6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d
TIN205 – EKONOMI TEKNIK Materi #10 h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Pendahuluan … (1)
2
Seandainya
anda
menginvestasikan
senilai
($1.650) dalam rekening tabungan 6% per tahun.
Kemudian anda hanya memperoleh $9.477 pada
Januari tahun 2000.
Apa arti dari 6%
interest
disini?
Ini adalah
opportunity cost
jika menyimpan uang
pada rekening tabungan, dan merupakan suatu
tindakan yang terbaik yang dapat dilakukan saat
itu.
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Pendahuluan … (2)
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik3
Kemudian, pada tahun 1970, anda memperoleh
tawaran untuk investasi lain dengan
interest
lebihdari 6% untuk investasi lain, anda akan mengambil investasi tersebut?
Dalam hal ini, 6% dipandang sebagai
minimum
attractive rate of return
/MARR (rate of return
yang dibutuhkan). Maka, anda dapat menetapkan aturan keputusan
berikut untuk memperoleh investasi yang diusulkan yang terbaik jika:
ROR > MARR h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Definisi #1 ROR
4
Rate of return
(ROR) merupakan interest
rate yang diperoleh pada unpaid balance
dari angsuran suatu pinjaman.
Contoh:
Sebuah
bank
meminjamkan
$10.000
dan
menerima
pembayaran
pertahun sebesar $4.021 selama 3 tahun.
Dalam hal ini, bank dikatakan memperoleh
penghasilan kembali
(return of)
10% dari
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Loan Balance Calculation
A = $10.000 (A/P, 10%, 3) = $4.021
Year Unpaidbalance at beginning of year Return on unpaidbalance (10%) Payment received Unpaid balance at the end of year 0 –$10.000 –$10.000 1 –$10.000 –$1.000 +$4.021 –$6.979 2 –$6.979 –$698 +$4.021 –$3.656 3 –$3.656 –$366 +$4.021 0 Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 5
TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
A return of 10% on the amount still outstanding
at the beginning of each year
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Contoh #1 (ROR)
6
John membeli barang seni seharga $80.000
dan menjual kembali seharga $53,9 juta
pada 40 tahun kemudian.
Berapa
rate of return
dari investasi John ?
$80.000
$53,9juta
0
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Solusi Contoh #1 (ROR)
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
7
Diketahui:
P
= $80.000 ;
F
= $53,9juta ;
n
= 40 tahun
Ditanya:
i
Jawab:
1
i
40$80.000
$53,9juta
17,69%
i
1
i
nP
F
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a nContoh #2 (ROR)
8
Pada awal 1985, suatu investasi dari 100 saham
seharga $1.650 menjadikan sebuah perusahaan
terbuka (
go public
). Investasi tersebut akan
menjadi $13.312.000 pada 31 Januari 2015.
Berapa
rate of return
pada investasi tersebut?
$1.650
$13.312.000
0
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Solusi Contoh #2 (ROR)
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
9
Diketahui:
P
= $1.650 ;
F
= $13.312.000 ;
n
= 30 tahun
Ditanya:
i
Jawab:
1
i
30$1.650
0
$13.312.00
34,97%
i
1
i
nP
F
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a nDefinisi #2 ROR
10
Rate of return (ROR) is defined as
break-even interest rate (i*), which equates the
present worth of a project’s cash outflows
to the present worth of its cash inflows.
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Definisi #3 ROR (Return on Invested Capital)
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
11
Return on invested capital is defined as the
interest rate earned on the
unrecovered project
balance
of an investment project. It is commonly
known as
internal rate of return (IRR)
.
Contoh: A company invests $10.000 in a
computer and results in equivalent annual labor
savings of $4.021 over 3 years. The company is
said to earn a return of 10% on its investment of
$10.000.
