vii ABSTRACT
Matuate, Vitha Ama, (2015). A Set of Supplementary English Materials using
Infographic for Seventh Grader of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
BOPKRI 1 Junior High School is one of the schools that applies English as the school subject. The writer found some of learning and teaching problems
based on the writer’s experience as the PPL teacher and based on the result of the interview with the English teacher. The first problem is that some students did not learnt English in the elementary school. The second problem is that the students have some difficulties in learning grammar, vocabulary mastery and English skills. To overcome those problems, the writer decided to design English infographic supplementary materials to help the students in English learning.
There are two problems in this study. They are (1) How is a set of supplementary English materials using infographic media for seventh graders of
BOPKRI 1 Junior High School designed?, and (2) What does the set of English supplementary materials using infographic for seventh graders of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School look like? To answer the first research problem of this study, the writer used five out of ten steps from research and development of Borg and Gall (1983) and combined it with six steps of instructional media design by Kemp (1977) to produce the writer’s research model. The research model are (1) pre-design survey and data analysis, (2) planning the pre-design material needs (3) designing the design material (4) post design survey and designed material evaluation, and (5) designing the design material.
To answer the second research problem, the writer presented the supplementary designed materials that consisted of seven titles. The titles are (1) Help me, Please, (2) What do you do?, (3) I like your dress, (4) My favorite singer I Afgan, (5) How many apple that you have?, (6) Show me how to make mango juice, (7) I got your message. Each unit of the supplementary deigned materials consisted of three main contents, namely “Let’s get started”, “Let’s focus, and
“Let’s review. In “Let’ get started” were asked to observe the introduction of each topic. In “Let’s focus”, the writer presented the infograpfic and the learning activities. The learning activities were consisted of individual work, partner work, and group group work activities. In “Let’s review”, the students were asked to review the material by reading the short summary of each unit and doing the exercises. The writer added two additional contents for the supplementary designed materials. The contents were “Fun Time”, and “Did You Know?”
In the end of the research, the writer had the evaluation of the designed material from the evaluators. The result of the evaluation showed almost all the evaluators’ opinion were between agree and strongly agree (degree of agreement). This means that the designed material was appropriate to be used for the seventh grader of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School.
viii
ABSTRAK
Matuate, Vitha Ama, (2015). A Set of Supplementary English Materials using
Infographic for Seventh Grader of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School. Yogyakarta: Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma
SMP BOPKRI 1 merupakan salah satu sekolah yang menerapkan Bahasa Inggris dalam matapelajaran sekolah. Dari pengalaman penulis sebagai guru PPL dan dari hasil wawancara informal dengan guru Bahasa Inggris, terdapat beberapa masalah dalam proses belajar mengajar bahasa Inggris. Pertama, tidak semua siswa belajar bahasa inggris di sekolah dasar. Kedua, siswa masih kesulitan dalam belajar struktur bahasa, kosakalata dan kemampuan berbahasa Inggris. Untuk mengatasi masalah tersebut, penulis memutuskan untuk mendesain material tambahan Bahasa Inggris menggunakan Infographic dalam membantu siswa belajar bahasa Inggris.
Terdapat dua rumusan masalah dalam studi ini. Pertama (1) Bagaimana desain materi tambahan Bahasa Inggris menggunakan Infographic untuk kelas tujuh SMP BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta, dan (2)Seperti apa materi tambahan Bahasa Inggris mengunakan Infographic untuk kelas tujuh SMP BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta?” Untuk menjawab rumusan masalah pertama, menggunakan 5 dari sepuluh tahap dari teori penelitian dan pengembangan Borg dan Gall (1983) dan mengkombinasikannya dengan desain media instruksional Kemp (1977) dalam menentukan tahapan-tahapan penelitian penulis yang antara lain (1) pre-design survey and data analysis, (2) planning the design material needs (3) designing the design material (4) post design survey and designed material evaluation, (5) designing the design material, and (6) revising the design material.
Untuk menjawab rumusan masalah kedua, penulis memperkenalkan materi tambahan yang terdiri dari tujuh judul. Materi yang dihasilkan adalah (1) Help me, Please, (2) What do you do?, (3) I like your dress, (4) My favorite singer I Afgan, (5) How many apple that you have?, (6) Show me how to make mango juice, (7) I got your message. Setiap unit terdiri dari tiga bagian utama yaitu
“Let’s get started”, “Let’s focus, and “Let’s review. Dalam “Let’ get started” Para siswa diajak untuk mengamati perkenalan dari setiap unit. Dalam “Let’s focus”, penulis memperkenalkan infographic, dan aktivitas-aktivitas belajar. Aktivitas belajar terdiri dari kegiatan individual, kegiatan berpasangan, dan kegiatan kelompok. Dalam “Let’s review”, para siswa diajak untuk mengulang kembali pelajaran yang telah dipelajari. Penulis memasukan dua konten tambahan dalam materi tambahan. Konten tersebut adalah “Fun Time”, and “Did You Know?”
Penulis mendapakan evaluasi materi pembelajaran dari beberapa evaluator. Dari hasil evaluasi tersebut menunjukkan hampir semua pendapat evaluator berada diantara di pilihan setuju dan sangat setuju(tingkat kesepakatan. Ini menunjukkan materi yang dihasilkan sesuai untuk diterapkan di kelas tujuh SMP BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta.
A SET OF SUPPLEMENTARY ENGLISH MATERIALS
USING INFOGRAPHIC FOR SEVENTH GRADERS
OF BOPKRI 1 JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Vitha Ama Matuate Student Number: 111214126
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS AND TRAINING EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
iv
DEDICATION PAGE
MAKE A WISH, TAKE A CHANCE
AND
MAKE A CHANGE
(Vitha Ama Matuate)
v
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work or parts of the work of other people, except those cited in the quotations and the references, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, August 10, 2015 The Writer
vi
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASIKARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswi Universitas Sanata Dharma: Nama : Vitha Ama Matuate
Nomor Mahasiswa : 111214126
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
A SET OF SUPPLEMENTARY ENGLISH MATERIALS USING INFOGRAPHIC FOR SEVENTH GRADERS
OF BOPKRI 1 JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL
Beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada) dengan demikian, saya berikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikannya secara terbatas dan mempublikasikannya di internet ataumedialain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin maupun royalty kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sebenarnya.
Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal: 10 Agustus 2015 Yang menyatakan,
vii ABSTRACT
Matuate, Vitha Ama, (2015). A Set of Supplementary English Materials using
Infographic for Seventh Grader of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
BOPKRI 1 Junior High School is one of the schools that applies English as the school subject. The writer found some of learning and teaching problems based on the writer’s experience as the PPL teacher and based on the result of the interview with the English teacher. The first problem is that some students did not learnt English in the elementary school. The second problem is that the students have some difficulties in learning grammar, vocabulary mastery and English skills. To overcome those problems, the writer decided to design English infographic supplementary materials to help the students in English learning.
There are two problems in this study. They are (1) How is a set of supplementary English materials using infographic media for seventh graders of
BOPKRI 1 Junior High School designed?, and (2) What does the set of English supplementary materials using infographic for seventh graders of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School look like? To answer the first research problem of this study, the writer used five out of ten steps from research and development of Borg and Gall (1983) and combined it with six steps of instructional media design by Kemp (1977) to produce the writer’s research model. The research model are (1) pre-design survey and data analysis, (2) planning the pre-design material needs (3) designing the design material (4) post design survey and designed material evaluation, and (5) designing the design material.
To answer the second research problem, the writer presented the supplementary designed materials that consisted of seven titles. The titles are (1) Help me, Please, (2) What do you do?, (3) I like your dress, (4) My favorite singer I Afgan, (5) How many apple that you have?, (6) Show me how to make mango juice, (7) I got your message. Each unit of the supplementary deigned materials consisted of three main contents, namely “Let’s get started”, “Let’s focus, and “Let’s review. In “Let’ get started” were asked to observe the introduction of each topic. In “Let’s focus”, the writer presented the infograpfic and the learning activities. The learning activities were consisted of individual work, partner work, and group group work activities. In “Let’s review”, the students were asked to review the material by reading the short summary of each unit and doing the exercises. The writer added two additional contents for the supplementary designed materials. The contents were “Fun Time”, and “Did You Know?”
In the end of the research, the writer had the evaluation of the designed material from the evaluators. The result of the evaluation showed almost all the evaluators’ opinion were between agree and strongly agree (degree of agreement). This means that the designed material was appropriate to be used for the seventh grader of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School.
viii
ABSTRAK
Matuate, Vitha Ama, (2015). A Set of Supplementary English Materials using
Infographic for Seventh Grader of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School. Yogyakarta: Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma
SMP BOPKRI 1 merupakan salah satu sekolah yang menerapkan Bahasa Inggris dalam matapelajaran sekolah. Dari pengalaman penulis sebagai guru PPL dan dari hasil wawancara informal dengan guru Bahasa Inggris, terdapat beberapa masalah dalam proses belajar mengajar bahasa Inggris. Pertama, tidak semua siswa belajar bahasa inggris di sekolah dasar. Kedua, siswa masih kesulitan dalam belajar struktur bahasa, kosakalata dan kemampuan berbahasa Inggris. Untuk mengatasi masalah tersebut, penulis memutuskan untuk mendesain material tambahan Bahasa Inggris menggunakan Infographic dalam membantu siswa belajar bahasa Inggris.
Terdapat dua rumusan masalah dalam studi ini. Pertama (1) Bagaimana desain materi tambahan Bahasa Inggris menggunakan Infographic untuk kelas tujuh SMP BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta, dan (2)Seperti apa materi tambahan Bahasa Inggris mengunakan Infographic untuk kelas tujuh SMP BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta?” Untuk menjawab rumusan masalah pertama, menggunakan 5 dari sepuluh tahap dari teori penelitian dan pengembangan Borg dan Gall (1983) dan mengkombinasikannya dengan desain media instruksional Kemp (1977) dalam menentukan tahapan-tahapan penelitian penulis yang antara lain (1) pre-design survey and data analysis, (2) planning the design material needs (3) designing the design material (4) post design survey and designed material evaluation, (5) designing the design material, and (6) revising the design material.
Untuk menjawab rumusan masalah kedua, penulis memperkenalkan materi tambahan yang terdiri dari tujuh judul. Materi yang dihasilkan adalah (1) Help me, Please, (2) What do you do?, (3) I like your dress, (4) My favorite singer I Afgan, (5) How many apple that you have?, (6) Show me how to make mango juice, (7) I got your message. Setiap unit terdiri dari tiga bagian utama yaitu “Let’s get started”, “Let’s focus, and “Let’s review. Dalam “Let’ get started” Para siswa diajak untuk mengamati perkenalan dari setiap unit. Dalam “Let’s focus”, penulis memperkenalkan infographic, dan aktivitas-aktivitas belajar. Aktivitas belajar terdiri dari kegiatan individual, kegiatan berpasangan, dan kegiatan kelompok. Dalam “Let’s review”, para siswa diajak untuk mengulang kembali pelajaran yang telah dipelajari. Penulis memasukan dua konten tambahan dalam materi tambahan. Konten tersebut adalah “Fun Time”, and “Did You Know?”
Penulis mendapakan evaluasi materi pembelajaran dari beberapa evaluator. Dari hasil evaluasi tersebut menunjukkan hampir semua pendapat evaluator berada diantara di pilihan setuju dan sangat setuju(tingkat kesepakatan. Ini menunjukkan materi yang dihasilkan sesuai untuk diterapkan di kelas tujuh SMP BOPKRI 1 Yogyakarta.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I want to give my greatest gratitude to Jesus Christ for His loves, blessings, and supports so that I can accomplish this thesis. He makes me believe that I can do all of these. I also would like to express my biggest gratitude to my family especially my father Drs. B. Ahie and my mother Trifonnia Henny Alon, S.Pd., who always support me in everything that I did for my life. I also thank my little sister Maria Adol Fina Balomahu, and for all my family for their support while I was studying and doing my thesis in Yogyakarta.
My special gratitude and deep appreciation go to my thesis advisor Paulus Kuswandono, Ph.D., who guided me in writing my thesis. I would like to thank him for the time, support, advice and patience during my thesis process.
