RANCANG BANGUN ALGORITMA DETEKSI
GERAK ADAPTIF BERBASIS WEB
DENGAN MENGGUNAKAN METODE
FRAME
DIFFERENCES
DAN
DYNAMIC TEMPLATE
MATCHING
Naskah Publikasi
untuk memenuhi sebagian persyaratan
mencapai derajat Sarjana S-2
Program Studi S2 Teknik Elektro
Konsentrasi Sistem Komputer dan Informatika
Jurusan Teknik Elektro dan Teknologi Informasi
diajukan oleh
Muhammad Ihsan Zul
10/305739/PTK/06833
kepada
PROGRAM PASCASARJANA
FAKULTAS TEKNIK
UNIVERSITAS GADJAH MADA
YOGYAKARTA
DESIGN OF WEB BASED ADAPTIVE MOTION
DETECTION ALGORITHM USING
FRAME DIFFERENCES AND DYNAMIC
TEMPLATE MATCHING METHODS
Computer and Informatic Systems
Department of Engineering Science
Faculty of Engineering
Proposed by:
Muhammad Ihsan Zul
10/305739/PTK/06833
To
GRADUATE SCHOOL
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
GADJAH MADA UNIVERSITY
Naskah Publikasi
RANCANG BANGUN ALGORITMA DETEKSI GERAK
ADAPTIF BERBASIS WEB DENGAN MENGGUNAKAN
METODE
FRAME DIFFERENCES
DAN
DYNAMIC
TEMPLATE MATCHING
yang dipersiapkan dan disusun oleh
MUHAMMAD IHSAN ZUL
10/305739/PTK/06833
Pembimbing Utama
………..
Widyawan, S.T., M.Sc., Ph.D
Pembimbing Pendamping
………..
Ir. Lukito Edi Nugroho, M.Sc., Ph.D
Pengelola Program Studi : S2 Teknik Elektro
Ir. P. Insap Santosa, M.Sc., Ph.D.
NIP. 196101081985031002
Mengetahui,
Ketua Jurusan / Wakil Penanggung Jawab Program Studi Teknik Elektro
DESIGN OF WEB BASED ADAPTIVE MOTION
DETECTION ALGORITHM USING FRAME
DIFFERENCES AND DYNAMIC TEMPLATE
MATCHING METHODS
Proposed by :
MUHAMMAD IHSAN ZUL
10/305739/PTK/06833
Supervisor
………..
Widyawan, S.T., M.Sc., Ph.D
Co-Supervisor
………..
Ir. Lukito Edi Nugroho, M.Sc., Ph.D
Programme Director : Magister of Electrical Engineering
Ir. P. Insap Santosa, M.Sc., Ph.D.
NIP. 196101081985031002
Head of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology Department
Rancang Bangun Algoritma Deteksi Gerak yang Adaptif Berbasis Web
Menggunakan Metode Frame Differences dan Dynamic Template
Matching
Design of Web Based Adaptive Motion Detection Algorithm using Frame
Differences and Dynamic Template Matching Methods
Muhammad Ihsan Zul
1, Widyawan
2, Lukito Edi Nugroho
3Program Studi S2 Teknik Elektro
Program Pascasarjana Universitas Gadjah Mada
INTISARI
Ada banyak cara yang dilakukan untuk mendeteksi gerak dalam kajian
computer vision
.
Metode yang umum digunakan untuk mendeteksi objek yang bergerak dilakukan dengan
membandingkan dua atau lebih citra yang ditangkap berurutan. Pembandingan dengan
melakukan analisis setiap piksel dari dua atau lebih citra dikenal dengan nama
Frame
Differences
. Selain, template matching juga dikenal dengan sebuah metode penentuan citra
pembanding atau citra referensi. Citra referensi yang ditentukan secara dinamis dikenal
dengan nama dynamic template matching. Penelitian ini mengajukan algoritma penentuan
citra referensi secara adaptif dengan menggunakan metode
dynamic template matching
.
Algoritma ini menggunakan tiga metode penentuan citra referensi berdasarkan perbuahan
kondisi area tangkapan kamera. Algoritma ini direalisasikan dengan menggunakan bahasa
pemrograman web dan menggunakan IP Camera sebagai alat pendeteksi gerakan. Algoritma
ini menghasilkan akurasi pendeteksian hingga 95,5%.