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a nProject Balance Calculation
12
0 1 2 3
Beginning project balance –$10.000 –$6.979 –$3.656 Return on invested capital –$10.000 –$6.979 –$3.656 Payment received –$10.000 +$4.021 +$4.021 +$4.021 Ending project balance –$10.000 –$6.979 –$3.656 0
The firm earns a 10% rate of return on funds that remain internally invested in the project. Since the return is internalto the project, we
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Metode Perhitungan ROR
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
13 Metode Solusi Langsung (Log) Metode Solusi Langsung (Quadratic) MetodeTrial & Error Metode Solusi Grafik Komputer n Proyek A Proyek B Proyek C Proyek D 0 –$1,000 –$2,000 –$75,000 –$10,000 1 0 1,300 24,400 20,000 2 0 1,500 27,340 20,000 3 0 55,760 25,000 4 1,500 h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Metode Solusi Langsung (Log) Proyek A
14$1,000 = $1,500(P/F, i, 4)
$1,000 = $1,500(1 + i)
–40.6667 = (1 + i)
–4ln 0.6667/–4 = ln (1 + i)
0.101365 = ln (1 + i)
ℯ
–4= (1 + i)
i = ℯ
0.101365– 1
i = 10.67%
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Metode Solusi Langsung (Quadratic)
Proyek B
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
15 h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Metode Trial & Error Proyek C
… (1)
16
Langkah 1: Guess an interest rate, say, i = 15%
Langkah 2: Compute PW(i) at the guessed i value.
PW (15%) = $3,553
Langkah 3: If PW(i) > 0, then increase i. If PW(i)
< 0, then decrease i.
PW(18%) = –$749
Langkah 4: If you bracket the solution, you use a
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Metode Trial & Error Proyek C
… (2)
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
17 3,553 0 -749 15% i 18% 749 3,553 3,553 3% 15% i 17.45% i h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Metode Solusi Grafik Komputer Proyek D
Langkah (a): Create a NPWplot using Excel.
Langkah (b): Identify the
point at which the curve crosses the horizontal axis closely approximates the i*.
Catatan: This method is
particularly useful for projects with multiple rates of return, as most financial softwares would fail to find all the multiple i*s.
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Situasi
Multiple Rates of Return
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
19
Aturan keputusan dasar, jika ROR > MARR, maka terima
proyek.
Aturan ini tidak berlaku untuk situasi dimana investasi
mempunyai“multiple rates of return”.
Contoh: Cari rate(s) of return dari CF diagram berikut.
$1,000 $2,300 $1,320 0 1 2 PW i( ) $1, i i $2, $1, ( ) 000 300 1 320 1 0 2 h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Solusi Contoh
Multiple ROR
20
Let Then,
Solving for yields,
or
Solving for yields or 20% x i PW i i i x x x x x i i 1 1 000 300 1 320 1 000 300 320 0 10 11 10 12 10% 2 2 . ( ) $1, $2, ( ) $1, ( ) $1, $2, $1, / /
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
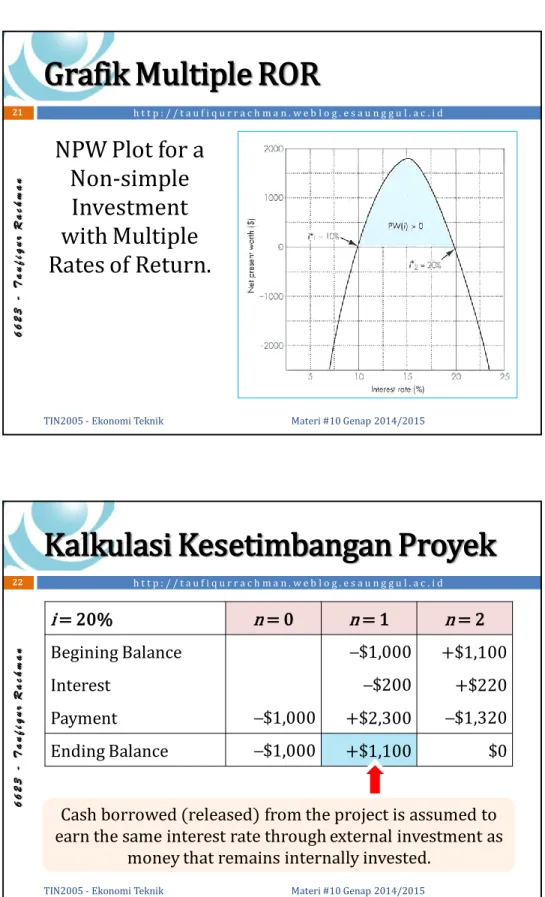
Grafik Multiple ROR
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
21
NPW Plot for a
Non-simple
Investment
with Multiple
Rates of Return.
