ABSTRACT
Lidya Revianti, Siska. 2014. A Moodle Learning Model for Introduction to College English Classes. Yogyakarta: Graduate Program on English Language Studies, Sanata Dharma University.
Learning models which are based on Information and Communication Technology (ICT) are becoming more popular lately. The use of ICT in education has provided many opportunities for teachers and students to get information as well as to share information quickly and easily. Electronic learning (e-learning) using Learning Management System (LMS) Moodle is one alternative that can be used by the teachers to maximize the use of ICT in education. LMS Moodle has many useful features such as document sharing, various learning activities, automatic assessment, search engine and entertainment.This phenomenon has inspired the researcher to offer an online supplementary material for Introduction to College English (ICE) classes based on LMS Moodle application.
This research was aimed at designing the iconic model which was used as an online supplementary material in ICE classes Level 2 of Duta Wacana Foreign Language Training Center. There were two research problems in this study, namely: (1) What is the theoretical model of the Moodle learning model for ICE class Level 2 like?, and (2) What is the iconic model of the Moodle learning model for ICE class Level 2 like?
To answer the problems, the researcher reviewed relevant literature and has designed an online supplementary material for ICE class Level 2 using the ADDIE Instructional Design model. There are five phases which are used in this instructional model, they are: Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation and Evaluation. The phases were integrated into the Borg and Gall’s cycles of Research and Development. The cycles consisted of Research and Information Collecting, Planning, Developing Preliminary Form of Product, Preliminary Field Testing, Main Product Revision, Main Field Testing and Operational Product Revision.
The theoretical model and the iconic model of A Moodle Learning Model for Introduction to College English Classes were the results of the research. The theoretical model presented the selected features and widgets based on their suitability with CALL principles and the syllabus in ICE Level 2. The CALL principles used in this research were Authenticity, Literacy, Interaction, Vitality and Empowerment principles. Based on those principles, the researcher designed a learning model using the features offered by Moodle: Resource Module, Assignment, Quiz, Forum and Chats. The widgets added were BBC World news, Test Your English, Cambridge Online Dictionary, clock, game, on-line radio, Yahoo! Messenger and Facebook linker. The iconic learning model could be accessed on
http://www.iceportal.tk .
The Moodle-based Learning Model for ICE class Level 2 had been proven as useful and acceptable. This portal can also be used as a useful source for a supplementary material in ICE class. The research would be useful and beneficial for students of a similar program, especially to equip the process of teaching and learning in the classroom with e-learning material. Finally, the research can give great contribution to English language teaching and further research.
ABSTRAK
Lidya Revianti, Siska. 2013. A Moodle Learning Model for Introduction to College English Classes. Yogyakarta: Program Pasca-Sarjana Kajian Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Model pembelajaran yang didasarkan pada Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi (TIK) menjadi lebih populer belakangan ini. Penggunaan TIK dalam pendidikan telah memberikan banyak kesempatan bagi guru dan siswa untuk mendapatkan informasi serta berbagi informasi dengan cepat dan mudah. Electronic learning (e-learning )yang menggunakan Sistem Managemen Pembelajaran (LMS) Moodle merupakan salah satu alternatif yang dapat digunakan oleh para guru untuk memaksimalkan penggunaan TIK dalam pendidikan. LMS Moodle memiliki banyak fitur yang bermanfaat seperti berbagi dokumen, berbagai kegiatan pembelajaran yang bervariasi, penilaian secara otomatis, mesin pencari dan hiburan. Kenyataan ini telah mengilhami peneliti untuk menawarkan sebuah bahan tambahan online untuk kelas Introduction to College English (ICE) berdasarkan LMS Moodle.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk merancang model ikonik yang dipakai sebagai sebuah bahan tambahan online dan berdasarkan pada aplikasi Moodle dalam kelas ICE Level 2 di Pusat Pelatihan Bahasa Asing Duta Wacana. Ada dua masalah penelitian dalam penelitian ini, yaitu:(1) Seperti apakah model teoritis dari model pembelajaran Moodle di kelas ICE Tingkat 2?, dan (2) Seperti apakah model ikonik dari model pembelajaran Moodle di kelas ICE Tingkat 2?
Untuk menjawab permasalahan, peneliti melakukan studi pustaka dan telah merancang sebuah bahan tambahan online untuk kelas ICE Level 2 menggunakan model Instructional Design ADDIE. Ada lima tahap yang digunakan dalam model pembelajaran ini, yaitu: Analisis, Desain, Pengembangan, Implementasi dan Evaluasi. Fase-fase tersebut diintegrasikan ke dalam siklus-siklus penelitian dan pengembangan milik Borg dan Gall. Siklus-siklus terdiri dari Penelitian dan Pengumpulan Informasi, Perencanaan, Pengembangan Bentuk Awal Produk, Pengujian Awal di Lapangan, Revisi Produk, Pengujian Utama di Lapangan dan Revisi Produk Operasional.
Model teoritis dan model ikonik dari Sebuah Model Pembelajaran dengan Moodle untuk Kelas-Kelas Introduction to College English merupakan hasil-hasil penelitian. Model teoritis menyajikan fitur-fitur dan widget terpilih berdasarkan kesesuaian dengan prinsip-prinsip CALL dan silabus di ICE tingkat 2. Prinsip-prinsip CALL yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah Authenticity, Literacy, Interaction, Vitality and Empowerment. Berdasarkan prinsip-prinsip tersebut, peneliti mendesain sebuah model pembelajaran dengan menggunakan fitur-fitur yang ditawarkan oleh Moodle: Resource Module, Assignment, Quiz, Forum and Chats. Fitur yang disajikan dalam model pembelajaran Moodle adalah Resource Module, Assignment, Quiz, Forum and Chats. Widget yang ditambahkan adalah BBC World News, Test Your
English, Cambridge online dictionary, clock, game, on-line radio, Yahoo! Messenger and Facebook. Model pembelajaran ikonik dapat diakses pada http://www.iceportal.tk..
Model Pembelajaran yang berbasis Moodle untuk kelas ICE tingkat 2 telah terbukti berguna dan dapat diterima. Portal ini juga dapat digunakan sebagai sumber yang berguna untuk bahan tambahan di kelas ICE. Penelitian ini akan berguna dan bermanfaat bagi mahasiswa yang menjalani program yang sama, terutama untuk melengkapi proses belajar mengajar di kelas dengan materi pengajaran berbasis e-learning. Akhirnya, penelitian ini dapat memberikan kontribusi yang besar bagi pengajaran Bahasa Inggris dan penelitian lebih lanjut.
