i A Thesis
Presented as a Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the Attainment of Sarjana Pendidikan Degree in English Language Education
By:
SARI WAHYUNING TYAS
12202241060
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT FACULTY OF LANGUAGES AND ARTS STATE UNIVERSITY OF YOGYAKARTA
v
“
Man Jadda Wa Jadda
”
(Whoever strives shall succeed)
-Arabic Proverb-
“
Man Shabara Zhafira
”
(Those who persevere will get lucky)
-Arabic Proverb-
“When you want something, all the universe conspires in helping
you to achieve it.”
vi
I fully dedicate this thesis to:
♥
My beloved parents (Ibu Sartini and Bapak Kadiri)
Thank you very much for your encouragement, endless
prayers, motivation, and love.
♥
My younger sister (Arsita Novianti)
viii
RATIFICATION SHEET... iii
PERNYATAAN ... iv
MOTTOS ... v
DEDICATIONS ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ... vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... viii
LIST OF TABLES ... xi
LIST OF FIGURES ... ... xiii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xiv
ABSTRACT ... xv
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Identification of the Problem ... 3
C. Problem Limitation ………... 4
D. Formulation of problem ... 4
E. Research Objectives ... 5
F. Research Significances ... 5
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW ... 6
A. Literature Review ... 6
1. Teaching English in Vocational High School ... 6
a. English Curriculum of the Vocational High School ... 6
b. Nursing Department ... 8
2. English for Specific Purposes ... 6
a. Definition of English for Specific Purposes ... 9
b. The Need Analysis ... 10
ix
a. Definition of Materials ... 14
b. Criteria of Good Materials ... 15
5. Material Development ... 17
a. Definition of Material Development ... 17
b. The Model of Material Development ... 18
6. Unit Design Development ... 20
a. Component of a Unit ... 20
b. Developing Unit of Work ... 20
c.Task grading, Sequencing, and Integrating ... 21
7. Task Development ... 22
a. Definition of Task ... 22
b. Task Continuity ... 22
8. Materials Evaluation ... 23
B. Relevant Studies ... 23
C. Conceptual Framework ... 24
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD ... 26
A. Type of the Research ... 26
B. Setting and the Subjects of the Research ... 26
C. Research Procedure ... 27
D. Data Collection ... 28
1. Type of the Data ... 29
2. Data Collection Techniques ... 30
3. Data Collection Instruments ... 30
x
3. The Unit Design... 53
4. The First Draft Materials ... 56
5. The Expert Judgement ………... 57
B. Discussions ... 71
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS A. Conclusion ………..…… 78
1. Target Needs ... 78
2. Learning Needs ... 79
3. Characteristics of Appropriate English Materials for the Tenth Graders of Nursing Department at the Second Semester ……... 80
B. Suggestions ... 81
1. For English Teacher in VHS ... 82
2. For Other Materials Developers ... 83
xi
Table 3.1. the Organization of the first questionnaire for needs analysis Table 3.2. Data conversion table
Table 4.1. Students’ goal in learning English
Table 4.2. Students’ view Students’ View of Need in Target Situation Table 4.3. Students’ current levels of English proficiency
Table 4.4. Students’ View about Target Proficiency
Table 4.5. Students’ Wants of Language Skill in Learning English Table 4.6. Students’ Wants of Language Knowledge in Learning English Table 4.7. Learning needs (listening input)
Table 4.8. The length of listening input Table 4.9. Learning needs (speaking input) Table 4.10. Learning needs (reading input) Table 4.11. The length of reading input Table 4.12. Learning needs (writing input) Table 4.13. The length of writing input
Table 4.14. Students’ view about topics they want to learn in learning English Table 4.15. Learning needs (listening activities)
Table 4.16. Learning needs (speaking activities) Table 4.17. Learning needs (reading activities) Table 4.18. Learning needs (writing activities) Table 4.19. Learning needs (vocabularies activities) Table 4.20. Learning needs (grammar activities) Table 4.21. Learning needs (pronunciation activities) Table 4.22. Setting
Table 4.23. Setting in completing tasks Table 4.24. Learners’ role
xii
xiv C. Course Grid
D. Tasks Description of the First Draft Materials E. First Draft Materials
xv By:
Sari Wahyuning Tyas 12202241060
ABSTRACT
The objectives of this study are 1) to find out the target needs of the tenth graders of Nursing department in the second semester, 2) to find out the learning needs of the tenth graders of Nursing department at the second semester, and 3) to develop the appropriate English materials for the tenth graders of Nursing department at the second semester.
This study belongs to Research and Development (R&D). The subjects of this study were the tenth graders of nursing department at SMK Kesehatan Rahani Husada. This study adapted the materials development procedure from Jolly and Bolitho in Tomlinson (1998). The steps of this study were conducting the need analysis, developing the course grid, developing the first draft materials, materials evaluation, revising the first draft materials and writing the final draft materials. There were two types questionnaires used to collect the data. The first questionnaire was made for collecting data in need analysis while the second questionnaire was made for collecting the data about the appropriateness of the materials through the expert judgment. The collected data was analyzed through descriptive statistics.
1
Nowadays, vocational high school becomes popular as the option to
continue the education after Junior High Schools. That statement was based on
the Act of the Republic Indonesia number 20 year 2003 on National Education
System which stated that vocational high school is one of the secondary
schools which is the continuation of the basic education like Junior High
Schools (SMP or MTs). Thus, vocational high schools were expected to give
students the skills that they will need for their job in the future according to the
department. In Indonesia, vocational high school had many kinds of
departments as stated in the Government rule no. 17 year 2013 article 80 about
the categorization of departments in vocational high schools. The departments
are categorized into technology and engineering; information, communication
and technology; health; agribusiness and agri-technology; fisheries and
nautical; business and management; tourism; arts and crafts; and performing
arts.
SMK Kesehatan Rahani Husada was one of the vocational high schools
that is located in Klaten regency. It only had one department, which was
nursing department. It had two classes for each grade with around 35 students
in each class. The students of nursing department were expected to have
enough knowledge about nursing when they are graduated. After graduating,
department and become professional nurses. Whether becoming novice nurses
or professional nurses, they have to deal with medical terms that mostly are in
English. They also had to deal with various patients which possibly those who
cannot speak Indonesian. Since English is the international language, so the
ability to interact with English is very important for the students in nursing
department.
The students of nursing department can learn English that they will use
for their future job in school, but unfortunately the English lesson from school
was not sufficient for them since the lesson that they receive was general
English. However, they need English materials which can support them as
nurses in the future. The English lesson in school was not specifically designed
for nursing department, but it was designed for senior high school. The
textbook used for English lesson is Pathway to English and worksheet or
“LKS” for students. The book uses School Based Curriculum that matches with
the curriculum used in SMK Kesehatan Rahani Husada, but the contents are
not suitable for nursing department because nursing department has special
materials that are not being taught in general senior high schools.
