vi ABSTRACT
Sukesi, Retno. Designing a Set of English Speaking Materials for Guides and Instructors in Banyu Sumilir Using Communicative Language Teaching. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program. Sanata Dharma University.
In these recent times Indonesian government is trying to promote Indonesia to the world through its tourism. The government gives authority to local governments to explore their potential including the tourism aspects. The promotion works very well and it can be seen trough the increasing the number of foreign tourists who come to Indonesia. Nowadays, there is a tendency where tourists do not merely want to watch and enjoy tourism objects, but they want to be involved in the activities. The government fulfills the demand by developing Tourism Village where the guests can be involved in the villagers’ activity. One of those is Banyu Sumilir, an outbound area which is located in Desa Wisata Sorowulan. Since there are more and more tourists come to Banyu Sumilir, the guides and the instructors should be able to communicate with tourist guests. They are responsible for giving information to the tourists. That is why being able to communicate using English is badly needed.
The purpose of designing materials in this study is to help the guides and instructors in Banyu Sumilir to improve their English speaking ability so they can communicate with foreign guests.
There were two problems formulated in this study. The first problem deals with how a set of English speaking materials for guides and instructors in Banyu Sumilir using CLT was designed. The second problem deals with how the design materials look like.
In answering the first question the writer combined the instructional models from Kemp and Yalden to determine the step in designing the materials. There were seven steps conducted in this study. Those steps were (1) needs analysis, (2) stating goals, topic and general purpose, (3) stating learning objectives, (4) selecting the syllabus type, (5) listing the subject content, (6) selecting teaching learning activities, (7) evaluation.
The answer of the second question was the presentation of design materials. The materials consisted of seven topics which were presented in eight units. The activities of each unit were divided into five activities called subject content. The subject contents were Brain Storming, Read this dialogue, Expression, Today’s magic words and Time for grouping
vii
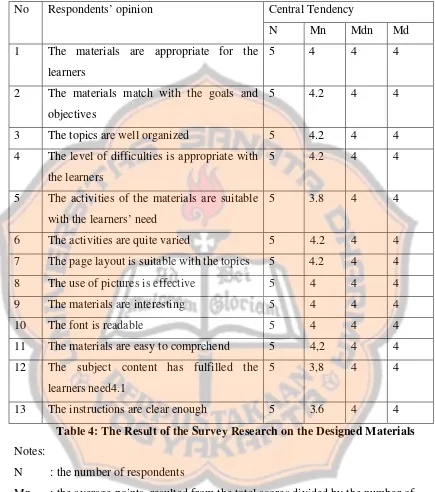
The result of the survey showed that the designed materials were acceptable. It can be seen from the average points of agreements of the respondents’. The average point was 4.1 from the scale 5.0.
viii
ABSTRAK
Sukesi, Retno. Designing a Set of English Speaking Materials for Guides and Instructors in Banyu Sumilir Using Communicative Language Teaching. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Dewasa ini pemerintah Indonesia sedang berusaha mempromosikan Indonesia melalui bidang pariwisata. Pemerintah memberikan wewenang kepada pemerintah daerah untuk mengembangkan daerahnya termasuk dalam segi pariwisata. Usaha ini mendapat sambutan baik terbukti dengan banyaknya wisatawan asing yang datang ke Indonesia. Sekarang ini ada kecenderungan bahwa turis yang datang ke Indonesia tidak cukup hanya melihat dan menikmati objek wisata, akan tetapi sekarang mereka ingin terlibat dalam kegiatan masyarakat. Pemerintah berusaha memenuhi permintaan itu dengan mengembangkan Desa wisata dimana pengunjung bisa terlibat dalam kegiatan penduduk setempat. Salah satunya adalah Banyu Sumilir yang terletak di Desa Wisata Sorowulan. Seiring dengan semakin banyaknya tamu asing yang datang ke Banyu Sumilir maka pemandu dan instruktur harus bisa berkomunikasi menggunakan Bahasa Inggris. Mereka diharapkan bisa memberikan informasi yang dibutuhkan oleh para tamu termasuk kepada turis asing. Itulah sebabya bahasa Inggris sangat dibutuhkan untuk meendukung pekerjaan mereka.
Tujuan dari pembuatan materi ini adalah untuk membantu pemandu dan instruktur di Banyu Sumilir untuk meningkatken kemampuan mereka berbicara menggunakan Bahasa Inggris sehingga mereka mampu berkomunikasi dengan tamu asing.
Studi ini membahas dua masalah. Masalah yang pertama adalah bagaimana seperangkat materi pembelajaran berbicara bahasa inggris untuk pemandu dan instruktur di banyu Sumilir tersebut dibuat. Masalah kedua adalah seperti apakah materi pembelajaran itu.
Untuk menjawab masalah yang pertama penulis memadukan model pembelajaran Kemp dan Yalden untuk menentukan langkah-langkah penyusunan materi. Langkah-langkah tersebut adalah (1) analisis kebutuhan, (2) menentukan sasaran, topik san tujuan umum, (3) menentukan tujuan pembelajaran, (4) menentukan tipe silabus, (5) menyusun bagian materi, (6) menentukan aktivitas pembelajaran, (7) evaluasi.
Untuk menjawab masalah yang kedua, penulis menampilkan hasil desain materi. Materi pembelajaran terdiri dari tujuh topik yang dikembangkan dalam delapan unit. Aktivitas dalam setiap unitnya dibagi menjadi lima bagian yang disebut “Brain storming”, Read this dialogue”, “expressions”, “today’s magic words” dan “Time for grouping”.
ix
lapangan yang kedua dilakukan setelah materi selesai dibuat. Penulis membagikan kuisioner kepada guru dan dosen bahasa inggris. Tujuan dari studi lapangan ini adalah untuk mengevaluasi apakah materi yang sudah disusun sudah sesuai dengan kebutuhan siswa.
Hasil dari studi ini menunjukkan bahwa materi pembelajaran diterima dengan baik. Terbukti dengan hasil yang menunjukkan angka dari antara 4,1 dari total 5
DESIGNING A SET OF ENGLISH SPEAKING MATERIALS
FOR GUIDES AND OUTBOUND INSTRUCTORS
IN BANYU SUMILIR
USING COMMUNICATIVE LANGUAGE TEACHING
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By Retno Sukesi
041214026
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
i
DESIGNING A SET OF ENGLISH SPEAKING MATERIALS
FOR GUIDES AND OUTBOUND INSTRUCTORS
IN BANYU SUMILIR
USING COMMUNICATIVE LANGUAGE TEACHING
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By Retno Sukesi
041214026
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
iii
vi ABSTRACT
Sukesi, Retno. Designing a Set of English Speaking Materials for Guides and Instructors in Banyu Sumilir Using Communicative Language Teaching. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program. Sanata Dharma University.
