PRAGMATIC
ANALYSIS
OF
SPEECH
ACTS
IN
BULLYCHAPTERS
I
AND
II
VIDEO
GAME
A THESIS
Presented as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Attainment of a Sarjana
Sastra Degree in English Language and Literature
by:
ARIF TRIWIDIATMOKO 10211141027
ENGLISH LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE STUDY PROGRAM ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGES AND ARTS YOGYAKARTA STATE UNIVERSITY
v
DEDICATION
vi
MOTTO
viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE ... i
APPROVAL SHEET ... ii
RATIFICATION SHEET ... iii
SURAT PERNYATAAN ... iv
DEDICATION ... v
MOTTOS ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... viii
LIST OF FIGURE AND TABLES ... x
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS ... xi
ABSTRACT ... xii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Research ... 1
B. Focus of the Research ... 3
C. Objectives of the Research ... 6
D. Significance of the Research ... 6
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW AND CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK A. Literature review ... 7
1. Pragmatics ... 7
2. Speech Acts ... 14
3. Video Game and Bully Video Game... 21
4. Previous Studies ... 22
B. Conceptual Framework ... 24
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD A. Type of the Research ... 27
ix
C. Instrument of the Research ... 28
D. Technique of Data Collection ... 29
E. Data Analysis ... 30
F. Data Trustworthiness ... 31
CHAPTER IV FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION A. Findings ... 33
B. Discussion ... 37
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS A. Conclusion ... 85
B. Suggestions ... 86
REFERENCES ... 88
APPENDICES A. Data Sheet of a Pragmatic Analysis of Speech Acts in Bully Chapters I and II Video Game ... 90
x
LIST OF FIGURE AND TABLES
Figure 1. Analytical Construct ... 26 Table 1. An Example of Data sheet of A Pragmatic Analysis of Speech Acts in
Bully Chapter I and II Video Game ... 29
Table 2. Types of Speech Acts Based on Searle’s Classification Found in Bully Video game ... 34 Table 3. The Way Speech Acts Delivered by the Main Character in Bully Video
xi
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
Rep: Representatives
a. Reporting b.Confirming c. Arguing d.Informing e. Explaining f. Stating g.Lying h.Convincing i. Predicting j. Describing
Dir: Directives
a.Questioning b. Requesting c. Warning d. Commanding e. Insisting f. Inviting g. Suggesting h. Negotiating
Com: Commissives
a.Agreeing b.Promising c.Threatening
Exp: Expressives
a.Complaining b. Insulting c. Thanking d. Boasting e. Greeting f. Complimenting g. Stating Apathy
h. Stating Disappointment i. Stating Impression j. Stating Irony k. Stating Relief l. Stating Disgust m. Stating Surprise n. Stating Dislike o. Stating Diffidence No: Data Number
Di/InD: Direct/Indirect Type: Speech act types Cha: Chapter
xii
A PRAGMATIC ANALYSIS OF SPEECH ACTS IN BULLY
CHAPTER I AND II VIDEO GAME
By: Arif Triwidiatmoko
10211141027
ABSTRACT
This research studies the phenomenon of pragmatics especially speech acts found in Bully video game. The objectives are to find out the types of speech acts based on Searle’s classification and the way speech acts delivered by the main character in the game.
The quantitative-qualitative method was used in this research. The method was used to describe the data in the form of utterances and to present the finding in percentage or number of occurrences. The key instrument of this research was the researcher. In addition, the researcher used data sheet as the secondary instrument to help identify and analyze the data. The data were in form of lingual units such as words, phrases, clauses, and sentences. The contexts of the data were the dialogues from the main character. The data were collected by recording the mission scenes. In this research the researcher (1) identified the data, (2) classified the data, (3) analyzed and grouped the data (4) described and interpreted the data, and (5) checked the accuracy of data then report and drew conclusion. The researcher also consulted the research and also has peer discussion to ensure the trustworthiness of this research.
There are four out of five types of speech acts based on Searle’s classification found in the data. They are representatives, directives, commissives, and expressives. Declaratives are not found in the data since the main character has no authority to perform them. Directives hold the highest frequency and then followed by representatives and expressives. Commissives come last. The illocutionary force of questioning occurs the most followed by commanding. Then, it is followed by illocutionary force of confirming and arguing. Illocutionary force of agreeing comes last. Both the direct and indirect speech acts are found in the data. However, direct speech acts are the most frequently used by the main character. It implies that the main character tends to direct others via language. He is also unaware of his surroundings or lack of information. In delivering his act, the main character does not like being complicated.
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Research
Language as the part of communication becomes an important aspect in humans life. Humans use language as a medium to communicate with each other. Language could be in terms of sign or sound which contains meaning. According to Taylor (1990:5) language is a set of system of signs (speech, sound, gestures, and letters) which are used to communicate messages. People read, write, and speak through language. They share ideas and informations and build relationships in social interaction because humans are considered as social beings and cannot live solitarily. By using language people reveal their sense of identity, character, and background. They share their opinions, express their feelings, command someone, influence someone, ask for request, and etc. using language.
2
by a speaker to a listener who sits near the window and the condition is unpleasant. It means that the speaker asks the listener to open the window. The utterance could be interpreted differently depends on the context. It becomes inseparable for language to be studied without the context of people as communicator or the users of language.
In linguistics, there is a field of language that studies the language in context which is known as pragmatics. According to Mey (2001:6), pragmatics is the study of human language usage in communication as determined by the society conditions, which means it explores the language in communication and the context surrounds it. Because pragmatics does not only study about certain linguistic form, the social and the surrounding context are considered in pragmatics. It is possible for an utterance to mean differently, from different speakers, to different listeners, at different times, and places.
According to Yule (1996:21), context means the physical environment or the situation surrounding the production of an utterance. It includes what is present around the speaker or the listener at the time of communication occurs, such as where the communictaion takes place, what is going on, and etc. Context is needed to understand the meaning of an utterance. The listener who has limited knowledge about the context of the utterance might find difficulties to interpret the correct message from the speaker.
3
language. Any spoken language that contains speech acts has functions such as to command, to warn, to request, or to express speaker’s intentions.
The usage of language also takes part in the aspect of entertainment such as video games. In which, language becomes the key part that shapes the story of the games. One of them is Bully, also known as Canis Canem in Latin, which means „dog eats dog’. It is an open world action-adventure video game released by Rockstar Vancouver for PlayStation 2 in 2006. The setting is in a school environment. The player plays as James "Jimmy" Hopkins, who is a student with a difficult background. The game starts with the moment when Jimmy enters Bullworth Academy. Jimmy is enrolled at the school when his newly married mother and stepfather go on a year-long honeymoon cruise.