Developing English learning materials is very important to be
conducted because there are no English learning materials which can fulfill
their need and interest to be used by teachers of nursing department to teach
their students. This condition needs to be fixed to give the nursing department
B. Identification of the Problem
Materials are one of the important aspects of teaching and learning
process both for teachers and students. For teachers, materials help them to
teach their students. By the existence of materials, teachers can choose what to
teach and how to teach those to their students. While for students, materials
help them to decide what to learn so they can focus on certain points. As a
result, good material is needed to be provided to help teachers and students
achieve the learning goals. Good materials are the materials that appropriate for
students to learn because it covers their needs and interests. Therefore, English
materials for vocational high school are different from those used in general
senior high school since there are various departments in vocational high
school.
However, based on the interview and observation conducted on
February 2016, the researcher found that the English teachers of SMK
Kesehatan Rahani Husada did not use English textbook that was specifically
designed for vocational high school of nursing department. The reason was
because she could not find the suitable textbook. The book used for English
learning process was Pathway to English and worksheet or “LKS” for students. The book mentioned was designed for Senior High School students in general.
Therefore, the contents were general English, which mostly were not related to
nursing. Moreover, because the teacher explained the materials used Pathway
nursing. As a result, the materials and practices were separated and it was not
practical because based on the interview with some students, sometimes they
lost the practices.
C. Problem Limitation
According to the problems mentioned above, the researcher
focused on developing learning materials for tenth graders of nursing
department of SMK. It was because after graduating from senior high school of
nursing department, the students are expected to be able to communicate in
English with foreign patients or at least be able to understand and respond to
foreign patients‟ grievance. Besides, they are also expected to be able to
understand medical terms in English so they can do their job professionally.
Therefore, they need materials that can prepare them for the expected skills
mentioned. Considering the time constraint, the researcher only developed the
materials for the second semester with the integrating skill tasks based on the
School-Based Curriculum.
D. Problem Formulation
The problems can be formulated into:
1. What are the target needs of the tenth graders of nursing department in
the second semester?
2. What are the learning needs of the tenth graders of nursing department in
3. What are the characteristics of appropriate English materials for the tenth
graders of nursing department in the second semester?
E. Research Objectives
1. to identify the target needs of the tenth graders of nursing department in the
second semester.
2. to identify the learning needs of the tenth graders of nursing department in
the second semester
3. to develop the appropriate English materials for the tenth graders of nursing
department in the second semester
F. Research Significances
This research is expected to give beneficial contributions for:
1. The English teachers of nursing department
The English teachers of nursing department can use the result of this
research to support them provide the materials and practices in English
learning process.
2. The students of nursing department
The result of this research can be used by the students of nursing
department to help them focus on learning the English materials needed.
3. Other researchers
For other researchers, the result of this research can be used as references
6
1. Teaching English in Vocational High School
a. English Curriculum of the Vocational High School
One of the most important aspect in teaching and learning process is
curriculum. In Indonesia, it has been stated in the Law number 20 year 2003
about National Education System that curriculum is a set of plans and rules
about the goals, content and materials of lessons and the method to conduct
the learning process to achieve the given education goals. In line with Tyler
(1949), curriculum can be defined as a plan for action or a written document
that includes strategies for achieving the wanted goals or ends.
In Indonesia, the government always try to develop the curriculum in
order to make good quality of education. As a result, curriculum is changed in
some years if the previous curriculum was not suitable with the current
condition. There was Competency-Based Curriculum in 2004. Two years
later, the new curriculum was applied. It is called School-Based Curriculum.
That curriculum was applied for seven years before the government
announced the new developed curriculum with scientific approach,
Curriculum of 2013.
In the process of curriculum changing, there are many problems
appear. One of them is the lack training for the teachers to apply the
curriculum in school. That problem is also happened in SMK Kesehatan
is not quite mastered the Curriculum of 2013 so do some other teachers in that
school. Therefore, SMK Kesehatan Rahani Husada decided to not use the
Curriculum of 2013 and back to use the School-Based Curriculum.
According to the National Education Department (2006), English is
an adoptive subject, in which its goal is to provide students the ability to
communicate in English in the communicative materials contexts needed for
the students‟ program, either in written and spoken form. In the School-Based Curriculum, there are two aims of English lesson:
1. to master the basic knowledge and skill of English to support the
competence achievement according to the study program
2. to apply the skill and competence of English to communicate either in
spoken or written form in the intermediate level.
In School-Based Curriculum, the area of English is included the aspects
of the basic communication of English in novice level, the basic
communication of English in elementary level, and the basic communication
of English in intermediate level. For grade ten, the English lesson is in the
novice level. The Standards of Competences and the Basic Competences are
different for each level. As for novice level, the Standards of Competences
Table 2.1. Standard of Competences and Basic Competences for Grade X of Vocational High School
Standard of Competence Basic Competence
1. Able to communicate in English in the novice level.
1.1. Comprehending basic expressions in the social interactions for daily life.
1.2. Mentioning things, people, characteristics, times, days, months and years.
1.3. Describing things, people, characteristics, times, days, months and years.
1.4. Producing complete simple discourse that enough for basic functions.
1.5. Describing activities using present continuous sentences.
1.6. Comprehending memo, simple menu, schedules of public transportation and traffic signs. 1.7. Comprehending words and foreign technical terms as well as simple sentences based on formula.
1.8. Writing simple invitation.
b. Nursing Department
Nursing department, students are expected to be able to look after patient.
The patients are sometimes foreigners. Then, to be able to look after those kinds
of patients, students must able to speak English. Therefore, the English knowledge
from school were expected to give enough skills for students. After graduating,
they can be a novice nurse or continue their study to the college with the same
department and become professional nurses. Whether becoming novice nurses or
professional nurses, they have to deal with nursing terms that mostly are in
English. They also have to deal with various patients which possibly those who
2. English for Specific Purposes (ESP)
English for nursing students can be categorized as English for specific
purposes because what they need is English for nursing field, not general English.
This part presents the definition of English for Specific Purposes, need analysis
and syllabus design.
a. Definition of English for Specific Purposes
By learning English, Vocational High School Students are
expected to be able to apply the knowledge they have learnt in their field.
Therefore, they need English material that specifically designed for them
related to their need and interest so they can focus only learn about it. In
English Learning Teaching, teaching English for special needs is included in
the approach of English for Specific Purposes (ESP).
Hutchinson and Waters (1987: 19) states that English for Specific
Purposes (ESP) is an approach to language teaching in which all the content
and method are based on the learners‟ reason for learning. In their book, Hutchinson and Waters (1987:8) also mention that one of the main reason to
the existance of ESP is learning that focus in the learners. It emphasizes the
most importance in learning English are the learners attitudes towards
learning. It views towards learners is that they have different needs and
interests that can influence their motivation to learn and the effectiveness of
their learning. In short, this approach was believed that the suitability of the
materials to their needs will increase their motivation so the learning will
There is also other definition of ESP by Dudley-Evans and St. John (1998)
who proposed some absolute and variable characteristics to explain what ESP
is.
