i
LEARNING ENHANCING FUNCTIONS OF TEACHERS
CODE SWITCHING IN THE ENGLISH FOREIGN
LANGUAGE CLASSROOM
THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan
Gayatri Agung Yunantohati 112011019
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION PROGRAM
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE
SATYA WACANA CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
SALATIGA
iii
COPYRIGHT STATEMENT
This thesis contains no such material as has been submitted for examination in any course or accepted for the fulfillment of any degree or diploma in any university. To the best of my knowledge and my belief, this contains no material previously published or written by any other person except where due reference is made in the text.
Copyright@2015. Gayatri Agung Yunantohati and Elisabet Titik Murtisari, M.TransStud., PhD
All rights reserved. No part of this thesis may be reproduced by any means without the permission of at least one of the copyright owners or the English Language Education Program, Faculty of Language and Literature, Satya Wacana University, Salatiga.
v
A. Definition of English Foreign Language Classroom ... 5
vi
LIST OF TABLE
1
LEARNING-ENHANCING FUNCTIONS OF TEACHERS CODE SWITCHING IN THE ENGLISH FOREIGN LANGUAGE CLASSROOM
Gayatri Agung Yunantohati
ABSTRACT
Code switching is used by Indonesian teachers to teach English in the English Foreign Language Classroom for years. During this practice, not many studies have tried to evaluate the functions of code switching which enhance English learning in the country. Thus, this current study aims at evaluating the functions of teachers‟ code switching in enhancing English learning process. The participants were two teachers. Six observations in two classrooms and two teachers-interviews were conducted. The findings show seven functions of code switching were used by the teachers to teach English in the classroom. There were directive function, metalinguistic function, translation function, phatic function, referential function, expressive function, and poetic function. The functions consisted of the most learning enhancing functions of code switching and least enhancing ones, respectively. The most enhancing functions of code switching were directive function, metalinguistic function, and translation function because they had big role in learning process in term of students‟ comprehension. The less enhancing functions of code switching were referential function and expressive function, mainly because the teachers could refer to English language since the utterances were familiar for students, so they would have understood what the teachers said.
Key words: Code Switching, EFL, Functions of code switching
INTRODUCTION
2
students learn in an environment where there is only a little natural use of the language (Yletyinen, 2004). Consequently, foreign language learners will find difficulties in learning English. Therefore, Indonesian teachers strategize it by using code switching in the classroom. They insert or change words, phrase or sentence of the first language while teaching English.
In line with code switching occurrences in the classroom above, I have experience related with it. Based on my own experience, I found that code switching is important for teaching English in English Foreign Language classroom (EFL) especially young learners. I have experiences teaching English to Kindergarten and Junior High School students. I tried to use English to introduce new vocabulary or new material, but the students did not understand completely. This was clearly seen on their face that the material was too difficult for them to understand, thus they needed more explanation. It was very frustrating at that time, so I decided to insert the students‟ first language (Indonesian language) to explain teaching material clearer. Unexpectedly, it was helpful for me as a teacher to teach the material easily and it was easy for the students to understand the material easier. Then, I realized that the students‟ lingua franca may be a great resource for language teaching. Cook (2001) agreed that when the students found difficulties or the teachers had limited of time while teaching English, the teachers could use L1 in the classroom.
3
this idea, Fakeye in Ruiz (2012) supports code switching in teaching English. Fakeye mentioned three benefits of code switching the following:
a. to provide essential means to create successful lessons across the curriculum and work with texts that are mostly written in English, b. to learn new vocabulary in the classroom, and
c. to establish a relationship with students or assert the authority of the teacher
It supports the idea that code switching can enhance English Foreign Classroom by using it effectively. However, English-only pedagogy has been questioned and some research studies show that L1 is also beneficial in English learning classrooms (Pei Shi, 2000). On the other hand, some believe that code switching should not be used in English class because it can be perceived as language interference in the classroom (Lesley, n.d). They believed that English class has to be English only. For this reason, the study was conducted to evaluate all of teachers code switching‟s functions which can enhance learning process.
