SMA MUHAMMADIYAH ENGLISH TEACHERS OF SURAKARTA
PUBLICATION ARTICLES
Submitted as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for Getting Bachelor Degree of Education
in English Department
by:
ARWIN ADIN PRASETYO
A 320 080 223
SCHOOL OF TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION
MUHAMMADIYAH UNIVERSITY OF SURAKARTA
A STUDY ON THE QUALITY
OF LESSON PLANS ON GENRE DEVELOPED BY
SMA MUHAMMADIYAH ENGLISH TEACHERS OF SURAKARTA
PUBLICATION ARTICLES
By:
ARWIN ADIN PRASETYO
A 320 080 223
Accepted by the Examiners Board of School of Teacher Training and Education
Muhammadiyah University of Surakarta
Team of Examiners:
1. Dra. Siti Zuhriah Ariatmi, M. Hum. ( ) (Consultant I)
2. Dra. Dwi Haryanti, M. Hum. ( )
(Consultant II)
Surakarta, March 2012
School of Teacher Training and Education
Muhammadiyah University of Surakarta
Dean
Arwin Adin Prasetyo
Dra. Siti Zuhriah Ariatmi, M. Hum
Dra. Dwi Haryanti, M. Hum
English Department, FKIP-UMS
Jl. A. Yani Pabelan Kartosuro Tromol Pos 1 Surakarta 57102
Telp. (0271) 7177417 Fax. (0271) 715448
ABSTRACT
This research purposes to describe the quality of lesson plans of genre developed by English teachers in Surakarta. The research type is descriptive evaluative research. The data are lesson plans of genre and the data source of this research is document.
The writer employs documentation as the method of collecting data with steps: seeking, collecting data, and giving code. In analyzing the data, the writer identifies three main components of lesson plans such indicators, teaching learning process, and evaluation from English teachers in Surakarta.
Based on the PERMEN 41, the percentage of indicator in narrative, hortatory exposition, and spoof are 30, 99%. The percentage shows that the quality of the design of indicators is bad quality based on the theory of Suharsimi. The percentage of teaching learning process in narrative, hortatory exposition, and spoof are 62, 59%. The percentage shows that the quality of teaching learning process is good quality based on the theory of Suharsimi. The percentage of evaluation in narrative, hortatory exposition, and spoof are 24, 77%. The percentage shows that the quality of the design of evaluation is bad quality based on the theory of Suharsimi.
Keywords: lesson plans, indicators, teaching learning process, narrative, hortatory exposition, spoof, social function, language feature, generic structure, operational verbs.
A. Introduction
Lesson plans are developed to facilitate the teaching and learning process
under the direction and guidance of school, college, or university and its staff
member. In an Interactive Approach to Language Pedagogy by Brownstated that
lesson plans are set of activities that cover a period of class room time, usually
ranging from forty to ninety minutes (2001: 149).
It shows that lesson plans are a planning of learning system in a period of
class room time. That time is from forty to ninety minutes. The lesson plan is
arranged by some activities in class room.
From all statements, it can be inferred that lesson plans are planning of
teaching in a time and contains the activities. Lesson plans are made by a teacher
which is suitable with students need and condition of class.
On the other hand, all lesson plans must be standardized based on the
regulation of the government. It relates to the process and quality of lesson plans
itself. The standard of lesson plans here refers to PERMENDIKNAS (Peraturan
Mentri Pendidikan Nasional) number 41 in 2007. The decision of education
ministry of Indonesia as regulation could be seen from the quoted statement
below.
Process standard is a part of standard rules to improve the development of
education. These standards are provided to be used by the teachers in developing
lesson plans arrangement, implementing learning process, assessing the result of
learning, and maintenance learning process. Process standards are provided to be
used by the teachers in learning, and maintenance learning process. The teachers
should use these standards. Those are also intended to achieve the effective and
efficient learning process.
Later on, the writer found that the teachers’ lesson plans are not based on
government regulation even they do not find difficulties in teaching. The work of
lesson plans created by teachers of English especially in SMA Muhammadiyah
senior high school are not suitable with the standard of lesson plans, mainly in
Supported by government regulation about lesson plans, there are three
main functional texts in XI grade of second semester SMA Muhammadiyah of
Surakarta. They are narrative, hortatory exposition, and spoof.