I also would like to thank BOPKRI 1 Junior High School. I thank Paryadi, S.Pd., as the headmaster of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School, for letting me do the research in BOPKRI 1 Junior High School. I thank Daru Kurniwan, S.Pd, and Madyasari Widianti, M.Pd. for helping me in doing my design. I thank them for their ideas, criticism, comments, feedback and support. I also would like to thank them as my evaluators for the post-design survey.
I am also indebted to the other evaluators: Marwati, S.Pd., I thank her for the evaluation and feedback. Her evaluation and feedback help me in revising the supplementary material.
x
studying in Yogyakarta. I thank my besties Agatha Lisa, Sonia Alexandra Pereira, Josephine Fanny Damayanti, Nurita Sekar Asri, Nadia Gitya, Priska Wardani, Arum Galih Rahayu, Tusita Maina Dewi, kak Vania Williany and all my friends from the English Language Education Study Program batch 2011 who always give me support in everything that I do.
xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
DEDICATION PAGE ... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... v
PERNYATAAN PERSETUTUAN PUBLIKASI ... vi
ABSTRACT ... vii
ABSTRAK ... viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... xi
LIST OF TABLES ... xiv
LIST OF FIGURES ... xiv
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xiv
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Research Background ... 1
B. Research Problems ... 3
C. Problem Limitation ... 4
D. Research Objectives ... 5
E. Research Benefits ... 5
xii
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 8
A. Theoretical Description ... 8
1. Infographic ... 9
2. Kemp’s Instructional Media Design ... 11
3. Visual Information in Learning ... 19
4. Task Based Learning ... 27
a. The Meaning of Task Based Learning ... 27
b. The Framework of Task Based Learning ... 28
5. Parameters of Book Activities ... 30
B. Theoretical Framework ... 31
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 34
A. Research Method ... 34
B. Research Setting ... 41
C. Research Participants ... 42
D. Instrument and Data Gathering Technique ... 42
E. Data Analysis Technique ... 45
F. Research Procedure ... 48
CHAPTER IV: RESUTLS AND DISCUSSION ... 50
A. The Design Process of Supplementary Material Using Infographic ... 50
1. Pre-design Survey and Data Analysis ... 51
xiii
3. Designing the Designed Material ... 63
4. Post-design Survey and Designed Material Evaluation ... 70
5. Revising the Designed Material ... 79
B. The Presentation of the Supplementary Material Using Infographic .... 79
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 82
A. Conclusions ... 82
B. Suggestions ... 84
REFERENCES ... 86
xiv
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
3.1 The Description of the Participant for the Pre-design survey ... 42
3.2 The Format Description of the Participants of the Post-design Survey (blank) ... 43
3.3 The Format of the Participants’ Opinion in Pre-design Survey ... 47
3.4 The Format of the Evaluators’ Opinion in Post-design Survey ... 47
4.1 The Points of Agreement for the Pre-design survey Questionnaire ... 54
4.2 The First Part of the Questionnaire for the Pre-design Survey ... 55
4.3 Some Focuses from the Syllabus ... 62
4.4 The Objectives of the Supplementary Material ... 69
4.5 The Description of the Evaluators for the Post-design Survey ... 70
4.6 The First Part of the Post-Design Survey Questionnaire ... 71
4.7 The Strengths and the Weakness of the Supplementary Design Material ... 75
xv
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
2.1 The Adjectives’ Infographic ... 10
2.2 Kemp’s Instructional Design Model ... 18
2.3 Visual Information about Brain ... 19
2.4 Examples of Sign Language ... 21
2.5 The Example of Flash Card... 23
2.6 Highlighting Text with Highlighter ... 24
2.7 Example of Chart ... 24
2.8 Example of Diagram ... 25
2.9 Examples of Illustration ... 25
2.10 Example of Map ... 26
2.11 Example of Venn Diagram ... 26
2.12 Example of Historical Photograph ... 26
2.13 Examples of Avatar, Pictograph and Music notes ... 27
2.14 Components of the TBL framework ... 29
2.15 Kemp Instructional Design Model steps ... 32
xvi
LISTS OF APPENDICES
Appendix Page
Appendix A: Permission Letter (from the Secretariat) ... 89
Appendix B: Research Permit Letter (from BOPKRI 1 Junior High School) 91 Appendix C: The Result of Pre-design Questionnaire ... 93
Appendix D: Appendix D: Questionnaire (post-survey) ... 97
Appendix E: Syllabus ... 100
Appendix F: Lesson Plan ... 115
1 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, the writer introduces the basic information of this study. There are six parts of this chapter. They are the research background, the research problem, the problem limitation, the research objectives, the research benefits, and the definition of terms.
A. Research Background
English nowadays becomes very important as the international language for communicating used by people around the world. In Indonesia, English becomes one of the important subjects at school. English is taught from the kindergarten up to the university. In this era, it is important for the students to learn all the language elements to improve their language skills.
However, there are few of the students who started learning English in junior high school. In language learning, the students need to master and understand the basic elements of language first before they learn more about the language. They need more materials to help them in learning English, which should be easy to be remembered and understood so those materials can grab the students’ interest in learning English. That is why the writer decided to design the English supplementary grammar and vocabulary for seventh grader of BOPKRI 1
Junior High School.
In BOPKRI 1 Junior High School, not all of students learnt English in their elementary school. For some students, English is a new subject. It is difficult for them to follow their friends who already had the basics English. They always find some difficulties in the learning process. On the other side, teaching English as the second language has its own difficulties for the teachers. It is about choosing the appropriate materials and learning activities to teach English, so that all of the students will fully understand the material.
problems, this study designed a set of English supplementary material using infographic.
In this study, the writer designed a supplementary book contains the infographic and combined it with Task-based learning as the learning technique in the supplementary book. Task as stated by Richards, et al (1986) usually involves the teacher to identify the purpose of the completion of task. Using various kinds of tasks in language learning helps the readers or the students to be more communicative since the task also contains various kinds of learning activities that require the readers or the students to practice the language by themselves (as cited in Nunan, 2004, p. 2).
B. Research Problems
The problems of this study are formulated in two questions. The problems are:
1. How is a set of English supplementary materials for the seventh graders of
BOPKRI 1 Junior High School using infographic media designed?
