i
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS TO TEACH VOCABULARY BASED ON TASK BASED LEARNING FOR SEVENTH GRADERS
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Brigitta Estianasari Windyaningrum Student Number : 061214044
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
v
I dedicate this thesis to those whom I love much, Jesus Christ & Virgin Mary, who always care about me My parents, who love me My sisters, who support and love me All of my friends, who always help me People are often unreasonable, illogical, and self-centered;
Forgive them anyway.
If you are kind, people may accuse you of selfish ulterior motives; Be kind anyway.
If you are successful, you will win some false friends and some true enemies; Succeed anyway.
If you are honest and frank, people may cheat you; Be honest and frank anyway.
What you spend years building, someone could destroy overnight. Build anyway.
If you find serenity and happiness, they may be jealous; Be happy anyway.
The good you do today, people will often forget tomorrow; Do good anyway.
Give the world the best you have, and it may never be enough; Give the best you've got anyway.
You see, in the final analysis, it is between you and God; it was never between you and them anyway.
vii ABSTRACT
Windyaningrum, Brigitta E. 2011. Supplementary Materials to Teach Vocabulary Based on Task Based Learning for Seventh Graders. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Vocabulary is an important element in language learning. Yet, it is probably difficult to learn and teach since it depends on many factors such as unfamiliar words, classroom atmosphere, students’ capability, unavailability of the materials and the complicated language. The most common problem encountered by the students in learning English is when they find the unfamiliar words or vocabulary. Teaching vocabulary is still important although it is not mentioned in the recent curriculum because vocabulary is taught through the skills’ learning. Having sufficient vocabulary mastery will assist the students to be able to develop their skills such as to comprehend the reading texts or to write an essay.
This study was aimed at helping Junior High School teachers provide interesting supplementary materials by designing supplementary vocabulary materials based on integrated skills-task based for seventh graders. The supplementary materials were presented in various activities and tasks to avoid the students’ boredom. There were two problems to be discussed in this study: 1) how is a set of supplementary materials to teach vocabulary based on task based instruction for seventh graders designed? and 2) what do the designed supplementary vocabulary materials based on task based instruction for seventh graders look like?
This study employed Educational Research and Development (R & D). Due to the time and resource limitation only four steps of R & D model were employed, namely research and information collecting, planning and developing product, preliminary testing and product revision. This study also adapted Kemp’s instructional design model and considered relevant theories related to vocabulary, task-based learning, young learners’ characteristics and School-Based Curriculum to design the materials based on task-based learning for seventh graders.
To acquire the information for developing the supplementary materials, the writer distributed questionnaire to the students of SMP BOPKRI 2 Yogyakarta and interview the English teacher. Having designed the supplementary materials, the writer distributed questionnaire to the English teacher and lecturers to obtain feedback, comment and evaluation on the designed supplementary materials.
viii ABSTRAK
Windyaningrum, Brigitta E. 2011. Supplementary Materials to Teach Vocabulary Based on Task Based Learning for Seventh Graders. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Kosakata adalah elemen penting dalam pembelajaran bahasa namun kadang kosakata juga sulit untuk dipelajari dan diajarkan tergantung pada beberapa faktor diantaranya kosakata baru, suasana kelas, kemampuan siswa, materi dan bahasa. Masalah yang kerap kali ditemui siswa dalam pembelajaran bahasa Inggris adalah saat mereka menemui kata-kata baru. Belajar kosakata tetap penting meskipun pembelajaran kosakata tidak disebutkan dalam kurikulum yang baru karena kosakata tidak lagi diajarkan terpisah namun pembelajarannya dijadikan satu dengan pembelajaran ketrampilan. Dengan mampu menguasai kosakata yang cukup banyak para siswa diharapkan dapat terbantu dalam mengembangkan ketrampilan yang dipelajari seperti dalam memahami bacaan maupun dalam membuat esai.
Studi ini bertujuan untuk membantu guru SMP dalam penyediaan materi kosakata tambahan yang menarik dengan membuat materi berdasarkan prinsip task-based learning untuk siswa SMP kelas VII. Materi ini diberikan dalam berbagai kegiatan dan tugas agar siswa tidak bosan. Ada 2 rumusan masalah yang dipaparkan dalam studi ini: 1) bagaimana materi tambahan untuk pengajaran kosakata dengan menggunakan task based untuk siswa SMP kelas VII dirancang? dan 2) bagaimanakah penyajian materi tambahan untuk pengajaran kosakata yang telah disusun tersebut?
Studi ini menggunakan metode penelitian dan pengembangan (R & D), namun karena keterbatasan waktu dan sumber hanya empat langkah dari model R & D yang digunakan yakni penelitian dan pengumpulan informasi, perencanaan dan pembuatan materi, evaluasi dan revisi. Dalam mendesain materi tambahan, penulis juga mengadaptasi model desain materi Kemp dan mempertimbangkan beberapa teori yang terkait dengan pengajaran kosakata, task-based learning, karakteristik siswa, dan Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan.
Untuk mendapatkan informasi yang dibutuhkan dalam pembuatan materi tambahan ini, penulis menyebarkan kuesioner pada para siswa SMP kelas VII dan melakukan interview kepada guru bahasa Inggris SMP kelas VII. Setelah membuat materi, penulis menyebarkan kuesioner kepada guru bahasa Inggris SMP kelas VII dan dosen untuk mendapatkan masukan, komentar dan evaluasi tentang materi yang telah disusun.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Praise be to God, my Lord Jesus Christ who never leaves me alone everytime and everywhere. I am so grateful for the gift of beautiful life, valuable experiences, miraculous blessings, amazing miracles, worth time, everlasting love, friendship, brotherhood and everything He grants for me. I thank Him for giving me the chance to do all things in my best and for bringing me to all wonderful moments I ever had. I also thank Virgin Mary, who always teaches me kindness, willingness, honesty, love and strength.
From my deepest heart, I thank the great people in my life whom I can learn and get many things from, my father, Bapak Matheus Poniman and my lovely mother, Ibu Fransisca Christina Sri Suharni for the care, love, prayer, understanding, patience, and for everything that I can not mentioned one by one. I warmly thank them for the endless love they gave to me. I know I will not be here now without them. I also thank my twin sisters, Rina and Rini for their love, support, and prayer. I am very pleased that they are willing to listen to me and tell me valuable things that make me get all my best. I thank them endlessly for the warm home and for every single beautiful moment I ever had.
x
My gratitude also goes to Mr. Yulius, the headmaster of SMP BOPKRI 2 Yogyakarta, who has permitted me to do a research. Special gratitude is directed to Ariaty Puji L., S.Pd. who has helped me during my research. I thank her for the time, guidance, suggestions and chance to conduct this study. Students of SMP BOPKRI 2 Yogyakarta also deserve my appreciation for being the participants of my study.
