BRAINSTORMING SKILL IN TEACHING READING BY
STUDENT-TEACHERS OF ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT AT SMKN 1 SURABAYA
THESIS
Submitted in Fulfillment of The Requirement For the Degree of Sarjana
Pendidikan (S.Pd) in Teaching English
By:
Siti Musfiroh
D05211025
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF EDUCATION AND TEACHER TRAINING
SUNAN AMPEL STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
ABSTRACT
Musfiroh, Siti. 2016. Brainstorming Skill in Teaching Reading by Student-teachers of English Teacher Education Department at SMKN 1 Surabaya. A Thesis. English Teacher Education Department, Faculty of Education and Teacher Training, Sunan Ampel State Islamic University. Advisors: Dra. Irma Soraya, M.Pd and Hernik Farisia M.Pd.I.
.
Keywords: Brainstorming Activities, Brainstorming Skill
ABSTRAK
Musfiroh, Siti. 2016. Brainstorming Skill in Teaching Reading by Student-teachers of English Teacher Education Department at SMKN 1 Surabaya. Skripsi. Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri Sunan Ampel Surabaya. Dosen Pembimbing: Dra. Irma Soraya, M.Pd and Hernik Farisia M.Pd.I.
.
Kata Kunci: Brainstorming Activities, Brainstorming Skill
D. Scope and Limitation ... 10
E. Significance of the Study ... 12
F. Definition of Key Term ... 14
CHAPTER II : REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Review of Related Literature ... 16
1. Brainstorming ... 16
a. Definition of Brainstorming ... 16
b. Types of Brainstorming Activities ... 19
1) The Stepladder Techniques ... 19
2) Brainwriting ... 20
3) The Crawford’s Slip ... 20
4) Brain-netting ... 21
5) Round Robin Brainstorming ... 21
6) Mind Mapping ... 21
c. Significance of Brainstorming in ELT ... 24
2. Teaching Reading... 25
a. Definition of Reading ... 25
c. Teaching Reading Components ... 26
3. Brainstorming as Activites in Teaching-Learning Practice ... 27
4. Brainstorming as Activites in Teaching Reading... 28
B. Review of Previous Study ... 30
CHAPTER III : RESEARCH METHODS A. Research Design ... 33
B. Research Subject ... 34
C. Data ... 35
D. Research Instrument ... 36
E. Data Collection Technique ... 37
F. Data Analysis Technique ... 38
G. Data Source ... 39
CHAPTER IV : FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION A. Findings ... 41
1. Brainstorming Activities ... 41
a. Student-teacher 1 ... 41
b. Student teachers 2 ... 58
2. Brainstormer Skill ... 63
B. Discussion ... 92
1. Brainstorming Activities ... 92
2. Brainstormer Skill ... 95
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION B. Conclusion ... 92
C. Suggestion ... 93
REFERENCES
LIST OF TABLES
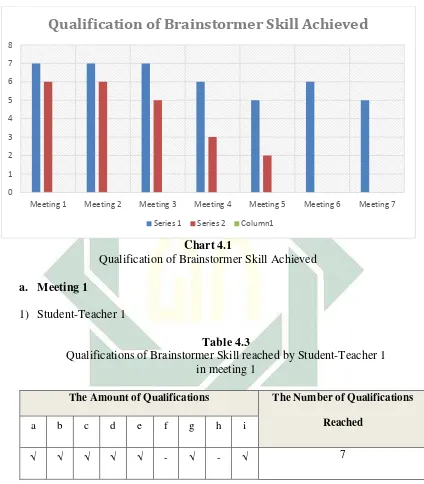
4.1. Brainstorming Activities of Student-teacher 1. ... 41
4.2. Brainstorming Activities of Student-teacher 2 ... 58
4.3. Qualification of Brainsormer Skill Reached by Student Teacher 1 in
Meeting 1 ... 65
4.4. Qualification of Brainsormer Skill Reached by Student Teacher 2 in
Meeting 1 ... 70
4.5. Qualification of Brainsormer Skill Reached by Student Teacher 1 in
Meeting 2 ... 73
4.6. Qualification of Brainsormer Skill Reached by Student Teacher 2 in
Meeting 2 ... 76
4.7. Qualification of Brainsormer Skill Reached by Student Teacher 1 in
Meeting 3 ... 78
4.8. Qualification of Brainsormer Skill Reached by Student Teacher 2 in
Meeting 3 ... 81
4.9. Qualification of Brainsormer Skill Reached by Student Teacher 1 in
Meeting 4 ... 83
4.10. Qualification of Brainsormer Skill Reached by Student Teacher 2 in
Meeting 4 ... 85
4.11. Qualification of Brainsormer Skill Reached by Student Teacher 1 in
Meeting 5 ... 87
4.12. Qualification of Brainsormer Skill Reached by Student Teacher 2 in
Meeting 5 ... 88
4.13. Qualification of Brainsormer Skill Reached by Student Teacher 1 in
Meeting 6 ... 89
4.14. Qualification of Brainsormer Skill Reached by Student Teacher 1 in
Meeting 7 ... 91
LIST OF CHARTS AND FIGURES
Figure 4.1. Brain-netting Media: Matching Words with Pictures ...46
Figure 4.2. Brain-netting Media: Person's Identity ...47
Figure 4.3. Brain-netting Media: Text about Personal Identity ...48
Figure 4.4. Brain-netting Media: Short Text about Person's Identity ...50
Figure 4.5. Brain-netting Media: Various Folklore ...51
Figure 4.6. Brain-netting Media: Bullying Questions ...56
Figure 4.7. Brain-netting Media: Imagine the Problems...61
Chart 4.1. Qualifications of Brainstormer Skill Achieved ...66
LIST OF APENDICES
Appendix 1
1. Brainstorming Activities Observation Checklist ... xv
2. Brainstormer Skill Rubric ... xviii
Appendix 2
1. Biography ... xxi
Appendix 3
1. Sample of Brainstorming Activities Observation Checklist ... xxii
2. Sample of Brainstorming Skill Rubric ... xxv
Appendix 4
1. Research Licensing Letter from SMKN 1 Surabaya ... xxix
2. Consultation Letter ... xxx
Appendix 5
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter discusses the area of the study that will be covered in some
headings (1) Background of the Study, (2) Research Questions, (3) Objectives of the
Study, (4) Scope and Limitation of the Study, (5) Significance of the Study, (6)
Definition of Key Terms.
