THE USE OF WEBQUEST IN BLENDED LEARNING
TO IMPROVE STUDENTS’
SPEAKING SKILLS FOR THE
ELEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF MAN SALATIGA
IN THE ACADEMIC YEAR OF 2018/2019
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a partial fulfillment of the requirement for
the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd)
By:
DIAN AMALIA
113-14-017
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
v MOTTO
Learning without thinking is useless, but thinking without learning is very
dangerous
vi
DEDICATION
This graduating paper is sincerely dedicated to:
My beloved parents, “Tusirah” and “Tipyani”; you are my inspiration and
my treasure.
My beloved sister “Devi Diana”, and my beloved brothers “Anang Fauzy and Habib Mubarizy” and my beloved partner “Imam Maliki”. Thanks for
your support and pray.
My best partners of graduating paper in Mrs. Setia Rini’s group that
support me to finish this graduating paper.
My big family TBI 2014 that support my education and finish this
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Bismillahirrahmanirrahim, Assalamu’alaikum Wr.Wb.
Alhamdulillahirobbil’alamin, all praises be to Allah SWT, the Most
Gracious, and The Most Merciful who always bless and help the writer so the writer can finish the graduating paper. Bless and mercy are upon great the Prophet Muhammad SAW for his guidance that leads the writer to the truth.
However, this paper will not be finished without supports, advices, help and encouragement from several people and institution. Hence, the writer would like to express special thanks to:
1. Mr. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M.Pd., the Rector of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) of Salatiga.
2. Mr. Suwardi, M.Pd, the Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty (IAIN) of Salatiga.
3. Mrs. Noor Malihah, Ph.D, the Head of English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty (IAIN) Salatiga.
4. My counselor, Dr. Setia Rini, M.Pd. who gives great attention, suggestion and guidance for this graduating paper from chapter 1 until chapter 5. 5. All of lecturers and staffs of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) of
Salatiga
Salatiga, August 21th 2018 The writer
viii ABSTRACT
Amalia, Dian. 2018. The Use of Webquest in Blended Learning to Improve Students’ Speaking Skills for the Eleventh Grade Students of MAN Salatiga in the Academic Year of 2018/2019. A Graduating Paper. English Education Department. Teacher Training and Education Faculty. State Institute for Islamic Studies Salatiga. Counselor: Dr. Setia Rini, M.Pd.
The objectives of the study were to find out the implementation of Webquest in Blended Learning and to know the improvement of students’ speaking skills by using Webquest in Blended Learning for the eleventh grade students of MAN Salatiga in the academic year of 2018/2019. The numbers of subject of the research were 21 students.
The methodology of research was classroom action research. The techniques of collecting data were pre-test and post-test (oral test) to find out the students’ skills by recording technique to find out the students’ pronunciation, intonation, fluency, grammar and vocabulary. The second technique of collecting data was observation to find out the students’, teachers’ activities, and the utilization of Webquest. The third technique of collecting data was field note to record all the detail activities while doing teaching and learning process in the classroom from the beginning until the end of the teaching learning process.
The writer finds that there was a significant improvement on students’ speaking skills after Webquest was implemented as media in Blended Learning in cycle I and cycle II. The result of pre-test cycle I was 52.37% of the students who reached the passing grade. The total presentation of the students who did not reach the passing grade in the post-test cycle I was 19.04%. T-test in the cycle I was 4.402 while t-table was 2.086 for df 20 and the significance 5%. Thus the sig. 2 (tailed) value < 0.05 and T-test was bigger than T-table. Thus, action hypothesis was accepted. Meanwhile, in pre-test cycle II there were 16 students who could pass the passing grade, and the presentation was 76.18%. Meanwhile, there were 23.80% who did not reach the passing grade. T-test in the cycle II was 9.954 while T-table showed 2.086 for df 20 and the significance 5%. The sig. 2 (tailed) value < 0.05 and T-test was bigger than T-table. Thus, action hypothesis was accepted. The target presentation of the passing grade had been achieved. The implementation of Webquest as media in Blended Learning was successful to improve students’ speaking skills.
ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS
DECLARATION ...Error! Bookmark not defined. THE ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR’S NOTE...Error! Bookmark not defined.
THE STATEMENT OF CERTIFICATION ...Error! Bookmark not defined.
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... vii
ABSTRACT ... viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... ix
LIST OF TABLE AND FIGURE ... xiv
CHAPTER I ... 16
INTRODUCTION... 16
A. Background of the Research ... 16
B. Research Questions ... 20
C. Objective of the Research ... 20
D. Significances of the Research ... 21
E. Hypothesis and Success Indicator ... 22
x
1. Research design ... 23
2. The subject of the research ... 25
3. The steps of the research ... 26
4. Techniques of Data Collection and Research Instrument ... 27
5. Data Analysis... 31
G. Graduating Paper Outlines ... 32
CHAPTER II ... 34
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ... 34
A. Supporting Theories ... 34
1. Speaking ... 34
a. The definition of Speaking... 34
b. Types of speaking ... 36
c. Elements of speaking ... 38
d. Aspects of teaching speaking skill ... 39
e. Teaching speaking in Senior High School ... 40
f. Problems with speaking activities... 42
g. Indicators of Succesful Speaking Skills ... 44
2. Webquest ... 46
a. Definition of Webquest ... 46
xi
c. Elements of Webquest ... 49
d. How to create Webquest in the classroom ... 51
3. Blended Learning ... 53
a. Description of Blended Learning ... 53
b. Levels of Blended Learning ... 56
c. Steps in Blended Learning ... 57
B. Review of the Previous Research ... 57
CHAPTER III... 62
IMPLEMENTATION OF RESEARCH ... 62
A. The Procedures of the Research ... 62
1. Cycle I ... 62
a. Planning ... 62
b. Acting ... 63
c. Observing ... 64
d. Reflecting ... 64
2. Cycle II ... 65
a. Planning ... 65
b. Acting... 66
c. Observing ... 67
xii
B. The minimal standard of successful ... 68
CHAPTER IV ... 69
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DATA ANALYSIS ... 69
A. The Result of the Research... 69
1. Research Finding ... 69
a. Cycle I ... 69
1) Planning ... 69
2) Acting... 71
3) Observing ... 82
4) Reflecting ... 89
b. Cycle II... 92
1. Planning ... 92
2. Acting... 93
3. Observing ... 102
4. Reflecting ... 110
2. Discussions ... 111
xiii
b. Improvement of students’ speaking skills by using Webquest in blended learning for the eleventh grade students of MAN Salatiga in
the academic year 2018/2019... 112
CHAPTER V ... 118
CLOSURE... 118
A. Conclusion... 118
B. Suggestion ... 120
REFERENCES... 122
xiv
LIST OF TABLE AND FIGURE
Figure 1.1 The Scheme based on Kemmis and McTaggart ... 23
Table 1.1 List of Students’ Name... 25
Table 1.2 Research Schedule ... 26
Table 1.3 Students’ Observation Checklist ... 28
Table 1.4 Teachers’ Observation Checklist ... 28
Table 1.5 The Use of Webquest Observation Checklist ... 29
Table 2.1 Speaking Assessment ... 41
Figure 2.1 Elements of Webquest ... 51
Table 4.1 Form the Result of Students’ Observation Checklist Cycle I ... 82
Table 4.2 Form the Result of Teachers’ Observation Checklist Cycle I... 83
Form 4.3 Form the Result of Using Webquest Checklist Cycle I... 84
Table 4.4 The students’s score of pre-test and post-test cycle I... 85
Table 4.5 Count of Passing Grade of Pre-Test and Post-Test in the Cycle I ... 87
Table 4.6 Descriptive Statistics ... 87
Table 4.7 Paired Samples Test ... 88
Table 4.8 Form the Result of Students’ Observation Checklist Cycle II ... 103
xv
Table 4.10 Form the Result of using Webquest Observation Checklist Cycle II
... 105
Table 4.11 The Students’ Score of Pre-Test and Post-Test Cycle II... 106
Table 4.12 Count the passing grade of Pre- Test and Post-Test in Cycle II ... 107
Table 4.11 Descriptive Statistics ... 108
Table 4.12 Paired sample test... 109
Table 4.13 Count Passing Grade of Pre-Test and Post-Test Cycle I... 113
Table 4.14 Analysis Table of Mean, Standard Deviation, T-Table and T-Test .. 114
Table 4.15 Count Passing Grade of Pre-Test and Post-Test Cycle II ... 115
16 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, the researcher presents the background of the research, research questions, objectives of the research, significances of the research, hypothesis and success indicator, research methodology and graduating paper outlines.
