i
A Sarjana Pendidikan Thesis
Presented as the Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
by
Lucky Trias Widhiatmoko Student Number: 991214065
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAMME DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING EDUCATION SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA 2006
ii by
Lucky Trias Widhiatmoko Student Number: 991214065
Approved by:
Major Sponsor
iv
I honestly declare that this thesis which I wrote does not contain the works or part of the works of other people, except those cited in the quotations and bibliography, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, 13 November 2006 The Writer,
v
I think about it every night and day
Spread my wings and fly away
I believe I can soar
I see me running through that open door
…
I believe I can fly
…
…
I believe I can fly
…
…
I believe I can fly
…
(I Believe I Can Fly)
dedicated to:
My beloved family,
vi
SWT, who has given me faith and strength so that I am able to overcome all of the obstacles in my life.
I would like to show my great thank and appreciations to P. Kuswandono, S.Pd, M.Ed., as my only sponsor for the advices that he gave to me and also for to be a very patient person in motivating me to finish my thesis.
I would also like to show my deepest gratitude to both of my parents, Widodo, B.Sc., and Tri Redhiati Retnowati for giving me love and caring me for my lifetime, and also support me, even sometimes in embarrassing ways, in finishing my thesis.
My great thank is addressed to my only brother Lutfi Triesnawan Widhiantoro for lending me his computer whenever I broke mine.
My deepest gratitude is addressed to Desi Lembah Hati, SE, MM., the General Manager of Language Center Institution, for being my working partner and also for giving me a chance to do my research in her institution.
My deepest gratitude is also addressed to Budi Suko Wardoyo, S.Pd., the Education Manager of Language Center Institution, for being my mentor and supervisor in my very first teaching experience.
My great thank go to my best friends, known as THE THREE MUSKENTHIR, Danang Wahyu Nugroho, Lukas Yargo Sadewo, S.Pd, and Justinus Irwin Ardiyanto, S.Pd., for being my truest soul mates.
vii
I am really grateful to my beloved girlfriend, Chrispina Irni Widyasari, who always supports me and lifts me up whenever I get myself lost. She is the one who always beside me during my thesis writing and become my “supervisor” that keeps pushing me to do my best.
Finally, I would like to show my deepest gratitude to everyone who was not only helping me in finishing my thesis writing but also being a part of my life that I cannot mention one by one.
viii Dharma University.
Vocabulary mastery is believed to be the basic knowledge in learning a new language. Thus, most of the institutions, which deal with foreign language teaching, put vocabulary as the first subject to be taught. In this research, the writer concluded that the best phase of human life to learn a new language is in their critical period, which is described by some previous researchers, that is shown by children in the age of 5 – 12 years old. The critical period is the period when the brain develops its capacity. The writer also concluded that the learners in this phase are having difficulties in understanding the abstract words. Thus, in teaching vocabulary to the learners in this phase, the language instructors need media in order to give the concrete understanding of the words supposed to be learned. Thus, the writer designed a movie-based instructional material to match the needs of the learners.
This study has two questions to be solved. (1) How is the design of a set of movie-based Instructional material to teach vocabulary for children in Language Center Institution constructed? (2) How do the designed materials look like?
To answer both questions, the writer conducted a library research and a survey research. The library research mainly used to find out data which supported the writer’s research. In doing his survey research, the writer conducted two different surveys which were addressed to two different respondents. The first survey was done in order to find out the needs of the learners. Thus, the writer chose the English instructors of Language Center Institution as the respondents. The second survey was done in order to evaluate the designed material. The writer chose the English instructors from various English courses in Yogyakarta in order to gain more reliable data.
To answer the first question, the writer applied an instructional model which is combined from Kemp’s model and Yalden’s model. This model consists of 7 steps. Those steps were (1) Need survey (2) Stating the Goal, topics and general purpose (3) Stating the instructional objectives (4) Building the subject content (5) Developing the instructional objectives (6) Evaluation and (7) Revising and improving the designed material. For the second question, the writer presented 8 units of movie – based instructional materials. Each unit consists of four parts, namely Let’s Watch the Movie, Let’s Learn More, Exercises, and Song (Appendix 6), in order to help the learners in understanding the lesson well.
The writer evaluated the design using descriptive statistics. The result showed that the average is 4.06 in using Likert scale. This means that the material designed is acceptable and applicable.
ix Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Penguasaan kosakata dianggap sebagai kemampuan dasar dalam pembelajaran bahasa asing. Maka, sebagian besar lembaga yang terkait dalam pengajaran bahasa asing, menjadikan pengajaran kosakata sebagai bahan pembelajaran pertama bagi siswanya. Dalam penelitian ini, penulis menyimpulkan bahwa masa yang ideal dalam mempelajari bahasa asing adalah pada masa kritikal, sebagaimana telah dijelaskan oleh beberapa peneliti terdahulu, yaitu pada masa antara 5 – 12 tahun. Masa kritikal ini adalah masa dimana otak berada dalam proses pengembanga n kapasitasnya. Penulis juga menyimpulkankan bahwa siswa dalam usia ini memiliki kesulitan dalam menggambarkan suatu benda abstrak. Maka dalam proses pambelajaran kosakata bagi siswa usia ini, guru memerlukan alat bantu dalam memberikan gambaran atau bentuk konkret dari kata – kata yang yang akan dipelajari. Karena itulah penulis merancang materi pembelajaran yang menggunakan film sebagai media yang sudah disesuaikan dengan kebutuhan siswa.
Penelitian ini ditjukan untuk menjawab dua permasalahan pokok, yaitu (1) Bagaimana program pembelajaran dengan menggunakan film sebagai media dalam pengajaran kosakata pada anak – anak di Language Center Institution dirancang? (2) bagaimana bentuk program pengajaran tersebut?
Penulis menggunakan library research dan surve y research untuk menjawab kedua pertanyaan tersebut. Library research atau studi pustaka digunakan untuk mengumpulkan data – data atau teori – teori yang berhubungan dengan penelitian yang dilakukan oleh penulis. Penulis melakukan dua macam penelitian yang ditujukan terhadap dua subjek yang berbeda. Pertama, penulis melakukan penelitian terhadap pengajar dari Language Center Institution untuk mengetahui kebutuhan siswanya. Penelitian kedua dilakukan terhadap beberapa pengajar dari beberapa lembaga bahasa di Yogyakarta untuk mendapatkan evaluasi rancangan materi pembelajaran.