A. Background of the Study
Reading is an important skill that could be mastered. It gives language
learners a chance to confirm expectation. Reading will create knowledge in
more scientific ways rather than listening.1 Someone can know everything
scientifically better by reading because it can give detail information about
particular issue rather than listening in which speaker’s opinion influence the
information too much.
In addition, different from listening which requires speakers to deliver
particular message, reading can be done independently, everywhere and every
time. So, nowadays there is no excuse for not getting the knowledge. This
statement is also supported by Stephanova who says that reading also creates
1
2
the more space for learners to conduct independent learning, moreover in
today’s cyber era.2
Thus, this current study focuses on reading.
The success of learning English, especially learning reading, cannot be
separated from teaching process. Brown defines the concept of teaching which
explains that teaching guides, facilitates, encourages, and also sets the
condition for the effectiveness of learning.3 Therefore, a teacher must have
good strategies or ways to support the effectiveness of learning.
In line with the previous statement, every student is also expected to
build knowledge by their own idea or mind. That statement is also explained
by Kolb which says that one of four kinds of abilities to reach successful
learning is by forming and re-forming and processing learner’s ideas.4
Meanwhile, the teachers need to facilitate students by giving a chance for
them to find and apply their own ideas.
By means of those two things, mainly students are expected to have
ability to think (encouraging idea) and to share the idea. Besides, teachers also
have to find any solution to achieve the aim of teaching-learning process
which can encourage students’ idea and can provoke them to share their ideas.
Surely, the strategy and activity which encourage student’s idea is very
2 Helen Stephanova, “
Receptive skill: Resourcess for Independent Learning”. English Language Teaching. Oxford University Press, 21st May 2013, 1.
3
Brown H.D, Principles of Language Learning and Teaching (4thedition) (NewYork: Addison Wesley Longman,Inc, 2000), 7.
4
3
needed as problem solving of that case.5 Then, it is important to provide
various activities in supporting the successful of teaching learning process,
including the activities that can encourage students’ ideas.
Dealing with the activities to encourage students’ ideas, brainstorming
can be chosen as one of any alternative options to apply. Orlich says that
brainstorming activity must be used as an important rule of teaching-learning
activity because brainstorming is the simple and effective skill-building
technique for using.6 Brainstorming is an activity that is useful to create a
chance for students to encourage their own ideas.
Brainstorming will be one of the solutions to pursue students for sharing
their ideas. It has been documented in Labiod's study stating that prior
knowledge triggering through brainstorming increases learners' reading
comprehension.7 In some cases, high expectation of providing brainstorming
in teaching learning often does not work properly. It is showed by
phenomenon of student-teachers in 6th semester of English Teacher Education
Department of State Islamic University Sunan Ampel in Surabaya who have
not been maximum yet in providing the activities which can brainstorm
students’ thinking to produce ideas in Practice Teaching Class (PPL 1).8 To
5
Deborah L. Ulrich and Kellie J. Glendon, Interactive Group Learning: Strategies for Nurse Educators (Springer Publishing Company, 2005), 10.
6
Donald Orlich et al., Teaching Strategies: A Guide to Effective Instruction (Cengage Learning, 2012).
7 Zargham Ghabanchi and Saeedah Behrooznia, “The Impact of Brainstorming on Reading
Comprehension and Critical Thinking Ability of EFL Learners”. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 98. 2014. 513 – 521. (www.academia.edu, accessed on May 5th 2015).
8
4
give a kind of follow up to the previous case, a preliminary research was
conducted. It is important to prove that brainstorming had not run optimal in
Practice Teaching Class (PPL 1).9
In providing the sufficient data for previous statement, a preliminary
research and interview to the student-teachers in 6th semester of English
teacher education department of State Islamic University Sunan Ampel in
Surabaya had been conducted to prove that statement. The aim of the
preliminary research was to know how many students used brainstorming as a
strategy or activity in teaching-learning practice especially in Practice
Teaching Class (PPL 1) to encourage student’s idea.
The result is that from 59 participants who filled the sheet of
preliminary research, only 18 students used brainstorming in
teaching-learning practice. From that case, it was known that there was only 30% of
students who conducted brainstorming in their teaching-learning process.
Besides, those 18 students did brainstorming only in the first session. This
case showed that there was 70% of participants who did not apply
brainstorming in all the stages of their teaching.
Then, the secondary preliminary research was examining about
students’ perspective related to brainstorming was conducted as the follow up.
The secondary research was a preliminary interview about students’
understanding of brainstorming. The second result shows that from 11
9
5
interviewees; 3 interviewees did not know about brainstorming and 8
interviewees knew brainstorming as only warming up activity or just in the
beginning of teaching-learning practice. Whereas, according to Mongeau and
Claire, brainstorming is also often used in a generic sense in producing a list
of ideas10. As brainstorming having its generic sense, it can be conducted in
every session of teaching process.
In contrast, students of Practice Teaching (PPL 1) supposed that
brainstorming can be conducted in the initiation only. Thus, it is clear that the
students did not really catch the point of brainstorming. Considering this
reason, brainstorming is taken as the object of the study to bridge between
students’ understanding and the theory of Mongeau and Claire.
Talking about English learning which becomes one of the subjects in
Indonesian school curriculum, there is a case that happened in education,
teaching-learning process still cannot be reached as expected. It is proven by
the evidence that there are many students in vocational school (SMK) who
cannot use English practically although they have learned it since elementary
until high school.11 This case however influences their ability to comprehend
specific terms in their field, to communicate globally, and to compete with
other people all over the world. Whereas, based on Directorate of Vocational
10 Paul A. Mongeau, and Mary Claire Morr, “Reconsidering Brainstorming”.
Group Facilitation: A
Research and Applications Journal. Vol.1, No.1, Winter 1999.
(http://69eisenhower.csub.edu/~rdaniels/Mongeua%20and%20Morr%201999.pdf, accessed on December 12th 2014).
11 Herman Dwi Surjono and Heni Rita Susila, “
Pengembangan Multimedia Pembelajaran Bahasa
6
School Development which stated that the procurement services for
vocational school (SMK) aimed to establish vocational graduates are
entrepreneurial, intelligent, competent, competitive, and nationalist in the
local advantages development and the global market competition.12
In other words, the requirement to face global market is not only skill in
job and knowledge, but also the ability to communicate especially by using
English as the international language. It is also supported by the Minister of
Education and Culture of Indonesian Republic which stated that the second
main competence in curriculum 2013 of English also states that the purpose of
teaching English in vocational school is to make students aware on the way
how to behave in global interaction.13 The term “behavior” is not only seen
from the attitude but also from the way to communicate with other people.
