improvement and teaches students the value of self-assessment, editing, and revision. A student portfolio can include:
journal entries and reflective writing peer reviews
artwork, diagrams, charts, and graphs group reports
student notes and outlines rough drafts and polished writing
e. Self-Assessment
Self-assessment requires students to evaluate their own participation, process, and products. Evaluative questions are the basic tools of self-assessment. Students give written or oral responses to questions like:
What was the most difficult part of this project for you?
What do you think you should do next? If you could do this task again, what would you
do differently?
What did you learn from this project?
Educators often use rubrics, or established sets of criteria, to assess student work.
Because authentic assessment emphasizes process and performance, it encourages students to practice critical-thinking skills and to get excited about the things they are learning.
Types of Authentic Assessments
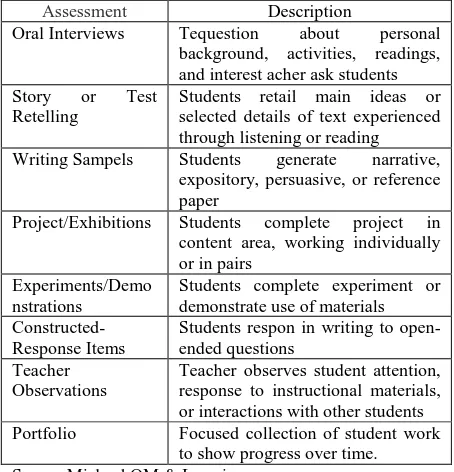
Authentic assessments include a variety of measures that can be adapted for different situations. These are some examples of authentic assessment. See table 2
Table 2 Type Authentic Assessment
Assessment Description
Oral Interviews Tequestion about personal background, activities, readings, and interest acher ask students Story or Test
Retelling
Students retail main ideas or selected details of text experienced through listening or reading Writing Sampels Students generate narrative,
expository, persuasive, or reference paper
Project/Exhibitions Students complete project in content area, working individually or in pairs
Experiments/Demo nstrations
Students complete experiment or demonstrate use of materials
Constructed-Response Items
Students respon in writing to open-ended questions
Teacher Observations
Teacher observes student attention, response to instructional materials, or interactions with other students Portfolio Focused collection of student work
to show progress over time. Source Michael OM & Lorraine
2.2 Project-based learning (PBL) Approach PBL refers to any programmatic or instructional approach that utilizes multifaceted projects as a central organizing strategy for educating students. When engaged in project-based learning, students will typically be assigned a project or series of projects that require them to use diverse skills such as researching, writing, interviewing, collaborating, or public speaking to produce various work products, such as research papers, scientific studies, public-policy proposals, multimedia presentations, video documentaries, art installations, or musical and theatrical performances, for example. The execution and completion of a project may take several weeks or months, or it may even unfold over the course of a semester or year.
Closely related to the concept of authentic learning, PBL experiences are often designed to address real-world problems and issues, which requires students to investigate and analyze their complexities, interconnections, and ambiguities. Students also typically learn about topics or
produce work that integrates multiple academic subjects and skill areas.
In this case, even if the project is assigned in a science course, students may be required to read and write extensively (English); research local history using texts, news stories, archival photos, and public records (history and social studies); conduct and record first-hand scientific observations, including the analysis and tabulation of data (science and math); and develop a public-policy proposal for the conservation of the ecosystem (civics and government) that will be presented to the city council utilizing multimedia technologies and software applications (technology).
In PBL, students are usually given a general question to answer, a concrete problem to solve, or an in-depth issue to explore. Teachers may then encourage students to choose specific topics that interest or inspire them, such as projects related to their personal interests or career aspirations.
PBL goes beyond generating student interest. Well-designed projects encourage active inquiry and higher-level thinking (Thomas, 1998). Brain research underscores the value of these learning activities. Students' abilities to acquire new understanding are enhanced when they are "connected to meaningful problem-solving activities, and when students are helped to understand why, when, and how those facts and skills are relevant" (Bransford, Brown, & Conking, 2000, p. 23).