In these recent times Indonesian government is trying to promote Indonesia to the world through its tourism. The government gives authority to local governments to explore their potential including the tourism aspects. The promotion works very well and it can be seen trough the increasing the number of foreign tourists who come to Indonesia. Nowadays, there is a tendency where tourists do not merely want to watch and enjoy tourism objects, but they want to be involved in the activities. The government fulfills the demand by developing Tourism Village where the guests can be involved in the villagers’ activity. One of those is Banyu Sumilir, an outbound area which is located in Desa Wisata Sorowulan. Since there are more and more tourists come to Banyu Sumilir, the guides and the instructors should be able to communicate with tourist guests. They are responsible for giving information to the tourists. That is why being able to communicate using English is badly needed.
The purpose of designing materials in this study is to help the guides and instructors in Banyu Sumilir to improve their English speaking ability so they can communicate with foreign guests.
There were two problems formulated in this study. The first problem deals with how a set of English speaking materials for guides and instructors in Banyu Sumilir using CLT was designed. The second problem deals with how the design materials look like.
In answering the first question the writer combined the instructional models from Kemp and Yalden to determine the step in designing the materials. There were seven steps conducted in this study. Those steps were (1) needs analysis, (2) stating goals, topic and general purpose, (3) stating learning objectives, (4) selecting the syllabus type, (5) listing the subject content, (6) selecting teaching learning activities, (7) evaluation.
The answer of the second question was the presentation of design materials. The materials consisted of seven topics which were presented in eight units. The activities of each unit were divided into five activities called subject content. The subject contents were Brain Storming, Read this dialogue, Expression, Today’s magic words and Time for grouping
vii
The result of the survey showed that the designed materials were acceptable. It can be seen from the average points of agreements of the respondents’. The average point was 4.1 from the scale 5.0.
viii
ABSTRAK
Sukesi, Retno. Designing a Set of English Speaking Materials for Guides and Instructors in Banyu Sumilir Using Communicative Language Teaching. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Dewasa ini pemerintah Indonesia sedang berusaha mempromosikan Indonesia melalui bidang pariwisata. Pemerintah memberikan wewenang kepada pemerintah daerah untuk mengembangkan daerahnya termasuk dalam segi pariwisata. Usaha ini mendapat sambutan baik terbukti dengan banyaknya wisatawan asing yang datang ke Indonesia. Sekarang ini ada kecenderungan bahwa turis yang datang ke Indonesia tidak cukup hanya melihat dan menikmati objek wisata, akan tetapi sekarang mereka ingin terlibat dalam kegiatan masyarakat. Pemerintah berusaha memenuhi permintaan itu dengan mengembangkan Desa wisata dimana pengunjung bisa terlibat dalam kegiatan penduduk setempat. Salah satunya adalah Banyu Sumilir yang terletak di Desa Wisata Sorowulan. Seiring dengan semakin banyaknya tamu asing yang datang ke Banyu Sumilir maka pemandu dan instruktur harus bisa berkomunikasi menggunakan Bahasa Inggris. Mereka diharapkan bisa memberikan informasi yang dibutuhkan oleh para tamu termasuk kepada turis asing. Itulah sebabya bahasa Inggris sangat dibutuhkan untuk meendukung pekerjaan mereka.
Tujuan dari pembuatan materi ini adalah untuk membantu pemandu dan instruktur di Banyu Sumilir untuk meningkatken kemampuan mereka berbicara menggunakan Bahasa Inggris sehingga mereka mampu berkomunikasi dengan tamu asing.
Studi ini membahas dua masalah. Masalah yang pertama adalah bagaimana seperangkat materi pembelajaran berbicara bahasa inggris untuk pemandu dan instruktur di banyu Sumilir tersebut dibuat. Masalah kedua adalah seperti apakah materi pembelajaran itu.
Untuk menjawab masalah yang pertama penulis memadukan model pembelajaran Kemp dan Yalden untuk menentukan langkah-langkah penyusunan materi. Langkah-langkah tersebut adalah (1) analisis kebutuhan, (2) menentukan sasaran, topik san tujuan umum, (3) menentukan tujuan pembelajaran, (4) menentukan tipe silabus, (5) menyusun bagian materi, (6) menentukan aktivitas pembelajaran, (7) evaluasi.
Untuk menjawab masalah yang kedua, penulis menampilkan hasil desain materi. Materi pembelajaran terdiri dari tujuh topik yang dikembangkan dalam delapan unit. Aktivitas dalam setiap unitnya dibagi menjadi lima bagian yang disebut “Brain storming”, Read this dialogue”, “expressions”, “today’s magic words” dan “Time for grouping”.
ix
lapangan yang kedua dilakukan setelah materi selesai dibuat. Penulis membagikan kuisioner kepada guru dan dosen bahasa inggris. Tujuan dari studi lapangan ini adalah untuk mengevaluasi apakah materi yang sudah disusun sudah sesuai dengan kebutuhan siswa.
Hasil dari studi ini menunjukkan bahwa materi pembelajaran diterima dengan baik. Terbukti dengan hasil yang menunjukkan angka dari antara 4,1 dari total 5
x
I Turn To You
When I'm lost in the rain
In your eyes I know I'll find the light
To light my way, when I'm scared losing ground
When my world is going crazy you can turn it all around
And when I'm down you're there pushing me to the top
You're always there giving me all you've got
For a shield, from the storm for a friend, for a love
To keep me safe and warm, I turn to you
For the strength to be strong, for the will to carry on
For everything you do, for everything that's true, I turn to you
When I lose the will to win
I just reach for you and I can reach the sky again
I can do anything 'cause your love is so amazing
'Cause your love inspires me
And when I need a friend you're always on my side
Giving me faith taking me through the night
For the arms to be my shelter through all the rain
For truth that will never change for someone to lean on
But for a heart I can rely on through anything
For the one who I can run to
I turn to you
Warren, Diane;
xi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
My deepest gratitude is addressed to Allah S.W.T who guides me all the time and gives me strength to finish this work, for the blessing by sending me great people and make my life so great and wonderful.
I dedicate my deepest gratitude and appreciation to my sponsor, Mr. Y.B Gunawan, M.A for the guidance, corrections, advice, criticism to improve the
thesis, and for the support and encouragement to finish the thesis soon.
I would like to say thank you to my beloved parents, Bapak Sualman and Ibu Sumarti thanks for struggling very hard and send me to school till I achieve
this degree. For my sisters, Mba Tuti and Mba Susi thanks for being nice friends to share. For my brothers Mas Danang, Mas Silih, Mas Dono, and Rendra thanks for nice jokes support and being good friends so I feel comfortable being at home. I thank to God for sending me to this lovely family.
My high appreciation goes to Mr. Yanto, the Manager of Banyu sumilir. Thanks for giving permission to conduct a research in Banyu Sumilir and let the guides and instructors in Banyu Sumilir be the respondents of my research.