The researcher is interested in the way the main character interacts in this game. This interaction will be studied using pragmatic approach to find the types of speech acts based on Searle’s classifications and to find the way speech acts delivered in the conversations.
B. Focus of the Research
The analysis of Bully using pragmatic approach aims to uncover the speech act features based on Searle’s classification and the directness of speech acts in the game. This research focuses on analyzing the “Chapter I: Making New Friends and Enemies” and “Chapter II: Rich Kid Blues” as the objects of the data. These chapters
4
environment. In order to limit focus and context of the study, the researcher thinks it is sufficient to take the data from these chapters.
There are some problems found when the researcher analyzing the game. First is speech acts. There are three related acts which are divided into locutionary, illocutionary, and perlocutionary act. Locutionary act is the act of saying something. Illocutionary act is what one does in saying it. Perlocutionary act is the desired effect by saying it. Based on Searle’s classifications in Yule (1996:53-54), there are five types of general functions of speech acts. They are declaratives, representatives, expressives, directives, and commissives. The way speech acts delivered are divided in to two types. They are direct speech acts, and indirect speech acts. Direct speech acts deliver action directly through language, while indirect speech acts perform act implicitly which leads the listener to have deeper interpretation about the speaker intention.
Second is the context of the utterances. Context is the physical or social setting that becomes the background knowledge to interpret speakers’ intentions. The listener must understand the context of the dialogues in order to decrease the possibility of miss interpretations. Context helps the listener to interpret the implied meaning of the speaker’s utterances.
5
informative, right and perspicuous. However, in communication sometimes speaker breaks the cooperative principles and flouts the cooperative maxims that cause unclear information.
Last is deixis or in Greek language means pointing via language. In conversation deictic expression often occurs and the interpretation depends on the speaker and listener who shares the same context. According to Yule (1998:9-14), there are three types of deixis. They are person deixis, spatial deixis, and temporal deixis. The use of deixis is important since it points clear aspects of utterance that needs to be inferred from the context.
From the identifications above there are some pragmatic characteristics found
in Bully video game. It is impossible for the researcher to explain all of them since
limitation of time and researcher’s skill in analyzing the topics. In order to keep the research focus, this research emphasizes on two points that will be studied. They are the types and the directness of speech act.
Based on the identification and limitation of problems, the formulation of the research are formulated as follows:
1. what are the types of speech acts based on Searle’s classifications found in dialogues from the main character in Bully video game?
6
C. Objectives of the Research
Based on the focus of the research discussed above, the objectives can be formulated as follows:
1. to describe the types of speech acts based on Searle’s classifications found in dialogues from the main character in Bully video game.
2. to describe the types of speech acts based on the way speech acts delivered in Bully video game.
D. Significance of the Research
The results of this research are expected to give contribution to theoretical and practical use of language:
1. Theoretical Contribution
By conducting this study, it is hoped that the finding will enrich comprehension and understanding of pragmatics, especially about speech acts. It is also expected to give additional reference to other researchers in pragmatics who are interested in analyzing speech acts.
2. Practical Contribution
a. The English Department
This research is expected to give contribution to the study of linguistics, especially pragmatics.
b. The Readers
7
CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW AND CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
A. Literature Review
This chapter presents theories used in this study. It includes pragmatics, scope of pragmatics, speech acts, Austin and Searle’s categorization of speech acts, felicity conditions, types of speech acts based on the way they are delivered,
and Bully video game as the object of the research.
1. Pragmatics a. Definition
The study of language is called linguistics as it concerns with language phenomenon including its form, sound, and the way a speaker produces it in communication. Communication cannot be separated from its context. Context is needed to study language in use. Pragmatics studies language in context. According to Yule (1996:3), pragmatics is the study of meaning in particular context. It studies more about what speakers mean by their utterances in the interpretation of the particular context and how the context influences what is said. Thus, pragmatics is also called the study of contextual meaning.
8
that description. On the other hand, pragmatics allows humans into the analysis. It studies the linguistic forms and the users. It takes us to make sense of people and what they have in mind. Moreover, Griffiths (2006:1) states that pragmatics and semantics are inseparable, because pragmatics is related to semantic knowledge and knowledge of the world, including context. Furthermore, Widdowson (1996:61) says semantics is the study of meaning or is concerned with the meaning of language while pragmatics is what people mean by the language use or how they actualize its meaning.
In accordance with Yule, Morris in Mey (2001:4) defines pragmatics as the study of the relation of sign to interpreters. It tends to be the study of message and language user. It is different from traditional linguistics which studies the form or the structure. Pragmatics focuses on the process of producing language and its producer. In addition, Mey (2001:6) states that pragmatics studies the way humans use their language in communication and how the language is intertwined in interaction or society. The way humans communicate using language is also affected by the society. Therefore, the condition of a society can also be observed by pragmatics.
9
In other words, pragmatics is the study of language meaning and the users. Furthermore, context is involved in pragmatics, since it influences language production and interpretation. Thus, pragmatics studies language in context. b. Scope of Pragmatics
Pragmatics has some topics of study. They are deixis, reference and inference, presupposition, cooperative principle, politeness, and context since pragmatics studies language and context. The topics of discussion of pragmatics are as follows:
1) Context
Mey (2001:58) states that pragmatic thinking is context-bound. No matter how natural language facilities or how convention bound they use, as language users, humans always operate in context. Context according to Yule (1996:21) is the physical environment. In addition, Leech (1983:13) considers context to be any background knowledge shared by speakers and listeners. It contributes to listeners’ interpretation of what speakers mean by the given utterance. In other
words, context is the decisive factor in pragmatics.
Halliday and Hassan (1989:5), state that there is text and other texts accompanies it, namely context. The notion of context goes beyond what is said and written. It includes the non-verbal in surrounding environment in which text occurs. It serves as the connector between text and situation.
10
theory. The first one is the participants in the situation, they refer as the persons who take part in the conversation and their personalities. These corresponds more or less toward sociologist would regard as status and roles as participants. Second, there is the action of the participants, it is what the participants doing, including verbal action and non-verbal action. Third, the other relevant features of the situation, they belong to the surrounding objects and events. Fourth, is the effect of the verbal action, it refers to the changes brought by what participants say in the situation.