Before we discussed the use of code switching in the classroom, we should know the definition of code switching. Gumperz (1982) defines code switching as “the use of more than one codes or languages in the course of a speech event.”.
4
switching is product oriented. I shall only focus on the form that the teacher is produced. In line with this idea, John Gumperz (1964) said that “the term of „code switching‟ has been used to refer to what speakers do, not whether they do it
consciously.” Nevertheless, code-switching cannot be used all the time in English
class. The teacher should consider the usage of L1 while the use of English should be used effectively to motivate and improve their English skills. Hence, code switching should be used appropriately by understanding the certain functions which beneficial, suitable also effective for students‟ comprehension in enhancing English learning in the classroom.
The study is conducted to answer the research questions: „What are the functions of code switching that the teachers used in the classroom?‟ and „What are the functions of code switching that enhance learning process?‟ These questions will find out various functions that teachers used in the classroom and the enhancing functions of teachers‟ code switching. It is also expected to
discover the beneficial functions of code switching to enhance English learning process. This study will hopefully provide more knowledge about the beneficial functions of code switching in order to enhance English learning process optimally and make English classroom more effective and comprehensible.
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
This section will discuss about the definitions of English Foreign Language (EFL) classroom and Code Switching in EFL classroom, encompassing the functions of code switching.
5
Definition of English Foreign Language Classroom
Yletyinen (2004: 4) explains that “in the English Foreign Language (EFL) classroom, the learners learn English in an environment where there is only a little natural use of language”. Then, Boey (1975) also adds that English foreign classroom only taught English a subject in school where English is not the mother tongue of any community within it.
Code Switching in the English Foreign Language (EFL) Classroom
Code switching is a common phenomenon in teaching English as a Foreign Language classroom, not only in Indonesia but around the world. It is very normal for people who have developed two or more languages to use it frequently at the same time (Ruiz, K.M.R, 2014).
6
The study focuses on finding various functions in order to assist teachers comprehend about the usage of code switching. This present study uses Appel and Musyken‟s (2006) typology which presents six functions of code switching; referential function, directive function, expressive function, phatic function, metalinguistic function and poetic function as a basis of the study. Another typology is presented by Hymes (1962) which has similar functions of code switching. There are five functions of code switching; expressive function, directive function, metalinguistic function, poetic function and referential function. These two classifications are suitable for the Indonesian context of this study. Furthermore, the framework was valid because it was recently published. If we compared to the other typologies, it would perform different finding that will be difficult to analyze and examine. The other study did not categorize the functions specifically. It can be seen in Kasperczyk‟s (2012) study, she categorized the function of code switching into three functions; topic switch, affective functions and repetitive functions. Those functions did not define specifically like Appel and Musyken‟s study (2006) and Hymes‟s (1962) study. Those functions were too broad to analyze, thus it may affect the findings of code switching‟s functions in the study in particular. As a result, it was not suitable
with the study. Therefore, the study uses Appel and Musyken‟s (2006) and Hymes (1962) typologies.
7 a. Referential Function
Referential function is code switching that is used when the speaker refers to the familiar utterance in L1 (Indonesian language) instead of English. It often involves lack of knowledge of one language or lack of facility in that language (p.118). It made the speaker conscious that he/she switches their language when speaking. In line with this idea, Appel and Musyken (2006) also said that this type of switching is the one that bilingual speakers are most conscious of. Example of this function is taken from a pre-observation which is conducted by the researcher in 7th grade
T: Kalau („if/ how about?‟) confident?
The familiarity of certain utterance in his first language of this student made him switch the utterance into his L1. Teacher used „ya‟ instead of „yes‟ also used Indonesian conjunction „kalau‟ instead of „if‟. He believes
8
(2006) further explained that when the speaker asks why they tend to switch into the other language, they answered that it is because they do not know the suitable word for talking about a given subject (p.118). In addition, Hymes (1962) as secondary reference also raise the same idea. He added that referential function may be due to three reasons; lack of readily available expression in the other language, lack of semantically appropriate expression, the more familiarity of L1 than foreign language.
b. Directive function
Directive function is used in a situation to direct someone, such as for requesting help, giving exercise, moving one activity to another activity and giving instruction. According to Appel and Musyken (2006), this function involves the listener directly to be directed. It may either excludes or includes the listener. An example of directive function which was conducted by a teacher to one student in the classroom:
T: „Bayu, please move the chair to the front of the classroom‟
S: *silent*
T: Bayu? Can you help me to move kursi ke depan? („the chair in front of the classroom?‟)
S: Oh yes, Sir.