A. Background of the Research
As the technology expands faster, people in the world can upgrade any information easier and faster through internet facility. In recent years, the internet becomes one of the most powerful technologies for communication and information (Vacca, 2009:430). Additionally, Jati (2016:1) states that technology is not only become the basic motive of the change in globalization era but also in education environment. This reality forces teachers to make a good use of internet and benefit the internet as one of advanced technology in providing sources for students in learning English.
17
that the change of technology makes a long lasting innovation and new activity in teaching and learning English. One of those innovations is Web-based education or usually named as E-learning.
Lamy and Hampel in Rodrigues (2007:4) states that online learning or E- learning has been broadening either in written discourse or oral discourse. Additionally, online learning’s existence is expectable to give a different color in the educational environment. Internet technology has a great influence on the educational environments, especially in the English classes. Surely, the internet has a great role in the second or foreign language teaching and learning. In addition, Tinio et.al as cited in Rodrigues & Vethamani (2015:3) mention that the effect of Internet and Communication Technology (ICT) is able to create teaching and learning to be more interesting, interactive, meaningful and motivating.
A new style of combining face to face and online learning which is called as blended learning is applicable for any courses. Blended learning is considered as the impact of the advancement of technology. Thorne (2011:16) sees that blended learning is the reasonable and common learning. It gives a solution to adjust learning process and enhance individual needs. Blended learning integrates and innovates the advancement of technology by doing online learning and interaction by traditional learning.
18
the internet media is Webquest. Webquest is one of teaching media by making a good use of internet in teaching and learning process. Webquest should be a good media in improving students’ English skills; such as speaking, writing, reading and listening. In this study, the researcher focuses on the speaking skill.
Speaking is one the four language skills which is very important to be mastered. Speaking is the most difficult skill to be mastered for the majority of English learners and still incapable in communicating in English orally (Al Hosni, 2014:3). Ur (1996:99) mentions there are many factors that cause difficulty in speaking, the first is inhibition. It means students are worried about making mistakes, fearful, or seven simple shy. The second is nothing to say, the students have no motive to express themselves. In the other hand, Rababa’h (2005) cited in Al Hosni (2014:4) adds the other factors that cause difficulty in speaking are related to the students themselves, inadequate teaching strategies, the curriculum, and the environment. For the example, the students are lack of vocabulary; students cannot keep the interaction going on. Some students lack of motivation to speak English.
19
enough and students have not mastered speaking yet. Based on the interview, the students’ inability to speak English fluently is caused by a
number of factors. First, students do not have a lot of vocabularies. Second, the students have low mastery of grammar and pronunciation. Third, the students are afraid of making mistakes, because they never practice to speak English formally or even informally with their friends. Fourth, the students feel embarrassed and sometimes feel confused in stringing up the words to make a good sentence or dialogue. Moreover, they do not feel confident; therefore self confidence is an important way to improve our language skills. Self confidence is related to something spoken or something told. It becomes the main factor in affecting students’ speaking skills and has a crucial contribution in speaking skills.
The second question is about media used by the teacher in teaching speaking. Commonly, in teaching speaking, the teacher used video and power point presentation. The teacher also applied pair work discussion but it did not work well.
The last question is about Webquest. The teacher said that she never used Webquest as media in teaching English. The media is unfamiliar for the teachers in MAN.
20
materials which provides the real example of videos, link websites which contain of dialogue or phrases or sentences or another online source, thus the students can imitate it, and the sources can be accessed by the students easily. Thus, the need to improve students’ speaking skills has been intriguing researchers’ interest.
From the previous explanation mentioned above, the researcher conducted a Classroom Action Research in MAN SALATIGA. In conducting the research, the researcher proposes a research entitled “The Use of Webquest in Blended Learning to Improve Students’ Speaking
Skills for the Eleventh Grade Students of MAN Salatiga in the Academic
Year of 2017/2018”
B. Research Questions
Based on the background of the research, the researcher formulates the research questions as follows:
1. How is the implementation of using Webquest in blended learning to improve students’ speaking skills for the eleventh grade students of
MAN Salatiga in the academic year of 2018/2019?
2. How far is the improvement of students’ speaking skills by using Webquest in blended learning for the eleventh grade students of MAN Salatiga in the academic year of 2018/2019?
C. Objective of the Research
21
1. To find out the implementation of using Webquest in blended learning to improve students’ speaking skills for the eleventh grade students of MAN Salatiga in the academic year of 2018/2019.
2. To find out the improvement of students’ speaking skills by using Webquest in blended learning for the eleventh grade students of MAN Salatiga in the academic year of 2018/2019.
D. Significances of the Research
Hopefully, the result of this research is expected to be some points in teaching and learning process of English. The significance of the research will be useful for the teachers, the students, the researcher, and the other researchers.
1. Practical benefit
a) For the students, the use of Webquest will not only give the students in learning how to speak well but also guide the students through a set of processes and instructions in the right order. In addition it will make the speaking process easier, especially finding the sources of materials.
b) For the teacher, Webquest can be an alternative tool in teaching English, especially to teach speaking. The teachers’ creativity in
22 2. Theoretical benefit
a) The finding of this study can be used to develop the application of the Webquest in teaching learning process of speaking.
b) The finding of the research may be used by the other researchers who want to conduct a research of students’ speaking mastery using Webquest.