A MOODLE LEARNING MODEL
FOR INTRODUCTION TO COLLEGE ENGLISH CLASSES
A THESIS
Presented as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Magister Humaniora (M.Hum.) Degree
in English Language Studies
by
Siska Lidya Revianti 106332033
THE GRADUATE PROGRAM OF ENGLISH LANGUAGE STUDIES SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
A MOODLE LEARNING MODEL
FOR INTRODUCTION TO COLLEGE ENGLISH CLASSES
A THESIS
Presented as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Magister Humaniora (M.Hum.) Degree
in English Language Studies
by
Siska Lidya Revianti 106332033
THE GRADUATE PROGRAM OF ENGLISH LANGUAGE STUDIES SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA 2014
A THESIS
A MOODLE LEARNING MODEL
FOR INTRODUCTION TO COLLEGE ENGLISH CLASSES
by
Siska Lidya Revianti 106332033
Approved by
Dr. J. Bismoko _______________________
Thesis Advisor Yogyakarta, February 10, 2014
A THESIS
A MOODLE LEARNING MODEL
FOR INTRODUCTION TO COLLEGE ENGLISH CLASSES
by
Siska Lidya Revianti 106332033
Defended before the Thesis Committee and Declared Acceptable
THESIS COMMITTEE
Chairperson : Dr. J. Bismoko _________________________ Secretary : Dr. B.B. Dwijatmoko, M.A. _________________________ Members : 1. F.X. Mukarto, Ph. D _________________________ 2. Jaslin Ikhsan, Ph. D _________________________
Yogyakarta, February 10, 2014 The Graduate School Director
Prof. Dr. A. Supratiknya
STATEMENT OF ORIGINALITY
This is to certify that all the ideas, phrases, and sentences, unless otherwise stated, are the ideas, phrases, sentences of the thesis writer. The writer understands the full consequences including degree cancellation if she took somebody else’s
ideas, phrases, or sentences without a proper reference.
Yogyakarta, February 10, 2014
Siska Lidya Revianti 106332033
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswi Universitas Sanata Dharma: Nama : Siska Lidya Revianti
Nomor Mahasiswa : 106332039
Demi perkembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
A MOODLE LEARNING MODEL
FOR INTRODUCTION TO COLLEGE ENGLISH CLASSES
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan. Dengan demikian, saya memberikan hak kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikannya secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya maupun memberikan royalti kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sebenarnya. Yogyakarta, 10 Februari 2014
Siska Lidya Revianti
“ Education’s purpose is to replace an empty mind with an open one”
(Malcolm Forbes)
I dedicate the thesis to God the Almighty,
to the world of education,
to my beloved grandparents, parents and family,
to all of my best friends and my students, and most of all
to SHEVA,my beautiful princess.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
It has been a great moment for me to express my deepest gratitude to all of those who have supported me to finish my study. Firstly, I would like to address my deepest gratefulness to God the Almighty, for His eternal love, guidance and grace so that I was able to finish my thesis. I am truly blessed by Him so that I could struggle to do my best efforts in accomplishing this thesis.
I would like to express my sincere thanks to my thesis advisor, Dr. J. Bismoko, who is willing to give his valuable guidance and support for my study. I am also deeply grateful to Barli Bram, Ph.D, for his willingness to spend his precious time in giving me the feedback during my thesis writing. He has given extraordinary suggestions and criticism to my thesis. My greatest thanks also go to my beloved lecturers in this graduate school, F.X. Mukarto Ph.D, Dr. B.B. Dwijatmoko, M.A., Dr. Francis Borgias Alip, M. Pd., M.A. and Dra. Novita Dewi, M.S., M.A (Hons)., Ph.D. for sharing their knowledge and expertise in my study time. They have taught me very well and have given great encouragement for me to finish my study.
Next, I am deeply grateful to Dr. Ir. Gatot Hari Priowirjanto and the SEAMOLECteam for the scholarship and the funding so that I was able to continue my study in English Language Studies of Sanata Dharma University. I am so thankful to Bu Dewi, Pak Zubeir, Pak Aritonang, Pak Jaslin Ikhsan, Bu Cahya, Pak Rizal, Pak Jarwo and Pak Taufik for sharing the valuable knowledge and
experience in SEAMOLEC classes. I would like to extend my gratitude to Mbak Lely, Pak Mul, Wendy, Nimas, and Sisca for their fully assistance and kind attention to me.
I am indebted to all of the teachers, staff members and part timer students at the Center of Foreign Language Training (PPBA) of Duta Wacana Christian University. I acknowledge my big appreciation to Pak Andreas Winardi, Pak Moko, Bu Endang, Pak Punto, and Lisi Schrottner, for their willingness in spending their time evaluating my designed learning model. I am very grateful to Mbak Nia, Mbak Ambar, Bu Mega, Bu Ria Hapsari, Pak Ardhi, Bu Ninggar, Bu Kencana, Pak Jose, Pak Anton, Bu Mera, Bu Vero Widi, Bu Peppy, Bu Tia, Bu Lina and my other fellow teachers for their support, prayers, encouragement and feedback which always motivate me to finish my thesis.I also thank to all of my ICE students, especially to my ICE students in Level 2: Yulia, Vivi, Felix, Nando, Harta, Desy, Jeanette, Rolinda, Asniar, Devi, Endah, Pitriani, Amelia, Christiana, Victor, Stella, Okta, Chyntia, Riduwan, Anggi, Fanny, Widi, Sandra, Yuliyanti, Amanda, Johlin, Adiel, Lidwina, Ikhsan, Ari, Jeffin, Jian, Cahyo, Bili, Christanto, Erick, Kevin, Jessy, Alan, Angger, and many more. I do appreciate their active participation in ICE classes and their willingness to study together inside and outside class by joining themselves into my portal. Next, I would like to say thank you to all the part timer students at PPBA for their great assistance in helping me doing my research at PPBA. I hope they will be successful in their future.
Moreover, I wish to thank Alvin Setianugraha, my special saviour in my research. I would not be able to finish my thesis without his big help and kind attention. His willingness to spend his valuable time and his continuous support had given me high spirit to create a better portal for my students and finish this thesis. I warmly thank Edy Nugroho, SE. MSc as the Head of Statistic’s Center at Duta Wacana Christian University and his staff: Alfa, Heru, Ronny, and Tia for their patience, enthusiasm and support in helping me managing the statistics of my research.
I would like to thank all my classmates and other friends in English Language Studies: Pak Akbar, Pram, Arry, Muji, Edward, Patrice, Mega, Puri, Bu Irna, Bu Heni, Bu Mei, Nana, Orpha, Arina, Mawar and many others for our beautiful friendship and solidarity. We have grown together and shared bitter sweet memories through our classes and discussions. I wish to thank my best friends Passive Voicers: Tinon, Hayu, Anis, Unik, Yuli,Sari and Lulu for the priceless friendship and lovely attention through the ups and downs of my life. Their prayer, jokes, and caring have supported me emotionally and financially to finish this thesis.
My sincerest thanks go to my beloved family members; my super Mom and my super Hero Sri Suyanti, my greatest father M. Soebagiyo, my lovely sisters Dwi Riana Oktavia and Tri Ratna Kurniasari, my love of my life Shevarina Adiska Tirta Kirana and Adipermono. Their endless love and prayer always give me high spirit and strength to do my best efforts to finish my thesis. I also thank my uncle Soemardiyono and his family, my late grandparents Sanadi Sastro Hutomo
and Sardinem for their blessing, great affectionand precious guidance so that I was able. All of their love always cherish me and strengthen me in keeping my efforts up to finish my study in English Language Studies of Sanata Dharma University.
