commit to user
OPTIMIZING YOUTUBE VIDEOS TO ENRICH STUDENTS’
VOCABULARY
(An Action Research at the 5th Grade Students of SD Negeri Sanggrahan Surakarta in Academic Year 2009 / 2010)
ERNA TITIS ISMAWATI
X 2208514
A THESIS
Submitted to the Teacher Training and Education Faculty of Sebelas Maret
University as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement
for the Undergraduate Degree of Education
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
TEACHER QUALIFICATION PROGRAM
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
SEBELAS MARET UNIVERSITY
SURAKARTA
commit to user
commit to user
commit to user
iv
ABSTRACT
Erna Titis Ismawati. X2208514. OPTIMIZING YOUTUBE VIDEOS TO ENRICH STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY (An Action Research at the 5th Grade Students of SD Negeri Sanggrahan Surakarta in Academic Year 2009 / 2010). Teacher Training and Education Faculty. Sebelas Maret University. 2011. The objectives of the research are: (1) to identify whether or not and to what extent YouTube videos can enrich the students’ vocabulary; and (2) to describe the situation when YouTube videos are applied during the teaching learning process.
This research was carried out at SD Negeri Sanggrahan Surakarta. It was conducted from April up to June 2010. The subject of the research was the fifth grade students of SDN Sanggrahan Surakarta in the academic year of 2009 / 2010. The research method was Action Research and it was conducted in two cycles. In collecting data, she used interviews, observation, diaries, document, and test. Having collected the data, she analyzed them both qualitative and quantitative data.
To identify whether and to what extent YouTube videos can enrich the students’ vocabulary and to describe the situation, the research findings show YouTube videos can enrich: (1) The students’ vocabulary which includes: (a) The students could ponounce some English words correctly; (b) The students could mention words they already learn before; (c) The students could spell some English words correctly; (d) Thestudents could recognize words well and (e) The students know the meaning of some English words well; and (2) Classroom situation. The classroom situation shows that: (a) The students do not make noise in the class; (b) The students be active in answering tasks given by teacher; (c) The students take note to the important things taught; (d) The students give their attention to learn English and; (e) The students are not busy doing non academic things anymore.
The students’ achievement also increased. The enrichment of the students’ achievement can be seen from the students score from pre-test until post-test 2. In pre-test, they scored only 42.64 in average; in post-test 1 they scored 56.17 in average; and in post –test 2 they scored 74.64 in average, it is higher than the English passing grade (KKM /Kriteria Ketuntasan Minimal), that is 60.
commit to user
v
MOTTO
“
Ikhlas adalah kompetensi tertinggi dalam hidup”.
commit to user
vi
DEDICATION
This thesis is whole-heartedly dedicated for:
♥
My Beloved Father and Mother
♥
My Dearest Husband and Sons
commit to user
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Subhanallah Walhamdulillah Wa laailaaha Illa Allah Wallaahu Akbar. Maha suci Allah, Segala puji bagi Allah, Tiada Tuhan selain Allah, dan Maha Besar Allah who has given His blessing, charity, love, and guard, so it is possible for the writer to finish this thesis. Regarding the completion of this thesis, the writer would like to express her high gratitude to:
1. The Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of Sebelas Maret University for giving his permission to write this thesis.
2. The Head of Art and Language Education, and The Head of English Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty, for their approval of this thesis.
3. Dra. Hj. Dewi Rochsantiningsih, M.Ed., Ph.D., the first consultant, and Drs. A. Handoko Pudjobroto., the second consultant, for their priceless critical advice, guidance, encouragement, suggestion, correction, contribution, patience and support for the writer to complete this thesis.
4. Sri Idayati, A.Ma Pd, the Headmistress of SDN Sanggrahan Surakarta, Farida, SS, the English teacher and Dewi Chandra, the observer for permitting and helped her to carry out this study and collecting the data. 5. The fifth grade students of SDN Sanggrahan who have participated well
during the research and helped her by joining the test.
6. Her beloved mother, father, and brothers for their loves and best wishes. 7. Her beloved husband “M3” and her beloved sons “Teto and Hilmi” for their
love, spirit, time to share stories, smile and the beautiful days.
Finally, the writer hopes this thesis would be worth reading for all the readers and also can give contribution and advantageous in teaching learning process. This thesis is nothing but a senseless thesis without their help, support, and love. The most certainly, this thesis would not be finished without Allah’s Hands. The writer realize that this thesis is still far from being perfect. Any criticism from the readers for the improvement to this thesis will be gratefully accepted.
Surakarta, April 2011
commit to user
viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE... i
APPROVAL...ii
LEGITIMATION...iii
ABSTRACT...iv
MOTTO ...v
DEDICATION ...vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ...vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS...viii
LIST OF TABLES ...x
LIST OF ABBREVIATION ...xi
LIST OF APPENDICES ...xii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION ...1
A. Background of the Study...1
B.Problem Statements...3
C.The Objectives of the Study...3
D.The Benefits of the Study...4
CHAPTER II REVIEW OF THE RELATED LITERATURES ...5
A.Vocabulary ...5
1. The Definition of Vocabulary ...5
2. Kinds of Vocabulary ...7
3. The Importance of Vocabulary ...8
4. Vocabulary Test Scoring Rubric...9
5. Teaching and Learning Vocabulary...10
B. YouTube Videos ...12
1. The Benefits of Video...13
2. Teaching Vocabulary Using YouTube Videos...15
3. The Criteria for Selecting Video...17
C. Young Learners...17
commit to user
ix
2. Teaching Video to Young Learners ...20
D. Review of Related Researchers ...21
E. Rationale...23
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ...25
A. The Context of the Research...25
1. Research Setting ...25
2. Subject of the Research...26
B. The Method of the Research ...26
1. The Definition of Action Research ...27
2. The Characteristics of Action Research...28
3. The Model of Action Research ...29
4. The Stage of Action Research...30
C. Data Collecting ...32
D. Data Analysis ...34
CHAPTER IV RESEARCH FINDING AND DISCUSSION...37
A. Research Findings...37
1. Situation Before Research...38
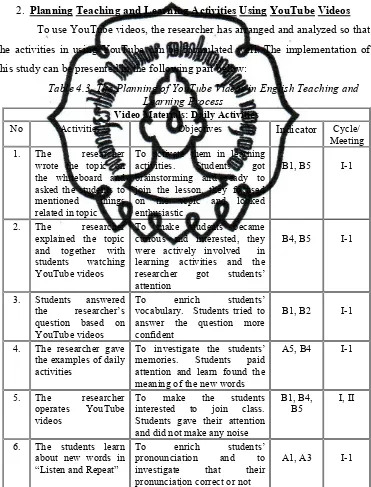
2. Planning TL Activities Using YouTube Videos ...40
3. Research Implementation...42
4. Research Findings ...64
a. The Enrichment of Students’ Vocabulary ...76
b. The Enrichment of Classroom Situation ...77
B.Discussion ...78
1. YouTube Video can Enrich Students’ Vocabulary ...79
2. YouTube Video Changes Classroom Situation ...80
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION, IMPLICATION AND SUGGESTIONS...84
A. Conclusion ...84
B. Implication ...85
C. Suggestions ...86
BIBLIOGRAPHY ...88
commit to user
x
LIST OF TABLES
