1
Phylogenic Tree Analysis of Angus Grade Cattle
Dwi Ahmad Priyadi
1, Yudi Adinata
2, Tety Hartatik
1,*1 Department of Breeding and Animal Reproduction Faculty of Animal Science, Universitas
Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta 66281, Indonesia,
2Loka Penelitian Sapi Potong, Grati, Pasuruan 6714, Indonesia
Corresponding author: [email protected]
Abstract: Studies about Indonesian cattle genetic purity should be encourage to determine the value of blood relationship and ancestors prediction, so the effort to improve livestock quality could be done correctly. This can be done by studies based on Cytochrome b gene that is only inherited maternally. The samples are 15 Angus Grade cattles from Sragen, Central Java, which have been reared since 1980s. The comparative datas were 54 Cytochrome b gene reference sequences from various breeds and countries (GenBank). The phylogenetic tree arranged by Mega 6 software with maximum likelihood method (Bootstrap values 1000, Tamura-Nei parameter) used 8 out-group Cytochrome b genes sequence comparators (GenBank). The results obtained that the Angus grade cattle had 2 branches ancestors, that branch belongs to Banteng (Bos javanicus) and branch belong to Domestic Cattle (Bos indicus; Bos taurus), with majority of the sample (n=13) were at the Banteng branch. The result indicates that most of Indonesian cattle presently, both crosses and local, had Banteng maternal ancestor and a small portion had close ancestor with Bos indicus or Bos taurus. Strong presumption that ancestors of native cattle in Indonesia and the surrounding regions are species of Bos javanicus, Bos sauveli,
Bos grunniens and Bos frontalis.
Keywords: Angus grade cattle, Banteng, cytochrome b, maximum likelihood tree, Indonesian cattle, the phylogenetic tree
Introduction
Studies related to the phylogenetic relationship and predictions ancestors of livestock is needed to
support the conservation efforts of a livestock breed as well as the development of cattle breeding.
One technique that developed to determine the degree of organism kinship is the genetic material
comparison technique, with the understanding that there are evolution rate and specialization rate of
a population, phylogenetic tree based on genetic material can reconstruct kinship, and maximum
likelihood method appropriately used in a scientific context by this time (Aprilanto and Sembiring,
2016). Genetic material in an eukaryotic organism divided into genetic material in the nucleus
(nuclear DNA) and genetic material in the mitochondria (mtDNA), studies on mtDNA is frequently
used to determine the rate of evolution, migration of population and relationship of organism (Karp,
2010), because mitochondria are inherited only from maternal lines (Griffith et al., 2005).
Cytochrome b (Cyt b) gene is mtDNA that frequently used for determine the genetic relationship in
2
the result of crossbreeding between Indonesian local cattle in Sragen region of East Java with
Angus cattle since the 1980s, this is similar to the development of Brangus cattle with the final
results of blood composition was 5/8 Angus and 3/8 Brahman (Neser et al., 2012). Cattles that exist
today can not be denied were from the domestication of wild cattle, during the domestication
process the genetic selection rate will occur towards the desired trait for human (Diamond, 2002).
The materials of this study were Cyt b gene of 15 Angus grade cattle, with comparator datas were
54 sequences (GenBank) Cyt b gene from various countries and various cattle breeds.
Material and Method
Sample collection and DNA isolation
Genome DNA obtained from the whole blood of 15 Angus grade cattle reared in Sragen regency,
Central Java province. Blood sampling using vacuum tubes containing K3EDTA (BD vacuntainer).