Last but not least, my greatest and deepest thank goes to everybody who has helped me in finishing my study and writing my thesis, either directly or indirectly. Their love has given me an enormous power that raised me up to continue my struggle in completing this thesis. Their kindness will be carved in my heart and I do hope we could always be a blessing for others. It is just like the everlasting love of the dew on the grass and leaves to the morning glory, it would always refresh our mind to start a new day with new hope and touch our heart with new accomplishments. May God bless us!
Siska Lidya Revianti
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ...…... i
APPROVAL PAGES... ii
THESIS DEFENSE APPROVAL PAGE………….………..……… iii
STATEMENT OF ORIGINALITY... iv
PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH... v
DEDICATION PAGE...vi
1.7 Research Benefits and Development...12
CHAPTER II. LITERATURE REVIEW………....15
2.1 Theoretical Review………...15
2.1.1 The Nature of Introduction to College English (ICE)...15
2.1.2 Theory of Learning and Language Learning………...23
2.1.2.1 Theory of Learning………...23
2.1.2.2 Theory of Language Learning………...…28
2.1.3 Adult Learning Principles………...30
2.1.4 Computer Assisted Language Learning and Electronic Learning ...32
2.1.4.1 Computer Assisted Language Learning (CALL)...32
2.1.4.2 Electronic Learning (E-Learning)...37
2.1.4.2.1 Definition………..…….……...……...37
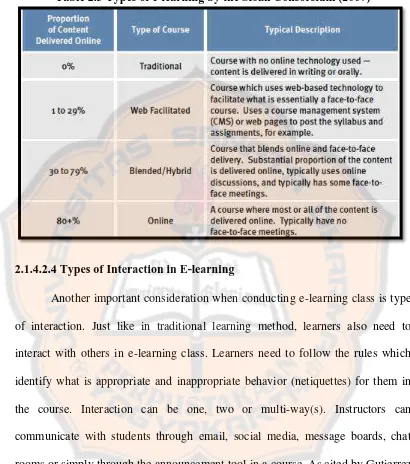
2.1.4.2.3 Formats of E-learning…………..……….40
2.1.4.2.4 Types of Interaction in E-learning………...41
2.1.4.2.5 Advantages and Disadvantages ……….…….44
2.1.5 Blended Learning……….……….………...46 2.1.6 Instructional Design Model………..48
2.1.7 Moodle……… ...55 2.1.7.1 Nature of Moodle………...………...…………55
2.1.7.2 Features of Moodle……….…..56 2.1.8 Learning Model………....62
2.1.9 Review of Related Study………..64
2.2 Theoretical Framework...65
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 3.1 Research Method...72
3.1.1 Research Information Collecting………..74
3.1.2 Planning………75
3.1.3 Developing a Form of Product………...76
3.1.4 Preliminary Field Testing……….76
3.1.5 Main Product Revision……….77 3.1.6 Main Field Testing ………..77 3.2 Setting and Research Participants...78
3.2.1 The Participants of Need Analysis………...79 3.2.2 The Participants of the Preliminary Field Testing………81
3.2.3 The Participants of the Main Field Testing………..82
3.3 Research Instruments...……….83
3.3.1 Questionnaire……….83
3.3.1.1 The Need Analysis Questionnaire………..84
3.3.1.2 The Preliminary Field Testing Questionnaire……….86
3.3.1.3 The Main Field Testing Questionnaire………87
3.3.2 Interview……….…..88
3.4 Data Gathering Techniques...90
3.5 Data Analysis Technique... ..92
3.6 Procedure…………...94
CHAPTER IV. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION………...96
4.1 Theoretical Model of the Designed Moodle...97
4.1.1 Research and Information Collecting……….…..97
4.1.1.1 The Result of Curriculum Investigation………...97
4.1.1.2 The Interview with the Coordinator of PPBA………..98
4.1.1.3 The Result of the Questionnaire from ICE Students in Level 2….100 4.1.1.4 The Result of the Questionnaire from PPBA Lecturers……...106
4.1.2 Planning………...111
4.1.2.1 Stating the Course Description of the ICE Portal………...111
4.1.2.2 Specifying the Topics and the Learning Objectives………...112 4.1.2.3 Choosing Teaching Activities and Instructional Event…………..113
4.2 The Iconic Model of Moodle Learning Model for ICE Class Level 2 ………...114
4.1.3 Developing Preliminary Product………...114
4.1.4 Preliminary Field Testing of the Material……..…………..……….122
4.1.4 Main Product Revision………..………....128
4.1.5 Main Field Testing………...………… 129
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS………...…….……131
5.1 Conclusions...131
5.2 Benefits………133
5.2 Suggestions...136
BIBLIOGRAPHY...138
APPENDICES...142
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
2.1 The General Objectives of ICE Classes Level 1-3………18
2.2 The Topics Presented in the Syllabus of ICE Level 2………..22
2.4 Summary of the Technology Adoption Hierarchy (Hooper & Rieber, 1999)…..52 3.1 Gender Table from the Student Group (the 1stBatch)………..…80
3.2 Gender Table from the Student Group (the 2ndBatch)………80
3.3 Description of Participants from the Lecturer Group………...81
3.4 Description of the Lecturers in Need Analysis Phase……….82
3.5 Gender Table from the Student Group………82
3.6 Degree of Agreement Value in the Questionnaire………...84
3.7 Blueprint for the Need Analysis from the Student Group……….84
3.8 Blueprint for the Need Analysis from the Lecturer Group………85
3.9 User Validation Blueprint for the Preliminary Field Testing………....86
3.10 Expert Validation Blueprint for the Preliminary Field Testing………...87
3.11 User Validation Blueprint for the Main Field Testing………88
3.12 Research Instrument and Data Collections………....89
3.13 Interpretation of the Degree of Agreement………94
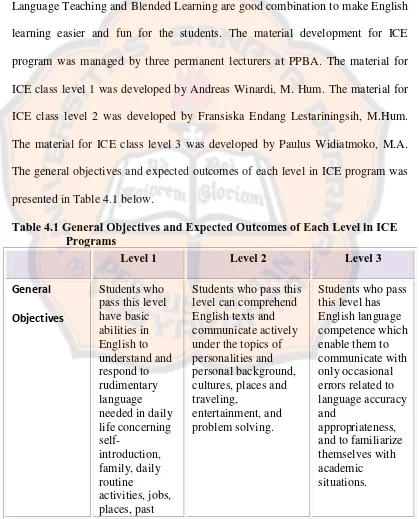
4.1 General Objectives and Expected Outcomes of Each Level in ICE Program...99
4.2 Statistic Results from Need Analysis Questionnaire ………….……….101
4.3 Result of Need Analysis Questionnaire from Lecturers………..108
4.4 Open-Ended questions of Lecturers Need Analysis Questionnaire……….109
4.5 Course Management in ICE Portal……….……….112
4.6 List of topics and objectives of ICE Level 2 in Moodle………..112
4.7 Types of activities related to Moodle Features………..……….113
4.8 Content of ICE Level 2 in Moodle Learning Model………...114
4.9 Result of Expert Validation Statistic………...123
4.10 Result of User Validation Statistic………127
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
2.1 Connectivism (Siemens, 2004)……….27
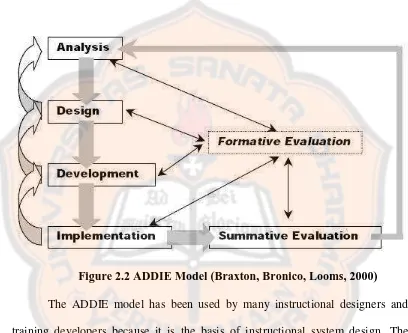
2.2 ADDIE Model (Braxton, Bronico, Looms, 2000)………..51