1. Table 2.1 Student Oral Language Observation Matrix _______________ 10 2. Table 3.1 The Schedule of the Research__________________________ 25 3. Table 3.2 The Data Collecting _________________________________ 32 4. Table 4.1 The Overall Process of Research _______________________ 37 5. Table 4.2 Situation Before Research_____________________________ 38 6. Table 4.3 The Planning of YouTube Videos in English TLP __________ 40 7. Table 4.4 List of Indicators of Problems as Being
Enriched by the Learning Activities Using YouTube Videos _________ 42 8. Table 4.5 Summary of Research Implementation___________________ 43 9. Table 4.6 The List of Daily Activities ___________________________ 51 10. Table 4.7 The Enrichment of Meaning Aspect Cycle 1 ______________ 53 11. Table 4.8 The Enrichment of Spelling Aspect Cycle 1_______________ 54 12. Table 4.9 Enrichment of Pronunciation Aspect Cycle 1______________ 54 13. Table 4.10 The Examples of the Sentences Using in
YouTube Videos ____________________________________________ 58 14. Table 4.11 The Enrichment of Meaning Aspect Cycle 2 _____________ 61 15. Table 4.12 The Enrichment of Spelling Aspect Cycle 2______________ 61 16. Table 4.13 The Enrichment of Pronunciation Aspect Cycle 2 _________ 62 17. Table 4.14 The Comparison between the Situation before
commit to user
xi
LIST OF ABBREVIATION
commit to user
xii
LIST OF APPENDICES
No. List of Appendices
1. Pedoman Wawancara Dengan Siswa Dan Guru
2. Transkip Hasil Wawancara Dengan Guru (Pre Research) 3. Transkip Hasil Wawancara Dengan Siswa (Pre-Research) 4. Catatan Lapangan Hasil Observasi (Pre-Research)
5. Transkip Wawancara Dengan Pengamat (After Research) 6. Transkip Wawancara Dengan Siswa (After Research) 7. Catatan Lapangan Hasil Penelitian
8. Lembar Pengamatan Jalannya KBM
9. The Researcher’s Diary
10. Lesson Plan
11. Daftar Nilai Siswa
12. The Photographs
13. Transkip of YouTube Videos
14. Transkip of Pre-Test, Post-Test 1 and Post-Test 2 15. Keys for Worksheets and Tests
16. Blue Print
commit to user
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study
Vocabulary is an important element in second language acquisition. It is an element that links the four skills of language like listening, speaking, reading and writting all together, that is why it is undeniable that vocabulary has been considered the crucial component of learning a foreign language. “Without grammar very little can be conveyed, without vocabulary nothing can be conveyed.” This is how the linguist David Wilkins summed up the importance of vocabulary learning. Vocabulary is the first step to be taught before teaching other aspects of the language because vocabulary as one of the most aspects and becomes a central part of the foreign language learning.
SDN Sanggrahan Surakarta is one of elementary school that has decided to include English as a local content in its curriculum. In reality, English especially for the beginners level are often faced with the problem of vocabulary. It is proved from the observation done by the writer to the fifth grade students in SDN Sanggrahan Surakarta. The writer found that children as the learners face some obstacle in vocabulary competence, and it can be seen from the students’ answer when they are asked about English, i.e. Bahasa Inggris sulit, Bu, membacanya
beda sama tulisan, artinya juga tidak tahu, sering lupa dan gak asyik, etc. From
these statements, the writer concludes that some problems come up dealing with vocabulary. The indicators are: (1) The students usually make mistakes in pronouncing the words; (2) The students get difficulties to mention words they already learn before; (3) The students get difficulties to spelling the words; (4) Thestudents get difficulties in recognizing words; (5) The students get confuse in meaning of English words.
commit to user
By doing so, the writer found some factors causing those problems. They are: (1) The students usually make noise in the class; (2) The students passive in answer tasks given by teacher; (3) The students do not take note the important things taught; (4) The students’s attention to learn English is not optimal; (5) The students busy doing non academic things with their friends.
After observing the instructional process at the fifth grade students of SDN Sanggrahan, it can be identified that several problems occured during the teaching-learning activity. They are: (1) The technique applied by the teacher is not appropriate enough related to the topic or material, situation and condition. The teacher only gives some English words then translate them; (2) The teacher only focuses on the writing skill. The students asked to remember letter of words, write the words mentioned by the teacher, that is the teacher tends to use written form first than oral in introducing the English words; (3) There is no media use in teaching and learning process. From the interview and observation, the researcher find out that the teacher does not use any media in teaching and learning process. The teacher only uses text book in teaching and learning process. The teacher finds that the students are not interested in learning English. The low interest in learning causes the students pay little attention to the teacher’s explanation.
commit to user
to the study already under way about to be undertaken. Also, learning can be increased by repeated showing on the video as well as pre-testing and post-testing.
In conducting vocabulary activity, teacher can enrich learning video by providing for participation or repetitive experiences related to video content. Here, the researcher uses YouTube videos. YouTube as one of the video sharing website which users can upload and share videos, and view them in various format (ComScore, 2007. Accessed from internet on Wednesday January 20th 2010).
This study explores the use of YouTube videos in teaching vocabulary for elementary school students. By using YouTube videos, it is hoped that the students feel more interested in learning English, it gives the students opportunities to recall new words easily and finally, it is also hoped that YouTube videos can be used as one of the enjoyable alternatives in teaching English vocabulary to the elementary students especially at the fifth grade of SDN Sanggrahan Surakarta.
B.Problem Statements
The problems of this study that will be analyzed are:
1. Does and to what extend the implementation of YouTube videos can enrich the students’ vocabulary?
2. What is the situation if YouTube videos applied during teaching learning process at the fifth grade students of SDN Sanggrahan Surakarta?
C.The Objectives of the Study
The objectives of this research are:
1. To identify whether or not and to what extent YouTube videos can enrich the students’ vocabulary.
commit to user
D.The Benefits of the Study
In writing this thesis, there are some benefit to gain such as the followings:
1. For the English teacher.
This thesis is expected that through this study the English teacher know the problem that arise during teaching and learning process in enriching vocabulary, it may help the English teacher in choosing an appropriate technique so that the students can get better result in competencing English vocabulary.
2. For the students.
By applying YouTube videos, the students at the fifth grade of SDN Sanggrahan Surakarta is expected can enrich their vocabulary, so they can enjoy the teaching learning process and they do not think that English is a difficult lesson anymore.
