THE EFFECT OF APPLYING SEMANTIC CLUSTERING
TECHNIQUE ON STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY MASTERY
A THESIS
Submitted to the English Department, Faculty of Languages and Arts, State University of Medan in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirement
for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan
By:
Tiarmayanti Novita Sonia
Registration Number 2103321045
ENGLISH AND LITERATURE DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGES AND ARTS
i
ABSTRACT
Sonia, Tiarmayanti Novita. 2103321045. The Effect of Applying Semantic Clustering Technique on Students’ Vocabulary Mastery. A Thesis. English Department. Faculty of Languages and Arts. States University of Medan. Medan: 2015.
This study deals with The Effect of Applying Semantic Clustering Technique on Students’ Vocabulary Mastery. This study used the experimental design. The population of the study was the first grade of SMP Swasta Masehi Medan. There were sixty students of first grade junior high school as the sample of the research. This study was conducted with two groups, experimental and control group. The experimental group was taught by applying Semantic Clustering Technique and the control group without applying Semantic Clustering Technique. The data were acquired by adminitered the pre-test and the post-test. The data were analyzed by using SPSS 17.00. The mean score of the experimental group in pre-test =58.20, control group = 50.87. In the post-test, mean score of the experimental group = 76.23, while the control group = 64.53. The result of this study showed that teaching by applying Semantic Clustering Technique significantly affected the students’ vocabulary mastery.
ii
ACKNOWLEDMENT
The greatest thanks to the Almighty Jesus Christ for His love, blessing and
guidance that enable the writer to complete this thesis as a partial fulfillment for
the requirement for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan at the English Department of
Faculty of Language and Arts, State University of Medan.
During the process of writing, the writer realizes that she cannot
accomplish her writing without God guidance and supporting from many people,
therefore the writer would like to express her sincere gratitude to:
Prof. Dr. Ibnu Hajar Damanik, M.Si., as the Rector of State University of Medan.
Dr. Isda Pramuniati, M.Hum., as the Dean Faculty of Languages and Arts, State University of Medan.
Prof. Dr. Sumarsih, M.Pd., as the Head of English and Literature Department and also Dra. Meisuri, M.A, as the Secretary of English Department and as her Examiners.
Dra. Masitowarni Siregar, M.Ed., as the Head of English Education study Program.
Dr.Anni Holila Pulungan, M.Hum, as her Advisor.
Dr. Siti Aisah Ginting, M.Pd., as her Academic Advisor.
Dra. Tjut Ernidawaty, M.Hum, as her Examiners.
Dra. Meisuri, M.A., as her Examiners.
Mahmud Layan Hutasuhut, M.Hum., her Examiners.
All the Lectures of English Department who gives new knowledge, advices in facing life, and for giving gorgeous study experiences.
Mam Eis, as the administration staff of English Department, for her attention, assistance, and information in completing it.
Ir. Usman Sembiring as the Headmaster at SMP Swasta Masehi Medan for giving permission and helping the writer to do this research.
The Teachers and students of SMP Swasta Masehi Medan, thanks for their helping, assistance and guidance during the research.
The deepest thanks are expressed to her beloved parents, Ir. Simson Girsang and R.E. Simanjuntak, for everything given in order to finish her study. Thanks also given to her splendid sisters and brothers: Erika Margaretha Girsang, Ruth Helena Girsang, Hanna Girsang, Daniel Frans Jordan Girsang, Arnold Abednego Girsang, Jeremia Deo Haganta Girsang. And also for all family members who supported her.
iii
her study and her writing thesis. Thankyou for your kindness, praying, support, and love for her.
Special thanks to her best friend, Icha Ramadhani Butar-butar, S.Pd., Fitri Handayani Lubis, Yenni Rofina Simanjuntak, Sri Agus Murniasih, Gustinavira, Asri Rumiris Panjaitan, Yusniar, Misida Marpaung for their support, praying, love, laugh, care, and wonderful friendship.
The writer realizes that this thesis still has the paucity, he conveniently welcomes anysuggestions, comments critics, and advices that will improve the quality of this thesis. He hopes that this thesis would be useful for those who are read and interested in the field of this study.
.