Untuk menjawab pertanyaan pertama, penulis menerapkan model instruksional dengan mengadaptasi gabungan model instruksional Kemp dan Yalden. Model tersebut terdiri dari 7 langkah, yaitu: (1) Analisis kebutuhan siswa (2) Menentukan Tujuan, topik, dan tujuan umum (3) menyatakan tujuan pembelajaran (4) Mengembangkan isi materi (5) Mengembangkan tujuan pembelajaran (6) Evaluasi, dan (7) Revisi dan perbaikan materi pembelajran. Untuk menjawab pertanyaan kedua, penulis menyajikan rancangan materi pengajaran yang setiap unitnya terdiri dari 4 bagian pokok yaitu: Mari Menonton Film, Mari Belajar Lebih Banyak Lagi, Latihan, dan Bernyanyi (Apendiks 6), untuk membantu para siswa dalam memahami materi pembelajarannya.
Penulis mengevaluasi hasil rancangan dengan menggunakn descriptive statistics. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan rata – rata penilaian adalah 4 dalam skala 1 – 5. karena itulah penulis menyimpulkan bahwa rancangan ini dapat diterima dan dapat diterapkan.
x
STATEMENT OF ORIGINALITY………... iii
DEDICATION PAGE………. iv
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT……….. vi
ABSTRACT……… viii
ABSTRAK... ix
TABLE OF CONTENT………. xi
LIST OF FIGURES………... xiii
LIST OF TABLES………. xiv
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION...Error! Bookmark not defined. A. Background ...Error! Bookmark not defined. B. Problem Limitation...Error! Bookmark not defined. C. Problem Formulation...Error! Bookmark not defined. D. Objectives of the Study...Error! Bookmark not defined. E. Benefits of the Study ...Error! Bookmark not defined. F. Definition of Term...Error! Bookmark not defined. CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL REVIEW...Error! Bookmark not defined. A. Theoretical Description ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 1. Children as the Learners ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 2. Vocabulary...Error! Bookmark not defined. 3. Media or Teaching Aids ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 4. Instructional Design Model ...Error! Bookmark not defined. B. Theoretical Framework...Error! Bookmark not defined. CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY...Error! Bookmark not defined. A. Types of Study...Error! Bookmark not defined. 1. Library Research...Error! Bookmark not defined. 2. Survey Research ...Error! Bookmark not defined. B. Research Subjects and Respondent ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 1. Subject of the Related Literature ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 2. Respondents of the Research...Error! Bookmark not defined. C. Research Instrument ...Error! Bookmark not defined. D. Information and data Gathering ...Error! Bookmark not defined. E. Data Analysis ...Error! Bookmark not defined. F. Procedure of the Study ...Error! Bookmark not defined. CHAPTER IV
xi
3. Stating the Instructional Objectives ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 4. Building the Subject Content ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 5. Developing the Instructional Material...Error! Bookmark not defined. 6. Evaluation...Error! Bookmark not defined. 7. Revising and Improving the Designed MaterialError! Bookmark not defined. B. Findings of the Designed Material EvaluationError! Bookmark not defined.
1. Description of the Respondents ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 2. Data Presentation...Error! Bookmark not defined. C. Discussion on the Designed Material EvaluationError! Bookmark not defined. D. Presentation of the Designed Materials ...Error! Bookma rk not defined. CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION...Error! Bookmark not defined. A. Conclusion...Error! Bookmark not defined. B. Suggestion...Error! Bookmark not defined.
BIBLIOGRAPHY...Error! Bookmark not defined. APPENDICES
xii
xiii
Table 4 1: The List of Basic Competencies ...Error! Bookmark not defined. Table 4 2: The List of the selected Indicators...Error! Bookmark not defined. Table 4 3: The Description of The Respondent ...Error! Bookmark not defined. Table 4 4: The Data Presentation of Evaluating the designed MaterialsError! Bookmark not defined.
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
The first chapter of this research discusses the background, the problem limitation, problem formulation, objectives of the study, benefits and also definition of terms of the research conducted by the writer.
A. Background
Learning an L2 (a new language or foreign language besides mother tongue (L1)) also means learning a new pattern and rules of the new language. It also means that when someone learns a new language, he looks like as if he were a baby, in which he starts to do the process of learning, step by step. In learning an L2, there are some phases in human life, which are divided based on the age of the person him/herself. And the best phase to learn an L2 or a new language is the critical period, which will be explained by some researchers as follow.
cited in Intisari at September edition (1998: 28), which said that the children in the age of 5 – 12 years old (critical period) ha ve a good opportunity to learn a new language because of the brain plasticity. As one learns the new language, he cannot acquire the new language instantly and the first step to learn a new language is by learning its vocabulary.
Learning the vocabulary of the new language is very important, since one cannot deliver his or her ideas to someone else or vice versa because he doesn’t know the meaning of the transmitted or received messages. Wilkins states as quoted by Bird (1994: 237) that without grammar very little that can be conveyed, but without vocabulary nothing can be conveyed. It implies that when someone learns a new language, he should learn the vocabulary of the new language first before he learns the other part of the language itself as stated by Carmelita as quoted by Sutanto (2003: 4)
Learning a language, among others, is learning its vocabulary, since vocabulary should be mastered before being able to speak or produce a sentence. Vocabulary plays an important role in giving the children basic knowledge, because it will be useful and helpful to prepare the children to learn English in the next level.
The above statement shows us that learning vocabulary becomes the base of further learning of a language. But then, learning vocabulary, especially for learners at very young age, requires media to show or to expose the materials more clearly. Thus, the learners need what so called learning media.
need media which is not only able to show them what is the meaning of a word in their own language or their mother tongue language, but also to show them the concrete form of the word itself. In other words, the learners are not only able to imagine the thing or something that they try to learn, but are also able to recognise the thing itself. By using a medium, for example the word “car,”, the learner will be able to recognise the concrete form of the word car as a means of transportation which has four wheel, engine, steering wheel, etc. One of the most largely used media nowadays is audio-visual media and the most commonly used of this type of media is the movie media.
Prihatin (2003: 13) states that the video films have a great capability in presenting complete communicative activities, in which this kind of media is constructed based on the combination of sound and vision. It implies that when a learner uses this type of learning media, the media enables the learner not only to learn the form or the syntax of the language, but also to learn how the language usages in term of communication with others. The audio-visual media also enables the learner to observe the relation between the characters involved in the materials, which are designed into a story, which has the purpose to entertain the learner, beside as the learning media, so that the learner would feel enjoy and satisfied in the learning process. Hamalik (1994: 84) states that using the audio- visual media is not only to provide the learners with the facts, but also to provide the answers to problems and to give a better understanding about the learners themselves and their environment.
(1995: 46) state that introducing vocabulary through a visual context is very effective, especially for the lower level students and the children. Therefore, the aim of the writer is to construct a set of movie-based instructional material to teach vocabulary for children in Language Center Institution.