E. Hypothesis and Success Indicator
Based on the interview with the English teacher, the students have problems to speak fluently, pronounce the words in correct manner, and the chosen of vocabulary and grammar. The researcher tries to overcome those problems by implementing Webquest in blended learning. By conducting this research, the researcher proposes an action hypothesis: Using Webquest in blended learning can improve students’ speaking skills.
The success indicator of this research was taken from the students’ Basic Competence shown in Lesson Plan (see appendix 3 and 4). The students’ success and failure in doing activities in cycle I and II were
23 F. Research Methodology
1. Research design
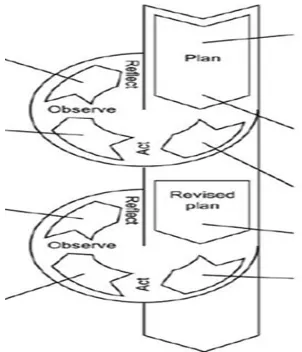
This research was CAR (Classroom Action Research). Action research tried to take a study since it explored whether something caould be done in a better way or not. This type of research was done for the purposes to improve classroom practices. Action research provided a chance for teachers to reflect on their own practices (Cresswell, 2005:550). The researcher used Classroom Action Research because the research wanted to know the implementation of Webquest in blended learning and how far was the improvement of students’ speaking skills after using Webquest in blended learning.
Figure 1.1 The Scheme based on Ke mmis and Mc Taggart (in Mc Niff, 2 002:58)
24
these phases is validated by the previous phase, and looks forward to the next. For example, the action phase is validated b y the planning phase, and look forward to the observation. The cycle can be begin at any stage, and does not stop after one cycle has been completed, but rather begins another one; hence it is a “spiral” rather than “cycle”.
a. Planning
At the planning stage, the researcher formulates some procedural acts how to improve speaking skill by using Webquest in blended learning. The procedures are put in two lesson plans.
b. Acting
At the acting stage, it is the implementation of techniques/procedural acts that have been planned at planning stage.
c. Observing
25 d. Reflecting
Reflection is a research finding analysis. This is used to analyzed based on the data that have been collected in determining the next action. Reflection is used to evaluate teaching- learning process in order to know the improvement of speaking skill.
2. The subject of the research
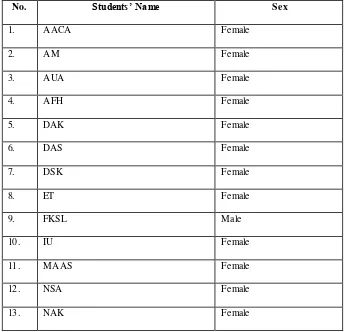
The subject of this study is the eleventh grade students of MAN Salatiga XI MIPA 5 in the academic year of 2018/2019.
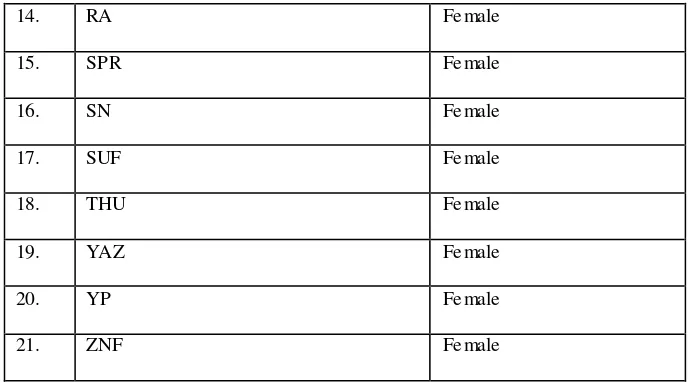
Table 1.1 List of Students’ Name of XI MIPA 5 Class of MAN Salatiga
No. Students’ Name Sex
1. AACA Fe male
2. AM Fe male
3. AUA Fe male
4. AFH Fe male
5. DAK Fe male
6. DAS Fe male
7. DSK Fe male
8. ET Fe male
9. FKSL Male
10. IU Fe male
11. MAAS Fe male
12. NSA Fe male
26
3. The steps of the research
In conducting the research, the researcher listed the steps by summarizing the following research schedule. The research was done on July 2018 until August 2018. The table of the research schedule was arranged as follows:
Table 1.2 Research Sche dule
No. Date and ti me Acti vi ties Place and ti me
1. April, 6th 2018
Giv ing observation letter to one of the admin istration staff at MAN
Salatiga
Giv ing consultation sheet to the head of Curriculu m MAN
Salatiga.
Office staff MA N Salatiga (09.00
WIB)
4. July, 18th 2018
Interview with the English teacher in the preliminary study (before
27
classroom action research) (10.00 WIB)
5. July, 23th 2018 Meet the English teacher to do a
consultation about the lesson plan
Teacher room
Doing action in the c lass (cycle 1) Treat ment
In the classroom of XI MIPA 5 (07.45-09.15)
8. August, 7th 2018
Doing action in the c lass (cycle 1) Post-test
4. Techniques of Data Collection and Research Instrument
Data collecting is used to gather information. In this study the researcher uses four data collection methods namely; observation, tests, and documentation.
a. Observation
28
In conducting action research, the researcher observes the learning process. The learning process is taught by the teacher, while the researcher only observes the teaching learning process. The observation consists of two cycles. There are the cycle I, and cycle II. The researcher uses observation checklist in order to make more systematic and field notes to get more detail information in teaching and learning process. The observation sheet consists of students’ observation checklist, teachers’ observation checklist and
the use of Webquest checklist. The observations checklist are written as follows:
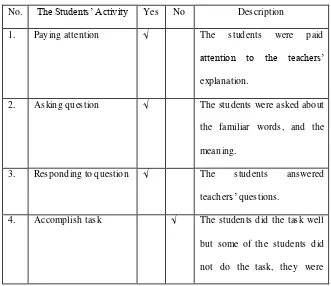
Table 1.3 Students’ Observation Checklist
No. The Students’ Activity Yes No Description
1. Paying attention
2. Asking question
3. Responding to question
4. Accomplish task
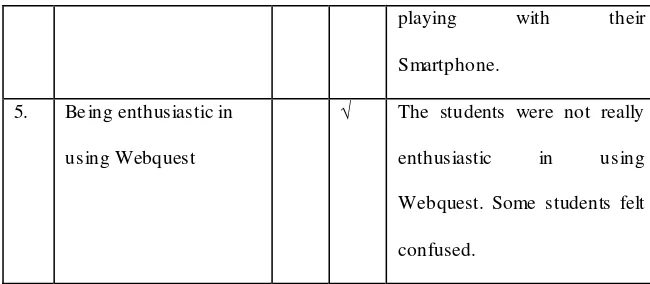
5. Be ing enthusiastic in application
Webquest
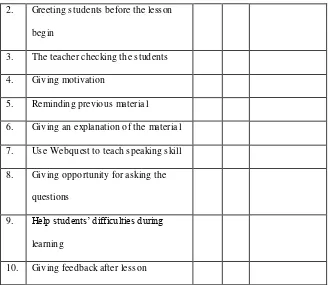
Table 1.4 Teac hers’ Observation Checklist
No. The teachers’ activity Yes No Description
29
2. Greeting students before the lesson
begin
3. The teacher checking the students
4. Giv ing motivation
5. Re minding previous materia l
6. Giv ing an e xplanation of the materia l
7. Use Webquest to teach speaking skill
8. Giv ing opportunity for asking the
questions
9. Help students’ difficulties during learning
10. Giv ing feedback after lesson
Table 1.5 The Use of We bquest Obser vation Checklist
No. Criteria Yes No Description
1. The teacher and the students have
internet access
2. The teacher uses smart phone/laptop
3. The students use smart phone to access
Webquest link
4. The students can access the Webquest
well.