9
is Indonesian language, to make him understand and did what the teacher asked to.
c. Expressive function
This function serves to express the various feelings of the speaker. Examples of the expressive function are correcting her/his self while teaching and expressing certain feelings like being happy and disappointed. The researcher found the example in the observation which was conducted by the researcher.
T: Kenapa lho rame terus biasanya tidak seperti ini (Why are you behaving like that, it‟s unusual)
The teacher complained about the noisiness that students made while she was explaining the material. The use of Indonesian language in this sentence expresses the disappointment of the teacher.
d. Phatic function
10 An example of the phatic function is,
T: Classroom. Siswa di dalam ruang?(„Where‟s students when they are studying in the school?‟)
S: Kelas
T: Kelas. („Classroom‟) What…hmm probably they do? What they
do?
In this conversation, the teacher changed the tone when said „kelas‟ („classroom‟) and repeated the code switch which he used to emphasize
the utterance that he would like to explain about. In this conversation, he would like to correct the students‟ answer.
e. Metalinguistic function
Metalinguistic function of code switching occurs when the speaker comments directly or indirectly on the language involved (p, 120). It encompasses in term of explaining language functions, grammar also highlighting learning points. An example of this function presents below,
T: Jadi kalimat perintah is expression atau kalimat atau ungkapan yang diberitahu atau tell someone. Jadi kalimat perintah adalah kalimat yang diberikan seseorang untuk memberikan pekerjaan. („Imperative sentence is expression or sentence to tell someone. So, imperative sentence given to someone to ask him/her to do something‟)
The utterance above represents how the teacher explained the language function of „imperative sentence‟ using Indonesian language in the
11 f. Poetic function
This function is used when the speakers insert some puns, jokes or stories as a part of some kind of unofficial interaction. The unofficial interaction mostly did not relate with the teaching material. This function usually occurred to build the relation with students occasionally.
Example of poetic function provides below,
T: Alex please complete the sentence number 7 Alex: If I …. enough money, I will go with you. T: and your answer please, lex.
Alex: *thinking*
T: Wah kamu mikirnya lama lex, kalau punya uang gak ajak- ajak temen ya? („You think for a long time. I think that if you have much money, you will spend money for yourself not sharing it with your friends. Am I right?‟)
S: *laugh*
The code switching was used by the teacher to make students more relax in answering the question, since the student seemed to find it difficult to answer it. Thus, the teacher used joke to overcome this problem.
THE STUDY
Context of the study
12
was conducted in two classes as a comparison of the functions of code switching that both teachers produced.
Participants
The participants were two teachers in 7th grades. The researcher observed and interviewed two teachers who teach in the same level to get know more about functions of code switching which is used in each classroom. Different classes and different teacher may use different functions of code switching.
Data Collection Instrument
This research used observation and interview as the methods of data collection.
Observation
13 The event-observation present below: No Functions of teachers‟ code
switching
Frequency Total frequency
1. Referential functions 2. Directive functions 3. Expressive functions
4. Phatic functions
5. Metalinguistic functions 6. Poetic functions.
Interview
The second instrument was used in this study was interview. Interview was conducted to obtain the perspective‟s respondent toward the findings of
observation. Besides that, this interview was aimed to know the teachers‟ educational background, code switching, why the teachers used particular functions of code switching in teaching English and how the teachers used code switching in teaching English. The researcher was conducted the interview based on two teachers from 7th grades using semi-structured interview. The interview took 10-15 minutes recorded.
14
2. What is the purpose of using code switching in teaching English?
3. In your opinion, is the use of code switching beneficial for foreign language students? Why/Why not?
Data Collection Procedure and Analysis
The first step that the researcher did to collect data was asking a permission letter to English Department Administration Office for SMP N 2 Salatiga. After that, the researcher asked permission from the headmaster of SMP N 2 Salatiga. Then, the headmaster asked two teachers to be responsible in the study, both from 7th grades.