2.3 Modified Instructional Design Model for Teacher Designer (Rogers, 2002)…..54 2.4 Resources Features in Moodle………..57
2.5 Activity Features in Moodle ………58
2.6 Assignments and Quiz Setting Page in Moodle………59
2.7 Forum Setting Page in Moodle………60
2.8 Chat Setting Page in Moodle……….61
2.9 The Framework of the Theoretical and Iconic Model Developments…………..70
3.1 R & D Adopted Method Collaborated with ADDIE ………...78
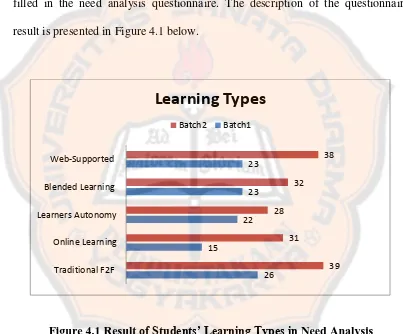
4.1 Result of the Students’ Learning Types………...101
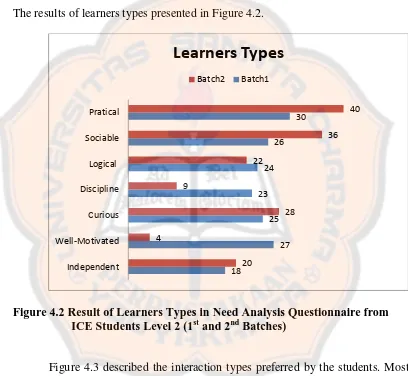
4.2 Result of the Students’ Learners Types………...102
4.3 Result of Interaction Types……….……….103
4.4 Result of the Use of Technology………104
4.5 Result of Learners Autonomy……….105
4.6 Result of Students’ Problem Solving……….……….105
4.7 Result of the Students’ Preference in Moodle………106
4.8 Result of the Syllabus Analysis……….107
4.9 Result of the Teaching System………..108
4.10 Result of the Use of Multimedia……….108
4.11 Result of the Students’ Motivation………..109
4.12 Content and Flowchart of ICE Portal using Moodle Learning Model………..116
4.13 General Description about the Portal……….117
4.14 Home Page Interface……….118
4.15 Login Page……….119
4.16 Course Category Page……….…………..120 4.17 Topic Page ………...……….121
4.18 Quiz Page………...………122
4.19 Learning Indicator……….122
4.20 Learning Material………..123
4.21 Elaboration of language Skills………...123
4.22 Features and Activities………..124
4.23 Overall Evaluation……….124
4.24 Material in the Portal……….126
4.25 User Interface ………...….127
4.26 Interaction and Communication…………...……….127
4.27 Flexibility………...128
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix Page
Appendix 1 Percentage of the ICE Students who passed and Failed………...…….142 Appendix 2 ICE Level 2 Syllabus ………....143 Appendix 3Grading competence of ICE Students in Level 2………...146 Appendix 4 Need Analysis Questionnaire from the Students (1stBatch)……..…...148 Appendix 5 Need Analysis Questionnaire from the Students (2ndBatch)………...154 Appendix 6 Need Analysis Questionnaire from the Lecturers ……….160 Appendix 7 User Validation Questionnaire………..………….164 Appendix 8 Expert Validation Questionnaire….………...166 Appendix 9 User Validation Questionnaire (Main Field Testing) ……..………….169 Appendix 10 Result of the Open-Ended Questions (Need Analysis) ………...171 Appendix 11 Result of Open-Ended Questions (Expert Validation) ………...173 Appendix 12 Result of the Expert Validation Questionnaire……….………...177 Appendix 13 Result of the Open Ended Questionnaire (User Validation)…………181
ABSTRACT
Lidya Revianti, Siska. 2014. A Moodle Learning Model for Introduction to College English Classes. Yogyakarta: Graduate Program on English Language Studies, Sanata Dharma University.
Learning models which are based on Information and Communication Technology (ICT) are becoming more popular lately. The use of ICT in education has provided many opportunities for teachers and students to get information as well as to share information quickly and easily. Electronic learning (e-learning) using Learning Management System (LMS) Moodle is one alternative that can be used by the teachers to maximize the use of ICT in education. LMS Moodle has many useful features such as document sharing, various learning activities, automatic assessment, search engine and entertainment.This phenomenon has inspired the researcher to offer an online supplementary material for Introduction to College English (ICE) classes based on LMS Moodle application.
This research was aimed at designing the iconic model which was used as an online supplementary material in ICE classes Level 2 of Duta Wacana Foreign Language Training Center. There were two research problems in this study, namely: (1) What is the theoretical model of the Moodle learning model for ICE class Level 2 like?, and (2) What is the iconic model of the Moodle learning model for ICE class Level 2 like?
To answer the problems, the researcher reviewed relevant literature and has designed an online supplementary material for ICE class Level 2 using the ADDIE Instructional Design model. There are five phases which are used in this instructional model, they are: Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation and Evaluation. The phases were integrated into the Borg and Gall’s cycles of Research and Development. The cycles consisted of Research and Information Collecting, Planning, Developing Preliminary Form of Product, Preliminary Field Testing, Main Product Revision, Main Field Testing and Operational Product Revision.
The theoretical model and the iconic model of A Moodle Learning Model for Introduction to College English Classes were the results of the research. The theoretical model presented the selected features and widgets based on their suitability with CALL principles and the syllabus in ICE Level 2. The CALL principles used in this research were Authenticity, Literacy, Interaction, Vitality and Empowerment principles. Based on those principles, the researcher designed a learning model using the features offered by Moodle: Resource Module, Assignment, Quiz, Forum and Chats. The widgets added were BBC World news, Test Your English, Cambridge Online Dictionary, clock, game, on-line radio, Yahoo! Messenger and Facebook linker. The iconic learning model could be accessed on
http://www.iceportal.tk .
The Moodle-based Learning Model for ICE class Level 2 had been proven as useful and acceptable. This portal can also be used as a useful source for a supplementary material in ICE class. The research would be useful and beneficial for students of a similar program, especially to equip the process of teaching and learning in the classroom with e-learning material. Finally, the research can give great contribution to English language teaching and further research.