Kata Kunci -
frame
differences
,
dynamic template matching,
deteksi gerak berbasis web
1
Fakultas Teknik, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
2Fakultas Teknik, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
3Design of Web Based Adaptive Motion Detection Algorithm using Frame
Differences and Dynamic Template Matching Methods
Rancang Bangun Algoritma Deteksi Gerak yang Adaptif Berbasis Web
Menggunakan Metode Frame Differences dan Dynamic Template
Matching
Muhammad Ihsan Zul
1, Widyawan
2, Lukito Edi Nugroho
3Program Studi S2 Teknik Elektro
Program Pascasarjana Universitas Gadjah Mada
ABSTRACT
There are many ways to detect the moving object in term of image motion detection. A
common method that is used to detect moving object recognize by comparing two or more
sequence images. Comparing image by analysing all of image pixel is known as
frame
differences
method. Template matching is a method that used to determine the reference
image. Reference image which determined dynamically is known a dynamic template
matching. This research proposes an algorithm to determine the reference image by using
dynamic template matching adaptively. In the system, there are three ways to determine the
reference image base on environment condition. This research realizes an algorithm by using
web based system and using IP Camera as measures device. This algorithm provide detection
accuracy rate 95.5%.
Keywords- frame differences, dynamic template matching, web based motion detection
1
Faculty of Engineering, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia.
2Faculty of Engineering, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia.
3I. PENDAHULUAN
Kamera pemantau merupakan perangkat yang digunakan untuk memantau suatu area atau objek. Terdapat berbagai jenis kamera pemantauan yang digunakan untuk sistem keamanan. Salah satu kamera pemantau yang umum digunakan dalam pemantauan adalah IP Camera. Penerapan sistem pemantauan memiliki fitur pendeteksian gerak berdasarkan citra yang terdeteksi. Pendeteksian gerak ini dilakukan dengan menganalisis citra-citra yang ditangkap.
Mekanisme pendeteksian gerak dimulai dari penentuan citra referensi dengan citra pembanding. Citra pembanding dianggap sebagai kondisi normal sebuah ruangan. Citra tersebut dibandingkan dengan kondisi setelah dilakukan penangkapan citra. Proses penangkapan citra dilakukan secara berkala sesuai dengan kebutuhan sistem.
Menurut penelitian yang dilakukan oleh Mishra et al. [1] ada tiga metode yang umum digunakan untuk mendeteksi gerak. Metode tersebut adalah background subtraction, optical flow dan temporal differences. Background subtraction dilakukan dengan membandingkan citra tertentu dengan citra yang dijadikan sebagai referensi. Background subtraction melakukan pendeteksian gerak dengan menggunakan teknik penentuan gambar referensi secara statis [2, 3, 4].
Penelitian [5, 6, 7, 8] menggunakan optical flow dalam penelitian tentang deteksi gerak yang dilakukan. Penelitian tersebut cukup sulit diterapkan untuk real time video surveillance. Penerapan optical flow membutuhkan perangkat keras tambahan untuk mendukung kinerja dan performa sistem pemantauan. Metode temporal differences juga dikenal dengan nama frame differences. Metode ini dilakukan dengan membandingkan frame-frame citra yang ditangkap. Penelitian lain yang dilakukan oleh Kenchannavar et al. [9] menjelaskan tentang algoritma yang diterapkan dalam metode background subtraction dan frame differences. Penelitian yang dilakukan dengan menerapkan konsep SAD. SAD merupakan singkatan dari Sum of Absolute Difference. SAD inilah yang digunakan untuk menyatakan ada atau tidaknya pergerakan suatu pasang citra.
Metode frame differences menggunakan citra referensi tertentu dalam mendeteksi gerak. Metode yang digunakan dalam penggunaan citra referensi ini dikenal dengan nama template matching. Ada dua metode penentuan template yang digunakan, antara lain : static template matching (background subtraction) dan dynamic template matching.
Penelitian ini menggunakan metode dynamic template matching dalam menentukan citra referensi. Metode dynamic template matching dikembangkan dan dimodifikasi agar adaptif terhadap perubahan lingkungan. Metode ini selanjutnya disebut dengan nama dynamic and adaptive template matching. Pendeteksian gerak dengan menggunakan metode ini dikembangkan dan diimplementasikan untuk aplikasi berbasis web, sehingga bahasa pemrograman yang digunakan adalah bahasa pemrograman web.
II. PENELITIAN TENTANG DETEKSI GERAK
Penelitian yang dilakukan oleh Yong et al. [10] menggunakan empat metode pendeteksian gerak. Metode-metode tersebut antara lain Metode-metode frame differences, background subtraction, pixellate filter dan blob counter. Metode frame differences menggunakan citra ke t-1 sebagai citra referensi. Penelitian ini menggunakan bahasa pemrograman C# dalam melakukan pendeteksian. Support Vector Machine (SVM) juga diterapkan dalam mendeteksi gerak [4]. Penelitian ini tidak hanya melakukan pendeteksian gerak, akan tetapi juga melakukan segmentasi terhadap objek-objek tersebut. Pendeteksian ini dirancang dengan menggunakan bahasa pemrograman C++ dan OpenCV.