B. Problem Limitation
The writer limits his study in designing a set of movie-based instructional materials for children in Language Center Institution. In this study, the writer clarifies that he constructs his design based on the already existing videos, and reconstructs them based on the units decided by the writer based on the need analysis. The writer also realises that it will take some time to find out whether the designed materials are appropriate for the students or not. Thus, the writer considers that it is impossible for the writer to decide whether the design will be the most appropriate design for the children or not, before the design is applied in the real situation. It means that the writer is not going to discuss whether this design is the most appropriate design for the children or not, because as we know that everything always changes.
C. Problem Formulation
As the starting point in designing a set of movie-based Instructional material to teach vocabulary for children in Language Center Institution, the writer found some questions that should be revealed. Therefore, the aim of this study is to answer the two following questions:
2. How do the designed materials look like?
D. Objectives of the Study
The objective of the study is to provide a design of Movie-Based Instructional Materials to teach vocabulary for children in Language Center Institution which are aimed to help the children learn English more enjoyable, so that hopefully it will increase the knowledge of the children. This study will also reveal about how the design will be constructed and also the result of the design.
E. Benefits of the Study
Hopefully, this design can make beneficial effects for the following people. 1. The children as the learners
As what has been mentioned before, that with the existence of this design, it will ease the learning process of the learners and it provides a systematic and enjoyable way of learning. The design provides steps, which has to be taken by the learners in order to gain the main purpose of learning English.
2. The teachers or mentors
3. The writer
This research that is conducted by the writer is the part of the writer's learning development. So, this research would bring the writer into a phase in which the writer could improve himself in the term of his working field.
4. The English teaching in General
This research is conducted based on the writer's discipline that is English Education Program, in which the writer is trained to be a teacher. This research is constructed based on the theories of learning, in which those theories have been found by some former researchers, and the truth of those theories is approved by the world of teaching. So this research becomes the improvement of the English teaching in general. Hopefully, the existence of this research could bring a new branch of English teaching, in this case teaching English for children.
F. Definition of Terms
In order to avoid some misunderstanding in interpreting the result of the research, the writer has already made a clarification of some terms, which are considered as important terms in this research. Those terms are:
1. Media
addition, with the existence of the media, the message is not in limited by spaces or times, in other word media are repeatable.
Romiszowski (1981: 339) defined media as the carrier of messages, from the transmitting object (which may be a human being or an inanimate object) to the receiver of the message. It implies that the carrier interact with the receiver through the senses.
Hamalik (1994: 12) defined media as tools, methods and techniques which are used to create more effective environment in term of communication and interaction, between the teacher and the learners.
From the definitions above the writer concluded that media is a tools that can be used to deliver messages. The existence of the media would ease the teacher or instructor in delivering their materials. Thus, the aimed of the writer is to construct a kind of media which is going to be used by the instructor of Language Center Institution, in their teaching process.
2. Movie
Heinich, Molenda, and Russell (1988:186) defined movie or motion picture is a film consists of a sequence of slightly different still pictures called frames, which are projected on a screen at a certain speed, causing the images to be appear in continuous motion.
Hamalik (1994:84) stated that movie media is actually developed from the still pictures, which are called as frames, which are projected through a mechanical projector creating a motion pictures that creates a continuous visual process.
from a certain amount of still pictures, which are projected creating a single continuous motion. The writer also concludes that movie-based material means that the designed material is built using this kind of media.
3. Instruction
Banathy (1976: 15) defined the instruction as the interaction between the learner and his environment through which the learner is making progress toward the attainment of specific and purposed kno wledge, skills and attitude.
Gagne and Briggs (1979:17) stated that instruction is the mean employed by the teachers, designers of materials, curriculum specialists and others whose purpose is to develop an organised plan to promote learning. Romiszowski (1981: 4) proposed that instruction is a goal directed teaching process which is more or less pre-planned. It implies that the instruction will bring a clearly guidelines for the teachers or instructors in delivering their material, in which the instruction itself is well-constructed and well-planned.
From the definitions above the writer concluded that instruction is a tool used by a designer in beginning his design, in order to create a proper design.
4. Instructional material
From the definitions above the writer concluded that instructional material is the material used by the designer in delivering his design or lesson.
5. Instructional Design
Gagne and Briggs (1978: 34) defined the instructional design as the entire process of analysis of learning needs, goals and the development of delivery system to meet the needs, including the development of instructional material, activities, try out, revision of all instruction and learner assessment activities.
From the definitions above the writer concluded that instructional design is the whole process taken by a designer in developing his design, from the first step until he gets the final version of his design
6. Vocabulary
Burton (1982: 99) proposed that vocabulary is a stock of words in a language that can support the learners to learn the skill of the language.
Hornby (1974: 95) stated that vocabulary item is a total of words, which make up a language. Vocabulary item also can be defined as a word known to or used by a person in trade and profession and it also can be defined as a list of words.
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL REVIEW
This section mainly discusses the theoretical description, which explains the theories which are used by the writer as the basis of his research, and the theoretical framework, which explains the steps taken by the writer in conducting his research.
A. Theoretical Description
In the first part of the theoretical description, the writer thinks that it is necessary to recognize the nature of the children as the learners, in order to be able to decide what kind of material to be designed.
1. Children as the Learners
Before the writer learns furthermore about the nature of the children as the learners, the writer believes tha t it is very important for him to understand the characteristics of the children, so that the writer able to know the characteristics of the children to whom he makes the design for.
a. Characteristics of the Children
Since the children who are going to be the object of this study in the range of 6 to 12 years old, the researchers consider them as the intermediate level of cognitive development, in which they are now still in the middle between the childhood and adolescence.
the children have already outgrown their infantile characteristics, but they have not developed the desire for complete independence and the heterosexual interest of adolescence. Furthermore, he says that in this phase, the children show the increased stability, motoric ability, higher intellectual capacity, intense curiosity about all kinds of things, including the new language, etc.
Cole (1956:125-132) also proposed that in this stage of characteristics development covers the physical, intellectual, emotional and social aspect that will be explained as follow:
1) Physical Characteristics
The students’ physical characteristic of this phase is described as a slower growth in height, but faster in weight. In this stage of development, girls usually taller than boys, and because of the increasing size and strength of the muscles and better nerves control, children at this stage can do many things easily than they did before.
2) Intellectual Characteristics
The children in this stage have a great sense of curiosity of many things. They have a great desire to learn and to know about many things that interest them as fast and as many as they can.
3) Emotional Characteristics
In this stage, words take an important role as the basic effective communication tools. In this stage children also having two contradicting characteristics in which at one side each child becomes a highly individualistic person in both interests and desires. While at the other side they also become highly interdependent upon others.