5. The students can follow the
Webquest’s instructions
6. The Webquest is well design and
30
7. The teacher does teaching and learning
process by combining Webquest and using traditional method
b. Test
According to Arikunto (2010:193), test is series of the question as excercises and other tools use to measure the skill, knowledge, intelligence, ability or talent posesed by individuals or group. The researcher uses pre-test and post test.
1) Pre-test
In this research the pre test will be given in the first time. Pre-test is given to the students before the teacher using her media in the teaching- learning process. The objective is to know about the students’ speaking skill before treatment.
2) Post-test
Post test will be given in the last sessions after the media will be applied. The goal of the post-test is to know the improvements of speaking skill after the students got a treatment.
c. Documentation
31
and record videos in doing pre-test and post-test as the documentation of the research.
5. Data Analysis
In analyzing data, the researcher uses mixed methods to analyze the data (Creswell, 2012:16).
a. Qualitative Data
In analyzing qualitative data collected based on words from a small member of individual, thus the participants’ views are
obtained and analyzed the data for description (Creswell, 2012:16). In this research, the data of observation checklist is analyzed by qualitative.
b. Quantitative Data
In the other hand, quantitative technique data analysis is used to process the data. The quantitative data is processed by the teacher and the researcher to get the score of the students. The maximum score is 100. The process measurement based on: 1) Score the students’ test
There are five components in scoring speaking; they are pronunciation, intonation, fluency, grammar, and vocabulary. The researcher uses an analytical scoring rubric to analyze the data related to the students’ speaking test (see appendix
32
2) Calculate the result of the test
After the scoring of students’ test, the researcher calculates the data using the t-test to determine there was a significant difference in cycle I and cycle II. This research uses Statistical Package for the Social Science (SPSS) for analyzing the data. In practice, the researcher will use SPSS version 16.0.
G. Graduating Paper Outlines
This graduating paper has five chapters. Each chapter has different elements as follows:
Chapter I is an introduction. This chapter consists of the background of the research, research questions, objectives of the research, significances of the research, hypothesis and success indicator, research methodology, and graduating paper outlines.
33
the types of Webquest, the elements of Webquest, and how to create Webquest and the previous studies.
Chapter III is the implementation of the research. This chapter consists of procedures of the research.
Chapter IV is research findings. This chapter consists of the research findings and discussion of the research in implementing Webquest in blended learning to improve speaking skill for the eleventh grade students of MAN Salatiga in the academic year of 2018/2019.
34 CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
In this chapter consists of supporting theories and the review of previous research. Supporting theories describe some information related to speaking, Webquest and blended learning.
A. Supporting Theories
1. Speaking
a. The definition of Speaking
According to Nematovna (2016:3) states that “speaking is an active skill”. Additionally, speaking belongs to productive skill because the speakers’ idea, words, feeling etc. are expressed in orally
35
The principle thing in learning English is mastering speaking skill (Ampa, 2013:6). Mostly students presume that they have been succeeding in learning English when they have enhanced their oral language skill. According to Richard (Ampa, 2013:6) proposes that speaking has three functions namely; interaction, transaction and performance function. Interaction function related to the basic social interaction such as greeting and conversation. Transaction function focused on getting goods and services, while performance function refers to the public talk.
According to Thornbury (2005:8) cited in Akhyak & Anik (2013:2) states that speaking is spoken product that related to our daily activities. Speaking relates to the three areas of knowledge; grammar, pronunciation, and vocabulary (Akhyak & Anik, 2013:2). In the other definition, Mart (2012:1) adds that speaking is the skillful in delivering speech, stating or exchanging ideas by using language. Thus, speaking seen as the capability in uttering the words, stating an expression or idea that related with our daily activities which is organized as spoken language production by regarding knowledge, grammar, pronunciation and vocabulary.
36
an interactive process of arranging message which is consists of producing and accepting information (Brown, 1994; Burns & Joyce, 1997 cited in Kosar & Bedir, 2014:2). Therefore, Efrizal (2012:1) emphasizes that speaking is a way to convey the ideas and deliver the message in oral language. Therefore, Eagan (1998) in Kosar &Bedir (2014:2) points out that speaking is the heart of learning second language among the four skills in learning English.
From those definitions, it can be concluded that speaking is a productive skill where speaking in produced from reading and listening. In other words, speaking is a way to communicate, to express feeling, thought, emotion, etc. o the addressee or listener orally. Moreover, speaking is one of the crucial skill among the four skills; reading, listening, and writing, because speaking is used for communication. Whereas, the first thing in learning speaking is be able to apply in daily activities.
b. Types of speaking
According to Brown (2004:271), there are six types of speaking: 1) Imitative
37 2) Intensive
The second type of speaking is designed to demonstrated grammatical or phonological aspect. It can be self- initiated or it can form work activity.
3) Responsive
This type of speaking includes interaction and comprehension at limited level of very short conversation, standard greetings, small talks, and short questions or comments.
4) Transactional (dialogue)
This type of speaking is nearly similar to responsive. The purpose of transactional is for conveying or exchanging certain information. The conversation may have more discussion activity than responsive.
5) Interpersonal (dialogue)
This type of speaking has the purpose for maintaining social relationship than for the transmission of facts and information. 6) Extensive (monologue)
38 c. Ele ments of speaking
The four crucial elements of speaking according to Harmer (2001:269) are the following:
1) Connected speech
The effective English speaker is required not only be able in producing the individual English phonemes (Example: I would have gone) but also in using connected speech (Example: I’d have gone).
2) Expressive devices
English native speaker sometimes change the pitch and stress of utterances. Expressive devices assist the capability in conveying the meaning of the utterances.