Based on the statement above, the students of vocational school is
prepared to work in certain field. Whereas, senior high school does not
prepare students to work because it points to the scientific optimalization in
order that students can continue to a higher education. Those things are
explained explicitly in the academic manuscript about standard content in
senior high school which mentioned that senior high school curriculum never
12
Direktorat Pembinaan Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan, Direktorat Jendeal Pendidikan Menengah, dan Kementrian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan Tahun 2014. Garis-garis Besar Program Pembinaan SMK.(http://www.ditpsmk.net/juknis/files/00_GarisGaris_Besar_Program_Pembinaan_SMK_2014. pdf, accessed on July 3rd 2015).
13
7
gives the certain experience or skill to work.14 Instead, the certain experiences
or skills to work in certain field are arranged in vocational school. Therefore,
the teaching learning process in vocational school ought to provide
appropriate material and teaching method for students based on their field.
Dealing with the way how vocational school students communicate
using English, an interview to previous students-teacher at SMKN 1 Surabaya
was conducted. That interview stated that the skill of English especially in
reading and speaking of SMKN 1 students is not quite good. The reason is
that because just few students could reach the goal of those subjects.
There are some studies related with this current study. The first study
was done by a professor assistant of University of Jerash, Jordan, Walid
Mahmoud Sdouh, in 2012-2013. The result of this research showed that there
were significant differences in term of academic achievement and the
development of creative thinking skills among the averages between the two
observed groups; the group that used the strategy of brainstorming and the
group that used the strategy of computer education. Besides, this research also
shows that both groups of students have different attitudes towards learning
the engineering unit in mathematics.15 The differences between this previous
study with the current study are the subject material used. The previous study
14
Departemen Pendidikan Nasional Badan Peneitian dan Pengembangan Pusat Kurikulum 2007,
Naskah Akademik Kajian Standar Isi Pendidikan Menengah. Jakarta: Depdiknas, 2007, 12.
15Walid Mahmoud Sdouh, “
The Effect of Using Strategies of Brainstorming and Computer Education in Academic Achievement and The Development of Creative Thinking Skills Among The Students of Sixth Grade and Their Attitudes towards Learning The Engineering Unit in Mathematics”.
8
is mathematics and this current study is English. Then, the previous study
tried to compare between two strategies; brainstorming strategy and computer
education and this current study tried to identify the types of brainstorming
provided by student-teachers and their brainstorming skills to do it.
The next study was conducted by Bilal Adel Al-Khatib. This study was
eager to analyze the effect of using brainstorming strategy in developing
creative problem solving skills among female students in princess Alia
University College.16 This study showed that there are statistical significant
differences at the level of (α = 0.05) between the experimental group and the
control group. This difference indicates any effectiveness of using
brainstorming strategy in developing creative thinking skill. Then, the
difference of Al-Khatib’s research with this current study is the design of
method used. The previous research used quantitative method which
employed experimental design. In contrast, this current research used
qualitative design.
The last study was conducted by Mahdum which attempted to describe
and test whether brainstorming can increase students’ reading ability at
English Department FKIP UR Pekanbaru.17 This study showed that students’
reading ability, students’ interest, and students’ motivation could be improved
16
Bilal Adel Al-khatib, “The Effect of Using Brainstorming Strategy in Developing Creative Problem
Solving Skills among Female Students in Princess Alia University College,” American International Journal of Contemporary Research. vol. 2, No.10, 29-38.
17
Mahdum, undergraduated thesis: “Penggunaan Brainstorming dalam Meningkatkan Kemampuan
9
by using brainstorming technique. The similarity of this study and the
previous one is that both of them used observation and interview as
instruments, but previous study examined the effect of brainstorming in
classroom research. In contrast, this current study elaborated more on the
brainstorming activity employed by student-teacher.
Dealing with the previous studies which showed the effect of using
brainstorming strategy in solving the problem and also in increasing students’
reading ability, it is important to provide brainstorming activities in teaching
learning process especially in teaching reading.
B. Research Questions
As a creative strategy to solve the problem in teaching-learning reading,
brainstorming becomes the important activities to provoke the creative
thinking of students. Considering that mentioned reason and the research
background, this study was intended to answer the following questions:
1. What types of brainstorming activities are used by student-teachers
of English Teacher Education Department at SMKN 1 Surabaya in
teaching reading of Internship Program?
2. How are brainstormer skill of student-teachers of English Teacher
10
C. Objectives of the Study
Considering the question arisen on this study, this study is intended to
reach the following objectives:
1. To find what types of brainstorming activities used by
student-teachers of English Teacher Education Department at SMKN 1
Surabaya in teaching reading of Internship Program.
2. To know how are brainstormer skill of student-teachers of English
Teacher Education Department in teaching reading.
D. Scope and Limitation of the Study
This research had two scopes to examine. The first scope was to
examine student-teachers’ activities in providing brainstorming in teaching
reading for specific purpose. In brief, this research examined the activities run
by student teachers doing internship in SMKN 1 Surabaya to provide
brainstorming in teaching reading. Then, as the second scope, this study
intended to examine to what extent the brainstorming activities provided by
students in teaching reading for specific purpose fulfill the qualifications of
good brainstorming.
Dealing with the scopes stated above, it was also important to set some
limitations in order that this research could reach its objectives. For that
11
limited to twelve activities adapted from some theories and experts. The
activities are: Stepladder Technique, Brainwriting, The Crawford’s Slip Approach, Brain-netting, Round Robin Brainstorming, Mind Mapping, Reverse brainstorming, Starbusting, Charette Procedures, Random input, Free-Wheeling, and Group ideation.
Furthermore, the second scope in which examining the extent of
brainstorming skill provided was also limited as well. The limitation was on
the qualifications of a good brainstorming adapted from Osborn and
Hutchinson and Waters’s theory. There are 9 qualifications chosen as the
indicators, they are:18
a. Teacher creates the positive attitude towards reading material in
which teacher behave not to be a teacher of the subject but an
interested student of the subject matter.
b. Teacher demonstrates the proper background knowledge.
c. Teacher does not criticize or express negative evaluation of any idea
presented, such as by saying “No” or “wrong” to correct students’
ideas.