In addition, Dell Hymes in Wardaugh (2006:247-248), purposes an ethnography framework. It describes all the factors that are relevant in understanding how particular communicative event achieves its objectives. He uses the word SPEAKING as the acronym for the various factors that is believed to be relevant. They are:
a) The setting and scene (S)
Setting refers to the time and place or the concrete physical circumstances in which speech takes place. Meanwhile, scene refers to the abstract psychological setting, or the cultural definition of the occasion.
b) The participants (P)
It includes the various combinations of speaker-listener, addressor-addressee, or sender-receiver that generally fill certain socially specified roles.
c) Ends (E)
11
d) Act sequence (A)
It refers to the actual form and content of what is said including the precise words usage, how they are used, and the relationship of what is said to the actual topic at hand.
e) Key (K)
Key refers to the tone, manner, or spirit in which particular message is conveyed, such as light-hearted, serious, precise, pedantic, mocking, sarcastic, pompous, and so on. It is also marked nonverbally by certain kinds of behavior, gesture, posture, or even deportment.
f) Instrumentalities (I)
Instrumentalities refers to the choice of channel, such as oral, written, or telegraphic, and form of speech, such as language, dialect, code, or register that is chosen.
g) Norms of interaction and interpretation (N)
They refer to specific behaviors and properties which are attached to speaking and also how these may be viewed by someone who does not share them, such as loudness, gaze return, silence, and so on.
h) Genre (G)
Genre refers to clearly demarcated types of utterance such as poems, proverbs, riddles, sermons, prayers, lectures, and editorials.
2) Deixis
12
interpretation depends on the speaker and the listener who share the same context. Furthermore, Yule (1996:9-14) also states there are three types of deixis: person deixis such as „he’ and she’, spatial deixis such as „here’ and „there’, and temporal deixis such as „now’ and „later’. In addition, Levinson (1983:54) says that deixis is the most obvious way in which language and context are reflected in the structure of language. The use of deixis is important since it points clear aspects of utterance that needs to be inferred from the context.
3) Reference and Inference
Referring expression is another way of pointing via language. According to Yule (1996:17-18), reference is an act in which a speaker, or writer, using linguistic form to enable a listener or reader to identify something. The examples of linguistic form of referring expression are proper nouns, definite noun phrase, indefinite noun phrase, and pronoun. Reference is based on the speaker’s context. The speaker assumes that information is already known by the listener. Meanwhile, inference is the indirect relationship between entities and words. Listener needs to infer speaker’s intention correctly by seeking information from the context given by speaker.
4) Presupposition
13
a proposition which truth is taken for granted by the speaker and must be known and taken account of the utterance to make sense to the listener. For example, the utterance Mary’s dog is cute (Yule 1996:26) presupposes that Mary has a dog, even if this is not explicitly stated.
5) Cooperative Principle
Grice in Yule (1996:37) states that conversation is based on shared principle of cooperation, “Make your conversational contribution as required, at
the stage at which it occurs, by the accepted purpose or direction of the talk exchange in which you are engaged.” In addition, Cruse (2006:40) says that conversation is a co-operative activity in which participants agree in bound with certain rules. In other words, participants of a conversation can obey a general cooperative principle. Cutting (2002:34-35) proposes four rules of cooperative principle called maxims. Maxim of quantity, the information given should not be too few or too much. Maxim of quality, the speaker is demanded to speak according to reality. Maxim of relevance, the speaker must say things relevant to what the speaker states previously. Last is maxim of manner, it demands speakers to speak briefly and orderly to avoid obscurity and ambiguity.
6) Politeness
14
(solidarity and deference strategy). Hence, Cruse (2006:131) states that politeness is the matter of minimizing the negative effect and maximizing the positive effect of what one says to other. In other words, politeness is the way of showing awareness of other’s face. There is also another topic of discussion in pragmatics, namely speech acts. The explanation of speech acts are shown in the following section.
2. Speech Acts
Speech act is one sub domain of pragmatic study. It studies the phenomenon of doing things with language. Therefore, speech acts become the main theory to analyze the language phenomena found in the data.
a. Definitions
Griffiths (2006:148) states that basic unit of linguistic interaction such as giving warning, greeting, applying for, telling what, confirming an appointment, the acts of those interaction and not the label are called speech acts. In accordance with Griffiths, Cruse (2006:167) defines speech acts as the acts which are involved in the production of language. In other words, speech acts are the actions done through language. They give impact to the real world and its surrounding. In addition, Mey (2001:95) says that speech acts are the verbal action happening in the world. Speaker performs an activity that intentionally changes the existing state of affair.
15
in Mey (2001:93) says that linguistically communication is not only based on basic unis such as symbols, words or sentences, but also the performance in producing these units. Thus, speech acts are produced in actual language use, by people having something „in mind’.
b. Speech acts Categorization
According to Austin in Levinson (1983:236), there are three basic acts of speech acts, they are explained as follows:
1) Locutionary act
Locutionary act is the utterance of a sentence with determined sense and reference. In accordance with Austin, Cruse (2006:167) says that locutionary act is the production of an utterance, with a particular intended structure, meaning, and reference. Furthermore, Yule (1996:48) states that the locutionary act is the basic act of utterance which produces a meaningful linguistic expression. Similar to Yule, Cutting (2002:16) states locution is what is said by the speaker or the form of words uttered. The act of saying those words is called locutionary act. Peccei (1999:44) says that it is the actual word forms used by speaker. In other words, locutionary act is the speaker’s meaningful utterance.
2) Illocutionary act
16
performed by speaker in saying something in appropriate intention and context. In accordance with Yule, Cutting (2002:16) states that illocutionary act is the action, the function of the words, or the specific purpose of what speaker has in mind. Peccei (1999:44) says that it is what speaker is doing by uttering the words. 3) Perlocutionary act
Perlocutionary act is the effect of the speaker’s utterance on the listener. In addition, Cutting (2002:16) states that perlocutionary act is the results of the speaker’s words or it is what is done by uttering the words. In accordance with
Cutting, Cruse (2006:168) says that it is a speech act which depends on the production of specific effect. Furthermore, Yule (1996:48) states the perlocutionary act is the intended effect of an utterance, on the assumption that listeners will recognize the speakers’ intended meaning. Peccei (1999:44) says that perlocution is the real result of illocution. It is the impact on the listener or the listener’s reaction.
17
On the other hand, Searle in Peccei (1999:51) categorizes speech acts based on the relationship between the words and the world and on who is responsible to make that relation work. The five categories of speech acts by Searle are shown below:
1) Representatives
Speaker represents eternal reality by making their words fit the world as they believe it to be. Yule (1996:53) says that it is the kind of speech acts that states what speaker believes to be the case or not. The same view is shared by Cutting (2002:17), he states it is the act in which the words state what the speaker believes to be the case. In addition, Levinson (1983:240) says that it commits the speaker to the truth of expressed propositions such as asserting, concluding, describing, claiming, and insisting. The examples are as follows.
a) The earth is flat.
b) It was a warm sunny day.
c) Chomsky did not write about peanuts.
Yule (1996:53) 2) Commissives
18
a) We will not do that.
b) I am going to get it right next time. c) I will be back.