3) Lexis and grammar
Lexis and grammar refers to the use of common lexical phrases in the performance language function. The teacher should provide a variety of phrases which have different function. 4) Negotiation language
The negotiation language is required to ask for the clarification when someone is speaking and show the structure from what we are saying.
39
students; 1) pronunciation, 2) grammar, 3) vocabulary, 4) fluency, and 5) comprehension.
d. Aspects of teaching speaking skill
According to Al Hosni (2015:1) states that the main focus in teaching speaking is to enhance students’ spoken language production.
Therefore, the objective of teaching speaking is students are expected be able to communicate English orally (Yustina, 2015:2). Nematovna, (2016:8) says that teaching speaking become a crucial part in learning English as a second language.
In relation of teaching speaking, Brown (2001:275-276) proposes some principle in designing techniques for teaching speaking. Those principles are presented as follows:
1) Use techniques that cover the background of learners needs, from language-based on accuracy, to message-based focused on interaction, meaning and fluency.
2) Provide motivating techniques intrinsically. 3) Encourage the use of authentic language. 4) Giving appropriate feedback and correction.
5) Give students opportunities to start oral communication. 6) Encourage the development of speaking strategies, such as:
a) Asking for clarification (What?).
b) Asking someone to repeat something (Huh? Excuse me?).
40
d) Using conversation maintenance signs (such as; uh, huh, right, yeah, okay, hm).
e) Getting someone’s’ attention (such as; hey, say, so). f) Using paraphrases for structures.
g) Collecting for a help from the interlocutor. h) Using the formula of expression.
i) Using mime and nonverbal expression to convey meaning.
e. Teaching speaking in Senior High School
MAN Salatiga has implemented Curriculum 2013 in the academic year 2018/2019. Kusumaningrum (2013:30), states that in senior high school, the aim of curriculum is, to achieve the communication proficiency. Based on the Standard Competencies and Basic Competencies of curriculum of 2013, English subject involves four basic skills as the main foundation in mastering English. The basic skills that students must achieve are; listening, speaking, reading and writing. Those four skills are the language target development. It means that the students are able to use English as the informational language. There are five components for speaking skills’ assessment;
41
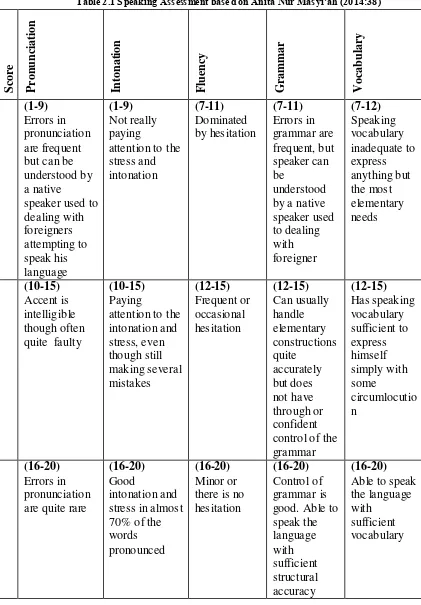
Table 2.1 S peaking Assessment based on Anita Nur Mas yi’ah (2014:38)
42
Categories Score
Very Good 90-100
Good 80-89
Medium 76-80
Enough 70-75
Poor Under 70
f. Proble ms with speaking activities
Students are usually faced by some problems in speaking. Ur (1996:121) mentions several problems with speaking activities as written below:
1) Inhibition
Learners are worried in making mistakes, feel afraid, and even fell shy when getting attention from their classmates on their speech.
2) Nothing to say
Learners cannot think anything to say, they cannot express anything when they feel that they should speak on unfamiliar topic.
3) Low or uneven participation
There is only a participant who dominates to speak during the time, while the other learners have a little speaking time.
4) Mother tongue use
43
Rababa’h (2005) cited in Al Hosni (2014:4) mentions the
other factors that cause difficulty in speaking as written below: a) Students themselves
The students lack of vocabulary and they cannot keep the interaction going on.
b) The teaching strategies
Inadequate teaching strategies and do not emphasize on speaking. Therefore, in changing teachers’ methodology, the
teacher training programs are not successful. c) The curriculum
English is taught separately, the syllabus is not completed and suitable with the students’ communicative
needs.
d) The environment
The lack of environment can be another reason of difficulty in speaking. The huge number of students in a classroom is not appropriate with English teaching periods. e) Lack of motivation to speak English
The students do not realize the real need to learn or speak English. Motivation becomes the important strength which determines the students improve their speaking competency. The developments of speaking skills are laid on students’
44
g. Indicators of Successful Speaking Skills
Learners as the speaker must be able to anticipate and produce the expected patterns of specific discourse situation. They must also manage other elements such as rephrasing, providing feed-back, turn-taking, or redirecting. They must choose the correct vocabulary to describe things, rephrase or emphasize words to clarify the description, and use appropriate facial expressions (Burn & Joyce in Florez, 1991:1).
According to Florez (1999:3-4), the indicators of speaking skills are described as follows:
1) Producing sounds, stress patterns, rhythmic structures, amnd intonations of the language.
2) Using grammar and structure correctly.
3) Selecting vocabulary which is understandable and appropriate for the audiences.
4) Applying strategies to enhance comprehensibility such as rephrasing and emphasizing key words.
5) Using gestures or body language.
6) Paying attention to the success interaction and adjusting components of speech; such as vocabulary, rate of speech, grammar, and structure to maximize the listeners’ comprehension
45
According to Ur (1991:120), states that there are four characteristics of successful speaking as follows:
1) Learners talk a lot
Give much of the period of time for the activity which is filled out by learners’ talk. However, most of the time is filled out by teacher talk or pauses.
2) Participation
Classroom activity is not dominated by talkative learners, all learners have a chance to speak, and there is distribution of speaking time.
3) Motivation is high
Learners have desire to speak, event they have intrinsic motivation to speak, since they are interested on the topic, they have some ideas to express it even they want to take a part to achieve the objective.
4) Language is of an acceptable level
Learners express their self in utterances which are relevant, understandable for others or might be the acceptable of accuracy’s level.
In the other hand, Nunan (1989:32) characterize the indicators of successful speaking as follows:
46 c) An acceptable fluency’s level.
d) Transactional and interpersonal skill. e) Taking short and long speaking shift’s skill. f) Management interaction skill.
g) Negotiation meaning skill.
h) Conversational learning skill (successful conversation consists of good listener as well as good speaker).
i) Comprehension about and negotiation the objective of the conversation.
j) Using appropriate formula and filler.