18
Olga Goldenberg and Jennifer Wiley. (2011). “ Quality, Conformity, and Conflict: Questioning the
12
d. Teacher provides brainstorming activity to encourage students’ ideas
(the more ideas generated by students, the better brainstorming
activity provided).
e. Teacher records each idea from students.
f. Teacher sets a limit of time.
g. Teacher provides the atmosphere in which all students are involved
to encourage idea freely, being active in discussion, or invention
(finding the solution).
h. Teacher provides new ideas and situation for students, and gives
them motivation to generate the new ones.
i. Teacher starts the activity with students’ interest in, comments,
questions, etc.19
Then, providing brainstorming activities in teaching reading for specific
purpose by student-teachers in SMKN 1 Surabaya became the focus of the
study.
E. Significance of the Study
This study attempted to give both theoretical and practical contribution.
Thus, the following are the details on how this study implies any effect:
13
1. Theoretically, for teacher and student, this study is intended to
contribute research on informing the types of brainstorming
activities used.
2. Practically, this research gives some significances for teacher and
students of English Teacher Education Department Faculty of
Education and Teacher Training Sunan Ampel State Islamic
University Surabaya. This is hoped that this study gives any
understanding on how the student-teachers provided brainstorming
activity creatively (relating with types of brainstorming activities)
to provoke critical thinking of students and to build atmosphere of
class.
For students, this study attempted to show that brainstorming is not
only the activity or strategy in the beginning of the
teaching-learning process but also in the other sessions of it.
For student-teachers of sixth semester who will face the real activity
in the next teaching on internship program, because if
brainstorming activities is applied by all of teachers; it will be an
attractive activity in the teaching-learning practice.
For students of SMKN 1 Surabaya, they will become creative,
brainstorming above, the researcher considers that brainstorming is the
kind of activities to produce large ideas which can be found not only in
the beginning of the teaching-learning process but also in the other of it.
Here are brainstorming steps: clearly define topic to be brainstormed,
generating as many as ideas, dont changing, criticizing or evaluating any
idea, encouraging each member to present the idea, and presenting the
ideas.21 In this study, selecting topic, encouraging much ideas then
developing it are the main step in brainstorming activity.
2. Reading English for Specific Purpose: According Borg and Gall
statement that reading for specific purpose is kind of reading which
specifically conducted to fulfill students’ need by providing particular
reading comprehension material.22 In this research, reading for specific
purpose is defined as reading activity providing a specific material to
meet students’ speciality focus based on their field.
20
Paul A. Mongeau, and Mary Claire Morr. “Reconsidering Brainstoring.pdf.”. A Research and Applications Journal 1. Vol. 1, No. 1, 1999. 13-20.
21Suzanne Murphy. “5 Steps to Effective Brainstorming”
2016 Work Systems Affiliates International, Inc, (www.wsa-intl.com, accessed on January, 19th 2016).
15
3. Internship Program (PPL 2): As stated in the guideline of real classroom
teaching 2015 which is published by faculty of education and teacher
training of Islamic State University Sunan Ampel Surabaya, real
classroom teaching is a sequence of activity to apply kinds of education
theory manifested teaching learning process in school.23 In this research,
internship program (PPL 2) is the exercise practice in teaching which is
faced to the real teaching performance in the certain school (this curent
study is at SMKN 1 Surabaya).
4. Student-teacher: student who meet the requirements as student teacher in
real classroom teaching.24 One of the requirement is the student have
passed practice teaching subject (PPL1). In other words, student-teacher
is student who will teach in real classroom of Internship program with the
certain school.
23
Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Keguruan UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, Pedoman Praktik Pengalaman Lapangan II (PPL II) Tahun 2015. (Sidoarjo: Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Keguruan UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, 2015), 1.
24
CHAPTER II
Review of Related Literature
In this chapter, the researcher explicates several theories through reviewing
some literatures related to this study. This theoretical construct deals with some main
areas: (1) Brainstorming; definition of brainstorming, types of brainstorming, and
significance of brainstorming in ELT, (2) Teaching Reading; definition of reading,
types of reading, and teaching reading components, (3) Brainstorming in Teaching
Learning English, (4) Brainstorming as activities in teaching reading.
A. Theoretical Framework
1. Brainstorming
a. Definition of Brainstorming
Brainstorming is one of the most popular strategies in provoking
creative and solving problem in every field whether in educational,
commercial, industrial, and political fields. Brainstorming is defined as
the activity of thinking that includes the breaking up the old ideas,
17
onset of great ideas.1 In other words it can be said that in brainstorming
emphasized on calling the prior knowledge, linking it with the novelty
ideas, and generating more ideas. Another statement claimed that
brainstorming in creative problem solving probably becomes one of the
most popular tools stated by Fernald & Nickolenko, and Leclef, and
Stein.2 It showed that brainstorming will become a creative way to solve
students’ problem because it provides the activities will attract point of
view of students. Introduced by Alex Osborn, brainstorming becomes
solution of the inconvenience of traditional business meetings. In his
book under the title “Applied Imagination”, Osborn explained the
various tools and approaches creative problem solving.3
In one study, a group using brainstorming is more useful in
generating ideas than individuals thinking up suggestions.4 That study
also supported by Al-Maghrawy which defines brainstorming as a
creative group forum in producing general idea. Then, Jarwan defines
brainstorming as the active way to solve the problem and the session of
brainstorming heads for producing a list of ideas that can solve the
1
Bilal Adel Al-khatib, “The Effect of Using Brainstorming Strategy in Developing Creative Problem
Solving Skills among Female Students in Princess Alia University College,” American International Journal of Contemporary Research. vol. 2, No.10, 29.
2
Zargham Ghabanchi and Saeedah Behrooznia, “The Impact of Brainstorming on Reading
Comprehension and Critical Thinking Ability of EFL Learners”. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 98. 2014. 513 – 521. (www.academia.edu, accessed on May 5th 2015).
3Scott G. Isaksen and John P. Gaulin. “A R
eexamination of Brainstorming Research: Implications for
Research and Practice”. Creative Problem Solving Group. Vol. 49, No. 4. 2005. 315-329.
4
18
problem under discussion. Based on the studies and statements above,
brainstorming is defined as a creative and an active way to provide
solution for the problem solving that might appear in teaching learning
process. In detail, producing ideas, discussing it, and sharing it under the
discussion are the activities in brainstorming.