I warmly thank all of my relatives and friends for the encouragements and inspiration. Gratitude goes to those who have colored my life and have supported me, my wonderful friends, PBI 2006 The Glitters (Nita, Beti, Stella, Nisa, Berlin, Jati, Ragil, Kurnia, Jojo, Ardi, Christin, Emiko, Henny, Homo), The Fireflies (Nonok, Aldi, Adven, Riris, Satrio), KKN (Aya, Arum, Vincent, Doni, Bayu, Galih), Mudika St. Vinsensius a Paulo and Mudika St. Bonaventura for the support, help, strength, laugh, smile, friendship, togetherness and understanding. I am so lucky to have them in my life.
xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page TITLE PAGE ………
APPROVAL PAGES ………
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ……….
DEDICATION PAGE …..……….
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN ………..
ABSTRACT ………..
ABSTRAK ………..
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ………...
TABLE OF CONTENTS ………..
LIST OF TABLES ………
LIST OF FIGURES ………...
LIST OF APPENDICES ………... i ii iv v vi vii viii ix xi xiv xv xvi
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION ……….... 1
A. Research Background ………... 1
B. Problem Formulation ……….. 4
C. Problem Limitation ………. 4
D. Research Objectives ……….... 5
xii
F. Definition of the Terms ………... 6
1. School-based Curriculum ………. 6
2. Task Based Learning ..……….. 6
3. Vocabulary ……… 7
4. Seventh Graders ……… 7
5. Supplementary ……….. 7
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ………... 8
A. Theoretical Description ……… 8
1. Instructional Design ……….. 8
2. Teaching Vocabulary ……… 10
a. The Nature of Teaching Vocabulary ……….. 10
b. Principles on Teaching Vocabulary ………... 11
3. Task Based Learning ………... 13
a. The Definition of Task Based ……….. 13
b. Framework of Task Based Learning ………..………….. 14
c. The Types of Tasks ………….………. 16
4. Students’ Characteristics ………... 18
a. Physical Development ………. 19
b. Social Development ………. 19
c. Cognitive Development ………... 19
d. Emotional Development ……….. 20
5. School-based Curriculum ……….. 20
xiii
CHAPTER III: METHODOLOGY ………. 25
A. Research Method ………. 25
B. Research Respondents ………... 27
C. Research Instruments ………... 28
D. Data Gathering Technique ………... 30
E. Data Analysis Technique ………. 31
F. Research Procedures ……… 33
CHAPTER IV: RESULTS AND DISCUSSION ………..…... 35
A. Steps on Designing English Vocabulary Materials ……….…….…… 35
1. Research and Information Collecting ……… 35
2. Planning and Developing Product ……….. 42
3. Preliminary Testing ………. 50
4. Product Revision ……… 55 B. The Presentation of English Vocabulary Materials Based on Task Based for Seventh Graders ………..…… 57
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS ……… 61
A. Conclusion ……… 61
B. Suggestions ……….. 63
REFERENCES ……… 65
xiv
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
2.1 Basic Competence and Competency Standard ... 22
3.1 The Form of the Result of Participants’ Questionnaire ... 33
4.1 Data of Respondents ... 38
4.2 The Result of the Questionnaire ... 40
4.3 Topics and General Purposes ... 43
4.4 Learning Topics ... 44
4.5 Learning Indicators of the Materials ... 45
4.6 The Organization of Subject Contents ... 47
4.7 The Description of the Respondents……….51
4.8 The Result of the First Part of the Post-Designed Questionnaire...52
xv
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
2.1 Kemp’s Instructional Design Model ………... 9
2.2 Task Based Learning Framework ………... 16
xvi
LIST OF APPENDICES
Page
Appendix 1: Letters of Permission ... 68
Appendix 2: Instruments for Need Analysis ………...……70
a.List of Questions for Interviewing the Teachers ……… 71
b.Questionnaire for Need Analysis ……….…….. 72
Appendix 3: Questionnaire for Materials’ Evaluation ... 74
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents detailed information about the research background that leads to the study, the problem formulation in a form of questions and the limitation of the problem. Besides, this chapter also presents the research objectives, the research benefits, and definition of the terms which includes some terms related to the study.
A. Research Background
their skills such as to comprehend reading texts, to understand listening passage or to write an essay. Considering the importance of vocabulary role in students’
learning, the mastery of this element should be developed.
Since 2006 Indonesia has applied the curriculum namely School-Based Curriculum or Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP). As the consequences, all levels of education are expected to use School-Based Curriculum in carrying out their teaching learning process. Based on the curriculum, English becomes one of the subject matters that should be taught in Junior High School. As stated in the curriculum, the main objective of learning English for Junior High School students is that the students can come to the functional level. The English taught in Junior High School includes four skills, listening, speaking, reading and writing as stated in the School-Based Curriculum, while vocabulary and grammar are taught through the skills’ learning.
SMP BOPKRI 2 is one of the junior high schools which teaches English in its teaching learning process. This school has applied School-Based Curriculum or Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP) in its teaching learning process
since 2006. Based on the writer’s observation, most of the seventh graders seem
Most of them have learned English for one to three years and there were only few of them who have learned English since they were in the first grade of elementary school. There are also few of them who just learned English in Junior High School. To make the students participate actively in the class activities, the writer thought that they first should master the language elements including vocabulary. It is why the writer decided to design vocabulary materials to the seventh graders of SMP BOPKRI 2.
For the teacher, teaching vocabulary is difficult since the teacher becomes one of the important factors that makes the successful teaching learning process. The teacher should consider many things, for example what kind of teaching technique she or he will use. Teacher must determine the most efficient and effective methods (Kemp, 1977: 55). Kemp further stated that teacher needs to know the strengths and weaknesses of the alternative methods and then make selections in terms of the students characteristics and needs that will best serve the objectives. In other words, to create enjoyable teaching learning process, the teacher should select an interesting teaching technique without forgetting the students’ needs and level.
in his article Redesigning Non Task-Based Materials to Fit a Task-Based Framework, task based allows for the need analysis. It means that the course
content can be matched to the students’ need. He also stated that student-centered is the main principle in teaching learning process by using task-based. Task based also enables the students to learn vocabulary in natural context based on the language used.