Absolute Characteristics
1. ESP is defined to meet specific needs of the learners.
2. ESP makes use of underlying methodology and activities of the discipline it serves.
3. ESP is centered on the language appropriate to these activities in terms of grammar, lexis, register, study skills, discourse and genre.
Variable Characteristics
1. ESP may be related to or designed for specific disciplines.
2. ESP may use, in specific teaching situations, a different methodology from that of General English.
3. ESP is likely to be designed for adult learners, either at a tertiary level institution or in a professional work situation. It could, however, be for learners at secondary school level.
4. ESP is generally designed for intermediate or advanced students.
5. Most ESP courses assume some basic knowledge of the language systems.
After reviewing some definitions and characteristics of ESP above, it is
clear that ESP is designed to provide the approach of English learning with
materials that related to the learners‟ need and interests. Therefore, knowing learners‟ need in learning English is very important. The activity to identify
learners‟ need called need analysis. It was discussed in the next point of this
thesis.
b. The Need Analysis
What makes ESP different from English for general purpose is the
need to conduct need analysis. Need analysis can be simply defined as the
activity to identify the learners need to learn in the learning process.
Richards and Schmidt (2002:353) defines needs analysis as the
process of deciding the needs of learners who learn language and arranging
the needs based on priorities. Furthermore, needs analysis is needed to find
out:
a.the situations when a language will be used
b.the aims and goals for which the language is needed
c.the types of communication which will be used
d.the level of proficiency needed
According to Richards (2006: 12) needs analysis is an activity to
decide the specific characteristics that will be used in specific purposes rather
than general purpose. Furthermore, needs analysis can be conducted through
surveys, observation, interviews, and situation analysis in the target setting.
The result of the need analysis can be used to consider the vocabulary,
grammar, texts, functions, and other skills for developing the materials.
Hutchinson and Waters (1987 : 54) states two types of needs: target need
and learning need. Target need is viewed as what the learners needs to do in
the target situation. What included in target needs are necessities, lacks, and
wants. Necessity is what the learner must know so they can be functioned
effectively in target situation. Then, there is lack which can be defined as the
last aspect that includedin target needs is wants. Want is what learner asks to
learn.
The second type of needs is learning needs. Hutchinson and Waters (1987:
60) define learning needs as what knowledge and skill will the learners need to
be able to perform nicely in the target situation.
3. Task-Based Language Teaching
a. The Nature of Task-Based Language Teaching
Teachers and learners need textbook or coursebook to support them in the
learning process. The textbook or coursebook provide materials, task,
activities, and practice for the learners. The tasks in the textbook or coursebook
is based on the theory of Task-Based Language Teaching.
Willis and Willis (2007:1) states that those who agree with Task Based
Language Teaching argue that the most effective way to teach a language is by
involving learners in authentic use of language in the classroom. That activity
can be done by designing tasks that can give opportunity to learners in using
the real language use such as discussions, problems solving, games, and so on
which the learners need to use the language for themselves.
Besides, Nunan (2004:12) states that the basic concept for task-based
language teaching is experiential learning. This approach is to use the learner‟s personal experience directly as the starting point of the learning experience.
that suitable to get the natural process that is „learning by doing‟. Furthermore, Willis (1996:40) states:
“task-based learning is not just about getting learners to do one task then another tasks and then another. If that were the case, learners would probably become quite expertat doing tasks and resourceful with their language, but they would almost certainly gain fluency at the expense of
accuracy.”
By using these kinds of tasks, learners are expected to improve
their English proficiency through the exposures which are provided by the
tasks. Moreover, learners can finish the task through group activity that can
give them chance to learn from their peer. Therefore, the existence of tasks is
very important in the teaching-learning process.
b. Principles of Task-based Language Teaching
In applying task-based language teaching during the learning
process, knowledge about how to apply this approach in the learning process is
necessarry. One of the knowledge that should be known by teachers is the
principle. By understanding the principles of task-based language teaching, the
learning process is expected to be effective.
One of the theory about the principles of task-based language teaching is
proposed by Nunan (2004:1) who state that there are some principles in the
application of task-based language teaching:
a. To select the content, a needs-based approach is needed.
b. An emphasis on learning to communicate by interacting using the target
language.
d. Providing chances for learners to focus not only on language but also on
the learning process itself.
e. An enhancement of the learner‟s own personal experiences as important aspects to classroom learning.
f. There is relation of classroom language learning and language use outside
the classroom.
Thus, this approach is emphasizing the practices not the product. The
product of the English language ability can be achieved through drilling and
practices. By this approach, students are expected to be able to use English in
for their job in the future.
4. English Learning Materials
a. Definition of Materials
The aspect that cannot be separated from teaching is the
availability of materials. Materials can be from many sources, such as
textbooks, pictures, videos, audios, and so on. Richards and Schmidt
(2002:322) defines materials as anything that can be used by teachers or
learners to make the learning process of a language easier. Materials may be
linguistic, visual, auditory, or kinesthetic, and they may be presented in print,
audio or video form, on the Internet or in live performance or presentation.
In line with the definition above, Tomlinson (1998: 2) states that materials
can be anything which is used to increase the learners‟ knowledge of the
dictionaries, grammar books, readers, workbooks, photocopied exercises,
newspapers, food packages, photographs, live talks by invited native speakers,
instruction given by a teacher, tasks written on cards or discussions between
learners.
In addition, Richards (2001: 251) defines instructional materials as the
language input for learners and the language practice used in the classroom.
The materials may take the form of (a) printed materials such as books,
workbooks, worksheets or readers; (b) non print materials such as cassette or
audio materials, videos, or computer-based materials; and (c) materials that
comprise both print and non print sources such as self-access materials and
materials on the internet.
After reviewing the definitions of materials above, we can conclude that
materials are anything that can help teachers and students in the learning
process. Materials can be in the form of printed materials (e.g. textbook,
newspaper, magazine), non-printed materials (e.g. audios, videos, recordings),
or the collaboration of printed and non-printed materials (e.g. self-access
materials and materials on the internet).
b. Criteria of Good Materials
In order to support learning process better, good materials is needed to be
provided. Hutchinson and Waters (1987:107) state some criteria of good
materials that are contain:
a. interesting texts
c. opportunities for learners to use their existing knowledge and skills d. content which both learners and teachers can cope with
Furthermore, Hutchinson and Waters (1987:107) also propose some
principles in writing the materials:
1) Materials should support the learners to learn.
2) Materials help arranging the teaching learning process.
3) Materials put a view of the nature of language and learning.
4) Materials reflect the nature of the learning task.