To make successful brainstorming activities, there are guidelines
which are built by Osborn: (1) no Criticism or Evaluation. Express no
negative evaluation or critics. (2) "Freedom" in expressing idea is
welcomed. The large idea is expected. (3) quantity is wanted. The
greater number of ideas shows the more the likelihood of winners. (4)
combination and improvement are sought. Thus, those four guidelines
are important in providing brainstorming. In addition to contributing
ideas, participants should suggest how ideas of others can be turned into
better ideas; or how two or more ideas can be joined into still another
idea.5 By that activities, list of brilliant ideas can be produced and from
those ideas, students can find the solution of the problem.
b. Types of Brainstorming Activities
Types of brainstorming activities become options for students to do
Brainstorming. Surely, types of Brainstorming can help students to
5 Paul A. Mongeau, and Mary Claire Morr, “Reconsidering Brainstorming”.
Group Facilitation: A
Research and Applications Journal. Vol.1, No.1, Winter 1999.
19
encourage their ideas. There are some types of Brainstorming can be
applied in teaching-learning process. Here are the details:
1) The Stepladder Techniques: this activity is developed by
Rogelberg, Janet, Barnes-Farrell, and Lowe. This activity has
basic steps. They are 6:
a) Present the task or problem to all members. Then, giving
them sufficient time to think and to form their opinion to
solve the problem.
b) Create a main group consist of two members. Ask them to
start the discussion about the problem or topic
c) Add the third member to the main group. The third member
has to present the ideas before knowing those ideas from two
members before. After all three members sharing their ideas,
they discuss about their options together.
d) Repeat the same process by adding the fourth member, and
so on, to the main group. Give the time for discussion after
new member has shared his or her ideas.
e) Reach a final decision after all members have been given and
shared their ideas.
6
20
2) Brainwriting: it emphasizes the silent production of ideas in
writing. Brainwriting was developed by Geschka, Schaude, and
Schlicksupp and the variation have been developed by Goodman.7
Here are the basic rules of brainwriting8:
a) Each person begins writing the ideas on paper, card, or board
by limiting the time.
b) When time is up, everyone must share the ideas to someone
else.
c) The second person must read all the ideas of first person and
add the new ideas.
3) The Crawford’s Slip: this brainstorming activity was developed by
Professor C.C. Crawford at the University of Southern California.
This activity involves collating input from people on slips of
paper. There are steps to do this activity 9:
a) Teacher gives students a scratch pad or paper
b) The teacher presents a problem, for example in “how to”
Christine Hogan, Practical Facilitation: A Toolkit of Techniques. (Kogan Page, 2005), 269.
8
Chauncey Wilson, Brainstorming and Beyond A User-Centered Design Method. (Morgan Kaufmann Publications, 2013), 52-53.
9Donald C. Mosley Jr., Donald C. Mosley Sr., and Paul H. Pietri. “
Supervisory Management: The Art
of Inspiring, Empowering, and Developing People”. Decision Making, Problem Solving, and Ethics.
21
d) Teacher asks students to place the slip of idea into the idea
bank(box).
e) Teacher asks students to arrange and to select the slips using
judgement to throw the weak ideas out.
f) Then, teacher asks all students to develop the good ideas and
to present the recommendation to the larger group.
4) Brain-netting: this activity is similar to brainwriting, but it uses an
electronic document stored.10
5) Round Robin Brainstorming: it was popularized by Spencer
Kagan.11 This brainstorming activity facilitate students to generate
ideas in turn. If the students have no idea, they feel free to “pass”.
The session overs if everyone passes.
6) Mind Mapping: This activity was popularized by Tony Buzan.12
11 David Fulton. “Teaching Contemporary Themes in Secondary Education”.
In Helen Gadsby and Andrea Bullivant (Ed.). Global Learning and Sustainable Development”. (New York: Routledge,
2011), 149.
12
Suzan Norman, Transforming Learning: Introducing SEAL Approach (London: Saffire Press, October 2003), 31.
13
22
images, symbols, and key words. That tool aims to scribe
responses or to organize information, then simply listing ideas on
flipchart.
7) Reverse Brainstorming: This activity was developed at the
Hotpoint Company, as a group method for discussing all possible
weakness of an idea, or what might happen when an idea is
implemented.14 Here are basic steps to do this activity:
a) Identify the problem
b) Reverse the problem or challenge by asking about the
solution or something that make that problem worse.
c) Brainstorm the reverse problem to generate reverse solution
ideas.
d) Evaluate those solution ideas.
8) Starbusting: is a form of brainstorming that focuses on producing
questions rather than answer. It can be used continuously, with
further question to get more ideas. It uses six component of
questions; Who? What? How? When? Where? and Why?15
9) Charette Procedures: This activity was derived from the Frensh
word for Wagon. It comes from the architecture students in the
14
Tony Proctor. Creative Problem Solving for Managers: Developing Skills for Decision making and Innovation (Taylor & Farncis e-Library, 2010), 236.
15
23
early 1800s. Then, introduced by Mind Tools CEO, James
Manktelow.16Here are the steps to do this activity”
a) Set the issues
b) Divide the larger group into small groups
c) Give the issue to each group
d) Try to have a recorder for each group
e) Record all ideas and set a time limit
f) Start to record brainstorming of the next group.
g) Discuss all the ideas to get the good ideas.
10)Random Input: is a lateral thinking activity. This activity tries to
link the thinking pattern into the other to generate the ideas. The
variations are all involve stating a challenge and comparing it to
some randomly selected words, pictures, phrases, objects, and
activities.17 Random input entails using a random word, picture, or
even sound to open the new ideas of thinking. This activity
associated by Edward the Bono.
11)Free-Wheeling: according to Osborn, it is an activity which
encourages people to recommend the ideas.18 In this activity
encourages the students to call out ideas freely and randomly until
16 James Manktelow. “Brainstorming Toolkit”
Mind Tools Limited, (www.heftfaculty.co.uk or
www.mindtools.com, accessed on January 20th 2016).
17
Chester Davis, Six Steps tp Better Acivism (Booktango, 2013).
18
24
none has anything further to add. This activity is spontaneous and
open in producing all the ideas.
12) Group Ideation: is introduced by Alex Faickney Osborn, the
founder of Brainstorming. The steps to do this activity are to form
a groups brainstorming then start to produce the ideas together.19
c. Significance of Brainstorming in ELT
Some of the significances of brainstorming are summarized below:
1) Brainstorming can generate or create greater number of ideas
and alternative responses. This statement is supported by
Arivananthan, in her journal said that brainstorming is a quick
and easy technique to generate the ideas for problem solving
and innovation.20
2) Brainstorming train critical thinking to solve the problem. It
helps the students to see other points of view and all students
have equal opportunity to participate. Alam Khan said that
brainstorming can encourage learners to think freely and
19Karen E. Burris, “Leading Brainstorming Session: How to facilitate Ideation and creative Problem Solve”. Society for Healthcare Strategy & Market Development of The American Hospital Association.