ABSTRAK
Lidya Revianti, Siska. 2013. A Moodle Learning Model for Introduction to College English Classes. Yogyakarta: Program Pasca-Sarjana Kajian Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Model pembelajaran yang didasarkan pada Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi (TIK) menjadi lebih populer belakangan ini. Penggunaan TIK dalam pendidikan telah memberikan banyak kesempatan bagi guru dan siswa untuk mendapatkan informasi serta berbagi informasi dengan cepat dan mudah. Electronic learning (e-learning )yang menggunakan Sistem Managemen Pembelajaran (LMS) Moodle merupakan salah satu alternatif yang dapat digunakan oleh para guru untuk memaksimalkan penggunaan TIK dalam pendidikan. LMS Moodle memiliki banyak fitur yang bermanfaat seperti berbagi dokumen, berbagai kegiatan pembelajaran yang bervariasi, penilaian secara otomatis, mesin pencari dan hiburan. Kenyataan ini telah mengilhami peneliti untuk menawarkan sebuah bahan tambahan online untuk kelas Introduction to College English (ICE) berdasarkan LMS Moodle.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk merancang model ikonik yang dipakai sebagai sebuah bahan tambahan online dan berdasarkan pada aplikasi Moodle dalam kelas ICE Level 2 di Pusat Pelatihan Bahasa Asing Duta Wacana. Ada dua masalah penelitian dalam penelitian ini, yaitu:(1) Seperti apakah model teoritis dari model pembelajaran Moodle di kelas ICE Tingkat 2?, dan (2) Seperti apakah model ikonik dari model pembelajaran Moodle di kelas ICE Tingkat 2?
Untuk menjawab permasalahan, peneliti melakukan studi pustaka dan telah merancang sebuah bahan tambahan online untuk kelas ICE Level 2 menggunakan model Instructional Design ADDIE. Ada lima tahap yang digunakan dalam model pembelajaran ini, yaitu: Analisis, Desain, Pengembangan, Implementasi dan Evaluasi. Fase-fase tersebut diintegrasikan ke dalam siklus-siklus penelitian dan pengembangan milik Borg dan Gall. Siklus-siklus terdiri dari Penelitian dan Pengumpulan Informasi, Perencanaan, Pengembangan Bentuk Awal Produk, Pengujian Awal di Lapangan, Revisi Produk, Pengujian Utama di Lapangan dan Revisi Produk Operasional.
Model teoritis dan model ikonik dari Sebuah Model Pembelajaran dengan Moodle untuk Kelas-Kelas Introduction to College English merupakan hasil-hasil penelitian. Model teoritis menyajikan fitur-fitur dan widget terpilih berdasarkan kesesuaian dengan prinsip-prinsip CALL dan silabus di ICE tingkat 2. Prinsip-prinsip CALL yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah Authenticity, Literacy, Interaction, Vitality and Empowerment. Berdasarkan prinsip-prinsip tersebut, peneliti mendesain sebuah model pembelajaran dengan menggunakan fitur-fitur yang ditawarkan oleh Moodle: Resource Module, Assignment, Quiz, Forum and Chats. Fitur yang disajikan dalam model pembelajaran Moodle adalah Resource Module, Assignment, Quiz, Forum and Chats. Widget yang ditambahkan adalah BBC World News, Test Your
English, Cambridge online dictionary, clock, game, on-line radio, Yahoo! Messenger and Facebook. Model pembelajaran ikonik dapat diakses pada http://www.iceportal.tk..
Model Pembelajaran yang berbasis Moodle untuk kelas ICE tingkat 2 telah terbukti berguna dan dapat diterima. Portal ini juga dapat digunakan sebagai sumber yang berguna untuk bahan tambahan di kelas ICE. Penelitian ini akan berguna dan bermanfaat bagi mahasiswa yang menjalani program yang sama, terutama untuk melengkapi proses belajar mengajar di kelas dengan materi pengajaran berbasis e-learning. Akhirnya, penelitian ini dapat memberikan kontribusi yang besar bagi pengajaran Bahasa Inggris dan penelitian lebih lanjut.
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This thesis is about designing a Moodle-based learning model for Introduction for College English (ICE) classes. This Moodle-based learning model is an online learning model which specifies the materials of general English in ICE programs for university students in the Foreign Language Training Center (PPBA) of Duta Wacana Christian University (UKDW). This chapter is arranged into seven parts, namely: research background, problem identification, research limitation, research questions, research goals, product specification and research benefits.
1.1 Research Background
Knowledge should be equally and fairly distributed to everybody but unfortunately not all people get the access in having good education. The difficult geographical conditions and the expensive education are some of the problems in education which cause unequal distribution in educating people. One way to overcome this situation was by creating Open Education as an alternative solution. At first, there was only one form of distance learning format in a formal higher education that was Open University. However, it was regarded as an alternative education which was less prestigious than the traditional one with face to face method somehow. This phenomenon has changed with the advancement of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in education.
One obvious technological development is the Internet technology that enables information dissemination to the global world becomes more possible without many restrictions that were faced before. The Internet has emerged to overcome the barriers in the distribution of education because the access to the global world becomes very easy, efficient, and flexible.
These changes in education since the arrival of new technologies in schools in the 1980s had big impact on the way that teachers planned and taught the lessons (Pritchard, 2007). The way of how the teaching material is prepared and presented, including the way of how the homework is issued and submitted using new technologies are some examples of education system in Postmodernism Era. Sarup (1993) stated that Postmodernism era refers to the incipient or actual dissolution of those social forms associated with modernity. Modernization is a diverse unity of socio economic changes generated by scientific and technological discoveries and innovation. This means that in Postmodernism Era, people are demanded to be able to actualize themselves better by using technology.
The Internet provides great access to search any information needed by lecturers and students. Lecturers and students from different institutions can share ideas, great resources and information quickly. Students can find information that they think is worthwhile anywhere they can, share it as soon as possible, and search for meaning through discussion. Education in the future will be optimized by information network that allows interaction and collaboration between lecturers and students. As it is stated by Prensky (2007):
future. Modern technology fits perfectly with the students because they can collaborate the learning process with the community. (p.1)
Munir (2009) also described that this new paradigm has changed face to face method in teaching-learning activity into the possibility of distance learning or computer-based learning which can be done by anyone, at anytime and anywhere. By integrating ICT into learning activities thus the quality of the teachers and the students will be better. Teachers will have the opportunity to develop their skills and competence to improve the quality of education in their classes. From distance learning, students will also have more opportunity to get better knowledge and understanding. They can access the materials based on their needs and preferences so that they will find the learning process as a fun experience (p. 42).
autonomous learners. Teachers can also update the web with new information every time (p. 110).
This phenomenon is related with the constructivism and connectivism theories. E-learning, in consructivism and connectivism theories, involves the process of learning which is constructed through the learners‟ personal
experiences and interactions with various learning sources outside the classroom. Students are exposed to create meaning from the knowledge they get actively and to express their opinion freely in a better social context.
LMS Moodle doesn‟t require special web knowledge about how to build a web using PHP, HTML and JAVA programs. LMS Moodle also serves as a media for on-line learning which develops the students‟ learning autonomy and focuses on the students-centered approach. The students can access the resources, do the exercises, join in discussion forums, and moreover contact the other students and the teacher via email and messaging.To conduct better learning using a web-based learning portal, a high-speed Internet connection and a good computer processor are required.
The next discussion covers the importance of learning foreign language for international communication. Language, as social symbol of humanity, plays an important role in human life. People can express their feeling and ideas, as well as exchanging information by means of language. As one world language, English is considered as an international language. English, the most frequently-learned second language at the moment, has a vital role in all aspects of life, particularly in science and technology. Brumfit (1982:1; also cf. Lieberson 1982; Noss 1983; Bryson 1990; Pennycook 1994; and Crystal 2004) summarizes well the source of English‟s present dominance in the following:
“English is an international language in that it is the most widespread medium of international communication, both because of the number and geographical spread of its speakers, and because of the large number of non-native speakers who use it for part at least of their international contact”
students. Just like other universities, Duta Wacana Christian University (UKDW) facilitates its students through the Foreign Language Training Center (PPBA). In English program, PPBA offers Introduction to College English (ICE) classes.