3. For the school.
This thesis is expected to give contribution to elementary school to increase its quality in teaching the second language, especially can be useful input for teaching English in SDN Sanggrahan Surakarta.
4. For the other researcher.
commit to user
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF THE RELATED LITERATURES
A.Vocabulary
1. The Definition of Vocabulary
Vocabulary is one elements of language that should be learnt and taught. It takes such as important basic role in mastering English as a foreign language. Vocabulary is important for someone or learner to master it of language because it is essential part of communication. Krashen (1995: p.155) said that vocabulary is basic to communication. If acquirers do not recognize the meaning of the key words used by those who addresses them, they will be unable to participate in conversation. According to Hatch and Brown (1995: p.1), the term vocabulary refers to a list or sets of words that individual speakers of a language might use. Another definition is states by Burns and Browman (1975: p.295) they state that vocabulary may be defined as the stock of words used by a person, class, or profession. Then they added that words are symbols of ideas; to express and communicate ideas, one needs facility in the use of words, it influences how one sees the world and what one may think of it. Hornby (1995: p.1331) states that vocabulary is the total number of the words (with their meaning and with the rules for combining them) make up the language. Caroline (2006: p.121) says that vocabulary is the collection of words that an individual knows
Another definition of vocabulary is stated by Ur (1996: p.60), She states that vocabulary as the words we teach in a foreign language. She also gives some elements that need to be taught in teaching vocabulary as follows:
(a) Form: Pronunciation and Spelling.
The learner has to know how a word is pronounced (its pronunciation) and what it looks like (its spelling). These are fairly obvious characteristics, and one or two other will be perceived by the learner when encountering the item for the first time. In teaching, the teacher needs to make sure that both these aspects are accurately presented and learned.
commit to user
(b) Grammar.The grammar of a new item will need to be taught if this is not obviously covered by general grammatical rules. An item may have an unpredictable change of form in certain grammatical contexts or may have some idiosyncratic way of connecting with other words in sentences; it is important to provide learners with this information at the same time as the teacher teach the base form.
(c) Collocation.
The typical collocations of particular items are another factor that makes a particular combination sound “right” or “wrong” in a given context. So, this is another piece of information about a new item which it may be worth teaching. Collocation are also often noted in dictionaries, either by providing the whole collocation under one of the head–words, or by a note in parenthesis.
(d) Aspects of Meaning (1): denotation, connotation, appropriateness.
The meaning of a word is primarily what it refers to in the real world, its denotation; this is often the sort of definition that is given in a dictionary. For example, dog denotes a kind of animal; more specifically, a common, domestic carnivorous mammal; and both dank and moist mean slightly wet. A less obvious component of the meaning of an item is its connotation: the associations, or positive or negative feelings it evokes, which may or may not be indicated in a dictionary definition. The word dog, for example, as understood by most British people, has positive connotations of friendship and loyalty; whereas the equivalent in the arabic, as understood by most people in Arab countries has negative associatios of dirt and inferiority. (e) Aspects of Meaning (2): meaning relationships.
commit to user
Hyponyms: items that serve as specific examples of a general concept; dog,
lion, mouse, are hyponyms of animal; 4) Co-hyponyms or co-ordinates: other
items that are the “same kind of thing”; red, blue, green, and brown are co-ordinates; 5) Super ordinates: general concepts that “cover” specific items;
animal is the super ordinates of lion, dog, mouse, etc; 6) Translation: words
or expressions in the learners’ mother tongue which are (more or less) equivalent in meaning to the item being taught.
Based on the definition above it can be concluded that vocabulary is total numbers of words in a language that individual speaker might use to convey their meanings. There are some aspects of vocabulary which are proposed by Ur, namely: 1) form 2) grammar; 3) collocation; and 4) aspects of meaning
2. Kinds of Vocabulary
Haycraft quoted by Hatch & Brown (1978: p.370) divides two kinds of vocabulary, namely receptive and productive vocabulary.
a. Receptive Vocabulary
Receptive vocabulary is words that the learners recognize and understand when they occur in context, but which cannot produce correctly. It is vocabulary that the learners recognize when they see it in reading context but do not use it in speaking and writing. The receptive vocabulary is also called a passive process because the learner only receives thought form others. In language application, the receptive vocabulary is considered as the basic vocabulary. It is much larger than productive vocabulary because there are many words recognized when the learner hears or reads but do not use when he speaks or writes. b. Productive Vocabulary
commit to user
From the explanation above, it can be concluded that there are two kinds of vocabulary: a receptive vocabulary and productive vocabulary. The receptive vocabulary as the words known when the learner listens and reads. It is also called a passive process because the learner only receives thought from others. In language application, the receptive vocabulary is considered as the basic vocabulary. Later, productive vocabulary is defined as the words used when the learner speaks and writes.
3. The Importance of Vocabulary
By having rich vocabulary, students can enrich their listening, speaking, reading, and writing abilities; not only in the way they comprehend but also in the way they produce language. With these points mentioned above, it is undeniable that vocabulary plays a very important role in the language acquisition. It can be denied that it will hard to master the language, without mastering or understanding a certain numbers of vocabularies. Zimmerman in Coady and Huckin (1997: p.5) state that vocabulary is central to language and critical importance to the typical language learner. McCharty and Schmitt (1997: p.140) state that vocabulary is necessary in every stage of langauge learning. He added the importance of vocabulary in language learning as follows:
No matter how well the students learns grammar, no matter how successfully sounds of L2 are mastered, without words to express a wider range of meanings, communication in an L2 just cannot happen in any meaningful way. (McCarthy, 1990:viii).
Knowing words is the key to understanding and being understood. The bulk of learning a new language consists of learning new words. Grammatical knowledge does not make for great proficiency in a language. (Varmeer, 1992: 147).
commit to user
language. The learners feel that many of their difficulties in both receptive and productive language use result from inadequate vocabulary.
4. Vocabulary Test Scoring Rubric
According to Mertler (2001), rubrics are rating scales-as opposed to checklist-that are used with performance assessments. They are formally defined as scoring guides, consisting of specific pre-establishes performance criteria, used in evaluating students work on performance assesments. Rubrics are typically the specific form of scoring instrument used when evaluating student performances or products resulting from a performance task.
Brookhart in Moskal (2000) Scoring rubrics are descriptive scoring schemes that are developed by teachers or other evaluators to guide the analysis of the products or processes of students’ efforts.
