i
THE EFFECT OF LECTURER’S ELICITING TECHNIQUE
TOWARD STUDENTS’ ACTIVENESS IN SPEAKING
CLASS ACTIVITY OF SECOND SEMESTERAT ISLAMIC
STATE UNIVERSITY SUNAN AMPEL SURABAYA
A THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for the degree of
SarjanaPendidikan (S.Pd) in Teaching English
By
NOR ROHMAN
NIM:D05211040
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHER TRAINING
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITYSUNAN AMPEL
SURABAYA
2016
ii
iii
iv
v
vi
DEDICATION SHEET
This Thesis I dedicate to
My parents whom I love
H. Sholeh/Muniri and Hj. Nur/Hadirah
My Brother and Sister
Ruba’ie Sholeh, S.Pd.I, Syaifah and Shophia
And my dear fiancée
Siti Rahayu
Who have been supporting me all the times and loving me all my ways.
vii
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Alhamdulillah, I would like to express my gratitude to Allah SWT, who had given me mercies and blessing to accomplish this thesis. In addition, I would like to express my gratitude to those who have contributions toward the accomplishment of this thesis:
1. Prof. Dr. H. Abd. A’la, M.Ag as the Rector of Sunan Ampel State Islamic University Surabaya
2. Prof. Dr. H. Ali Mudlofir, M.Ag as the Dean of Faculty of Education and Lecturer Training. 3. Rizka Safriyani, M.Pd as the Head of English Lecturer Education Department.
4. Rakhmawati, M.Pdas my thesis advisor. This special thank is to appreciate your patience, kindness, and wisdom in guiding me to do my best in completing my thesis.
5. Rizka Safriyani, M.Pd, M.A as the proposal examiner of my study. I am so grateful for your kindness sparing your time to give me information and suggestion toward my proposal. 6. Ana Nurul Laila, M.TESOL as validator of instruments used in this study. I am so grateful
for your kindness in giving me information and suggestion toward my instruments.
7. Sigit Pramono Jati, M.Pd., as the lecturer in Every day Communication Class who allowed me to take the data and patiently guided me doing academic procedures during my study. 8. All of my lecturers of English Lecturer Education Department.
9. My friends of PBI (Alfan Hariri, S.Pd, Zakaria Aditya Warman S.Pd and Bustanul Arifin S.Pd as Madura Avenger). Thank you for your time to help share with me everything related academic, especially thesis.
Those people’s kindness of encouraging the writer absolutely means as the great motivation for accomplishing this thesis. Ultimately, the writer hopes that may Allah SWT always give mercies and blessing to all of kind people mentioned above.
viii
Surabaya, July 31th, 2016 The writer
NOR ROHMAN NIM: D05211040
ABSTRACT
Rohman, Nur, (2016). The Effect of Lecturer’s Eliciting Technique toward Students’ Activeness in Speaking Class Activity of Second Class at Islamic State University Sunan Ampel
Surabaya. A thesis. English Teacher Education Department Faculty of Tarbiyah and
Teacher Training, SunanAmpel State Islamic University, Surabaya. Advisor: Rakhmawati, M.Pd
Key Words: Eliciting Techniques, Students’ activeness and Speaking Class.
This research was done in second semester of English Department. In the semester, the speaking class named Everyday Communication. The goal of this class is to improve their speaking ability, especially for daily communication. Therefore, the lecturer should be able to facilitate and expand students’ opportunity to practice speaking because this is the very beginning step to build up the students’ confidence before stepping to the next speaking class called Speaking for Group activities. For this reason, this thesis analyzes the lecturer’s eliciting technique in Everyday Communication class, UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya. In this research, the research was done to know eliciting techniques that used by the lecturer and the effect of eliciting technique used by the lecturer for the students in Everyday Communication class. This research used qualitative method because the researcher started from the theory of the Eliciting technique to encourage the students. Furthermore, data was collected through the transcription of the class and interview from the lecturer and the students.The eliciting techniques that the lecturer used are; Polar Closed Question, Closed Question, Open Question, and Socratic Question, while the effects of eliciting techniques used by the lecturer in “Everyday Communication Class” are in the form of thier responses and actively responded by the students. However, responses of the students were in the form of short answer. As matter of fact, Polar closed question led students to answer in form of “yes/no” response. In addition, for closed question, the students’ responses are based on the factual information that they knew. Furthermore, in open question, here the students have more opportunity to participate and Socratic question is one to lead students to realize or discover something. Moreover, in the eliciting techniques that students exactly have more opportunity was not maximizing by the lecturer.As example, the lecturer just used once Socratic question and none of catalytic question. For this reason, the lecturer must be able to create suitable question with the student’s level in order that, the students will easily understand the question and engage the opportunity of learning.
xiv
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE SHEET ……….….………...i
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIYAH...ii
ADVISOR APPROVAL SHEET...……….…………...iii
APPROVAL SHEET...iv
PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN PENULISAN………...v
ABSTRACT………...xiii
TABLE OF CONTENTS………...…xiv
LIST OF TABLE………..…..xvi
CHAPTER I………...1
A. Background of Study………1
B. Research Question……….6
C. Object of study………...6
D. Significant of Study………...6
E. Scope and Limitation………7
F. Definition of Key Terms………7
CHAPTER II………..9
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE………..9
A. Eliciting Techniques………11
a. Kinds of Eliciting Technique………12
1. Polar Closed Question……….12
2. Closed Question………13
3. Open Question………..13
4. Socratic Question……….14
5. Catalytic Question………15
b. Effect of Lecturer’s Eliciting Technique………..15
1. The Effect of Polar Closed Question………..…16
2. The Effect of Closed Question………17
3. The Effect of Open Question……….………..17
4. The Effect of Socratic Question……….……….17
5. The Effect Catalytic Question……….17
xv
C. Students Activeness in Speaking………20
D. Previous Study………..21
CHAPTER III………..24
A. Approach and research Design………...24
B. Research Presence………25
C. Research Location………25
D. Data and Source of Data………..26
a. Observation………....26
b. Transcription………..27
c. Interview……….27
E. Research Instrument………...28
F. Data Analysis Technique...………..28
G. Checking Validity of Findings………....30
H. Research Stage……….30
CHAPTER IV………..32
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION………32
A. Research Finding……….32
a. The Lecturer’s Eliciting Techniques Used in Everyday Communication Class.33 1. Polar Closed Question……….33
2. Closed Question………37
3. Open Question………..42
4. Catalytic Question………46
5. Socratic Question……….47
b. The Effect of Lecturer’s Eliciting Techniques Used in Everyday Communication Class…..………..49
1. The Effect of Polar Closed Question………..49
2. The Effect of Closed Question………49
3. The Effect of Open Question………..50
4. Socratic Question……….50
B. Discussion...………..53
a. The Use of Polar Closed Question and Its Effect………...53
b. The Use of Closed Question and Its Effect………..54
c. The Use of Open Question and Its Effect………56
d. The Use of Socratic Question and Its Effect………58
CHAPTER V A. Conclusion...……….61
xvi
List of Tables
Table 4.1...69
Table 4.2...74
Table 4.3...79
Table 4.4...85
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of Study
As English department, the students are not only demanded to master the grammar, writing and reading but also speaking competence. Therefore, the department provides step by step speaking class to equip the students with adequate speaking skills. In the first semester, the English department did not definitely determine the class of the speaking but Intensive Course (IC). In IC, the subject is the basic of all English competences which the purpose, is to give the general view and foundation about English.