Before doing a real observation, the researcher conducted a pre-observation in order to survey the environment. The researcher also did not want to interfere with teacher and students during the learning process. In addition, the researcher wanted to make them unaware of my present. The observations were conducted four times in teacher A‟sclass and three times in teacher B‟s class, in total the researcher conducted seven times observations. Then, the researcher conducted interviews to check their perspectives about code switch and also gain more clarification and explanation about their code switching usage. The interviews were recorded and the recordings are then transcribed.
15
code switching based on the result of observation and interview transcription. Then, each function was described and presented in detail. In analyzing the findings, all of the functions of code switching that had been stated in the literature review were presented in the observation. However, the study emerged one function of code switching which was found in the observation. After checking the result of observations and interviews, the data was analyzed based on the mostly functions which was used by teachers from observations. The researcher tried to analyze the beneficial functions which were enhanced language learning. The last step on the research was drawing conclusion.
DISCUSSION
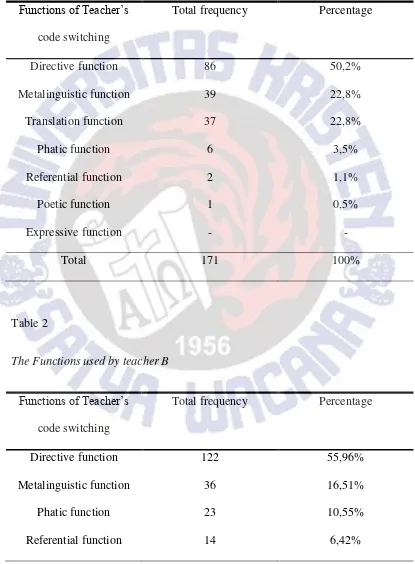
16 Table 1.
The Functions used by teacher A
Functions of Teacher‟s
code switching
Total frequency Percentage
Directive function 86 50,2%
Metalinguistic function 39 22,8%
Translation function 37 22,8%
Phatic function 6 3,5%
Referential function 2 1,1%
Poetic function 1 0,5%
Expressive function - -
Total 171 100%
Table 2
The Functions used by teacher B
Functions of Teacher‟s
code switching
Total frequency Percentage
Directive function 122 55,96%
Metalinguistic function 36 16,51%
Phatic function 23 10,55%
17
Expressive function 12 5,5%
Translation function 10 4,58%
Poetic function 1 0,45%
Total 218 100%
Based on the observation, the entire functions were categorized into Appel and Musyken‟s typology, which are referential function, directive function,
expressive function, phatic function, metalinguistic function and poetic presented in the study. However, this study emerged one function which was found in the observation, which is translation function.
The study found that the function of code switching which is mostly used is directive function. The findings on functions of code switching were discussed in detail below.
1. Directive function
Directive function of code switching was used to direct someone to do something or say something. This function has the highest percentage of occurrences on two classes. Based on the observation, the researcher found directive function was used by Teacher A 50, 2% and Teacher B 55, 96%. Both teachers used this function of code switching mostly in their classroom.
18
material or instruction and check their understanding toward the material which is given to them in the classroom.
During the observation, teacher A used this function to give instruction to the students in learning process. He said,
„dengarkan baik-baik‟(„listening carefully‟)
„kemudian tambahkan this‟ („then, add this in the sentence‟)
„Kamu lihat ke gambar‟, what is the picture said about?‟ („Look at the
picture‟).
Besides asking the students to do something, teacher A also directed them using Indonesian language when asking for their opinions toward the material which was being discussed. As an example was presented below,
„Kalimat perintah apa yang diberikan guru oleh anaknya?‟ („What is the
suitable imperative sentence that the teacher should give to the students?‟)
The last part of directive function that was used for checking understanding by demanding the students‟ answers toward the material. It presented on the first observation,
„Contohnya apa tadi?‟ (Can you mention the other example?‟)
19
The other teacher, teacher B, also used code switching for a directive function on the highest percentage. During the first, she used this function to give instruction to students to do the exercise. An example was provided below,
„Sekarang coba kamu tulis kalimatnya yang kita bahas tadi.” („Now, let‟s
try to write the sentence that we have been discussed‟).