There are two types of rubrics: holistic and analytic. A holistic rubric requires the teacher to score the overall process or product as a whole, without judging the component parts separately. In contrast, with an analytic rubric, the teacher scores separate, individual parts of the product or performance first, and then sums the individual scores to obtain a total score (Moskal and Nitko in Mertler, 2001).
commit to user
Tabel 2.1. Student Oral Language Observation Matrix (The English Language Learner Knowledge Base, 2004)
Aspect 1 2 3 4 5
Pronunciation
Pronunciation problems so severe as to make speech virtually unintelligible
Very hard to understand because of pronunciation problems. Must frequently repeat in order to make him/herself understood Pronunciation problems necessitate concentration on the part of the listener and occasionally lead to misunderstanding Always intelligible, although the listener is conscious of a definite accent and occasional inappropriate intonation patterns Pronunciation and intonation approximate that of a native speaker
5. Teaching and Learning Vocabulary
Teaching vocabulary is among the least important of a teacher’s jobs, and it is important to know about learner’s strategies. Schmitt and McCharty (1997: p.208) divide the taxonomy of vocabulary learning strategies into four groups:
1) Discovery Strategies
In this stage, when learners do not know the words, they must discover their meaning by guessing from structural knowledge of the language, guessing from L1 cognate, guessing from context, using reference materials, or asking someone else.
2) Social Strategies
A second way to discover new meaning employs the social strategy of asking someone who knows. Teachers are often in this position. They can be asked to help in a variety of ways.
3) Memory Strategies
Most memory strategies involve relating the word to be retained with some previously learners’ knowledge, using some form of imagery or grouping. The strategies used in this stage are pictures / imagery, related words, unrelated words, grouping, etc.
4) Cognitive Strategies
commit to user
classifying, comparing, predicating, repeating and using mechanical means to study vocabulary.
Brown and Payne (in Hatch and Brown, 1995: p.372) propose strategies in teaching vocabulary. Brown and Payne say that the teachers have always been naturally interested in how learners go about learning vocabulary. If they know more about learner strategies and what works and what does not work well, they can help learners acquire more profitable strategies. Intuitively, they have always given advice about how to learn vocabulary.
Brown and Payne divide the procedure in learning vocabulary into five essential steps: (1) having sources for encountering new words; (2) getting a clear image, either visual or auditory or both, for the forms of the new words; (3) learning the meaning of the words; (4) making a strong memory connection between the forms and meanings of the words; and (5) using the words.
Different from Brown and Payne, Cross (1991: 11-13) proposes three stages of procedure of teaching vocabulary as follows:
a. Presentation
In this stage, the teachers can use various techniques. However, the teachers have to be careful in selecting the techniques that they use in teaching activity. Dealing with it, the teachers must consider about the students’s need of vocabulary, the area of vocabulary, which is appropriate to the students’ level and how vocabulary can be stored in the students’ mind. Therefore, teaching vocabulary is a complex process.
b. Practice
It is not enough just to present words and have them repeated. The students must use words if they are to internalize them. In this stage, the teacher gives exercises to the students in order to practice the subject items being learnt, making completion, matching, words classification, etc. Those are several of exercise that can be used by the teacher in this stage.
c. Production
commit to user
needs to walk around while the students write to ensure they are all trying. Then the students may appoint one of them to write on the board. The other students can compare this with their own versions. Having copied those illustrative sentences just a few days later, they are unlikely to make mistake, so they get a sense of achievement. This stage expects the students to apply the newly learnt vocabulary through the speaking or writing activities.
Based on the two theories above, it can be concluded that the procedures of teaching vocabulary are: 1) presentation (having sources for encountering new words and getting a clear image for the forms of the new words); 2) practice (learning the meaning of the words and making a strong memory connection between the forms and meanings of the words); 3) production (using the words).
B. YouTube Videos
There are growing demands on almost everyone who live in ICT era to become technologically literate. It provides many kinds of media which can be used in teaching learning process. Internet not only gives benefits for society, but also for students in learning process. Students can do their tasks or looking for any kinds of information easily by using the web in the internet that provides millions of pages of information from any resources in a fast, cheap, and easy way. In addition, the ability in term of ICT must be mastered well by students as early as possible by conducting teaching and learning process that have a base in ICT (Information and Communications Technology).
commit to user
specific code for playing each video that can be embedded on a web page. (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/YouTube accessed on February 10th 2010).
YouTube videos also make a specially contribution to the process of language learning, they are to interest and stimulus, a sense of the language and to motivate the students in teaching learning process.
From the definition above, it can be understood that YouTube video is a kind of short video existing in internet. By using YouTube video, teacher can create activities which more enjoyable and fun.
1. The Benefits of Video
Video is the technology of electronically capturing, recording, processing, storing, transmitting, and reconstructing a sequence of still images representing scenes in motion (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/benefits accessed on January 20th 2010). Video is something switched on to present language without teacher’s intervention. It can be a valuable and possible under used classroom tool. Although, there is always the temptation to simply put a video on at the end of term and let the students watch a video without even challenging them to be actively involved.
Smaldino (2002: p.283) defines video as electric storage of moving images, He adds that any electronic media that employs “motion pictures” to present a message can be reffered to as video.
Video, a kind of multimedia material, consist of verbal and nonverbal presentations displaying simultaneous images, narration and on-screen text. (Hu and Deng (2007) indicated that multimedia (video) could improve students’ ability to memorize words because multimedia transmitting information through auditory and visual modalities attracted learners’ attention, and accordingly improve their word retention.
commit to user
c) A useful variation in delivery-can help keep learners attention and concentration when used alongside other delivery methods; d) Ready-made and easily reusable or shareable resource; e) Video equipment is relatively simple to operate.
Adapted from Willis’6 roles for video (accessed from internet on January 20th 2010), there are four possible roles for video: 1) Developing listening skills, that are listening for global understanding and listening for detail; 2) To provide information. To provide content relevant to students’ needs and interest; 3) Presenting or reinforcing language, that are grammar, vocabulary, and functions; 4) Stimulating language production, here video used as a basis for discussion, a model for learners to follow, and a visual aid.
Through video, students, can also see the gestures and facial expressions which play an essential role in clarifying the part of the meaning which is conveyed by intonation and tone voice. Jones (2004) investigated second language vocabulary recognition and recall from one control group and three treatment groups that provided written, pictorial, or both written and pictorial annotations while listening. She found that the pictorial and written annotations group recalled more vocabulary than those without access to written annotations. Vocabulary recognition and recall would be more effective if new words were placed in a context, using sound and image combination.
commit to user
2. Teaching Vocabulary Using YouTube Videos
Teaching vocabulary must be easy and enjoyable for the students. It is intended so the students easy to keep the new words in their mind. English teachers have to use good method and technique in teaching vocabulary to young learners. There are many kinds of techniques that can be applied in teaching vocabulary such as by using pictures, videos, games, etc. Allen (1983) states some techniques of vocabulary teaching that can be prepared and chosen as follows: a) Demonstration.