In the second semester, there was the specification of the English skills, including speaking. In the semester, the speaking class named Everyday Communication. The goal of this class is to improve their speaking ability, especially for daily commutation. Therefore, in this class, a lecturer should be able to facilitate and expand students’ opportunity to practice speaking because this is the very beginning step to build up the students’ confidence before stepping to the next speaking class called Speaking for Group activities.
2
Those purposes of every day communication class, of course they rely on the lecturer’s capability in conducting communicative interaction with the students. For this reason, the lecturer must be able to provide opportunity for the students in speaking through effective interaction. In brief, the lecturer play vital role in improving the students’ speaking ability through the classroom interaction.
In the class, the students will be taught basic speaking aspects such as introducing students’ identity, describing students’ daily activity, social life, unforgettable moment and etc. These activities enable students to interact and describe one another. As an example, in Me and Myself activity, the lecturer provided some questions and got students to look for information about the other student’s identity then describe it in front of the class. Furthermore, through this activity the students are able to practice basic grammar that they got in the previous class. As matter of fact, the students will use simple present to ask and describe the information. In addition, students will use simple past tense to tell about the unforgettable moment.
3
conversation. In short, the Everyday Communication class, the students begin to build the foundation of their speaking. In addition, from the preliminary research, the researcher found that most of the students of the Everyday Communication class expect to gain the better understanding and practice of the language taught. For example, although the students grammatically know the correct use words arrangement but most of them still confused in implementing the grammatical order. Furthermore, the researcher assumed that the use of eliciting techniques during the teaching learning can be improved to encourage greater participation of the students. Moreover, the lecturers’ teaching styles were demanded to encourage interactive language used. By that way, the students would have many opportunities to practice the skill they are learnt.
By that purpose, the role of lecturer was very crucial to prepare and train the students to know the basic speaking before continuing to the higher one, whether how the lecturer determined the objective of the class, the lecturer designed the classroom activities or the lecturer brought the class onto the pedagogic goals.1 In addition, the lecturer’s should not only pay attention to the design classroom activities but also pay attention on the implementation through the lecturer’s’ interaction.
When there is factual information that students need to know, simply telling them is the fastest way to transfer the information. However, if this technique is used repeatedly, the class will be monotone and lecturer centered class. In addition, when the lecturer is telling about the information, it does not guarantee
1
SteveWalsh.,Investigating classroom discourse(USA and Canada: Rout ledge, 2006)
4
that the students will listen, understand and learn. For this reason, it is important to use another strategy in making the students understand the information.
One of the strategies that can be used by the lecturer is eliciting technique. Eliciting technique is how the lecturer draws a thing from students by the purpose that the students will be involved in the classroom activities. By the eliciting technique, the student will be led to greater thinking and interest to learn toward making discoveries for themselves.2
Naturally, university students have higher level than senior high school and they get different materials presence. It means that they are demanded to make their own discoveries. In this case, they need to be accustomed in participating the classroom activities. By this fact, the researcher intended to make this research in the Everyday Communication class.The researcherconsiders that the Everyday Communication class students need more training in speaking fluency and accuracy.Thus, eliciting technique, hopefully will help them to actively participate in the classroom activities. Furthermore, this research is intended to help the lecturer in knowing the appropriate eliciting technique.
In addition, the researcher chose the speaking activity because researcher would like to know the effect of the eliciting technique implemented in the speaking class activity. It means that the eliciting techniques that were used by the lecturer in the speaking class activity will hopefully help the lecturer to reach the goal of the lesson. In this case, the eliciting techniques gave the effect to students’ activeness in participating the classroom activities in which, students would be encouraged to 2
Jim Scrivener. Classroom Management Technique. (UK: Cambridge University Press.2012)
5
express their ideas more to make the students more motivated to actively participate in classroom activities. Therefore, the researcher focused on the speaking activity only.
Actually this research was ever done by some researchers such asa research that was done by Rahayu under the title,The use of elicitation technique in learning to improve students’ speaking skill.3 In this research, the researcher analyzed lecturer’s eliciting technique compared with eliciting theory. Also researcher found other research which is done by Quyen Thi Thauc Bui. With the title, The effect off attitude toward speaking English and exposure to oral communication in English on use of communication strategies by English majors in
Vietnam.4 In the same way, Huyen, investigated technique used by the teacher to elicit tenth grade students’ talk in Hanoi.5Concluding that students’ opportunities are one of the three factors in excelling the students’ ability in speaking. In Quyen’s research, the focus is on the some factors that influence toward the students’ activeness.6Also, Chu ThiHuyenMi, with the title teacher’s use of elicitation techniques to teach speaking skill to first-year students of UET, VNU focused on the
ineffective use of eliciting technique for Vietmen students.7 So in this research, the researcher would like to know about eliciting technique used by the lecturer in
3
Siti Rahayu. The use of elicitation technique in learning to improve student’s speaking skill. (Bandung Universitas padjadjaran. 2013)
4
QuyenThiThauc Bui,The effect off attitude toward speaking English and exposure to oral communication in English on use of communication strategies by English majors in Vietnam(Hanoi ThS Nguyen Minh Tuan, 2012)
5
Huyen. Investigated technique used by the lecturer to elicit tenth grade students’ talk in Hanoi.(Hanoi 2006) 6
Quyen Thi Thauc Bui, The effect off attitude toward speaking English and exposure to oral communication in English on use of communication strategies by English majors in Vietnam(Hanoi ThS Nguyen Minh Tuan, 2012)
7
Chu Thi Huyen Mi, with the title lecturer’s use of elicitation techniques to teach speaking skill to first-year students of UET, VNU(htunkTuH press, 2011)
6
speaking activity. Since the lecturer’s eliciting will decide how students opportunity learning, especially in speaking. In this case, the researcher focused on how the lecturer’s eliciting technique used and how it affects the students’ activeness.