C. Problem Limitation
This study aimed to design the supplementary material which can help students to improve their English skills. These components help the students to develop their listening, reading, speaking, and writing skills. The designed material are designed in the form of supplementary book using infographic to learn grammar, vocabulary and other language functions (expressions and text genre). The materials are designed for second semester of junior high school. This designed material used the syllabus, competence standard and basic competence of the seventh grade of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School that will be adjusted to the students’ level and interest.
D. Research Objectives
There are two research objectives of this study. The first research objective is to find out how a set of English supplementary materials using infographic for the seventh graders of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School is designed. The second objective is to find out what the English supplementary materials using infographic for the seventh graders of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School looks like.
E. Research Benefits
The results of this research are expected to be useful for those who are concerned and willing to be an English teacher since infographic can be used as an alternative way in teaching and learning grammar, vocabulary and the other language functions in learning English. There are some other groups who may get benefits from this study.
First, for the English teachers, this study can help the teachers in developing their technique in teaching grammar, vocabulary and language function especially for junior high school students. The designed material will help them improves their technique and strategies in teaching. The book also has various kinds of activities and exercises that can be used as the source of teaching material for the teacher.
easily. Therefore the students will be prepared to learn the other components of English when they reach the higher levels of their education.
For the other researchers, this study may help the future researchers as the reference to develop better instructional materials design using the other methods that used in teaching and learning process.
F. Definition of terms
In order to avoid the misinterpretation, the terms of this study need to be defined. There are some specific terms related to this study. The explanation about the definition of terms is described a follows.
1. Instructional Material Design
The instructional material design is creating the new materials that will be useful for teacher in their teaching performances. The main concern of this material design has been with methods of teaching, rather than with learning that means rather than the outcomes of education (Kemp, 1977, p. 6).
2. Supplementary Materials
3. Infographic
Smiciklas (2012) on his book says that infographic is formally defined as “the visualization of data or ideas that tries to convey complex information to an audience in a manner that can be quickly consumed and easily to be understood” (p. 3). It means that infographic shows the information in a practical way, therefore the audience or the reader can understand the information easily.
4. Task-based learning
Task-based learning is one of the techniques in language teaching which aims to provide the learner with the natural context of the language, so if the learners need to complete the task they have to encourage themselves to interact with others (Larsen-Freeman, 2000, p.2). Cadlin and Murphy (1987) also added that the main focus of the task-based learning is the language learning which are presented in a problem-solving form, so the students can expand the knowledge that they know and the new knowledge that they get from the learning process (as cited in Larsen-Freeman, 2000, p. 144).
5. The Seventh Grader Students of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School
In this study, the materials are designed for the seventh grade students of
8 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter was divided into two parts, namely the theoretical description and the theoretical framework. The theoretical description states some related literature which are useful in document analysis and designing the material. The theoretical framework puts the writer’s concepts based on the theoretical description in conducting this study.
A. Theoretical Description
1. Infographic
Infographic is used to visualize the data. Infographic is information graphic that represents the data, knowledge or other information visually with images, graphics, tables and colors. Smiciklas (2012) says that “infographic is defined as the visualization of the information or thoughts that carry the complicated information to a group of people in a practical way which is easy to use and understand”(p. 3). “They are concise, easily digestible, and aesthetically
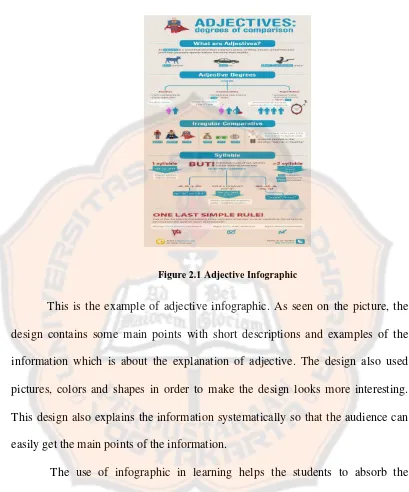
Figure 2.1 Adjective Infographic
This is the example of adjective infographic. As seen on the picture, the design contains some main points with short descriptions and examples of the information which is about the explanation of adjective. The design also used pictures, colors and shapes in order to make the design looks more interesting. This design also explains the information systematically so that the audience can easily get the main points of the information.
The infographic presented the material in exciting and powerful ways so that the students can be more interested in learning (Davis & Quinn, 2014, p. 16). Sometimes infographic used as the focus of the learning material. If the infographic given by the teacher is interesting, it will stimulate the learner’s interest, and can motivate the learner to explore more information (Bellato, 2014). Furthermore, Rotrkl (2014) from British Council noted that the best way to use the infographic is with interactive whiteboards. In the whiteboard, the teacher can display the information and explain it. It also can be in a form of printed explanation which is used colorful, and attractive vectors. In English learning, infographic can give an inspiring approach to set homework for students which used for them to learn English more. For example, they can see the grammar explanation and then doing some exercises and learning activities related to the infographic explanation. This was the idea of the supplementary material that the writer designed for this study.
2. The Instructional Design Model
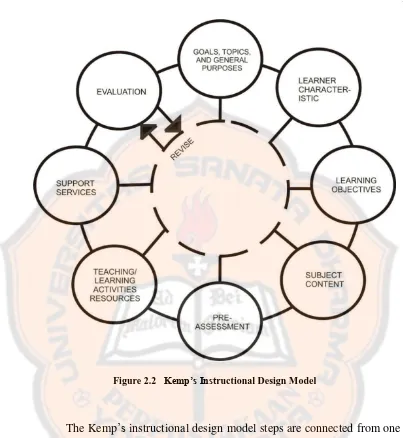
The instructional design model that used in this study is Kemp’s instructional design model. As stated by Kemp’s (1977), this type of model can be implemented in any educational level. This model is designed to supply the answers which are considered as the important elements of the instructional technology. There are:
a. Objectives (What must be learned)
c. Evaluation (How will we know when the required learning has taken place?)
The process of Kemp’s instructional design plan is flexible, which
means the writer can start the process from the element that the writer is ready with. The writer can choose the step whenever the writer need for research. In this theory, Kemp (1977) divides the instructional design into eight parts. The eight parts are as follows:
1) Choose the Goals, the List of Topics, and Starting the General Purposes As stated by Kemp (1977), the writer should start the design by considering the goal first. It begins with the recognition of the school system. In identifying the goals, it may be derived from the society, the students and the subject areas. The society determined the goals include the changes of personal values in living with the society, the development of responsibility and concern for self and others. The students determined the goals include the job preparedness, problem solving skills, or the constructively of using the leisure time, so the goal can be more specific.