The technique, which belongs to demonstration, is gesture and action performing. The teacher can use real object and command. Teacher may demonstrate the material using of real objects available in the classroom such as door, windows, clock, desk, etc.
b) Visual Aids
Visual means something visible. Teacher may use visual aids in the teaching of vocabulary to enable students to observe and identify the objects vividly. Beside that, visualization may interest the students in their learning vocabulary. c) Verbal Explanation
Verbal explanation can be carried out through definition and translation. Teacher can use explanation in the students’ own language, definitions in simple English, and using vocabulary that students have already known to show the meaning.
d) Word List
When using word list technique, teacher should pay attention to vocabulary selection. The words taught should relate and appropriate to the students need and relate to their level.
commit to user
According to Sherman (2003: p.1), video allow us to introduce any aspect of real life into the language learning environment, contextualizing the learning process. Besides, it can be used in many different instructional settings, from the classroom to online distance learning campuses. The great value of video lies in its combination of sounds, images, and sometimes text (in the form of subtitles), together with the socio-cultural information about habits, traditions, culture, etc. All this makes it a very comprehensible tool for teaching vocabulary to foreign language students.
Teaching English using video will give a fun atmosphere to the students, especially young learners. They can learn unconsciously while they are watching the film, so that they enjoy language learning. Tomalin (1991: p.48) states one of the aims of teaching English to young children is to instill in them the idea that language learning is a happy experience, and video creates an attractive enjoyable learning environment. It means that it is important to make children feel comfort and happy first in order to make language learning run effectively.
Basically, there are two main uses of video have been distinguished: instructional video, specifically created to teach foreign languages, and authentic video materials, such as films, TV series, commercials, etc., originally created for native speakers of the language. Even if it can sometimes be more difficult to handle, it is in fact very functional to use authentic video in the foreign language class, since students can profit more efficiently from this type of input, given its presentation of real (not manipulated) and complete communicative situations, that is what learners really need in real life.
Authentic videos for young learners will often contain a lot of repetition. This is a good lesson for lower levels because students only have to focus on a minimum of spoken dialogue. Students watch a scene from a film which has lots of things that they can see and therefore write in their vocabulary books.
commit to user
obvious advantage over conventional audio tapes and the visual dimension that makes understanding easier through gestures and context.
In addition, teaching English using YouTube video will be appropriate to young learners since it provides an entertainment to the students therefore it will not only leads the language learning learnable but also enjoyable.
3. The Criteria for Selecting Video
When selecting a video for used in the classroom, certain general criteria should be kept in mind. There are several criteria in selecting video, they are: 1) Watchability. It is related to the question is the video interesting, would a young learner want to watch this; 2) Completeness. Tomalin (1991: p.50) states the ideal video clip tells a complete story or a section of a story. This idea of completeness is important for young learners whose primary motivation for watching a video is enjoyment; 3) Length. The length of the clip is important. It shouldn’t be long, perhaps between 30 seconds and 10 minutes depending on the learning objective; 4) Appropriateness of Content. The content should be suitable for young learners. It should also be suitable for viewing in all cultures; 5) Level of Maturity. Children mature very quickly. It is should be matched with their level of maturity in order to make them understand the concepts in the video; 6) Availability of Related Materials. Many authentic videos now come with readymade materials that can be used for language teaching. Other videos may have been adapted from books, which could be used in the classroom to support the video.
C.Young Learners
1. The Characteristics of Young Learner
Young learners have their own characteristics that dirrefentiate them from adult learners. By knowing their characteristic, it is hoped that teacher would treat their students well and be able to use an appropriate technique of teaching in order to make the objective of teaching learning process successful.
commit to user
are five to seven years old and the eight to ten years old. Both of them are assumed as the beginner’s stage. They also states that the characteristics of Young Language learners are. They are: a) They can plan activities; b) They can argue for something and tell you why they think what they think; c) They can use logical reasoning; d) They can use their vivid imaginations; e) They can use a wide range of intonation, patterns in their mother tongue; f) They can understand direct human interaction.
Other characteristics of the young learner are:
a. They know that the world is governed by rules. They may not always understand the rules, but they know that they are there to be obeyed, and the rules help to nurture a feeling of security.
b. They understand situations more quickly than the language used. c. They use language skills long before they aware them.
d. Their own understanding comes through hands and eyes and ears. The physical world is dominant at all times.
e. They are very logical-what you say first happens first. f. They have very short attention and concentration span.
There are also general characteristics of children around eight to ten years old. Children of five are little children. Children of ten are relatively mature children with an adult side and a childish side. Many of the characteristics listed above will be things of the past.
a. Their basic concepts are formed. They have decided views of the world b. They can tell the difference between fact and fiction
c. They ask questions all the time
d. They rely on the spoken word as well as the physical world to convey and understand meaning
e. They are able to make some questions about their own learning f. They have definite views about what they like and don’t like doing
g. They have a developed sense of fairness about what happens in the classroom and begin to question the teacher’s decision
commit to user
Eight to ten years olds have a language with all the basic elements in place. They are competent users of their mother tongue and in this connection they are aware of the main rules of syntax in their own language.
By the age of ten children can: a) understand abstracts; b) understand symbol (beginning with words); and c) generalize and systematize.
This refers to children’s general language development. There are many similarities between learning one’s mother tongue and learning a foreign language in spite of differences in age and the time available. So far no body has found a universal pattern of language learning which everyone agrees with. Much seems to depend on which mother tongue the pupils speak and on social and emotional factors in the child’s background. What is clear here is that most eight to ten years olds will have some sort of language awareness and readiness which they bring with them into the foreign language classroom.
The students at Elementary School that belong to young learners have their own characteristics which are different from adults. They, as young learners need different teaching and learning process that is more various and interesting.
Those opinions above give the writer some important notes about children’s special characteristics in learning the language. They are:
1. Children respond the language from the concrete things (visual things) to abstract thing.
2. Children are able to work together.
3. Children need more fun and interesting atmosphere in their teaching and learning process.
4. Children need physical movements and real activities to stimulate their thingking.
commit to user
2. Teaching Video to Young Learners
Compared with other teaching tools, such as audio tapes, textbooks, and the basic blackboard, video is a relatively new option for the language teacher. In the twenty years or so since then, video has become an even more widely available teaching aid, although its penetration into everyday classroom practice and course or syllabus design hasn’t been as deep as many had anticipated.
According to Tomalin (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/benefits accessed on January 20th 2010), some benefits of using video to teach young learner are: 1) Young learner enjoy language learning with video. One of the aims of teaching
English to young learner is to instil in them the idea that language learning is a happy experience, and video creates an attractive enjoyable environment. 2) Video is an effective way of studying body language. Younger language
learners are still learning about the world around them.
3) Young learner gain confidence through repetition. Young learner love to hear stories again and again and the same goes for video. By watching a video several times young learner can learn by absorption and imitation.
4) Video communicates meaning better than other media. Video presents language in context in ways that a cassette can’t. Young learner can see who is or what is speaking, where the speakers are, what they are doing, etc. All these visual clues can help comprehension.