I would like to say thanks to Ms. Murti, Mr. Andre, Ms. Mita, Bu Yuseve, and Mr. Nugraha for giving opinions and suggestion to my design
materials. It is very useful to improve the materials. I would like to thank other PBI’s teaching staff who educated me, shared their knowledge and guided me during my study. I also address my sincere gratitude to Sr. Margaret SCJ who is willing to correct my grammatical mistakes. For the staff of PBI secretariat, Mba Tari and Mba Dani thank you for the good services related to my study.
My deepest thanks go to my friends in KKN (Riko, Novi, Gustin, Hendrik, Angga, Duma, Tia, Thomas, Yunika), my friends in PPL (Hening,
Ayu, Herlin, Yanti, Tuti), my friends in SPD (Oki, Maya, Tya, Dian, Joni,
xii
Deeply from my heart I want to address my gratitude to my best friends (Dita, Tami, and Maya) who are willing to give their time to share happiness, sadness and to support one another. For all my friends in PBI especially from 2004 thank you for the very nice friendship. Every moment we share will be unforgettable.
At last but not the least, I would like to say thank you to Mas Adith, for always giving me support, keeping asking me about the progress of my thesis, giving me unpredictable but brilliant idea, and thanks for being by my side during the hard times.
Finally I would like to say thank you to everyone who helps me during the process of finishing my thesis.
xiii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE ... .i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... iv
LEMBAR PERYNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI... v
ABSTRACT... vi
ABSTRAK ...viii
DEDICATION PAGE... .x
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ... .xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS...xiii
LIST OF TABLES ... xvi
LIST OF FIGURES ... xvii
LIST OF APPENDICES ...xviii
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION 1
A. Background ... 1
B. Problem Identification ... 4
C. Problem Limitation... 5
D. Problem Formulation ... 5
E. Research Objectives... 6
F. Research Benefits... 6
G. Definition of Terms... 7
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE 9
A. Theoretical Description ... 9
1. Instructional Design Model... .9
a. Kemp’s Instructional Material Design Model... 9
b. Yalden’s Instructional Material Design Model... 13
xiv
a. The Nature of Speaking…... .17
b. The process of Speaking ... 17
c. The Principles of teaching speaking…... 18
d. Activities ... 19
3. Communicative Language Teaching... .21
a. Characteristics of CLT ... 22
b. Learners’ and teacher’s role ... 24
c. The role of Instructional Materials in CLT ... 25
d. Theory of Learning ... 26
e. Types of Learning and Teaching Activities ... .26
4. English for Specific Purpose... 27
a. The reasons that initiate ESP program ... 27
b. The characteristics of ESP program... 29
5. Syllabus ... .31
B. Theoretical Framework ... 34
CHAPTER III. METHODOLOGY 38
A. Research Method... 38
B. Research Respondent... 43
C. Setting... 44
D. Research Instruments ... 44
E. Data Gathering Technique... 45
F. Research Procedure... 46
CHAPTER IV. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS 49
A. The Elaboration of steps in designing the materials ... 49
B. Result of Survey Research... 64
1. The Results of the Needs Analysis... 64
2. The Result of the Survey on the Designed Material ... .69
C. Discussions ... 72
xv
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS 75
A. Conclusions ... 75 B. Suggestions... 78
xvi
LIST OF TABLES
1. Basic Competence……… 54
2. Learning Indicators………..………..56
3. The data of the respondents………...69
xvii
LIST OF FIGURES
1. Kemp’s Model……….13
2. Yalden’s Model………...14
3. The similarities between the writer’s model and R & D……….42
xviii
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1:
Surat Ijin Penelitian
Appendix 2:
Questionnaire for Needs Survey………80
Appendix 3:
Questionnaire for Material Evaluation………..83
Appendix 4:
Overview……….………..85
Appendix 5:
Syllabus……….90
Appendix 6:
Lesson Plan………97
Appendix 7:
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter covers the background of the study, problem limitation, problem Formulation, Objectives of the study Benefits of the Study, and Definition of the terms, which includes designing a set of English materials, Speaking, outbound, instructors, and communicative Language Teaching.
A. Background of Study
In these recent years the Indonesian government focuses on developing tourism. Indonesia tries to attract foreigners to come to Indonesia. The latest program is Visit Indonesia 2008. This program shows that the government seriously invites foreigners to come to Indonesia. Attracting people to come means that Indonesia has to provide attractions to satisfy the guests. Right now Indonesia is concerned about developing the tourism aspects.
and many others. Unfortunately now the interest is not only put on the objects itself. It is not enough for the visitors just to come and see and go back home without any experience of cultures.
Now Sleman, one of the regencies in Yogyakarta, tries to support the government’s effort to invite as many foreigners as possible. Sleman focuses on developing a tourism village as a new innovation of tourism. Tourism village is hoped to offer different attractions for visitors. The area which is located far away from the city and crowd is hoped to be a suitable place for those who want to feel different atmosphere. In tourism village, visitors not only enjoy seeing the object but also get involved in the villagers activities. It will give them new experiences.
Banyu Sumilir, one of the tourism objects which is located in Desa Wisata Sorowulan offers attractions. There visitors are involved in many activities, and one of which is games. Banyu Sumilir provides a lot of challenging games for visitors both for individual and team. The games do not merely give fun to visitors but it has something to learn, such as leadership, concentration, and cooperation. Visitors will be safe because it is completed with security facilities and is guided by professional instructors.
(Aseli, Lokal, Unik and Indah). During the past six years there has been lots of visitors come to Sorowulan from both local and International. They can enjoy all the activities and facilities provided in this village at a reasonable price.
In the development of Banyu Sumilir, the owner promotes Banyu Sumilir not only in Indonesia but also in other countries. It brings a new problem since there are no guides or instructors who are able to speak English fluently. It becomes a serious problem because the guides and the instructors are those who are in charge of accompanying and guiding visitors. They have to explain all the activities and things related to the village. If the visitors come from other countries, of course, the explanation is conveyed in English.
In Banyu Sumilir, the guides and instructors have different roles. They become instructors when they have to be facilitators in playing games, and they will change their role as guides when they have to guide tourists. Both instructors and guides have to be able to give clear instructions and explanations to tourists. That is why being able to speak English fluently is very important.
Communicative competence is the focus of the classroom goals and not restricted to grammatical or linguistic competence.
Communicative Language Teaching is an approach that can be applied in English Language teaching as a second language. Since this study focuses on teaching speaking skill to enable the learners to be able to communicate with foreigners, CLT is the appropriate basic theory for language teaching methodology to be applied in this study.
B. Problem Identification
Being able to speak English is very important. The real world requires that everybody is supposed to be able to speak in English. Those who are not able to communicate in English will lose out in the competition. From the background of this study we can see that a good service is badly needed. In this case, giving a good service means being able to speak English in order to serve foreign tourists during their vacation in the village.