3) Directives
Speaker directs a listener to perform some future act which will make the world fit the speaker’s words. In accordance with Searle, Yule (1996:54) says that
directive is the kind of speech acts which a speaker uses to get someone else to do something. In other words, it expresses what a speaker wants. The same view is also shared by Levinson (1983:240) who says that directives are the acts performed by the speaker to get the listener to do something. The examples of directive act are requesting, questioning, ordering, suggesting, and commanding. In addition, Cruse (2006:168) says that directives are the acts which are used to order someone to act in a certain way. The examples are as follows.
a) Gimme a cup of coffee. Make it black. b) Coul you lend me a pen, please? c) Don’t touch that.
Yule (1996:54) 4) Expressives
19
of speech act that states what the speakers feel. It expresses a psychological state of pleasure, pain, likes, dislikes, joy, or sorrow. It may be caused by something the speaker does or listener does, but it is about the speaker’s experience. The
examples are presented as follows. a) I am really sorry! b) Congratulations! c) It hurts!
5) Declarations
Declaration is the act of uttering the words that change the world. It requires the speaker to have authority to perform this act. According to Levinson (1983:240), declaration act is the act which affects immediate changes on the institutional state of affair such as christening, declaring a war, and firing from employment. In addition, Cruse (2006:169) says that it is the act which produces a change of some sort in the world. Furthermore, Yule (1996:53) says it is the kind of speech act that changes the world via utterances. These are the examples of declarations.
a) Priest: I now pronounce you husband and wife. b) Referee: You are out!
c) Jury Foreman: We find the defender guilty. c. Felicity Conditions
20
the language being used and they are not acting or being nonsensical. Content conditions are related to the contents of an utterance. For instance, if the utterance is a promise and warning both contents must be about future event.
Searle in Geis (1995:6) categorizes the felicity conditions into four types. They are preparatory conditions, sincerity conditions, propositional content conditions, and essential conditions. It is an example of the felicity conditions of request. The propositional content condition of request is the future action of the listener. The preparatory condition of the request is the listener’s ability to do the action and the speaker believes that the listener is able to do it. In occasion, it is not clear for both speaker and listener that listener will do the action requested. The sincerity condition of the request is that the listener is willing to do the action requested. The essential condition is the attempt of the listener to do the action. d. Type of Speech Acts Based on How They Are Delivered
There are other ways in analyzing speech acts by distinguishing the types of speech acts on the basis of their structure. Those are direct and indirect speech acts.
21
to the representative act of describing, since it describes the current condition outside the place is winter and snowy.
Meanwhile, indirect speech acts occur when there are indirect relationships between the form and function (Yule, 1996:55). Furthermore, Searle in Peccei (1999:55) says that indirect speech acts are speech acts which are performed indirectly through performance of another speech acts, even though the surface form looks like particular direct speech acts. In this case, the felicity condition is obviously violated. At the same time, one or more real felicity condition of the underlying act has been questioned or mentioned by the locution to give a hint as a true illocutionary force.
3. Video Game and Bully Video Game a. Definition
Video games are variously referred to as computer games, electronic games, and even digital entertainments. These terms cannot be taken to be strictly equal. Computer game sometimes refers to games on a personal computer. Electronic game might also refer to toys. While video game is sometimes used to refer exclusively to console games such as those on the X-Box or Playstation. This research adopts video game as the general term, because this term dominates the current usage and it has the essence of referring to its crucial definition.
22
enjoyable for the player. It also provides an objective for the player and a guideline for the rules of the game. This information is then used to create the game's manual. In many cases, the inspiration for a story is derived from popular movies or books.
Bully video game has a good story line which is interesting to be studied.
The story is studied using speech act approach to find the speech acts based on Searle’s classification and speech acts based on the way they are delivered, and
describe it in descriptive qualitative way. b. Bully Video Game
Bully is an open world action-adventure video game set in a school
environment. The player takes control of James "Jimmy" Hopkins, who from the opening cut scene is revealed to be a difficult student. The game tells about the events that follow Jimmy as he enters Bullworth Academy. Bully received highly positive reviews from critics including the voice acting, gameplay and side missions which made it to the Top 10 Games of '06 in PlayStation Magazine. In 2016 Rockstar re-released the anniversary edition on mobile devices with android and ios platform. This mobile version comes up with some new updates of additional graphical effects, higher resolution textures, better lightning, and new multi-player mode.
4. Previous Studies
23
She analyzed speech acts in“Date Night” movie. The research objectives were to find out the types of speech acts focusing on illocutionary act and also to analyze the conversational implicature.
The results of the study showed that there were two important points. First, there were four kinds of illocutionary acts performed in Date Night based on Searle’s categorization. They were representatives, directives, commissives, and
expressive. Second, there were two types of conversational implicatures found in the main character’s speech. They were generalized conversational implicature in which the main character’s intention was explicitly uttered and particularized conversational implicature in which the main character’s intention was implicitly
uttered.
Another pragmatic analysis of speech acts was conducted by Rayi Denok Sunestri (2012) in her thesis entitled “A Pragmatic Analysis of Speech Acts of Hester Prynne in Roland Joffe’s The Scarlet Letter as Reflection of American
Society in 17th Century”. Her research had two objectives. The first was to find out the classification and functions of speech acts based on illocutionary act. The second was to identify the characteristic of American society in 17th century based on the theory of context by Holmes.
24
American society in 17th century was reflected by Hester’s speech acts in the society dominance of religion in society, since religion controls all things in the society including controlling how to communicate, how to dress, how to decide one’s punishment, how to control the mourning times, and how religion control
women’s lives in society.
Similar to previous research, the researcher also analyzes pragmatics in term of speech acts. This research tries to find out the types of speech acts based on Searle’s classification and the way they are delivered. The differences between
this research and the previous research are in the object of the research and the objectives. These differences will lead to different discussion and findings.
B. Conceptual Framework
This research uses pragmatic approach since this research studies language in use and its context. The language used by people consists of utterances which contain action. Most of what people say have intended or desired goal. In other words, the language people use contains action that changes its participant or world.
25
used to classify and analyze the data found in the conversation from the main character in the game.
This research also finds out the types of speech acts based on the way they are delivered by using language. When the speaker clearly states their intention, the listener will easily understand the purpose. However, sometimes utterances mean differently from what the speaker is intended to say or the speaker indirectly say what he or she means. Thus, the listener needs to pay more attention on the utterances made by the speaker. This language phenomenon is called indirect speech act. The research employs Searle’s theory of indirect speech act. In analyzing indirect speech act, there are some felicity conditions which are violated and at the same time, there are true felicities that give the clue of the real illocutionary force.