5) Video represents a positive exploitation of technology. Young learner have a positive attitude towards television and video. It is seen as being “modern” compared to books.
Other benefits of using video in teaching and learning process are: 1) Teacher just need to download video through the internet.
2) By using video, students can get benefit of audio and visual supports at the same time to catch the whole message.
commit to user
Based on the explanation above, teaching young learners is hard. Before deciding to become a teacher of young learner, everyone should recognize that the children are different to adult. Teacher can create activities which can be attracted by using the video. Video gives young learners an opportunity to acquire new vocabulary and react to what they have heard and have seen. That is why video is a very good way of stimulating young learners in learning process.
D. Review of Related Researchers
There are some studies conducted to enrich vocabulary. Lu Fang Lin (2010) writes “ English Learners’ Incidental Vocabulary Acquisition in the Video
based CALL Program” This study investigated the effects of video-based
commit to user
There are also some articles related to the use of video in foreign language class. The first article entitled “Learning Vocabulary Through Authentic
Video and Subtitles”. It states that subtitles can be used together with authentic
video to improve word recognition and vocabulary acquisition skills in the EFL class.
This atmosphere provides authentic input through three different channels (written text, oral text and images) that contribute to offer a better and potentially longer-lasting mental representation of new and old lexical items. The great value of video lies in its combination of sounds, images, and sometimes text (in the form of subtitles), together with the socio-cultural information about habits, traditions, culture, etc. All this makes it a very comprehensible tool for teaching vocabulary to foreign language students.
Tatsuki (1999) writes about “Video in the Language Lab: Teaching
Vocabulary”. She states learners who read illustrative sentences (sentences
capturing a scene in the movie and model the correct usage of a target vocabulary item) scored better on a multiple choice test than did those who read the narrative only or read the narrative and watched the video. This would indicate that if vocabulary learning is going to be measured by productive use, video is certainly facilitative. If, on the other hand, vocabulary gain is going to be measured via multiple choice testing, video will be most efficient if learners are provided with contextualized sentence models. Either way, video is a useful part of vocabulary learning.
McKinnon writes “Teaching Technologies: Teaching English Using
Video”. It is an article offering advice and suggestions on how to teach English
using video. He states that video is a valuable and possibly underused classroom tool. There is always the temptation to simply put a video on at the end of term and let our students watch a film without even challenging them to be actively involved. Then, he concludes that the use of video is an advantage here as it is an emotional scene with lots of gestures, adding weight to the situation.
Constantinescu (2007) writes “Using Technology to Assist in Vocabulary
commit to user
the relationship between vocabulary knowledge and reading comprehension. Then, it has been increasingly argued that computer technologies can support learning in a number of ways. Many features of the computer are considered to enhance vocabulary development and reading comprehension: multimedia is one of them. Multimedia refers to computer-based systems that use various types of content, such as text, audio, video, graphics, animation, and interactivity. Chun and Plass in Constantinescu (2007) states that visual multimedia advance organizers were found to help not only recalling new words, but also act as facilitators of reading comprehension, which stresses the close relationship between vocabulary and reading.
Irina (2010) writes “Using YouTube Videos in Teaching English”. She states that video material taken from YouTube can be a very useful source and asset for the language teaching-learning process because it combines both fun and pedagogic instructions in an authentic material that reflect real interaction. Using videos in the English class is a very helpful and stimulating method to motivate the students to get the most of the lesson. By employing videotaped material teachers can always create an indefinite number of language teaching activities. The devised activities above are mere examples based on one short segment and each focuses of a different language skill that EFL students need to acquire.
E. Rationale
commit to user
The problem in learning vocabulary is the student’s low vocabulary competence. It is indicated by the result of the test. The mean score of the vocabulary test in pre research is 42.64. 1) The students usually make mistakes in pronouncing the words; (2) The students get difficulties to mention words they already learn before; (3) The students get difficulties to spelling the words; (4) the students get difficulties in recognizing words; (5) The students get confuse in meaning of English words.
Considering to the characteristics of young learners who are like something which is fun, the teacher has to find an interesting activity in teaching and learning process to solve the problem. An interesting activity can be created by the use of media that is YouTube videos which can be used in presenting vocabulary to young learners clearly. By optimizing the use of YouTube videos, it becomes motivator for the students to learn. It is because YouTube videos are interesting, a very useful tool in linking fantasy and the imagination of the children’s world. Thus, YouTube videos can motivate the students to learn and will reduces students’ stress and create a positive mood of the learners. It will bring much joy and give the students opportunites to remember the words and understand the new words easily and it will be easier for young learners to learn the English words.
commit to user
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter discusses the research method that is used in this study. It covers the research setting, the subject of the research, the methods of the research, the technique of collecting data, and the technique of analyzing the data. Each of the item is discusses in the following section
A.The Context of the Research
1. Research Setting
The research is conducted at SDN Sanggrahan, Surakarta. This elementary school is located at Kartika street number 6 Jebres, Surakarta. This school building is simple with a field in front of the building as school yard and sport hall. It consists of six classrooms, a teacher’s room, a headmaster’s room, a school health center or UKS, a school guard’s room, a canteen, three toilets, a library, a hall and parking space for students and teachers. Some of the classrooms are not in a good condition, they can be seen from some of the walls that are hollows and not all of rooms in ceramic tiles. For teaching learning process, this school supported by comfortable surrounding atmosphere, each room have some big windows along the wall, and the location is in a quite enough village.
[image:37.612.132.511.196.462.2]The research was conducted in three months from April 2010 to June 2010. This research includes the pre-research, action, and activities after the action. It can be arranged as follows:
Table 3.1 The Schedule of the Research
No Activity Time of Research
1. Pre-research (observation, interview) April 2010 2. Preparation of pre-test April 2010
3. Pre-test April 2010
4. Action May to June 2010
5. Post test June 2010
commit to user
2. Subject of the Research
The subject of the research is the fifth grade students of SDN Sanggrahan Surakarta. There are 42 students in the class which consist of 22 boys and 20 girls. Most of students in SDN Sanggrahan Surakarta are coming from the middle-low economic level, their parents’ occupation mostly as labor and employees which is make their time spend only to work and no much time for more attention to their children. The reason the writer chooses the fifth class is because of the fact that the students’ vocabulary was still low. It is proven by the result of interview with the teacher. The teacher said that the fifth grade students were active in making noise and passive learners. They usually do not pay full attention to their study, They look sleepy in class and less concentrate. The atmosphere of the teaching learning process are boring and going monotonous. The result of pre-observation in the teaching learning process also showed that the students’s achievement were not satisfying. During the teaching and learning process, the students looked bored and did the tasks or English learning activities unenthusiastically. They were passive in answer the teacher’s question and usually busy doing non academic thing. It influenced their result of study. It can be seen from their achievement of the vocabulary test which was not satisfying enough or it can be called so bad. They got some difficulties in pronouncing, spelling, and understanding the English words.