5) Materials can help teacher in developing the teacher method, by
introducing teacher to new techniques.
6) Materials provide the example of correct and appropriate language use.
Therefore, good materials should provide the real-world communication
on it so the students can use the knowledge from the materials in their work or
in the field they are in so it suitable to their needs.
5. Material Development
a. Definition of Material Development
Tomlinson (1998: 2) defines materials development as anything
which is done by writers, teachers or learners to provide language input and
to use those sources to maximize the available information to conduct
language learning. Instructional development provides a process and
framework for planning, developing, and adapting instruction based on the
development means creating, choosing or adapting, and organizing materials
and activities to help the students reach the learning goals.
Thus, materials development refers to the effort of making or
developing the materials in the form of writing or creating, adapting, and
organizing to achieve the goals of learning.
b. The Model of Material Development
Nunan (2004: 41) presents the simple model of an effective task in
a diagram below:
As presented in the diagram above, there are six components of
task. They are goals, input, procedures, teacher role, learner role and
setting.
1) Goals
Goals are general purposes of learning activities. Nunan (2004: 44)
states that the most useful goal is those that related to the students and
those that can be expressed through performance. One of the examples of
the effective goal related to this research is to improve the students‟
2) Input
Input refers to the spoken, written and visual data that learners use
in completing a task. The input can be provided by a teacher, a textbook or
some other sources. In addition, Hutchinson and Waters (1987: 108) notes
that input can be in the form of a text, dialogue, video recording, diagram,
and any piece of communication data based on the results of needs
analysis. Further, input provides:
a) Stimulus materials for activities b) New language items
c) Correct models of language use d) A topic for communication
e) Opportunities for learners to use their information processing skill f) Opportunities for learners to use their existing knowledge both of the
language and subject matters. 3) Activities
Activities or procedures are described by Nunan (2004: 52) as what
learners will actually do with the input that forms the starting point for the
tasks. Nunan (2004: 57) also mentions task types into three activities:
a) Information gap activity
b) Reasoning gap activity
c) Opinion gap activity
4) Teacher and Learner role
Nunan (2004: 64) defines role of learners and teachers are in
learning task and in the social and interpersonal relationship between the
participants, Breen and Candlin as stated in Nunan (2004: 67) propose
facilitator of the communicative process, as a participant and as an
observer and learner.
Meanwhile, learners‟ role depends on the approach used in
teaching and learning process in the classroom. For example, in
communicative approach the learners have to be active, negotiating roles
and should contribute as well as a receiver.
5) Setting
Nunan (2004: 70) propose that setting refers to the classroom
arrangements in completing the tasks and it also needs consideration of
whether the task is to be carried out entirely or partly, inside or outside the
classroom.
6. Unit Design Development
a. Component of a Unit
In developing a unit, the components that are developed by the researcher
are (1) title which is related to the students‟ need according to their study program; (2) objective which tells the students what language function, and
what texts they will learn in that unit; (3) sequence of tasks which consists of
introduction, main lesson, and reinforcement. The introduction part is to show
them the preview of what they will learn in that unit and build the schema
building of the materials. It also used to prepare students or as the warm up
activity. The second part is the main lesson. There are the tasks that has been
made to improve the four skills mentioned that will help them in their job in
the future. The tasks there was designed from guided production tasks and
gradually to free-guided production task. The last part is the reinforcement. It
consists of enrichment, evaluation, reflection, summary, and vocabulary list.
Enrichment is aimed to give students opportunity to have more practice in
order to fully understand the materials. While evaluation is to test themselves
about their understanding of the materials. Then, the purpose of reflection is to
give them the chance to recognize their own success or lack after learning the
materials. Next, the summary is to summarize the materials presented in the
unit. Finally, the vocabulary list is to show the meaning and the kind of some
words that might be unfamiliar to students used in the unit.
b. Developing Unit of Work
Nunan (2004: 31-33) proposes six-step pedagogical sequence for
introducing tasks.
1. Schema building
Schema-building tasks are created to introduce initial vocabulary, language
and context for the task.
2. Controlled practice
Controlled practice is given to the learners in the form of target language,
vocabulary, structures and functions.
3. Authentic listening practice
4. Focus on linguistic elements
The step is focusing on linguistic elements, e.g. grammar and vocabulary
after the students have seen, heard and spoken the target language within a
communicative context.
5. Provide freer practice
In this step, the students are encouraged to use whatever language that they
have learned to complete the task.
6. Introduce the pedagogical task
This step includes the group work discussion and decision making task in
order to complete the task.
c. Task grading, Sequencing, and Integrating
According to Nunan (2004: 13) the decision of what come first in a unit
depends on the belief of the materials developer or syllabus designer about
grading, sequencing and integrating content. Grading, according to Richard,
Platt and Weber (1986) in Nunan (2004), is the arrangement of the content of
materials so that it is presented in a helpful way. In line with Richard, Platt,
and Weber, Nunan (2004) states that grading and sequencing tasks are
decisions on what to teach first, what second, and what last of the materials.
Tasks must be graded and sequenced from the easy one to the difficult
one. In reading and listening skills, input becomes an important part that must
be sequenced. Tasks must also be sequenced from the less demanding to the
production activities and exercises, and finally to ones requiring authentic
communicative interaction (Nunan, 2004).
7. Task Development
a. Definition of Task
The task, as what Nunan (2004: 4) called as a pedagogical task is a
piece of classroom work that helps learners in comprehending,
manipulating, producing or interacting in the target language while they
are focusing on drilling their grammatical knowledge to express meaning,
and in which the purpose is to convey meaning.
In addition, Richards and Schmidt (2002:539-540) defines task as
an activity which is designed to help achieve a particular learning goal.
These include goals, procedures, order, pacing, product, learning strategy,
assessment, participation, resource, and language.
b. Task Continuity
The terms „continuity„ refers to the interdependence of tasks, task components and supporting enabling skills within an instructional sequence.
When planning instructional sequence, Nunan (2004: 125) proposes the same
steps to make activities gradually increase from demanding, moving from
comprehension-based procedures to controlled production activities and
8. Materials Evaluation
After designing the materials, the materials need to be evaluated to find
out the effectiveness for learning. Tomlinson (1998: 3) defines materials
evaluation consists of efforts to predict whether the students will be able to use the
materials without many difficulties and will enjoy doing activities or not. In
addition, Hutchinson and Waters (1987: 96) note that evaluation is a matter of
judging the appropriateness of something for a specific purpose.
In Indonesian context, the material evaluation is conducted by referring to
Badan Standar Nasional Pendidikan (BSNP). There are four aspects of evaluation as listed below:
1. The appropriateness of content.
2. The appropriateness of presentation.
3. The appropriateness of language.
4. The appropriateness of graphic.
B. Relevant Studies
Some researchers have conducted similar research. Rahayu (2014)
conducted research on developing English learning materials for grade XI
students of Fishery study program. She designed three units for three basic
competences. Murtafi‟ah (2014) conducted research on developing English learning materials for grade X students of Nautical Fishing Vessel study program
at SMKN 2 Cilacap. She also designed three units for three basic competences.
materials for the tenth grade students of boga department at SMK N 4 Yogyakarta. She also designed three units for three basic competences.