26
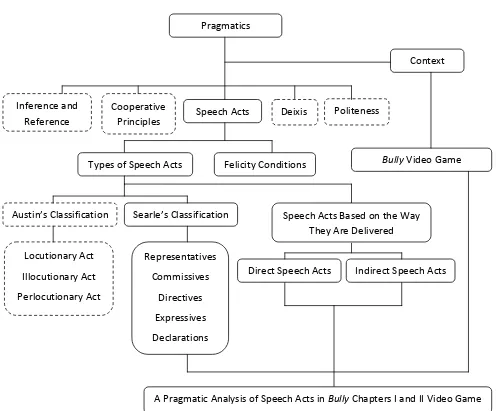
Figure 1. Analytical Construct
Pragmatics
Speech Acts
Context
Bully Video Game Deixis
Cooperative Principles
Politeness Inference and
Reference
A Pragmatic Analysis of Speech Acts in Bully Chapters I and II Video Game Felicity Conditions
Types of Speech Acts
Speech Acts Based on the Way They Are Delivered
Direct Speech Acts Searle’s Classification
Austin’s Classification
Indirect Speech Acts Locutionary Act
Illocutionary Act
Perlocutionary Act
Representatives
Commissives
Directives
Expressives
27
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHOD
The objectives of this research were to identify the type of speech acts based on Searle’s classification and to identify the way they were delivered, as
reflected by the main character in Bully video game. In accordance with the objectives, an appropriate methodology is needed to achieve the goal of the research.
A.Type of the Research
This research employed a descriptive qualitative research. According to Vanderstoep and Johnston (2009:310), qualitative research is making a narrative or textual descriptions on the phenomena under study. In other words, qualitative research describes the phenomena found in the study without making a modification or manipulating the data. In addition, Bogdan and Biklen in Sugiyono (20012:13) state that qualitative research occurs in natural setting and it is descriptive. It produces descriptive data of people’s own written or spoken
words and observable behavior.
28
B.Source, Form and Context of the Data
According to Vanderstoep and Johnston (2009:48), data is a collection of variables from a research sample. Qualitative research is descriptive, therefore the data in qualitative research are in the form of words rather than number, Bogdan and Biklen in Sugiyono (2012:13).
The source of the data was the Bully video game’s script. The source of the data of this research were taken from the scenes which appeared in each mission through Chapters I and II of the game. Thus, in this research the data were in the form of lingual unit, such as words, phrases, clauses, or sentences which contained speech acts. Meanwhile, the context of the data was dialogue since the research’s object was video game.
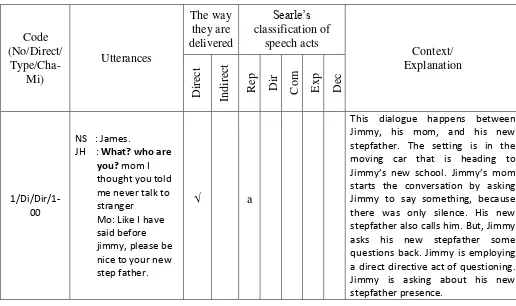
C. Instrument of the Research
29
Bully Chapter I and II Video Game
D. Technique of Data Collection
The data of the research were collected from the utterances which were
30
deep comprehension and also to find out the information related to the objectives of the research. The researcher recorded each mission and rewrote the subtitles of the main character dialogues that were presented in the game since the researcher was not able to find the script on the internet. The researcher had reread the transcript of the subtitles many times and classified the relevant data based on particular classification into the data sheet.
E. Data Analysis
According to Bogdan in Sugiyono (2012:244), data analysis is the process of systematically searching and arranging the dialogue script, notes, and other materials that researcher accumulates to increase the understanding and to enable to present what researcher has discovered to others. In addition, Vanderstoep and Johnston (2009:258) say that qualitative researchers usually think of their findings as an analysis, interpretation, and themes rather than objective results. The procedure which were used to analyze the qualitative data should be reported in order to make reader understand and trust the procedure of the research.
The steps of data analysis in this research were as follows:
1. The data from the subtitle script of Bully video game were identified. 2. The data were classified based on the formulation of the problems.
3. The data were analyzed and grouped into their own types and transferred into data sheet.
31
5. During the process of analysis, the researcher applied the trustworthiness of the data and analyzed the data to gain the result of the research.
F. Data Trustworthiness
There are some strategies in achieving trustworthiness of the research which Creswell (2009:191) states as a validity strategy. The credibility, dependability, transferability and conformability are the strategies which are done in order to gain the trustworthiness of the research. Credibility is concerned with the accuracy of the data. Dependability refers to the stability and track ability of the changes of data. Transferability means that the research generalization in fittingness of the data is related to each other. Conformability means that the result of this research represents the condition in the game and does not represent the researcher’s mind.
32
33
CHAPTER IV
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter consists of two sections. The first section is the findings which present all the result from the data about speech act found in the game, especially about the types of speech acts and the way they are delivered. The second section is the discussion which present further explanation in detailed analysis of findings.
A. Findings
1. Types of Speech Acts Based on Searle’s Classification
Action done through language is called as speech act. There are three related acts. The first is locutionary or the speaker meaningful utterance. It is what the speaker says by producing a meaningful linguistics expression. The second is illocutionary or the force of an utterance. It is the intended action expressed by the speaker. Last is perlocutionary, which is the effect from the utterance on the listener. Searle in Peccei (1999:51-53) categorizes speech acts into five categories. They are representatives, directives, commissives, expressives, and declarations. Representatives are the act that represent eternal reality by making their words fit the world as they believe it to be. Directives are the act which are used by speakers to direct listeners to perform some future acts which will make the world fit the speaker’s words. Commissives are used when the speaker commits him or
34
represent their internal psychological world. Declarations are the act of uttering the words that change the world.
Based on the findings of the research there are some types of speech acts based on the Searle’s classification found in the data. The findings of these types
of speech acts based on Searle’s classification found in Bully video game are presented in Table 2.
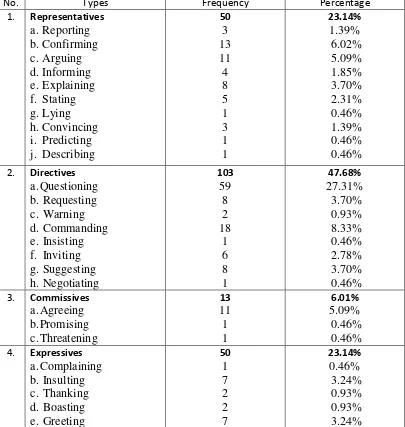
Table 2. Types of Speech Acts Based on Searle’s Classification Found in
Bully Video Game
35
From the table above there are four out of five types of speech acts found. Those types of speech acts are representatives, directives, commissives, and expressives. The types are based on Searle’s classification found in the data of
Bully video game. There are total 36 kinds of illocutionary force and total 216
speech acts found.