Considering with the fact above, the researcher thought that by applying YouTube videos in English class, it will changing the situation being more alive and interesting.
B. The Method of the Research
commit to user
1. The Definition of Action Research
Action research is a group activity. There are some definitions of action research proposed by some experts. Kemmis and Mc Taggart (in Nunan, 1992: p.17) argue that the three defining characteristics of action research are that it is carried out by practitioners (for the purposes, classroom teachers) rather than outside researchers; secondly, that it is collaborative; and thirdly, that it is aimed at changing things. Meanwhile Stephen (in Hopkins, 1993: p.44) defines action research is a form of self-reflective enquiry undertaken by participants in social including educational situation in order to improve the rationality and justice of (a) their own social or educational practices; (b) their understanding of these practices and ; (c) the situations in which the practice are carried out.
Cohen and Manion (in Nunan, 1992: p.18) offer a similar set of characteristics. They argue that action research is first and foremost situational, being concerned with the identification and solution of problems in a specific context. They also identify collaboration as an important feature of this type of research, and state that the aim of action research is to improve the current state of affairs within the educational context in which the research is being carried out.
Similarly, Elliot (in Hopkins, 1993: p.45) says that action research as the study of a social situation with a view to improving the quality of action within it.
Wallace in Burns (1999: p.30) views that action research is done systematically collecting data on your everyday practice and analyzing it in order to come to some decision about what your future practices should be.
commit to user
2. The Characteristics of Action Research
These definitions suggest a number of common features which can be considered to characterise action research. They are:
(a) Action research is contextual, small-scale and localised-it identifies and investigates problems within a specific situation;
(b) It is evaluative and reflective as it aims to bring about change and improvement in practice;
(c) It is participatory as it provides for collaborative investigation by teams of collegues, practicioners and researchers;
(d) Changes in practice are based on the collection of information or data which provides the impetus for change.
In this research, action research is conducted in order to enrich the students’ vocabulary by optimizing YouTube videos, develop teacher’s creativity in teaching vocabulary, so the students are motivated in teaching-learning process. It also aimed that the research effects positive change of the social and educational situation on the fifth grade class of SDN Sanggrahan Surakarta.
The writer also prefers conducting a classroom action research to other educational research because of the following reasons:
1. Classroom action research is continuous process that produces open-ended result. So that this research enable the researcher to become continuous learners to change and enrich their quality in teaching
2. The researchers are committed to take action and positive educational change based on their findings rather than being satisfied with reporting their conclusions to others.
3. Classroom action research not only change and enrich students’ vocabulary but also to change and improve teacher’s technique variation in teaching vocabulary.
commit to user
3. The Model of Action Research
The model of classroom action research used in this study is based on the model developed by Kemmis and McTaggart (in Burns 1999: p.32) who state that action research occurs through a dynamic and complementary process which consists of four fundamental steps in a spiralling process. They are as follow: a. Planning
Before implementing the action, the researcher needed to make general plan. Develop a plan of critically informed action to improve what is already happening. The researcher also prepared equipments needed in doing the action in order to enrich the students’ vocabulary competence.
b. Action
Act to implement the plan. The researcher did the planning which had been made. The researcher carried out the lesson plans the researcher had made. In this research, the researcher applied YouTube videos in teaching learning process in order to enrich students’ vocabulary competence.
c. Observation
Observe the effects of the critically informed action in the context in which it occurs. The researcher observes all activities happening in the class situation and make notes related to the process of teaching and learning. The researcher did observation during teaching learning process.
d. Reflection
commit to user
O B S E R V EO B S E R V E
AC
T
ACT
REF
L
ECT
R
EF
LEC
T
R E V I S E D P L A N
[image:42.612.177.444.101.468.2]P L A N
Figure 3.1. An Illustration of Action Research Spiral
4. The Stage of Action Research
The four steps at the model above can be expanded into six steps which included in the procedure of action research. The procedures are: 1) Identifying the problem; 2) Planning the action; 3) Implementing the action; 4) Observing the action; 5) Reflecting the action; and 6) Revising the plan. For each step will explained as follows:
1) Identifying the problem
The problems were identified before planning the action. The problems reffered to the factors making the low of vocabulary competence. The problems can be identified by using:
a) Test
commit to user
b) Interview with the teacherThe interview was held in order to obtain the problems faced by the teacher during teaching learning process.
c) Observation
The observation was held in order to obtain the students’ vocabulary, the students’ behavior during teaching-learning process and also to obtain the class management.
2) Planning the Action
Generally, the plan will be made before implementing the action. The researcher will prepare everything related to the action as follows:
a) Firstly, the researcher gave the students pre-test and evaluates the result. b) Secondly, the researcher prepared the materials and sheets for observation.
It done to obtain the situation of TLP when the technique is applied. c) Thirdly, made lesson plan and designed the steps in doing the action. d) Fourthly, prepared the teaching aids (LCD, laptop, camera and speaker). e) Then, the researcher prepared exercises and post-test to obtain whether
students’ vocabulary enrich or not.
f) Next, the researcher implemented the lesson plans which she had made. g) After implemented the first cycle, the researcher gave first post test and
evaluated the result to decide the next cycle action.
h) After the researcher had finished applying all the lesson plan, she gave the second post test or can be called final test then evaluated the result.
i) Finnaly, the researcher compared the result of the pre test, the first post test and the second post test then identified the scores comparison.
3) Implementing the Action
The researcher implementing the plan, implementing the teaching and learning process by using YouTube videos based on the planning.
4) Observing the Action
commit to user
5) Reflecting the ActionThe researcher analyzed the collected data, determining whether the action is successful of unsuccessful. The result of this step will be the basic of the next activity of cycle.
6) Revising the Plan
Revising plan was needed when the action cycle did not make any enrichment on the students’ vocabulary acquisition based on the weaknesses which were found in reflecting process for the next cycle.
This research was conducted in two cycles. Each cycle used YouTube videos in vocabulary activity. Pre-test was held in the beginning of cycle to measure students’ vocabulary before implementing the action. In the end of every cycle, there was post-test. Students’ enrichment was seen in the results which were compared from the pre test and post test.