2) Identify the Learner’s Characteristics and Needs
In this part, the writer recognized the characteristics and needs of the learners. It is an important step before the writer designs the supplementary materials. This part also helps the writer to select the suitable methods and material for the students. In finding the learners’ characteristics, it is must to obtain the information about the learners’ capabilities, needs, and interests. These
should be affect the emphases in the selection of the topics and levels, the choice and the sequence of the objectives, the depth of treatment, and the variety of learning activities (Kemp, 1977, pp.18-19).
3) Specify the Learning Objectives
In this part, the learning objectives become important instructional design’s step. By stating measurable objectives that the teacher knows specifically about what the teacher wants to teach for example, can later determine whether we have to accomplish it. Kemp (1977) states that the objectives of the learning can be divided into three major categories which are include cognitive, psychomotor, and affective domains (p. 9). First is cognitive domain which is the most important domain for educational program. Bloom at al. (1956) have developed a taxonomy for the cognitive domain which contains of knowledge (ability to memorize, recall, and repeat the information presented earlier), comprehension (ability to interpret or restate the information, application ability to use or apply the information, theories, principles, or laws to new situation), analysis (ability to divide complex knowledge into separate parts and to recognize the relationships of those parts), synthesis (ability to bring together separate elements of knowledge to form new patterns or wholes), and evaluation (ability to make judgments based on knowledge).
attitudes become part of an individual’s practicing value system. However, this
domain has a problem in translating the feelings into identifiable and observable behavior which makes the writing of attitudinal objectives very difficult.
In this learning objectives part, the writer should recognize that those three domains are closely related in two ways. First, the single objective can involve learning in two or more domains. Second, attitudinal development may precede successful learning in the other domains.
4) List the Subject Contents that Support Each Objective.
Subject contents are very important in the students’ learning experiences. It must closely relate to the objectives and to the students’ need. The subject content is the traditional starting point in teaching. It usually used as the subject-centered in teaching. The textbook, for example, is used by the teacher as the primary instructional resource, which often determines objectives, content, and teaching sequence.
In instructional design plan, Kemp (1977) says that subject content is selecting and organizing the specific knowledge which includes fact and information, skills which includes the steps of procedures, conditions, and requirements, the last one is the additional factors of any topic (p. 44). All of these elements of subject contents must be related to the learners’ need and
interest.
5) Develop Pre-assessment to Identify the Students’ Background
will answer these questions: first, is the student prepared to learn about the topic or unit? Second is the student already competent in some of the stated objectives? (Kemp, 1977, p. 50) Through this pre-assessment, the writer will know about the students’ background and the students’ level of knowledge about the topic.
6) Select Learning and Teaching Activities
After the writer developed the pre-assessment, the next step is that the writer have to do is selecting the learning activities, teaching activities, and instructional resources. This part of instructional design is planned to find the method to accomplish the objective. The teacher must determine the most efficient and effective methods and then select the materials to provide learning experiences that will utilize the content associated with each objective (Kemp, 1977, p. 55).
After deciding the plans and also the teaching learning activities, teacher must select the supporting and instructional material resources which can help to explain and motive the students in learning, so the students can easily understand the materials. Not only the materials, teachers must consider the selection of media which is closely associated with the planning of teaching and learning activities. This will be explained more in the next part of the instructional design.
7) Organize the Support Services
educator often make plans using certain instructional methods and for the preparation the teacher did not consider about the support services that they will require later in their teaching performance. As stated by Kemp (1997), considering the appropriate planning is very important in making the design materials. It means that it is important to make some survey before the writer starts to design the materials.
8) Evaluate Students’ Learning towards the Designed Material
This part of design model is needed to measure the students’ accomplishment about how far the students achieve the objectives of the design material. It helps the writer to revise and re-evaluate the designed material that still needs improvement. There will be two kinds of part that will help the writer in gathering data for evaluation. First is formative evaluation which takes place during developments and try-outs. The formative evaluation allows teacher to determine in any point in the instructional sequence. If the students know the material, so the design does not require too much attention of the students.
The second evaluation is summative evaluation. This evaluation is concern with evaluating the degree of students’ final achievement of the
Figure 2.2 Kemp’s Instructional Design Model
3. Visual Information in Learning
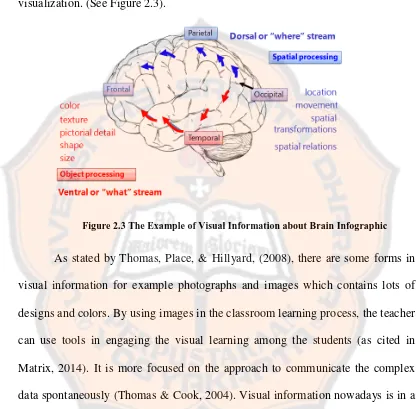
[image:37.595.95.512.172.581.2]Infographic is categorized as information visualization or data visualization. (See Figure 2.3).
Figure 2.3 The Example of Visual Information about Brain Infographic
As stated by Thomas, Place, & Hillyard, (2008), there are some forms in visual information for example photographs and images which contains lots of designs and colors. By using images in the classroom learning process, the teacher can use tools in engaging the visual learning among the students (as cited in Matrix, 2014). It is more focused on the approach to communicate the complex data spontaneously (Thomas & Cook, 2004). Visual information nowadays is in a form of descriptive rather than comparative with the meaning of context of data.
always think in the physical term and very aware of everything around them (as cited in Lane, 2012).