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a nKalkulasi Kesetimbangan Proyek
i = 20% n = 0 n = 1 n = 2 Begining Balance –$1,000 +$1,100 Interest –$200 +$220 Payment –$1,000 +$2,300 –$1,320 Ending Balance –$1,000 +$1,100 $0 22
Cash borrowed (released) from the project is assumed to earn the same interest rate through external investment as
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Critical Issue Kesetimbangan Proyek
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
23
Can the company be able to invest the money
released from the project at 20% externally in
period 1?
If your MARR is exactly 20%, the answer is
“yes”
, because it represents the rate at which the
firm can always invest the money in its investment
pool. Then, the 20% is also true IRR for the project.
Suppose your MARR is 15% instead of 20%. The
assumption used in calculating i* is no longer valid.
Therefore, neither 10% nor 20% is a true IRR.
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
How to Proceed Kesetimbangan Proyek
24
If you encounter multiple rates of return, abandon
the IRR analysis and use the NPW criterion.
If NPW criterion is used at MARR = 15%.
PW(15%) = –$1,000 + $2,300 (P/F, 15%, 1)
– $1,320 (P/F, 15%, 2 )
= $1.89 > 0
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Aturan Keputusan Non-Simple Investment
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
25
Kemungkinan multiple ROR
Jika PW(i) seperti Gambar
1, maka IRR = ROR.
Maka jika IRR >
MARR, terima proyek.
Jika PW(i) seperti Gambar
2, maka, IRRROR (i*).
Dapatkan IRR sebenarnya, atau Gunakan method PW. i* i i i* i* PW (i) h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Aturan Keputusan Non-Simple Investment
26h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Incremental Investment
n Proyek A1 Proyek A2 Incremental Investment (A2 – A1)
0 –$1,000 –$5,000 –$4,000
1 $2,000 $7,000 $5,000
ROR 100% 40% 25%
PW(10%) $818 $1,364 $546
Assuming MARR of 10%, you can always earn that rate from other
investment source, i.e., $4,400 at the end of one year for $4,000 investment.
By investing the additional $4,000 in A2, you would make additional
$5,000, which is equivalent to earning at the rate of 25%. Therefore, the incremental investment in A2 is justified.
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015
27
TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Incremental Analysis (Procedure)
28
• Compute the cash flows for the
difference between the projects
(A,B) by subtracting the cash flows
for the lower investment cost
project (A) from those of the higher
investment cost project (B).
Langkah 1:
• Compute
the
IRR
on
this
incremental investment (IRR).
Langkah 2:
• Accept the investment B if and only
if IRR B-A > MARR.
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Contoh Incremental ROR
Diketahui MARR = 10%, proyek mana yang menjadi pilihan terbaik?
n B1 B2 B2 – B1 0 1 2 3 –$3,000 1,350 1,800 1,500 –$12,000 4,200 6,225 6,330 –$9,000 2,850 4,425 4,830 IRR 25% 17.43% 15% Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 29
TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
Karena IRRB2-B1=15% > 10%, dan juga IRRB2 > 10%, pilih B2.