Medan, Januari 2015 The writer,
iv
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF LITERATURE A. Theoretical Framework ... 5
7. Semantic Clustering Technique ... 16
a. Justification for Semantic Clustering ... 18
b. The Example of Semantic Clustering Technique ... 20
c. The Steps of Semantic Clustering Technique ... 21
8. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Semantic Clustering Technique ... 22
B. Relevant Studies ... 23
C. Conceptual Framework ... 24
D. Hypothesis ... 25
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHOD A.Research Design ... 26
B. Population and Sample ... 27
1. Population ... 27
2. Sample ... 27
C. The Source of Data and The Data ... 27
D. The instrument for Collecting Data ... 28
v
E. The Procedure of Research ... 29
1. Pre –Test ... 29
2. Treatment ... 29
3. Post- test ... 33
F. Scoring of the Test... 33
G.Data Analysis... 33
1. Data Analysis on Pre-test ... 34
a. Normality Distribution ... 35
b. Homogeneity Variance ... 35
c. Independent T-test Computation ... 35
CHAPTER IV. THE DATA AND THE DATA ANALYSIS A.The Data ... 36
B. The Data Analysis ... 36
1. Pre-Test Score Analysis ... 36
2. The Post-Test Score Analysis ... 39
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS A.Conclusions ... 43
B. Suggestions ... 43
REFERENCES ... 44
LIST OF TABLES
Pages
Table 1.1. The Seventh Grade (VII) Students’ Score of Vocabulary Test ... 2
Table 3.1. The Research Design ... 26
Table 3.2. The Treatment for Experimental Group ... 29
Table 3.3. The Treatment for Control Group ... 32
Table 4.1. Descriptive Statistics of Pre-test ... 36
LIST OF FIGURE
Page
iv
LIST OF APPENDICES
Pages
Appendix A. The Pre-Test Score of Experimental and Control Group... 47
Appendix B. The Post-Test Score of Experimental and Control Group ... 48
Appendix C. The Pre-test and Post-test of Experimental Group ... 49
Appendix D. The Pre-test and Post-test of Control Group ... 50
Appendix E. Descriptive Statistics of Pre-test ... 51
Appendix F. Test of Normality Pre-test ... 53
Appendix G. Test of Homogeneity of Variances Pre-test ... 54
Appendix H. Paired Sample T-Test of Pre-test ... 55
Appendix I. Descriptive Variables of Post-test ... 56
Appendix J. Test of Normality Post-test ... 58
Appendix K. Test of Homogenenity of Variances Post-test ... 59
Appendix L. Paired Sample T-Test of Post-test... 60
Appendix M. Observation sheet ... 61
Appendix N. Interview sheet ... 63
Appendix O. Lesson Plan (Control Group) ... 65
Appendix P. Lesson Plan (Experimental Group). ... 67
Appendix Q. Vocabulary Test ... 74
Appendix R. Answer Key. ... 79
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. The Background of the Study
One of the essential for success in comprehending the language well, good
speaking, and composing a good writing is vocabulary. Vocabulary has an
important role in teaching and learning English as a foreign language.
At the present day, everybody approves the value of vocabulary in learning a
language. Vocabulary as the basic element of language, is accepted as even the
backbone of the language system. But unfortunately, vocabulary knowledge is not
attached importance according to its desertsin language study area in the
beginning. Vocabulary teaching was a matter of secondary importance in foreign
language programs. Today, almost all second language theorists and practitioners
admit vocabulary is crucial for language teaching.
Vocabulary knowledge also plays a significant role in overall academic
success (Lehr et al, 2004). Students’ lack of academic vocabulary ultimately
translates into shallow interaction with print and spoken word, fewer job
opportunities, and less income.
Vocabulary is the basic element of four skills, listening, speaking, reading and
writing. Students who are rich in vocabulary will be better in listening, speaking,
reading and writing a foreign language (Ekawati:2014). Therefore, vocabulary
affects the student’s ability in learning foreign language. According to Marzano
2
significant in our daily life and can have practical as well as social and emotional
consequences. It is supported by Beck (2002) who estimates that better readers
may learn as many as seven new words a day, while struggling readers and low
achievers learn one or two new words per a day. Not surprisingly, students with
rich vocabularies find more enjoyment in reading and more willing to spend time
reading. It supported by Pikulski (2004:4) that the learners have to increase their
vocabulary by around 3.000 words a year. The number of vocabulary will
influence how well someone masters the language.