Penelitian yang terkait dengan deteksi gerak juga dilakukan oleh Zheng et al [11]. Penelitian ini menggunakan metode frame differences yang digabungkan dengan pengaturan ambang batas yang adaptif (adaptive threshold). Pendeteksian gerak juga direalisasikan dengan menggunakan metode statistical correlation method [12]. Metode ini digunakan setelah dilakukan proses temporal differences dalam menganalisis beberapa frame citra. Pendeteksian gerak dengan mengkombinasikan teknik frame differences dengan optical flow. Metode ini dilanjutkan dengan teknik morphological filter [13].
Penelitian yang dilakukan oleh [14] menerapkan konsep vektor untuk mendeteksi pergerakan. Metode ini dilakukan dengan membandingkan beberapa frame dan menandai titik-titik perbedaan antar frame. Metode ini juga menghasilkan informasi tentang arah pergerakan objek. Zheng et al. [11] menjelaskan bahwa terdapat metode lain yang digunakan untuk mendeteksi gerak. Metode ini dikenal dengan nama Statistical Learning Algorithm. Penelitian dengan menerapkan metode serupa juga dilakukan oleh Murali dan Girisha [12]. Sama seperti optical flow, metode ini membutuhkan waktu komputasi yang besar. Hal ini terjadi karena algoritma ini membutuhkan langkah-langkah yang kompleks.
Terkait dengan teknik penentuan citra referensi, salah satu metode pendeteksian gerak dilakukan dengan menggunakan teknik double differences. Teknik komparasi citra ini dikembangkan oleh Kameda dan Minoh [15]. Double differences dilakukan dengan membandingkan citra dengan waktu t dengan citra t-1, selanjutnya dilakukan pembandingan kedua antara citra t-1 dengan citra t-2. Berbeda dengan metode yang dikembangkan oleh Collins et al. [16], pembandingan dilakukan antara citra t dengan citra t-1, dan antara citra t dengan citra t-2.
Berdasarkan tinjauan tersebut, disimpulkan bahwa terdapat banyak penelitian yang dilakukan dalam pendeteksian gerak dengan menggunakan citra. Penelitian yang diajukan di dalam paper ini memiliki perbedaan dalam hal metode, teknik penentuan citra referensi dan bahasa pemrograman yang digunakan dalam pendeteksian gerak.
III. PENELITIAN DETEKSI GERAK
Penelitian ini menggunakan metode frame differences yang dilakukan dengan membandingkan piksel rata-rata komponen RGB. Pengujian dengan langkah ini dilakukan dengan menggunakan persamaan 1 dan persamaan 2.
3
komponen RGB citra referensi. fodango adalah nilai rata-rata
dari penjumlahan nilai komponen warna RGB. T merupakan threshold atau ambang batas nilai RGB.
Selanjutnya dilakukan penghitungan persentase piksel objek yang terdeteksi. Pendeksian ini dilakukan dengan menggunakan persamaan 3. jumlah piksel yang terdeteksi berbeda berdasarkan komponen
warna RGB.
fR,
fG,
fB adalah jumlah pikselkeseluruhan citra yang diambil dari tiga komponen warna.
B. Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching
Terkait dengan penenetuan citra referensi, penelitian ini mengajukan sebuah metode penentuan citra referensi dengan teknik yang berbeda. Metode referensi yang digunakan adalah kombinasi antara referensi pada saat t-1, t-n dan penetapan citra referensi baru jika lingkungan (area tangkapan kamera) mengalami perubahan yang signifikan.
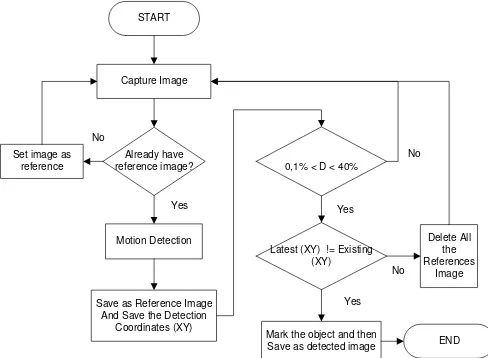
Perubahan-perubahan signifikan yang dimaksudkan dapat berupa: (1) perubahan kecerahan objek, dalam hal ini bisa terjadi jika lampu ruangan dimatikan atau ruangan diterangi cahaya matahari, (2) perubahan area tangkapan kamera, kondisi ini terjadi jika posisi kamera diubah, (3) perubahan kondisi lingkungan jika terdapat objek yang datang dan secara statis berada di posisi tertentu secara terus-menerus. Algortima penentuan citra referensi ini selanjutnya disebut dengan nama teknik dynamic and adaptive template matching. Algortima dynamic and adaptive template matching bekerja berdasarkan diagram pada gambar 1.