PBL is an instructional model that involves students in investigations of compelling problems that culminate in authentic products. Projects that make for stronger classroom learning opportunities can vary widely in subject matter and scope, and can be delivered at a wide range of grade levels. Nonetheless, they tend to share defining features. Projects grow out of challenging questions that cannot be answered by rote learning. Projects put students in an active role such as: problem solver, decision maker, investigator, or documentarian. Projects serve specific, significant educational goals; they are not diversions or adds-ons to the "real" curriculum.
Buck Institute for Education (BIE) said, PBL is a model for classroom activity that shifts away from the usual classroom practices of short, isolated, teacher-centred lessons. PBL activities are long-term, interdisciplinary, student-centred, and integrated with real-world issues and practices.
enables the teacher to manage classroom learning with work involving the project. Project work based problems and requires students to design, solve problems, make decisions, conduct investigations, and to provide opportunities for students to work independently.
According to the definitions found in PBL handbooks for teachers, projects are complex tasks, based on challenging questions or problems, that involve students in design, problem-solving, decision making, or investigative activities; give students the opportunity to work relatively autonomously over extended periods of time; and culminate in realistic products or presentations (Jones, Rasmussen, & Moffitt, 1997; Thomas, Mergendoller, & Michaelson, 1999).
Other defining features found in the literature include authentic content, authentic assessment, teacher facilitation but not direction, explicit educational goals, (Moursund, 1999), cooperative learning, reflection, and incorporation of adult skills (Diehl, Grobe, Lopez, & Cabral, 1999). To these features, particular models of PBL add a number of unique features.
PBL is an instructional approach that involves students in investigations of compelling problems that culminate in authentic products (Wardani Naniek Sulistya, 2013).
Steps in PBL as developed by The George Lucas Educational Foundation (2005) consists of: a. Starts With the Essential Question
b. Design a Plan for the Project c. Creates a Schedule
d. Monitor the Students and the Progress of the Project.
e. Assess the Outcome. f. Evaluate the Experiences.
Inside, conclution Heide Spruck Wrigley (1998) in his research below:
In the meantime, we may have to take the project-based learning on faith and see it as a promising approach that are acts much of what we know about the way adults learn.
2.3 Social Studies
The IPS learning discusses a lists of events, facts, concepts, and generalizations those related with social issues so that the IPS learning scope is so wide those consists of place, time, social system, and behavior.
Social studies seeks to examine and understand communities, from the local to the global, their various heritages, physical systems, and the nature of citizenship within them. Therefore, social studies discuss social and physical environment.
3. Research Methodology
Research is a descriptive research. The data used are primary data, where researchers must
collect data through observation and focus group discussion (FGD). Data are analyzed qualitatively. Subjects of this research are student PGSD second semester student. Research variable was the PBL and assessment of authentic learning. The stages of PBL are (1) the essential question; (2) design a plan the project; (3) creates a schedule; (4) monitor the students and the progress of the project; (5) assess the outcome and (6) evaluate the experiences.
Authentic learning assessment consists of (1) reading authentic materials texbok; (2) writing for an audience (report); (3) communicating of the classroom (presentation); (4) teamwork; and (5) giving to one's opinions (opinions), and (6) literacy.
4. Results and Discussion
This study aims to determine how to assess authentic learning social studies through PBL approach students PGSD
Social studies learning with PBL approach using the following steps
a. The Essential Question. Learning begins with the essential question about environment. b. Design a Plan for the Project. Learners are
expected to made observation sheet and angket c. Creates a Schedule.Teachers and learners
collaboratively construct a schedule activities in the form of a field study.
d. Monitor the Students and the Progress of the Project. Students collect data in the field. Teacher is responsible for monitoring the conduct activities.
e. Assess the Outcome. In the assessment, the lecturer make observations on the activity of the students in the data collection .
f. Evaluate the Experiences. Teachers and learners to reflect on the activities and results of the project. The process of reflection is done either individually or in groups.