In this study, the writer chooses vocabulary as her topic because when she
observed to the VII grade students at 2013/2014 academic year and interviewed
the English teacher in SMP Swasta Masehi Medan she found that the students
cannot comprehend a text and do the exercises from the textbook because their
vocabulary were still low. The students’ achievement in learning English is very
low especially in vocabulary. Most of them have many problems in
understanding, memorizing, and pronouncing the words and it makes them lazy to
study English because most of the students get the score below Minimal
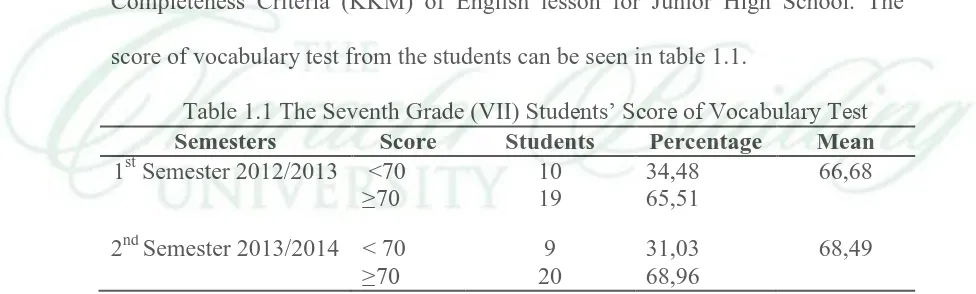
Completeness Criteria (KKM) of English lesson for Junior High School. The
score of vocabulary test from the students can be seen in table 1.1.
Table 1.1 The Seventh Grade (VII) Students’ Score of Vocabulary Test
Semesters Score Students Percentage Mean
3
The Minimal Completeness Criteria (KKM) applied for the seventh grade
(VII) by school is 70. From the data above, it can be fulfilled that the students’
ability in vocabulary in that class is still low. It can be seen from the mean of the
students’ score where the mean is still under the Minimal Completeness Criteria.
The problems are most of the students still have limited vocabulary in
English. The students felt bored with the teachers’ way of teaching vocabulary, in
which they were asked to find out the meaning of difficult words in the dictionary
and then memorize the words. The teaching method is not effective and students
need something different. Harmer (2001) said that the role of teacher is crucial.
The teacher should find out a different method of teaching considered to solve the
problem.
From the reason which has been explained above, creative and engaged
technique should be used. Thus, in this study it is determined to conduct a
research by applying Semantic Clustering Technique to improve the students’
vocabulary.
Lizda and Zainuddin (2012:3) states that semantic clustering is a teaching
technique which can provide the best exercises for learning the meaning of words
and increase the number of students’ vocabulary. By semantic clustering
technique, it is expected that the students will get many new words. Another
benefit of using clustering technique is to stimulate and encourage the students to
search for new words to enlarge their vocabulary and also motivate them to learn
seriously. It is expected that students’ achievement in vocabulary will be
4
B. The Problem of the Study
Based on the background of the study, the research problem of this study is
formulated as the following: “Is there any significant effect of applying Semantic
Clustering Technique on Students’ Vocabulary Mastery?”
C. The Objective of the Study
The objective of the study is to analyze the effect of applying semantic
clustering technique on students’ vocabulary mastery.
D. The Scope of the Study
Based on the background above, this study is limited to the effectiveness
applying Semantic Clustering Technique in teaching vocabulary in grade VII at
SMP Swasta Masehi Medan.
E. The Significance of the Study
As this study concerns with the use of semantic clustering technique to affect
the students vocabulary mastery, the findings of this study are expected that:
1. Theoretically : It is useful for the teachers to improve the quality of
students’ vocabulary and for the researchers to use this study as reference
for next researches
2. Practically: It is useful to improve the students’ vocabulary and widen
their horizon about the function of semantic clustering technique in affect
43
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
A. Conclusions
Based on the results of the data analysis, it is found that the Semantic
Clustering Technique significantly affect the students’ vocabulary mastery. The
using of Semantic Clustering Technique enables the students to master of
vocabulary of English. On the other hand, the application of Semantic Clustering
Technique in teaching vocabulary is more effective because the result show that
students’ score is higher after treatment. Therefore, it is concluded that hypothesis
is accepted.