There are 10 kinds of illocutionary force of representatives with the total of 50 data or 23.2% found in the game. They are reporting, confirming, arguing, informing, explaining, stating, lying, convincing, predicting and describing.
Next, there are directives with 8 kinds of illocutionary force. They are questioning, requesting, warning, commanding, insisting, inviting, suggesting and negotiating. Directives hold the highest occurrence above all types of speech acts found in the data with total 103 or 47.5%.
Next, Commissives have only 3 kinds of illocutionary force. They are agreeing, promising and threatening. Commissives occur in 13 data or 6.1% of speech acts which are found in the data.
36
complimenting, stating apathy, stating disappointment, stating impression, stating irony, stating relieve, stating disgust, stating surprise, stating dislike and stating diffident. Expressives have the total of 50 data or 23.2% occurrences of speech acts.
There is one type of speech act that was not found in the data. It is declaration or the act that change the world via utterances. This act requires the speaker to have authority to perform it. Since the main character in Bully video game does not have the authority to perform it, he cannot use the declaration speech acts.
2. Speech Acts Based on the Way They Are Delivered
37
Both of these types of speech acts are found in the data in Bully video game. The findings of these types of speech acts based on the directness are presented in the Table 3.
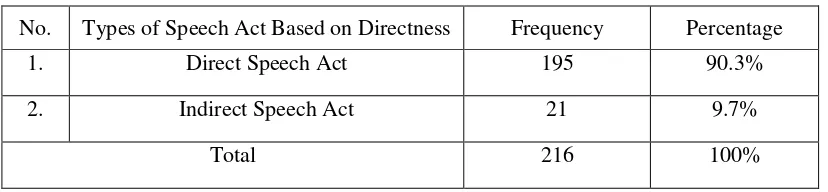
Table 3. The Way Speech Acts Delivered by the Main Character in Bully Video Game
No. Types of Speech Act Based on Directness Frequency Percentage
1. Direct Speech Act 195 90.3%
2. Indirect Speech Act 21 9.7%
Total 216 100%
These types of speech acts and the direct and indirect speech acts will be explained in the following section.
B. Discussion
The researcher analyzes the phenomena of pragmatics especially speech acts which are performed in Bully video game. There are two points of discussion present. The first point discusses the types of speech acts based on Searle’s classification. The second point discusses the way speech acts are delivered. 1. Types of Speech Acts based on Searle’s Classification
The findings of the data presents that there are four kinds of speech acts based on Searle’s classification performed by the main character in Bully video game. They are representatives, directives, commissives, and expressives. Declaratives were not found in the interaction among the character, because the main character has no privileges to perform them.
38
a. Representatives
Representatives are the kind of speech act that states what the speaker believes to be the case or not. It commits the speaker to the truth of expressed proposition such as asserting, concluding, describing, claiming, insisting. The findings on the type of representatives acts are 50 data or 23.14% from total data. There are 10 types of representatives acts found in Bully video game. Those are reporting, confirming, arguing, informing, explaining, stating, lying, convincing, predicting and describing. Each of those types is explained in the following paragraphs.
1) Reporting
Reporting is retelling something that one has heard, told or observed. Reporting occurs 3 times in the data or about 1.39% from total 216 data. These are the examples of reporting found in Bully video game.
M : Jimmy, please say something. NS : James.
JH : What? who are you? mom I thought you told me never talk to stranger.
(2/InD/Rep-Exp/1-00) The dialogue above happens between Jimmy, his mom, and his new stepfather. The setting is in the moving car which is heading to Jimmy’s new school. Jimmy’s mom starts the conversation by asking Jimmy to say something, because
there is only silence. His new stepfather also calls him. Instead, Jimmy responses it angrily and says to her mom that she told him not to talk to someone unfamiliar.
39
JH : Yeah, you could've fooled me. HM : What?
JH : I said you could've fooled me. This place is full of bullies and maniacs.
(28/Di/Rep/1-03) The example above happens in the third missions chapter 1. The dialogue occurs between Jimmy and the headmaster in the school yard. The headmaster is interrogating him about his adaptation with the school. Jimmy answers the questions, but he also says that the headmaster could have fooled him about the school. The statement demands an explanation. So, Jimmy retold the headmaster that he said the headmaster could have fooled him, because the school condition is different from what the headmaster had explained.
Here is another datum of reporting from Bully video game.
JH : Uhm… you’d better use that meat soon. The clerk said it expires at midnight.
Cook: Nonsense. There are no fussy eaters at Bullworth. It’ll last for a month.
(130/Di/Rep/2-16) The dialogue above happens in the kitchen between Jimmy and the cook. Jimmy has been asked to visit the cook by the headmaster. The cook sends Jimmy to help her to do some arrangements. One of them is to bring her some meats. Jimmy tells the cook that the clerk said the meat is going to expire by midnight. But, the cook ignored the fact.
2) Confirming
40
The examples from the acts of Confirming are as follows. Mo : That’s enough! Behave you little brat.
NS : You’ve upset your mother, I got to have a mind to beat you. JH : Have a mind is right, suddenly you realize.
(4/Di/Rep/1-00) The dialogue above is from the opening scene of the game. The characters in the dialogue are Jimmy, his mom and his new stepfather. The setting is in the moving car. There is a conflict between Jimmy and his new stepfather. From the previous conversation it shows that Jimmy doesn’t like his new stepfather. His stepfather angrily says to have a mind to beat him. Jimmy replies it by confirming that to have a mind is right.
Another example of confirming as follow. HM : Ahh, yes, so you must be Hopkins. JH : Uh, huh.
(10/InD/Rep-Exp/1-00) The conversation above occurs in the headmaster office between Jimmy and the headmaster. The headmaster is welcoming Jimmy in joining the school. The headmaster is clarifying Jimmy and Jimmy confirms it by saying uh huh. But the answer does not satisfy the headmaster, so Jimmy has to confirm it in better way.
This is another datum of confirming found in Bully video game.
Bt : Secondly, Mr. Hattrick saw me writing in my diary during class and he took it in his desk. And he says he's gonna give it to the principal tomorrow. If anyone sees what in there. I will just die.It's really personal.
JH : Yeah, well, nothing like having the whole school know your deepest secrets. Make your teenage years go by in flash.
41
the class. Jimmy approaches her and asks her condition. She explains that Mr. Hattrick is going to give the book to the principal tomorrow. She is so upset and distress, because the diary is something personal. Jimmy confirms it, as he says that having the other know your secret is really bad.
3) Arguing
Arguing is the act of having different view or against something which is being the case. It can be a fact or opinion. Arguing can also mean to deny or debate. Arguing occurs 11 times or about 5.09% from total 216 data in Bully video game.
The following are the examples from the acts of arguing found in Bully video game.