The directive function was also used to ask students‟ opinions. She
stimulated the students by asking their opinions in order to better understanding real meaning of studying. She asked them in the third observation,
“Bagi kalian belajar itu apa?” („In your opinion, what is studying?‟)
Teacher B also used directive function for checking their understanding toward the material which was given to them in the classroom. She used it to make sure that they understood well. The examples were found in the third observation.
„Seperti apa?‟ (What is it looked like?
„Yang kedua apa?‟ („What is the second example?‟)
Teacher B explained in the interview why the teacher use the directive function of code switching in teaching English,
20
explain in English but if they still do not understand. No other choice but we must use Indonesian” (Teacher B, Interview, July 10th
, 2015)
Based on the observation, students tended to be silent when they did not understand what the teachers said to them. As shown in the following example:
T: Do you still remember? The last meeting? S: Hah opo? Opo wi? (What do you mean by that?) T: Pelajaran yang lalu?(„What is our previous material?‟)
The teacher switched the question into Indonesian language when she knew that the students‟ did not understand. This function was likely to happen because they wanted to help the students to comprehend the instruction well and support the learning process well. Moreover, the students asked the teacher back what she means on her question. It supported Abbot and Wingard (1981)‟s idea that foreign language students demands explanation in mother tongue. Therefore, it was considered that code switching as directive function can be used for teacher in teaching English Foreign Classroom in order to enhance learning process.
2. Metalinguistic function
21
Metalinguistic function was the second rank percentage in the study. Teacher A used this function in 22, 8% and teacher B used this function in 16,51%.
In the first observation, the teacher used metalinguistic function to explain the meaning of imperative sentence. Teacher A said,
“Jadi kalimat perintah is expression atau kalimat atau ungkapan atau
yang diberitahu atau tell someone” („So, imperative sentence is the expression or sentence which is used to ask or tell someone‟).
Metalinguistic function was also on the second rank which was conducted by teacher B. The example was represented to explain the language function of verb,
“Kalau ada yang dikerjakan berarti itu termasuk verb, kalau tidak bisa
dilakukan berarti bukan verb Explanation” (If the sentence contain something that
you should do something, it‟s calledverb. If not, it‟s not verb‟)
Teacher B explained why she used explanation function in her teaching in the interview:
“I think sometimes we need explanation function because if we always use
22
question, that‟s mean that they are not understand” (Teacher B, Interview,
July 10th, 2015)
This is in line with teacher A that is,
“We should use mother language because not all students have English
lesson before, some of the students maybe did not get English lesson in their elementary school, because they lived far away, that‟s why I use
Indonesian language then English.” (Teacher A, Interview, July 5th, 2015)
Based on the observation and interview, explanation function takes an essential role when teaching English in English Foreign classroom. The students‟ comprehension was the main reason of this function occurred in the classroom. This idea support Spratt (1988)‟s statement, she said that English teachers may
want to use their first language while giving explanation and justification to make the students understand the explanation well. Moreover, it can avoid students‟ confusion and ambiguity toward the information. Thus, the teachers used this function optimally to achieve the learning goal successfully. It sums up that this function was considered in the enhancing function of teacher code switching in the classroom.
3. Translation function
23 and instruction. It was presented on the second observation.
T: … Pertama kali saya masuk tadi („First time, I enter the class‟), What I‟m ask..I‟ll to do. Saya minta kamu melakukan apa („What am I going to ask you to do?‟)? Saya minta kamu? („I‟m asking you to?‟) To? To? To move the? Saya minta kamu tadi untuk memindahkan kursi. („I‟masking you to move the chair‟) …
Another example was also performed by teacher B. She said on the first observation,
“Where do you do this activities? Dimana kamu melakukan kegiatan itu translation” („Where do you do this activities?‟).
She translated into Indonesian language in order to make student clearer with the instruction. She said the utterance in English then translated into Indonesian language exactly same.