B.Suggestions
In line with the conclusions and the result of the research, some suggestions are
stages as the following:
1. Theoretically : It is useful for the teachers to improve the quality of
students’ vocabulary and for the researchers to use this study as reference
for next researches
2. Practically: It is useful to improve the students’ vocabulary and widen
their horizon about the function of Semantic Clustering Technique in
44
REFERENCES
Adel, Z. AlShaikhi. 2011. The Effects of Semantic and Thematic Categorization of Vocabulary on Arabic-Speaking EFL Learners. Unpublished Thesis. English Department. Colorado State University
Ary, Donald. 2002. Introduction to Research in Education. Canada: Nelson Education
Beck, I. L., McKeown, M. G., and Kucan, L. 2002. Bringing Words to Life: Robust Vocabulary Instruction. Newyork: Guilford Press
Decarrico, J.S. 2001. Vocabulary Learning and Teaching. In M. Celce-Murcia (Ed.), Teaching English as a Second or Foreign Language (3rd ed., pp.285-299)
Ekawati, E. N. 2014. The Effect of Using Frayer Model on Students’ Vocabulary Mastery. Unpublished Thesis. English Department Faculty of Languages and Arts. State University of Medan (UNIMED)
Fikri, M. 2012. The Effectiveness of Clustering to Teach Reading Comprehension
Viewed from Students’ Interest. Unpublished Thesis. Indonesia University of
Education
Gairns, R., and Redman, S. 1986. Working with Words. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Gronlund, N. 2009. Measurement and Assesment in Teaching. New Jersey: Pearson Education
Harmer, Jeremy. 2001. The Practice of English Language Teaching. Cambridge: Longman Inc
Kamil, M. L., and Hiebert, E. H. 2005. Teaching and Learning Vocabulary: Bringing Scientific Research to Practice. Mahwah. New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates
Khoshnevis, Iraj. 2012. The Effect of Thematic versus Semantic Clustering of English Vocabulary. Unpublished Thesis. English Department. Islamic Azad University. Ardabil: Iran
Lavie, N., Briggs, S., Raht, C., and Denman, B. 1991. In Contact 2. Glenview, IL: Scott Foresman
45
Lizda, Y. Tumanggor. 2012. Improving Students’ Achievement in Vocabulary Through Clustering Technique. Unpublished Thesis. English Department Faculty of Languages and Arts. State University of Medan (UNIMED)
Lizda, Y. T and Zainuddin. 2012. Improving Students Achievement in Vocabulary Through Clustering Technique. Journal of Linguistics. Vol.2, No.4 (1-18)
Long, H. Michael and Richards, C. J. 2007. Modelling and Assesing Vocabulary Knowledge. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Mitchell, R., and Miles, F. 1998. Second Language Learning Theories. London: Arnold
Molinsky, S. J., and Bliss, B. 1989. Side by Side, 1. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall
Nation, I. S. P. 2000. Learning Vocabulary in Lexical Sets: Dangers and Guidelines. TESOL Journal, Vol.9, No.2 (6-10)
PavicicTakac and Vinsja. 2008. Vocabulary Learning Strategies and Foreign Language Acquisiton. Clevedon: Cromwell
Pikulski, John. J and Shane, T. 2004. Teaching and Developing Vocabulary: Key to Long-Term Reading Success. United State of America: Houghton Mifflin Company
Qian, D. 2002. Investigating the Relationship between Vocabulary Knowledge and Academic Reading Performance: An Assessment Perspective. Language Learning, Vol.52, No.16 (513-536)
Ramirez, A. 1995. Creating Contexts for Second Language Acquisition. White Plains, NY: Longman
Richards, J. C. 1998. Interchange, 1. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Seal, B.D. 1991. Vocabulary Learning and Teaching. In M. Celce-Murcia (Ed.),
Teaching English as A Second or Foreign Language. (2 nd
ed., pp. 296-311). Boston: Heinle and Heinle
46
Suharsimi, Arikunto. 2003. Prosedur Penelitian : Suatu Pendekatan Praktik: Edisi Revisi XIV . Jakarta: Rineka Cipta
Tankersley, Karen. 2005. Literacy Strategies for Grades 4-12: Reinforcing The Threads of Reading. Alexandria: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development
Tinkham, T. 1994. The Effects of Semantic and Thematic Clustering on the Learning of Second Language Vocabulary. Second Language Research, Vol.13, No.2 (138-163)
Thornbury, Scott. 2002. How to Teach Vocabulary. England: Bluestone Press
Tulving, E. 1962. Subject Organization in Free Recall of Unrelated Words. Psychological Review, Vol.3, No. 69 (344-354)
Tumanggor, Lizda. 2012. Improving Students’ Achievement in Vocabulary Through Clustering Technique. Unpublished Thesis. English Department Faculty of Languages and Arts. State University of Medan (UNIMED)
Wahana, K. 2010. Panduan Aplikasi dan Solusi Mengolah Data Statistik Hasil Penelitian dengan SPSS 17. Semarang: Penerbit Andi Offset