After knowing the characteristics of the children, the writer also believes that the children development phases also have an important role in determining the types of study of the children. Thus, the writer also needs to learn about the student’s development stage.
b. Student’s Development Stage
Piaget as quoted by Vasta, Ross, Haith, Marshall and Miller (1976:35) view that all children ha ve to pass the same stages of cognitive development in exactly the same order. Each stage has its own characterisation, in which each of them has a different function and structure. Piaget proposes that there are four stages of the cognitive development.
The first stage is the sensomotor period which occurs since the child has just been born until the age of two years old. At the initial stage of this period, the movements of the child are just simply reflexes. And as the child grows older, these reflexes are combined into larger and more flexible units of actions.
no longer physically. However, the children in this phase are still having some difficulties which are shown by their confusion in their attempt to understand something new.
The third stage is the concrete operation period which represented by the children in the range of 6 to 11 years old. At this phase, the children are already able to overcome their problem in the previous stage. At this stage, the children are able to perform the mental operation based on their previous knowledge, in which they are able to reorganise it.
The last stage is the formal operation period which extends from the age of 11 years old until the adulthood. At this stage, the children have already come to the phase of the highest level of abstract operations.
After knowing the development stage of the students to whom the materials are going to be designed to, the writer also needs to learn about the student’s cognitive development.
c. Student’s Cognitive Development
Hurlock (1978:28) states that the development of a learner is the result of the intrinsic maturity and learning process. What she called by intrinsic maturity is the release of individual’s potential characteristic, which is from his/her heredity. Whereas what she called learning is the development, which is from the practice and trial.
and vice versa, if the individual’s environment does not support the individual effort, then, the individual has a bigger chance to fail.
In this study the writer learns that in doing his research later, he also needs to consider about the environment interference in the learning progress of the learner. After knowing this fact, the writer also needs to know about how the children study, in order to be able to give the appropriate treatment to the children.
d. How the Children Study
Macomber (1954:32) proposed that the children’s learning behaviours depend on the stage of the cognitive development that has been reached by each child. Unlike the adults who can be directly told which one should be learned; children usually learn depend on how does the lesson attract them, and not because they need it. Caswell (1957:175) states that the children learn because they are interested in what they want to know.
Since they learn based on what is interesting, the children usually create their own ways, even in the way that the adult people, do not even think of. Moreover, Hort (1967:167-168) explains that children tend to create their own path into an unknown path (represents the knowledge that they want to learn) that the adults would never think of them and they would go faster and cover even broader territory than of what the adults could ever think they could cover.
of the children becomes higher when they feel that their environment, such as teachers, friends, parents, etc. support and give the children their appreciatio n towards the children’s achievement.
One thing that the adults should understand that the way the children learn is different from the way the adults learn. In adults’ way, they could start to learn something new by themselves, but in the children’s way, they still need the guidance. Since they still need the guidance, then they should have some appropriate treatment. But what we should remember is that in this phase their study behaviour is still depends on what they like and dislike, and any wrong treatments may caused them stop trying to learn for something more.
After the writer learns about the children, the writer also needs to reveal more about the subject that he wants to develop, in this case is the vocabulary itself.
2. Vocabulary
The first part of the vocabulary that the writer needs to learn is about the meaning of the vocabulary itself. It is very important, because by knowing the exact definition of the vocabulary, it will help the writer to design his material in the correct way.
a. Meaning
parts of the language. The relation of both grammar and the vocabulary can be described as if the grammar of a language becomes the skeleton of the language, than the vocabulary become s the vital organ of the language.
After knowing the exact meaning of the vocabulary, the writer wants to reveal about the importance of learning vocabulary.
b. The Importance of Learning Vocabulary
Krashen (1983: 155) proposed that the vocabulary is basic to communicate, in which it is also very important for the acquisition process. It means that the vocabulary provides the base for further learning of a language. This statement is also emphasised by Mc Keown (1984: 4) who stated that individual who knows many word meanings, knows much about the world. Meaning to say, any person who masters the vocabulary would have a better chance to reveal the knowledge related to the language usage.
Since vocabulary takes important role in one’s knowledge, the writer also wants to know the types of vocabulary so that he able to determine what kinds of vocabulary that he wants to use in his design.
c. The nature of Vocabulary Teaching
to use the words in the correct situation.
In order to fulfil those criteria, Lado (1964:121) stated that teaching vocabulary must involve these three steps. The first step is the learners hear the new word for several times. In this step the teacher has to repeat the new word for several times in order to let the learners recognise the sound of the new word. The repetition also takes an important role in giving example of a good pronunciation. The second step is
to let the learners pronounce the new word. This step provides the experience for the learners to produce the new word by themselves. The aim of this step is that by experiencing the production of the word, the learners will remember the word better. In this step the teacher should repeat the new word again and again if he found his learners produces the new word incorrectly. The last step is to let the learners grasp the meaning of the new word. In order to help the learners in getting the image of the new word, it would be better for the teacher to explain or to show the concrete form of the new word itself, for example by showing the picture or other media.
After knowing the nature of the vocabulary, the writer realises that he could not start his design without knowing the types of vocabulary. Thus, the next section will explain about the types of vocabulary that can be developed in order to accomplish the research of the writer.
d. Types of Vocabulary
The previous researchers have cond ucted some research to find out the segments of the types of vocabulary, and the followings are the findings of two of those researchers.
into two types as follow:
1) Vocabulary which has the Lexical Meaning
When a person is looking for the meaning of a word in a dictionary, it means that this person is looking for the word’s lexical meaning. In other words, lexical meaning of a word is the meaning that can be found in the dictionary. For example,
2) Vocabulary which has the Structural Meaning
In deciding a word’s structural meaning, a person cannot only depends on the dictionary, but he should also observe the context of the usage of the word itself. For example, the word “red.” The word “red” in the sentence of “Anna has a red balloon,” means that “red” as a kind or colour, but it differs from “The police have got a red code,” in which it means a kind of code which shows an urgent situation.
Sen (1983:12) divided the vocabulary in a different way from Fries, since he divided the vocabulary based on the use of the vocabulary.
1) Active vocabulary
The vocabulary, which is included to this type of vocabulary, is the type of vocabulary which is used when a person produces words and expressions in writing and speaking.
2) Passive vocabulary
The vocabulary, which is included to this type of vocabulary, is the type of vocabulary which is used for reading and listening.
e. Vocabulary Selection
the learning process of the learners. Sumardi (1974: 44), in relation to this topic, proposed some criteria to select vocabulary as follows:
1) Frequency
This criterion is considering of how often a word appears in daily use. The more often a word appears the easier the learners mastering it. For example is the use of the determiner a/an/the, in which each of the determiners has their own rules of usage. By using over and over the learners would save either the usage or the pattern and also the combination of personal pronoun in sentences in their mind.
