AN ANALYSIS OF CURRICULUM 2013 (K-13) LESSON
PLAN DESIGNED BY THE PRE-SERVICE ENGLISH
TEACHER
THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for the Degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in Teaching English
By:
Istianatul Khusniyah
NIM D05211010
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF EDUCATION AND TEACHER TRAINING
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
SUNAN AMPEL
AN ANALYSIS OF CURRICULUM 2013 (K-13) LESSON
PLAN DESIGNED BY THE PRE-SERVICE ENGLISH
TEACHER
THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for the Degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in Teaching English
By:
Istianatul Khusniyah
NIM D05211010
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF EDUCATION AND TEACHER TRAINING
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
SUNAN AMPEL
ABSTRACT
Khusniyah, Istianatul. (2015). An Analysis of Curriculum 2013 (K-13) Lesson Plan Designed by the Pre-Service English Teacher. A Thesis English Teacher Education Department, Faculty of Education and Teacher Training, State Islamic University (UIN) Sunan Ampel. Advisor I: Rakhmawati, M. Pd. Advisor II: Hikmatul Masykuriyah, M. Pd.
Key Word: Lesson Plan, Curriculum 2013
ABSTRAK
Khusniyah, Istianatul. (2015). An Analysis of Curriculum 2013 (K-13) Lesson Plan Designed by the Pre-Service English Teacher. A Thesis English Teacher Education Department, Faculty of Education and Teacher Training, State Islamic University (UIN) Sunan Ampel. Advisor I: Rakhmawati, M. Pd. Advisor II: Hikmatul Masykuriyah, M. Pd. Kata Kunci: Lesson Plan, Curriculum 2013
LIST OF CONTENTS
Page
TITTLE SHEET ... i
ADVISOR APPROVAL SHEET ... ii
APPROVAL SHEET ... iii
MOTTO ... iv
DEDICATION SHEET ... v
ABSTRACT ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... vii
PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN TULISAN ... viii
LIST OF CONTENTS ... ix
LIST OF TABLES ... xi
LIST OF FIGURES ... xiii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xiv
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION A. Background of The Study ... 1
B. Research Questions ... 7
C. Objectives of The Study ... 8
D. Significance of The Study ... 8
E. Scope and Limitation ... 9
F. Definition of Key Terms ... 10
CHAPTER II : REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Review of Related Literature ... 13
1. Definition of Lesson Plan ... 13
2. The Function of Lesson Plan ... 15
3. The Component of Lesson Plan ... 16
4. Requirements of Curriculum 2013 (K-13) ... 23
5. Principles in Designing Lesson Plan ... 33
6. Steps in Designing Lesson Plan ... 36
7. Difficulties in Designing Lesson Plan... 38
CHAPTER III : RESEARCH METHOD
A. Approach and Research Design ... 43
B. Setting and Research Subject ... 44
C. Data and Source of Data ... 46
D. Data Collection Technique ... 46
E. Research Instrument ... 49
F. Data Analysis Technique ... 50
G. Checking Validity of Findings ... 53
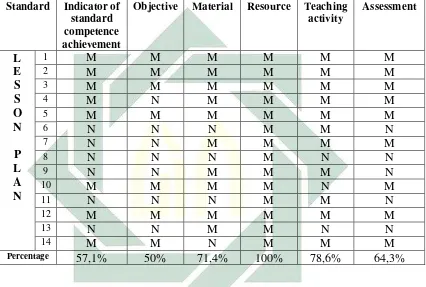
CHAPTER IV : RESEARCH FINDING A. Findings ... 54
1. The lesson plans designed by the pre-service English teachers met the requirements of K-13 or not ... 54
2. The difficulties faced by the pre-service English teachers in designing K-13 lesson plans ... 99
B. Discussion ... 102
1. The lesson plans designed by the pre-service English teachers met the requirements of K-13 or not ... 102
2. The difficulties faced by the pre-service English teachers in designing K-13 lesson plans ... 108
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion ... 112
B. Suggestion ... 115
BIBLIOGRAPHY
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter discusses about background of the study, research questions, objectives of the study, significance of the study to let the reader recognize about the value of the study result, scope and limitation of the study, and definition of key terms.
A. Background of The Study
2
designing the syllabus.1
This curriculum is aimed to prepare the learners to have the ability to live as individual and citizen who obedient, productive, creative, innovative, affective, and able to contribute in the society.2
Therefore, the teachers must find out the contextual need and curriculum standard in order to create effective educational system in Indonesia.
The Minister of National Education Regulation No. 103 Year 2014 about Curriculum 2013 Study Guide for Elementary School and Secondary School stated that there are six crucial aspects that must be considered in designing K-13 lesson plan; they are main competence and basic competence, indicator of standard competence achievement, material, resource, teaching activity, and assessment.3 This Curriculum 2013 also emphasizes the implementation of science approach and authentic assessment in learning process.4
In Indonesia, the curriculum has developed for several times as an attempt to improve its education quality. The curriculum development is accompanied with scientific approach including the new theories of study.5 Syllabuses, lesson plans, materials, methods, and strategies which have been designed and taught by
1
Badan Pengembangan Sumberdaya Manusia Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan dan Penjaminan Mutu Pendidikan Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, Materi Pelatihan Guru Implementasi Kurikulum 2013(Jakarta: PSDMPK-PMP Kemendikbud 2013), 74-78.
2
Badan Pengembangan Sumberdaya Manusia Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan dan Penjaminan Mutu Pendidikan Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan…..84.
3
Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan Nasional Republik Indonesia No. 103 Tahun 2014, Panduan Penyusunan Kurikulum 2013 Jenjang Pendidikan Dasar dan Menengah (Jakarta, 2013), 4.
4
Badan Pengembangan Sumberdaya Manusia Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan dan Penjaminan Mutu Pendidikan Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, Materi Pelatihan Guru Implementasi Kurikulum 2013….. 278.
5
3
the teachers previously must be developed and adjusted with the new curriculum. As the result, teachers and students are often confused with a new concept of curriculum applied in the classroom.
Syllabus and lesson plan, as the important component of curriculum, should be prepared and developed well and systematically by the teachers in order to create effectively, interesting and fun language learning in the classroom. Harmer stated that syllabus and lesson plan have a close relationship that cannot be separated. The lesson plan prepared by the teachers must be based
on the syllabus design and the students’ needs. It will lose direction if the lesson
plan is not developed based on syllabus design.6 As asserted by Joseph and Leonard, “teaching without adequate written planning is sloppy and almost always ineffective since the teacher has not thought out exactly what to do and
how to do it.”7
It signs that without syllabus and lesson plan, the process of teaching learning will be disorganized because the teachers do not have appropriate concepts and aims of teaching. Therefore, students lose chance to get effective language learning and appropriate knowledge and skills.