Isolation of DNA performed using Extaction Kit (Genetic Science) in the Laboratory of Genetics
and Animal Breeding Faculty of Animal Science UGM. The quality of the isolation product
determined using gel electrophoresis (1%), the thick and clearly DNA bands was the prefered result
(Lee et al., 2012). Fifty-four GenBank sequence comparison of various countries (Cambodia,
America, China, India, Germany, France, New Zealand, Sri-Lanka, and some unmentioned
countries) and the various cattle breeds (Bos javanicus; Bos taurus: Angus, Angus -X, Minnan,
Bohai Black, Heinan, Jiaxian, Leizhou, Xuanhan, Luxi, Yanbian, Qinchuan, Mengu; Bos indicus:
Ongole, Zwerg Zebu, Leiqiong, Sri-lanka native, and some unmentioned breeds) collected from
NCBI sites (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov).
Amplification of DNA by Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) method
Primer arranged based on full-genome mitochondrial cattle (GenBank accession No:
AF492350.1) with targeting Cyt b gene, in order to obtain primer; forward (5'-AAA AAC CAT CAT
TCA ACTA TGT CGT-3') and reverse (5'-ATA TCA CAA GGA TGA TTC TGA GGA GCAA-3') to
amplify 464 bp DNA fragments. Polymerase Chain Reaction performed in a total reaction of 30 µl,
containing 0.75 µl of DNA, 1.5 µl of both forward and reverse primer, 15 µl PCR Kit (KAPA
BIOSYSTEMS), and 11.25 µl aquabidest (Otsuka). The reactions were performed using a thermal
cycle (PEQLAB Primus 25 advanced) with a predenaturation temperature at 95°C for 2 minutes,
followed with 35 cycle of reaction; denaturation at 95°C for 36 seconds, annealing at a temperature
of 51°C for 73 seconds, extension at 72°C for 84 seconds, and a final extension at 72°C for 3
minutes. The quality of the PCR product was determined using gel electrophoresis (2%), the thick
3
Sequencing and phylogenetic tree analysis
The 30 µl/samples of PCR product and 20 µl of primer sent to the PT. Genetics Science for
sequenced. A total of 69 sequences of Cyt b (15 Angus grade cattle, and 54 GenBank sequence),
aligned using Bioedit program (version 7.2.5) and grouped by the similarity of nucleotides.
Phylogenetic tree (Maximum likelihood; bootstrap value 1000; Tamura-Nei parameters) was
conducted using the program Mega 6 to reconstruction the phylogeny between samples by adding
sequences of out group Cyt b (Bos gaurus (Gaur; domestication Mitun), Bos frontalis (Mitun), Bos
sauveli (Kuprey), Bos grunniens (Yak), Bison bonasus, Bison priscus, Ovis aries and Capra hircus)
as a comparison.
Result and Discussion
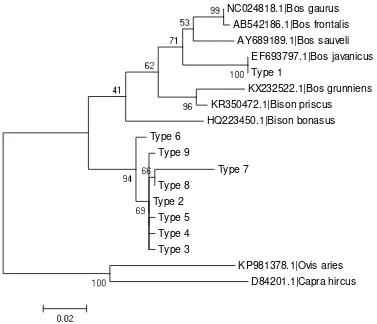
The alignment results of 69 Cyt b gene sequences showed similarity genotype, so it can be
classified into 9 type. Type 1 consists of Angus grade cattle (n = 13) and Bos javanicus (n = 1),
Type 2 consists of Angus grade cattle (n = 2), Bos taurus (n = 11), and Bos indicus (n = 15), Type 4
to 6 consists of Bos taurus (n= 1; 1; 1; 20; respectively), and Type 7 to 9 consists of Bos indicus (n
= 1; 1; 2; respectively).