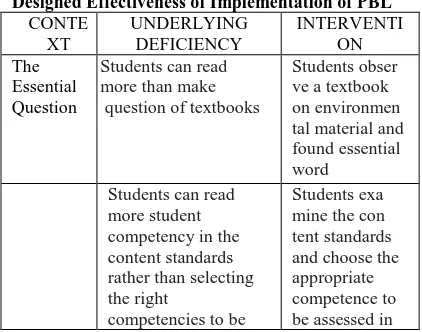
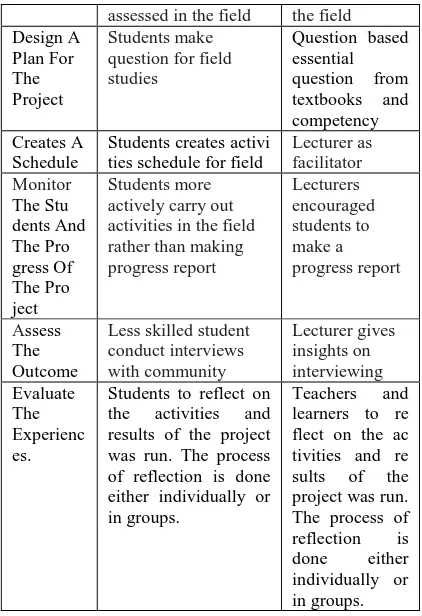
Design effectiveness of implementation of PBL is presented by Table 3 below.
Table 3
Designed Effectiveness of Implementation of PBL CONTE
Students can read more than make question of textbooks
assessed in the field the field ties schedule for field
Lecturer as activities in the field rather than making either individually or in groups.
Authentic assessment is provides information about the particular tasks that are worthwhile, significant, and meaningful in short authentic, and related to real life provide the relevance students need to find meaning in what they are studying.
The task of social studies given in the form of a field study of the environment. The one's opinions and (6) literacy.
Implementation assess is combine various methods of assessment so that the strengths of one offset the limitations of the other, which are called balanced assessments. Balanced assessment in the research consists of assessment tradisional for focus test (knowledge) and rubric reading, writing, presentation and literacy (skill), assessment portfolio for focus teamwork and giving opinion (proses) dan report (product), and assessment performance focus standards (tasks, criteria, rubric). See table 1.
From the class interval, it is known that the thresholds of each class and then the value of each student will be included as in Table 3
The results PGSD student have score of the authentic assessment are presented in Table 4 below:
Table 4
Categories of the score rubric (Reading, Writing, Presentation, Literacy, Teamwork, Opinion and Report)
Interval Category Value 4,21<mean≤5,00 Very good 5 3,41<mean≤4,20 Good 4 2,61<mean≤3,40 Pretty good 3 1,81<mean≤2,60 Poorly 2 1,00<mean≤1,80 Not good 1
Result authentic assessment from assess rubric are presented in Table 45 below:
Table 5
Result Authentic Assessment from Assess Rubric
N
Total Average Value 3,85 Good
Based on table 5, student has score assessment which has a total average value of 3,85 is included in the good category, it means that students of PGSD have assess is good. Meanwhile, in detail, each of the indicators is as follows: Student has score for writing which has mean of 3,23 and mean score literacy 2,7 is included in the pretty good category, it means that students of Ele PGSD have assessment score is pretty good. In addition, for reading, report and presentation which has mean value of 3,83; 3,97 and 4,15 is score is very good.
The test results of social studies, the lowest score is 69.95 the highest score is 96.45, with an average of 83.04.
Implementing PBL in Elementary School Teacher Education
In PBL. teachers are facilitators who help students if they ask for it. A PBL teacher acts more as a resource, than a disseminator of information. PBL challenges students to solve problems, become decision makers and presenters rather than remaining passive listeners. Students learn teamwork, communication and collaboration as well as critical thinking and problem solving. Students will be able to present their ideas or results to their peers, parents and community.
manage a complex project in a limited amount of time, and how to collaborate with members of a group.
(http://darkwing.Uoregon.edu/moursund/PBL/). In the following I will introduce my concept of how to implement PBL in students of PGSD in the second semester.
First step, think about the goals, what you want your students to know, to learn, and to be able to do. The goals are based on the curriculum is examine the interaction between physicall and social environment. In this step the students were asked to formulate the problem the interaction between physicall and social environment. The problem in terms of the arts, culture, technology, economics and law. From this activity, it appears the entire group can formulate the problem correctly. This is the first step in the PBL, is starts with the essential question. Learning begins with the essential question, namely the question which can give students assignments in conducting a activity.