This study aims at helping the English teacher of Junior High School to provide interesting materials in learning vocabulary. It also helps the students to learn vocabulary in communicative ways.
B. Problem Formulation
Considering the background presented above, the writer formulates the problems of the study as follows.
1. How is a set of supplementary materials to teach vocabulary based on task based learning for seventh graders designed?
2. What do the supplementary materials to teach vocabulary based on task based learning for seventh graders look like?
C. Problem Limitation
interact naturally in the target language and to participate in active and communicative task in English.
D. Research Objectives
This study is to bring about some objectives that are presented as the following.
1. To find out how a set of supplementary vocabulary materials based on task based learning for seventh graders is designed.
2. To present the supplementary materials to teach vocabulary based on task based learning for seventh graders.
E. Research Benefits
This study is expected to be able to give several contributions. The contributions are formulated as follows.
1. For the material designers
The results of the study can give a reference to the material designers to guide them in selecting and designing a set of supplementary materials to teach vocabulary for the seventh graders.
2. For the teachers
3. For the seventh graders
This study is to present a set of supplementary vocabulary materials which can help the learners in vocabulary practice. It is supposed to give opportunities for the learners to learn actively and communicatively by using the designed supplementary materials presented.
F. Definition of the Terms
There are some important terms related to the study. Those are as follows. 1. School-based Curriculum
According to Pusat Kurikulum Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Pendidikan Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, School-based Curriculum is a new
curriculum developed and carried out by each level of education under the coordination and supervision of Department of Education. The curriculum requires the teacher to make their own teaching materials based on the competence standards and basic competencies. In this study, the writer uses curriculum which is used in SMP BOPKRI 2 YOGYAKARTA namely School Based Curriculum. The curriculum is used as the reference in designing the materials. The materials in this study are designed by considering the Competency Standards and Basic Competences.
2. Task Based Learning
of language tasks as the central key in learning (Richards and Rodgers, 2001:223). Freeman and Larsen (2000:44), in the book entitled Techniques and Principles in Language Teaching, add that a task-based instruction has aims in providing the
students a natural context for language use. In this study, task based deals with the technique used in classroom by motivating the students to learn language by themselves.
3. Vocabulary
Hornby (1974: 959) defines vocabulary as the words that make up a language which can stand alone or together and they may have different meaning. In this study, the vocabulary refers to the vocabulary in the English curriculum to the seventh grade students of Junior High Students.
4. Seventh Graders
Seventh graders are students who are in the first grade of Junior High School. They are usually 12-13 years old. They are categorized as adolescence who develop emotionally, socially, cognitively and personally. In this study, seventh graders are students who are in the seventh year of formal education held in Indonesia. The students are the students of SMP BOPKRI 2 Yogyakarta.
5. Supplementary Materials
8
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter is divided into two main parts, namely theoretical description and theoretical framework. In the theoretical description, the writer reviews some theories used as the references of the study. Then, the writer draws a theoretical framework based on the theoretical description which is used as the guideline to answer the problems of this study.
A. Theoretical Description
In the theoretical description, the writer discusses some theories which will be used as the guidance to the development of the vocabulary materials. They are instructional design, vocabulary, task based, students’ characteristics and
School-based Curriculum. 1. Instructional Design
In this study, the writer would consider Kemp’s instructional design
model to design and develop the vocabulary materials since Kemp’s model of
instructional design is a flexible one. The flexibility of Kemp’s model means that
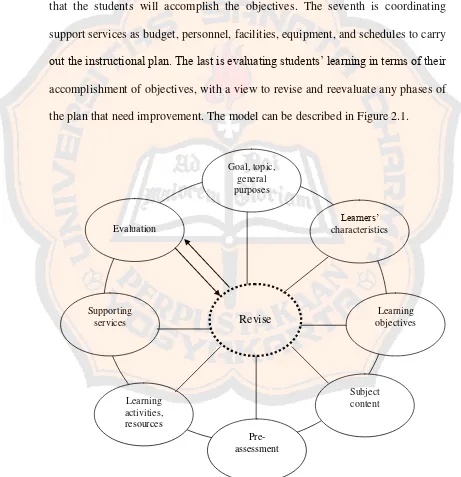
the instruction is to be designed. The third is specifying the learning objectives to be achieved. The fourth is listing the subject contents that support each objective. The fifth is developing pre-assessments to determine the students’ background and present level of knowledge about the topic. The sixth is selecting teaching learning activities and instructional resources that will treat the subject contents so that the students will accomplish the objectives. The seventh is coordinating support services as budget, personnel, facilities, equipment, and schedules to carry out the instructional plan. The last is evaluating students’ learning in terms of their
accomplishment of objectives, with a view to revise and reevaluate any phases of the plan that need improvement. The model can be described in Figure 2.1.
Figure 2.1. Kemp’s instructional design model Goal, topic,
general purposes
Learners’ characteristics
Revise objectives Learning
Subject content
Pre- assessment Learning
activities, resources Supporting
2. Teaching Vocabulary
a. The Nature of Teaching Vocabulary
Teaching vocabulary is not easy for some teachers. One of the reasons is that vocabulary teaching and learning must fit into the broader framework of a language course. It means there should be a balanced range of learning opportunities. Nation (2003:133-134) suggests four strands to see whether there is a balanced range of opportunities or not in the language course. They are as follows.
1. Learning from meaning-focused input
This strand involves learning from listening and reading. The focus of learning vocabulary in this strand is that learners need to know 98 percent of running words already. It means that , at most, there should be only one unknown word in every fifty running words (Nation, 2003: 133).
2. Deliberate Learning
The deliberate learning strand, which is sometimes called form-focused instruction or language-focused learning, involves paying deliberate attention to language features such as sounds and spelling. Memorizing students’ first
language translation is considered as the most obvious deliberate learning technique in learning new vocabulary.
3. Learning from meaning-focused output
In this strand, the students’ main attention is on communicating messages
vocabulary productively can strengthen learning and can push students to focus on aspects of vocabulary knowledge that they did not need to attend to when listening and reading (Swain, 1985).
4. Fluency Development
The aim of this strand is to help students make the best use of what they already know. It is important to see fluency as being related to each of the four skills of listening, speaking, reading and writing with fluency needed to be developed independently in each of these skills (Nation, 2003: 134).
b. Principles on Teaching Vocabulary
Nation suggests some principles the language teachers can use for teaching vocabulary (2003:135-141). They are as follows.