One of the principles of tourism village is that all the services are done by the villagers themselves, including the guides if there are visitors from other countries. From the background it can be seen that the problem in the development of tourism village and Banyu Sumilir is that the villagers and the instructors are not able to speak English.
communicate in English. In this study the writer tries to develop materials for guides and instructors in Banyu Sumilir.
C. Problem Limitation
This study is limited to the teaching of speaking materials for instructors in Banyu Sumilir and the materials focus on how to guide tourists to do games and activities conveyed in English..
To be able to give a satisfying service to the guests, the guides should be able to know what the guests need. In this case the ability to communicate in English is much needed. Guides should be able to use English properly. This means that they have to know how to use English in their daily work.
Considering the importance of English for tourist guides, the writer tries to develop speaking materials for guides and instructors in Banyu Sumilir.
D. Problem Formulation
Based on the background, problem identification and problem limitation above, the problems of this study are formulated as follows:
1. How is a set of English speaking materials for guides and outbond instructors in Banyu Sumilir using Communicative Language Teaching designed?
E. Research objectives
The objective of the study is to find out how designing a set of English speaking materials for guides and instructors using Communicative Language Teaching in Banyu Sumilir is designed and to present the designed set of English speaking materials.
F. Research Benefits
The writer hopes that this study will give benefit as follows: 1.For English teachers
This study can be used as a guideline to teach speaking especially for English for specific purpose
2. For guides and the instructors
This research can be used as a means to improve English speaking skill 3. For Banyu Sumilir
If the instructors and the guides are able to speak English they can promote Banyu Sumilir to other countries.
4. For the writer
G. Definition of terms
In order to have a clear understanding of the study, the writer includes some definitions of important terms. Those are:
1. Design
Instructional design is a systematic planning of instruction in which attention is given to the related elements (Kusumo & Willis, 1989: 55). Designing also means instruction development. Instruction development is managing the planning, development, and implementation procedure for instruction or training (Kusumo & Willis, 1989: 55).
Design is the general arrangement of a developed plan to guides educational activity in situation (Howe, 1978:230). In this study it means as an overall plan to facilitate teaching learning activities in the classroom. In this study, designing means a process of making materials, activities which is begun with a theory in order to achieve a certain goal.
2. Speaking
Speaking is the process in which people address each other to form their communication process (Joyce, 1980: 242). In this study speaking is used by tourist guides to communicate with foreigners.
3. Guides and Instructors
4. Communicative Language Teaching
9
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter reviews the related literature underlying this study. It consists of theoretical description and theoretical framework. The theoretical description discusses basic theory of instructional material design, communicative language teaching, speaking skill, ESP and syllabus.
A. Theoretical Description
This part discusses theory of Instructional material design. The first discussion is about models of Instructional Material Design which are used in this research. The next discussion is about Communicative Language Teaching because the design uses CLT approach, and the design concern in speaking skill. Since the study is going to provide materials for a certain group, the writer also discusses the theory of ESP to determine the syllabus.
1. Instructional Design model
Hutchinson and Waters state that designing material is creating a set of materials that fits the specific subject area of particular learner. This study follows the models presented by Kemp.
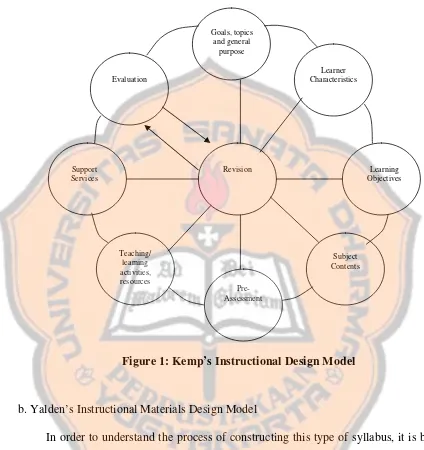
a. Kemp’s Instructional Material Design Model.
1) Goals, Topic, and General Purpose
Determining goals may be the basic aspect for the understanding and skill the society expect .the basis of instructional planning often straight teacher oriented statement of general purpose of topic (Kemp, 1997)
2). Learner characteristic
In making instructional planning, including selecting topic, determining objectives, and choosing learning activities, an instructional designer should consider learners’ capabilities, learners’ interest in order to adjust the instructional material design with learners’ condition.
a) Academic factor
It includes number of students, academic background, grade point average, level of intelligence scores on standard achievement, motivation for studying the subject, expectation of the course.
b) Social Factor
It includes age, maturity, special talent, relation among students, socio-economic factor.
3). Learning objectives
Learning objectives concerning with learning as the result of instruction. In order to be the learning guideline, all objectives must be stated in the forms of activities that will guide the learning process.
The benefits of objectives are:
b) Objective helps the planning team to think in specific term and to organize and sequence the subject matter
c) Objectives provide a basis for evaluating both the students’ learning and the effectiveness of the subject matter.
d) Objectives indicate the type and extent of activities that are required for successfully carrying out the learning.
e) Objectives the best means for communicating to your colleagues, parents and others what is to be taught and learned.( Kemp, 1997)
In other words we can say that objectives tell the students the goal they have to achieve.
4). Subject Content.
Determining the subject content is the next step after the goals and the topics have been stated. In details, subject content includes the organization of the content and the organization of the task. (Kemp, 1997:44)
5). Pre Assessment
This step has two kinds of test. The first one is requisite testing. It is done to determine whether the students already have the background and preparation for the topic. The second one is pre testing. It is aimed to measure which objective have already mastered or achieved. (Kemp, 1997: 51-52)
6). Teaching Learning Activities
to a group, individualized learning and teacher-students interaction, as the basic method of the learning activities.
There is a development of teaching learning activities.
a) Presenting information to a group of students at one time than to have each student study the materials independently.
b) Many students learn satisfactorily on their own at their own pace, whereas other students prefer highly structured teaching learning situation in which they are systematically guided through lesson.
c) Making small group interaction in order to give opportunity face to face teacher-student relationship.
7). Support Service
This step includes funding, personal, facilities, equipment, tools and time, for the schedule of the instructional plan. (Kemp, 1997:85) Support service should be well prepared to avoid any possible constrain in designing the plan.
8). Evaluation
The test is used to measure whether the materials are successfully implemented for the students or not (Kemp,1997: 91). The teacher should have the criteria of making the test item in order to measure the learning outcome.
Figure 1: Kemp’s Instructional Design Model
b. Yalden’s Instructional Materials Design Model
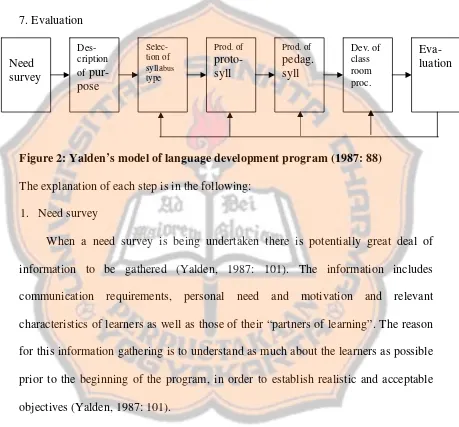
In order to understand the process of constructing this type of syllabus, it is by examining the overall process planning a second-language program. Yalden’s stages for the instructional plan can be divided into seven stages (Yalden, 1987: 100).