Regarding to this function, teacher A clarified deeply in the interview,
“… I found in that situation some of the students did not understand what I mean. So, I‟m translated into Indonesia but when I use
24
So, I don‟t need to translate into bahasa Indonesia.” (Teacher A,
Interview, July 5th, 2015)
Teacher A feels that translation function of code switching is needed when they are not understood what he said. Thus, he translated the utterances from English into Indonesian language.
Based on the observations and interview which focused on this function, the researcher feels that this function is quite important in teaching English Foreign Language Classroom. As Atkinson (1993) suggests that using L1 for translation can be a teaching technique. It can save the teachers‟ time to explain the material. So that, the learning process can optimal in term of time management. In addition, translation function can be used to confirm students understanding because the teachers repeated the utterances in L1. This idea was supported by some researchers; Macaro, 1977; Spratt, 1988 and Urgese, 1987. According Spratt (1988) a teacher may want to use L1 when he/she want to give explanation and justification about his/her material.. Macaro (1977) also raised similar idea about this function, the teacher often uses L1 to check students‟ understanding by repeating the utterances. Urgese (1987) emphasized that checking students‟ comprehension is useful to help the learners to become more
25 4. Phatic Function
Phatic function is the function of code switching which was used to emphasize the certain utterance or to change the tone when speaking. Phatic function is the fourth rank that was used in this study. Teacher B used this function in higher percentage than teacher A. Teacher B used phatic function in 10,55% whereas teacher A used it in 3,5%.
The teacher used this function mostly for emphasizing some utterances in the conversation. Like presented in the first observation below,
S: Humoris („funny‟)
T: Ya suka bercanda. („Yes, that‟s right. The one who like joking‟) Teacher A changed his tone when he said „Ya suka bercanda‟ („Yes, that‟s right. The one who like joking‟) to correct the students
answer.
In this study, teacher B used this function more than teacher A. She switched the language into Indonesian language when the students cannot be managed. The example was presented below,
“Sudah cukup, pertanyaan nya cukup ya. Now guess, what is it?” („It is
enough for the guessing questions. Now guess, what is it?‟)
26
Based on the finding which is performed in the observations above, the researcher feels that phatic function is less important in teaching English. We as teacher can change the utterance in English without changing the intention or the meaning of emphasizing certain utterance. We can simply say the English utterance by changing our tone higher to attract their attention or to emphasize the meaning of utterances.
5. Referential function
Referential function of code switching has occurred when the teacher feels that the students are more familiar with the certain utterance in L1 rather than English utterances. It often involves lack of knowledge of one language or lack of facility in that language.
Referential function has fewer occurrences in this study. Teacher A only used twice in 1,1% whereas teacher B used fourteen times in 6,42%.
In the first observation was found teacher A referred to use „disini‟ instead
of „in this sentence‟. He told to the students, “No verb disini” („there/in this
sentence‟). Disini in the context means „in the sentence that being discussed‟ in
the classroom. The other example was presented by teacher B in the first observation. Teacher B chose the utterance „terus‟ instead of „then‟ or „next‟ while asking to the students. On the second observation, the researcher also found three uses of referential functions. All of them contained the same word, which is „ya‟ instead „yes‟.
27
English. It is because the utterances which performed by the teachers are not essential point. The teachers should try to use English utterances as much as possible. It supports Harbord (1992) opinion that the communication in the classroom should take place as far as possible in English. The researcher think that it is possible for the teachers to refer in English utterances instead of the mother tongue especially toward referential function of code switching to give richer vocabulary to the students.
6. Expressive function
The sixth expression which was found in the study is expressive function of code switching. This function means the use of L1 in order to express the feelings of speaker in another language. The speaker can use this function to show his/her angriness, his/her sadness even happiness. This function was presented by teacher B twelve times in 5,5% while teacher A did not use it at all.
The finding found that teacher B used this function as expression of her disappointment when the students did not pay attention to her sayings in the classroom.