B. Research Question
Based on the background of the study above, there are two problemsthat accured:
1. What are eliciting techniques that used by the lecturer in “Everyday Communication” class?
2. What is the effect of eliciting technique used by the lecturer for the students in “Everyday Communication” class?
C. Objective of the Study
Based on research questions above, in this research the researcher would like to find out about:
1.The lecturer’s eliciting techniques that are practiced in Everyday Communication class.
2.The effect of the lecturer’s eliciting techniques to the students’ activeness in Everyday Communication class.
D. Significance of the Study
7
lecturer’s eliciting technique engaging the students in participating to the speaking activity. As a consequence, this study is expected to give beneficial information for the lecturer toward the eliciting technique used in the classroom speaking activity. In hance, the lecturer can improve the eliciting technique in conducting active speaking class.
E. Scope and Limitation of the study
There are some terms in this study that need to specify. There are a lot of ways in eliciting technique such as Socratic question, catalytic question, polar question, closed question and open question. In this case, the researcher overviewed the general eliciting technique in teaching learning activity. Consequently, the researcher will notify each eliciting technique used by the lecturer in speaking classroom activity.
The researcher did his research only in speaking activity time. In the other word, it is not for the other classroom activities. Also, this research will be done in two classes.
F. Definition of key terms
There are some terms that need to be specified in this research to avoid the misunderstanding. Those are:
8
themselves.8In addition, eliciting is a technique where it can encourage the students to actively think and make their own discoveries therefore, the researcher will analyze about the lecturer’s eliciting technique in speaking activities of intensive class.
2. Everyday Communication: is English language class carried by language of UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya class that must be taken in the second semester which focuses on the improvement of speaking skill.
3. Student’s activeness: in this research refers to the activeness of the students to join the speaking activities of the classroom in other words, the students is being active to express their opinion dealing with the material given.
4. Effect: according to the Cambridge dictionary is the result of particular influence.9 In this case, effect refers to the influence made by the lecturer’s elicitation toward students’ activeness in speaking.
8
Jim Scrivener. Classroom Management Technique. (UK: Cambridge University Press.2012)
9
Cambridge advanced learner’s dictionary 3rd edition. Cambridge. Cambridge university press, 2008.
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
A. Lecturer interaction
Interaction is not usually included in consideration of classroom management. Whereas, the way how lecturer says and acts, leads the students to do the instruction, is a central positive and communicative classroom.1 By this purpose, lecturer’s instruction should pay attention to every single instruction in conducting teaching and learning activity, especially through the lecturer’s elicitation.
In wider scheme the lecturer eliciting technique is in the form of lecturer interaction including the lecturer initiation and feedback.2 In the classroom interaction, there are some activities such as; checking the error, initiating the interaction, giving feedback etc. furthermore the lecturer interaction may carry several purposes: command, clarification, and heuristic. To this purpose it is important for the lecturer to pay attention to each interaction used in conducting classroom activity.
Coulthard assumed that a through interaction lecturer will enable the student to access new knowledge, practice and maintain new skill, establishing
1
Robert C. Di Giulio. Positive Classroom Management, (United State of America. Corwin Press 2007) 2
10
relationship and so on.3 Similarly, lecturer is like a conductor of an orchestra. In orchestra, each move of the conductor hand, the orchestra will deliver different music and tone.4Likewise, the lecturer’s interaction, each interaction that the lecturer makes will lead the student to different activities and skill practice. Hence, lecturer should be able to facilitate communicative interaction to provide students’ with more time to practice the speaking skill. In short, the students’ participation relies on how the lecturer uses interaction particularly eliciting the students’ response.
Traditionally, lecturer’s interaction is in the form of initiation, respond, and feedback (IRF Pattern). Initiation refers to where the lecturer starts an interaction by questioning, eliciting, and instructing to invite the students’ participation in form of respond.5 For the example, the lecturer asked the students about the lesson, asking opinion, eliciting the information, etc.In addition, respond refers to how the students reply toward the lecturer’s initiation. Automatically, the students’ respond is influenced by lecturer’s initiation. As an example, when the lecturer’s initiation in the form of closed question, the students’ answer is in “Yes/No”, also when the lecturer’s initiation is in the form of opened question, will encourage students to give long answer.
The performance or production stage of the lesson should provide the students with the opportunity to use the language previously presented and practiced during the lesson in a communicative context. Students should be encouraged to express their ideas, opinions, and feelings in discussions and debates.
3
Coulthard, M. Advances in spoken discourse analysis (USA and Canada. Routledge.2002).
4
Coulthard, M. Advances in spoken discourse analysis (USA and Canada. Routledge.2002). 5
11
Sinclair et al. assumed that eliciting process is not only in the form of initiation-response (IR) but also in the form initiation-response-feedback, IRF, it means that the feedback is to evaluate the response. Actually, the occurrence of the third part, called feedback is something that should be happen because, the feedback will confirm whether the response is appropriate or inappropriateby that way, the role of the feedback is very powerful to tell students about the response that given.
A. Eliciting Technique
Eliciting is the technique of drawing things from students, mainly by asking questions, rather than using lecturer explanation.6 It leads to greater involvement, encourages thinking and nudges the learners toward making discoveries for themselves. To elicit instead of tell, we simply need to turn our statement into question, leaving it up to the students to look, think, decide and say the answer. For example, the lecturer can use a picture to encourage students’ activeness in participating the classroom activity, by introducing the picture in this way; the students will be actively involved.
Adrian Doff assumed that the there are some advantages of eliciting. First, it helps to focus the students’ attention and make them think. For example, here the students are demanded to focus and think of the eliciting given. Second, it helps students make the connection between what they already know and what they are about to learn. Automatically, the students encourage recalling what they already
6
12
know about background knowledge and connect that to what they will learn about. Third, it helps the lecturer assess what the students already know.7 Here the lecturer will easily recognize to measure the ability dealing with the material given.