Step 2 is design a plan for the project. Students makes planning for the project. Student makes instrument observation sheet for observation natural phenomenon, and students make a questionnaire about local economic activity, students perform mapping of attractions in Pacitan , and student identification regulations around sights. Planning is done collaboratively between teachers and learners. Thus learners are expected to be felt "Have" for the project. Then,
Step 3, students creates a schedule for field study. Teachers and learners collaboratively construct a schedule activities to complete the project for one day. The next step, monitor the students and the progress of the project. Teacher is responsible for monitoring the conduct activities for learners completing the project, and student construct the progress of the project is field study. So all the activities done by the students, always monitored by the lecturer and were scored as assessment materials.
Step 5 is to assess the outcome
The authentic assessment was conducted to assist teachers in measuring achievement standards, a role in evaluating the progress of each student, provide feedback on the level of understanding that has been achieved learners, assist teachers in developing learning strategies next. In step 5, all groups can report progress in a timely and complete reports as a reference is given.
The final step is evaluate the experiences. Teachers and learners to reflect on the activities and results of the project was run. The process of reflection is done either individually or in groups. The results obtained from this final step is the student has gained a lot of experience, ranging from reading, to formulate the problem,
make a plan of field studies, preparing instruments, collecting data, analyzing the data, create reports and make revisions. Although the results are not optimal in substance, but the spirit, motivation and curiosity of the students is very high. Basing on the above results, the PBL is implemented by the students well and smoothly.
The advantages gained from PBL are :
PBL gives students a more “integrated”
understanding of the concepts and knowledge they learn, while also equipping them with practical skills they can apply throughout their lives. The interdisciplinary nature of PBL helps students make connections across different subjects, rather than perceiving, for example, math and science as discrete subjects with little in common.
Because PBL mirrors the real-world situations students will encounter after they leave school, it can provide stronger and more relevant
preparation for college and work. Student not only acquire important knowledge and skills, they also learn how to research complex issues, solve problems, develop plans, manage time, organize their work, collaborate with others, and persevere and overcome challenges.
PBL reflects the ways in which today’s
students learn. It can improve student engagement in school, increase their interest in what is being taught, strengthen their motivation to learn, and make learning experiences more relevant and meaningful. Since PBL represents a more flexible approach
to instruction, it allows teachers to tailor assignments and projects for students with a diverse variety of interests, career aspirations, learning styles, abilities, and personal backgrounds.
PBL allows teachers and students to address multiple learning standards simultaneously. Rather than only meeting math standards in math classes and science standards in science classes, students can work progressively toward demonstrating proficiency in a variety of standards while working on a single project or series of projects.
Disadvantages obtained from PBL are :
PBL may not ensure that students learn all the required material and standards they are expected to learn in a course, subject area, or grade level. When a variety of subjects are lumped together, it’s more difficult for teachers to monitor and assess what students have learned in specific academic subjects.
learning of learning progress and schools may not have the funding, resources, and
capacitythey need to adopt a PBL model. The projects that students select and design
may vary widely inacademic rigor and quality. PBL could open the door to watered-down learning expectations and low-quality coursework.
PBL is not well suited to students who lack self-motivation or who struggle in less-structured learning environments.
PBL raises a variety of logistical concerns, since students are more likely to learn outside of school or in unsupervised settings, or to work with adults who are not trained educators.
Learning social studies were designed using the PBL approach, consequence assessment to assess authentic learning. Outcome PBL authentic approach and the assessment can improve the effectiveness of learning and increase student competence.
5. Conclusion
It is argued that one of the most important thing for improving competency student, spesialy students of PGSD is innovation in teaching. PBL can improve the competency of PGSD, because for PBL steps include (1) Starts With the Essential
Question; (2) Design a Plan for the Project; (3) Creates a schedule teachers and learners collaboratively; (4) Monitor the students and the progress of the project; (5) Assess the outcome and (6) Evaluate the Experiences. As for the competency owned by students is good.
