Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- Hepy Yudo Hartoto
- Pengajar:
- Drs. Amir Sisbiyanto, M.Hum
- Drs. Ahmad Sofwan, PhD
- Sekolah: Semarang State University
- Mata Pelajaran: English
- Topik: The Errors of English Pronunciation Among The Second Grade Students of Tersono Junior High School Tersono Batang
- Tipe: Final project
- Tahun: 2010
- Kota: Semarang
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. Introduction
This study investigates English pronunciation errors among second-grade students at Tersono Junior High School in Tersono, Batang. The introduction establishes the context by highlighting the importance of English as a subject in Indonesian junior high schools and the emphasis on developing all four language skills (speaking, listening, reading, and writing) within a competency-based curriculum. The researcher notes a widespread observation of poor pronunciation among young learners, often attributed to limited practice, the inherent difficulty of English phonetics, and differences between the English and Javanese sound systems. The study aims to contribute to improved English language teaching by analyzing the specific types and sources of pronunciation errors.
1.1 Background of the Study
The section underscores the significance of pronunciation in effective English communication, emphasizing its crucial role in both speaking and listening. It highlights the gap between students' actual pronunciation abilities and teacher expectations, leading to the identification of numerous errors. The researcher observes students struggling with various aspects of pronunciation, including differentiating sounds with similar pronunciation and correctly producing vowels and diphthongs. The limited practice time and potential demotivation among students are also considered as contributing factors to the prevalent pronunciation issues.
1.2 Identification of the Problem
This section delves into the linguistic differences between Javanese (the students' native language) and English, explaining how these differences contribute to pronunciation errors. The researcher points out disparities in consonants, vowels, diphthongs, stress patterns, and spelling rules between the two languages. The transfer of Javanese sound systems into English pronunciation is identified as a key source of errors, highlighting the complexities of learning a second language with a significantly different phonetic system. The discussion touches upon the need to understand these linguistic differences to effectively address pronunciation challenges.
1.3 Statement of the Problem
The study emphasizes the scarcity of research focusing on pronunciation errors among young English language learners, particularly in the Indonesian context. The researcher identifies a gap in understanding the specific pronunciation challenges faced by young learners and the need for more focused research in this area. By focusing on the production of vowels, diphthongs, and intonation in simple questions, the study aims to provide data that will be beneficial to teachers in improving their students' pronunciation.
1.4 Formulation of the Problem
This section clearly articulates the two main research questions: Firstly, it asks to identify the specific types of pronunciation errors (vowels and intonation) made by the students. Secondly, it aims to determine the underlying causes of these errors, considering both interlingual (Javanese interference) and intralingual (within English) factors. These questions guide the research process and focus the analysis on key aspects of pronunciation difficulties.
1.5 Objectives of the Problem
The stated objectives directly correspond to the research questions, clearly outlining the study's aims. The first objective is to comprehensively describe the observed pronunciation errors in vowels and intonation. The second objective focuses on analyzing and discussing the sources of these errors, investigating the interplay between Javanese/Indonesian and English sound systems, and determining the influence of both interlingual and intralingual factors on student pronunciation.
1.6 Significance of the Study
The significance section explains the expected contributions of this research. The findings are anticipated to provide valuable insights for junior high school teachers, informing the development and improvement of English language teaching methodologies. The study also aims to contribute to the broader field of language education by offering data that can support future research into young learners' pronunciation development.
1.8 Outline of the Report
This section provides a concise overview of the thesis structure, outlining the content of each chapter. It summarizes the key topics covered in each chapter, providing a clear roadmap for the reader. This allows readers to quickly understand the organization and flow of the research, facilitating a more efficient understanding of the study's methodology and findings.
II. Review of Related Literature
This chapter delves into existing theories and research on pronunciation errors, drawing upon various sources to establish a theoretical framework for the study. It begins by defining the concepts of 'error' and 'mistake,' differentiating between systematic errors reflecting incomplete learning and random slips. The chapter then explores the significance of error analysis in language acquisition, highlighting its role in assessing learning and informing teaching strategies. Various taxonomies of errors are reviewed, including linguistic categories (phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics), surface strategies (omission, addition, misinformation, misordering), and communicative effect categories (local and global errors).
2.1 Definition of Error
This subsection provides various definitions of 'error' from established linguistic literature. It clarifies the distinction between errors and mistakes, identifying errors as systematic deviations from target language norms, while mistakes are defined as performance errors resulting from temporary lapses. The discussion also introduces the concepts of interlingual errors (influenced by the native language) and intralingual errors (stemming from the target language itself). Different theoretical perspectives on the sources of these errors are presented.
2.2 Significance of Error
This section emphasizes the crucial role of errors in language learning, highlighting that errors are an inevitable and necessary part of the acquisition process. It discusses the insights that error analysis can provide into learners' strategies and levels of language mastery. Error analysis is presented as a valuable tool for teachers to assess learning, inform their teaching, and identify areas for improvement. The connection between error analysis and effective language instruction is clearly established.
2.3 Rule of Pronunciation in Learning
This subsection defines pronunciation and discusses its significance in language learning. It explains the multifaceted nature of pronunciation, encompassing individual sounds, stress, rhythm, and intonation. The section also presents a description of the articulatory phonetics of English, classifying vowels and consonants based on their articulation and discussing the complexities of the English sound system. The discussion lays the groundwork for understanding the difficulties that learners face when acquiring English pronunciation.
2.4 Errors in Pronunciation
This section examines the various sources of pronunciation errors, synthesizing information from different theoretical perspectives. It explores interlingual transfer, phonological universals, avoidance strategies, overgeneralization, hypercorrection, elision/epenthesis, letter-to-sound rule confusion, and the developmental model. The diverse factors contributing to pronunciation errors are presented, offering a multifaceted understanding of the challenges faced by learners. The discussion is further enriched by a consideration of Jenkins' proposal for prioritizing error correction based on the communicative needs of non-native speakers.