Pre-service teacher program or Microteaching class, Praktik Pengalaman Lapangan 1 (PPL 1) is a training subject that used to practice and learn how to
teach well. It engages real teaching situation to develop skills and helps to get
6
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching, Third Edition (New York: Longman, 1991), 295.
7
4
deeper knowledge of the art of teaching.8
It is also one of the steps of students’ teachers to develop competence in performing and teaching practice in real terms till the students ready to become a professional teacher.9
The teachers are required to have the pre-service teacher program since it often provides the first step in the professional development of teacher.10
Curriculum 2013 has presented the component required for the teacher with an expectation that this curriculum would create better learning process. Subarman said that a teacher at least must have three basic competences. They are competence of understanding subject or instructional materials, planning a teaching and learning program, and applying the teaching and learning program.11 Regarding with this statement, the pre-service English teachers as candidates of the real teachers should be able to understand how to organize the teaching and learning process before teaching in the class of formal school.
However, there are some problems related with Curriculum 2013 especially in designing K-13 lesson plan. As asserted by Muhammad Nuh, the Minister of National Education in 2013, some teachers have difficulties in making authentic assessment that is part of K-13 lesson plan. In making authentic assessment the teacher not only gives the score but also provides the evidences why the students
8Ambili Rames, “Microteaching; An Efficient Technique For Learning Effective Teaching”.
Articles from Journal of Research in Medical Sciences. Vol. 8 No. 2, 2013. 163.
9
Tim Penyusun Pedoman PPL II Tahun 2014, Pedoman Praktik Pengalaman Lapangan (PPL) II Tahun 2014 ( Surabaya: FakultasTarbiyah dan Keguruan UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, 2014.), 1.
10
Sylvia Chong, et.al., Pre-Service Teachers’ Beliefs, Attitudes and Expectation: A Review of the Literature (National Institute of Education: Nanyang Technological University), 1.
11
5
can get that score.12 Another difficulty is the teachers do effort hard in combining Main Competence (KI) to Basic Competence (KD).13 Besides, teachers have difficulties in designing K-13 Lesson Plan because of the change of some components from the previous lesson plan.14 In addition, According to Daya Negri Wijaya, there are several things that cause less skilled teachers in designing K-13 lesson plan, such as the limited time in designing lesson plan, the ability in understanding the syllabus, the ability in developing the indicators, the ability in designing teaching method, and the ability in making authentic assessment.15 Furthermore, Marsigit stated in his study that some teachers have difficulties to develop syllabus and lesson plan and yet they are inactive to join the programs related to the socialization of lesson plan which is held by the school institution or government.16 Moreover, Badianti in her study clarified that most of teachers were not able make appropriate lesson plan because of her weakness in the formulating indicators, the instructional objectives, the teaching learning activities, the materials, and the assessments. Therefore, it is required
12
Muhammad Nuh, “Guru Sulit Lakukan Penilaian Autentik”,
(http://www.republika.co.id/berita/pendidikan/eduaction/14/07/22/n92vqz-guru-sulit-lakukan penilaian-otentik/, accessed on June 21, 2015).
13
Nurul Hidayati, “Guru Mengaku Kesulitan Terapkan Kurikuum 2013”,
( http://edisicetak.joglosemar.co/berita/guru-mengaku-kesulitan-terapkan-kurikulum-2013-149276.html, accessed on Juni 21, 2015).
14
Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan Nasional Republik Indonesia No. 81 ATahun 2013, Implementasi Kurikulum 2013 (Jakarta, 2013).
15Daya Negeri WIjaya, “
Seputar RPP Kurikulum
2013”,(https://mathyess.wordpress.com/2014/07/12/seputar-rpp-kurikulum-2013/, accessed on June 21, 2015).
16
6
more seminars and counseling of how to make a good lesson plan to teachers. From those theories, it can be concluded that the teachers in Indonesia have difficulties in designing K-13 lesson plan.
The students of Microteaching class (PPL 1) of English Teacher Education Department academic year 2015 are chosen as the subjects since they have taken all the courses emphasizing pedagogical competence, such as Teaching English of Foreign Language (TEFL), Curriculum Development (CURDEV), and Instructional Material (INMALT). Then, they are also expected to have better understanding of K-13 since K-13 is the current curriculum which has the change of some components from the previous curriculum. For that reason, it is considered to know whether the lesson plans designed by students of this department meet the requirements of K-13 or not and find out the difficulties in designing K-13 lesson plans.
Some studies have shown that many pre-service English teachers had difficulties in designing their lesson plan particularly in their training subjects such as matching goals, objectives, and form of evaluation.17
Based on the
researcher’s preliminary research to ten pre-service English teachers of English
Teacher Education Department in PPL 1 academic year 2014, four of them faced difficulties in making authentic assessment. Two students had difficulty in
17 Peter D. John, “Lesson Planning and
7
selecting resource. One student confused in formulating indicator. Three students had difficulty in applying scientific approach in the lesson plan.
Knowing that reason, the researcher was interested to conduct this research to the pre-service English teachers at English Teacher Education Department of State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya academic year 2015 to know whether K-13 lesson plans designed by students of this department meet the requirements of K-13 or not in order to be awareness and reflection for them to improve their knowledge and skills especially in designing a systematic and good lesson plan based on the governments’ rules before conducting the English teaching at the real class of formal school which applies K-13. In this research, the researcher took K-13 lesson plans designed by the pre-service English teachers in PPL 1 of English Teacher Education Department of State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya academic year 2015.
B. Research Questions
Based on the problems stated in the background of the study, the researcher composed the research questions as follows:
1. Do the lesson plans designed by the pre-service English teachers meet the requirements of K-13?
8
C. Objectives of The Study
The objectives of this study are:
1. To know whether the lesson plans designed by the pre-service English teachers meet the requirements of K-13 or not
2. To find out the difficulties faced by the pre-service English teachers in designing K-13 lesson plans
D. Significance of The Study
The findings of this study explain whether the lesson plans designed by the pre-service English teachers meet the requirements of K-13 or not and the difficulties faced by the pre-service English teachers in designing K-13 lesson plans. They can be used as beneficial input for the lecturers of English Teachers Education Department, the pre-service English teachers of English Teachers Education Department, and the researcher.