2015.
20 Meena Arivananthan, “Brainstorming: Free
25
innovatively each other than they were doing routine classroom
situation.21
3) Brainstorming is an activity to create a student-centered activity.
Students manage their own group to generate the ideas, develop
rating criteria, responsible with the movement of the group. In
his book, Jones said that one of the activity that is used in
student-centered activity is brainstorming.22
2. Teaching Reading
a. Definition of Reading
Reading is the activity that cannot be separated with the existence of
reader and text or writing work. It can be said that there is an
“interactive” process between a reader and a text when the reader reads
something. In reading process, the reader interacts with the text and
attempts to provoke the meaning and where various kinds of knowledge
are being used: linguistic or systemic knowledge (through bottom-up
processing) as well as schematic knowledge (through top-down
processing).23 Then, Reading is process from reading a words in a group
21Intakhab Alam Khan, “Relevance of Brainstorming in an EFL Classroom”.
Elixir Social Science.
54A, January 2013, 12880-12883.
22
Leo Jones, The Student-Centered Classroom (Cambridge: Cambridge Universuty Press, 2007), 40.
26
of sentences and then link it to find the information or knowledge from
it.
b. Types of Reading
There are two types of reading; extensive and intensive reading.
Hafiz and Tudor defined in a journal of Alyousef that extensive reading
is kind of reading program which provoke the students learn to write
through reading. While intensive (or creative) reading, usually students
read a page to discover the meaning and to be acquainted with the
mechanisms of writing.24
From the explanation above, teaching reading in English has to
include the six components of reading process and using the appropriate
activities and strategies dealing with the types of reading to make
reading become interactive process.
c. Teaching Reading Components
Seen as a complex process, reading, in a statement of Grabe that
many researchers try to know and describe the fluent of reading process
by examining a set of element skills in reading process; so at least there
are six general component skills and knowledge areas25:
1. Automatic recognition skills
2. Vocabulary and structural knowledge
24 Hesham Suleiman Alyousef, “Teaching Reading Comprehension to ESL/EFL Learners”. The Reading Matrix. Vol.5, No.1, September 2005. 66.
25
27
3. Formal discourse structure knowledge
4. Content/world background knowledge
5. Synthesis and evaluation skills/strategies
6. Metacognitive knowledge and skills monitoring
Those six components skills and knowledges that become
requirement to know and describe the reading fluency. So, it is
important for teacher to master it in teaching reading.
3. Brainstorming in Teaching-Learning Practice
One of activities in the teaching learning process is brainstorming.
This activity trains students’ critical and creative thinking to solve the
problem. Ganji and friends state that brainstorming is considered as the
importance thing in ELT because it can enhance critical abilities of
student, social intelegence, novelty ideas, solution, and also provide the
chance to discuss in language learning areas. Based on that statement,
brainstorming is regarded as a beneficial activity in language learning
process.
There are the steps in providing brainstorming which are stated by
Simmon in a thesis of Mahdum, teacher have to : (1) deciding the topic
which will be discussed or for the next topic the students can decide it,
(2) making a list or concept related with the topic; meanwhile dealing
with the words and idea related with the topic are students ‘job, (3)
28
develop the ideas related with the topic, (4) choosing the topic which
will be developed and students is given the opportunity in developing
their ideas based on the topic discussion.26 Dealing with the previous
statement, the Simmon’s steps of brainstorming, there are some
important things to be highlighted, such as deciding topic, making a list
or concept, developing a set of concept, and developing idea that have to
be completed in doing brainstorming activity.
4. Brainstorming as activities in Teaching Reading
Evolving as one of the popular strategy, the main purpose of
brainstorming is to develop and enhance communication skill, to help in
encouraging ideas and to train the skill in making decision of sharing
and delivering viewpoints and opinions. That statement also supported
by Feather which said that brainstorming offered to make prediction of
many materials.27 Furthermore, it is such that brainstorming is one of
strategies which involve students in generating the ideas concerned what
prior knowledge about the topic of text given before reading it.
26
Mahdum, Thesis: “Peggunaan Brainstorming dalam Meningkatkan Kemampuan Membaca
Mahasiswa S1 Semester 1 Program Studi Bahasa Inggris FKIP UR Pekanbaru”. Pekanbaru: FKIP UR Pekanbaru, 2013.
27
29
Brainstorming is also can motivate student’s communication skill.28
There are identifying marks that will be used to sign good brainstorming
activities. They are
a. Teacher expresses good comment: no negative evaluation of any idea presented.
b. Teacher does for quantity, not quality--the longer and more the list of ideas, the better.
c. Extending on each other’s ideas, piggyback, hitch on, elaborate whenever possible.
d. Increasing the thinking out of the box.
e. Teacher records each idea of students, at least by a key word or phrase.
f. Teacher sets a time limit and holds strictly to it.29
In addition, to achieve the successful brainstorming activities,
brainstormer (student-teachers) should have the skill in brainstorming.
There are some capacities that student-teacher should have:
a. Creating the positive attitude towards ESP content
b. Demonstrating the proper background knowledge relevant to the subject area
c. Mastering all the requirements of the Brainstorming session
d. Providing the positive and permissive atmosphere that encourages idea generation, discussion, and invention
e. Providing students with novelty ideas and situations and giving motivation to them in generating novelty ones
f. Reflecting their satisfactory command of scientific and technological English
g. Initiating activities which students interest in, comments, questions, etc.
h. Appreciating the scientific point of view and the role of science and technology in modern society
28
Rita S. Dunn and Kenneth J, “Practical Approaches to Individualizing Instruction: Contracts and
Other Effective Teaching Strategies”. BRAINSTORMING APPROACH, 1972, (http://www2.maxwell.syr.edu/plegal/crit3/a12.html, accessed on April 16th 2015).
29
30
i. Mastering the linguistic, technical, and psychological aspects of ESP teaching and learning.
Hutchinson and Waters state that all of the capacities above can be
used for improving the level of student’s comprehension in ESP reading.