Flemming (2001) in his Visual Audiotory Kinesthetic (VAK) learning style model presents some of visual learning characteristics. They are:
a. The visual learners think in pictures and need to create vivid mental images to retain information. They become understand if they try to imagine the information, for example, the process of rain. Rather than reading it from books which in narrative form, the visual learners understand the process of the rain by imagining it. It helps them to understand the information easily.
b. Visual learners enjoy looking at maps, charts, pictures, videos, and movies. Everything that are visual, something that they can see or watch.
c. They also have some visual skills for example demonstrated in puzzle building, reading, writing, understanding charts and graphs, a good sense of direction, sketching, painting, creating visual metaphors and analogies (perhaps through the visual arts), manipulating images, constructing, fixing, designing practical objects, and interpreting visual image.
picture of a person rather than the names. Visual learners need quiet study time. They cannot be disturbed with noises. They like to study in a quiet place, so they can concentrate more on their study. Visual people had difficulties to work with audio and kinesthetic people. Visual learners have to think awhile before understanding lecture. This is the way when they tried to understand the information by create their own imagination. Visual learner is good at spelling. They are good in remembering letters. Visual learners like colors and fashion. The colors can attract people visually with different kinds and characteristic of the colors itself. Visual people dream in color. It means that color help the visual people in creating the imagination of something. Visual learners understand charts. Charts can help them in summarizing the information that the visual learner get. It is easier for them to absorb the material easily. The last characteristic of visual learner is good with sign language (See Figure 2.3).
Figure 2.4 Examples of sign language
1) Draw a map of events in history or draw scientific process. It will create visual form information which can be easy for the visual learner to understand.
2) Make outlines of everything. By writing the point or the focus of the information can help the visual learner to arrange the information. Then from those points, the visual learners can elaborate the points by their own. This usually helps in writing essays and presentations.
3) Copy what is on the board. This will help the visual learner to repeat the information once again. To make it easier to understand, sometimes they will copy the information that they get in their own way by creating a mind map or make a short summary by using color, graphic or picture. 4) Ask the teacher to make the diagram of the learning material. So the
visual learner can absorb the information easily through the diagram. 5) Make diagram sentences. For example mind map. Mind map is one of
alternative ways in memorizing some information. It is a diagram/graphic that people usually draw in order to summary the information.
6) Take notes, make lists of the important. This can help the visual learner to memorize the material well by writing the point as the focus of the material that they get before.
8) Color code words, research notes. This characteristic helps the visual learners to remember the main points of the information. Usually color code word is used to highlight the important part of the information. 9) Outline reading. This helps the visual learner to get more understanding
in reading. Outline reading lead the visual learners to read the reading text. Sometimes, outline reading are provided in a form of worksheets. 10) Use flashcards. Flash card can be an alternative tool in learning. For
[image:41.595.99.512.252.601.2]example, the use of flash card in English learning is used in order to learn and memorize the English vocabularies. It is easy for the learners remember the vocabulary by using flash card. (See Figure 2.5)
Figure 2.5 The Example of Flash Card
Figure 2.6 Highlighting Text with Highlighter
In order to help the teachers to understand the use and the process of making the infographic, they have to understand some elements of visual. As stated by Lamb and Callison (2012) (as cited in Lamb & Johnson, 2012, p. 57), there are seven categories of visual elements.
a. Charts and graphs. As stated by Lamb and Callison (2012), survey is often represented in form of charts and graphs.
b. Diagram. Diagram is useful in showing the simplified visual representation of an idea, object or concept. Diagram work well for showing relationships such as part and wholes.
Figure 2.8 Example of Diagram
c. Illustration. For example cartoon sketch and technical drawings.
Figure 2.9 Examples of Illustration
Figure 2.10 Example of Map
e. Organizers. For example concept maps, cause/effect organizers and Venn diagram. Organizers are effective to show the relationships among data connection, chronologies of events, and comparison.
Figure 2.11 Example of Venn Diagram
f. Images. For example the historical photograph or satellite images.
g. Symbol. For example traffic sign, music notations, avatar, pictograph etc. Symbols are visual tools that are used to represent ideas, concept, or other abstractions. Avatar can be used to represent human and pictograph can be used to represent chat and maps.
Figure 2.13 Examples of avatar, pictograph and music notes
4. Task-based Learning
In this study, the writer combines the infographic supplementary material with one of the learning techniques. The writer used task-based learning in this study and made the infographic in a form of book to make the students easier to learn English. In this discussion, the writer divided the explanation into two parts. a. The Meaning of Task-based Learning.
In the task-based learning, the term of task as the main focus of the learning process is important. Long (1985) said that the term of the tasks that is used in task-based are based on everything that people do in everyday life activities (as cited in Nunan 2004, p.2). Richards, et al, (1986) added that the task may or may not involve the production of the language. The use of various kinds of activity in task-based learning is to make it more communicative in the learning process (as cited in Nunan, 2004, p. 2).
b. The Framework of the Task-Based Learning
In task-based learning, the daily activities that we do are transformed into tasks in language learning process. The focused of the task- based learning enables the language learners to develop the language skills and also the knowledge of the language itself through the learners’ interaction in
communicating the language. The skills that enable the language learners in developing their skills are language exercises and communicative activities (Nunan 2004, p. 22). Various language exercises can be used in language teaching. The language exercises come in many shapes, forms and can be focused on the lexical, phonological and grammar.
Figure 2.15 Components of the TBL framework (Willis 1996: 52)
In the pre-task, the students discussed the topic with teacher. Then the students highlight the useful words and phrases that help them in understanding the task instructions. As stated by Willis (1996), a good textbook will have ideas for introducing the topic and task, and will also include the preparatory activities for the learner which can be done before they move further in learning the language (p. 46). Willis (1996) also added some activities for the pre-task such as classifying words and phrases, matching phrases to pictures, memory challenge, brainstorming, and mind maps. These activities help the teacher to introduce the topic to the students.
Task cycle consists of three stages. First stage is a task, where the students do the task in pair or in small groups. The task helps students to develop fluency in the target language and strategies in communication. Through the task, the students are expected to become better communicators and also learn new words and phrases so they can enrich their knowledge in learning English. Second stage
PRE-TASK
Introduction to topic and task
TASK CYCLE Task, Planning and Report
is planning, which comes after the task. It describes how the students to plan the report effectively. After the students finish the task, the students tell the answer and discuss it with the teacher and the whole class. Here the teacher encourages the students to speak, check the answers and give feedback for the students’ answers. The role of the teacher in this step is as the language adviser, helping students shape their meanings and express more exactly what they want to say. In the process of this stage, teachers are allowed to correct the students’ language in their speaking. The last stage of the task cycle is report which deals with the report as the conclusion of the task cycle. The teacher as the chairperson summarizes the whole learning and teaching activity.
5. Parameters for Book Activities
parameters for book activities to choose the sub-part for each unit in supplementary material book.