2) Range
The range of a word is related to the ability of a word to be found not only a certain situation. For example personal pronouns, in which this type of word is very often appears in any kind of situation. A pronoun can be found in past, present and future situation or any kind of situation.
3) Availability
The availability of a word is considering that the word to be taught should be suitable for a certain condition. For example the word “seat” and “wheel” have close relationship with the word “vehicle”.
4) Coverage
In order to facilitate an effective learning the teacher should teach words of which meaning can cover the general definition.
5) Learnability
After able to have a guidance in selecting the types of vocabulary, the writer also would like to reveal more about the media or aid that can help the instructors later in delivering the materials.
3. Media or Teaching Aids
Hamalik (1994: 1) said that learning media or teaching aids are one integrated part of the learning process of the learner and it needs to be mastered by professional teachers. From this statement it shows that learning media or teaching aids cannot be separated from the learning process itself. Thus, the writer thinks that it is important for him to take this topic.
a. Types of Media or Teaching Aids
According to APEID (1986: 5-6) there are 5 categories of teaching aids: 1) Non –Projected Visual Aids
The non-projected visual aids can be divided into three types as follow: a) Graph
Graph is a set of illustrations other than pictures of reality. b) Display Board
Display board is element for building concept on felt or magnetic boards. c) Study Print or Still Picture
Study print or still picture is a picture that represents photographic or printed illustrations of reality.
2) Projected Visual Aids
3) Audio Program
Audio program can be defined as a means of recording and transmitting the voice of human sound. The messages contained in this type of aids or media are coded into audio verbal or non verbal or even the combination of both.
4) Picture With Sound
This type of media also known as audio visual media. There are two kinds of media, static audio visual aid and dynamic audio visual aid.
5) Objects and Three-dimensional (3D) media
Objects cover all kinds of things in the environment. Three dimensional (3D) is the type of media that present the real things.
After knowing the types of media, the writer decided to use the picture with sound media or audio visual media. In the next section, the writer would reveal about the benefits on using this type of media.
b. Benefit of using movie as media
Beatty (1981: 18-20) stated that by using the movie as media, there will be some benefits that can be taken. The benefits on using the movie media are shown as follow:
1) Movie can help to overcome intellectua l barriers to learning because they depend little upon skills of reading. It means, by using the movie media, the learners who have some difficulties in imaging something abstract, can be helped by using this media, since it able to show the thing as a concrete thing.
seeing this type of media.
3) Movie media is able to provide the class with a common experience. The movie media becomes the bridge of background differences for members of the same and different ethnic groups.
4) Movie may be used to overcome many physical limitations in the learning process and to extend the limited range of the normal human senses. It means that the movie media able to show all things that hard to be seen by the learners such as the deep ocean life or the other existing planets.
5) The motion pictures film can control the time factor in operations or series of event. It means that by using the movie media, the user of this type of media are able to control the time by fast- forwarding or slow motioning or event repeating the movie again.
6) The movie media are able to keep the sustained attention of the learners. The reason is in the darken room, most outside distraction are reduced. Moreover, the motion picture may attract the learners’ attention to keep focus on it.
7) Most movies are edited version of reality. This editing, which involves the manipulation of time, space and objects, heightens reality by eliminating distractions and pointing up key relationships.
8) Most films can develop an understanding of abstract relationships. It means that the movie media are able to present, in a matter of a few minute, some events which actually took thousand years to happen.
4. Instructional Design Model
Gagne and Brigg (1973:3) define instructional design as a process of how an instructional material is planned and organised. What meant by the instruction here refers to all events, which have direct effect on learning.
a. Jerrold E. Kemp’s Model
Jerrold E. Kemp in his books proposed that an instructional design plan should provide the answers of these following three questions, which are considered as the core or the essential elements of instructional technology. Those questions are:
First, what must be learned? This question is related to the objectives of the designed material. It means that when a designer wants to start his works, he should be able to recognise and to construct the objectives of his works.
Second, what procedures and resources will work best to reach the desires learning levels? This question is related to the activities and the resources that the writer will use in developing his instructional design plan. The most important thing is that the writer should be able to decide and to choose the kind of activities which are matched to the level of the learners, so it will help the users of the material design in gaining the objectives.
make an improvement of their own ways of teaching.
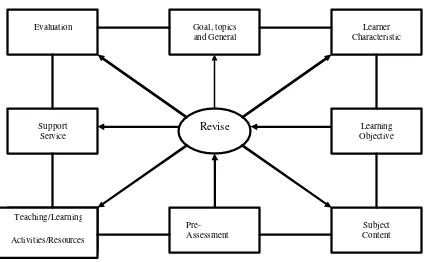
Kemp proposed that there are eight parts of his plan in constructing the instructional design. Those parts are shown as follow:
The first part of the plan consists of three elements. First, the instructional design writer must consider the goals that he wants to gain from his works which may be derived from the society, students, and subject areas. It means that in deciding the goals of the instructional design, the writer has to consider not only the students’ needs and expectation, but also the society’s expectations and also provides competencies which are needed, in which the purpose of the learning behaviour of the students is that they able to participate in their social lives. Second, the writer must consider the topics choosing and sequencing. In choosing the topics, the writer should consider the time available, the relevancy between the topics and the goals, the characteristics of the learners, the budget limitations, facilities, etc. in sequencing the topics, the writer has to consider the difficulty level of each topics, the previous learning experience of the learners, and also the teaching experience of the teacher. Third, the writer has to consider about listing the general purposes which represent each topics. Actually this is not included into the instructional designer writer’s working field, but the writer may give his contributions in the way of clarifying the statements of the purpose and also to translate those statements into more detailed behavioural terms.
Third part of the plan is to state the specific and measurable learning objectives to be achieved in the course which later can be the determiner whether we have already accomplished it or not.
Fourth part of the plan is to determine and to list subject content that support the learning objectives. The subject content should be constructed from the selection and organisation of the specific knowledge, which includes the fact and information, skill, and attitudinal factors of the each existing topic.
Fifth part is to conduct the pre-assessme nt in order to find out and to measure the students’ readiness and preparation to study the planned instruction. It is also necessary to find out the students previous competencies in some of the stated objectives.
Sixth part is to select the teaching- learning activities that are most effective, efficient and applicable to the planned topics. The instructional design writer also has to select the materials refers to the subject content which support the attainment of the stated objectives
Seventh part is to view and to coordinate the supporting services, which include the funds, facilities, equipment, and personnel who are involved in the instructional plan.
Eighth part is to construct the evaluation of both the learning outcomes and the instructional material.
The relation between each parts of the instructional design is shown in figure 2.1 on page 26.