The ICE program serves as general English course for the new students at UKDW. The ICE program is a matriculation program, compulsory but non-credit, as a prerequisite of the credit-bearing in English for Specific Purposes (ESP) offered in each faculty. ICE classes are designed to prepare the students in their basic English skills before they join English for Specific Purposes (ESP) class in each department. The students who pass these basic levels are expected to able to understand and respond to basic language needed in daily communication. ICE students come from most faculties in the university except the Faculty of Theology.
The freshmen should join ICE class and take the placement test first. Then, they will be categorized into three levels: Level 1, Level 2, Level 3. The material given in ICE classes is integrated material which develops the students‟ reading,
writing, listening and speaking skills and also enhance the students‟ vocabulary and grammar mastery. In the regular system, the students will join ICE class for 1 semester in each level. There are two lecturers who teach in one class. Meanwhile in the short semester program, the ICE class will be conducted only in a three week-period for each level. The material given is the same, in 24 meetings, but in the short semester the time is shortened and more intensive.
fact, some students have to take the subject more than twice. Based on the data taken from PPBA in even semester period in 2010/2011 until odd semester period in 2012/2013, the number of ICE students who failed in even and odd semesters in all levels was more than 20%. The data of the students who passed and failed is presented in Appendix 1.
This phenomenon makes the researcher feel challenged to improve this situation. The researcher has been teaching ICE classes Level 1 until 3 in PPBA since 2004. As one of the lecturers in PPBA then there was a big motivation to give some contributions in improving the situation. To improve the situation, the researcher proposed a web-based distance learning model. This researcher is about creating an online Moodle learning model to help the students accessing more helps to understand the material given in ICE class better. The online learning model is used as a supplementary material to enrich the materials given in class. The design of this Moodle learning model supports the implementation of „blended learning” method in teaching ICE classes. The Moodle learning model is
specifically designed for ICE class level 2 which covers three topics presented in the syllabus of ICE level 2. The language learning theory in the design also complies with the the course description and course objectives in the syllabus, that uses communicative approach. This research would be very beneficial as there has not been any learning model using Moodle for ICE classes.
1.2 Problem Identification
Indonesia. Some of them have already got sufficient English knowledge, but some others have not got it yet. To minimize the problems arise in teaching English in class, then PPBA conducts placement tests. The placement tests will put the students into three categories: Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3. The syllabuses are based on the learning objectives in each level. They are designed to accommodate the students‟ need in using English communicatively and actively inside and
outside the class. In fact some students still fail and must retake the subject more than once somehow.
The greatest challenges and concerns in ICE class are not only about the students‟ English background but also about the students‟ lack of motivation.
Because of the students‟ low motivation the students do not really care about their
progress in learning English. Some of the students do not consider English as an important subject. The students do not really want to participate fully in class. Some of them have problems in their attendance so that they do not do the progress tests fully and are not allowed to do the final test.
Based on the background of the study and realizing the fact that some students still fail in ICE classes, then the researcher was motivated to improve the teaching-learning process in ICE classes. The new paradigm in teaching –learning method using ICT, especially the Internet, is believed as a breakthrough which can overcome the problems in ICE classes. The concept of “blended learning” is applied. The researcher integrated the material used in class ICE Class Level 2 with the use of ICT in an Open Source Website called Moodle.
The approach of language learning used in PPBA is Communicative Language Teaching (CLT). The emphasis of teaching English at PPBA is the communicative functions which are expressed and performed with language. The class activities involve the ICE students in realistic communication such as in role-play and simulation. Harmer (2007: 69) states that plentiful exposure to language in use and plenty of opportunities to use it are vitally important for a student‟s development of knowledge and skill. Then, the researcher proposed Moodle learning model as a supplementary material in ICE classes as one of the media for the students to expose the language more outside class.
1.3 Research Limitation
2. The materials in Moodle application that would be discussed in this thesis were only for 3 topics given in level 2. The goals, objectives and topics of the materials are arranged in accordance with the syllabus as formulated by the material coordinator of Level 2 and it has been approved by the coordinator of PPBA.
Actually, there were some classes offered in ICE program in each level per semester. However, the research only used four ICE classes in level 2. The research was started in the odd semester period in July-December 2012 and was continued for the even semester period in January-May 2013 in ICE classes level 2. The researcher only used two classes of ICE class level 2 offered in the odd semester in July – December 2012, namely: 2C and 2D classes. For the even semester period in January-May 2013, the researcher used 2 classes of ICE class Level 2, namely: 2C and 2E classes. Then, the researcher gave the students an opportunity to use the suggested supplementary material and negotiated the feedback from the students and the other lecturers.
1.4 Research Questions
As it has been discussed in the background that ICE students still have some difficulties in learning English in ICE classes, this research is aimed to find the answers of these two questions namely:
1. What is the theoretical model of the Moodle learning model for ICE class Level 2 like?
1.5 Research Objectives
The objectives of the study are to answer the questions stated in the
statement of Research Questions. The first objective of this research is to present
theoretical model which can be applied as a supplementary material in ICE class
level 2 using Moodle learning model. The theoretical model will elaborate the
discussion of what the design of an online supplementary material in ICE class level 2 using Moodle application is like and how the portal is designed, based on the need analysis and related theories. The theoretical model will be used as the
basis for developing the iconic model.
The second objective of this research is to develop the iconic model and
the practical online supplementary material using Moodle application in ICE class
level 2. There are some features offered by Moodle application which are finally
selected to be included in the iconic model, namely: Resources,
Assignments/Quiz, Forum, Links and Widgets. The chosen features and additional
widgets are designed by considering the students’ need and the students’
characteristics in ICE classes. The final version of the iconic model is the
improved model that has been revised based on the feedback from the targeted
users and the expert.
1.6 Product Specifications
presented in the portal are based on the topics given in the syllabus of ICE program in Level 2. The targeted users are the students of ICE program in level 2 of PPBA at Duta Wacana Christian University. This model is developed to facilitate the students‟ learning autonomy in using a web-based material and to improve the students‟ ability to understand the material given in class better.
1.7 Research Benefits and Development
This research is expected to give some contributions to English teaching and learning in global world of education in term of theory and practice.
1. Theoretical Benefit
2. Practical Benefits
This research is also valuable for the students, the lecturers and the curriculum developers because they can get some practical benefits. First, the research provides the ICE students level 2 an online supplementary material so that the students have more opportunity and can use it outside class as a self-study to get better understanding for the material given in class. The experience will enhance the students to be more independent and ready to become autonomous learners. The students can do the exercises and also play the video or other sources more than once. From this experience, the students will get a new experience of using Moodle application to support their learning method in their academic life. The online Moodle application hopefully can help the students to improve their English mastery and increase their grades in ICE class level 2.