2.4 Conceptual Framework
This section outlines the theoretical framework guiding the research. It posits that while young learners have the potential to acquire understandable pronunciation, they often encounter difficulties due to their beginner status. This leads to various errors, such as addition, omission, misordering, and misinformation. The framework distinguishes between interlingual errors (caused by native language interference) and intralingual errors (due to complexities within the target language). The discussion connects the types of errors observed with the possible underlying causes, establishing a clear connection between theory and the practical aspects of the study.
III. Research Method
This chapter details the research design and methodology employed in the study. It specifies the research setting (Tersono Junior High School), timeline, and target population (second-grade students). The researcher explicitly states the use of a descriptive case study approach, employing qualitative data gathered through a pronunciation test. This chapter systematically guides the reader through the steps taken to collect and analyze data.
3.1 Place and Time of the Research
This subsection clearly states the location and timeframe of the research. The researcher specifies the school and grade level of the participants and provides a timeline detailing the various stages of the research process, including preparation, data collection, analysis, and report writing. The concise presentation makes the research context and timeline readily accessible to the reader.
3.2 Research Method
This section defines the research methodology, clarifying the use of a descriptive case study approach and the qualitative nature of the data analysis. The researcher explains that the data is primarily collected through a pronunciation test, supplemented by qualitative observations. The choice of methodology is explicitly justified in relation to the research questions and objectives.
3.3 Population and Sample
This section identifies the population (all second-grade students at Tersono Junior High School) and explains the rationale for selecting this specific group. The researcher's decision to focus on this population is justified by their linguistic background (Javanese speakers) and their status as beginner-level English learners. The clarity and precision in this section ensure that the reader understands the scope and limitations of the study.
IV. Research Findings
This chapter presents the results of the study, detailing the identified pronunciation errors and their sources. The findings are presented systematically, with descriptions and interpretations of both the types of errors and their underlying causes. The data analysis would likely involve categorizing errors based on the frameworks discussed in the literature review (interlingual vs. intralingual errors, surface strategy taxonomy).
4.1 Description of the Data
This section would present an overview of the collected data from the pronunciation test. This might include descriptive statistics, such as the number of participants, the types of errors observed, and the frequency of different errors. The data presentation should aim to give the reader a clear understanding of the overall pattern of pronunciation errors.
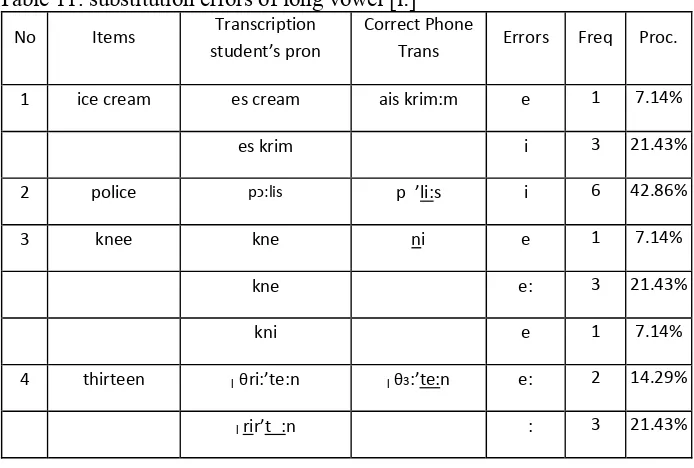
4.2 Description and Interpretation of Errors of the Learner’s Pronunciation
This section would detail the specific types of pronunciation errors identified in the students' speech. The errors are categorized and described, potentially using a table or other visual aid to organize and present the data effectively. The interpretation of these errors would likely refer back to the theoretical frameworks discussed in the literature review, providing insights into the linguistic mechanisms underlying the errors.
4.3 Description and Interpretation of the Sources of the Learner’s Pronunciation Errors
This section analyzes the sources of the identified errors, distinguishing between interlingual (first language interference) and intralingual (target language-specific) factors. It would explain how the students' native language (Javanese) influences their English pronunciation and also how internal factors within the English language system contribute to their errors. The discussion would integrate theoretical concepts from the literature review to provide a deeper understanding of the underlying causes.
V. Conclusion and Suggestion
This final chapter summarizes the key findings of the study and offers recommendations for improving English language teaching. The conclusions reiterate the main findings, emphasizing their implications for educational practice. The suggestions would offer practical strategies based on the identified error patterns and their sources.
5.1 Conclusion
This section summarizes the key findings of the study, restating the main types of pronunciation errors identified and their underlying causes. The conclusions should directly address the research questions and objectives, synthesizing the results of the data analysis and relating them back to the theoretical framework. This section should present a concise and clear summary of the research findings.
5.2 Suggestion
This section offers practical recommendations based on the study's findings. The suggestions might include specific pedagogical approaches for improving pronunciation instruction, such as incorporating more focused pronunciation practice, contrastive analysis activities, or the use of specific teaching materials. The recommendations should be grounded in the research findings and be feasible for implementation in the classroom.
Referensi Dokumen
- Theoretical implications of an Error Analysis of Second Language Phonology production ( Altenberg, E.P. & Vago, R.M. )
- Qualitative Research for Education: An Introduction to theory and Methods ( Bodgan, R. and Biklen, S.K. )
- Aspect of Language ( Bolinger, D. )
- An Investigation into the Generation of Mouth Shapes for a talking Head ( Breen A., Bowers E., Welsh W. )
- Questions of intonation ( Brown, G., Curie, K. L., & kenworthy, J. )