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
IRR Increment Investment 3 Alternatif
n D1 D2 D3 0 –$2,000 –$1,000 –$3,000 1 1,500 800 1,500 2 1,000 500 2,000 3 800 500 1,000 IRR 34.37% 40.76% 24.81%
1. Langkah 1: Tetapkan IRR untuk tiap proyek untuk mngeliminasi tiap project yang gagal memenuhi MARR.
2. Langkah 2: Bandingkan D1 dan D2 berpasangan.
30
IRRD1–D2=27.61% > 15%, pilih D1.
3. Langkah 3: Bandingkan D1 dan D3. IRRD3–D1= 8.8% < 15%, pilih D1.
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Incremental Borrowing Analysis
If the difference in flow (B-A)represents an increment of investment, then (A-B) is an increment of borrowing.
When considering an
increment of borrowing, the rate i*A-B is the rate we paid to borrow money from the increment.
If BRR B-A <
MARR, select B.
If BRR B-A =
MARR, select either one.
If BRR B-A >
MARR, select A.
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015
31
TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
Principle: Decision Rule:
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Borrowing Rate of Return
32 n B1 B2 B1–B2 0 –$3,000 –$12,000 +$9,000 1 1,350 4,200 –2,850 2 1,800 6,225 –4,425 3 1,500 6,330 –4,830
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Incremental Analysis for Cost-Only Projects
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
33
Items CMS Option FMS Option
Annual O&M costs:
Annual labor cost $1,169,600 $707,200
Annual material cost 832,320 598,400
Annual overhead cost 3,150,000 1,950,000
Annual tooling cost 470,000 300,000
Annual inventory cost 141,000 31,500
Annual income taxes 1,650,000 1,917,000
Total annual costs $7,412,920 $5,504,100
Investment $4,500,000 $12,500,000
Net salvage value $500,000 $1,000,000
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Incremental Cash Flow (FMS – CMS)
34
n CMS Option FMS Option Incremental(FMS–CMS) 0 –$4,500,000 –$12,500,000 –$8,000,000 1 –7,412,920 –5,504,100 1,908,820 2 –7,412,920 –5,504,100 1,908,820 3 –7,412,920 –5,504,100 1,908,820 4 –7,412,920 –5,504,100 1,908,820 5 –7,412,920 –5,504,100 1,908,820 6 –7,412,920 –5,504,100 $2,408,820 Salvage + $500,000 + $1,000,000
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Solusi (FMS – CMS)
PW(i)FMS–CMS= –$8,000,000 + $1,908,820(P/A, i, 5) + $2,408,820(P/A, i, 6) = 0 IRRFMS–CMS = 12.43% < 15%, pilih CMS Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 35TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Predicting Multiple RORs
36
–100% < i* < infinity
Net Cash Flow Rule of Signs:
No. of real
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Contoh
n Net Cash flow ChangeSign
0 –$100 1 –$20 2 $50 1 3 0 4 $60 5 –$30 1 6 $100 1
No. of real i*s = 3.
This implies that the
project could have
(0, 1, 2, or 3) i*s but
NOT more than 3.
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015
37
TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Accumulated Cash Flow Sign Test
Find the accounting sum of net cash flows at the
end of each period over the life of the project.
Period (n) Cash Flow (An) Sum (Sn)
0 A0 S0= A0
1 A1 S1= S0+ A1 2 A2 S2= S1+ A2
n An Sn= Sn–1+ An
38
If the series
S
starts
negatively
and changes sign
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Contoh
n An Sn Perubanhantanda 0 –$100 –$100 1 –$20 –$120 2 $50 –$70 3 0 –$70 4 $60 –$10 5 –$30 –$40 6 $100 $60 1Jumlah tanda
berubah =
1, indicating
a unique i*.
i* = 10.46%
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 39TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Contoh Incremental B/C Ratios
40
A1
A2
A3
I
$5,000
$20,000
$14,000
B
12,000
35,000
21,000
C’
4,000
8,000
1,000
PW(i)
$3,000
$7,000
$6,000
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Solusi
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 41TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik A1 A2 A3 BC(i) 1.33 1.25 1.40 Ranking Base A1 A3 A2 I +C’ $9,000 $15,000 $28,000 h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Cost-Effectiveness Studies
… (1)
42General Procedure
Step 1: Establish the goals to be achieved by the analysis.