The writer is interested in conducting research related to the lesson plans in
SMA Muhammadiyah of Surakarta because first, many lesson plans made by
English teachers do not have standard on genre. Second, there are many mistakes
in part of lesson plans on genre. Third, the English teachers could not mix and
match how to make the lesson plans on genre. Fourth, there are some gaps in part
of lesson plans on genre. Fifth, there have not qualities in English lesson plans on
genre.
From all reasons, the writer researches the quality of lesson plans. The
writer looking for the weaknesses and the strengths in Lesson plans. The writer
hopes that the results of this research encourage the teachers to improve their
lesson plans.
Related to the background of the study, the problems which are proposed
by the writer as how are the qualities of the indicator on genre formulated by the
teachers of SMA Muhammadiyah, How are the qualities of the design of learning
activities on genre by the teachers of SMA Muhammadiyah, and how are the
qualities of the design of evaluation on genre by the teachers of SMA
Muhammadiyah.
In this research, the writer proposes three major objectives to be described
as to describe the qualities of the indicator on genre formulated by the teachers by
the teachers of SMA Muhammadiyah, to describe the qualities of the design of
learning activities on genre by the teachers of SMA Muhammadiyah, and to
describe the qualities of the design of evaluation on genre by the teachers of SMA
Muhammadiyah.
Those are three previous studies from the author. The first, Hadi analyzed
the development of curriculum at national standard school at SMP N 40
Semarang. He describes the curriculum development model of NSS. The main
informants or research are the principle, vice principal of the curriculum and
The second previous study, Aziza explained the teachers’ lesson plans with the principle of school level-based curriculum in SMPIT Nurhidayat
Surakarta. They compare the teachers’ lesson plans with the principle of school level-based curriculum.
The third previous study, Sukiran described the implementation of KTSP
in the teaching of English in SMK Negeri 2 Surakarta . The implementation of
KTSP has some supporting factors from the syllabus and creativities of teachers’
teaching strategy. The teachers have rights to arrange their syllabus which are
appropriate to the school’s need and the condition and the teachers are free to improve and apply any teaching strategy which is the most appropriate and
effective for the students to learn.
B. Research Method 1. Data and Data Source
The data of the research are lesson plans written by English teachers. The
data source of the research is taken from SMA Muhammadiyah 1 Surakarta, SMA
Muhammadiyah 3 Surakarta, and SMA Muhammadiyah 5 Surakarta.
2. Method and Collecting Data
The methods of collecting data are (1) the writer seeks the data from
English teachers at SMA Muhammadiyah 1 Surakarta, SMA Muhammadiyah 3
Surakarta, and SMA Muhammadiyah 5 Surakarta. (2) The writer collects the data
from English teachers at SMA Muhammadiyah 1 Surakarta, SMA Muhammadiyah
3 Surakarta, and SMA Muhammadiyah 5 Surakarta then are classified based on
their type. (3) The writer gives data code. To give the reader easier in
understanding about the information related the data, the writer would like to
encode the data by using formulation as bellow.
Instance/Skill/Text/Number of Lesson plan
From the formulation above, it clearly can be read as follow
Lesson plan in SMA Muhammadiyah 1 Surakarta (M01) is on listening skill
3. Method of Analyzing Data
The process of analysis is done together with the process of collecting
data. According to Sutopo (2002: 91), there are three components of analysis by
using the rest of time. They are (1) reduction of the data, (2) presentation/display
the data, and (3) verification/drawing conclusion.
C. Findings and Discussion 1. Finding
a. Indicators
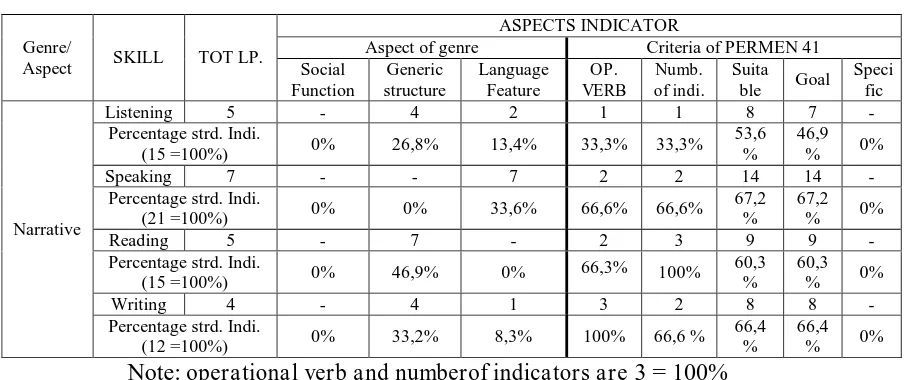
Table 1
Percentage Indicators of Narrative
Genre/
Aspect SKILL TOT LP.