Figure 2.1: Kemp’s Instructional Design Model (Kemp, 1977: 9)
element may affect the other elements. Based on this reasons, the instructional designer is free to decide from which point that he wants to start his design with.
There are two benefits those are underlined by the writer. Those benefits are: first, the model can be applied to all education level. Second, the model can be applied for an instructional unit or for a single subject.
b. Janice Yalden’s Model
Yalden (1983:7) said that after knowing the type of syllabus that will be applied, the teacher should prepare himself in developing the instructional materials.
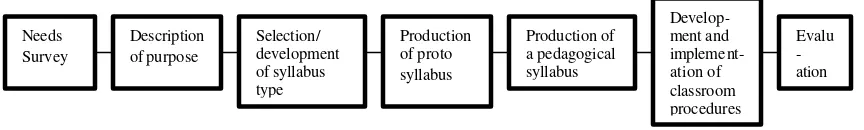
Yalden (1983:88) proposed that there are 8 stages in developing the instructional
Evaluation Goal, topics
and General Purposes
Learner Characteristic
Support Service
Teaching/Learning
Activities/Resources
Pre- Assessment
Subject Content Learning Objective
materials. Those steps are mentioned below.
The first stage is to hold the need survey to find the learners’ needs. The second stage is to make the description of the program.
The third stage is to select or to develop the syllabus type to be used. The fourth stage is to produce a proto syllabus.
The fifth stage is to produce a pedagogical syllabus. In this stage, the teaching materials will be developed as far as possible.
The sixth stage is to develop the classroom procedures that include the exercises, teaching techniques, lesson plans, weekly schedules, etc.
The seventh stage is to evaluate the learners’ achievement, the programs and the teaching activities.
The eighth stage is to evaluate the whole comp onents of the program.
The relation between each parts of the instructional design is shown in this following figure.
Figure 2.2: Yalden’s Language Program Development (Yalden, 1983: 88)
B. Theoretical Framework
In developing the instructional material, the writer proposes his work based on his theoretical framework, which consists of five steps, in which these five steps are the combination of the Jerrold E. Kemp’s instructional design model and the Janice Yalden’s instructional design model. The seven steps, which are taken by the writer,
are conducting a need survey, stating the goal, topics and general, stating the instructional objectives, building the subject content, developing the instructional materials, evaluation, and revising and improving the design. Those seven stages are explained as follows:
Stage 1: Need Survey. (Yalden)
This stage is important to find out what our learners’ needs in which it would determine what should be learned by the learners. In conducting the need survey, the writer also needs to find out in what level and cognitive development stage the learners are, since it will also determine the kinds of treatment should be given to the learners in order to facilitate them in an effective and efficient learning behaviour. And this instructional material design is proposed for the children, in which the learners still have a big sense of curiosity which also become the basic characterisation which characterised their learning behaviour. The learners usually try to make sense out of things, to find out how every things work, to have a big sense of competition among each other and to control over themselves and their environment.
Stage 2 : Stating the Goal, Topics and Basic Competencies.
on the need survey Stage 3: Stating the Indicators
This stage is adapted from the third step of Kemp’s model, Stating the Learning Objective, and revised based on the type of curriculum used in Indonesia.In this stage, the writer specifies the learning objectives to be achieved in term of measurable learners’ behavioural outcomes. In other words, all objectives stated must be in the form of manageable activities, which promote learning.
Stage 4: Building the Subject Content (Kemp)
In this stage, the writer develops the objectives to construct the subject content. Meaning to say, the writer decides what needs to be inserted in order to support the learning objectives itself.
Stage 5: Developing the Instructional Materials (Yalden)
In this stage, the writer develops the instructional materials into three types of activities, namely
a. Pre-activities b. Main-activities c. Post-activities Stage 6: Evaluation (Kemp)
After getting the results of the research, the writer uses those opinions as the feedback, which enable s him to find out which parts need to be improved to get the final version of his design.
The stages in designing the instructional materials could be seen in this following figure.
Figure 2.3: Revised Instructional Materials Design Model Need Survey
Developing the Instructional Materials
Revising and Improving the Designed Material
Evaluation Stating the Goal, Topics
Basic Competencies-+++++++++++++++++++
Stating the Indicators
Building the Subject Content
Developing the Instructional Materials
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
This section elaborates the methodology used in this study. This section contains the subjects, respondents, setting and instruments of the research. This section also presents how the writer gathers and analyses the gathered data.
A. Types of Study
In doing his study, the writer conducted two types of study, namely reviewing the related literature method (finding theories and information related to the research) and conducting the research. Bismoko as quoted by Sutanto (2003:37) stated that there are five types of research, namely qualitative-quantitative research, primary-secondary research, statistical research, survey research, ex post facto research and experiment research. The type of research, which was chosen by the writer, was a survey research (non-experimental research) in which the uses of the research were to describe and to interpret the results of the research itself. Moreover, according to Jaeger (1988: 303-304) the survey research is used to describe the specific characteristic of the whole group. The methods of study are divided into two as follows:
1. Library Research
method, the writer tried to compile and focus his study on books, which revealed about children development stages, material design, and media design. Other sources, which were used by the writer, were sources, which were related to some previous instructional material design, which were considered useful and having relations to the new instructional material design.
2. Survey Research
According to Sprinthall, Schumte and Sirois (1991: 93) the survey research is designed in order to gather information from samples or respondents by using questionnaires, interview or conducting a class observation. Moreover, Sprinthall, Schumte and Sirois also imply that the main concern of the survey research is to examine the relationship between the variables measured or the differences between samples in their response pattern.
B. Research Subjects and Respondent
1. Subject of the Related Literature
As mentioned previously in the other part of this chapter, the writer conducted the literature review in order to have a strong theoretical base in developing his instructional design. And in developing his ins tructional material design, the writer focused his attention on the books and other sources related to the research.
The books used by the writer were the books and other sources, which contained the theories related to his research and also needed by the writer in order to develop his instructional material design. The aim of reviewing such sources was that the writer would be able to construct a strong and reasonable framework in his research. These theories also helped the writer to make his design more reliable, because the writer had based his study on theories which had been found and used by some previous researchers, in which they also developed their own design. All books and other sources, which were used by the writer, cover the field of instructional design, instructional design development, children development, the teaching methodology, and also the analysis of the data which helped to improve the designed material.
2. Respondents of the Research
whether the designed material would meet the need and fulfilled the goal of the study process of the learners or not.
There were two groups of respondents in this study. The first group was the respondents of the needs survey who were taken from the instructors of Language Center Institution as the teachers of the children who learned English at Language Center Institution. The writer believes that instructor is the first person who deals with the children. The instructor is the person who builds the knowledge of the learning child. Moreover, the instructor should also know the level of his learners or the needs of his learners before he taught his learners.