1. Need survey
2. Description of purpose
3. Selection of development of syllabus type Goals, topics
and general purpose Evaluation
Learner Characteristics
Support Services
Revision Learning
Objectives
Teaching/ learning activities, resources
Pre- Assessment
4. Production of proto-syllabus 5. Production of pedagogical syllabus
6. Development and implementation of classroom procedures 7. Evaluation
Figure 2: Yalden’s model of language development program (1987: 88)
The explanation of each step is in the following: 1. Need survey
When a need survey is being undertaken there is potentially great deal of information to be gathered (Yalden, 1987: 101). The information includes communication requirements, personal need and motivation and relevant characteristics of learners as well as those of their “partners of learning”. The reason for this information gathering is to understand as much about the learners as possible prior to the beginning of the program, in order to establish realistic and acceptable objectives (Yalden, 1987: 101).
information is face-to-face interview. The writer conducts this kind of interview to understand the variety of learners’ expectation.
2. Description of purpose
After information of the needs survey was collected, the next step is getting expected and specific purpose of the learners. By identifying the purpose of their needs, the writer could form the appropriate language content from simplest till the wider scope. Robinson (1980) divided general purpose into two kinds of purposes, namely educational and occupational purpose (Yalden, 187: 107). Understanding the learner’s purpose will guide the teacher to design the instructional materials that is suitable in the learner’s field.
3. Selection of development of syllabus type
Yalden describes the syllabus as an instrument by which the teacher can achieve a degree of fit between the needs and aims of the learner and the activities that will take place in the classroom. Yalden also has classified as number of communicative syllabus types, such as notional or structural syllabus that focus on the grammar understanding, functional syllabus that involves developing skill and structural-functional syllabus that involves combination between grammar and skill development (Yalden, 1987: 108).
4. Production of Proto-Syllabus
functions, discourse and rhetorical skill, variety of language, role sets and communicative events as well as grammar and lexis.
5. Production of Pedagogical syllabus
The pedagogical syllabus provides a repertoire of words and phrases chosen as exponents of functional and suitable to the topics identified as important to the learners (Yalden, 1987: 143-144). Such syllabus creates a convenience in terms of the matched between the knowledge and appropriate content and teaching technique, the learner’s actual purpose and needs in the classroom.
6. Development and Implementation of Classroom Procedure
Yalden (1987: 89) gave a brief description on the development and implementation of classroom procedure that can be divided into:
a. Selection of exercise type and teaching techniques b. Preparation of lesson plans
c. Preparation of weekly schedules
Those three procedures are meant to be monitored weekly by the teacher to assess the classroom progress.
7. Evaluation
From the above points, Yalden stages are started from the importance of conducting communicative need survey from whom the program is prepared. Those stages represent discrete operations for the sake of clarity in Yalden’s model.
In this study the writer combined those two models to determine the steps in designing the materials. The writer took some steps from Kemp’s model and some steps from Yalden’s model.
2. Teaching Speaking Skill
This part will discuss the basic theory of speaking skill. There are three parts that are going to be discussed in this section. Those are:
a. The Nature of Speaking
First of all, spoken language and written language are different basically. Brown and Yule as quoted by Nunan (1989:26-27) discuss the difference between them. Written language is characterized by well-formed sentences, which are integrated into highly structured paragraphs. On the other hand, spoken language consists of short, often fragmentary utterances, in a range of pronunciations. It is a skill that generally has to be learned and practiced.
b. The process of speaking
Through speech, someone expresses his emotion, communicates his intention, reacts to other persons situation, influences other people, and finally enables him to examine, and rearrange impression and association so that he involves new relationships and purposes. ( Rivers, 1986: 162)
c. The Principle of Teaching Speaking
Teaching speaking skill can not be separated from the idea of teaching communicative ability. Communicative ability is the production of specifies ability to communicate in target language. (Paulston and Bruder, 1976: 56)
The principles of teaching speaking will be clarified as follows:
1) Be aware of the differences between second language and foreign language learning context.
A foreign language context is one where the target language is not the language of communication in the society, while a second language context is one where the target language is the language of communication in the society. Learning speaking is very challenging for the students in Foreign Language because they have very few opportunities to use the target language outside the class.
2) Give students practice with both fluency and accuracy.
3) Provide opportunities for students to talk by using group work or pair work, and limiting teacher talk.
Pair work and group work activities can be used to increase the amount of time that learners get to speak in the target language during the lessons.
4) Plan speaking tasks that involve negotiation for meaning
Research suggests that learners make progress by communicating in the target language because interaction necessarily involves trying to understand and make your self understood. It involves checking to see if you’ve understood what someone has said, clarifying your understanding, and confirming that someone has understood your meaning.
5) Designing classroom activities that involves guidance and practice in both transactional and interactional speaking.
Interactional speech is communicating with someone for social purpose. Transactional speech involves communicating to get something done. According to Nunan, interactional speech is much more fluid and unpredictable than transactional speech.
The writer needs to understand the principles of teaching speaking to be bale to apply suitable method in conducting teaching learning process. These principles will be used as a guide in conducting the lesson.
d. Activities
The aim of this activity is for the learners to discover their classmates’ secret choices. This activity can be used to practice almost any structure, function or notion.
2) Dialogue and role-play
By doing role-play the learners may participate more willingly and learn more thoroughly than when they are told to repeat a given dialogue in pairs or in a group.
3) Matching activities.
The task for the learners is to recognize matching items, or to complete pairs or sets.
4) Communicative activities
This activity is designed to encourage the learners to practice communication strategies like paraphrasing, using gesture, and asking for feedback.
5) Pictures and picture stories
Communication activities can be stimulated through the use of pictures. 6) Puzzles and problems
This requires the learners to make guess, draw from their general knowledge and personal experience, use their imagination and test their power of logical reasoning.
7) discussion and decision
The writer will apply most of these activities in the design materials since the focus of the study is to teach speaking skill. Questions and answers activity will be applied in information gap activity. The learners need to ask questions to their friends to complete the information. Dialogue and role-play is very useful to be applied. The learners will practice some of the activities similarly with the real situation.
Matching and puzzle activities would be applied in vocabulary mastering. The learners match the English words with its meaning or its synonyms. The writer also used pictures during the learning process. Pictures were an effective means to lead the learners to have an idea about the topic. Communicative activity was another important activity that would be applied. This activity was suitable with the approach that the writer used in this study. Communicative activity gave a good chance for the learners to practice their speaking ability using the target language.
3. Communicative Language Teaching
In conveying the materials, the writer uses Communicative Language Teaching. The writer uses this approach to give opportunities for the learner to practice their ability to communicate with others.