1. Focus on the most useful vocabulary first
2. Focus on the vocabulary in the most appropriate way
This principle gives explanation at how new vocabulary should be taught and learned. There are many learning strategies that can be used to teach vocabulary. Nation suggests four most important vocabulary learning strategies to teach low frequency words, namely using word parts, guessing from the context, using word cards and using dictionaries. The ways of helping students with high frequency words can be simpler that with low frequency words. These ways includes directly teaching the words, getting students to speak and write using the words and getting students to study words and do exercise based on the words (2003: 138-139).
3. Give attention to the high frequency words across the four strands of a course High frequency vocabulary needs to occur in all strands. It should get deliberate attention through teaching and study and should be met and used in communicating messages in listening, reading, speaking and writing (Nation, 2003:139).
4. Encourage learners to reflect on and take responsibility for learning
responsibility for their own vocabulary learning, students need to choose words that will be useful for them.
3. Task Based Learning
In this discussion, there are two parts that will be discussed. Those are the definition of task based and the framework of task based.
a. The Definition of Task Based
There have been many advocates or researchers defining and explaining the task based instruction. According to Freeman and Larsen (2000:44), in his book entitled Techniques and Principles in Language Teaching, a task-based instruction has aims in providing the students a natural context for language use. Using task-based, it is expected that the students are able not only do or complete the task given but also interact with other students and teacher. Interaction in task-based aims at facilitating the learners’ acquisition of language in which the
learners have to express their own understanding.
In addition, Long and Crookes (1993) mentioned three different types of task-based instruction. The first is procedural, in which the teacher at first gives example to the teachers the ways how to do or complete the tasks. The second type is language learning should be seen as a process through communicative interaction. In this type, the students and teacher decide together the tasks to do. The last type is task-based language teaching which is made by the students. It focuses more on the meaningful interaction between the students.
b. Framework of Task Based Learning
According to Willis (1996), the components of task based are divided into three phases. They are as follows.
1. Pre Task
In this phase, the teacher introduces the topic to the students and helps the students to understand the task instructions. Harmer (2002:87) added that in the pre task the teacher discusses the topic with the class and may highlight useful words and phrases. Before giving pre task language activities, the teacher should help the learners to define the topic area and then help the students to recall and activate words or phrases that will be used both during the task and outside the classroom.
2. Task Cycle
This phase consists of three stages, namely task, planning and report. a) Task
In this stage, the students do the task. They can perform the task in pairs or in small groups. The students also have chance to choose and use whatever language they already had and whatever they want to say to express themselves. The teacher, in this stage, is as the monitor. She or he monitors and encourages the students when the students are doing the task.
b) Planning
In this phase, the teacher helps the students to plan their report effectively. The students are expected to maximize their learning opportunities in the task cycle. After doing task, the students tell the whole class what they did in the form of both oral presentation and written presentation. During the planning stage, the teacher becomes the language adviser. The teacher should help the students to shape the meanings and express exactly what they want to say. She or he is allowed to correct their language and give advice for them. c) Report
3. Language Focus
This phase consists of two stages, namely analysis and practice. In analysis stage, the students analyze and discuss the listening passage or reading text which they have to look up for the task. In practice stage, the teacher may conduct some form of practice of specific language features such as words, phrases, patterns and sentences.
The components of task based can be summarized as follows.
The Figure 2.2 The Components of TBL Framework (Willis:1996)
c. The Types of Tasks
1. Listing
This task involves two processes namely brainstorming and fact-finding. In the first process, the students draw on their own knowledge and experiences either as a class or in pairs/groups, while in the second process, the students are asked to find the things in their own ways, either by asking other people or referring to books.
2. Ordering and Sorting
The task involves four processes. The first is sequencing items, actions, or events in a logical or chronological order. The second is ranking items according to personal values or specified criteria. Categorizing items in given groups or grouping them under given headings is the third process. The last is classifying items in different ways, where the categories themselves are not given.
3. Comparing
There are three processes in this task. The first is matching to identify specific points and relate them to each other. The second is finding similarities and things in common. The third is finding differences.
4. Problem Solving
5. Sharing Personal Experiences
The aim of this task is to encourage the students to talk more freely about themselves and also to share their experiences with others.
6. Creative Tasks
These tasks are often called projects and involve pairs or groups of learners in some kind of free creative work. These tasks can involve the combination of task types such as listing, ordering and sorting, comparing and problem solving.
4. Students’ Characteristics
Junior High School consists of three grades namely grade seven, grade eight and grade nine. In this case, the writer will only concern with grade seven. According to Hurlock (1980:185), the students of grade seven are of the age 12 or 13 where they are in the puberty stage. They are considered as adolescence. Adolescence is a transition period that is a period of individual’s life when they
a. Physical Development
In adolescence stage, the growth of body is rapid although it is varied among the students. Their body changes markedly in form and function during this stage of development. Boys and girls have differences in their growth. Boys develop wider shoulders for example while girls develop wider hips. Hamachek (1990: 107) says that in adolescence, strength and stamina increase and correspondingly, so does the capacity for work and play.
b. Social Development
Much adolescence spends their time more outside their home. They prefer spending time with their friends or groups than with their family. Adolescence searches their identity through the value given by other people. Many activities, which are usually done in groups or peers, aim at knowing themselves through feedback from others. Hurlock (1980:213) says that the individuals get more influence to their behavior, attitude, interest and appearance from their friends rather than their family. Pikunas (1976:263) adds that discussion with peers facilitates the students to improve their communication skills as well as to generate new interest and attitudes, broaden viewpoints, and enrich personality resources.
c. Cognitive Development
everyday, concrete here and now happening to complex issues and the meaning of life (Hamachek 1990: 127).
They are already able to think, hypothesize and imagine. They are able to think from the concrete issues to the complex ones, develop hypothesis based on certain situation and imagine something based on their point of view. Hamachek (1990: 123) adds that it is during adolescence that one develops the capacity for imagining and hypothesizing when a certain situation exists.
d. Emotional Development
In this stage, there is an increasing of emotional which is apparent in various ways. Emotionally, adolescents tend to be unstable since they are in the transition period from childhood into adulthood. They become sensitive and react easily to certain situation. The series of fluctuating ups and downs is the main characteristic of emotional development in adolescence. Hamachek (1990:121) adds that depression is the common emotional experience in adolescence.