1. For lecturers of English Teacher Education Department
9
2. For the pre-service English teachers of English Teacher Education Department
The result of this research can be used by the pre-service English teachers of English teacher Education Department as a measurement to know how well they design their lesson plan and reflection on their work so that they can revise and improve their lesson plans for better work next time, especially in the case of designing K-13 lesson plan.
3. For the researcher
Since the result of this study is considered as essential instrument of teaching and learning process, it is important for the researcher as the future English teacher to be able to design a good lesson plan based on government’s rule. After conducting this study, the researcher will know how to design and use the lesson plan well based on the requirements of K-13. Moreover, another researcher can use this study as one of the references to similar study related to lesson plan.
E. Scope Limit of The Study
10
plans designed by the pre-service English teachers meet the requirements of K-13 or not. The researcher analyzes the lesson plans by matching them to the requirements of K-13 using checklist of K-13 lesson plan analysis adapted from the Minister of National Education Regulation No. 103 Year 2014 about Curriculum 2013 Study Guide for Elementary School and Secondary School and focuses on six aspects in the lesson plans. They are indicator of standard competence achievement, objective, material, resource, teaching activity, and assessment. Actually, objective is not crucial component which stated in K-13 but the researcher analyses objective because the pre-service English teachers are recommended to formulate objectives in K-13 lesson plans by lecturers in PPL 1. The researcher also examines the difficulties faced by the pre-service English teachers in designing K-13 lesson plans.
F. Definition of Key Terms
In this study the researcher provides definitions of some key terms to help the reader understand easily. They are described as follows:
1. Lesson plan is considered as a blue print, a guide map for action, or a comprehensive chart of classroom teaching learning activities. It is defined as
elastic but a systematic approach to teaching of the concepts, skills, and
attitudes.18 Lesson planning is described as considering the students, thinking
18
11
of the content, materials, and activities that could go into a lesson to ensure the lesson is good.19 In this study, the lesson plan is produced by the pre-service English teachers in PPL 1 academic year 2015 and designed as guidance in preparing an effective daily plan organizing content, materials, and activities in the classroom.
2. Curriculum 2013 (K-13) is the Autocomes-Based Curriculum which has been applied since 2013 in Indonesia and an advanced curriculum which developed from KBK (Kurikulum Berbasis Kompetensi) or Competence-Based Curriculum and KTSP (Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan) or School-Based Curriculum. This curriculum development aimed to achieve the competences which are formulated from SKL (Standart Kompetensi Lulusan) or Grading Competence Standard. In addition, this curriculum
includes the competence of attitude, knowledge, and skills in an integrated manner.20
Besides, K-13 emphasizes the implementation scientific approach and authentic assessment in learning process.21 In this study, the lesson plan is analyzed based on the requirements of K-13 determined by the Minister of National Education Regulation No. 103 Year 2014 about Curriculum 2013 Study Guide for Elementary School and Secondary School. There are six
19
Tessa Woodward, Planning Lessons and Courses (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2009), 1.
20
Badan Pengembangan Sumberdaya Manusia Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan dan Penjaminan Mutu Pendidikan Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, Materi Pelatihan Guru Implementasi Kurikulum 2013…..74–75.
21
12
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter describes the theories related to the problems of this study, which are used as foundation and reference in order to give relevant knowledge in the field. This chapter also presents several similar previous studies. The analysis conducted in this research depends on some theories discussed in this chapter.
A. Review of Related Literature
1. Definition of Lesson Plan
There are several definitions of lesson plans have been provided. Reiser and Dick stated that lesson planning is an activity that teachers and students will do. Teachers can plan their lesson while they are in shopping, driving even when they are walking to the class.1 Harmer clarified that lesson planning is the art of combining some different elements into a coherent whole so that a lesson has an identity which students can recognize, work within, and react to whatever sign and gestures teachers may use to visualize and create that identity.2 It can be inferred that planning a lesson means the time for teachers to design what activities, materials, or skills that will be delivered to the students.
1
Baylor A. L., et.al., “The Instructional Planning Self-reflective Tool IPSRT): A Method for
Promoting Effective Lesson Planning, Educational Technology”. 41(2), 2001, 59.
2
14
Mulyasa stated that lesson plan is a plan which describes procedures and management of research in order to reach one or more basic competence regulated in the Standard Content and extended in the syllabus.3 It means that there are steps and organizations developed by a teacher in a plan of course in order to achieve Competence-Based that stated in the curriculum. The steps deal with the chain works conducted by the teacher in developing the lesson plan such as establishing the objective of research, indicators, materials, and methods. They should be done structurally in order to meet students’ needs,
interests, and be able to adjust students’ ability appropriately.
According to the Minister of National Education Regulation Number 103 Year 2014 said that the lesson plan is developed lesson plan in detail on particular subject matter or theme that refers to the syllabus.4 In addition, Ginting asserted that lesson plan is teaching scenario which is as reference for teacher to prepare, do, and evaluate the result of teaching-learning process.5
In conclusion, lesson plan is a sequence of lessons which are prepared by teacher based on the curriculum. It is a detailed description of a syllabus which is developed by a teacher as an effort to reach main competence and basic competence in the curriculum.
3
Mulyasa, Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan……212.
4
Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan nasional Republik Indonesia No. 103 Tahun 2014, Panduan Penyusunan Kurikulum 2013 Jenjang Pendidian Dasar dan Menengah (Jakarta, 2014).
5
15
2. The Function of Lesson Plan
The Planning a lesson is an essential process in an instruction because this process will help teacher to manage instruction effectively. As asserted by Richards, “planning a lesson before teaching is considered essential in order to
teach an effective lesson.” It should enable students to learn effectively in the classroom and to gain specific competencies after teaching-learning process. It should also provide an appropriate quality towards language learning so that the students can obtain the quality of language skills as well.6
Harmer argued that teachers and students will find the lesson not meaningful and interesting without lesson plan. The worst condition is the students are undermined to learn English. If teachers do not think what they are going to do, it means they do something useless at all.7 Those are the reasons why lesson plan is essential.
According to the Minister of National Education Regulation Number 65 Year 2013 about the Standard Process, every teacher must develop lesson plan completely and systematically so that teaching-learning can be administered interactively, fun, challenging, and can encourage students to participate actively as well as can give sufficient space for their creativity and autonomy based on their interests, innates, and also their physic and psychology
6
J.C. Richards - D. Bohlke, Creating Effective Language Lessons (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2011), 35.
7
16
development.8 It means that a teacher as the agent of change in the classroom is required to be able to develop his lesson plan systematically in order to create interactive and effective learning based on students’ interests, ability,
and so forth as well as to encourage students to be active and creative in their learning activities.