ASPECTS INDICATOR
Aspect of genre Criteria of PERMEN 41 Social
Note: operational verb and numberof indicators are 3 = 100%
In table indicators of narrative (table1), four skills (listening, speaking,
reading, and writing) have not indicators that focus on social function.
Speaking skill also has not indicators in generic structure as (orientation,
complication, and resolution).
Indicators of narrative text just have one operational verb in listening skill,
two operational verbs in speaking skill, two operational verbs in reading skill,
and three operational verbs in writing skill. As the example:
1) Describe the social function of narrative text.
The numbers of indicators have one indicator in listening skill, two
indicators in speaking skill, three indicators in reading skill, and two
indicators in writing skill. As the example:
1) The learners identify the generic structure of narrative text.
2) The learners apply past tense in narrative text.
Four skills (listening, speaking, reading, and writing) have not indicators
in specific purpose as “social function, generic structure, and language
feature”.
From the data above, it means that the indicators in narrative text are not
complete. The teachers should develop the indicators in aspect of genre and
indicator criteria.
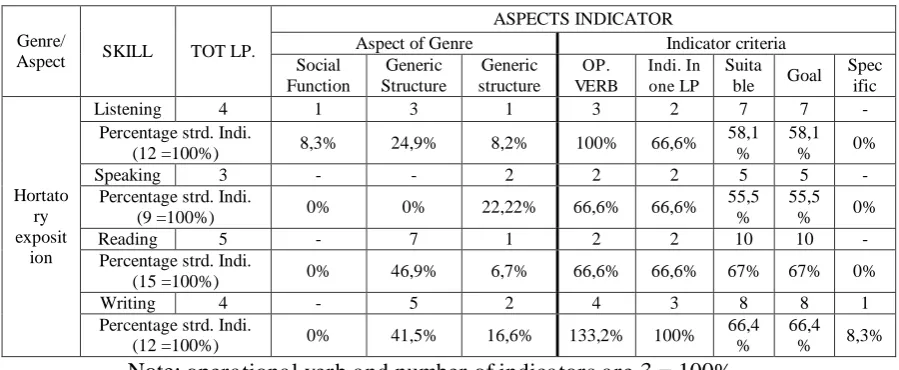
Table 4
Indicator of Hortatory Exposition
Genre/
Aspect SKILL TOT LP.
ASPECTS INDICATOR
Aspect of Genre Indicator criteria Social
Note: operational verb and number of indicators are 3 = 100%
In table indicators of hortatory exposition (table 4), three skills (speaking,
reading, and writing) have not indicators that focus on social function.
Speaking skill also has not indicators in generic structure as (Thesis,
argumentative 1, argumentative 2, and recommendation). As the example:
Indicators of hortatory exposition text just have three operational verbs in
listening skill, two operational verbs in speaking skill, two operational verbs
in reading skill, and four operational verbs in writing skill. As the example:
1) Analyze the social function of hortatory exposition text.
2) Identify the generic structure of hortatory exposition text.
The numbers of indicators have two indicators in listening skill, two
indicators in speaking skill, two indicators in reading skill, and three
indicators in writing skill. As the example:
1) The learners classify the generic structure of hortatory exposition text.
2) The learners repair present tense in hortatory exposition text.
Three skills (listening, speaking, and reading) have not indicators in
specific purpose as “social function, generic structure, and language feature”.
As the example:
1) The learners retell problems of story in hortatory exposition text.
From the data above, it means that the indicators in hortatory exposition
text are not complete. The teachers should develop the indicators in aspect of
genre and indicator criteria.
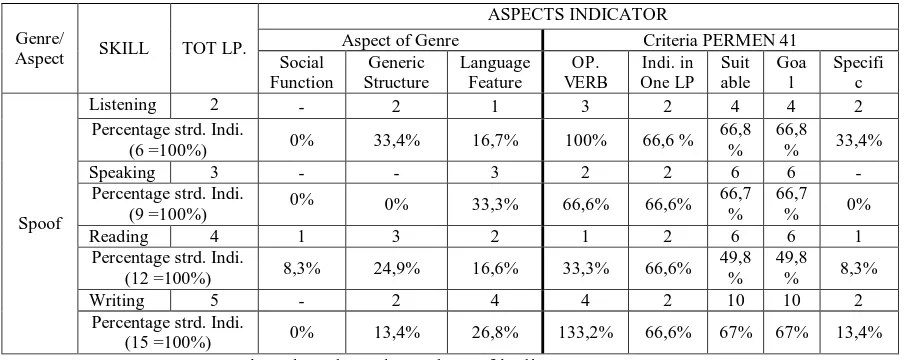
Table 7
Indicators of Spoof Text
Genre/
Aspect SKILL TOT LP.