T: Kenapa lho rame terus biasanya tidak seperti ini („Why are you so noisy today? You never behave like that‟)
Teacher B explained on why she used this function in her teaching,
28
Based on the observation and interview above, the expressive function is often used in her classroom. Teacher B feels that changing the expressive sentence into Indonesian language is suitable. But, I do not think so. The expressive function can be changed into English without changing the purpose. The teacher can use English expression in the classroom to express her feelings. In addition, it can make the students more familiar with the English expression that the teacher used.
7. Poetic function
Last function of code switching which was found in the observations is poetic function. Poetic function is used when the speaker switches their language into the other language in informal way. It includes jokes, stories, even ice breaker. This function was found in each teacher once. Teacher A used poetic function once in 0,5% while teacher B used this function once in 0,45%.
Teacher A used this function in the third observation while explaining descriptive text about Tukul Arwana, Indonesian comedian artist. The finding of poetic function was presented in dialogue below,
T: ……. Who is that? S: Tukul
T: Okay Tukul Riyanto. Bukan Priyanto. („He‟s Tukul Riyanto not Priyanto‟)
29
Teacher A inserted jokes in the middle of explaining the descriptive text by saying „bukan‟ instead of „he‟s not‟. Teacher B also inserted jokes in her teaching which was found in the first observation. She said,
S: Makan bu („Eating ma‟am‟)
T: Emangnya kamu („It‟s you. Not us)
This function was used by both teachers to make the students laugh in the middle of learning process. It made them relax and enjoy the lesson even not bored while learning. This function also explained by teacher A in the interview,
“I use jokes in Bahasa Indonesia, because if I used jokes in English, I don‟t think they will understand. In addition, it can get their attention and refresh their mind for a while. So, they will not get stress and under pressure. So, I need some jokes to make them more relax and I used English since they are not familiar with English jokes.”(Teacher A, Interview, July 5th, 2015)
Teacher B also had similar opinion with teacher A.
“I insert some jokes in Indonesian language because sometimes they don‟t understand when we use English to joke. I want to use English, but if I say it in English they like, „What?‟ There is no reaction.”(Teacher B, Interview, July 10th, 2015)
Both of the teachers explained the same reason why they used jokes in Indonesian language. It is because the students cannot understand English jokes. In addition, they are not familiar with English jokes. I also think that joke is quite important in learning process. But, I don‟t agree that this function is useful for learning. It will be much better if the teacher can reduce the Indonesian language slowly. It is useful to enrich the students‟ English vocabulary in enhancing
30
In line with the idea of Bowen (2004) said that the teacher should have policy to avoid over dependence on the L1 in order to limit excessive and automatic use of L1 in the class. It is also useful to make the students‟ English vocabularies richer.
CONCLUSION
Code switching in teaching English as a foreign language (EFL) classroom has been used for a long time. Regarding to the practice of code switching between L1 and English in teaching English, the study aimed to evaluate the functions of code switching which enhance English learning, as well as further maximizing English usage in teaching English. In addition, the study will hopefully provide more knowledge about the beneficial functions of code switching in order to enhance English learning process optimally and make English classroom more effective and comprehensible.
31
teachers overcome this matter to change the utterances into their L1. In addition, the students have limited command of English, it can cause misunderstood or it might lose its effectiveness. Thus, the use of L1 would be more effective (Moskowitz, 1971). It can be concluded that the directive function proved to be an enhancing function of teachers‟ code switching in order to enhance English learning in EFL classroom.
The second biggest of code switching functions which was used by the teachers is metalinguistic function. Metalinguistic function was used by teacher A 22,8% whereas teacher B 16,51%. Explanation has a big role in teaching process. As cited in (Moppondi, 1995 in Novotna n.d ), “The role of an explanation is to make clearer the meaning of an object (method, term, assignment) maintaining formally the necessary distance between the object of the action or study and the tools.” To avoid explanation errors and manifest the explanation clearer, the
teachers used the function to make students understand the material well. It sums up that explanation function includes in enhancing function of teaches code switching in EFL classroom.
The third rank of function teachers‟ code switching is translation function.
32
Beside directive function, metalinguistic function and translation function, the study found another functions of code switching in the observations. There are phatic function, referential function, expressive function, and poetic function. Those functions were categorized as less enhancing functions of teachers‟ code switching. It can be eliminated during learning process, since it was considered that it is less important for improving and enhancing English skill.