5. School-Based Curriculum
According to Pusat Kurikulum Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Pendidikan Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, School-based Curriculum is a new
curriculum developed and carried out by each level of education under the coordination and supervision of Department of Education. The curriculum includes Content Standard (Peraturan Menteri No.22) and Graduates’ Competency
framework, curriculum structure, learning content, and academic calendar while Graduates’ Competency Standard involves the minimum graduates’ competency
standards of subject matters.
It is stated in the curriculum that the teaching of English covers four skills namely listening, speaking, reading and writing, while the elements of English are taught implicitly. It means that the teaching of English elements coincides with the teaching of English skills. In this study, the writer focuses on one of English elements, namely vocabulary.
The basic competence for seventh graders of junior high is basically to respond meaning in transactional and interpersonal conversation, monologue and functional text accurately and fluently based on the topics discussed. The competency standards used in this study is general competence standards used in the second semester. Those are to comprehend transactional and interpersonal conversation and to comprehend meaning in oral functional text and monologue in the real daily life context. However, the vocabulary materials taught in classroom should deal with the competency standards and the basic competences stated in the school-based curriculum.
Competency Standard Basic Competences
to comprehend transactional and interpersonal conversation and to comprehend meaning in oral functional text and monologue in the real daily life context.
Be able to respond the meaning in simple functional text about family
Be able to respond the meaning of things in classroom and instructions
Be able to respond the meaning in simple functional text about things in shops in a form of shopping list
Be able to respond the meaning in simple descriptive text about animal
Be able to respond the meaning in simple text on one’s job and responsibility
Be able to respond the meaning in simple sentences of dislike and like about hobby Be able to respond the meaning in simple descriptive text about people
Be able to respond the meaning in simple procedure text
Table 2.1 The List of Basic Competence and competency Standard
B. Theoretical Framework
This section discusses the synthesis of theories discussed in the previous subchapter. This theoretical framework consists of the steps for developing and designing the vocabulary materials by adapting Kemp’s instructional design
To find out the answer of the first objective of the study, the writer has to understand some principles, namely teaching vocabulary, task-based learning, students’ characteristics and the curriculum. In teaching vocabulary, the writer
should design material which is adjusted to the students’ characteristics. Vocabulary teaching and learning should be a balanced range of learning opportunities in language course. Focus on the most important and useful vocabulary is one of the principles in teaching vocabulary.
In task based learning, tasks are considered as the core unit of planning and instruction. The framework of task-based learning consists of three phases namely pre task, task cycle and language focus phase. In these phases, the students function as active language users while the teacher functions as the facilitator and monitor.
To achieve the learning goals and objectives, the writer chooses the interesting and contextual activities. There are many kinds of tasks used in the designed materials. Listing, ordering and sorting, comparing and creative tasks are chosen since those tasks can be done both individually, and in pairs or in groups.
The steps used in this study based on the Kemp’s model but only some steps are used. Kemp’s model is chosen since it is flexible. We can start and go forward from whichever element we are ready to start with and then move to the other steps. The explanation of the steps is as follows.
a. Learners’ Characteristics
Knowing the learners’ characteristics is important to design and develop materials because learners’ characteristics are an input and basis for the writer to
design the materials. The writer obtains information about learners’ capabilities, needs, interest, learners’ academic, social and emotional factors such as academic background, learners’ participation in class, level of intelligence through interview
and questionnaire.
b. Stating Goals, Topics and General Purposes
Learning goals are something that the students should achieve in their learning process. To state the goals, general purposes and topics, the writer observed the recently curriculum used that is School Based Curriculum.
c. Specifying Learning Objectives
After having known and understood the goals, the objectives must be stated in terms of activities that will best promote learning. The writer uses the stated goals, topics and general purposes to specify the learning objectives.
d. Listing Subject Content, Learning Activities and Resources
25
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
This chapter presents detailed information about the methodology used to accomplish the study. It consists of research method which provides the information about the method used for the study, research respondents and research instruments that show the instruments used in the study. This chapter also includes data gathering technique that is about the technique used, data analysis that is how the data obtained is analyzed, and research procedures that are the steps conducted in the study.
A. Research Method
1. Step of Pre-Design
In this category, there was a step which was done before the writer designed and developed the materials, namely research and information collecting. The step, research and information collecting, was to find the relevant information and to study the research findings in relation to the materials to be designed and developed. In this study, it involved review of related literature and needs analysis survey.
2. Step of Main Design
In this category, there was a step which was done when the writer designed and developed the materials, planning and developing product. The step, planning and developing product or materials included stating the objectives as what stated in School-based Curriculum as competency standards and basic competencies and developing materials based on the research findings. It also involved planning for tasks to be developed. Then, the writer designed and developed vocabulary materials based on the needs analysis and the goals that the students should achieve.
3. Steps of Post-Design
In this category, there were two steps which were done after the writer designed and developed the materials. These steps included preliminary testing and product revision. The explanation of each step was as follows.
a. Preliminary Testing
teaching field. It was hoped through preliminary testing, the writer could gain criticisms and suggestions that led to changes and improvements of the preliminary materials.
b. Product Revision
The final step was product revision which aimed at revising and making improvement of the designed materials based on the feedback obtained. Product revision was needed to determine whether the materials have been complete and met the objectives to be achieved.
B. Research Respondents
In this study, the writer would divide the respondents as follows. 1. Respondents in Research and Information Collecting
The respondents of this step were they who were needed for gaining information and data needed for the need analysis. The respondents were the English teacher and the seventh graders of SMP BOPKRI 2 YOGYAKARTA. The writer expected valuable information and input from the teacher especially about the students’ characteristics and the students’ needs.
2. Respondents in Preliminary Testing
obtain feedback, evaluation and comment on the designed materials which would help the writer in making revision and improvement on the materials.
C. Research Instruments
In order to obtain data and information, the needs’ analysis, feedback and
effects of the designed supplementary materials, the writer needed some instruments. The instruments used are presented as follows.
1. Instrument for research and information collecting
In order to obtain data and information of needs’ analysis, the writer
conducted interview. Interview is one kind of qualitative researches that involves the collection data through direct verbal interaction between individuals. Ary et al (2002:434) states, “interview provides insight on participants’ perspectives, the
meaning of events for the people involved, information about the site, and perhaps information on unanticipated issues. It allows immediate follow-up and clarification of participants’ responses”. There are there common types of
interview namely, structured interview, semi-structured interview and unstructured interview (Borg, 1963:222).
the learners’ characteristics, teaching learning activities, materials and curriculum used that would be useful to design and develop the materials.