ASPECTS INDICATOR
Aspect of Genre Criteria PERMEN 41 Social
In table indicators of spoof (table 7), three skills (listening, speaking, and
writing) have not indicators that focus on social function. Speaking skill also
has not indicators in generic structure as (orientation, event 1, event 2, and
twist). As the example:
1) The learners read the social function of spoof text.
Indicators of spoof text just have three operational verbs in listening skill,
two operational verbs in speaking skill, one operational verb in reading skill,
and four operational verbs in writing skill. As the example:
1) Explain the social purpose of story in spoof text.
2) Arrange the generic structure of spoof text.
The numbers of indicators have two indicators in listening skill, two
indicators in speaking skill, two indicators in reading skill, and two indicators
in writing skill. As the example:
1) The learners describe the generic structure of spoof text.
2) The learners analyze past tense in spoof text.
Speaking skill has not indicators that specify in specific purpose as “social
function, generic structure, and language feature”. As the example:
1) The learners listen problems of story in spoof text.
2) The learners use noun phrase in spoof text.
From the data above, it means that the indicators in spoof text are not
complete. The teachers should develop the indicators in aspect of genre and
indicator criteria.
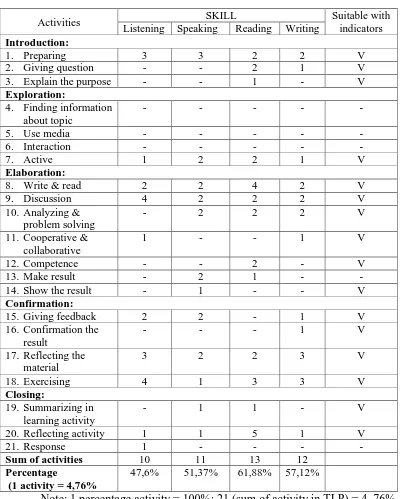
b. Teaching Learning Process
Table 2
Teaching Learning Process of Narrative Text
Activities SKILL Suitable with
indicators Listening Speaking Reading Writing
Introduction:
2. Giving question 4 1 3 5 V
Note: 1 percentage activity = 100%: 21 (sum of activity in TLP) = 4, 76%
Based on table 2 (teaching learning process of narrative), four skills
(listening, peaking, reading, and writing) have not activities as “using media
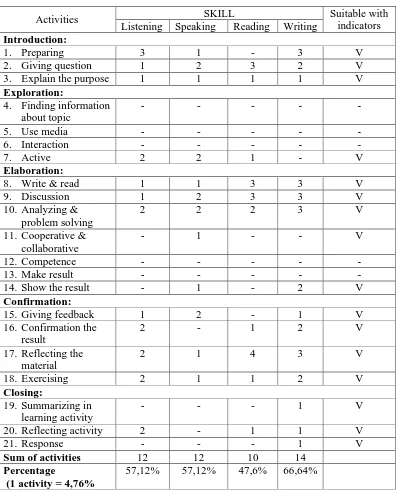
Table 5
Teaching Learning Process of Hortatory Exposition
Activities SKILL Suitable with
indicators Listening Speaking Reading Writing
Introduction:
Note: 1 percentage activity = 100%: 21 (sum of activity in TLP) = 4, 76%
Based on the table 5 (teaching learning process of hortatory
exposition), four language skills (listening, speaking, reading, and writing)
interaction, and response”. The teachers should give some activities such like
“the learners read the definition of hortatory exposition”, “the teachers give simple question about the material”, and “the teachers give positive response to the learners”.
Table 8
Teaching Learning Process of Spoof Text
Activities SKILL Suitable with
indicators Listening Speaking Reading Writing
Note: 1 percentage activity = 100%: 21 (sum of activity in TLP) = 4, 76%
Based on the table 8 (teaching learning process of spoof), four skills
(listening, speaking, reading, and writing) have not activities as “finding information about the material, using media, interaction, competence, make
result”. The teachers should make activities such like “the learners discuss about spoof text” and “the learners make result in spoof text”.
c. Evaluation
Table 3
Evaluation Base on the Language Feature and Generic Structure on
Narrative Text
Evaluation of Narrative listening speaking reading writing
1. Contain nouns as pronouns, animals, and certain sequences, such as here, in the mountain, happily, ever, before, etc.
- - - -
5. Use of past tense V V - V
6. Action verbs such as in past tense: stayed,
climbed, jumped, etc. V V - V
7. Response verbs indicating utterance such as promised and thinking verbs identifying thought, perception of characters in the story, such as thought, understood, felt, and seemed.