According to Richards and Rodgers (1986: 64) CLT opens up wider perspective on language. They consider language not only in terms of its structure, but also in terms of communicative function. CLT also opens up wider perspective on language teaching. In particular, it makes us more strongly aware that it is not enough to teach learners how to manipulate the structure of the foreigner language.
a. The characteristic of CLT
Littlewood (1981: 1) mentions some characteristics of CLT. He says that the most characteristic features of CLT is that CLT pays systematic attention to functional as well as structural aspects of language, and then combine these aspects into a more fully communicative view.
Different from Littlewood, Brown (1994: 245) offers the interconnected characteristic of CLT:
1) Communicative competence is the focus of the classroom goals and not restricted to grammatical or linguistic competence.
2) The design of language techniques involves learners in the pragmatic, authentic, and functional use of the language for meaningful purpose.
3) Fluency and accuracy are emphasized as complementary principles underlying communicative techniques.
4) The classroom goal is to use the language productively and appropriately in a spontaneous way.
a) To make communicative competence the goal of language teaching
b) To develop procedure for teaching of the four language skills that acknowledge the interdependence of language and communication.
Teaching points are introduced in dialogue form, grammatical items are isolated for controlled practice, and then freer activities are provided. Pair and group work are suggested to encourage the students to use and practice functions and forms (Richards and Rodgers, 1986)
The methodological procedures reflect a sequence of activities represented in Littlewood (1981, p. 86) as follows:
Structural activities Pre-communicative activities
Quasi communicative activities
Functional communicative activities
Communicative activities
Social interaction activities
Littlewood (1983) distinguishes subcategories of communicative activity called functional communication activities and social interaction activity
¾ Functional communicative activities: this activity places the learners in a situation where they must perform a task by communicating as best as they can. ¾ Social Interaction activities: the learners are also encouraged to take account of
The goal of CLT is that, at the end of the course, the learners have communicative competence. This approach helps the learners to be able to communicate using the target language understandably.
b. Learners’ and teacher’s role 1) Learner’s role
Communicative Approach emphasize on the process of communicative. Breen and Candlin (1980: 110) describe the learner’s role in CLT as below:
“The role of the learner is as negotiator – between the self, the learning process, and the object of learning – emerges from and interact with the role of joint negotiator within the group and within the classroom procedures and the activities that the group undertakes. The implication for the learner is that he should contribute as much as he gains, and thereby learn in an interdependent way.”
2) Teacher’s role
According to Breen and Candlin teacher has several roles: a) Facilitator
A teacher has to facilitate a communication process between all participants in the classroom, and between participants and various activities.
b) Participant
Teacher should act as an independent participant within the teaching-learning group. c) Counselor.
d) A group process manager.
The teacher organizes the classroom as a setting for communication and communicative activities.
CLT requires the teacher to be active and creative in designing the activities that give opportunities to speak in the classroom activities.
c. The Role of Instructional Materials in CLT
The instructional materials in CLT play an important role in promoting communicative language use. The instructional materials should help the learners in achieving the objective of the program. The materials should encourage the learners to be active and creative.
According to Richard and Rodgers (1986:79-80), there are three kinds of materials currently used in CLT, namely text-based materials, task-based materials and realia.
1) Text-based materials
Text-based materials are materials, which are designed to direct and support CLT. They are written in structural syllabus with reformatting to be based on a communicative approach and created to help teachers to initiate conversation among learners. Some examples of text-based materials are visual cues, tape cues, pictures, and sentence fragments to initiate conversation.
2) Task-based materials
handbooks, cue cards, activity cards, pair communication practice materials, and student-interaction practice booklets. These materials are sometimes complementary which mean that students should cooperate with their partners to complete the tasks.
3) Realia
Realia is authentic materials or the ones taken from real life. The realia might include language-based realia such as signs, magazines, advertisements, newspapers, graphics, and tables. It is also suggested that the teachers use visual sources around which communicative activities can be built such as maps, pictures or photograph, and symbols.
d. Theory of learning
Elements of an underlying learning theory can be discerned in some CLT practices. One such element may be described as the communication principle: activities that involve real communication promote learning. A second element is the task principle: Activities in which the language is used for carrying out meaningful tasks promote learning (Johnson 1982). A third element is the meaningfulness principle: language that is meaningful for the learners supports the learning process. Learning activities are consequently selected according to how well they engage the learner in meaningful and authentic language use (rather than merely mechanical practice of language patterns), (Richard, Rodgers 2001:165).
e. Types of learning and teaching activities
communicative objective of the curriculum, engage learners in communication, and require the use of such communicative processes as information sharing, negotiation of meaning, and interaction. Classroom activities are often designed to focus on completing tasks that are mediated through language or involve negotiation of information or information sharing (Richard, Rodgers 2001:165).
The writer used Communicative language teaching approach in this study. The writer applied some principles of this approach. One of the principals of CLT is that communicative competence becomes the focus of the classroom goals and not restricted to grammatical or linguistic competence. It is suitable with the goals of this study. By the end of the course the learners were expected to be able to communicate with foreign guests understandably. They do not have to focus on their grammar.
The writer also applied the sequence of activities in CLT. The writer divided the activities in each unit into two main activities, Pre-communicative activities and Communicative activities. The writer also used the activities from CLT such as information gap activity.
4. English for Specific Purpose
In this section the writer wants to discuss two parts. They are the reasons that initiate the ESP program, and the characteristic of ESP.
a. The reasons that initiate ESP program
The first reason is the demand of instrumental use of English. The expansion of the development of science, technology and commerce requires more and more people to learn English as international language. People learn English not only because of the expansion of technology and commerce but because they need English for their everyday communication.
The demands and requirement have resulted in the expansion of one particular aspect of English Language Teaching (ELT) namely the teaching English for Specific Purpose (ESP). The demand for English has often come from groups of learners with no need for ‘general’ English. This general English is usually provided by secondary-school English course. Some learners wish to learn English for a particular reason which concern their studies or jobs.
This study is involved in ESP program since this study .concerns with designing materials for guides and instructors. They do not need to learn the whole English program, but only some restricted areas of English that is relevant to their need.
should be possible to determine the features of specific situation and make them the basis of the learners (Hutchinson and Waters, 1987: 7).
The third reason of the emergence of ESP program is that the ESP program should be focused on the learners. A new development in educational psychology that emphasizes on the central importance of learners and their attitudes toward learning contributed to the rise of ESP (Hutchinson and Waters, 1987). In this case, learners with all their different needs and interest become the important consideration in determining the course content. (Hutchinson and Waters, 1987: 19) said that ESP is an approach to language teaching in which all decisions as to content and method are based on the learners’ reason for learning. Moreover, the emphasize on the word “specific” in English for Specific Purpose should be placed firmly on the purpose of the learner for learning the language, not on the language he is learning (Mackey and Mountford 1987).
b. The characteristic of ESP Program
In order to design the instructional materials for guides and instructors, the writer should be able to understand the characteristic and the criteria of the learners. The understanding of the learners’ characteristic will be useful to place the level of the learners in the course.