The researches mentioned above were done successfully. All the units
which they developed meet the students‟ need in English learning process. It means that the research on materials development for vocational schools is needed
to facilitate students with sufficient and appropriate inputs and tasks based on
their target situation.
C. Conceptual Framework
Students of vocational high school are expected to have skills according to
their field including the communication skill. They are expected to not only able
to communicate in their first language, but also English as the international
language. Nowadays, English language ability is very important to be possessed
since in this globalization era people are able to go to places around the world
easily. Since English is a „lingua franca‟ or language as the bridge of
communication for people around the world, this language uses for many sectors
of life especially that involved people with different languages.
In nursing department, students are expected to be able to look after
patients. The patients are sometimes foreigners. Then, to be able to look after
those kinds of patients, students must able to communicate in English. Therefore,
English knowledge from school were expected to give sufficient skills for
students. Unfortunately, English skills that were being taught in school were not
textbook that actually designed for Senior High School, it was not specially
designed for vocational high school. However, the students of nursing department
need the kind of English lesson that related to their needs and interests in nursing
field.
Related to this problem, the researcher developed English learning
materials for nursing department since that was urgent to be conducted regarding
the unavailability of English materials for nursing department. The English
materials established the students need. This research was expected to provide
English learning materials that could help students to use English for their future
work. Therefore, the researcher focused on developing learning materials for the
second semester of the tenth graders of nursing department in SMK Kesehatan
Rahani Husada in the form of learning materials based on the School-Based
Curriculum.
The contents of the materials followed the Task-Based Language
Teaching. The materials in this research were arranged according to the nursing
term by providing appropriate tasks and vocabulary related to nursing field. The
process of material development used the model proposed by Jolly and Bolitho as
cited in Tomlinson (1998: 98) with some changes to match the steps of
26
research; population and sample of the research; setting of the research; data
collection technique and instrument; data analysis technique; and procedure of the
research.
A. Type of the research
This research is categorized as Research and Development (R & D). As
stated by Borg and Gall (2003: 569) that the findings of the R & D research are
used to design new products and procedures or develop the product that already
made. It is systematically field-tested,evaluated, and refined until they are in the
best condition or ready to be published. However, this research were only until the
expert judgment step, not to be tried out and published.
B. Setting and the Subjects of the Research
The research was conducted in SMK Kesehatan Rahani Husada which
located in Pilangsari, Gondang, Kebonarum, Klaten, Central Java. The reason why
this school was chosen as the setting of the research was because it had nursing
department which had not have the appropriate English materials yet.
The subjects of the research were class KPR XB students of nursing
C. Research Procedure
This research used the research procedure proposed by Jolly and Bolitho in
Tomlinson (1998).
Since the model above was only focused on the material design, so there
were some additions in the procedure according to the research needs. As a result,
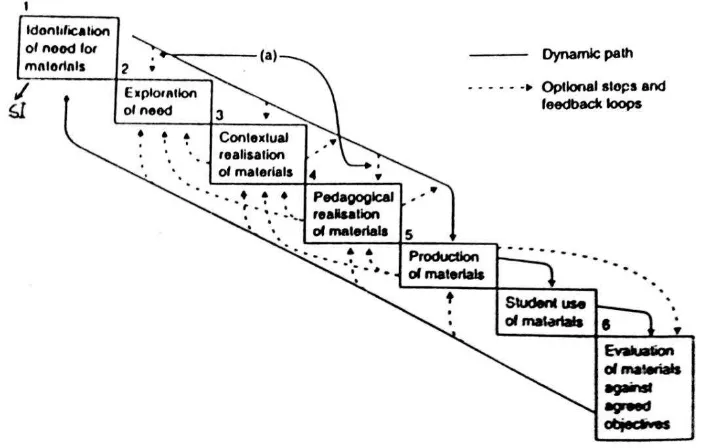
[image:42.595.133.487.200.424.2]the procedure of the research was as follow:
Figure 3.1: Research procedure by Jolly and Bolitho’s material development model in Tomlinson (1998: 98) with some additions to the research needs
Conducting needs analysis
Developing the course grid
Designing materials (first draft)
Expert Judgment
1. Conducting needs analysis
This step was conducted to get information about the learners:
target need and learning need. This step was done by giving questionnaires
to the students of nursing department.
2. Developing the course grid
The course grid was developed based on the School-Based
Curriculum with the content related to nursing field.
3. Designing the materials
After making the course grid, the process was continued to design
the materials. This process was also called as first draft.
4. Expert Judgment
The first draft then was consulted to the expert. The expert can be
lecturer of English education department who can judge the materials and
have experience in material development.
5. Writing the final draft
After getting judgment from the experts, the materials were revised
based on the suggestions given by the expert. This was also called as final
draft.
D. Data Collection
1. Data collection Techniques
In the research, there were two questionnaires used. The first
the needs analysis. This questionnaire was in the form of multiple choices.
The second questionnaire was created for the experts, in this research it
was a lecturer of English Education study program who are able to
evaluate the learning materials to do the evaluation step of the materials.
The questionnaire was in the form of a check box. The experts were
required to give a check to the column that represented their opinion. The
scale of the check box was explained in the data analysis technique.
2. Data collection instruments
In this research, there were two questionnaire used. The first
questionnaire was addressed to the students to conduct the need analysis.
In the first questionnaire that is for the students of nursing department, the
subject that was asked several questions related to their learning needs by
answering multiple choice questions. This questionnaire was given to
collect learners‟ needs. The organization of the first questionnaire is
presented on the table below.
Table 3.1: The Organization of the Questionnaire
No. Aspects Item
Number
The Purpose of the
Questionnaire References
1. Students‟ identity Part A To find some information about
Part B 2.
T
ar
ge
t
Ne
e
d
s
Learners‟ goals 1 To find out the
learners‟goal inlearning English Brown (2001: 142) Nunan (2004: 174)
3. Necessities 2 To find out the
learners‟ needs in
terms of target situation
Hutchinson and Waters (1987: 55)
Lacks 3, 4 To find out the gap
between students‟
current
proficiencyand the target proficiency
Hutchinson and Waters (1987: 55-56)
Wants 5, 6 To find out what the
learners want in order to be included in thematerials Hutchinson and Waters (1987: 56) 4.