V V - V
1 percentage of evaluation = 100%: 9 (sum of evaluation) = 11, 11%
Based on the data above, reading skill has not the evaluation in narrative
text. Three language skills (listening, speaking, and writing) has not the
teachers should make the evaluation as “the teachers check the adverbial of
time”.
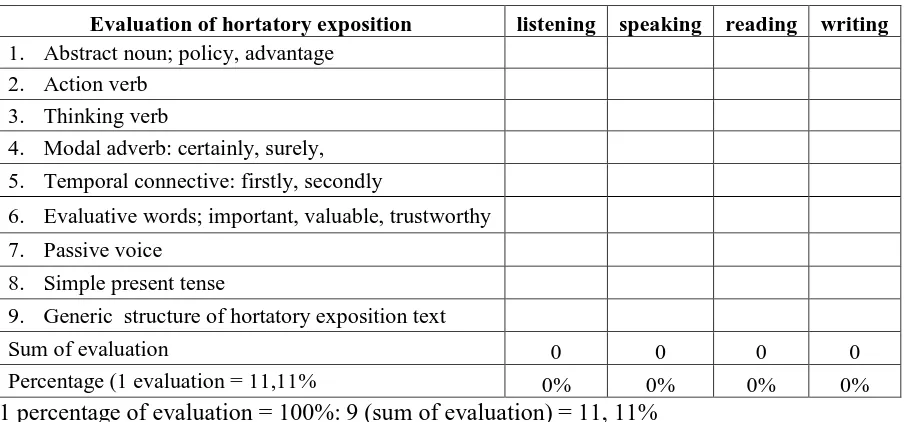
Table 6
Evaluation Base on the Language Feature and Generic Structure on
Hortatory Exposition Text
Evaluation of hortatory exposition listening speaking reading writing
1. Abstract noun; policy, advantage
2. Action verb
3. Thinking verb
4. Modal adverb: certainly, surely,
5. Temporal connective: firstly, secondly
6. Evaluative words; important, valuable, trustworthy
7. Passive voice
8. Simple present tense
9. Generic structure of hortatory exposition text
Sum of evaluation 0 0 0 0
Percentage (1 evaluation = 11,11% 0% 0% 0% 0%
1 percentage of evaluation = 100%: 9 (sum of evaluation) = 11, 11%
Based on the data above, there are no evaluations of hortatory exposition
text especially in four language skills (listening, speaking, reading, and
writing). The teachers should give evaluation such like evaluate in present
tense.
Table 9
Evaluation Base on the Language Feature and Generic Structure on Spoof Text
Evaluation feature of spoof listening speaking reading writing
1. Focusing on people, animals or certain things V
2. Using action verb: ate, ran, V
3. Using adverb of time and place
4. Generic structure of spoof text V
Sum of evaluation 0 0 0 3
Percentage (1 evaluation = 25% 0 0 0 75%
Based on the data above, there are no evaluations that focus on “focusing people, action verb, adverbial of time, and generic structure” especially in three language skill (Listening, speaking, and reading). The teachers should
make the evaluation such like “correct the generic structure of spoof text, evaluate in adverbial of time, and give simple question about past tense”.
2. Discussion a. Indicators
From the analysis above, the writer finds the total percentage of
indicators below:
= (tot. Narrative + tot. Hortatory exposition + tot. Spoof) / 3
= (36, 98% + 45, 48 % + 41, 52%) / 4
= 123, 98 / 4
= 30, 99%
The total amount of percentage is 30, 99%. It means that the quality of
indicators in SMA Muhammadiyah of Surakarta is categorized as bad
result.
b. Teaching Learning Process
From the analysis above, the writer finds the total percentage of
teaching learning process below:
= (narrative + hortatory exposition + spoof): 3
= (76, 16% + 54, 49% + 57, 12%
= 187, 77%: 3
= 62, 59%
The final percentage is 62, 59%. It means that the quality of teaching
learning process in SMA Muhammadiyah of Surakarta is categorized as
c. Evaluation
From the analysis above, the writer finds the total percentage of
evaluation that could be seen below:
= (narrative + hortatory exposition + spoof): 3
= (55, 56% + 0% + 18, 75%): 3
= 74, 31%: 3
= 24, 77%
The result is 24, 77%. It means that the quality of evaluation in SMA
Muhammadiyah of Surakarta is categorized as bad result.