2. Webquest
a. Definition of Webquest
47
In defining Webquest, March (2003) in Marco (2015:7) adds that Webquest provides scaffolding organized as web pages resources and the original task to encourage students to do activity in learning English more skillfully. Marco (2015:18) adds that Webquest needs computer and internet access. At least a group or students have a computer to work with, so that the students will work it at home autonomously
Nowadays, Webquest has got a great attention for teachers or educators. Therefore, the use of technological tool and internet such as Webquest may help students to overcome the difficulties in learning English and improving students’ speaking skill. Abbit & Ophus as
cited in Balkissoon et al. (2014:2) prove that Webquest can improve students’ specific subject skill by using internet technology to access
the web resources. Al Masri et al. (2011:2) reinforce that Webquest is designed not only for looking at it, but also focus ing on the information because through Webquest can enhance students’ level of
evaluation, synthesize and analysis the data.
Web-based learning offers a wide of chances for teaching and learning and getting a broad internet access to find new knowledge and information (Sadikin, 2015:2). In add ition, Chang et al. (2011:2) reinforce that combining Webquest can bring about the new learning environment for the students and Webquest can improve students’
48
any information required to complete their task well. Therefore, Viddoni & Maddux (2002) as cited in Chang et al. (2011:2) explore that the advantage which can benefit from Webquest is; foster the students’ learning skill by permitting the students in searching for any
information that related to the task rather than searching for it alone.
Webquets has many advantages, as stated by Irzawati and Asiah (2013) cited in Sorcia et al. (2017:4) conclude that Webquest is beneficial, attracting, enjoyable, and motivated students in learning grammar. They teach English course for TOEFL, Webquets is designed to help their students study grammar. It proves that Webquest is applicable for any courses. In identifying another advantage of Webquest, Gonzales in Sorcia, et al. (2017:4-5) mentions that he designed Webquest to teach vocabulary and grammar, Webquest can bring successful activity because the students were motivated and participated.
49 b. Types of Webquest
Marco (2015:8) identifies that there are two kinds of Webquest based on the task duration where each type has different purposes but the same methodology.
1) Short-term Webquest
Short-term Webquest means that one class session is wrapped up into three class sessions. The primary aim is that students be able to achieve knowledge through the organization and acquisition of the information obtained.
2) Long-term Webquest
On the one hand, long-term Webquest commonly take for a week and a month classroom session. The main purpose is to process the knowledge about certain topics, but learners must process the new knowledge through involutes process. Additionally, they will be able to transform and understand it through online or offline (Dodge, in Marco, 2015:8).
c. Elements of Webquest
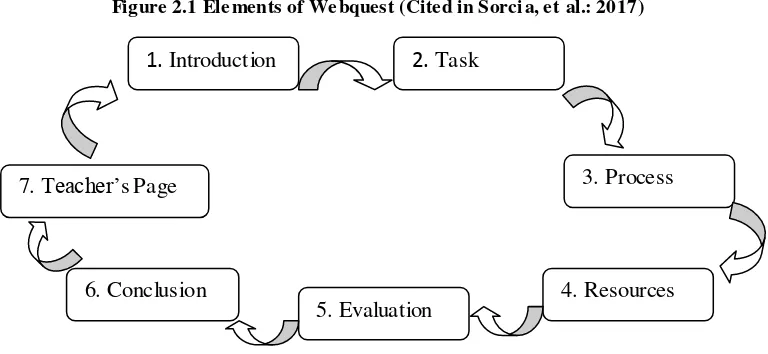
Dodge (1997) in Sorcia et al. (2017:2-3) states that there are six processes are well designed as follow:
1) Introduction
The objective is to attract student’s attention in order to make it
50
presents topic visually more attractive, relevant to the learners and the goal.
2) Task
This part is focused on what learners must to do; it could be problems or situation to be solved.
3) Process
This phase is where teacher guides the students by doing different steps in order to reach the goal by tasks itself. Additionally, the tasks can be divided into some sub-tasks. It may include students’ role or teacher’s guide.
4) Resources
This section the teacher provides a list of web pages which is relevant to the topic to complete the tasks. The students must read, watch, or search for more information. The teacher not only provide a number of web pages but also another resources; video, songs, maps etc.
5) Evaluation
Evaluation uses different evaluating sc ale to measure the quantity of student’s works.
6) Conclusion
51
it used to encourage students to keep on searching about the topic they get.
7) Teacher’s page
In the last part of Webquest consists of the identity or curriculum vitae of teacher. It might be included to the Webquest itself or not.
Figure 2.1 Ele ments of We bquest (Cite d in Sorci a, e t al.: 2017)
d. How to create Webquest in the classroom
According to Suraya (2011:32) Webquest can be used in for students, individual, small group and even a big class. Webquest also can be used on- line and off- line by using a set of computer. There are many ways to create Webquest in the classroom which written as follows:
1) Using the computer lab-whole class access (a) Class teams
Classes are divided into teams, working on different Webquest but doing the same topic.
1. Introduction 2. Task
5. Evaluation 4. Resources 3. Process 7. Teacher’s Page
52 (b) One Webquest focus
Classes can work together by accessing one Webquest, but each group will conclude its own result.
(c) Limited access to the laboratory
Classes only have weekly access in the lab, thus the students have to do on-line research activities and leave off- line session in the classroom or library.
2) Computer stations-part class access (a) On-line and off- line work
If there is limited access for on- line, some of students could take turn in using the computers while the others could use another method.
(b) Using the library
The library can be used a place where some groups work in off- line way with a teacher, while the other groups work in on-line way.
(c) Rotation
Webquest can be used for classes in rolling; all activities might be focus on the same topic.
3) Access to one or two on- line computers- individual students access (a) Everyone has a turn; it means that individuals rotate their teams in
53
(b) The teacher chooses on students in each group to investigate using the computer, the teacher limits the usage of computer. 4) No computers available on- line – no students access
(a) Working on community members (b) Involving parents or guardians (c) Using stand alone computers (d) Downloading information
3. Blended Learning
a. Description of Blended Learning
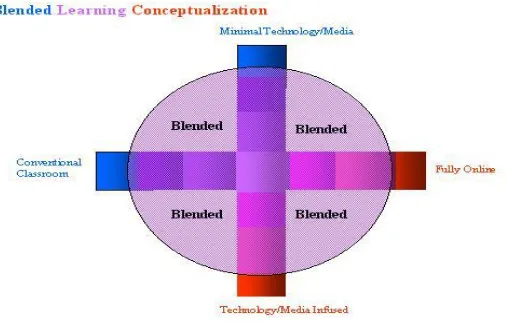
Blended learning is being popular in education context. According to AbouRezk (2014: 7), explicates that blended learning integrates face to face teaching method with computer based activities to make an integrated teaching approach. Kennedy (2014) in AbouRezk (2014: 6) , mentions that blended learning called as a strategy in helping teachers to achieve the things what must done in order to get a deeper comprehension and make the students to work with. Moreover, Torris et al. (2013:3) point out that actually the term blended learning refers to the utiliz ing of technology and face to face teaching interaction.