In elicitation, a lecturer can use picture, realias, gestures, and visuals to encourage student participation. Mostly the lecturer elicited students’ response by using question. There are some kinds of questions that commonly used by the lecturer: Socratic question, Catalytic question, polar closed question, and open question.
a. Kinds of Eliciting Techniques
Question is central classroom activity that should be considered to encourage students’ activeness. With the appropriate use, a question can be one of the main engines of classroom activity, by becoming more aware of the range of question types and the different ways that can be exploited. Here are the types of question.
1) Polar closed question.
This is a question to lead student to have “Yes/No” answer. For an example: ‘Did parker buy car?’, ‘Is the word arrangement correct? According to Matthew S. Dryer, Polar questions are ones to which the expected answer is the equivalent of “yes” or “no” (and which are thus sometimes called “yes-no
7
13
questions”).8 Such question can be form whether in positive or negative form. Of course this kind of question does not necessary an alternative answer which mean the response is very simple, which not more than three word.
2) Closed question.
This is a question that often asked by using WH-question (e.g. what, who, whom, where, why, how.) this is called closed question because there is typically one correct answer or very limited number of limited answer. Closed question invites short focused answer which often (but not always) either right or wrong9. Usually, closed question are easily to answer because based on the certain information. Automatically, the response will be simple since it is questioning about fact finding scenario.10 For example: ‘When did the parker come from America?’, ‘When have Hariri gone?’
Some researchers show this is the most commonly used question by the lecturer to interact with the students. Unfortunately, this type of this question just invites minimal participation from the students because it requires simple answer.11
3) Open question.
This question can let the students to answer in different ways; there will be some possible answers can be ooccurred. Open question allows for them to have
8
Matthew S. Drayer, Polar Question in Teaching Learning (UK, TWAC Press 2005). 9 Robert J Marzano et al,
Classroom Interaction that Works.( USA, ASCD 2001)
10
Skills you need. com.Types of Questions. Accessed on 16/06/2016
11
Mohamet E Osman & Michael J Hannafin, Effect On Advance Organizing Questioning and prior knowledge in science learning, (USA. Florida State University. 1994)
14
longer response and therefore encourage more creative and various responses12 For example: ‘How can we be healthier?’, ‘How can the machine work?’
A fair amount of research indicates that question which require students to analyze information frequently called higher level question produce more learning than question that simply require students to recall or recognize information frequently referred to as lower order question.13Unfortunately, most of the questions that the lecturer used in teaching learning are lower order of question.14 For this reason, it is important for the lecturer to extend the use of open question in order to encourage students’ participation toward classroom activities.
4) Socratic questions
Socratic question is one of the way how the lecturer can use to elicit the students, it can lead the students to realize or discover something for themselves.15It is possibly something that they did not fully know aboutor they may do something contradicted, inconsistency, or false assumption in their understanding.16 In this case, the students need to increase theirknowledgefor what they know about. Inhence, the lecturer should clarify by using the Socratic question here.
12
Frank J Guszak, lecturer questioning and reading ( University of Texas 1976)
13
Redfield AG, The Effect of Lecturer Questioning level on students (GSTOR 1999)
14
Fracesco Fillipone, Questioning at Elementary Level (ERIC 1998)
15
Oxford, R. Language Learning Strategies: What Every Lecturer Should Know, Boston, MA: Heinle and Heinle(1990)
16
Jim Scrivener. Classroom Management Technique. (UK: Cambridge University Press.2012)
15
5) Catalytic question
Catalytic question is to encourage students’ learning and self-exploration dealing with the materials given. In other word, catalytic question helps the students to make their own decision rather than the lecturer tells them what to do.17
Catalytic question is lecturer’s agenda that implemented in his/her teaching activities where that leads to the way and controls something happen in the class. In this case, the lecturer should plan the lesson activities, structure and instruct through the lesson. In the other word, it is based on what the lecturer wishes to implement the catalytic question in the classroom activities that decide and guides.
b. The effect of lecturer’s eliciting techniques.
Lecture’s eliciting techniques effect refers to the influence made by the lecturer’s elicitation toward students’ activeness in speaking. Scrivener proposes that the way how the lecturer elicits the question will influence the students’ response.18Automatically, when the lecturer’s eliciting technique usedsimplequestion, the students’ response is inform of one or two word(s) only. In the other hand, when the lecturer’s eliciting technique demands long answer, the students’ responses will be more communicative.19 For example, when the lecturer uses opened question and closed question. For that reason, the eliciting technique requires the lecturer understands toward appropriate expectation of students in each
17
Jim Scrivener. Classroom Management Technique. (UK: Cambridge University Press.2012)
18
Jim Scrivener. Classroom Management Technique. (UK: Cambridge University Press.2012) 19
Krashen, S., & Terrell, T. The Natural Approach: Language acquisition in the Classroom(Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1983)
16
step of language development.20 Eliciting techniques were used on regular basis to elicit students’ talk. The manners of elicitation which were paid the most attention to included “combining types of question”.21 In this case, this is what going to be focus of this research that is the effect from student toward the elicitation made by lecture.
The effect of eliciting techniques on students’ responses differs from to which types of questions lecturer used. It is noticed that the participation of students are greatly influenced by the nature of these questions.22Walsh (2013) believes that elicitation entails asking questions and that questioning is one of the principal ways in which lecturer control the classroom discourse. Many researchers investigate the types of questions selected by lecturers and kind of responses to these questions. Lecturer questions are categorized into: open and closed questions, polar closed question, Catalytic question and Socratic question.23
1) The effect of Polar closed question
According to Matthew S. Dryer, Polar questions are ones to which the expected answer is the equivalent of “yes” or “no” (and which are thus sometimes called “yes-no questions”).24 Of course this kind of question does not necessary an alternative answer which mean the response is very simple, which not more than three word.