The objective should be closely specified and related to the time available. It implies the collaboration and negotiation among those who are involved in the course, for example, student, teacher, and organizer.
2) ESP students are likely to be adult rather than children
As adult learners they can think of the reason why they learn English. The adult learners will learn fast when they realize that English course is useful for their needs. Strevens (1980) stated that adult learners would be motivated and may learn fast when they realize that English course is relevant to their needs.
3) ESP course consists of identical students
It means that all the learners in class of ESP are involved in the same work. There are some criteria of ESP program. The first criterion is that normally ESP program is goal directed, that is they learn English not because they are interested in English language, but because they need it for study or work purposes. The guides and instructors learn English to support their work, therefore, their purpose to learn English is already goal directed.
Seeing the characteristics of CLT, this study belongs to ESP. The characteristics are the course usually has clearly specified period of the course, ESP students are likely to be adult rather than children, ESP course consists of identical students. The learners of this study are guides and instructors who need to learn English to support their job. They are expected to be able to speak with foreign guests using the target language.
5. Syllabus
Hutchinson and Waters (1994: 80) defines a syllabus as a document or statement of what will (or at least what should) be learned and taught. Syllabus is very crucial for teachers because syllabus is a plan of work as well as guideline and content for class content. For students, syllabus can be “a route map” of the course. The effect may be similar to that of using a published textbook for the course (rather than a series of hand out) that is the students can see that there is a plan and how the individual lesson fit together (Hutchinson and Waters, 1994: 81)
Types of syllabus
Krahnke (1987) stated that there are six types of syllabus. The types of the syllabus are clarified as follows:
a. A structural (or Formal) syllabus.
statement, questions, subordinate clauses, complex sentences, past tenses, and so on. They may include other aspects of language from such pronunciation and morphology.
b. A Notional (functional) syllabus
A Notional (functional) syllabus is a syllabus in which the content of language teaching is a collection of function as those are performed when language is used, or of the notions that language is used to express. Examples of functions include informing, agreeing, apologizing, requesting, promising, and so on. Examples of notions include size, age, color, comparison, and so on.
c. A situational syllabus.
A situational syllabus is a syllabus in which the content of language teaching is a collection of real or imaginary situation in which language occurs or used. A situation usually involves several participants who are engaged in some activities in a specific setting. The primary of a situational language teaching syllabus is to teach the language that occurs in the situations. Examples of situations include: seeing the dentist, complaining to the landlord, buying a book at the bookstore, meeting a new student, asking direction in a new town, and so on.
d. A skill-Based syllabus.
skill-based introduction is to learn the specific language skills. A possible secondary purpose is to develop more general competence in language learning incidentally only information that may be available while applying the language skills. Skill-based syllabus group teaches linguistic competencies (pronunciation, vocabulary, grammar, socio linguistics, and discourse) together into generalized types of behavior, such as listening to spoken language for the main idea, writing the well-performed paragraph, giving effective oral presentations, reading texts for main ideas or supporting details, and so on.
e. A task-based Syllabus
A task-based Syllabus is a syllabus in which the content of language teaching is a series of complex and purposeful tasks that the students want or need to perform with the language they are learning. Task-based teaching has the goal of teaching students to draw on a variety of language forms, functions, and skills, often in as individual and predictable way in completing the tasks. Tasks then can be used for language learning are generally tasks that the learners actually have to perform in any case. Examples are applying for a job, taking with a social worker, getting housing information over the telephone, completing bureaucratic forms, collecting information about preschool to decide which to send a child to, preparing a paper for another course, reading a textbook for another course, and so on.
f. Content-Based syllabus
content or information using the language whatever content is being taught. The subject matter is primary, and language learning occurs incidentally to the content learning. The content teaching is not organized around the language learning, but vice versa. Content-based language teaching is concerned with communicative and cognitive processes. An example of content-based language teaching is a science class, which is taught in the language that students need or want to learn. It is possibly with linguistics adjustments to make the science more comprehensible.
From the elaborations of the syllabus types above the writer would like to choose the most appropriate one. Since the content of the language teaching in this study is a collection of functions, the writer would apply a functional syllabus as the syllabus type in this study.
B. Theoretical Framework
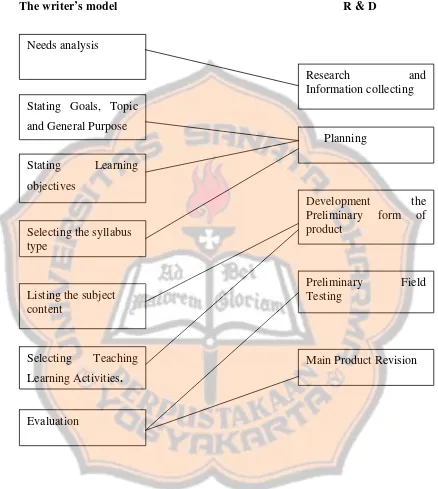
Some steps are required to make a set of instructional design materials to teach speaking to the guides and instructors in Banyu Sumilir. In order to make an effective instructional material for tourist guides and instructors in Banyu Sumilir, the writer adapts the steps of Kemp’s model and Yalden’s model.
product, preliminary field testing and main product revision. The following are the writer’s model.
1. Needs analysis
Usually a group of learners do not need general English. They learn English for a particular reason. Since this study is concerned with English for tourist guides in tourism village, the material will be relevant to the learner’s need and purpose. It means that the aim of the study is first identified by learners need analysis. The writer conducted needs analysis based on the theory of ESP. ESP emphasizes the central importance of the learners and their attitudes to learning (Rodgers, 1969).
2. Stating Goals, Topic and General Purpose
This step is aimed to determine the goals of instructional material design. After stating the goals, the topics should be listed as the scope of the course and the basic needs of instruction. The topics in the instructional materials should be selected based on the situation.
The topics should express the general purpose as to what the learners’ expect as a result of instruction. So topics, goals, and general purpose are an important aspect in making instructional material.
3. Stating Learning objectives
the students needs. It implies the collaboration and negotiation among those who are involved in the course, for example, students, teacher and organizer.
4. Selecting the syllabus type
Selecting the syllabus type used in this study is the next step after stating learning objectives. Since the basis of these instructional materials is speaking, so the appropriate syllabus type is functional syllabus. The content of the language teaching in this study is a collection of function.
5. Listing the subject content
The aim of this step is to clarify the learning objectives. It involves the selection and the organization of the specific knowledge, skill, and attitudinal factors. Well-designed subject content will lead to communicative and interactive teaching learning activities. The writer selected the subject content based on the sequence of activities in CLT. The activities were divided into two sections, Pre- Communicative activities and Communicative activities. Teaching points are introduced in dialogue form, grammatical items are isolated for controlled practice, and then freer activities are provided. Pair and group work are suggested to encourage the students to use and practice functions and forms (Richards and Rodgers, 1986).