3. The Component of Lesson Plan
The main focus of lesson plan is to decide what teachers and students will do in the classroom, to get the effective instruction, and to increase students’ achievement. As Brown clarified that key questions in planning, he
indirectly pointed out the content of a lesson plan. They are:9 a. What kinds of things do you want the pupils learn? b. What are your precise instructional objectives?
c. What is the most appropriate sequence of the topics and the tasks (procedure)?
d. What are the most appropriate methods?
e. How should the teaching and learning be evaluated?
In addition, according to Reiser and Dick there are six components of lesson plans which can be criteria in lesson planning: indicators, objectives,
8
Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan Nasional Republik Indonesia No. 65 Tahun 2013, Standar Proses untuk Satuan Pendidikan Dasar dan Menengah (Jakarta: Badan Standar Nasional Pendidikan, 2007), 1.
9
17
activities, materials, instructional media, and assessment.10 They are described:
1) Indicators
Reiser and Dick clarified that the criteria of indicators; match with the objectives, reveals the specific skill, considering the domain of learning, and measurable.11
On the other hand, Rowntree listed some observable (measurable) and non-observable (immeasurable) verbs. Observable (measurable) verbs mean the verb that used in instructional goals can help the goals to be easy to see, assess, or observe by the learners.12 Reiser and Dick stated about the using of measurable instructions. They argued that measurable instruction for goals must use measurable verbs. Some examples of the measurable verbs are state, describe, list, and others. The observable and non-observable verbs are presented in the table below.13
10
As cited by Bidaria, Thesis: “Teaching English for Young Learners” (Jambi: Universitas Jambi, 2013), 13.
11
As cited by Miftah Farid, Thesis: “Teachers Difficulties in Lesson Planning” (Bandung: Universitas
Pendidikan Indonesia, 2014), 17.
12
As cited by A. Rejeki, Thesis: “Case Study of Lesson Plans of Two Elementary Schools in Bandung Kulon, West java” (Bandung: Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, 2009), 14.
13
18
Table 2.1
Observable and non-observable objective verbs based on Rowntree
Observable (measurable) Verbs Non-observable (immeasurable)
Verbs
Explain, list, evaluate, pick out, distinguish between, analyze, summarize, compare, apply, asses, suggest reasons why, give example of, carry out, demonstrate, etc.
Know, understand, really know, really understand, be familiar with, become acquainted with, have a good grasp of appreciate, be interested in, acquire a feeling for, be aware of, believe, have information about, realize the significant of, learn the basics of, obtain working knowledge of, believe in, etc.
2) Objectives
After having indicators, objectives are the second aspect that should be taken in the lesson plan. Objectives are explicit descriptions of what students will be able to do instead of what teachers are going to do as a result of the instructional activities they received. Based on Reiser and Dick proposed taxonomy to classify objectives into four types or domains of learning out comes, they are knowledge skills, intellectual skills, motor skills, and attitudes skills.14 Firstly, knowledge skills explain the ability to
14
19
recall and remember some specific in formations. It commonly refers to memorize specific information. The suggested verbs for this domain learning in objectives are list, state, describe, and recognize. Secondly, intellectual skills are those processes used by learners that go above and beyond the pure memorization to the actual use of the information. The suggested verbs for this domain learning objectives are classify, apply, and solve. Thirdly, motor skills are the next type which refers to any physical activities that requires a movement from the learners. The suggested verbs for this domain are perform and execute. Finally, attitude refers to the personal feelings and beliefs that outcome in a person’s preference to act in particular way. The suggested verb for this domain is choose. All of these domains should be incorporated in the objective of
lesson plan because they have been formulated in measurable verbs and helps students to achieve the objectives. The table below describes suggested verbs for various learning domains of objectives.15
15
20
Table 2.2
Suggested verbs for various learning domains of objectives based on Reiser and Dick
Learning domains Suggested verb
Knowledge List, state, describe, and recognize
Intellectual skills Classify, apply, solve
Motor skills Perform, execute
Attitudes Choose
In addition, Reiser and Dick said that the criteria of instructional objectives; stated explicitly, based on the relevant document, translated on the instruction, and measured on the assessment tools.16
3) Activities
Learning process will be successful if students’ needs are accommodated by the classroom activities that facilitate by the teachers. Reiser and Dick stated that many teachers spent a lot of time in planning activities in the classroom. It indicated that to plan activities to be relevant with objectives is not easy.17
16As cited by Miftah Farid, Thesis: “Teachers Difficulties in Lesson Planning”….. 17
21
In addition, Reiser and Dick clarified that the criteria of instructional activities; reflecting students-centered instruction, reflecting communicative method, motivate students to learn and to expose foreign language, helping students to recall prerequisite, presenting information and examples, integrating the four skills (reading, listening, speaking, and reading), and providing practice and feedback.18
4) Materials
Reiser and Dick asserted that the criteria of materials in lesson planning; appropriate with the goals and objectives, appropriate with student’s level, appropriate with student’s need, and appropriate with
student’s characteristics.19
5) Media
Some students have different span memories in learning. For that reason, media is important to help teacher to explain the materials especially in teaching language learners. According to Reiser and Dick, there are three principles of using media; effectiveness, practicality, and appropriateness. In terms of effectiveness, media should help students to get the purpose of materials. Beside that, it can be effective if it can
18As cited by Miftah Farid, Thesis: “Teachers Difficulties in Lesson Planning” …. 19
22
motivate students, inform students of objectives, and present information and example, provide practice and feedback, and summarize the lesson. Then, teachers should consider in selecting media whether it is practical to use or not. In this case, teachers are demanded to choose media smartly and creatively. Last, teachers should pay attention to the appropriateness of media. The media should be suitable for student characteristics.20
Furthermore, Reiser and Dick clarified that the criteria of instructional activities: practical, motivating students’ participation, relevant with material, relevant with the condition and students’ characteristics.21
6) Assessment
Assessment is an activity administered to examine learners’ progress. Teachers have to take assessment into their lesson plan since it provides information whether students achieve the objectives or not.22 By assessment, teachers know the progress of their students.
20
As cited by Bidaria, Thesis: “Teaching English for Young Learners”……18.
21As cited by Miftah Farid, Thesis: “Teachers Difficulties in Lesson Planning” …. 22
23
In addition, Reiser and Dick stated that the criteria of assessments tool in lesson planning; measure the objective, match with the material, match with the students’ grades, and reliable.23
4. Requirements of Curriculum 2013 (K-13)
There are several components guiding teachers in designing K-13 lesson plan which can also be criteria or requirement for constructing an effective K-13 lesson plan. The components which are based on the Minister of National Education Regulation Number 103 Year 2014 are as follow:24
a. Main competence (KI)
Main competence is description of students’ primary competences included knowledge, attitude, and skills to be achieved every class and/or semester in a certain subject or competence which have to be posed by students in a certain subject.