From the identifying marks and brainstormer skill above, it is important
to use those categories in doing the brainstorming activities of teaching
reading.30
B. Previous Studies
There are some studies related with the current study. The first study
is done by assistant professor of University of Jerash, Jordan, Walid
Mahmoud Sdouh, in 2012-2013, that investigated the effect of using
strategies of brainstorming and computer education in academic
achievement and the development of creative thinking skills among the
students of sixth grade and their attitudes towards learning the
engineering unit in mathematics. This previous study is the same as term
brainstorming, but in previous study using brainstorming as strategy but
this current study using brainstorming as activities. Then, another
difference is the subject material, the previous study is mathematics and
this current study is English. The first group of this previous study
included 34 students who used the brainstorming strategy. The second
30Mohammad Ahmed Manasrah, “T
he importance of Brainstorming in Improving ESP Reading
31
group included 35 students who used the strategy of computer
education. The result of the previous study showed differences with the
statistical significance in developing creative thinking skills. Then,
using strategy of computer education to learn the engineering unit also
showed the differences with statistical significance.
The next study is done by Bilal Adel Al-Khatib in 2012 that
analyzed the effect of using brainstorming strategy in developing
creative problem solving skills among female students in princess Alia
University College. This study is to investigate the effect of using
brainstorming strategy in developing creative problem skills. To find the
significant result, the researcher used a program of brainstorming
strategy and Torrance creative thinking test. The different things
between Al-Khatib’s study and current study is this current study
analyzed the brainstorming activities that will be done by
student-teachers and describe it by using rubric which contain the identifying
marks of brainstorming and the brainstormer skill items. There were two
classes in the previous studies. The first class represented the
experimental group totaling 47 students taught through brainstorming
strategy in the course of developing thinking skill. The second class
represented the control group totaling 51 students. The findings of
32
between those two classes. The result showed that using brainstorming
strategy is effective in developing creative thinking skills.
The last study was conducted by Mahdum which attempted in
describing and testing whether brainstorming can increase students’
reading ability at English Department FKIP UR Pekanbaru. This
previous study used quantitative and qualitative data in collecting data.
Whereas this study uses qualitative data. Besides, the previous study
used action research as research design, in contrast, this study uses
qualitative research. In previous study, the participants were 25 students
of the first semester S1 program. This study uses observation, interview,
and tests. The result of the previous study showed that brainstorming
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter discusses the area of the study that covered (1) Research Design,
(2) Research Subject, (3) Data, (4) Research Instrument, (5) Data Collection
Technique, (6) Data Analysis Technique.
A. Research Design
The employed method in this current research was qualitative. As the
reason of previous statement, this research examined and collected any data
related to the words behavior of a small of participants. As the consequence,
what was done by the participants was obtained more in this research. To support
the previous statement, Walliman says that the development and understanding
of qualitative approach tend to focus on behaviors, events, and etc. 1
In further, Sugiyono defines qualitative method as a method which is based
on positivism and examines natural things which face no changing, and the
researcher plays as the most important instrument inside.2 The definition of
qualitative arouse by Sugiyono is in line with this research which put the
researcher as the main instrument, as the key of research. In other term, this
qualitative research with its descriptive characteristic was purposed to describe a
1
Nicholas Walliman, Research Methods the basics (London and New York: Routledge, 2011), 102.
2
34
factual and certain situation systematically and accurately. Besides, this research
was devised to explain the individual phenomena or characteristic and certain
situation or group.
Moreover, the researcher used case study as a type of qualitative approach
in which case study attempts to understand clearly about a program, event,
activity, process of the subject of the study.3 In this case, the researcher identified
the internship program (PPL 2) by focusing on teaching learning activity
especially in providing brainstorming activities of teaching reading which
conducted by student-teachers at SMKN 1 Surabaya and also their brainstormer
skill. Furthermore, Ary stated that case study focuses on a single unit such as
individual, group, and organization.4 For this reason, the researcher took two
student-teachers at SMKN 1 Surabaya as subject of this study.
B. Research Subject
As mentioned previously on the research background, the subject of this
study was student-teachers of English Teacher Education Department of State
Islamic University Sunan Ampel Surabaya. However, not all of the
student-teachers were involved in this research. This study selects only two students who
teach in SMKN 1 Surabaya. The reason was that because this research just
3
John W. Creswell, Research Design Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Method Approaches (3rd edition) (USA: Sage Publication, 2009).
4
35
attempted to analyze the ability to conduct brainstorming activity of some
student-teachers who thought English in senior vocational school.
Relating with the previous words, in choosing the participants, purposeful
sampling, especially Extreme Case Sampling was employed. Extreme case sampling is a sampling technique which can enable the researcher to choose
research subject based on the different or extreme characteristic.5 The reason
why those two students teaching in vocational school were included into the
extreme one is that because student-teachers in SMKN 1 differ from other
students for they were the only one who thought English for specific purpose in
real classroom teaching. Thus, it was clear that those two students use the
different strategy, materials, and so on to include students’ focus, etc.
C. Data
The data is any information dealing with student-teachers’ ability in
providing brainstorming activity in teaching reading. From all meetings,
student-teacher 1 taught reading in seven meetings and student-student-teacher 2 taught reading
in five meetings. The primary data was the types of brainstorming activities
provided by teacher and the brainstorming skill item reached by
student-teacher which got through classroom observation result. Besides, the data also
reached through some notes from the video record of the classroom activities in
the class.
5
36
Then, to support the primary data, any supplementary data got from lesson
plan which will be held in their teaching was also employed. Furthermore, to
strengthen all the data got by, another secondary data relating to brainstorming
information taken from books, journal, etc. was also employed.
D. Research Instrument
In case study to gather the data, Ary suggested to use multiple method such
as interview, observation and archives.6 In conducting this research, the
researcher used some instruments. There were two instruments used to answer
both questions:
1. Instrument used for the first question
To answer the first research question, the instruments were:
Observation checklist of brainstorming activities used by students was to
examine the brainstorming activities through teaching practice. It consisted
of some types of brainstorming that were used by the student-teachers in
their teaching.
6
37
2. Instrument used for the second question
To answer the second research question, the instruments were:
Brainstormer skill rubric used to examine whether the activities meet with
the good items of brainstormer skill through brainstorming activities which
provided by student-teachers.
E. Data Collection Technique
In collecting the data, this research was divided into two parts and used two
instruments to collect the data. The first part was conducted to answer the first
question which used observation checklist of brainstorming activities. This
instrument was used to identify the types of brainstorming that provided by
student-teachers. Moreover, lesson plan also had a role as supporting instrument
to gain any related information about brainstorming. While observing students’
teaching performance using observation checklist, a lesson plan was used to
identify the teaching activities which were conducted by student-teachers and
other unpredictable activities related to brainstorming activity.