Analysis of the common ancestry using maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree method obtained
the results as shown in Figure 1. Genotype Type 2 to 9 are on the same branch, while Type 1 on the
separate branches. Angus grade cattle which were in the Type 1 (n = 13) had a maternal parent
derived from Banteng cattle (Bos javanicus; EF693797.1) this is similar to the previous research in
Madura and Java cattle(Hartatik et al., 2015). While the Angus grade cattle which were in the Type 2
(n = 2) had a close relationship with the Type 3, 4, 5, 8 and 9 that consists of Bos taurus and Bos
indicus. This statement is supported by the previous research results, which states that the majority of
Indonesian cattle had Banteng mtDNA, and only a small portion had Bos indicus mtDNA(Mohamad
4
Figure 1. The phylogenetic tree reconstruction using 8 out-group sequence comparison
Type 1 genotip were in the same branch with Bos gaurus, Bos frontalis, Bos sauveli, Bos
grunniens, Bison priscus and Bison bonasus. Genetic distance based on mtDNA showed the genus
Bos (Gaur, Banteng, Kuprey) have the same parent (2.6 million years ago), and split the pedigree in
a short time (between 2.6 to 2.3 million years ago), then they are possible became the ancestry of
present cattle in the Asia (Hassanin and Ropiquet, 2004). The proximity of genus Bos and Bison,
also shown by the discovery of similarities in mtDNA haplotip of Bison (40% of the population),
crosses among them can produce fertile offspring (Ward et al., 1999).
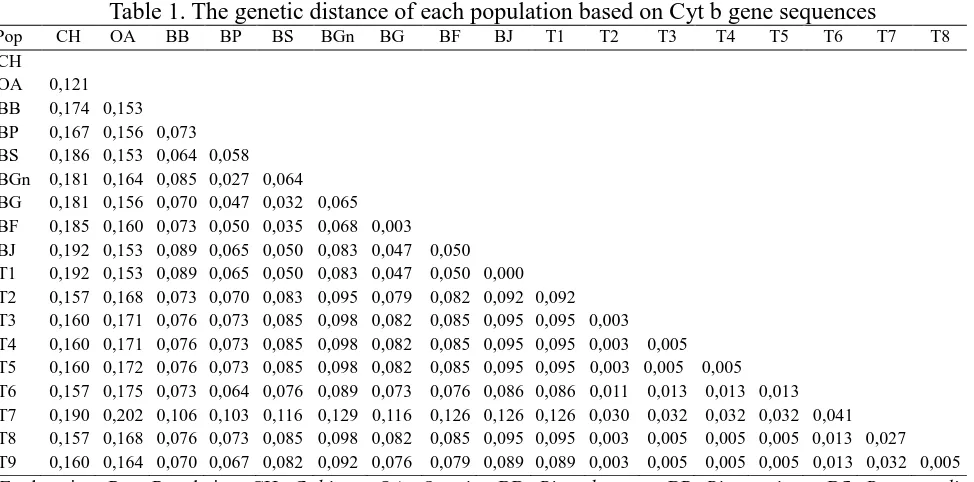
The calculation of genetic distance in 9 genotype and 8 out-group sequence shows the range
value between 0.192 to 0.000 (Table 1). The highest genetic distance shown between Capra hircus
with Type 1 and Bos javanicus. The smallest genetic distance and identical demonstrated between
Type 1 with Bos javanicus. Type 2 had the smallest genetic distances with type 3, 4, 5, 8, and 9, by
the value of 0.03, which consists of Bos taurus and Bos indicus. Among the genus Bos, the highest
distance was shown betwen Type 7 with Bos grunniens by the value of 0.129. While among 9 type
of genotype, Type 7 shows the highest genetic distance compared to Type 1 (0.126) as well as
compared to other types that were in a same phylogenetic tree branch (0,041).