In order to obtain data and information of needs’ analysis, the writer also
distributed questionnaires. According to Ary et al, there are two types of questionnaires: structured or close and unstructured or open questionnaires (2002:175). In the structured questionnaires, the questions has been structurally ordered with options which should be chosen by the respondents as the alternative answer, while in the unstructured questionnaires, the respondents are free to answer the questions by their own words.
In this study, the writer used the structured questionnaires in which the participants should choose one of the alternative answers provided. The questionnaires were conducted for the seventh graders of SMP BOPKRI 2 YOGYAKARTA. The students were asked to answer some questions concerning the materials they mostly liked and teaching learning activities.
2. Instrument for preliminary testing
answering the questions. The questionnaire was delivered in English since the teacher and lecturers had already had sufficient knowledge of the use of English.
D. Data Gathering Technique
The data gathering were conducted twice: in research and information collecting stage and in preliminary testing stage.
In research and information collecting, the writer used some techniques. To obtain the information and references needed for the study the writer found books and journals in the library and articles from the internet.
In order to gather data and information of the needs’ analysis, the writer
conducted interview. The interview was directed to English teacher of SMP BOPKRI 2 YOGYAKARTA. It was aimed at obtaining data on the learners’ characteristics, classroom activities and the curriculum being used. The questions included in the interview were the students’ difficulties in learning vocabulary, the
activities used in the classroom when the students learn vocabulary, the media used in the classroom, the sources the teachers usually use, and the technique applied.
In order to gather data and information of the needs analysis, the writer also distributed questionnaires. It was directed to the seventh graders of SMP BOPKRI 2 YOGYAKARTA. It was aimed at obtaining data on the materials the students mostly liked and the teaching learning activities.
the writer tried to find out the English teacher and lecturers’ opinions and
suggestions which were used as the means to evaluate and improve the designed supplementary materials. The questionnaires were intended to obtain the English lecturers and teacher’s arguments of the designed materials. The English lecturers
and teacher could also give criticism and suggestions so that the designed materials were useful for the students.
E. Data Analysis Technique
The technique used to analyze the data will be explained based on the instruments used. The explanation is as follows.
1. Interview
The data obtained from the interview of one English teacher of SMP BOPKRI 2 YOGYAKARTA was analyzed through description or called as qualitative data analysis. It was done by interpreting the answers and elaborating the information obtained. In addition, the writer could use the field notes that she had made during the interview for analyzing the data.
2. Questionnaire
In this study, questionnaires were used in two different steps. It was used in the research and information collecting and in the preliminary testing. Since the types of questionnaires used in those steps were different, the way to analyze them was also different.
The data obtained from the questionnaires was analyzed by calculating each item by percentage. According to Ary et al (2002:125), “The percentages are calculated by dividing the total number in one category by the total number in all categories and multiplying the result by 100.” Percentages, however, can express the
information in a clearer way as so it would be easier to interpret and understand the data presented. The formulation to find out the percentage is presented as follows.
n
x 100 % n
Note :
n = the number of respondents who choose certain statements
n = the total number of participants
Since the questionnaire conducted for preliminary testing was questionnaire which combined the two types, the data was analyzed in two different ways. In the first part, percentage was used to analyze the data. The formula of calculating the percentage is the same with the previous formula.
n
x 100 % n
Note :
n = the number of respondents who choose certain statements
After the percentage of each statement was found, the data were presented in the format displayed in Table 3.1.
Table 3.1 The Form of the Result of Participants’ Questionnaire
No. Participants’ Opinion
Frequency of Occurrence Percentage
1 2 3 4 N %
In the second part, the data were analyzed by summarizing and presenting the respondents’ answer into paragraphs. The result of the questionnaire was used to as the feedback to revise and improve the designed materials.
F. Research Procedures
The procedure of conducting the study was carried out through some steps. The procedures were as follows.
1. Doing library research for collecting information related to the study 2. Making proposal and asking for permission for conducting the research 3. Designing and conducting instruments used for the study
4. Obtaining the need analysis data and analyze the data 5. Planning and developing the materials
6. Conducting the designed materials evaluation survey 7. Analyzing materials evaluation data
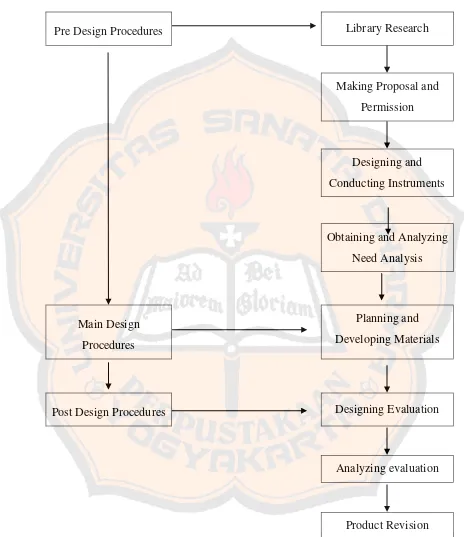
The writer’s procedures in designing in the materials can be illustrated in figure 3.1.
Pre Design Procedures Library Research
Making Proposal and Permission
Designing and Conducting Instruments
Obtaining and Analyzing Need Analysis
Main Design Procedures
Planning and Developing Materials
Post Design Procedures Designing Evaluation
Analyzing evaluation
35
CHAPTER IV
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents the research results and discussion of vocabulary materials based on task based learning. This chapter is divided into two main parts. The first part presents the steps on how to design English supplementary materials to teach vocabulary based on task based learning. The second part presents what English vocabulary materials for seventh graders look like.
A. Steps on Designing English Vocabulary Materials Based on Task Based Instruction for Seventh Graders
There were four steps on designing English supplementary vocabulary materials which were elaborated in this chapter. They were (1) research and information collecting, (2) planning and developing product, (3) preliminary testing, and (4) product revision. Each step will be elaborated as follows.
1. Research and Information Collecting
Before designing English vocabulary materials based on task based learning for seventh graders, the writers conducted an interview and distributed questionnaire, which aimed at obtaining data and information related to the students’ needs.
a. Interview the Teacher
obtained some information related to the students’ characteristics, interest and
need in learning English especially in learning English vocabulary.