A : No listen. I need your help, pretend we're friends, walk with me. I'll pay, I'll pay you two bucks.
JH : Two bucks... Are you crazy? Make it five.
(44/Di/Rep/1-05) The dialogue above is between Jimmy and Algie. The setting is in the school library. Jimmy is strolling around the library when suddenly meets Algie who has been looking at the book shelf. Algie is asking for Jimmy to help him reach the locker. He offers Jimmy two dollars, but Jimmy does not like the offer. Instead Jimmy asks five dollars for the price.
This one is another example of arguing.
T : Smashing! Now, tell me Hopkins… is it true you said I was inbred?
JH : No.
42
The dialogue above happens between Jimmy and Tad in Tad’s front yard.
Previously Tad is asking Jimmy to bring him some eggs to do the next mission. Suddenly, Tad asks Jimmy about he being inbreed. Jimmy boldly says no as the answer, because he is never gossiping about Tad being inbreed before.
Here is another arguing act found in Bully video game. Pi : So this is how you treat a girl? Well, not me! JH : What are you talking about?
Pi : We had a date, and you are three minutes late. JH : No we didn’t.
(151/Di/Rep/2-20) This dialogue occurs between Jimmy and Pinky in front of the cinema. Pinky is waiting impatiently for Derby when Jimmy approaches her. Pinky mad at Jimmy as he is being late for a date. Otherwise, Jimmy denies it because he is not come for a date. They were not planning for any date at that time. Pinky is mistaking Jimmy as Derby.
4) Informing
Informing is the act of giving or transferring knowledge to make someone aware of something, usually facts or occurrences. Informing occurs 4 times in the data or about 1.85%. The examples of this type are in these data.
G : Look at you "Leave me alone Gary! I'm really self important that I've finally hit puberty". What's your problem? I'm just being nice to the new kid as he passes through bullworth on his inevitable journey to prison.
JH : Look, I gotta unpack. Would you guys mind getting outta here?
G : Oh, now look what you've done, Pete , Jimmy can't stand you already.
43
The dialogue above occurs in the first missions of the game. The characters in the dialogue are Jimmy Hopkins, and his new friends Gary and Pete. The setting is in the Jimmy’s new dorm room. Jimmy is telling Gary and Pete that he is about to unpack his stuff. He tells them as a response of Garry previous statements and conflict between Gary and Pete.
Another example of representative acts of informing is in the following datum.
JH : Yeah, but unless you buy everyone's vote, you never gonna win. Because they're definitely gonna ruin your speech at the debate.
E : Ohhh.. Unless I had a security manager... Oh please! Please! Please! Please!
(73/Di/Rep/1-09) The dialogue above occurs in the school corridor while Jimmy is strolling around and he meets Earnest who had been bullied. Earnest was patching a poster in the wall when suddenly some bullies appeared and bullied him. Jimmy greets him by asking about his campaign. Earnest asks Jimmy if he is going to vote for him or not. Jimmy has no interest in voting for Earnest but he sues Jimmy by promising some money. Jimmy agrees, but Jimmy tells him that he still would not win the election unless he pays everyone voices.
This following dialogue also represents a representative act of informing as show.
E : Ohhh... Unless I had a security manager... Oh please! Please! Please! Please!
44
This dialogue is the part of previous dialogue above. The dialogue is in the same setting and context. Here, Jimmy responds Earnest statement about the need of security manager to handle the campaign. Jimmy tells him that he has no idea of security manager, because it is expensive.
5) Explaining
Explaining is the act of giving a full picture or extra features of the subject being explained. Explaining usually comes in the form of interrogative answer. There are 8 illocutionary force of explaining found in the video game or about 3.7% from total data.
These following examples are the examples of the acts of explaining. JH : Yeah, you could've fooled me.
HM : What?
JH : I said you could've fooled me. This place is full of bullies and maniacs.
(30/Di/Rep/1-03) The example above is taken from the third missions on the first chapter. The dialogue occurs between Jimmy and the headmaster in the school yard. The headmaster is interrogating him about his adaptation with the school. Jimmy answers the questions, but he also says that the headmaster could have fooled him about the school. He explains that the school condition is full with bullies and bad students.
This is another example of explaining acts. E : I always knew I was born leader!
JH : Yeah, but unless you buy everyone's vote, you never gonna win. Because they're definitely gonna ruin your speech at the debate.
45
The dialogue is taken from mission 9 on chapter 1. It occurs at the school corridor while Jimmy was strolling around and he met Earnest who had been bullied. Jimmy greets him by asking about his campaign. Earnest asked Jimmy if he is going to vote for him or not. Jimmy has no interest in voting for Earnest. But, he sues Jimmy by promising some money. Jimmy agrees. However, he is never going to win, because those bullies are going to ruin the speech at the debate.
Another example of explaining is in the following datum.
G : There you are. Come on, I found something incredible. JH : Hold on. Relax, man. I can't keep getting in trouble. I can't
get expelled again.
(99/Di/Rep/1-14) The dialogue above happens between Jimmy and Gary in the boy dorm living room. Gary is sitting alone restlessly as Jimmy comes by. He is so excited to see Jimmy. He invites Jimmy to do another bad stuff. However, Jimmy refuses it. Jimmy explains that he does not want to be involved in more troubles. He does not want to get expelled from the school.
6) Stating
Stating is the act of giving a statement or opinion on fact as regard of the circumstances. This type of speech acts occurs 5 times in the video game or about 2.31% from total 216 data. These are the example of stating found in Bully video game.
H : That's a long story, you got any liquor? JH : No, I'm 15.
46
boys are bullying poor Hobo, but they run away and left Jimmy alone. Hobo asks Jimmy about liquor. However, he tells him that he does not bring any with him, because he is only 15 and it is illegal.
This is another example of act of stating.
G : Oh Marion, show me your breast stroke again... Or wait.. Do you like the boys on the team?
P : Yeah you right Gary. G : Which is it Petey?
JH : I see you guys are getting along as usual.
(60/InD/Rep-Exp/1-07) This dialogue happens in the boy dorm living room. The characters in the conversation are Jimmy, Gary, and Pete. As Jimmy enters the room, he sees Gary disturbing Pete. He says that Gary and Pete are getting along as usual. Instead, they are always in dispute, but still get along one another.
Another example of stating is in the following datum.
G : I say do it is a good chance to show Russell who's in charge around here. Now, run along pee stain. Before you mark the carpet. Yes, we've got to take care of Russell and his boys them after that, take care of all other cliques. Soon this school will be ours.
JH : I don't want the school.
47
7) Lying
Lying is the act of giving false or different impression about the true fact. This type of speech acts only occurs 1 time or 0.46% from total data. This is the example of lying found in Bully video game.