B. Theoretical Framework
This part of the study explains the relation of theoretical description in solving problem which is mentioned in Chapter 1. It is important to include the related studies to analyze the object of the study. To answer the first research problem about how a set of supplementary English materials for BOPKRI 1 Junior High School using infographic media is designed, the writer has to understand about the principles in teaching grammar, vocabulary and the other elements in English language, understand about the students’ characteristics and needs, and also have some information about the curriculum which included the syllabus that used by the teacher.
As stated by Wisniewski and Fichter (2007), the infographic is as the visual media used to instruct, inform, illuminate and entertain readers (p. 57). In this study, the writer designed the infographic as the media to inform the language focus of each learning material. The infographic were combined with the task-based instruction in a form of supplementary book. To make the supplementary book using the infographic, the writer should consider the topics so that they can use the infographic to explore more the information of a topic easily (Lamb and Johnson 2014, p. 55)
material. Because of its flexibility, the writer can start to design the material from whichever step the writer is ready to start. The writer also can omit the step that is not needed for the research. Out of eight steps on Kemp’s instructional media
[image:50.595.99.508.249.610.2]design, the writer only used six steps; 1) Considering the goals, topics and general purposes, 2) Identifying learner’s characteristic and need by developing the pre -assessments 3) Specifying learning objectives, 4) List the subject content, 5) Selecting teaching learning activities and resources, and 6) design materials’ evaluation and revision.
Figure 2.16 Kemp Instructional Design Model steps
The content of the supplementary book that is designed by the writer is used the parameters of book activities by Willis (1996). Those parameters are goal/outcomes, pre-task activities, interaction pattern, and post-task activities. The last step of Kemp’s instructional design model is to evaluate the student’s
Considering the goals, topic and general purposes
Design materials’evaluation and revision Identifying Learner’s Characteristics and Needs
Specifying the Learning Objective
34
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter discussed the methods of the research analysis, the research procedure and also data analysis. This part of the study includes research method, research setting, research participant, instrument and data gathering technique, and data analysis technique and research procedure.
A. Research Method
There were two major problems found in this study. First, this study was conducted to know how supplementary English materials for seventh grade of
BOPKRI 1 Junior High School are designed using infographic media. Second, this study was also conducted to know how does the set of supplementary English materials for BOPKRI 1 Junior High School look like.
To answer the research question/problems of this study, the writer used the research and development (R&D) from Borg and Gall (1983) theory. The followings will explain more about this research.
learning activities for the deigned material. The data and the information about the students’ need in language learning was very important in order to help the writer designed the material.
After finding the data and information for the design, the writer conducted the research using Borg and Gall’s (1983) theory to achieve the research objectives in this study. This method was purposed by Walter R. Borg and Meredith Damian Gall (1983). As stated by Borg and Gall (1983) research and development is a process used to develop the educational product so that it can be acceptable to use in teaching learning process at school (p. 772). In this theory, Borg and Gall (1983) said that there are 10 stages of research and development cycles.
1. Research and Information Collecting
The first step that the writer used was analyzing the learning needs about the material that the writer wanted to design and develop. The data could be taken from the observation, interview, or questionnaire distribution.
2. Planning
3. Develop preliminary of product
From this step of the research and development method, the writer listed and chose the learning techniques that would be suitable for the designed material. In this stage, the writer chose and organized the content of the material.
4. Preliminary field testing
As stated by Borg and Gall (1983), the aim of the preliminary field testing is to find the evaluation of the designed product in the qualitative.
5. Main Product revision
This stage was for the revision of the designed material. The result would be in a qualitative research. It means that the writer analyzed the data and described it in a descriptive form. The evaluation of the deigned material would be more focusing on the process of the research.
6. Main field test
In this stage, the writer should have the field test to test the design so the writer would know whether the designed material was suitable or not.
7. Operational product revision
After conducting the test of the material, the writer did the revision to get the design material ready to be used.
8. Operational field testing
After the writer did the revision the writer did the test one more time. 9. Final product revision
10. Dissemination and implementation
This would be the last stage in the research and development method. The purposed of this stage was to develop the implementation of the design material.
In this study, the writer used the first five steps from Borg and Gall theory because the writer only had limited sources and time to conduct more steps of this study. Since it is flexible to use, the writer started the research from research and information collecting, planning, develop preliminary of product, preliminary field testing, and main product revision.
1) Research and Information Collecting
Research and information collecting aimed to get the relevant information in the process of developing the product. This step of the research is usually called as the pre-design survey where the writer conduct an observation, interviews the English teacher, and distributes the questionnaire to the students. The research and information collecting steps were held in BOPKRI 1 Junior High School. These steps were important in collecting the students’ learning needs and information for the material design. These needs helped the writer in designing the supplementary material activities. For the infographic, the writer also got some educational information from The information was gathered by conducting the informal interview.
2) Planning
material design. In this step, the writer reviewed the syllabus used by BOPKRI 1
Junior High School in order to identify the topics and the goals of the material. The syllabus helped the writer in planning the materials design. For the infographic, the writer chose to make the design based on the syllabus indicator on the syllabus. The infographic discussed the focus of each indicator. The indicators were divided into 7 units as the focus of each unit. Each units of the supplementary book discussed two or four indicators. Those indicators were depended on the topic that was provided by the writer. The writer also wrote some exercises related to the indicators. The next step that the writer did was developing preliminary of the product.
3) Develop preliminary of product
used communicative approach which required the students to practice their speaking skill.
4) Preliminary field testing
Preliminary field testing which is usually called as post-design survey, aimed to obtain the qualitative evaluation of the product (Borg & Gall, 1983, p. 782). The writer evaluated the materials and gathered some comment and suggestions about the supplementary designed material. Those evaluation elements would decide whether the designed materials were appropriate or relevant enough to be implemented as the teaching learning materials. In this study, the designed materials were assessed by distributing the evaluative questionnaire to two English teachers of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School, and one of English tutors from All plus Puri Kids who had some experiences in teaching junior high school students.
5) Main product revision
In this step, the designed materials were revised based on the feedback on the preliminary field testing step. The purpose of this step is to make the final version of the design before it was applied as teaching learning material. The materials were expected to be more appropriate and ready to be used in the classroom after passing some revision from the evaluators.
the theories for the design process. The combination of both theories can be seen in figure 3.1.