From the result, it was found that the students had different background of learning English. Generally, the students have already had background of learning English since they were in elementary school although it was different from one to the others because most of them have learnt English for one to three years and there were only few of them who have learnt English since they were in the first grade of elementary school. It can be said that the students were mostly in the low to medium level of intelligence.
According to the teacher, since the students had different background of learning English, they had different understanding, knowledge of English and vocabulary mastery. It was one of the difficulties found in learning English. The other difficulty was the students’ motivation in learning English,
especially in learning vocabulary. From the writer’sobservation and teacher’s
explanation, some of the students had less interest in searching words’
had to speak in front. Besides, the students sometimes did not actively involve in the teaching learning process.
Dealing with the teaching techniques used in classroom, the students felt excited, and active in learning English if the teacher delivered the materials by using pictures or games. Media also played important role in the teaching learning process. There were some media can be used in the classroom activity. Media helped the teacher to create fun and interesting teaching learning activity in class. Besides, media also helped the students to remember and understand the materials faster. In learning vocabulary, especially, the students were motivated when they had to find words through pictures, puzzle or crossword.
Based on the interview, there were 4 contact hours in a week of English class. The teacher taught the English language skills and elements including vocabulary in an integrative way. It was because the materials used were from handbook, which were constructed as integrated materials. However, the teacher sometimes provided certain time to discuss the vocabulary for example after they discussed the materials or in the end of the class. It aimed at recalling the vocabulary they have learnt during the class.
Dealing with the materials used in class, the teacher said that the materials were taken from some handbooks which adapted School Based Curriculum. Some handbooks were used because the teacher had to adjust the materials with the students’ capability. It was difficult to find book which
Although most of the activities and tasks were based on the handbook prepared, the teacher still created her own tasks to be given to the students. The teacher also provided some pictures or games which were not in the book.
b. Questionnaire
The need analysis questionnaire’s respondents were twenty students of
seventh graders of SMP BOPKRI 2 Yogyakarta. The data were recorded in Table 4.1.
Table 4.1 : Data of the Respondents
Respondents
Sex Ages
Male Female 12 13 14 Seventh graders of SMP BOPKRI 2
Yogyakarta
14 6 8 7 5
of them considered the teacher as the important factor why they liked to learn English. There were 8 students who did not like to learn English. They stated that English is difficult to be understood and to be learned.
The next two questions were about the vocabulary teaching. All of the students stated that the teacher taught vocabulary during the teaching learning process. The students were motivated to learn vocabulary through all skills but they chose reading and speaking as the priority. The fourth question was related to the difficulty the students found when they learn English. Most of the students considered new vocabulary as one of the difficulties they found in learning English. The students also felt difficult to learn English because they didn’t have much time to practice English. Two of the students wrote their own answers mentioning that the uncomfortable of the classroom situation and the uninteresting learning method used by the teacher became their difficulties of learning English.
The last question was related to the topic that the writer offered. From the result of the questionnaire, the students chose procedure, asking and giving information, like and dislike, family life, giving instruction, do and don’t, describing people and numbers. Those topics were considered as the wants of the students. The writer might reorder, add or reduce the topics based on the lacks of the students, the need of the students, the curriculum and the degree of the topics’ difficulties. The result of the questionnaire can be seen in Table 4.2
Table 4.2 : The Result of the Questionnaire
Questions Responses N Percentage
Do you like English?
a.Yes b.No 18 2 90 % 10 % Does your the teacher
teach vocabulary in class?
a.Yes b.No 20 - 100 % - What kind of activities do
you like when you learn vocabulary? (you may choose more than 1)
a. Listening b.Speaking c. Reading d.Writing 5 11 12 7 14 % 31 % 35 % 20 %
What are the
obstacles/difficulties you found in learning English?
a. Boring activities
b.The explanation aren’t really easily
understandable c. A new vocabulary
Questions Responses N Percentage
What are the
obstacles/difficulties you found in learning English?
e. Less practice f. Other answers
Uncomfortable class situation Uninteresting method 6 1 1 30 % 5 % 5 % What kinds the methods do
you like in learn English?
a. Lecture b.Discussion
c. Question and answer
3 8 9 15 % 40 % 45 % What are your favorite
activities in learning English? (you may choose more than 1)
a. Role Play
b.Question and answer c. Pair/Group discussion d.Problem solving e. Games 4 12 15 3 11 9 % 27 % 33 % 7 % 24 %
What are your favorite topics? (choose 5 of them)
a. Procedure
b.Asking & Giving Information
c. Like & Dislike d.Describing Animal e. Family Life
f. Numbers
g. Giving instruction h.Describing People i. Do & Don’t j. Thank you
2. Planning and Developing Product
After obtaining the data, the writer developed the framework of the materials to be designed. It consisted of stating goals, topics and general purposes, specifying learning indicators and organizing subject content.
a. Stating Goals, Topics and General Purposes
To state the goals, general purposes and topics, the writer observed the recently curriculum used that is School Based Curriculum. Since the goal of teaching vocabulary was not stated in the curriculum, the writer then created the goal. The goal of this study was to assist the seventh grade students of Junior High School to be able to master and learn English vocabulary related with certain topics so that they would find it easy in developing their skills.
Table 4.3 : Topics and General Purposes
Topics Basic Competences
Family
Be able to respond the meaning in simple functional text about family
Instructions
Be able to respond the meaning of things in classroom and instructions
Shopping List
Be able to respond the meaning in simple functional text about things in shops in a form of shopping list
Describing Animals
Be able to respond the meaning in simple descriptive text about animal
Profession
Be able to respond the meaning in simple text on one’s job and responsibility
Like and Dislike
Be able to respond the meaning in simple sentences of dislike and like about hobby
Describing People
Be able to respond the meaning in simple descriptive text about people
Procedure Be able to respond the meaning in simple procedure text
The writer also considered the teacher’s suggestions. The teacher
suggested that the topics should be based on the curriculum. Besides, the teacher also said the students’ level of proficiency should be considered.
She added it was better to develop topics which were familiar to the students.
There were 8 topics developed, in which five of them were selected by the respondents while the others were selected by the writer. The topics selected by the students were like and dislike, family life, instruction, procedure and describing people while the topics selected by the writer were describing animals, shopping list and profession. The writer organized the topics based on the level of difficulty of each topic. The topics were stated in Table 4.4.