20
Addrienne L. Herrell and Micheal Jordan.Strategies for Teaching English Language Learners Third Edition(Canada: pearson Education, Inc, 2008)
21
Chu ThiHuyen Mi. Lecturers’ use of Eliciting Techniques to Teach Speaking Skill to First-year of UET, VNU(Vietnam: UET Press 2012)
22
Ms. ShuruqAlsubaieAn Analysis of classroom discourse: elicitation techniques in Efl classrooms Language Instructor(ELI University of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 2015)
23
Walsh,S. Classroom Discourse and Lecturer Development, Edinburgh(Edinburgh University press, 2013) 24
17
2) The effect of closed question
Closed question invites short focused answer which often (but not always) either right or wrong. Automatically, the response will be simple since it is questioning about fact finding scenario.25
3) The effect of open question
This question can let the students to answer in different ways; for this reason there will be some possible answers that can be occurred. Open question allows for them to have longer response and therefore encourage more creative and various responses.
4) The Effect of Socratic question
It is possibly something that they did not fully know aboutor they may do something contradicted, inconsistency, or false assumption in their understanding.26 In this case, the students need to increase theirknowledgefor what they know about. For this reason, the student response is relied on how lecturer uses the Socratic question to encourage student to actively participate in the class.
5) The effect of Catalytic question
Catalytic question is to encourage students’ learning and self-exploration dealing with the materials given. In other word, catalytic question helps the students to make their own decision rather than the
25
Skills you need.com.Types of Questions. Accessed on 16/06/2016 26
Jim Scrivener.Classroom Management Technique. (UK: Cambridge University Press.2012)
18
lecturer tells them what to do. Similar to Socratic question, the student response is relied on how lecturer used the Socratic question to encourage student to actively participate in the class.
Considering the complication and importance of the classroom interaction toward the success of the learning, it is fair to say that to improve the quality of students’ learning is by paying attention to each lecturer’s eliciting technique to encourage students’ in participating to the classroom activity. Thus, the students will have more opportunity of learning in practicing the material thatl given. As a result, students will be able to work and active in the classroom activities that can help them in understanding the whole materials, weather theories or practices.
Furthermore, by students actively involved in classroom activities, the lesson got will be easily remembered and practiced by the students. For example, the lecturer can invite students to actively participate by giving comment or feedback toward the lesson and explanation. By involving the student in teaching learning activity the student will have more understanding toward the process of the lesson.
B. Speaking class
During the globalization, it is big demand for being able to communicate efficiently in English. For a language learner that ability requires communicative competence that can be got by practicing frequently. 27For this purpose, it is important to provide students in practicing students’ ability in speaking more
27
Chu ThiHuyenMi, with the title lecturer’s use of elicitation techniques to teach speaking skill to first-year students of UET, VNU (Hanoi ThS Nguyen Minh Tuan, 2012)
19
intensively, in this case in speaking class. In addition, through the practice will have to enhance students’ confidence in communication.
According to Skehan, Speaking enables students to reflect and to communicate their opinion, to express their feeling, to ask a question and others. Unlike the other productive skills, speaking needs more stimulation to interact rather than writing.28Moreover, there are many students who were not confident to communicate using the foreign language. According to Lam, the students who have the communicative competence tend to have more willingness to communicate and are not afraid of making mistake. As a result, they make use of more linguistic practice with higher frequency and wider range.29
Furthermore, opportunities to speak English enable students to drill their speaking competence. According to Bui, it is no doubt that the more opportunities students speak English, the more experience dealing with the problems they could face from the various situation and interlocutor.30 In short, students’ opportunities give big effect toward students’ fluency in speaking.
Based on the explanation above, it is important for the lecturer to lead the class that provides wider opportunities for students in speaking. For this purpose, it is relied on the lecturer’s creativity to make students actively participate in speaking activity. In this case, the lecturer can use the technique: eliciting technique.
28
Skehan.A cognitive approach to language learning, (Oxford: University press.1998)
29
MarianiLam.Communication strategies: learning and teaching how to manage oral interaction, (-: learning path tantevieper imparare.2010)
30
Chu ThiHuyenMi, lecturer’s use of elicitation techniques to teach speaking skill to first-year students of UET, VNU, (Hanoi ThS Nguyen Minh Tuan, 2011)
20
One of the main problems in speaking is a difficult contract to express. In speaking, it can be devided into some parts, such as; pronunciation and intonation, accuracy and fluency or it can be categorized into some strategies or related to the form of interaction and analyzed using the method of pragmatics or discourse analysis.31 Another problem, Sekhan found some differences when the students speak out of classroom are different when they speak in the classroom activity. Inhence, it causes some differences in defining the success of speaking.32
In this case, the researcher focused on students’ involvement in participating the classroom activity. Automatically, the researcher did not see the detail about the speaking construct produced by students since, the purpose of this research is not to test the speaking ability but to see students’ involvements. For this purpose, the researcher analyzed the lecturer’s eliciting technique to engage students’ activeness
C. Student activeness in speaking
In speaking evaluation the lecturer or the researcher will provide the aspects that are used to measure the student success toward the speaking ability. As an example, fluency, accuracy, and pronunciation are the common criteria that are used in speaking rubric evaluation. For the reason that in this research is focused on the analysis of student activeness from the elicitation made by the lecturer, the researcher provided some sources that provide the variety that
31
Steve Walsh. Investigating classroom discourse(USA and Canada: Rout ledge, 2006) 32
Sekhan.A Cognitive approach to language learning, (Oxford: University Press.1998)
21
student may participate during the teaching learning activity especially in speaking. James Dean Brown proposes some criteria that can be used for the student activeness in speaking activity: First, the students respond appropriately to elicitation given by the lecturer with ideas that relate to what is being discussed. The second, the students actively participate in classroom language activities. For the example: by asking questions, predicting the answer,expressing feelings, sharing ideas, and making personal connections.
Furthermore, the use of language to connect new experiences to what is already known became a consideration in measuring students’ activeness in addition, the students are able to demonstrate an interest in and willingness to use and experiment with language use newly learned vocabulary in own speech. As a matter of fact, Initiating conversations, taking turns in structured activities, raising hand to be recognized before speaking. Moreover, Sustaining conversation on a familiar topic for short periods of time and stay on topic would be an attention toward students’ activeness and using complete sentences when necessary or appropriate in speaking.33
D. Previous study
There are some researches that were done dealing with eliciting technique in teaching-learning activity. For the example, a research that was done by Rahayu under the title the use of elicitation technique in learning to improve students’ speaking skill. This research usedclassroom action research in which the researcher
33
James Dean Brown. Testing in Language programs: A comprehension guide to English language assessment (New York: Mc Graw Hill 2014)
22
used two cycles of implementation. In this research, Rahayu analyzed about the elicitation used by the lecturer in increasingstudents’ activeness. As a result of this research the students’ activeness in speaking classwere increased after the lecturer used eliciting technique.34While the focus of thisresearch analyzed teacher’s eliciting technique by using with elicitingtechnique theory and furthermore, in the other hand, this research focuses on the students’ activeness in speaking classroom activity.