The second group is the respondents of materials evaluation who were taken from various English course institutions'. The aim of the writer in gathering information from this second group is to find out the strength and the weakness of his design, so that the writer able to improve his design.
C. Research Instruments
Cates (1985: 97) proposes two types of instruments in gathering data in research, namely questionnaires and interview. Cates also states that by using questionnaires, a writer will get a reliably consistent presentation of items. The questionnaires contain forced response or structured response and open-ended response or unstructured response question. The writer of this study used both types of instruments to gather the data of the needs of the learners and also to evaluate the designed material.
the respondents do not understand the items being asked (Ary, 1990:418). Moreover, the interviewer was able to add some additional information to the incomplete or not entirely relevant responses. Cates (1985:97) also states that the major advantage of using the interview is that the interviewer can utilise both verbal and nonverbal cues in determining the response.
D. Information and data Gathering
The information and data gathering were achieved through the use of the research instrumentations. In this research, the writer used two kinds of instruments, namely interview and questionnaires. Both interview and questionnaires would bring a set of data that would be useful for the writer in his research. These two instruments were delivered before and after the design are designed. The first instruments delivery was meant to gather information about what types of materials should be inserted or discussed in the material design. This needs analysis was done by delivering the questionnaires and conducting the informal interview to the English instructors of Language Center Institution as the respondents. And the second instruments delivery was meant to gather the feedback about the already designed material in order to improve the content of the designed material. The second type of data was gathered by delivering the questionnaires to the mentors of Language Center Institution and the lecturer of English Education Program of Sanata Dharma University as the evaluator of the designed materials. Both research instruments contained items that evaluate and information about the already existed instructional material that was used before this research being held.
E. Data Analysis
The data analysis phase could be held only after the writer completed his information and data gathering. In doing the data analysis, the writer considered the answers of the respondent before he started to develop and to re-evaluate his own instructional material design.
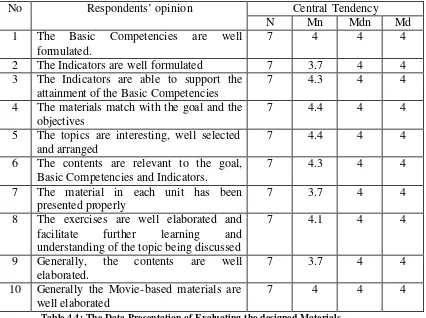
In the data ana lysis, the writer cultivated the data to relate the thought and the opinion of the respondents with the thought of the writer so that the writer able to construct a set of instructional material which at least able to fulfil the needs of the learners through the result of the research instrument. The data, which were analysed, came from the questionnaires which had been distributed to the respondents. Since the data gathered could be quantified, Cates (1985: 98) states that the finding could be displayed using descriptive statistics: mean, median and mode.
The writer used five-point agreement to measure the respondents’ opinions of the designed materials. The five-point agreement is shown as follow.
1 = strongly disagree with the statement 2 = disagree with the statement
3 = neutral
4 = agree with the statement
5 = strongly agree with the statement
The tendency of the respondents is presented in this following table. Central tendency No Respondent’s Opinion
N Mn Mdn Md
Note:
Mn : Means, it indicates the central tendency of the respondents.
Mdn : Median, it indicates the middle point that occurs in the gathered data. Md : Mode, it indicates the score that frequently occurs in the gathered data. The formula that is used in measuring the central tendency is presented as below.
Note:
Mn : mean S : the sum of X : the raw score
N : the number of the score
F. Procedure of the Study
Basically in doing his research the writer employed seven steps, which would be explained as follow.
1. The writer conducting a study to gather all information needed what so called reviewing the Library research. The writer studied theories and previous material designs which were designed by other previous writers to support the writer’s research.
2. The writer created a new instructional design model by adapting and combining the instructional model of Yalden’s and Kemp’s, which was believed by the writer as the appropriate model to develop his design.
3. The writer conducted a need survey in order to reveal the needs of the learners of Language Center Institution as the object of the writer’s study. The need survey
involved the two kinds of instrumentations, namely questionnaires and interview. 4. The writer composed a set of movie-based instructional materials to teach
vocabulary for children in Language Center Institution.
5. The writer delivered the designed materials and also the questionnaires in order to get the feedback as the evaluation of his designed to the English instructors of various institutions.
CHAPTER IV
DISCUSSION
This chapter presents the result and the discussion of the findings of the survey research and the designed material evaluation. This chapter is consisted of four parts. The first part describes the steps that were taken by the writer in designing a set of movie-based instructional materials to teach vocabulary for children in Language Center Institution. The second part describes the findings of the designed material evaluation. The third part presents discussion about the designed material evaluation, and the last part presents the designed materials.
A. The Steps of Designing a Set of Movie-Based Instructional Materials to Teach Vocabulary for Children in Language Center Institution.
In constructing the design, the writer employed seven steps. The elaboration of each step is stated as follow:
1. Need Analysis
sampling.
The writer found that before he started to construct his design, he should be able to address first to whom he constructed his design to. The data about the learners’ characteristics are gained using two kinds of sources, namely the library study, which involved the books, other thesis writing and other written sources, and the data gained from the questionnaires delivered to the respondents in the needs analysis.
The results of the study of the learners’ characteristics explained that the learners who are classified as Children in Language Center Institution as the objects of this study, are in the range of 6 -12 years old, in which they are in the level of intermediate of cognitive development. As stated by some previous researchers, the writer found that children in this phase have a big will in learning something new, including a new language, which is different from their mother tongue. In this phase, the writer found that it seemed that the children were always curious on what they see and what they hear. Moreover, the curiousness of the children governed them in their learning process.
The children were also able to choose or to learn something, but they still choose it based on what they like, not what they need. Thus, they needed adults to guide them in their learning process, in order to help them to determine what should be learnt. The writer also found that the children’s environment also ha s a strong relationship to the cognitive development of the children. It implied that the writer should be able to construct a design, in which able to attract both the children and the environment around them in order to create conducive learning environment.
used the materials that they chose by themselves and also the guideline of the institution, in this case Language Center Institution’s curriculum, as their base in teaching the children. It means that the instructors in this institutions are having freedom in choosing kinds of material, which they think useful and able to support them in the teaching process, as long as in the track of guideline, which is used by the institution. From this point, the writer thought that it would be very useful for the instructor, if the writer also constructed his design based on the guideline of Language Center Institution.