Table 4.4 : Learning Topics No Learning Topics
1. Family
2. Instructions
3. Shopping List
4. Describing Animals
5. Profession
6. Like and Dislike 7. Describing People
b. Specifying Learning Indicators
After stating the goals, general purposes and learning topics, the writer then specifies the learning indicators. The learning indicators were defined to measure the students’ achievement of the competency in every meeting, whether the students were able to achieve the general purposes. The learning indicators are presented in Table 4.5.
Table 4.5 : The Learning Indicators of the Materials Basic Competences Learning Indicators Be able to respond the
meaning in simple functional text about family
At the end of the lesson, the students are able to: 1.Mention the members of family
2.Draw a family tree
3.Write sentences based on the picture Be able to respond the
meaning of things in
classroom and
instructions
At the end of the lesson, the students are able to: 1.Mention the things in classroom
2.Mention words and its function 3.Write instructions
Be able to respond the meaning in simple functional text about things in shops in a form of shopping list
At the end of the lesson, the students are able to: 1.Name the words based on pictures
2.Write a shopping list
Be able to respond the meaning in simple descriptive text about animal
At the end of the lesson, the students are able to: 1.Mention and classify animal
Basic Competences Learning Indicators Be able to respond the
meaning in simple text on one’s job and
responsibility
At the end of the lesson, the students are able to: 1.Mention job/profession
2.Write a descriptive text
Be able to respond the meaning in simple sentences of dislike and like about hobby
At the end of the lesson, the students are able to: 1.Mention words related to hobby
2.Express like and dislike
Be able to respond the meaning in simple descriptive text about people
At the end of the lesson, the students are able to: 1.Mention adjectives used in describing people 2.Write a descriptive text
Be able to respond the meaning in simple procedure text
At the end of the lesson, the students are able to: 1.Mention words related to procedure
2.Rearrange procedure text 3.Write procedure text
c. Organizing Subject Content
Table 4.6 : The Organization of Subject Contents
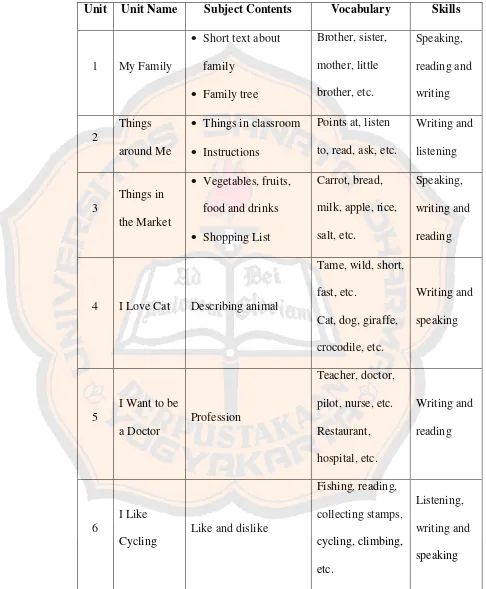
Unit Unit Name Subject Contents Vocabulary Skills
1 My Family
Short text about family
Family tree
Brother, sister, mother, little brother, etc. Speaking, reading and writing 2 Things around Me
Things in classroom
Instructions
Points at, listen to, read, ask, etc.
Writing and listening
3
Things in the Market
Vegetables, fruits, food and drinks
Shopping List
Carrot, bread, milk, apple, rice, salt, etc.
Speaking, writing and reading
4 I Love Cat Describing animal
Tame, wild, short, fast, etc.
Cat, dog, giraffe, crocodile, etc.
Writing and speaking
5
I Want to be a Doctor
Profession
Teacher, doctor, pilot, nurse, etc. Restaurant, hospital, etc. Writing and reading 6 I Like Cycling
Like and dislike
Unit Unit Name Subject Contents Vocabulary Skills 7 She is Beautiful Describing people Beautiful, lazy, friendly, curly hair, short, etc.
Listening, reading and writing 8 Show Me How Procedures
Boil, pour, heat, add, put, mix, etc.
Writing and speaking
After classifying and arranging the learning topics and the subject content, the writer described the content of each unit of the designed materials. The writer designed the learning materials based on the results of research and information colleting and the principles of task based learning. The principles of task based learning used in this study were based on the notion of the Task-Based Language Teaching framework proposed by Willis (1996:40). In order to design well-arranged vocabulary materials, the framework which consists of three phases namely pre-task phase, task-cycle and language focus, was adapted.
to prepare the students for the main task. The second phase, Work it out, served as the main task of the lesson. This phase tried to facilitate the students to learn and produce language by accomplishing the activities. The third phase, Make it better, included the language focus. The last phase, Do it over, was additional phase whose aim was to review the vocabulary given in the previous phases.
There were various kinds of tasks used in teaching learning activities. The writer designed the activities to be solved both individually and pair or group work. Since the task based learning was meant to be used with English as the language of classroom instruction, pair and group work would be helpful in achieving meaningful communication. Besides, pair and group works allowed the students to work together and the higher level students would help the lower level students in finishing the task. In the following the kind of tasks used in each phase of the designed materials as well as the purpose of each phase were discussed.
A. Come in
B. Work it out
This was where the main task takes place. The students were given tasks which were more complex than the previous phase. The students were asked to work individually or in pairs. The tasks would be problem solving, ordering and sorting, and some creative tasks. The focus of this phase was to provide the students to produce and learn the language. C. Make it better
This phase was used as repetition of the vocabulary items. The students would do the tasks which were almost the same with the previous phase. It provided supportive tasks so that the students could memorize the vocabularies. The students were also asked to work individually or in pairs. In this phase, the teacher corrected the students’ mistakes that they
might make during the lesson. D. Do it over
This phase was additional phase which aimed to review the vocabulary given in the previous phases. The students did the activities individually to know their understanding. This phase could also be done as homework for the students.
3. Preliminary Testing
appropriate, well-developed and well-designed. The evaluation was also needed to obtain comments and suggestion from the respondents on the designed materials. The comments and suggestion would be useful to make up the final version of the designed materials. The evaluation of the designed materials was conducted by distributing the post design questionnaire to one of English teachers of SMP BOPKRI 2 Yogyakarta and two English lecturers of the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. They were selected concerning their experiences and expertise in
English language teaching. The background of the respondents was presented in Table 4.7.
Table 4.7 : The Description of the Respondents
Respondents
Educational Background
Teaching Experience
Sex
S1 S2 S3 <5 5-10 >10 F M
Teacher 1 1 1 -
Lecturers 2 1 1 2 -
From the data above, the respondents of the post designed questionnaire were all female. There was no specific reason in choosing female respondents, because the main consideration of the respon