Similarly, Huyen,Iinvestigated technique used by the teacher to elicit tenth grade students’ talk in Hanoi.Asa result, Huyen found that mostly the lecturer’s
eliciting techniques were in the form closed question in which, it limit the students participation. For this reason, Huyen suggested that the lecturer must extend the use of eliciting technique to encourage students to be more active.35 However in this research, the researcher will focus on the eliciting technique that is used by the lecturer in the speaking activity.
In other research, Cao Thi, lecturers’ use Eliciting Techniques in English Speaking Lessons at Son Tay Upper Secondary School, Hanoi (2011) basically, the research analyze about the use of elicitation techniques in teaching speaking and overview the most command eliciting techniques used during the lesson. In the other hand, this research focused on the effect eliciting techniques toward students’ activeness.
34
SitiRahayu, the use of elicitation technique in learning to improve students’ speaking skill(Bandung: universitas Padjadjaran,2010)
35
Huyen,Investigated technique used by the lecturer to elicit tenth grade students’ talk in Hanoi(Hanoi ThS Nguyen Minh Tuan, 2012)
23
Chu Thi Huyen Mi, with the title teacher’s use of elicitation techniques to teach speaking skill to first-year students of UET, VNU focused on the ineffective use of eliciting technique for Vietmen students.36 As a result study shows a need to learn about the lecturer’s perceptionin the use of eliciting technique and the implementation in the class. However in this research, the researcher only focuses on the eliciting technique used by the lecturer in speaking activity whereas Hariri’s research focused on the lecturer’s interaction.
36
Chu ThiHuyenMi, with the title lecturer’s use of elicitation techniques to teach speaking skill to first-year students of UET, VNU(htunkTuH press, 2011)
24
CHAPTER III
RESEACH METHOD
A. Approach and research design
The design of this study used qualitative method because the researcher started from the theory of the Eliciting technique to encourage the students. Furthermore, data was collected through the transcription of the class and interview from the lecturer and the students. The purpose was to get fully understanding about the lecturer’s eliciting technique in the speaking classroom activities and the effect of the lecturer’s eliciting technique for the students.1
After that, the researcher used one of the qualitative interpretations: construction of patterns through analysis and re-synthesize of constituent parts.2
From this interpretation the researcher analyzed the data collection of the transcription of the lecturer’s eliciting technique with eliciting theory. For the reason that this research was done by beginning from the sources of elicitation then analyzed the existence in Everyday Communication class
1
Donald Ary, Cheser Jacobs, and Sorensen,C,. Introduction to Research in Education Eighth Edition(
Canada: Wadsworth, 2006)
2
Donald Ary, Cheser Jacobs, and Sorensen,C,. Introduction to Research in Education Eighth Edition(
25
(speaking), then this research was appropriately analyzed by qualitative approach.
B. Researcher presence
In this research, the researcher was as obsever of the research as well as data collector. By this purpose, researcher attended to the class and collected the data through instrument and made an observation about the classroom. Furthermore, the role of the researcher in the classroom was the pure observer which the researcher only observed the classroom activity without active participation. At the same time, the participants fully realized to the presence of the observer since the observer made a consolidation with the lecturer before the class about what was going to observe.
C. Research location
The researcher should take the appropriate object to come up with the valid result. Here, the researcher chose two classes in State University Sunan Ampel Surabaya, at A and B class as the object for the four considerations:
26
2. The students were demanded to master English language to face future challenge.
3. Thelecturer understood about the use of Eliciting techniques
4. The students had adequate ability that need more eliciting technique in order to be active.
Furthermore, there are 25students for A class and 18 students for B class. In both class, Mr. Sigit Pramono Jati is as the lecturer. The researcher had an overview to know how the eliciting technique couldbe used well in the speaking activities, and also, to help the lecturer to find effective technique for his/her teaching strategy.
D. Data and source of data
To gather the information about the subject of study, the researcher used three kinds of data collection technique. Those were documentation (recording), transcription and Interview.
a. Observation
27
context of the class and lecturer’s teaching behavior the researcher recorded the class for four meetings since the researcher is to fulfill the minimum amount of data collection in teaching the speaking activity. For this reason, the researcher assumed that to get fully portrayed of the lecturer’s eliciting technique; the researcher had extended the information from the interview.
In this research, the researcher observed eight meeting in two classes. The first meeting was on 15th of April, the second meeting was on 6th of May, the third meeting was on 13th of May and forth meeting was on 20th of May
b. Transcription
In this study the researcher transcribed the data as it could fulfill the required information of the classroom. Moreover the researcher made a note about the classroom activity that was useful for the more detail information about the class. In addition, the transcription processes are from the video recording, the researcher transcribed the data by himself then checked the transcription with some fellows in the English education department and finally validated the transcription to the lecturer being observed.
c. Interview
28
speaking classroom activity. In addition, to make sure about the impact of eliciting technique, the researcher interviewed the students to know students’ reflection about the lecturer’s eliciting technique. In this research, the researcher took five students in each class.
E. Research instrument
To help the researcher in collecting the data, the researcher used Video recorder to maintain the more detailed data about the classroom interaction the researcher interviewed the lecturer. For the instrument the researcher used mobile phone that has good quality video recording. Then the researcher transcribed the interaction among students and lecturer from the recording.
F. Data analysis technique
This is the most important step of the research as it leads the researcher to the interpretation about the data collected. For this reason we should choose the appropriate data analysis to come up with the valid result of the study.
29
the eliciting technique, the researcher examined whether the eliciting encouraged the students actively participates in the speaking classroom speaking activity.
The next step, to complete the understanding of lecturer’s eliciting technique the researcher used interview of the lecturer to know the reason why the lecturer use the eliciting technique in teaching learning process. Here researcher used qualitative research where the conclusion is derived from the data by making an analysis.3
Then, to answer the second research question, the researcher used the interview and observation toward the lecturer’s eliciting technique. For the observation, the researcher overviewed from the speaking activity whether in the class or from the recording. For the interview, the researcher asked the lecturer and the students toward the effect of eliciting technique used in speaking classroom activity.