d. Lesson Plans
From the analysis above, the writer finds the total percentage of lesson
plans. It is below:
= (Total indicators + total TLP + total evaluation): 3
= (31, 31% + 62, 59% + 24, 77%): 3
= 118, 67%: 3
= 39, 56%
The percentage of lesson plans is 39, 56%. It means that the quality of
lesson plan in SMA Muhammadiyah Surakarta is categorized as bad result
based on the theory of Suharsimi.
D. Conclusions and Implications
From all percentages, the last part for the discussion is lesson plans. This
obtains 39, 56% that shows bad result of lesson plans developed by English
teachers in SMA Muhammadiyah of Surakarta.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Arikunto, Suharsimi. 1993. Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan Praktek. Edisi Revisi. Cetakan 8. Rineka Cipta: Bandung.
Aziza. 2010. A Study on Teacher’sLesson Plan in SMPIT Nurhidayah, Surakarta Viewed from School Level-Based Curriculum. Unpublished Research Paper. Surakarta: Muhammadiyah University of Surakarta.
Callaghan M; Knapp P & G Noble (1993) "Genre in practice" in Cope B and Kalantzis M (eds.) The powers of literacy: a genre approach to teaching writing. The Falmer Press London.
Cuningsworth, Alan.1995. Choosing Your Course Book. Oxford: Henemann.
Douglas, H. Brown. 2001. An Interactive Approach to Language Pedagogy Second Edition. San Francisco: Logman.
Douglas, H. Brown. 2004. Language Assessment Priciple and Classroom Practices. San Francisco: Logman.
Ghofur, Abdul and all. Pola Induk Pengembangan Sistem Penilaian.
Hadi, M. Utomo. 2009. Development Curriculum of National Standards School (Site Study in SMP N 40 Semarang. Unpublished Research Paper. Surakarta: Muhammadiyah University of Surakarta.
Halliday, M. A. K & Hasan, R. 1989. Language, Context and Text: Aspects of Language in a Social-Semiotic Perspective. (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Hutchison, T. and Walter, A. 1987. English for Specific Purpose. A Learning Centered Approach: Cambridge University Press.
Kusuma, Dharma and all. 2011. Pendidikan Karakter. Bandung: Remaja Rosdakarya.
Macken-Horarik, M. 1997, 'Exploring the requirements of critical school literacy: a view from two classrooms', in S. Muspratt, A. Luke & P. Freebody (eds) Constructing Critical Literacies: Teaching and Learning Textual Practice, Allen & Unwin, Sydney.
Martin, James R. (1985) Factual Writing: exploring and challenging social reality (Sociocultural Aspects of Language and Education). Geelong, Victoria, Aus.: Deakin University Press.
PERMEN, No. 42. 2007. Standar Proses untuk Satuan Pendidikan Dasar dan Menengah.
Richards, J.C. and Rodgers, T.S. 2001. Approaches and Methods in Language Teaching. Cambridge:Cambridge University Press.
Saodih, Nana. 2007. Metode Penelitian Pendidikan. Bandung: Rosdakarya.
Sutopo, H. B. 2002. Metodologi Penelitian Kualitatif. Surakarta: Sebelas Maret Univerity Press.
Sukiran. 2010. The Implementation of Kurikulum Ttingkat Satuan Pendidikan in the Teaching of English (A Naturalistic Study in SMK Negeri 2 Surakarta). Unpublished Research Paper. Surakarta: Muhammadiyah University of Surakarta.
Suwarno, Wiji. 2009. Dasar-Da sar Ilmu Pendidikan. Jogjakarta: Ar-Ruzz.
Widodo, Ari. 2007. Lesson Study” Dalam Peningkatan Kemampuan Mengajar
Mahasiswa calon Guru. Unpublished Research Paper. Bandung: FPMIPA UPI Bandung.
Winecoff, Larry. 1988. Curriculum Development and Instructional Planning.
Bandung: University of South Carolina.
Zuhriah. A. Siti. 2011. Reading on English Text. Surakarta: Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta.
VIRTUAL REFERENCE
http://www.mumstudents.org/~matkinson/index.html. Accessed on 14 of March 2012 at 10.35 a.m.