In answering the second question, a video recorder was employed to
record the teaching performance of student-teacher joining real classroom
teaching in State Vocational School (SMKN) 1 Surabaya. After having the video
of student-teachers’ teaching performance, the rubric consisting of brainstorming
skill items was used to know to what extent brainstorming was provided by
38
In addition, during collecting the data, classroom observation related with
brainstorming activities in teaching reading was done in seven meetings of
student-teacher 1 and five meetings of student-teacher 2.
F. Data Analysis Technique
Data analysis technique plays an important role in conducting a research,
since analysis can help the researcher to get a valuable meaning to solve the
problem.7 In order to get a good understanding related to the data, there were
some steps that shall be done first:
1. RQ 1 Analysis Technique
a. The data was ordered into types of table of brainstorming activities
used by student-teachers in teaching reading. Here, the researcher
discovered which one indicated student-teachers’ activities related
to brainstorming activity by using observation checklists.
b. Then, the activities of brainstorming used by students were
classified into types of brainstorming activities provided in the
rubric, what activities which were used and not used.
2. RQ 2 Analysis Technique
a. Dealing with the second question, the teaching performance record
was analyzed using the rubric consisting of brainstorming items to
7
39
identify the brainstormer skill of student-teachers. This video
analysis was aimed to add the information about brainstormer skill
of student-teachers beside the data from brinstormer skill rubric
from classroom observation.
b. The data was filtered and separated by the researcher. Some tables
describing both activities and skills were presented.
c. After describing the brainstorming activities of student-teachers and
their brainstorming skills, the findings were discussed.
d. The research results were concluded based on all the findings.
G. Data Source
1. Primary source
The primer data of this research was the data got from brainstorming
activities checklist, brainstormer skill and the video of students’
teaching performance. The result of interpreting the data became the
answer of the questions raised. The data then would be analysis using
the procedures written in data analysis technique to arrive into the
research finding.
2. Secondary source
The secondary data of this research was the data from lesson plan and
40
observation, such as media and so on, students’ lesson plan and media
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDING
This chapter presents the research findings and discussions of the study. It
describes about the data result about types of brainstorming activities provided by
student-teachers and their brainstorming skills. While, the discussion of this study
deduces the findings to then concludes it.
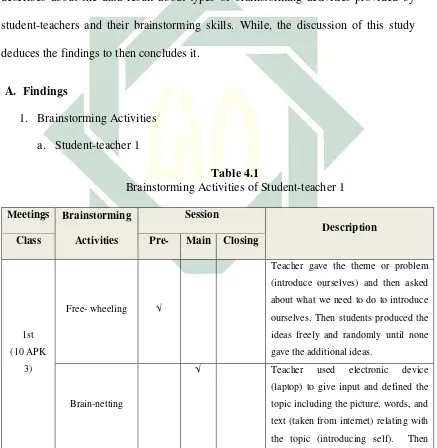
A. Findings (introduce ourselves) and then asked about what we need to do to introduce ourselves. Then students produced the ideas freely and randomly until none gave the additional ideas.
Brain-netting
in introducing ourselves and students tried to analyze about the information
Teacher showed two reading texts and she asked all of things related with the topic (introducing self) from the text.
Teacher asked students about what the meaning of folklore is by saying an example about folklore(Cinderella) then asked students to give another folklore.
Brain-netting √
Teacher provided pictures of various folklore, then asked about the things that they usually read inside each folklore (characteristic, setting, etc.) and teacher tried to clarify it with all of students.
43
4th (11 TKJ
1)
Free-wheeling √ Teacher asked the students about folklore and the examples of it
Brain-netting √
Teacher provided pictures of various folklore, then asked about the things that they usually read inside each folklore (characteristic, setting, etc.) and teacher tried to clarify it with all of students.
Each groups tried to give their opinion about moral value from the text, and had to present it in front of the class.
5th (11 TKJ
2)
Free-wheeling √
Teacher asked about students’ background knowledge about folklore then students mentioned the examples of folklore
Brain-netting √
Teacher provided pictures of various folklore, then asked about the things that they usually read inside each folklore (characteristic, magical features, setting, etc.) and teacher tried to clarify it with all of students.
Random input √
Each groups tried to give their opinion about moral value from the text, and what is the case of those video.
Free-wheeling √
Teacher gave some questions to students then they had to answer it by their own answer or ideas or opinion
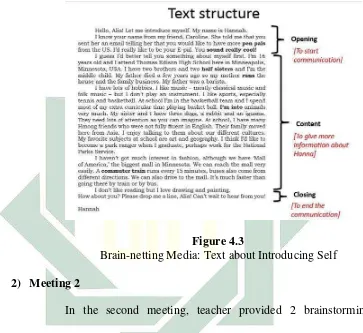
Group ideation √
Teacher divided students into 7 groups and gave them a paragraph for each
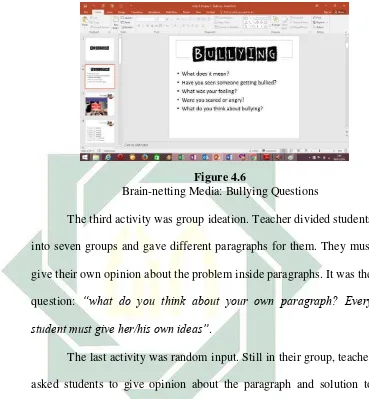
After giving opinion, teacher asked about students’ understanding toward topic (bullying) and they mentioned all the things related with it.
Group ideation √
Teacher divided students into 5 groups and gave them a different paragraph for each group. Then, they had to share about the main point of that paragraph Random input √ After sharing the main point of the
45
the opinion about the case in the paragraph and how to solve it.
1) Meeting 1
There were three activities that were provided in this meeting.
They were free-wheeling, brain-netting, and random input. The first
activity, free-wheeling, was conducted in pre-activity. In free-
wheeling activity, in the beginning, teacher told students the theme or
problem (introduce ourselves). Then, she asked them about what they
need to do to introduce theirselves. This offer resulted the production
of ideas freely and randomly among students. During that activity,
none gave any additional ideas. Here are the dialogues between
teacher and students during the classroom process:
T : “today we’re going to talk about our self. How to introduce
our self? what we need to do to introduce our self? What we’ve to mention?”
S : “name, class, address...”.
T : “Please, raise your hand!”.
S : “age”.
T : “Age. And then?”
S : “Number phone, number telephone...”
T : “Phone number..okay..what else? Only four?
S : “....”
T : “How about ‘hobby’?”