3
DonaldAry, Cheser Jacobs, and Sorensen, C, .Introduction to Research in Education Eighth Edition(
Canada: Wadsworth, 2006)
The researcher chose threliciting technique used by the lecturer.
30
G. Checking validity of findings
It is very important for a research to check the validity of the finding after having a final analysis of the research. By this purpose, the researcher re-checked the lecturer’s eliciting technique in recording, the note of the researcher and the transcription that made by researcher. This step enabled the researcher to overview the continuity and rationality among these instruments.
H. Research stages
Here is the research guide for the data analysis:
1. Collected the data from the class by recording then transcribe it. 2. Interviewed the lecturer and the some students.
3. The researcher encoded the eliciting technique used by the lecturer. 4. Made an analysis whether the eliciting technique is appropriate or
not.
Made an analysis whether the eliciting technique is appropriate or not.
Gave reasons, comments about the decision of the third step
Make a conclusion about the effectiveness of lecturer eliciting
31
5. Gave reasons, comments about the decision of the third step.
6. Made a conclusion about the effectiveness of lecturer eliciting technique.
32
CHAPTER IV
FINDINGAND DISCUSSION
In this chapter, the researcher presented two parts that will be discussed. They are types of elicitation techniques that were used by the lecturer and the effect toward students’ activeness in participating the classroom activities. Those two parts deal with the findings of the research and the discussion about what have been discovered by the researcher and also to answer the research questions.
A. Research Findings
As the researcher explained in the chapter three that the types of eliciting techniques were becoming main tool in analyzing the elicitation. The first: after the transcription, the researcher code the transcription based on five questions of eliciting techniques: polar closed question, closed question, open question, catalytic question, and Socratic question. Afterward, the researcher analyzed the questions by overviewing the students’ responds toward lecturer’s eliciting technique. As a result, the researcher could see to what extant lecturer’s question can engage the students’ activeness in participating the class activity.
In this case, the lecturer lecturer’s eliciting techniques analyzed in second semester A and B class of English department students at Islamic State University Sunan Ampel Surabaya. The lecturer that had been observed is Mr. Sigit Pramino Jati,MPd as English lecturer in English department of Islamic State University Sunan Ampel Surabaya. The student in Class A consisted of 25; 8 males and 17 females. Similarly, there are 18 students 5 males and 8 females. The class took three credits of System of the study. As the interview that was done by the researcher to
33
lecturer of the classes, the students are not in average abilities from the low to the high one.
Based on the research question, there are two research questions that the researcher divided into two points.
a. The lecturer’s eliciting techniques used in Everyday Communication Class. In this section is to fulfill data from first research question, in which analyzing eliciting techniques used by the lecturer. Thus, the researcher classifies the finding of the eliciting techniques proposed by Jim Scrivener: Polar closed question, closed question, open question, catalytic question and Socratic question.
1) Polar closed question
Polar closed question is one to which the expected answer is the equivalent of yes or no answer.1It means that this is a question to lead student to have “Yes/No” answe.
Here the researcher provides of polar closed question used by the lecturer.
Table 4.1
Lecturer Polar closed question and students’ responses
Me
eti
ng
Polar
closed
question
Frequen
cy
Examples of lecturer’s
Eliciting tecniques
Effect toward
students’
activeness
1
Matthew S. Dryer, Polar questioning in teaching learning (UK, TWAC Press 2005)
35
4 Polar closed question
Done?
Can you do it?
Shanaz, can you do
it with good intonation and the stressing?
Done
How about if
don’t have reason?
Yes sir, I’ll
try.
1 Polar closed question
Ready
Done?
Rusdi, ready now?
Do you get the
point?
Is that all true?
Is that right?
Raisa, is that right?
Yes
Yes, sir
No
oh yes
Yes
Yes
Yes. 10th of
37
Zakaria, you want
to choose?
Yes. the
round one.
From the transcription, the lecturer used polar closed question to ask confirmation about availability in doing something. As an example, can you do it? (See 1stObservation of class A utterance 33 extract 1.3), done? (See 3rd observation of class A utterance 60 extract 3.4), do you need to prepare? (See 3rd observation of class A Utterance 44 extract 3.3), you know what to do? (See 4th observation of class B utterance 66 extract 8.4) furthermore, polar closed question use to confirm about the student’s answer. As an example, is that right? (See 1st observation of class A utterance44 extract 1.9), so you say go rollerblading? (See 4th observation of class B utterance 45 extract 8.3), is that right? (See 2nd observation of class A utterance 17 extract 2.1).
2) Closed question
This is a question that often asked by using WH-question (e.g. what, who, whom, where, why, how.) this is called closed question because there is typically one correct answer or very limited number of limited answer. Below the researcher provides the table of Closed Question.
Table 4.2
42
7.1), what time do you watch sport? (See 2nd observation of class B utterance 53 extract 6.5), what time do you play music? (See 2nd observation of class B utterance 59 extract 6.5) what is the name of the song that we have last week? (See 2nd observation of Class A utterance 02 extract 2.1),are closed question as a techniques used by the lecturer to make sure that students really know about what they already learnt, about their activities, about the source of their knowledge and etc.
3) Open Question
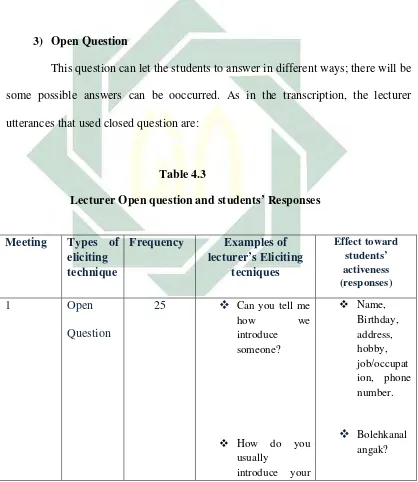
This question can let the students to answer in different ways; there will be some possible answers can be ooccurred. As in the transcription, the lecturer utterances that used closed question are:
Table 4.3
Lecturer Open question and students’ Responses
Meeting Types of eliciting technique
44
Question someone are?