54
of face to face teaching technique and online interaction. Therefore, Vernadakis et al. (2012:1) emphasizes that blended learning is teaching and learning process happened in both of face to face classroom and online. Moreover, blended learning is defined as the composite between web and individual interaction of teacher and students which use both of them; web and individual interaction (Aleksic & Ivanovic, 2013:1). According to Akkoyunlu & Soylu (2008:1) point out that blended learning atmosphere can combine the benefits in e- learning teaching method between the profits in traditional teaching method.
According to Sen (2011:1) defines that blended learning as follows: Blended learning can be seen as the combination of online and face to face learning, its aim is providing the efficient and effective teaching instruction by combining both of them. Blended learning called as hybrid learning where the face to face interaction combined with online activities. Blended learning is the combination of classroom face to face teaching and learning between online teaching and learning.
55
Figure 2.2 the c once pt of Blende d Lear ning as cite d in Picciano (2006:5)
As stated by Dziuban cited in Aleksic &Ivanovic (2013:1) mentions that blended learning has three advantages, such as better in accessing information, better of interaction and have a better pedagogic skill. Furthermore, Zhang & Han (2012:3) define that “Blended learning is rooted in the idea that learning is continuous process and blending provides more various benefits than using any single learning delivery type alone”. In addition, Le Kedong & Zhao Jianhua (2004) in Zang & Han
(2012:3) emphasize that blended learning used to apply for different media and method in transforming information. In the other hand, “the term
blended learning environment is commonly used to define as a learning environment which combine face to face (F2F) and online components”
(Kiraz, et al., 2012:2).
56
can be combined with traditional teaching method where the learning model still apply face to face classroom besides online activities.
b. Levels of Blended Learning
According to Graham (2006:11-12), there are four levels of Blended Learning namely:
1) Activity- Level Blending
This level occurs when the learning activities consist of face to face and computer mediated.
2) Course-Level Blending
Course level blending is the common way to blend. This level requires the combination of different face to face activities and computer mediated activities that used as a part of lesson.
3) Program-Level Blending
Ross and Gage (Graham, 2006:12) states that program level blending is occurred in higher education.
4) Institutional-Level Blending
Many institution or higher education creates models for blended learning. They blend face to face and computer mediated.
57
Students can be blended in face to face classroom and online learning activities environment. Students can be blended in face to face classroom with different students but in online environment. Students in face to face classroom are blended with other teacher or tutor through online environment.
c. Steps in Blended Learning
According to Soeakartawi in Felicia (2015: 13-14), there are six steps of blended learning. The steps are described as follows:
1) Determining teaching materials step.
2) The step of planning implementation of Blended Learning which is used.
3) Determining the format of online learning whether the materials are available in html format thus the materials can be cut and paste easily or in PDF format.
4) The implementation of Blended Learning while assigning instructor (teacher).
5) The testing of planning implementation which is made.
6) The criteria preparation for evaluating in doing Blended Learning.
B. Review of the Previous Research
There are some previous researches which are used in this research. The researcher takes three previous researches comparison.
58
teach writing descriptive text to grade XI of SMA Nasima Semarang and also to find out how well the use of Webquest as an alternative tool in teaching writing descriptive. The population of this study was grade XI of SMA Nasima Semarang. The number of the subject were 21 students. There were five meetings in the research. One meeting was for the pretest. Four meetings were for the treatments and the post test was hold in the last meeting. The students’ descriptive text in the second cycle was considered
as the post-test result. The result of this research showed that the post-test score was better than the pre-test score. The mean score of the pre-test was 64.57 and 82.42 in the post test. The difference between pre test and post test was 17.85.
The second research was conducted by Franco in 2016. The research was experimental study. The purpose of the research was to assess the impact of using Blogs and Webquets in students’ learning performance
59
hypothesis was accepted at the 0.5 level based on the post-test result. For the qualitative data, the researcher used the phenomenology type of qualitative research because it analyzed and described students’ reactions,
experiences, and feelings toward the tasks. The result of phenomenological presented students’ perceptions in terms of motivation
when being exposed to the blended learning instruction.
The third research was conducted by Abdulaal (2017). The method of the research was experimental study. The objective of the research was to identify the impact of multiple intelligences by using Webquest to develop speaking skill and provide teachers with effective methods and activities to teach speaking. The methodology of this research was experimental research. The subject of the research was first- year secondary female students (15-16 years old) of Al- Azhar Institute. The students were divided into two groups, experimental students (30 students) and control students (30 students). The researcher used pre-test and post-test to measure students’ speaking skill before and after the treatment. In data
60
could be concluded that students’ overall performance in speaking on the post-test as compared to the pre-test had improved.
The fourth research was done by Tuan (2011). The method of the research was Classroom Action Research. The objectives of this research were to examine the implementation of Webquest to enhance students’ reading skills, and to explore students’ attitude toward Webquest-based
teaching of reading. The participants were the second year students of University SSH-HCMC of Vietnam. The numbers of the participants were 44 students; 26 females and 18 males who attend Reading 3 course. The instruments of the research were; pre-test, post-test and online questionnaire to collect quantitative data. The findings of the research indicated that across all 44 students have improved by 12.14 points (41.91 – 29.77) after 14 weeks in applying Webquest in teaching reading.
Therefore, the significance value was less than 0.01. The result from the pos-test proved there was an effect of Webquest in teaching reading. Meanwhile, the questionnaire showed that over half of students (55%) agreed that they would continue to use Webquest and 45% of the students agreed that they would stop to use Webquest. Therefore, 60% of the students will tell about the use Webquest to others. The finding of the research proved that the use of Webquest could improve students’ reading
61
62 CHAPTER III
IMPLEMENTATION OF RESEARCH
A. The Procedures of the Research
The researcher uses the Classroom Action Research in collecting the data. There are four steps in one cycle for doing actions research those are planning, observing and reflecting. In this research, the researcher conducts the research into two cycles; cycle I, and cycle II. The researcher collaborated with the English teacher who teaches XI MIPA 5 students. The activities of each cycle as follows:
1. Cycle I
The researcher uses Webquest as media in blended learning which can improve the students’ speaking skills. The topic is asking and giving opinion. The procedures as below:
a. Planning
At planning stage, the researcher plans what actions will be done in using and applying Webquest in blended learning to teach speaking skills. The activities were presented as below:
1) Selecting the materials with teacher based on the syllabus. 2) Preparing the materials, making the lesson plans and designing
63
3) Preparing teaching aids by the theme “Giving opinion about the latest movies” and designing Webquest (example: video
about asking and giving opinion, picture, a sheet of paper and the website link of Webquest).
4) Preparing students’, teachers’ and the use of Webquest observation checklist of the cycle I (to know the situation of the teaching and learning process when the media is applied). 5) Preparing the pre-test and post-test in cycle I.