L
e
ar
n
in
g
Ne
e
d
s
Input 7, 8, 9,
10,11, 12, 13, 14
To find out the input, the topic, and the length of the text which is ideal for them
Nunan
(2004: 47-52)
Procedure 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21
To find out the activities that the students like the most
Nunan (2004: 52)
Setting 22, 23 To find out some information about the setting of learning that the learners preferred
Nunan (2004: 70 – 73 ) Hutcinson and Waters
(1987: 60 – 63)
Students‟
role
24 To find out learners„
preferred role in classroom
Nunan
Teacher‟s
role
25 To find out the teacher role in classroom that the learner‟s preferred
Nunan (2004: 64-69)
Then, the second questionnaire was made for the materials
evaluator. In the second questionnaire that was for the experts, the
questionnaire was aimed to get opinion regarding the materials designed.
The questions are divided into four parts; those are the appropriateness of
content, the appropriateness of language, the appropriateness of
presentation, and the appropriateness of graphic.
E. Data Analysis Technique
The data from the needs analysis and the expert judgment questionnaire
was analyzed quantitatively by using descriptive statistics. The data from the first
questionnaire was analyzed using the formula proposed by Suharto (2005) as
follow:
Interpretation:
P = Percentage f = frequency N = Total respondents 100 = fixed number
Then, the data from the second questionnaire was analyzed using Likert
scale. In the Likert scale, there are four-points scale that can be described as
follows:
1 = strongly disagree (SD)
2 = disagree (D)
3 = agree (A)
4 = strongly agree (SA)
The data from the second questionnaire then was measured by using mean
(central tendency) and analyzed by using a formula proposed by Suharto (2006)
that is:
R : range
Xh : the highest scale Xl : the lowest scale 4 : range of Likert-scale
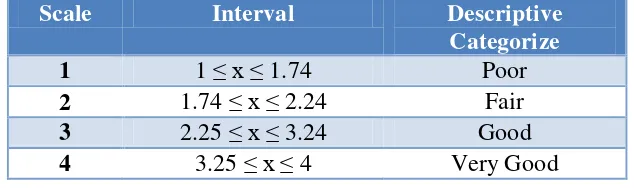
Then, the result of the calculation was converted into descriptive analysis.
To convert the data, data conversion table proposed by Suharto (2005) was used
[image:47.595.134.451.531.625.2]as the mean of the data had been calculated.
Table 3.2: Data conversion table
Scale Interval Descriptive
Categorize 1 1 ≤ x ≤ 1.74 Poor
2 1.74 ≤ x ≤ 2.24 Fair
3 2.25 ≤ x ≤ 3.24 Good
4 3.25 ≤ x ≤ 4 Very Good
x is mean obtained from expert judgment. To find x, the following formula
34
draft of the materials, the results of material evaluation by the expert, and the final
draft of the materials.
A. Research Findings
1. The Results of the Need Analysis
The need analysis process was conducted on March 30th, 2016 by
distributing questionnaire to grade X students of nursing department at SMK
Kesehatan Rahani Husada, Klaten. There are 25 questions in the
questionnaire. The questions in the questionnaires were divided into two
parts. There are questions about target needs in the first part, while the
second part were the questions about learning need questions. The total
respondents were 35 students from class KPR XB. The results of the need
analysis were used to guide the researcher in writing the course grid so the
materials were able to fullfil students of nursing department‟s learning preferance.
a. Target Needs
According to Hutchinson and Waters (1987 : 54), target needs vieved as
a) Necessities
One of the points in target need is students‟ goal. It can be described
as the students‟ reasons of learning English at school and the usage of their
knowledge of English for their future. The table below was the result of
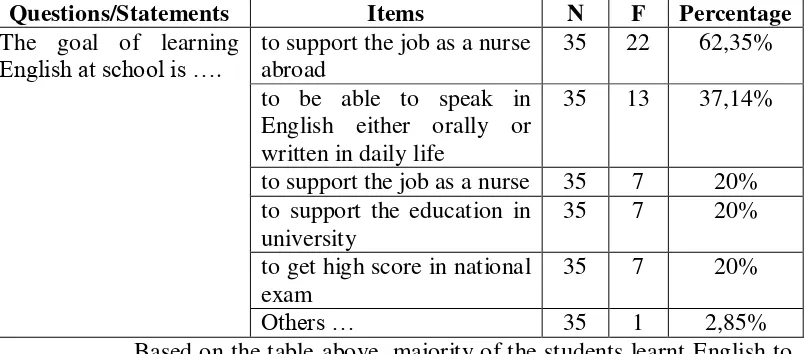
[image:49.595.114.516.280.457.2]students‟ goal in learning English.
Table 4.1: Students’ Goal in Learning English
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
The goal of learning
English at school is ….
to support the job as a nurse abroad
35 22 62,35%
to be able to speak in English either orally or written in daily life
35 13 37,14%
to support the job as a nurse 35 7 20% to support the education in
university
35 7 20%
to get high score in national exam
35 7 20%
Others … 35 1 2,85%
Based on the table above, majority of the students learnt English to
support them as a nurse with the percentage of 62,35% since the school has
signed the MOU (Master of Understanding) with a university of nursing in
China so the students want to continue the study there.
Therefore, according to the result above, the materials was
developed to make them able to speak English in daily life also to support
them for their future career as nurse, either in Indonesia or abroad. The
materials was developed based on the school-based curriculum or
curriculum of 2006 that also be used by most high school with nursing
By learning English, the students also had view on what are the
benefits of English for their future as nurse abroad that were more specific.
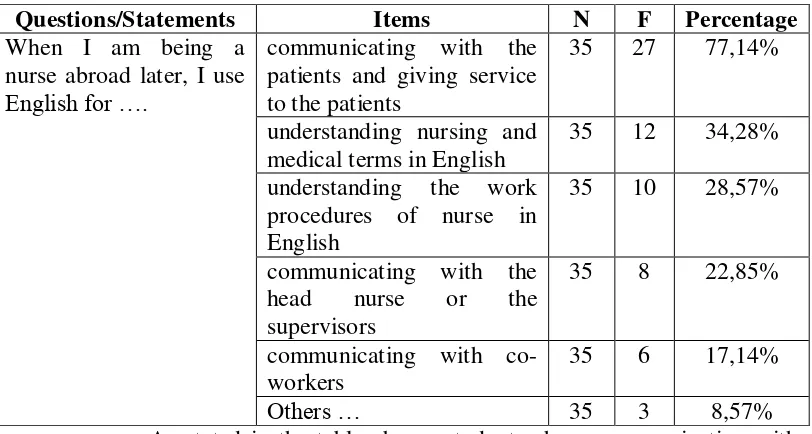
[image:50.595.111.517.222.439.2]The result was presented below.