Step 2: Identify the imposed restrictions on achieving the goals, such as budget or weight.
Step 3: Identify all the feasible alternatives to achieve the goals. Step 4: Identify the social interest rate to use in the analysis. Step 5: Determine the equivalent life-cycle cost of each
alternative, including research and development, testing, capital investment, annual operating and maintenance costs, and salvage value.
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Cost-Effectiveness Studies
… (2)
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik43
Step 6: Determine the basis for developing the cost-effectiveness index. Two approaches may be used;
(1) the fixed-cost approach and (2) the fixed-effectiveness approach.
If the fixed-cost approach is used, determine the amount of
effectiveness obtained at a given cost.
If the fixed-effectiveness approach is used, determine the cost
to obtain the predetermined level of effectiveness.
Step 7: Compute the cost-effectiveness ratio for each alternative based on the selected criterion in Step 6.
Step 8: Select the alternative with the maximum cost-effective index. h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Cost-Effectiveness Decision Criterion
44
Fixed Cost Approach
Maximize Effectiveness
Subject to:
Budget Constraint
Fixed Effectiveness
Approach
Minimize Cost
Subject to:
Must meet the
minimum effectiveness
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Case Study – Selecting An Weapon System
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
45 h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Weapon System Alternatives
46
Alternative Aj Advantage Disadvantage Probability of Kill A1: Inertial navigation
system Low cost, mature technology. Accuracy, target recognition 0.33 A2: Inertial navigation
system (Global positioning system)
Moderate cost,
nature technology Target recognition 0.70 A3: Imaging infrared
(I2R)
Accurate, target recognition
High cost, bunkered
target detection 0.90
A4: Synthetic aperture radar
Accurate, target
recognition High cost 0.99
A5: Laser detection / ranging
Accurate, target recognition
High cost, technical
maturity 0.99
A6: Millimeter wave
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Life-Cycle Costs for Weapon
Development Alternative
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
47
Expenditures in Million Dollars
Phase Year A1* A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 FSD 0 15 19 50 40 75 28 1 18 23 65 45 75 32 2 19 22 65 45 75 33 3 15 17 50 40 75 27 4 90 140 200 200 300 150 5 95 150 270 250 360 180 IOC 6 95 160 280 275 370 200 7 90 150 250 275 340 200 8 80 140 200 200 330 170 PW(10%) 315.92 492.22 884.27 829.64 1,227.23 612.70 h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n
Cost-Effectiveness Index
48Type Cost/Unit Probability of Kill Cost/Kill Kill/Cost
A1 $31,592 0.33 $95,733 0.0000104 A2 49,220 0.70 70,314 0.0000142 A3 88,427 0.90 98,252 0.0000102 A4 82,964 0.90 83,802 0.0000119 A5 122,723 0.99 123,963 0.0000081 A6 61,370 0.80 76,713 0.0000130
h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d 6 6 2 3 -T a u fi q u r R a ch m a n A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 60.000 70.000 80.000 90.000 100.000 110.000 120.000 130.000 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1.000 1.100 1.200 1.300 Co st /k ill
Present value of life cycle cost ($ million)
Cost-Effectiveness Graph
Materi #10 Genap 2014/2015 TIN2005 - Ekonomi Teknik
49 Maximize Effectiveness Fixed Cost Unacceptable Region 66 23 -T au fiq ur R ac hm an h t t p : / / t a u f i q u r r a c h m a n . w e b l o g . e s a u n g g u l . a c . i d