6) Preparing the list of students’ name and scoring of cycle I. Those preparations are designed to obtain the objective of the teaching and learning process. Students are supposed to improve their speaking skills through the materials were given.
b. Acting
After the preparation has been done, the teacher does teaching-learning process. At this section, the teaching-learning process is led by the teacher. In the acting phase as the implementation of the preparation, the researcher presented as written below:
1) Giving pre-test and post-test for students.
2) Giving the materials and explain the expression of asking and giving opinion, language feature of expression.
64
4) Explaining the materials and the implementation using Webquest as media in blended learning to teach asking and giving opinion expression.
5) Giving the Webquest link. Ordering the students to access Webquest link which consist of the materials about asking and giving opinion expression.
6) Giving occasion for the students to ask any difficulties accessing Webquest or the sites in the learning process.
7) Ask the students to make a dialogue using asking and givng opinion expression based on the Webquests’ tasks in a
workgroup discussion. At this phase, the teacher and the students are work together. Students obtained the materials deeply. Meanwhile, the teacher helps, guides and monitors the students.
8) Giving chance for the students to present their work in front of the class.
9) Giving post-test.
c. Observing
The researcher observes the students and teacher activity by using observation checklist.
d. Reflecting
65
process, problems, and real issues in the action. Reflection is an evaluation phase, it used to evaluate whether or not the media can be the problem solving and improve students’ speaking skill.
1) The researcher evaluated the activities that have been done. 2) The classroom teacher and the researcher discuss to make a
reflection what will they do to correct the problems.
3) Analyzing the data from the observation checklist and students’ score of the test in the cycle I.
2. Cycle II
The second cycle is done based on the reflections’ result of the
cycle I. If the result of the observation shows the low quality of students’ skills, thus it is needed another action which is aimed to create an improvement of students’ quality in the cycle II. The topic
will be different from the cycle I, the topic is asking and giving opinion about the famous figure. The procedures are presented as below:
a. Planning
In the planning phase of the cycle two, the researcher will do some activities that will be arranged as follows:
1) The researcher identifies the problem and makes the solution for the problems.
66
3) Preparing and reselecting teaching aids with the theme asking and giving opinion about famous figure (example: video, picture, illustration of the situation, Webquest link, and sheet of paper).
4) Preparing students’, teachers’ and the use of Webquest observation checklist of cycle II (in order to know the situation of teaching- learning process when the technique is applied). 5) Preparing pre-test and post-test of cycle II.
6) Preparing the list of students’ name and scoring of cycle II. The preparation is designed in order to gain the purpose of the teaching- learning process. Students are supposed to improve their speaking skills by the materials which are given.
b. Acting
In the cycle II acting phase is quite similar to the acting in cycle I. In this phase, the teaching and learning process is led by the teacher. The activities of acting phase in the cycle II are:
1) Giving pre-test for students.
2) Giving materials and explain asking and giving opinion expression and the language feature.
67
4) Giving more explanation about the materials and the implementation of using Webquest as a media in blended learning to teach speaking skill.
5) Giving the other example of asking and giving opinion through Webquest link.
6) Giving occasion for the students to ask any difficulties while using Webquest in the learning process.
7) Ask the students to make a dialogue by using asking and giving opinion expression based on Webquest Process in a workgroup discussion. At this phase, the researcher and the students are work together. The students obtain the materials deeply. Meanwhile, the teacher helps, guides and monitors the students.
8) Giving chance for students to present and discuss their knowledge in front of the class with their group.
9) Conclude the materials and giving feedback after the lesson. 10) Giving post-test
c. Observing
The researcher observes the students and the teachers’ activity by using observation checklist.
d. Reflecting
68
action. This is used to record what happened in the observation stage.
B. The minimal standard of successful
69 CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DATA ANALYSIS
This chapter focused on analyzing the collected data. The researcher collected the data from the eleventh grade students of MAN Salatiga. The researcher gave the details of the findings. This chapter was the main discussion of the research conducted. It presented the finding of the collected data starts from the beginning until the end of the research. The finding consists of the result of the cycle I and cycle II. Those two cycles were the treatments of the implementation using Webquest in blended learning to improve speaking skill.
A.
The Result of the ResearchThe research consists of two cycles, each cycle consists of planning, acting, observing and reflecting. The whole steps of the research would be explained in the description as follows:
1. Research Finding
The research consists of two cycles, each cycle consists of planning, acting, observing and reflecting. The whole steps of the research would be explained in the description as follows:
a. Cycle I
1) Planning
70 a) Lesson plan
The researcher used two lesson plans to control and manage the teaching and learning process in this research. It is aimed to manage in managing the time and activities during the teaching and learning process in the class (see appendix 3).
b) Observation checklist
Observation checklist was arranged to know the students’ and teachers’ activities during the teaching and learning
process. c) Material
The material of speaking skill was Asking and giving opinion which consists of the purpose, language feature and the example.
d) Teaching aid
The researcher prepared some instruments. They were board-marker, Power Point Presentation, LCD, laptop, speaker, Webquest link and handout for students (asking and giving opinion). The researcher also prepared the materials and tools in succeeding the action.
e) Pre-test and post-test
71
media to know the students’ speaking ability in asking and giving opinion.
2) Acting
The researcher conducted in three days. The action of the cycle I consist of three parts. The first part was done on Tuesday, July 24th, the second part was done on July 31th and the third part was done on August 7th, 2018 at 07.45 a.m until 09.15 a.m. The pre-test and treatment were conducted in day 1 and treatment and post-test was conducted in day 2. The researcher rolled as an observer and observed teachers’ and students’ activity in teaching
learning process. The researcher had a partner to take photos and videos in pre-test and pos-test for documentation.
The first part of cycle 1 was conducted o n Tuesday, 24th July 2018, at 07.45 a.m., the teacher and the researcher entered the class. Before started the lesson, the teacher informed the students that a few days later the class would be observed by the researcher. The teacher started the lesson by greeted and asked about their condition such the following short co nversation: Teacher: “Assalamu’alaikum?”
Students: “Wa’alaikumussalam, Miss”
72 Students: “Good morning Mom” Teacher: “How are you today?” Students: “I’m fine and you?” Teacher:“I’m fine too, thank you”
The teacher mentions the purpose of coming in the class; then the researcher introduced herself to the students. After that, the teacher checked the students’ attendance list. After checked the attendance list, the teacher told that they would have a pre-test. The teacher gave a sheet of paper for the students to give an opinion about the picture and give their own reasons (see appendix 5). Then the teacher gave 45 minutes for the students to practice in giving opinion about “the picture what they have chosen”. 10 minutes for preparing their answer, and 35 minutes
for practice one by one. The teacher asked the students to do by themselves, and also allowed the students to open dictionary and internet.
When the students were doing the pre-test, the teacher walked around the class to check the students while doing the test. Two boys, “DA and FM” who sit in the back chair did not focus; they