6. Selecting Teaching Learning Activities.
the learners chances to speak in order to be able to speak communicatively in the target language. The writer applied the activities in teaching speaking theory in designed materials. Those activities were questions and answers, dialogue and role-play, matching activities, communicative activities, pictures and pictures stories, puzzle and problems, and discussions.
7. Evaluation
38
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
There are seven sections discussed in this chapter. They are research method, research instruments, research respondent, research setting, data gathering technique, data analysis and research procedure.
A. Research Method
This research was carried out based on Research and Development ( R & D) theories. In this theory “the Research and Development is a process used to develop and validate the educational product” (Borg and Gall 1983: 772). These were the steps in Research and Development:
1. Research and Information Collecting
This step was about collecting information from many sources which was related to the research. According to R & D, this step included review of literature, classroom observation, and preparation of report of state of the art. The researcher tries to collect information about the learners by distributing questionnaires and interviewing the learners. The researcher collected information for two things:
a. Collecting information about related theory
theses, and internet. The writer tried to find information about designing materials, theory of speaking, and theory of CLT.
b. Collecting information about the learners
To collect information about the learners, the researcher distribute questionnaire and conduct interview to the learners. It is done to find what the learners exactly need, the learners’ background knowledge, and the learners’ interests toward English. It’s very important for the researcher to determine the suitable materials, the topic, the teaching learning technique, and the media.
In the writer’s step, this step is called needs analysis. In this step the writer conducted a survey to find out the learners’ need. The results of the survey were used as a consideration to develop suitable materials.
2. Planning
After collecting the information related to the research, the researcher should make a plan for developing materials. According to R & D theory, the planning referred to the statement of specific objectives that would be achieved after the course. In this step, the researcher focused on determining the goals that would be achieved. The researcher also prepared the syllabus and developed the materials based on the result of the information gathering.
topics, general purposes, learning objectives and also the syllabus type in order to fulfill the learners’ needs.
3. Development the Preliminary Form of Product
This step followed on from the previous step. In this step the researcher prepared the materials, handbook and evaluation. In designing the materials, the researcher referred to the principles by Waters and Hutchinson (1987). The designed materials will be based on the result of the needs analysis.
In the writer’s step this step was broken down into two steps. Those were listing subject contents and selecting teaching learning activities. The learners of this study were people who are responsible to give explanation to foreign tourists about the activities in Banyu Sumilir, so the topic and the materials will be related to the situation. The writer developed materials which provide exercises that enable the learners to practice their speaking ability.
4. Preliminary Field Testing
5. Main Product Revision
In this step the researcher revised and improved the designed materials based on the result of the questionnaire distributed in preliminary field testing. Then the last version of the materials was presented.
In the writer’s step, the writer combined Preliminary Field Testing and Main Product Revision into one step called evaluation. In this step the writer conducted a survey by distributing questionnaires to an English teacher, English lecturers, and English instructors to evaluate the materials. The writer used the results of the survey to make a final revision.
The writer’s model R & D
Figure 3: The similarities between the writer’s model and R & D Stating Goals, Topic
and General Purpose
Stating Learning objectives
Needs analysis
Selecting the syllabus type
Listing the subject content
Preliminary Field Testing
Planning
Development the Preliminary form of product
Research and Information collecting
Evaluation
Main Product Revision Selecting Teaching
B. Research Respondent
To gather the data, the researcher chose some respondents who were considered reliable to help the researcher to get information.
1. Research and information collecting.
In research and information collecting, the respondents were the guides and instructors in Banyu Sumilir. They were experienced in guiding and accompanying tourist guests. The guides and instructors knew the real situation, the difficulty in guiding tourist guests, and what they need to solve the difficulties, so the writer expected they could give suggestion to the writer to make the suitable materials. The writer also interviewed some of the instructors and the manager of Banyu Sumilir. The interview with the instructors aimed to get deeper information about the answer in the questionnaire, while the interview with the manager of Banyu Sumilir aimed to find out what the guests needed. Usually guests told the manager what their needs in tourism are.
2. Preliminary field testing
C. Setting
The researcher conducted the research in Banyu Sumilir in February 2008. Banyu Sumilir was located in Sorowulan Purwobinangun Pakem Sleman Yogyakarta.
D. Research Instruments
Before designing the materials, the researcher conducted needs analysis to get any information about the learners. The instruments were used in Research and information collecting to gather data about the learners and in preliminary field testing to evaluate the designed materials. The instruments were explained as follows:
1. Research and information collecting
In the first step the researcher conducted needs survey to collect information about the learners to obtain the information; the writer used instruments as follows:
a. Questionnaire
b. Interview
Another instrument that the wrier used to gather information from the learners was interview. The writer needed to get further information from the learners. Besides, the interview was done to get additional information from the learners and the problems that occured related to guiding tourist visitors from the manager of Banyu Sumilir.
2. Preliminary field testing
The writer distributed questionnaires to English lecturer, English teacher, and English instructors. Preliminary field testing questionnaire was used to evaluate the designed materials whether the materials had fulfilled the learner’s needs, whether the topics were suitable with the real situation, whether the activities provided opportunities to practice the learner’s ability to speak. The result of this questionnaire was very important to improve the materials before it was really applied.
E. Data Gathering Technique
The second step was conducting interview. The writer interviewed some learners randomly to clarify their answer in the questionnaire. The writer also interviewed the manager of Banyu Sumilir since the manager knew better about the guests and usually guests would convey their request to the manager.
The next step was preliminary field testing. This step aimed to evaluate the designed materials. In this step the writer distributed questionnaires to some English lecturers, English teacher, and English instructors. The questionnaire was about the relevance between the materials and the objectives.
F. Research Procedure
The procedures of this research are: 1. Conducting library research
In library research, the researcher read books, theses and other sources to understand the underlying theories related to the research.
2. Conducting need analysis
Before designing the materials, the researcher gathered information from the learners through needs survey. It was important to determine the method, topic, and media, for the teaching learning activities so that the materials will be applicable and suitable with the real situation.
4. Distributing the designed speaking materials and the questionnaires to evaluate the designed speaking materials.
In order to have good materials, the writer distributed the designed materials and questionnaire to some English lecturers, English instructors and English teacher to evaluate the materials. The questions of the questionnaire were asking about the lecturer’s opinion whether the materials had been relevant to the learners goals.
5. Revising and improving the speaking materials design
The researcher used the obtained data to improve and to revise the materials. 6. Making the final design of speaking instructional materials
The researcher made the final revision, and it was ready to publish.
G. Data Analysis
The data analysis in this research aimed to solve the problem of how the speaking instructional materials design for guides and instructors in Banyu Sumilir was carried out. In analyzing the data from sources above, the writer used figures and tables to organize them. While the questionnaires and interviews contain items of questions to evaluate the designed speaking m