Second, the other ICE lecturers can use the portal for supporting the teaching learning process in their own class. The lecturers can develop other material to bet included in the portal for different levels, level 1 and 3. The lecturers are still able to adapt or edit the material in the application to be updated with the students‟ need because the application is easy to be used and managed by the lecturers. The lecturers will be more aware to the students‟ progress and opinion because there are Self-Assessment and Pooling applications in Moodle application.
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW
This chapter is divided into two main sections; those are theoretical review and theoretical framework. In the theoretical review, there is a review of some theories and literatures that supports the process in conducting the research for Introduction to College English (ICE) program in Foreign Language Training Center (PPBA) of Duta Wacana Christian University (UKDW). In the theoretical framework, the framework of this research will be elaborated based on the discussed theories that support this research.
2.1 THEORETICAL REVIEW
In the theoretical review, the researcher provides the theoretical descriptions which are related and relevant to support this research. They are used as a guideline to design the Moodle learning model for ICE class level 2 at UKDW. Therefore, The Nature of Introduction of College English (ICE), Theory of Learning and Language Learning, Adults Learning Principles, Computer Assisted Language Learning (CALL) and Electronic-learning (E-Learning), Blended Learning, Instructional Design Model, Moodle, Learning Model and Review of Related Study are presented in this section.
2.1.1 The Nature of Introduction to College English (ICE)
UKDW is one of outstanding universities in Yogyakarta which concerns about high quality of its graduates to be able to compete both in local and international circumstances. This statement is stated in the UKDW‟s website at
to compete both in local and international circumstances. One of the requirements to succeed in the global marketplace is to master foreign languages. Realizing that mastering foreign languages has become the biggest need and one of the requirements to succeed in the global marketplace in the globalization era, thus, UKDW established a center for foreign language training or Pusat Pelatihan Bahasa Asing (PPBA).
PPBA has vision and mission to support the success of UKDW‟s vision that is to be an excellent Christian University that produces highly independent and professional graduates for the pluralistic world fortified by love. The missions are managing English language training for UKDW students through ICE program and English for Specific Purposes, training UKDW lecturers and staff based on special needs, running other programs for non-UKDW community (private courses, cultural events), running non-English language training (Mandarin, Korean), and maintaining the quality and services of the programs, as well as the quality of the teachers continually. The organizational structure at PPBA consists of a coordinator, some permanent lecturers and two administration staffs.
Remedial programs, today PPBA also administers other training programs open to the public such as General English, English for Specific Purposes, English for Academic Purposes, Mandarin courses, Korean courses, and Drop-in English.
ICE program is a training program which is set to improve the students‟
language in all skills comprehensively with a special emphasis on reading and speaking skills. Starting from the students in the batch of 1999/2000 academic year onwards, the program is a compulsory but non- credits. ICE classes are considered as matriculation programs for basic level of English. This program is a prerequisite of the credit-bearing in each Faculty of Applied English / Study Program.
Each semester PPBA trains ICE students in three different levels. Each level is based on placement test results when they follow the Admissions Test. Then, they will be categorized into three levels: Level 1, Level 2, Level 3. The ICE students will get a certificate after they complete one level. Each level consists of 24 sessions and the duration is 100 minutes per session. The maximum number of students is 30 students.
The materials for ICE classes are based on the syllabuses which are managed by the coordinator and the permanent lecturers at PPBA. The materials are designed based on blended learning theory and topic-based method. The general objectives for each level in ICE classes can be described in the following figure.
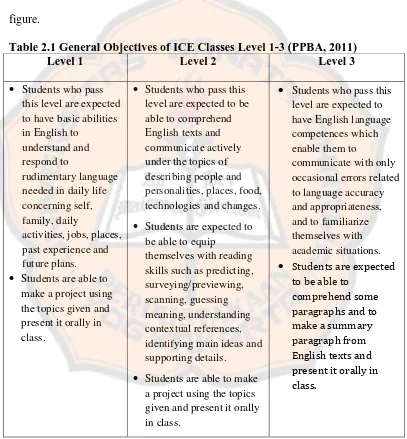
Table 2.1 General Objectives of ICE Classes Level 1-3 (PPBA, 2011)
Level 1 Level 2 Level 3
Students who pass this level are expected to be able to comprehend
Students are expected to be able to equip
Students are able to make a project using the topics given and present it orally in class.
Students who pass this level are expected to
ICE program are the students and also the lecturers. The students‟ low motivation
and willingness to be active in learning English are two great challenges in ICE classes. Because of the students‟ low motivation, then the students feel that ICE
program is only a compulsory subject with no credit so they just attend the class without strong motivation to learn English.
The ICE students also come from different background and area throughout Indonesia. This means that their level in English competence is varied, too. Therefore, there is a placement test system to put the students into three different levels, namely Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3. However, in certain cases, this placement test system unfortunately still cannot successfully put the students into the same level. So, some students need to put really hard efforts to pass the class and have to retake the same level again.
Wati (2006) also stated another problem in ICE program is about the time that the students needed to complete this program because the students have to repeat the same level. The time required to complete this program is not in accordance with what is planned, namely a maximum of 4 semesters for the lowest level. Another issue that stands out is the fact that there are students who repeat the same level, between 1 to 10 times. One of the reasons that have been successfully revealed from Puspindika (the unit in UKDW for gathering the students‟ data) is the lack of students‟ attendance in class. The students who are
This research is aimed to develop a product of a web-designed material utilizing Moodle application as an online supplementary material for ICE program level 2. The content of the web are based on the topics presented in the syllabus of ICE program in level 2. The general description of the course in ICE program level 2 covers the materials which can be used to develop the students‟skills in listening, speaking, reading and writing. The emphasis is in building the students‟ skill in speaking and reading from various interesting activities and drilling the language components so that the students will be trained to use their English more actively under certain topics.
The general objectives of the ICE program level 2 are training the students so that they will have basic competences in using English related to certain topics given in the syllabus. By the end of the course, the students are expected to be able to describe people‟s appearance and personality, describe places, describe food, describe technology development and describe changes. The students are also expected to apply reading strategies, such as predicting, surveying/previewing, scanning, guessing meaning, understanding contextual references, and identifying main ideas and supporting details. The evaluation of ICE program in level 2 consists of 5 Progress Tests (50%), Reading Test (15%) and Final Test (35%).
The topics given in the syllabus of ICE class level 2 is presented in Table 2.2 below.
Table 2.2 Topics Presented in the Syllabus of ICE Level 2
Meet Topics Sources
Describing People
1 Introduction World Link 1, pp.
2-6
7-Meet Topics Sources
Progress Test 1: Group discussion Active Skills for Reading: Book 2, pp.
7 Where’s that music coming from?
Active Skills for
9 What’s your city like?
Progress Test 2 Preparation (Homework)
World Link Intro, pp. 17-21
Reading 3: Scanning
10 Safe travel
Progress Test 2: Short Speech
Active Skills for
Progress Test 3: Guessing meaning
Active Skills for
15 Crazy about cell phones Progress Test 4: Role Playing
World Link 2, pp. 109- 113
Reading 5: Understanding Contextual References
16
Meet Topics Sources
18
Life is all about change.