Asses authentic learning using the balance assessment consisting of traditional assessment using tests (fokus kognitif), assessment using the portfolio teamwork and opinions (focus process) and reports (focus product), as well as performance appraisal using the assessment rubric skill to read, write, presentations, and literacy.
The test results of social studies, the lowest score is 69.95 the highest score is 96.45, with an average of 83.04. While social studies assessment results with the assessment rubric with pretty good category is writing and literacy which has mean of 3,23 and 2,7, good categories are reading, report and presentation which has mean score of 3,83; 3,97 and 4,15; and teamwork and opinions which has mean score of 4,56 and 4,55 is included in the very good category. Mean score assessment which has a total average value of 3,85 is included in the good category, it means that students of PGSD have assess is good.
REFERENCES
[1] Archbald, D. A., and Newman, F. M. 1988. Beyond Standardized Testing Assessing Authentic Academic Achievement in the Secondary School. Madison: University of Wisconsin, National Association of Secondary Principals.
[2] Bransford, Brown, & Conking, 2000. How people learn: Brain, mind, experience, and school. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
[3]Bruce B. Frey., Vicki L. Schmitt, and Justin P. Allen. 2012. Defining Authentic Classroom Assessment. Practical Assessment, Research and Evaluation. Volume 17, Number 2, January 2012.
[4]Chen and Mc Namee. 2007. Bridging Assessment for Teaching and Learning in Early Childhood Classroom, PreK-3. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin.
[5]Diehl, W., Grobe, T., Lopez, H., & Cabral, C. 1999. Project-based learning: A strategy for teaching and learning. Boston, MA: Center for Youth Development and Education, Corporation for Business, Work, and Learning.
[6]Ellysa Aryani. 2012. The Value of Project Based Learning in Primary School Indonesian Language. Proceeding International Seminar Faculty of Teacher Training and Education. Salatiga: Faculty of Teacher Training and Education Satya Wacana Christian University. 2012. pp 119
[7]Fogarty, R., and Stoehr, J. 2008. Integrating Curricula with Multiple Intelligences Teams, themes, and Threads (2nd ed.) Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin.
[8]Guskey, T.R. 2007. Using Assessments to Improve Teaching and Learning. In D. Reeves (Ed.). Ahead of the curve: The Power Of Assessments To Transform Teaching And Learning. Bloomington, In: Solution Tree.
[9] https://www.teachervision.com/teaching- methods-and-management/educational-testing/4911.html?page=1&2
[10] Jones, B. F., Rasmussen, C. M., & Moffitt, M. C. 1997. Real-life problem solving.: A collaborative approach to interdisciplinary learning. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
[11] Kay Burke. 2009. How to Assess Authentic Learning. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin.
[12] Michael O’Malley, J., & Lorraine Valdez Pierce. Authentic Assessment for English Language Learner Practical Approaches for Teachers. www.doe.in.gov/ englishlanguagelearning [13] Moursund, D. 1999. Project-based learning using
[14] Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan Nasional Republik Indonesia. 2006. No. 22 Standar Isi. Jakarta: Badan Nasional Standar Pendidikan.
[15] Popham, W.J. 2001. Teaching to the test? Educational Leadership. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
[16] The George Lucas Educational Foundation. 2005. Instructional Module Project Based Learning.
Retrieved July 10, 2007 from
http://www.edutopia.org/modules/PBL/whatpbl.p hp
[17] Thomas, J. W., Mergendoller, J. R., and Michaelson, A. 1999. Project-based learning: A handbook for middle and high school teachers. Novato, CA: The Buck Institute for Education.
[18] Thomas, J.W. 1998. Project-based learning: Overview. Novato, CA: Buck Institute for Education.
[19] Wardani Naniek Sulistya. 2013. The Effectiveness Of Inquiry Learning ApproachTowards The Enhancement Character Building Of 4th Grade Social Study Subject (IPS) Students Of Elementary School. Proceeding International Seminar On Primary Education (ISPE) PGSD and DIKDAS Study Programs. Yogyakarta: Primary Education and Elementary School Teacher Education.