Table 4.2: Students’ View of Need in Target Situation
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
When I am being a nurse abroad later, I use
English for ….
communicating with the patients and giving service to the patients
35 27 77,14%
understanding nursing and medical terms in English
35 12 34,28%
understanding the work procedures of nurse in English
35 10 28,57%
communicating with the head nurse or the supervisors
35 8 22,85%
communicating with co-workers
35 6 17,14%
Others … 35 3 8,57%
As stated in the table above, students chose communicating with
the patients and giving service to the patients as their main specific goal to
learn English with the percentage of 77,14%. It was because as nurse they
are always must to have direct communication with the patients. Then, the
next item was understanding nursing and medical terms in English the
percentage of 34,28% because as nurse they do not only service the
patients, but also having knowledge of nursing and undersanding medical
terms which are mostly in English.
b) Lacks
Hutchinson and Waters (1987 : 56) defined lacks as the gap
between current proficiency and the target proficiency. Students‟ lack of
Table 4.3: Students’ Current Proficiency
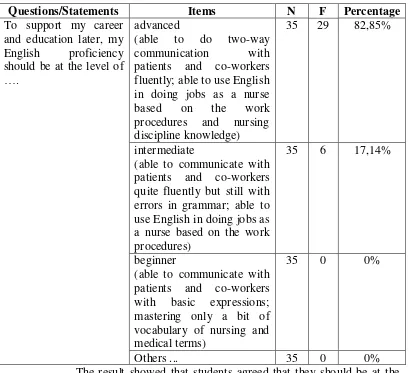
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
My current English proficiency is at the
level of ….
beginner
(able to communicate with patients and co-workers with basic expressions; mastering only a bit of vocabulary of nursing and medical terms)
35 30 85,71%
intermediate
(able to communicate with patients and co-workers quite fluently but still with errors in grammar; able to use English in doing jobs as a nurse based on the work procedures)
35 4 11,42%
advanced
(able to do two-way communication with patients and co-workers fluently; able to use English in doing jobs as a nurse based on the work procedures and nursing discipline knowledge)
35 0 0%
Others ... 35 1 2,85%
Most students, around 85,71% of the respondents thought that their
current English proficiency was in the beginner level. They were mostly
able to communicate in English with basic expression and mastering only a
bit of vocabulary of nursing and medical terms. Those who were in
beginner level need to be provided by drilling and practices. Some of them,
that was 11,42% claimed that their English proficiency was in the
intermediate level while no one was claimed that they were in the advenced
proficiency should be understood as well. The table below showed the level
[image:52.595.110.520.193.566.2]of prociency they should be at to support their future career and education.
Table 4.4: Students’ View about Target Proficiency
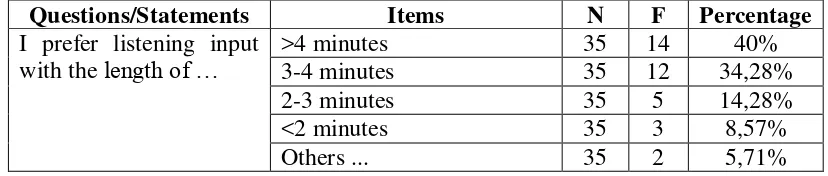
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
To support my career and education later, my English proficiency should be at the level of
….
advanced
(able to do two-way communication with patients and co-workers fluently; able to use English in doing jobs as a nurse based on the work procedures and nursing discipline knowledge)
35 29 82,85%
intermediate
(able to communicate with patients and co-workers quite fluently but still with errors in grammar; able to use English in doing jobs as a nurse based on the work procedures)
35 6 17,14%
beginner
(able to communicate with patients and co-workers with basic expressions; mastering only a bit of vocabulary of nursing and medical terms)
35 0 0%
Others ... 35 0 0%
The result showed that students agreed that they should be at the
advanced level of English proficiency. They agreed that in the future they
should be able to do two-way communication with patients and co-workers
fluently; able to use English in doing jobs as a nurse based on the work
procedures and nursing discipline knowledge. There were also 17,14% of
From the result above, it can be concluded that the average of
students‟ proficiency of English was in the beginner level while they were
acknowledged that they should at least in the intermediate level and the
target of English proficiency was in the advanced level. Therefore, they
have not acvhieved that target yet. As a result, they need to learn English
more so that when they graduated from senior high school and continue
their education or start their career, they can be in their target of English
proficiency.
c) Wants
In their book, Hutchinson and Waters (1987 : 54) defined wants as
what the learners ask to learn. In this aspect, they chose what they want to
learn that will be useful for them later on. Here was the result of the need
analysis in the term of their wants:
Table 4.5: Students’ Wants of Language Skill in Learning English
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
Language skill that I will usually use as a
nurse is / are ….
speaking 35 33 94,28%
listening 35 15 42,85%
writing 35 10 28,57%
reading 35 6 17,14%
Others ... 35 0 0%
Regarding the language skill that they will usually use as nurse,
almost all students chose speaking followed by listening with the
percentage of 42,85%. It was because as stated in the learning goals, they
want to be able to communicate in English, therefore speaking and listening
Besides the skill, language knowledge is also important to be
learnt. The table below presents the result of need analysis especially about
the language knowledge that the students claimed will usually be used
when they become nurse.
Table 4.6: Students’ Wants of Language Knowledge in Learning English
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
Language knowledge that I will usually use as
a nurse is / are ….
pronunciation 35 28 80%
grammar 35 19 54,28%
vocabulary 35 10 28,57%
Others ... 35 0 0%
In connection with the language skill that students want to learn
most, the language knowledge that they mostly preferred was pronunciation
that had been chosen by 80% of the students since it was essentials for
supporting speaking.
b. Learning Needs
Hutchinson and Waters (1987: 60) define learning needs as what
knowledge and abilities will the learners require in order to be able to perform to
the required degree of competence in the target situation.
a) Input
The first aspect of learning needs is input. Input can be used by the
learners to complete the tasks (Nunan, 2004). Input can be in the form of
written and spoken.
Table 4.7: Learning needs (Listening Input)
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
In listening activities, kind of input that I
monolog/dialog with the expressions that will be
preferred is/are … used
short monolog/dialog with pictures
34 12 34,28%
short monolog/dialog 34 8 22,85% monolog/dialog with new
vocabulary
34 4 5,71%
Others ... 34 0 0%
Monolog/dialog with the expressions that will be used was the
listening input that the students most preferred. There was also short
monolog/dialog with pictures that had been chosen by 34,28% of the
students. Related to the input, the length of the listening input that the
[image:55.595.110.518.112.218.2]students preferred was presented in the table below.