In addition, main competence is competence which can be performed by students for a certain subject/lesson or the macro-skills based on the government regulation in the curriculum. This main competence will be then translated into the basic competence that has several specific competences to be achieved by students. The macro-skills of English language are listening, reading, speaking, and writing. Each of these
23
As cited by Miftah Farid, Thesis: “Teachers Difficulties in Lesson Planning” ….
24
24
macro-skills is interpreted into basic competences which have to be achieved by the students. After that, the main competence and basic competence will be formulated in the syllabus and lesson plans.
b. Basic competence (KD)
Basic competence is several competences which have to be mastered by students for a certain subject as a basis for establishing indicator of competence.
c. Indicator of standard competence achievement
Indicator of standard competence achievement is behavior or performance which can be measured and observed to show the achievement of basic competence and main competence. In this notion, indicator of standard competence achievement is when students are able to perform their basic competence and it can be measured and observed through assessment execution covering cognitive (knowledge), psychomotoric (skill), and affective (attitude). The following table describes standard and its description of indicator of standard competence achievement:25
25
25
Table 2.3
Indicator of Standard Competence Achievement
No. Indicator of Standard
Competence Achievement
Description
1. The suitability with KI and KD.
The indicators of standard competence achievement are developed from KI and KD. They developed for basic competence in all main competences 1, 2, 3, and 4. 2. The suitability between
using operational verbs and competences.
The operational verbs used are suitable with the competences that want to be measured. 3. The suitability with attitude,
knowledge, and skill aspects.
The indicators of standard competence achievement are in line with attitude (affective), knowledge (cognitive), and skill (psychomotoric) aspects.
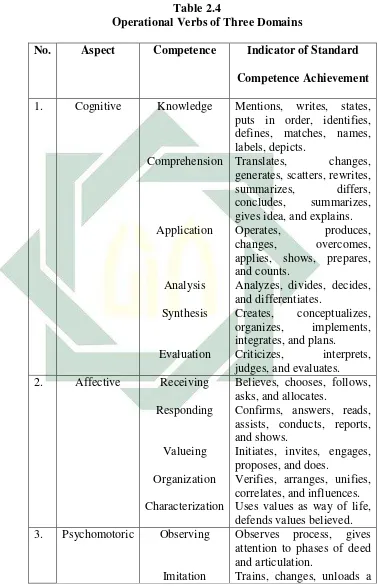
In educational activity, teachers must be able to extend the basic competence into indicator of standard competence based on these three types of learning, so that after a learning episode, students should have acquired new skills, knowledge, and/or attitudes. According to Moore and Rosyada, there are some operational verbs which can be used in indicator of standard competence achievement:26
26
26
Table 2.4
Operational Verbs of Three Domains
No. Aspect Competence Indicator of Standard
Competence Achievement
1. Cognitive Knowledge
Comprehension
Application
Analysis Synthesis
Evaluation
Mentions, writes, states, puts in order, identifies, defines, matches, names, labels, depicts. applies, shows, prepares, and counts.
Analyzes, divides, decides, and differentiates. 2. Affective Receiving
Responding
Valueing Organization Characterization
Believes, chooses, follows, asks, and allocates.
Confirms, answers, reads, assists, conducts, reports, and shows.
Initiates, invites, engages, proposes, and does.
Verifies, arranges, unifies, correlates, and influences. Uses values as way of life, defends values believed. 3. Psychomotoric Observing
Imitation
Observes process, gives attention to phases of deed and articulation.
27
Practicing
Adapting
structure, reconstructs a structure, uses a model. Familiarizes behavior already formed, controls habitual to be consistent. Adjusts model, develops model, and applies model. d. Objective
Objective is process and product of learning expected to be achieved by learners based on basic competence. In this regard, at the end of the course program, the students are able to achieve the aims which are relied on basic competence. The following table describes standard and its description of objective:27
Table 2.5 Objective
No. Objective Description
1. The suitability between objectives and the behavior of the result of the study.
The objectives contains behavior which is the result of the study. The behavior is formulated into the form of operational verbs. The objectives do not cause double interpretation and developed for basic competence in all main competences 1, 2, 3, and 4. 2. The suitability between
objectives and the indicator.
The objectives are developed from the indicator and basic competence which is in the curriculum.
27
28
e. Material
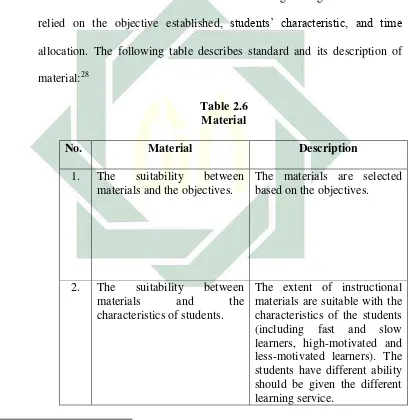
Material consists of relevant theory, facts, principles, and procedures which are written in point style based on the objective formulated, students’ characteristic, and time allocation. This means that materials are
related to what students will learn in the learning setting and have to be relied on the objective established, students’ characteristic, and time allocation. The following table describes standard and its description of material:28
Table 2.6 Material
No. Material Description
1. The suitability between materials and the objectives.
The materials are selected based on the objectives.
2. The suitability between materials and the characteristics of students.
The extent of instructional materials are suitable with the characteristics of the students (including fast and slow learners, high-motivated and less-motivated learners). The students have different ability should be given the different learning service.
28
29
3. The suitability between materials and time allocation.
The possibility of the materials can be achieved in time allocated.
f. Teaching activity
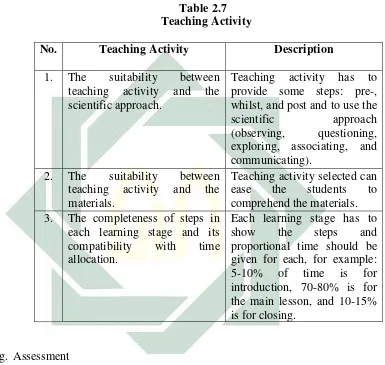
Teaching activity is divided into three stages: First, pre-teaching. It is conducted to encourage students’ motivation and to attract their attention in
learning participation. It can be interpreted that there are apperception and motivation conveyed to students in the beginning of teaching-learning process. Second, whilst-teaching. It is the process of teaching and learning to achieve basic competence which is conducted systematically through observing, questioning, exploring, associating, and communicating phases.