[image:58.595.100.522.177.592.2]Writer’s Research model Borg and Gall Theory Kemp’s Instructional Design
Figure 3.1 Writer’s Research Model
From the figure can be seen that the writer combined the research survey method and the instructional design model for the research study. Before designing the supplementary material, the writer did pre-design survey and data analysis (research and information collecting) by identifying the learner’s characteristics and needs. In this step the writer distributed the questionnaires and
Planning Identifying the learner’s characteristics and Design materials’ evaluation and revision Develop Preliminary of Product Preliminary Field Testing Main Product Revision Research and Information Collecting Pre-design Survey
and Data Analysis
Planning the Designed Material Contents Designing the Designed Material Post-design Survey and Designed Material Evaluation Revising the Designed Material Considering goals, topic and general
purposes
Specifying the learning objective
List the subject content
Selecting teaching learning activities and
analyzed the data. On the next step of the research study, the writer was planned for the designed material contents by considering the goals, topics and general purposes related to the participants answer from the pre-design survey. After planning the contents for designed material, the writer started to make the designed material (developing preliminary of product). The writer needed to consider about the learning objective specification, the list of the subject contents and selecting the teaching and learning activities for the supplementary book based on the students’ characteristics and needs.
The next step was post-design survey and designed material evaluation (preliminary field testing). After deigning the supplementary material, the writer met the evaluators to evaluate the designed material. The comments, feedback and suggestions by the evaluators helped the writer in revising the designed material (main product revision).
B. Research Setting
C. Research Participants
[image:60.595.98.519.250.586.2]This section elaborates on the participants of the research. For research participants, the writer chose the seventh grader students of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School. The participants were chosen from two classes of the seventh grade of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School which contain 24 students. The participants filled out the questionnaires in pre-design survey which were used as the data for this study. It helped the writer in making the designed material.
Table 3.1 The Description of the Participant for the Pre-design survey
Participants 7A 7D
Male Female Male Female
The Number of the participants 14 10 13 11
Before the writer conducting pre-design survey, the writer had an informal interview with the English teacher of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School who has educational background of S-1 degree and also had experience in teaching English. It aimed to get some information based on the teacher’s experience in learning English. After that, the writer gave the questionnaire to gain some information based on the students’ experience in English learning.
would be much more improved. The format of the participants was presented in Table 3.2.
Table 3.2 The Format Description of the Participants of the Post-design Survey (blank)
The Evaluators Description Sex
Educational Background
Teaching Experiences M F D3 S1 S2 <5 5-10 >10
1st evaluator
2nd evaluator 3rd evaluator
D. Instruments and Data Gathering Technique
This section explains the research instruments used to gather the data for this study. The types of instruments that were used in this study were informal interview, observation, and document analysis of the material. The writers also made the questionnaires that were used for evaluating the designed material. The explanations of the instruments and data gathering techniques were explained as follows.
1. The Description of Observation
7C, and 7D. Each class had the same amount of students which were 24 students. Because the writer was one of the PPL’s teachers at BOPKRI 1 Junior High School, it was not necessary for the writer to do the observation in the next semester.
2. The List of Interview
As stated by Kvale (1996), the use of interview in research is to state the opinion of a person’s knowledge through conversation (as cited in Cohen et al, 2003, p. 409). The writer used the informal interview in data collecting. This instrument was provided for English teacher of seventh grader of BOPKRI 1
Junior High School before the writer distributed the questionnaire to the students in order to gain some information about the students’ need in learning related to teacher experience in teaching processes.
3. Questionnaire
writer cannot predict all the possible answers. These types of questionnaires were used in all the design survey research steps. First, the questionnaires were used in the pre-design survey. It aimed to collect the data based on students’ motivation and needs in learning English. The second questionnaire was used in the post-design survey which is on the preliminary field testing (post-post-design survey). It aimed to have the evaluation and feedback toward the designed materials. This type of questionnaire were distributed to the evaluators who were two English teachers of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School, and one of English tutors from the All Plus Puri Kids who had the experience to teach the Junior High School students..
E. Data Analysis Technique
In survey research, descriptive data were taken from the result of the informal interview, observation and questionnaire. The writer did the observation to gather information about the students’ characteristics and needs in class. Since the writer was one of the PPL teachers in BOPKRI 1 Junior High School, the writer already knew the condition in seventh grader class. To find more information for this study, the writer gained some information from the English teacher in the informal interview.
were calculated and shown in descriptive form. After that, the writer explained the result of the questionnaire in a narrative form. The second result was about comments, feedback and suggestions of the participants that will be presented in a narrative form.
The data presentation for the post-design survey was also similar to the data presentation on the pre-design survey. The first part of the post-design survey questionnaire (the numeric data) was also presented in a descriptive and explained in a narrative form. The second part of the post-design survey questionnaire which contained comments, feedback and suggestions from the evaluators were also presented in a narrative form.
In the first part of the pre-design and post-design survey, the data from the questionnaires were calculated using the frequency of degree of agreement and calculated as follows:
Note:
N : the total number of the participant who chose the answer. ∑N : the total of all the participants.
format of the first part of the pre-design survey was presented in Table 3.3 and the format of the first part of post-design survey was presented in Table 3.4.
Table 3.3 The Format of the Participants’ Opinion in Pre-design Survey
No Participants opinion
Degree of Agreement Strongly
Agree Agree Disagree
[image:65.595.104.515.199.529.2]Strongly Disagree
Table 3.4 The format of the Evaluators’ Opinion in Post-design Survey
No Evaluators opinion
Degree of Agreement Strongly
Agree Agree Disagree
Strongly Disagree
F. Research Procedure
This section summarizes the steps that were taken in conducting this study. The steps are:
1. Requesting the permission letter from Sanata Dharma University to conduct the research in BOPKRI 1 Junior High School in order to collect the information about the learners’ needs in learning English.
2. Asking for permission to the headmaster of BOPKRI 1 Junior High School. The writer gave the permission letter to BOPKRI 1 Junior High School headmaster.
3. Conducting an informal interview with English teacher of the seventh grader of BOPKRI 1 Junior high School to gain some information about the syllabus, the students’ characteristic, and needs.
4. Distributing the questionnaire to the seventh grader students, to obtain the information needed for the designed material. It also asked some suggestions from the students as the addition for the designed material.