The implications of this study are to enhance English learning in EFL classroom. In addition, the teachers can be wise to use code switching which is useful for improving students‟ English skill and helps students in understanding
the material.
33 REFERENCES
Abbot, P. & Wingard, P (1981). Teaching English as an International Language. London: Biddles Ltd.
Appel, R., & Muysken, P. (2006). Language contact and bilingualism. Amsterdam University Press.
Atkinson, D. (1993). Teaching Monolingual Classes. Longman
Boey, L. Kiat. (1975). An Introduction to Linguistics for the Language Teacher. Singapore University Press.
Bowen, T. (2004). Using Mother tongue in the Classroom. Macmillan: Macmillan Publishers Ltd.
Brice,A.,&Brice,R.(2000).Language in the classroom: Comparisons of four bilingual environments. Retrieved October 2, 2005, from
http://www.asha.ucf.edu/SouthAfrica2000.html.
Chambers, J. K. (1992) Dialect acquisition. Language 68: 673–705.
Cook, V. (2001) Using the first language in the classroom. Canadian Modern
Gumperz,J. J. (1964) "Linguistic and Social Interaction in Two Communities", American Anthropologist, 66(S3): 137-153.
Gumperz, J. J., & Hernández-Chavez, E. (1975). Bilingualism, bidialectalism, and classroom interaction. In C. Cazden, V. P. John, & D. Hymes (Eds.), Functions of language in the classroom (pp. 84–107). New York: Teachers College Press.
Gumperz, J. J. (1982). Discourse strategies. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Harbord, J. (1992). The use of Mother Tongue in the Classroom. , ELT journal (46.4) : 350-355
34
Hymes, D. (1962). The ethnography of Speaking. In T. Gladvin and W. C. Sturtevant (Eds.), Anthropology and human behavior (pp15-53). Washington, DC: Anthropological Society of Washington.
Kasperczyk, L.A (2012) . What is Code Switching? Retrieved July 02, 2012 from
http://www.slideshare.net/maiye/code-switching-13522765.
Lesley, A. K., (n.d). Implementing Code Switching in the classroom.
Macaro, E. (1997). Target language, Collaborative Learning and Autonomy. Clevedon: Multilingual Matters Ltd
Mahootian, S. (2006). Code Switching and Mixing. Encyclopedia of Language & Linguistics, Vol.2, pp. 512-527.
Mopondi, B. (1995). Les explications en classe de mathématiques. Recherches en Didactique des Mathématiques, Vol. 15, n◦ 3, 7-52.
Moskowitz, G. (1971). Interaction Analysis-a New Modern Language for Supervision. Foreign Language annals 5(2), 211-212
Novotna, J (n.d). Teachers‟ Views and Use of Explanation in Teaching Mathematics. Prague:Charles University.
Ruiz, K. M. Algarin. (2014). Code Switching: A tool in the Classroom. State University of New York.
Spratt, M. (1988). English for the Teacher. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Urgese, T. (1987). L1 as a useful tool in Teaching Foreign Language. English teaching Forum, 25 (3), 39-40
Wardhaugh, R. (2006). An Introduction to Sociolinguistics (Fifth Edition). United Kingdom: Blackwell Publishing.
35
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Alhamdulillahirobill‟alamin. Foremost, I am grateful to Allah SWT for always helping me, blessing me and giving me the good health from the beginning of my study until the end of my thesis submission.
I wish to express my sincere thanks to my supervisor Dr. Elisabet Titik Murtisari, M.TransStud.,PhD for the continuous support of my study and research, for her patience, motivation, enthusiasm, and immense knowledge. My sincere thanks also goes to Christian Rudianto, M.Appling. as my examiner, for the sincere and valuable guidance and encouragement extended to me. I would also like to show my gratitude to SMP N 2 Salatiga principal and all the teachers and the students who have been cooperative in completing this research.
36 Appendix
Record Interview Questions of Teaching English in English Foreign Language Classroom for 7th grade
Name of teacher : ___________________________ Education : ___________________________
1. What do you think about code switching?
2. What is the purpose of code switching in teaching English?