Observing is in which students are facilitated to observe the object, questioning is in which students are engaged to ask about the result of observing the object, exploring and associating are in which students are facilitated to collect, to process, and to analyze the information, while communicating is in which students are confirmed, delivered, and
30
towards students. The following table describes standard and its description of teaching activity:29
Table 2.7 Teaching Activity
No. Teaching Activity Description
1. The suitability between teaching activity and the scientific approach.
Teaching activity has to provide some steps: pre-, whilst, and post and to use the scientific approach (observing, questioning, exploring, associating, and communicating). compatibility with time allocation.
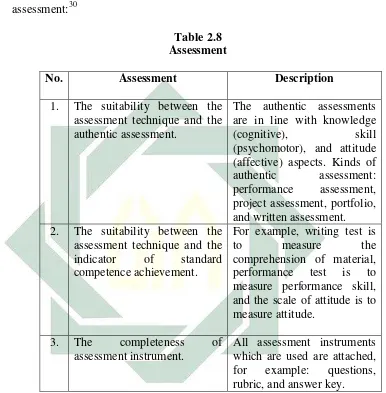
Each learning stage has to show the steps and proportional time should be given for each, for example: competence achievement. It can be inferred that assessment is required to execute using rubrics in order to evaluate students’ achievements towards
29
31
indicators determined. The following table describes standard of assessment:30
Table 2.8 Assessment
No. Assessment Description
1. The suitability between the assessment technique and the authentic assessment.
The authentic assessments are in line with knowledge (cognitive), skill (psychomotor), and attitude (affective) aspects. Kinds of authentic assessment: performance assessment, project assessment, portfolio, and written assessment. 2. The suitability between the
assessment technique and the indicator of standard competence achievement.
For example, writing test is
to measure the
comprehension of material, performance test is to measure performance skill, and the scale of attitude is to measure attitude.
3. The completeness of assessment instrument.
All assessment instruments which are used are attached, for example: questions, rubric, and answer key.
30
32
h. Resource
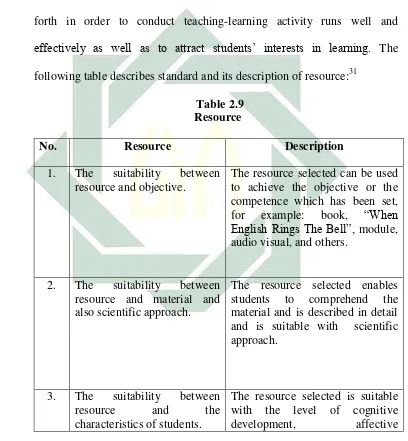
Resource is selected based on main competence and basic competence, objective, material, and scientific approach. In addition, resource is tool and media used such as textbook, projector, computer, internet, and so forth in order to conduct teaching-learning activity runs well and effectively as well as to attract students’ interests in learning. The
following table describes standard and its description of resource:31
Table 2.9 Resource
No. Resource Description
1. The suitability between resource and objective.
The resource selected can be used to achieve the objective or the competence which has been set, for example: book, “When English Rings The Bell”, module, audio visual, and others.
2. The suitability between resource and material and also scientific approach.
The resource selected enables students to comprehend the material and is described in detail and is suitable with scientific
33
characteristics, and psychomotoric skill of the students.
5. Principles in Designing Lesson Plan
Creating teaching learning process needs a good lesson plan. In developing a good lesson plan, teachers must obey the principles in order to achieve the objectives of teaching learning process. Harmer stated that there are two main principles behind good lesson planning; variety and flexibility”. Variety refers to students’ involvement in a number of different types of
activity and where possible they are introduced to a few selections of materials.32 It means that a lesson planning needs a variety so that learning is interesting and not monotonous for the students.
There are several important principles, based on the Minister of National Education Regulation Number 81 A Year 2013 about the implementation of curriculum 2013, which should be considered by the teacher before designing a lesson plan. The principles are as follows:33
a. Lesson plan is designed as curriculum idea and based on syllabus which had developed in national level to be realized in teaching learning process. b. Concern learners’ differences such as gender, prior ability, intellectual
level, interest, motivation of learning, aptitude, potential, social ability,
32
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching…..258.
33
34
emotion, learning style, special needs, learning speed, culture background, norms, values, and learners’ environment. This means that before
developing lesson plan, teachers have to consider many aspects related to students’ differences and their backgrounds in order to produce appropriate
and useful lesson plan for students.
c. Encourage students to be active participants. The process of teaching learning places students as the center by boosting motivation, interest, creativity, initiative, inspiration, autonomy, and learning enthusiasm. It is no doubt that this principle requires teachers to make their students become active by doing many useful efforts. It means, in designing a lesson plan, a teacher has to consider this principle.
d. Develop reading and writing culture. It ascertains that reading and writing culture are skills that are very rare to be taken into account either by teachers or students. Therefore, in designing a lesson plan, a teacher has to consider this principle.
e. Give feedback and follow-up such as develop draft program of positive feedback, empowerment, enrichment, and remedial. In this regard, after conducting teaching-learning activity or in post-teaching stage, teachers have to provide feedback and follow up towards students’ tasks or
performances.
35
teaching-learning activity, indicator of standard competence achievement, assessment, and resources united in learning experience. Lesson plan is also developed by accommodating thematic teaching learning, integration across subject and learning aspect, and culture diversity. It refers to the teachers have to make sure that the lesson plans developed must be relevant and coherent among the lesson plan’s components such as main
competence, basic competence, materials, and so forth as well as they are relevant with culture diversity.
g. Apply information of technology and communication based on situation and condition. It other words, in developing lesson plan, teachers may use information of technology and communication media such as internet, newspapers, and so forth in the teaching instruction as an attempt to attract students’ interests in learning.
h. It is appropriate with the aims of curriculum 2013.
i. Lesson plan is designed by paying attention the cohesiveness and relevance between KI and KD, material, teaching activity, assessment and resource. j. Lesson plan is designed by considering the applying information of
technology and communication systematically, and effectively.
In addition, according to Woodward, there are some criteria that need to be considered for good lesson and language course:34
34
Tessa Woodward, Planning Lessons and Courses: designing sequences of work for the language
36
1) Feeling comfortable physically, socially, and psychologically.
2) Knowing a little about each other, why teacher and learner are together and what teacher and learner want to get out of the experience.
3) Having awareness of some of what there is to learn. 4) Having awareness of some of things which have learned. 5) Having a notion about how teacher and learner learn best.