NC024818.1|Bos gaurus AB542186.1|Bos frontalis
AY689189.1|Bos sauveli EF693797.1|Bos javanicus Type 1
KX232522.1|Bos grunniens KR350472.1|Bison priscus
HQ223450.1|Bison bonasus Type 6
Type 9
Type 7 Type 8
Type 2 Type 5 Type 4 Type 3
5
Table 1. The genetic distance of each population based on Cyt b gene sequences
Pop CH OA BB BP BS BGn BG BF BJ T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8 BGn: Bos grunniens, BG: Bos gaurus, BF: Bos frontalis, BJ: Bos javanicus, T1: type 1, T2: type 2, T3: type 3, T4: type 4, T5: type 5, T6: type 6, T7: type 7, T8: type 8, T9: type 9. The datas analyzed using the program Mega 6 with Kimura 2-parameter models
Type 2 genotype cattle have a highly possiblility to have Bos indicus maternal ancestor, because
mtDNA taurine yet discovered in Indonesian cattle. So it could be interpreted that cattle with
Taurine phenotype appearance was the result of decline from male (bull or cement) introduction
(Mohamad et al., 2009). As comparative case, in Indonesian cattle, common mismatch between the
Cyt b (Bos javanicus) gene and Sex-determining Region Y (SRY) (Bos indicus) occure in 87.7% of
population of cattle with Zebu fenotype appearance, the case were also reported in Nepal, 16.7% of
population of cattle with Zebu fenotype appearance cattle had mtDNA Bos gruinense and SRY gene
Bos indicus. (Kikkawa et al., 2005). Cyt b gene Bos javanicus is also common in Indonesian
Brahman cattle (Hartatik et al., 2016).
Conclusion
Most of the Angus grade cattle that have long been reared in Sragen, Central Java has
similarities Cyt b gene with Banteng (Bos javanicus), and a small portion has Bos indicus. The
reconstruction of phylogenetic tree showed Angus grade cattle split into two branches, namely
Banteng branch, and Domestic cattle branch.
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by Loka Penelitian Sapi Potong Grati. Thank to Retno Setyawati for
isolating the DNA.
References
6
Diamond, J. 2002. Evolution, consequences and future of plant and animal domestication. NATURE., 418, 700 – 7007.
Griffiths, A.J.F., Wessler, S.R., Lewontin, R.C., Gelbart, W.M., Suzuki, D.T. and Miller, J.H. (2005). An introduction to genetic analysis, 8th ed. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company.
Hartatik, T., Putra, W.B.P., Volkandari, S.D. and Sumadi. 2015. Polymorphism of mtDNA Cytochrome b gene of local cattle in Indonesia. J-SustaiN.,3(1), 21 – 24.
Hartatik, T., Sumadi, Sidadolog, J.H.P. and Maharani, D. (2016) Identifikasi kemurnian sapi peranakan ongole kebumen berdasarkan marker gen Cytochrome b (Cyt-B) dan gen SRY. Laporan hasil hibah tematik laboratorium Fakultas Peternakan UGM. Yogyakarta.
Hassanin, A. and Ropiquet, A. 2004. Molecular phlogeny of the trible Bovini (Bovidae, Bovinae) and the taxonomic status of the Kouprey, Bos sauveli Urbain 1937. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 33, 896 – 907.
Karp, G. (2010) Cell and molecular biologi; concept and experiment, 6th ed. New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Kikkawa, Y., Takada, T., Sutopo, Nomura, K., Namikawa, T., Yonekawa, H. and Amano, T. 2005. Pylogenies using mtDNA and SRY provide evidence for male-mediated introgression in Asian domestic cattle. Anim. Genet., 34, 96 – 101.
Lee, P.Y., Costumbrado, J., Hsu, C. and Kim, Y.H. 2012. Agarose Gel electrophoresis for the separation of DNA fragments. J. Vis. Exp., 62, e3923.
Mohamad, K., Olsson, M., van Tol, H.T.A., Mikko, S., Vlamings, B.H., Andersson, G., Rodriquez-Martinez, H., Purwantara, B., Paling, R.W., Colenbrander, B., Lenstra, J.A. 2009. On the origin of Indonesian cattle. Plos One., 4 (5), e5490.
Neser, F.W.C., van Wyk, J.B., Fair, M.D., Lubout P. and Crook, B.J. 2012. Estimation of genetic parameters for growth traits in Brangus cattle. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci., 42 (5), 469 – 473.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A., and Kumar, S. 2013. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol., 30, 2725 - 2729.