JH : Enough, ok... I'll get your book back.
Bt : Then we can kiss! The cold sores aren't contagious once they start to scab over!
[Jimmy returns] oh there you are.. Did you get it? JH : Yes I did it, and I didn't read it... much.
(97/InD/Rep-Exp/1-13) The conversation above occurs between Jimmy and Beatrice. The setting is in the girl dorm front yard. Beatrice is asking help for Jimmy to retrieve her seizure diary. Jimmy succeed in getting the diary back. He says he did not read it much. In fact, he did read it when he took the book from the office.
8) Convincing
Convincing is the act of assuring someone. It is the act that makes someone believe by argument or evidence that it is true or certain. This type of speech act occurs 3 times in the video game or 1.39% from total 216 data. These are the example of convincing found in Bully video game.
HM : Really… and that you’ve been saying some entertaining things about me and some barnyard animals!
JH : No, I never said that!
48
He says that he is not being pugilist and he never says something bad behind people.
This is another datum about convincing.
Pi : We had a date, and you are three minutes late. JH : No we didn’t.
Pi : Yes, we did.
JH : No we really didn’t, but look I remembered how much you liked flowers
(152/Di/Rep/2-20) This dialogue occurs between Jimmy and Pinky in front of the cinema. Pinky is waiting impatiently for Derby when Jimmy approaches her. Pinky is mad at Jimmy as he is being late for a date. Otherwise, Jimmy denies it because he is not come for a date. They are not planning for any date at that time. Pinky mistakes Jimmy as Derby. Jimmy convinces her by arguing twice and stressing the last argument that they are not having a date.
This is the other example of convincing.
P : Well, for one moment, I had friends. Just one moment. You and Gary. Yeah, Gary’s a snake, and you’re a psychopath,
JH : Aww, come on.
P : And you both bullied me mercilessly. But at last I wasn’t left out. Now, I’m back on my own and I’m too cool to be a dork, am I’m too dorky to be anything else.
JH : You’re not on your own… where is everybody?
49
9) Predicting
Predicting is the act of thinking ahead what might happen in the future. This kind of representatives acts only occur 1 time or 0.46% from total data found
in Bully video game. This is the example of the data from the act of predicting.
P : I guess you want to kill Gary, now that he turned most of the school against you and got those rich kids to throw eggs at you JH : Gary will get what’s coming to him… what’s wrong with you?
(162/Di/Rep/2-21) The dialogue above is between Jimmy and Pete in the living room of boy’s dorm. Pete is sitting alone when Jimmy comes. Pete is asking Jimmy feeling toward Gary whether he is mad and seeks revenge. Jimmy replies that Garry will get what he is done, because thing that goes around will come around.
10)Describing
Describing is the act of giving details about person, thing, or event. Describing only occurs 1 time in the video game or about 0.46% from total 216 data. This is the example of describing found in Bully video game.
JH : Well, you’re sitting around watching TV by yourself like a
loser… someone craps in your bed? What’s wrong?
P : Well, for one moment, I had friends. Just one moment. You and Gary. Yeah, Gary’s a snake, and you’re a psychopath.
50
b. Directives
Directives are the acts by which speakers direct listeners to perform some future act which will make the world fit the speaker’s words. It is a kind of speech
act which the speaker uses to get someone else to do something. It expresses what the speaker wants. Directives hold the biggest portion of speech act found in Bully video game. There are 103 or 47.68% directives from total 217 speech acts found in the data. There are 8 types of directives found in the data. They are questioning, requesting, warning, commanding, insisting, inviting, suggesting and negotiating. Each of these illocutionary forces of directives will be explained as follows. 1) Questioning
Questioning is the act of seeking information through reply. The speaker demands for an answer from the listener to get information. This kind of speech act is dominant in the video game with 59 occurrences or 27.31% from total 216 data. The examples of questioning are as follows.
G : This is where I stand up to you my friend. JH : What are you talking about?
G : I know you hate me, Jimmy - boy, I know you've said all that stuff about me behind my back.
JH : What are you talking about?
G : Don't play innocent with me - you wanna run this school, I wanna run this school - only one of us is going to make it - and it's gonna be me...
51
what Garry says. Jimmy is wondering. He asks Garry about it twice, the same questions and he raises his intonation on the second question to stress his intention. But still, Garry wants to put a fight against Jimmy.
This is another example of questioning from Bully video game. Pi : Hey Jimmy Hopkins!
JH : Do I know you?
Pi : No, I’m Pinky, but I know all about you! Everybody’s talking about you. Everybody says that you’re mean and angry and you like fighting. Gary said you’re so mad because you’re sexually confused.
(134/Di/Dir/2-18) The dialogue above occurs between Jimmy and Pinky in front of the movie theater. Jimmy was passing by when Pinky stops and greets him. Jimmy who never met her before questions her. She confirms it. In other hand, Pinky knows a lot about Jimmy.
This one is another example of questioning. JH : Hey Pete. Where is everybody? P : Oh, Jimmy. It’s you.
JH : Yeah
(160/Di/Dir/2-21) The dialogue above is between Jimmy and Pete in the boy dorm living room. Pete is sitting alone when Jimmy comes. Jimmy greets him and asks him where the students are, since there is no one around the school. However, Pete does not answer the question instead of being surprised with Jimmy appearance.
2) Requesting
52
HM : Nonsense. That's just school spirit. High jinks. Why, in my day, we felt nothing of castrating the new boys. I want you to stop this nonsense Hopkins, I want you to behave yourself. You might learn something.
JH : Fine. Can I go now? Sir. HM : On your way
(32/Di/Dir/1-03) The dialogues above are between Jimmy and the headmaster in front of the school. The headmaster is lecturing Jimmy about his way on adapting with the new school. Headmaster asks him to behave and act appropriately. Jimmy agrees with the headmaster. Then, he asks for permission to be dismissed and the headmaster allows it.
This is another datum of requesting.
G : Hey, relax friend, you're all pent up. Go easy, or they'll put you on medication. They did to me, Boy - nearly sent me insane. JH : That’s fascinating... Now if you'll excuse me.
G : I said relax man.
(18/Di/Dir/1-01) The conversation above happens in the boy dorm when Jimmy enters and he is about to get change. Gary stops and greets him. However, Jimmy seems to have no interest with Garry and he tends to refuse him. He praises Gary approaches, but he asks him to leave, because he has something to do.
This one is also an example of requesting.
G : Look at you "Leave me alone Gary! I'm really self important that I've finally hit puberty". What's your problem? I'm just being nice to the new kid as he passes through bullworth on his inevitable journey to prison.
JH : Look, I gotta unpack. Would you guys mind getting outta here?
G : Oh, now look what you've done, Pete , Jimmy can't stand you already.