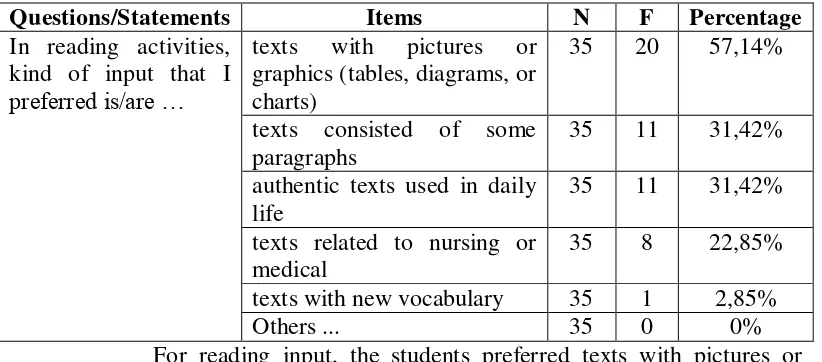
Table 4.8: The length of listening input
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
I prefer listening input with the length of …
>4 minutes 35 14 40%
3-4 minutes 35 12 34,28%
2-3 minutes 35 5 14,28%
<2 minutes 35 3 8,57%
Others ... 35 2 5,71%
Students mostly chose listening input with the length of more than
four minutes (40%). Then, 34,28% of the students prefer 3-4 minutes input
[image:55.595.104.518.379.467.2]for listening.
Table 4.9: Learning needs (Speaking Input)
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
In speaking activities, kind of input that I
preferred is/are …
authentic texts used in daily life
35 25 71,42%
simple monologue or dialogue
35 7 20%
monologue or dialogue with expressions
35 6 17,14%
monologue or dialogue with picture
35 3 8,57%
monologue or dialogue with new vocabulary
35 2 5,71%
The table above showed that more than half of the students, that
was 71,42% chose authentic texts used in daily life for the speaking input
since authentic texts are very practical. Then, 20% of the students claimed
that they want the speaking input in the form of simple monologue or
[image:56.595.109.520.278.459.2]dialogue.
Table 4.10: Learning needs (Reading Input)
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
In reading activities, kind of input that I
preferred is/are …
texts with pictures or graphics (tables, diagrams, or charts)
35 20 57,14%
texts consisted of some paragraphs
35 11 31,42%
authentic texts used in daily life
35 11 31,42%
texts related to nursing or medical
35 8 22,85%
texts with new vocabulary 35 1 2,85%
Others ... 35 0 0%
For reading input, the students preferred texts with pictures or
graphics (tables, diagrams, or charts). While 31,42% students chose texts
consisted of some paragraphs.
Table 4.11: The length of reading input
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
I prefer reading input
with the length of … 200-250 words 150-200 words 34 34 16 8 45,71% 22,85%
>300 words 34 7 20%
250-300 words 34 1 2,85%
Others ... 34 1 2,85%
The number of words for reading input the students chose mostly is
200-250 words with the percentage of 45,71%. Another option that got high
[image:56.595.114.519.559.648.2]Table 4.12: Learning needs (Writing Input)
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
In reading activities, kind of input that I
preferred is/are …
explanation of grammar and sentence structure that will be used to write texts
35 15 42,85%
examples of texts that will be written
35 11 31,42%
vocabulary related to nursing or medical that will be used to write texts
35 9 25,71%
texts with pictures or graphics (tables, diagrams, or charts)
35 7 20%
Others ... 35 0 0%
The table above showed the writing input that the students mostly
chose was explanation of grammar and sentence structure that will be used
to write texts with the percentage of 42,85%.
Table 4.13: The length of writing input
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
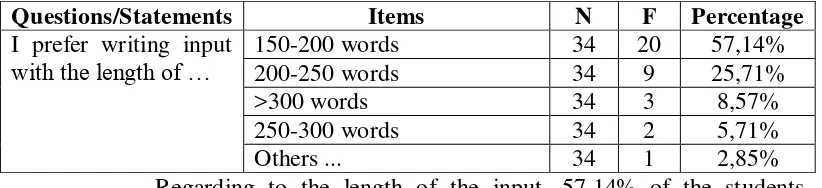
I prefer writing input
with the length of … 150-200 words 200-250 words 34 34 20 9 57,14% 25,71%
>300 words 34 3 8,57%
250-300 words 34 2 5,71%
Others ... 34 1 2,85%
Regarding to the length of the input, 57,14% of the students
preferred short passage with 150-200 words. There were also 25,71%
students chose 200-250 words. Therefore, the input in the learning materials
was developed with not so long passage for writing.
Not only the input and the length, the theme or topic is also
important to be considered so it can be suitable with the students‟ preferable.
Table 4.14: Students’ view about topics they want to learn in learning
English
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
Themes or topics that I preferred to be included in English learning materials
is/are ….
topics related to future career or nursing
35 21 60%
topics related to daily life in family, school, and society
35 18 51,42%
topics related to science (such as about plants, planets, new invention)
35 8 22,85%
topics related to teenager life 35 5 14,28% topics related to politics,
economics, and social cultures
35 4 11,42%
Others ... 35 0 0%
According to the table above, 60% of the students preferred the
theme or topics to be included in the textbook was the topics related to
future career or nursing so it could support their goal.
b) Procedure
Procedures can be defined as what the learners will actually do or
the activities that the learners will experience in carrying out the tasks.
Table 4.15: Learning needs (listening activities)
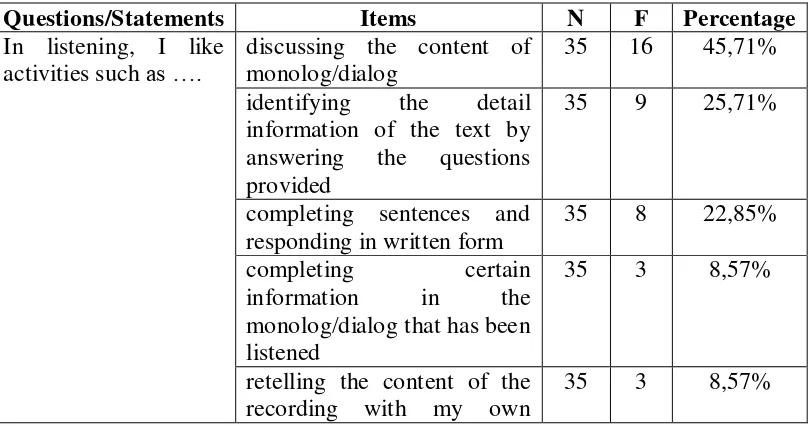
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
In listening, I like activities such as ….
discussing the content of monolog/dialog
35 16 45,71%
identifying the detail information of the text by answering the questions provided
35 9 25,71%
completing sentences and responding in written form
35 8 22,85%
completing certain information in the monolog/dialog that has been listened
35 3 8,57%
retelling the content of the recording with my own
[image:58.595.112.517.544.757.2]words
Others ... 35 2 5,71%
The table above showed that students mostly liked activities for
listening such as discussing the content of monolog/dialog (45,71%) and
identifying the detail information of the text by answering the questions
[image:59.595.110.520.279.461.2]provided (25,71%).
Table 4.16: Learning needs (speaking activities)
Questions/Statements Items N F Percentage
In speaking, I like activities such as ….
practicing model of dialog or monolog provided in the textbook
35 12 34,28%
making a dialogue then practicing it
35 10 28,57%
rol