6) Accepting that language is mixture of things (part instinct, motor skill, system, cultural artifact, music, part vehicle for content and part content itself), that it changes all the time and thus that teacher and learner need to teach and learn it in a variety of ways.
7) Knowing why teacher and learner are doing the activities teacher and learner are doing.
8) Doing things in class that would be worth doing and learn things that are worth learning for their own sake outside the language classroom. 9) Becoming more capable of taking the initiative, making decisions and
judging what is good and useful.
10) Starting useful habits which will continue after teacher and learner have left each other.
6. Steps in Designing Lesson Plan
Designing lesson plan needs to pay attention to some principles and
37
steps:35 Firstly, analyzing students’ needs and establish the specific objectives related to the context of students. Secondly, connecting the specific objectives with the general curriculum products and find the contexts to use the texts of genre from these outcomes. Thirdly, discovering and select what to be learnt by students in order to achieve the objectives determined. Fourthly, sequence the syllabus components into an effective development of teaching and learning. Fifthly, planning the way to observe students’ progress during the lessons and assess students’ achievement on the specific objectives at the end
of program. Finally, planning the way to report students’ achievement of the general curriculum products. According to Minister of National Education Regulation Number 103 Year 2014 about the Curriculum 2013 study guide, there are several steps in designing K-13 lesson plan, starting from lesson identity, core competencies, basic competencies, indicators of standard
competence achievements, learning materials, learning activities, learning
resources, and assessments.36 Moreover, the learning process in K-13 is
emphasized as a curriculum based on scientific approach that includes
observing, questioning, exploring, associating, and communicating. Lesson
35
S. Feez, “Curriculum evolution in the Australian adult migrant English program.” In D. R. Hall & A. Hewings (Eds).Innovation in English language teaching. Oxon: Routledge, 2001, 208-228.
36
38
plan is designed based on scientific approach dealing with the character of
subjects and students’ characteristics.37
7. Difficulties in Designing Lesson Plan
Designing lesson plan requires skill to think well in order to gain the best result and achieve the goal of teaching. There are some problems might be found when teachers and planners develop the lesson plan. Tashevska stated that those difficulties are timing, formulating lesson aims, sequencing activities, anticipating problem, and choosing appropriate teaching method.38
Furthermore, According to Kizlik, the most common problems in designing lesson plan in term of formulating the objective, selecting the assessment, selecting the material, selecting the instruction, and choosing the teaching activity.39 They will be described as follows:
a. The objective of the lesson: it does not specify what the student will actually do that can be observed. Objective is a description of what a student does that forms the basis for making an inference about learning. It means, poorly written objectives lead to faulty inferences.
b. The assessment: it is disconnected from the behavior indicated in the objective. An assessment in a lesson plan is simply a description of how the
37
Badan Pengembangan Sumberdaya Manusia Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan dan Penjaminan Mutu Pendidikan Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, Materi Pelatihan Guru Implementasi Kurikulum 2013…..291.
38
SvetlaTashevska, “Some Lesson Planning Problems for New Teachers of English”,
(http://eprints.nbu.bg/895/1/Some_Lesson_Planning_Problems.pdf), accessed on April 8, 2015).
39 Bob Kizlik. “Five Common Mistakes in Writing Lesson Plans(and How to Avoid
39
teacher will determine whether the objective has been accomplished. It must be based on the same behavior that is incorporated in the objective. c. The material specified in the lesson is extraneous to the actual described
learning activities.
d. The instruction in which the teacher will engage is not efficient for the level of intended student learning.
e. The teaching activity described in the lesson plan does not contribute in a direct and effective way to the lesson objective.
It can be concluded that when design a lesson plan, the planners and the teachers may find some difficulties related with its components.
B. Previous Study
There are some researches related with lesson plan. The first research was conducted by Asfaw, done in 2002 in Kafa Zone. It was conducted by analyzing 25 lesson plans collected from each of 15 teachers teaching English in grade seven, academic year 2001 in different schools in Ethiopia. The findings of this research showed that most of the lesson plans were not appropriate for successful teaching and learning interaction.40
The next research was done by Widyastono in 2011. The research entitled “Kemampuan Guru dalam Menyusun Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan”.
The researcher wants to get information about teachers’ ability to enact the
40
40
school-based curriculum. The research was conducted to 150 teachers from Jakarta, Bekasi, Depok, Bogor, and Tangerang. The result of the research indicates that the teachers’ ability in writing up the school-based curriculum
(syllabus) which encompasses standard competence, basic competence, instructional materials, learning activities, indicators, assessment, time allotment, and learning resource, was quite poor.41
The next research was conducted by Kodriyah in 2011. The research was conducted at two junior high schools, SMPN 1 Malang and SMPN 5 Malang. The researcher concluded the result of this study which showed that the teachers have already developed the competence standards and basic competence, the learning indicators, learning objectives, time allotment, the instructional materials, the teaching and learning methods, and the teaching and learning procedure, the assessment based on the KTSP curriculum to comprehend the curriculum to achieve the students’ competences.42
The next research was done by Anindita Badianti in 2013 entitled “The
Analysis of Junior High School English Teachers’ Lesson Plan”. In this research,
the researcher focused on to what extents are the indicators, the instructional objectives, the teaching learning activities, the materials, the assessments the lesson plan explicate. The research conducted to 5 English grade 7 lesson plans
41
Herry Widyastono, Thesis: “Kemampuan Guru Dalam Menyusun Tingkat Stauan Pendidikan” (Jakarta: Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kementrian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, 2012).
42
41
written by five different ex-international Junior High School Teachers and three different schools i.e. SMPN 6 Surabaya, SMPN 2 Jombang, and SMPN 3 Tuban. The result of the research indicated that only 2 of 5 lesson plans were closely appropriate. It means that most of teachers were not able make appropriate lesson plan. Therefore, it is required more seminars and counseling of how to make a good lesson plan to teachers.43
The next research conducted by Rini Budi Rahayu in 2013. The research entitled “An Analysis of the Pre-service English Teachers’ Ability in Designing
Lesson Plan”. In this research, the researcher wants to analyze KTSP lesson plan designed by the pre-service English teachers who took Internship Program year 2012, UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, focuses on the quality, strengths and the weaknesses of the lesson plans, and the causes of those strengths and weaknesses of the lesson plan. The result of this research indicates that the pre-service English teachers are quite good at designing lesson plan.44
The difference between those researches with this research was that the subject of the researches was the level of the school; junior high school. Meanwhile, this research was conducted in the state Islamic studies of bachelor degree which was similar with the last research conducted by Rini Budi Rahayu. Rahayu’s research analyzed the quality focused on strength and weakness of the
43
Anindita Badianti, Doctoral Dissertation: “The Analysis of Junior High School English Teachers’
Lesson Plan” (Surabaya: Universitas Negeri Surabaya, 2013).