C. Data Collecting
[image:44.612.133.507.209.467.2]In this classroom action research, the researcher combines the qualitative data and the quantitative data. The quantitative data are used to support the qualitative data. To collect the data, the researcher also using the some ways, that can be seen in the table bellow:
Table 3.2 The Data Collecting
Technique Participants Stage Data
Interview •Researcher
•Observer
•Identifying the problem
•Evaluating and reflecting
•Transcript of interview about TLP
•Students’ achievement
Observation •Researcher
•Students
•Observer
•Identifying the problem
•During the action
Field notes (model of teaching and students activities)
Documents •Researcher
•Students
•During the action •Photographs
•Students’ answer sheet Test •Researcher
•Students
•Planning
•Evaluating and reflecting
commit to user
Those techniques above can be explained by following means: 1) The Qualitative Data
a. Interview
According to Burns (1999: p.117), interview and discussion is face to face personal interactions which generate data about the research issue and allow specific to be discussed from other people’ perspectives. In this research, this technique is held in the beginning and ending of the research to obtain the teacher’s view of the teaching learning process, students’ vocabulary competence, students’ achievement before and after the action. b. Observation
Burns (1999: p.80) says that observation is taking regular conscious notice of classroom action and occurences which are particularly relevant to the issue or topics being investigated. In this research, observation was done by the teacher. Observations are ways of finding out more about the students’s response. Students’ behavior and activities were observed during English class. The observation was focused on the development of students’ vocabulary by using YouTube videos. A way reporting observation can be done by keeping field notes.
c. Documents
Some documents were taken in this research, they are: • Photographs
Photographs are record or activities happening in the class. It could give real description about teaching learning process.
• Field Notes
commit to user
classroom, whether they give attention, see the visual, read the word, touch the explanation or not.
• Students’ answer sheet
There are pre-test and post-test answer sheets in this research, pretest was given to identify the students’ vocabulary before the method applied while post-tests were given to measure the enrichment of students’ vocabulary after applying video in English class.
2) The Quantitative Data Test
The researcher gives tests to obtain how far the result of the technique that is used to enrich students’ vocabulary is. There are pre-test and post-test which are used to collect the data of the enrichment.
D. Data Analysis
Having collected data, the researcher then analyzed the data. The data from the observation are analyzed after the teaching process ended. The observation focuses on how teaching and learning process runs in the classroom.
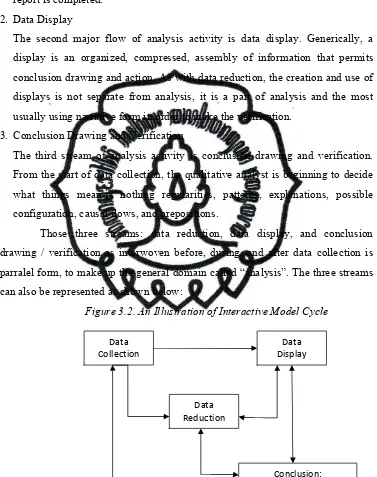
The data are divided into qualitative data and quantitative data. The qualitative data consists of the result of observation, field notes, interview, documents and photographs. To analyze qualitative data, the researcher uses Interactive Model. Miles and Huberman (1992: p.15) say that in general, the data analysis process includes:
1. Data Reduction
commit to user
coding, teasing out themes, making cluster, making partitions, writing memos). The data reduction / transforming process continues after fieldwork until a final report is completed.
2. Data Display
The second major flow of analysis activity is data display. Generically, a display is an organized, compressed, assembly of information that permits conclusion drawing and action. As with data reduction, the creation and use of displays is not separate from analysis, it is a part of analysis and the most usually using narrative form in order to make the verification.
3. Conclusion Drawing and Verification
The third stream of analysis activity is conclusion drawing and verification. From the start of data collection, the qualitative analyst is beginning to decide what things mean-is nothing regularities, patterns, explanations, possible configuration, causal flows, and prepositions.
[image:47.612.133.510.153.630.2]Those three streams: data reduction, data display, and conclusion drawing / verification as interwoven before, during, and after data collection is parralel form, to make up the general domain called “analysis”. The three streams can also be represented as shown below:
Figure 3.2. An Illustration of Interactive Model Cycle
The researcher analyzes the data from the result of observation, field notes, interview, documents, and photographs. The observation, field notes,
Data Reduction Data
Collection
Data Display
commit to user
interview, documents, and photographs describe how the process of teaching vocabulary using optimizing YouTube videos runs in the classroom. After studying notes of the data, she identifies progresses and advantages as well as problems and identifies possible solution in teaching vocabulary.
Then to analyze data in quantitative method, the researcher uses descriptive statistics to describe the main features of a collection of data. The aim is to quantitatively summarize a data set, rather than being used to support inferential statements about the population. The writer uses the mean score of every test that contains pre-test, and post-test. These are to observe whether there are significant differences between the students’ achievement before and after the action.
It can be calculated with the formula:
N x
x= Σ
_
In which:
∑x = The sum of students’ score before the action
∑y = The sum of students’ score after the action
χ = Means of students’ score before the action y = Means of students’ score after the action N = Number of sample (students)
N y
y = Σ
commit to user
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDING AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents the research findings and the discussion dealing with the problems formulated in Chapter I. This action research is conducted in order to investigate whether and to what extent the implementation of YouTube videos can enrich the students’ vocabulary at the fifth grade of SDN Sanggrahan. Besides, it is conducted to describe the situation of the class when the YouTube videos is applied during teaching and learning process.
A.Research Findings
[image:49.612.133.509.191.598.2]The research was conducted in collaboration with the English teacher in SDN Sanggrahan. The research was conducted in two sessions. The first was pre-research and the second was the implementation of action research. In brief, the overall process of the research can be seen in table below:
Table 4.1. The Overall Process of Research
1. Pre-research
Observing teaching and learning process Interviewing students and teacher Conducting pre-test
2. Research Implementation
Meeting 1: Explaining and Presenting YouTube video “Listen and Repeat” Meeting 2: Discussing the exercise and Presenting YouTube video “ Which one?”
Meeting 3: Modeling and Presenting YouTube video “ What do you do?”
Cycle 1
Conducting post-test 1
Meeting 1: Modeling, Disscussing the exercise and Presenting YouTube video “ Read the sentence”
Meeting 2: Discussing the exercise, Presenting YouTube video “Which one II?”
Cycle 2
Conducting post-test 2
3. Summary of Findings during the Research
The overall process of the research as summarized in Table 4.1. is described in more detailed as in the following. This section is divided into three main parts including description of the previous situation, research implementation, and summary of findings during the research. In pre-research, the researcher observed teaching and learning process, interviewed students and
commit to user
teacher, and conducted pre-test. While in Cycle I, she explained and presented YouTube videos in first meeting. In second meeting, she discussed the exercise and presented YouTube videos and she did modeling, presented YouTube videos also conducted post test 1 in the third meeting. Furthermore in Cycle II, she did modeling, disscused the exercise and presented YouTube videos in first meeting then in the second meeting she discussed the exercise, presented YouTube video and she conducted post-test 2 in the next day.
1. Situation Before Research
[image:50.612.135.504.202.701.2]In this section, the researcher describes the situation before the research was conducted. All are presented in Table 4.2.
Table 4.2. Situation Before Research
The Problems Descriptions
A. VOCABULARY COMPETENCE
1. Having difficulty in pronounciation
The students made mistakes in pronouncing the words. Some pronunciation of English words differs from pronunciation in Indonesian words.
2. Having difficulty in mention words