The respondents also explained that children were able to concentrate on the material in a very limited amount of time, namely between the range of 15 to 25 minutes. This fact implied that it is hard to keep the children stay and concentrate to the material, because they were getting bored very easily. Thus, the instructor needs a tool or media to keep the children concentrate so that they could follow the lesson efficiently. The fact that the children were having a time limitation in their relation with their study behaviour, was also became one of the writer consideration in designing the material, besides creating a more enjoyable learning for the learners.
The most frequently used techniques, which was used by the instructors in overcoming this situation, was using games or peer interaction. The instructors admitted that the success of using this kind of technique depended on the situation of the children, whether they were in a good or bad mood. It implies that the instructors still require a tool that able to increase the curiosity of the children, in order to stimulate the children’s intrinsic motivation to learn the new language. Thus, the writer intended to create such kind of tool or media in his design.
teaching- learning process, since with the existence of the media it would be easier for the teacher in delivering the material. Moreover, they agreed with the writer that using an audio-visual aid would be very useful for the teaching- learning process, since the audio- visual media had some special characteristics compared to other kind of media. The instructors said that the audio- visual aid would help the children to receive and to understand the topic being delivered, since this kind of media able to deliver both the message and the appearance of the material being discussed at the same time. Another characteristic of the media was that the media is repeatable without changing the message.
In this study, the writer intended to construct a design to teach vocabulary for children, therefore the writer needed the data of how important to learn vocabulary is. Based on the data, the instructors agreed that vocabulary takes an important role in the children’s language learning process. For this reason, the instructors gave this kind of material a bigger portion compared to the other kinds of material such as grammar, writing, reading, and etc. According to the instructors, good vocabulary mastery would bring the learners into a better further learning, since the messages received could be understood clearly.
2. Starting the Goal, Topics and Basic Competencies
Before the writer stated the instructional objectives, the learner thought that it was necessary for him to clarify once again about the goal of this study. The goal of this study was to design materials to help the children as the learners of the Language Center Institution in learning vocabulary using audio-visual media.
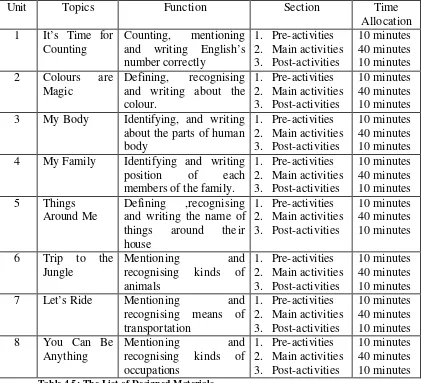
presented in each unit. In the Language Center Institution the instructors were allowed to decide the materials to be delivered as long as in the track of the Language Center Institution’s guideline. Therefore, the writer chose the topics based on the language Center Institution’s guideline and also the vocabulary around the learners, so that it would be easier for the children to recognise the material being discussed. The topics were as follows:
1. It’s Time for Counting 2. Colours are Magic 3. My Body
4. My Family
5. Things Around Me 6. Trip to The Jungle 7. Let’s Ride
8. You Can be Anything
After formulated the topics, then the writer formulated Basic competencies of each topics. The general purposes were stated as Basic Competencies. The complete Basic Competencies were drawn as follows.
No Topics Basic Competencies
1 It’s Time for Counting The learners are able to know English numbers. 2 Colours are Magic The learners are able to recognise the colours
correctly.
3 My Body The learners are able recognise the part of human body.
4 My Family The learners are able to understand the English family tree.
5 Things Around Me The learners are able to recognise things around them in their daily life.
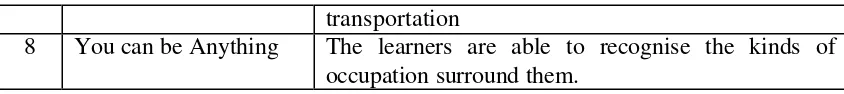
6 Trip to The Jungle The learners are able to recognise the kinds of animals
transportation
8 You can be Anything The learners are able to recognise the kinds of occupation surround them.
Table 4 1: The List of Basic Competencies
3. Stating the Indicators
The next step, which was taken by the writer after, was specifying the indicators of each unit. The complete indicators were drawn as follows:
No Topics Indicators
1 It’s Time for Counting At the end the lesson the learners are able to: 1.1.mention the English numbers in order. 1.2.write the English numbers.
2 Colours are Magic At the end the lesson the learners are able to: 2.1. recognise colours in English
2.2. apply the knowledge of colours in the exercises. 3 My Body At the end the lesson the learners are able to:
3.1. mention parts of their bodies correctly 3.2. identify and show parts of their bodies 4 My Family At the end the lesson the learners are able to:
4.1. recognise the position of someone in the family tree.
4.2. show and mention names and the position of each members of their family in their
own family tree.
5 Things Around Me At the end the lesson the learners are able to: 5.1.recognise things around their houses 5.2.mention things around their houses. 6 Trip to The Jungle At the end the lesson the learners are able to:
6.1. mention kinds of animals 6.2. recognise the kinds of animals
7 Let’s Ride At the end the lesson the learners are able to: 7.1. mention means of transportation
7.2. define the means of transportation 8 You can be Anything At the end the lesson the learners are able to:
8.1. mention kinds of occupations 8.2. define kinds of occupations Table 4 2: The List of the selected Indicators
included in order to facilitate the learning process. Thus, the writers started to build the subject content.
4. Building the Subject Content
In order to fulfil the objectives, the writer should provide the appropriate materials through a careful selection of the sources. In this step, the writer developed 8 lesson units.
Each unit had to be designed well in order to enable the learners in learning the material easily and in an enjoyable way. Each unit consists of 4 parts, namely: Let’s
Watch the Movie, Let’s Learn More, Exercise, and Song (the presentation of the
design can be seen in Appendix 6). The aim of the writer in dividing each unit into four part is to create a various, continuous and enjoyable learning activity. The pre-activity of the designed material would be in term of a speaking task. The instructors were supposed to deliver some questions related to each topic in order to put the basic knowledge for the learners before they started learning the materials (the example of the questions can be seen in APPENDIX 5)`. Thus, in the designed materials, the writer did not put any concrete material.
The Let’s Watch the Movie, Let’s Learn More and Exercise would be the main
“farmer” refers to a person who works in a farmland, using shirt, jeans and boots, and probably driving a tractor. While in Indonesia, the words “farmer” has a little bit differences in their appearance. For example, they usually wear a T-shirt, a three quarter trousers and a traditional hat called as “caping”. By watching the movie, and then see the highlight of the word, hopefully the learners will understand that the word “farmer” refers to the person who works in a farmland no matter what type of clothes they wear.
The Let’s Learn More consis ts of the list of pictures and the vocabularies. The
aim of designing these materials was to give the concrete vocabularies to the learners, which was suitable to the le