44
Rini Budi Rahayu, Thesis: “An Analysis on Pre-Service English Teachers’ Ability in Designing
42
lesson plan designed by the students of pre-service teachers of English Teacher Education Department. Meanwhile, this research was conducted to know whether the lesson plans met the requirements of K-13 or not.
Furthermore, the previous research by Asfaw was focused on knowing the quality of the lesson plans designed by the teachers and how the teachers applied the lesson plans in conducting teaching while this research was focused on knowing whether the lesson plans met the requirements of K-13 or not.
The difference between this research and Widyastono’s research was the subject of the research. This research was conducted to the pre-service English teachers in the state Islamic studies of bachelor degree while Widyastono’s research was conducted to the real English teachers from Jakarta, Bekasi, Depok, Bogor, and Tangerang. Furthermore, this research focused on analysis of K-13 lesson plans designed by the pre-service English teachers while Widyastono’s research focused on analysis of teachers’ ability in designing KTSP lesson plans.
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHOD
In this chapter, researcher described the research design which would be used in this study, research subject, data and source of data, data collection technique, research instrument, and data analysis technique. To make them clear, the researcher elaborated them one by one in this chapter.
A. Approach and Research Design
The goal of this research was to know and to describe whether the lesson plans designed by the pre-service English teachers met the requirements of K-13 or not, including the difficulties they faced in designing K-13 lesson plan. Considering the goal, this research was included as qualitative design using descriptive approach because it tried to describe or to get information about the K-13 lesson plans designed by the pre-service English teachers.
As asserted by Mardalis, descriptive approach is to describe or to get information about the current condition of certain objects. Hence, it includes describing, taking notes, analyzing, and interpreting the existing facts.1 In addition, Arikunto stated that descriptive approach is not aimed to testing a certain hypothesis, but only describes the phenomenon, situation, and condition that happen during the research.2 The descriptive approach is used to expose the
1
Mardalis, Metode Penelitian (Jakarta: Bumi Aksara, 1995), 26.
2
44
condition of the phenomena as clearly as possible without any special treatment.3 Descriptive approach is designed primarily to describe what is going on or what exists.4 Moreover, Whitney stated that descriptive qualitative approach is a data collection which interprets the fact truly.5
Therefore, the researcher tried to present the description, analysis, and interpretation of the existence of K-13 lesson plans which has been designed by the pre-service English teachers who taking PPL 1 academic year 2015 at State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya. The researcher explained the result of the study to know whether the lesson plans designed by the pre-service English teachers met the requirements of K-13 or not. Besides, the researcher also intended to know some difficulties faced by the pre-service English teachers in designing K-13 lesson plan.
B. Setting and Research Subject
This research was conducted in PPL 1 of English Teacher Education Department of State Islamic University Sunan Ampel Surabaya academic year 2015. There were seven classes of PPL 1. They were A class until G class. The
3
Indah Zakiyah Zamania, Unpublished Thesis: “Upaya Peningkatan Kompetensi Pedagogik Dalam Proses Belajar Mengajar Di Raudlatul Atfal Al-Ikhlas Sukodadi Lamongan” (Malang: UIN Malang, 2009), 121.
4
William M. K. Trochim, Research Methods Knowledge Base (Cincinnati, OH: Atomic Dog Publication, 2001), 5.
5
45
researcher selected the sixth semester students of English Teacher Education Department who taking PPL 1 academic year 2015 as the subject.
The purposive sampling was applied in this research. Ary explained that purposive sampling means that the researcher uses the experience and knowledge to select a sample of participants that can provide the relevant information about the topic or setting.6 In addition, as described by Miles and Huberman and in Marshall and Rossman, random purposeful sampling is one of several variations on purposive sampling which is used in qualitative research when the potential purposeful sample is too large and the credibility of the study can be enriched by randomly selecting participants or sites from the larger group.7 Random purposeful sampling is a technique of samplings which is for each sample or individual has same probability to be chosen randomly.8
Therefore, in this research, the researcher took fourteen K-13 lesson plans designed by pre-service English teachers from all classes of PPL 1, A class until G class, academic year 2015. For each class, the researcher took two K-13 lesson plans randomly based on the skills and sub-skills.
6
Donald Ary, et.al., Introduction to Research in Education (California: Wadsworth, Cengage Learning, 2010), 429.
7
As cited by Donald Ary, et.al., Introduction to Research in Education…..430.
8
46
C. Data and Source of Data
1. Data
The data which were needed in this research:
a. K-13 lesson plans designed by the pre-service English teachers. They reviewed based on six aspects; indicator of standard competence achievement, objective, material, resource, teaching activity, and assessment. The data was taken after those lesson plans were designed in PPL 1 academic year 2015. This data was included into documentation data.
b. The interviews results of pre-service English teachers about difficulties they faced in designing K-13. They reviewed relied on Kizlik’s theory.
2. Source of Data
The source of data in this recent study was fourteen students of sixth semester of English Teacher Education Department who taking PPL 1 academic year 2015.
D. Data Collection Technique
Ary said that the most common data collection techniques used in qualitative research are observation, interviewing, and document or artifact analysis.9 Thomas affirmed that there are three processes in the research method.
9
47
They are content analyses, observations, and interviews.10 Knowing the nature of this study, the researcher used documentation and interview. They were described as follows:
1. Documentation
Ary stated that documents can be classified into four categories; public records, personal documents, physical materials, and researcher-generated documents.11 Sukmadinata described documentation as “a technique to collect the data by assembling and analyzing the documents, either written documents, pictures, or electronic ones.”12 Furthermore, Creswell explained that document is a good source of the text (word) data in qualitative research. He also stated that one of the advantages of this technique is for analysis without needing to do transcription which required in interview collection.13
These definitions signed that documentation was one of collection data techniques to be analyzed and described based on either written or oral documents.
This research used documentation as a technique to get the information of K-13 lesson plan designed by the pre-service English teachers during PPL 1 academic year 2015. The documents of this study were obtained from the
10
R. M., Thomas. Blending qualitative and quantitative research methods in theses and dissertations (Thousand Oaks California: Corwin Press, 2003), 77.
11
Donald Ary, et.al., Introduction to Research in Education….. 442.
12
Nana Syaodih Sukmadinata, Metode Penelitian Pendidikan (Bandung: Remaja Rosdakarya, 2007), 221.
13