Progress Test 5: Free writing about a specific invention that has changed your life
World Link 3, pp. 12-16
Reading 6: Identifying Main Ideas and Supporting Details
19 How advertising uses psychology
Active Skills for Reading: Book 2, pp. 130-134
20
Reading TEST + teachers evaluation
Homework: bring samples of vacation brochure, city profile, house advertisement, gadget promotion, etc for group project.
Group Project
21
Checking artwork (vacation brochure, city profile, house advertisement, gadget promotion, etc) and writing draft for the project.
Homework: Bring all the equipment needed for the artwork
Teachers’ sources
22
Designing the artwork (vacation brochure, city profile, house advertisement, gadget
promotion, etc)
Students’ sources
23 Peer-feedback of students’ project draft
24 Final Test: Final presentation of students’ project
2.1.2 Theories of Learning and Language Learning 2.1.2.1 Theory of Learning
This chapter also describe the associated areas of learning and language learning theories used in the research and have an impact on the realisation of the expected learning outcomes. The advance in the field of Information and Communications Technology (ICT) has brought the breakthrough in the growing of awareness of the theory associated with e-learning. The electronic link between a teacher and students was established. Internet and mobile phones are new means to engage the students with the lessons they get in the classroom. The concept of learning in the implementation of conducting e-learning is a fundamental consideration. The design of the site, the tasks and other activities presented on websites including the ways in which teachers choose to encourage students to make use of websites, are supported by certain theoretical approaches to teaching and learning. Teachers need to be aware of the underpinning theory, which can have a big effect on the progress of learning.
There are two learning concepts that can be elaborated in relation to the use of ICT in teaching, they are behaviouristic and constructivist. Behaviorism and constructivism are the learning theories that most often used in the creation of instructional materials. As stated by Pritchard (2007):
Based on behaviouristic approach, all behaviour can be divided into small actions, each of which can be mastered by a process of training, rewards and sometimes punishments. In behaviourist theory, conditioning is the result of a three-stage procedure: stimulus, response and reinforcement (Harmer, 2007:51). Behaviourism emphasizes on drilling the students which follows the stimulus-response-reinforcement model. Learning is a mechanical process of associating the stimulus with response which produces a new behavior. The behavior is shaped by the reinforcement. Positive as well as negative reinforcement increase the probability of the repetition of behavior. Behaviorists view the learner as a passive person who responds to the stimuli. It is a teacher-centered approach because the students‟ learning process depends on the instruction given by the
teacher.
In contrast to earlier theory, the constructivist approach involves more thinking, more activity and more interaction with others. According to Pritchard (2007), the principles of constructivist learning are (1) learning is a process of interaction between what is known and what is to be learned, (2) learning is a social process, (3) learning is a situated process, and (4) learning is a metacognitive process. Based on constructivism, the knowledge is constructed through the learners' personal experiences and interactions with the outside world. The student takes in new information and gives meaning to it using his or her own prior attitudes, beliefs, and experiences as references (Stavredes, 2011). Students are responsible to make sense of a concept and to express their own perspectives.
There is no one correct meaning, since individuals differ in their sense-making
and viewpoints (Duffy & Jonassen, 1992). Students are active participants in the construction of knowledge while the teacher serves as a facilitator.Learners often select and pursue their own learning style and material (Siemens, 2004).
A constructivist also viewed learning as a social function and the focus is
on knowledge construction. As cited by Chao and Stovel in Patricia Roger‟s book
entitled Designing Instruction for Technology-Enhanced Learning (2002: 116),
Dewey (1944) stated that
“Knowledge and ideas emerge only from a situation in which learners are induced to draw them out of experiences which have meaning and importance to them. These situations have to occur in a social context, such as a classroom where students join in manipulating materials and thus create a community of learners who build knowledge individually and collectively.”
Vygotsky (1978) further states that learning is a social process. The
interactions with peers and with a subject expert help students to acquire
knowledge in the classroom. The teacher prepares a learning environment that provides a set of learning activities that can be chosen independently by learners to engage with the lesson given.
Another important principle in constructivism is active learning. It is more
effective for learners to build their own knowledge from their experiences than to
receive it passively (Perkins, 1992). Students are trying to create meaning actively
by constructing knowledge. They are more likely to retain it because they have
interpreted and assimilated it into their previous knowledge.
Nowadays, there is a new learning theory called Connectivism. Connectivism is a theory of learning which emphasizes the role of the social and cultural context opposed to a more essentialist notion which foregrounds the individual (Wikipedia, 2012). It has emerged because of the massive impact of the use of technology that has changed the way people live, communicate and learn.
Connectivism believes that knowledge exists outside of the learner, and the learner makes connections between information to build knowledge. Knowledge can be earned so quickly using various technologies offered by modern life style. Learning now occurs in a variety of ways – through communities of practice, personal networks, and through completion of work-related tasks. Through this connected web, learners will be able to stay up-to-date with content as it changes.
formal and informal education in gaining knowledge. Formal education no longer plays as the only source and the majority of learning. As it is stated by Siemen (2004):
“The starting point of connectivism is the individual. Personal knowledge is comprised of a network, which feeds into organizations and institutions, which in turn feed back into the network, and then continue to provide learning to individual.”
Figure 2.1 Connectivism (Siemens, 2004)
ideas, and concepts is a core skill to maintain and facilitate continual learning. Another important principle in connectivism is decision-making process. Choosing what to learn and the meaning of incoming information is seen through the process of a shifting reality. While there is a right answer now, it may be wrong in the future because of variations in the information which can affect the decision.
2.1.2.2 Theory of Language Learning
The next discussion presents theory of language learning in English Language Teaching (ELT). The approach applied in teaching English at PPBA is Communicative Approach. From the general objectives of ICE classes in level 1-3, it is stated that the students are expected to be able to use English in real communication in daily life under certain topics. Besides, the students are also expected to master English comprehensively in all skills so that they can use their English to make some projects and to do oral presentations well. Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) concerns the spoken functions as much as written grammar, and notions of when and how it was appropriate to say certain things were of primary importance (Harmer, 2007:69). Thus the teaching and learning activities in ICE classes should give the students some stimulus and exposure to perform the language in meaningful and communicative contexts to replicate real communication.
language focus. Then, the students practise the language using accurate reproduction techniques and drillings. Finally, the students use the new language items in more productive exercises and freer practices. This procedure was argued in the 1990s because it seems to assume that students learn “in straight lines‟- that is tsarting from no knowledge, through highly restricted sentence-based utterances and on to immendiate production (Harmer, 2007: 66). As cited by Harmer (2007), Woodward and Lewis (1993) noted that this procedure is not really suitable to the nature of language nor the nature of learning because human learning is more random and convoluted. Thus, Johnson (1982) suggested the “deep-end-strategy” as an alternative of PPP procedure. Moreover, Byrne (1986) suggested joining the three phases in a circle. Basically, the alternatives procedure of Johnson (1982) and Byrne (1986) state that teachers and students can decide at which stage to enter the procedure. If students are having problems during the production phase, then they can return to either presentation or practice phases.
2.1.3 Adult Learning Principles
The participants in this thesis are university students around 19 to 22 years old. They are considered as adults learners. Part of being an effective instructor also considers the understanding how adults learn best. To begin with, it is important to know the characteristics of adult learners. Then the discussion will be about the motivation of adult learners.