lecturer invited the students to actively joining in the all activities by using open question as the technique to make the students interesting to join. Such as in these
Question yourself when
46
examples: can you tell me how can you introduce someone? (See 1st observation of class A utterance 04 extract 1.1), how can you recognize someone in order that you can easily remember? (See 3rd observation of class utterance 04 extract3.1).Age, number of children, salary, measurement. You know what measurement? (See 1st observation of class B utterance 05 extract 5.1), can you tell me what the aspects to introduce someone? (See 1st observation of class B utterance 03 extract 5.1). Consequently, the student’s responds are based on the information that they knew. As an example: ok sir. She likes swimming because she wanted to be tall, having slim body and want to be a good looking girl and she can meet many view, people that the point, by swimming she can have sport refreshing. Cool girl! (See 4th observation of class B utterance 147 extract 8.6)
4) Catalytic Question
Catalytic question is to encourage students’ learning and self-exploration dealing with the materials given. In other word, catalytic question helps the studentsto make their own decision rather than the lecturer tells them what to do. Catalytic question is lecturer’s agenda that implemented in his/her teaching activities where that leads to the way and controls something happen in the class. In this case, the lecturer should plan the lesson activities, structure and instruct through the lesson or in other word, it is based on what the lecturer wishes to implement the catalytic question in the classroom activities that decide and guides.
In this technique, the researcher did not find any kind of this question. As in the interview with the lecturer, he did not use this kind of question by the
47
reason that this technique was not suitble anough to use in the class because the students’ English proficiency is still low. The lecturer also told the researcher that it is still basic for the just because in the first semester there was no specific class for speaking.
5) Socratic Questions
Socratic question is one of the way how the lecturer can use to elicit the students, it can lead the students to realize or discover something for themselves, it is possibly something that they did not fully know aboutor they may do something contradicted, inconsistency, or false assumption in their understanding.2 In this case, the students need to increase thier knowledge for what they know about. Inhence, the lecturer should clarify by using the Socratic question here.
Here the researcher provides table for the technique used by the lecturer:
Table 4.4
Lecturer Socratic question and students’ responses
Types of eliciting techniques
Frequency Examples of Lecturer’s Eliciting tecniques meet the person. It looks like I know him but I’m not sure I know him but his face not strange. Fortunately, he came to me and greet me. He said
48
“we meet in the international Seminar” and I asked him. “How can you recognize me?” “I got no reason to forget you just because you are very handsome”, how do you recognize someone in order that you can easily remember them?
In this technique, the lecturer told his past experience then followed by some question so that the students were interested to be in. here is the Socratic question used by the lecturer: You know it is funny when I meet the person. It looks like I know him but I’m not sure I know him but his face not strange. Fortunately, he came to me and greets me. He said “we meet in the international Seminar” and I asked him. “How can you recognize me?” “I got no reason to forget you just because you are very handsome”, how do you recognize someone in order that you can easily remember them? (See 3rd 0bservation of class A utterance 3 and 5 extract 3.1). In this question, the lecturer elicited the students by telling his experience about someone who knew him. This elicitation enabled the students to recall their experience or knowledge. As a result, the students would answer based on the experience that they underwent. As an example: I think very easy if the person is beautiful. It touches my hearth and always remember. In this
49
case, the students answer whether could be from the lecturer r experience background or their own experience.
b. The effect of eliciting techniques in every day Communication class
In this section is to fulfill data from second research question, in which analyzing effect from the eliciting techniques used by the lecturer. thus, the researcher classify the finding of the eliciting techniques proposed by Jim Scrivener: Polar closed question, closed question, open question, catalytic question and Socratic question.
1) The effect of Polar closed question
In this type of question, polar closed question expect yes or no answer from students. Sofor the effect, of course students’ answers are in form of yes or no. For example, right (See 2nd observation of class A utterance 17 extract 2.1.), yes, done (See 4th observation of class A utterance 29 extract 4.3).
2) The effect of closed question
50
3) The effect of Open question
Since the expected response of open question that is questioning about reason of how the students easily recognize someone, the student’s response tends to be longer because it did not have exact answer so that the student could find their own reason. Such as, “I think very easy if the person is beautiful. It touches my heart and always remember” (See 3rd observation of class A utterance 06 extract 3.1), Appearance (see 3rd observation of class A utterance 08 extract 3.1), body (See 3rd observation of class A utterance 10 extract 3.1), measurement (utterance 12 extract 3.1), accessories, sir (See 3rd observation of class A utterance 14 extract 3.1).
4) The effect of Socratic question
In this question, the lecturer elicited the students by telling his experience about someone who knew him. This elicitation enabled the students to recall their experience or knowledge. As a result, the students would be answered based on the experience that they underwent. As an example: I think very easy if the person is beautiful. It touches my hearth and always remembers. In this case, the students answer whether could be from the lecturer experience background or their own experience.
To sum up, the researcher provides table of eliciting techniques used by the lecturer in Everyday Communication class and the student’s response
Table 4.5
The sum up of lecturer eliciting techniques and students’ responses
the aspects to introduce someone?
The lecturer did not use this type of question Socratic
question
53
B. Discussion
In this discussion the researcher analyzed the lecturer’s Eliciting techniques implementation of Speaking in Every day Communication of second semester. Eliciting technique is the technique of drawing things from students, mainly by asking questions, rather than using lecturer explanation which focuses on lecturer’s questioning techniques and students response brought by Jim scrivener.3 There are fivekind of Eliciting techniques in Elicitation; 1) Polar closed Question, 2) closed question, 3) open question, 4) Catalytic question, and 5)Socratic question) . For this reason the discussion is classified based on the kinds of eliciting techniques.
a. The use of Polar closed question and its effect
Based on the finding from the transcription, the lecturer’s utterance which is categorized as polar closed question is when the lecturer asking a question that is the answer is only in the form of Yes or No answer. For example, do you need to prepare? (See 3rd observation of Class A utterance 44 extract 3.3). In this utterance, the lecturer was asking to the students about their preparation to do their work. This is suited with Matthew S. Dryer about definition of polar closed question; a question to lead student to have Yes/Noanswer.4 As a result, students’ responses are in the form Yes or No. for example, yes sir, moment (See 3rd observation of class A utterance 45 extract 3.3).
3
Jim Scrivener. Classroom Management Technique. (UK: Cambridge University Press.2012) 4
Matthew S. Drayer, Polar Question in Teaching Learning (UK, TWAC Press 2005).