START And Save the Detection
Coordinates (XY)
Mark the object and then
Save as detected image END Yes
Gbr 1. Diagram Alir Metode Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching (DATM)
IV.ANALISIS DETEKSI GERAK
A. Analisis Metode DTM t-1, Static Template Matching dan DATM
Dynamic Template Matching t-1
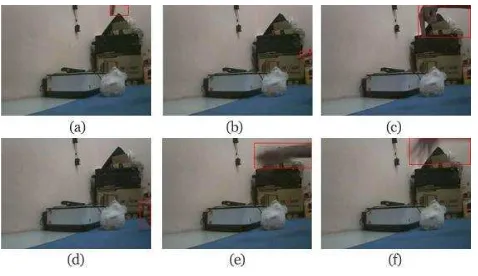
Gambar 2 dan gambar 3 merupakan hasil tangkapan objek yang teridentifikasi bergerak dengan menggunakan metode DTM t-1. Kedua gambar ditangkap secara berurutan dengan menggunakan IP Camera.
Pada gambar 2, gambar 2 (b) dan 2 (c) mendeteksi pergerakan yang telah terdeteksi pada citra 2 (a) dan 2 (b). Keadaan ini merupakan kelemahan dari metode DTM t-1. Jika diteliti lebih lanjut, kelemahan semakin terlihat pada gambar 3.
Gbr 2. Motion Detection t-1 Reference Image
Gbr 3. Deteksi Gerak dengan Referensi t-1 Ditandai dengan Kotak Merah
Gambar 3 merupakan pendeteksian gerak dengan metode DTM t-1 dengan dilengkapi penanda (marker) kotak merah. Gambar 3 (c) menandai objek kosong yang sebelumnya merupakan objek yang terdapat di gambar 3 (b). Pengujian ini semakin menegaskan kelemahan metode DTM t-1 dalam mendeteksi pergerakan.
Static Template Matching
Pengujian selanjutnya dilakukan dengan menggunakan citra referensi yang telah ditetapkan oleh sistem. Metode ini (1)
(2)
bisa disebut dengan nama static template matching. Pengujian dengan menggunakan metode ini dapat dilihat pada gambar 4.
Gbr 4. Metode Static Template Matching
Pada gambar 4, sistem berhasil menanggulangi kelemahan yang terjadi pada saat menerapkan metode DTM t-1. Setiap citra yang terdapat pada gambar 4 berhasil mendeteksi objek yang bergerak dan menandai persis pada area objek tersebut.
Namun, metode ini masih meninggalkan permasalahan ketika suatu objek datang dan secara terus-menerus berada di area tangkapan kamera secara statis. Hal ini terlihat pada gambar 5. Terdapat objek (mouse) yang masuk pada gambar 5 (b). Objek tersebut dideteksi bergerak oleh hasil tangkapan pada citra selanjutnya (gambar 5 (c), (d), (e)). Terlihat bahwa sistem tidak adaptif terhadap perubahan area tangkapan. Hal ini tentu akan menjadi masalah jika terjadi perubahan kecerahan karena faktor cahaya.
Gbr 5. Permasalahan Deteksi Gerak Pada Citra Referensi Statis
Berdasarkan pengujian yang dilakukan terhadap dua metode penentuan citra referensi sebelumnya, terdapat kelemahan yang terkait dengan metode penentuan citra referensi. Rancangan dan diagram alir algoritma metode penentuan citra referensi yang teradapat pada gambar 1, merupakan algoritma yang modifikasi dari metode dynamic template matching. Metode ini diperkenalkan dengan nama Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching (DATM). Metode ini bekerja dengan cara melakukan penyesuaian citra referensi berdasarkan kondisi area yang ditangkap.
Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching
Secara umum, sistem ini bekerja dengan menggunakan tiga metode penentuan citra referensi. Metode tersebut berubah-ubah secara dinamis dan adaptif. Metode pertama
adalah referensi saat t-1. Metode ini digunakan untuk kondisi ketika sistem pertama kali menangkap pergerakan, maka referensi t-1 akan bereperan sebagai pembanding untuk citra yang terdeteksi tersebut. Jika pada frame selanjutnya sistem masih mendeteksi pergerakan, maka referensi yang digunakan adalah citra pada saat t-2. Jika pada frame selanjutnya masih berlanjut dan mendeteksi pergerakan, maka citra referensi yang digunakan adalah pada saat t-3, begitu seterusnya. Metode ini disebut dengan teknik penentuan citra referensi saat t-n. Metode t-n merupakan metode kedua yang digunakan sistem. Dimana nilai n disesuaikan dengan urutan frame hasil pendeteksian secara berurutan
Metode ketiga yang digunakan adalah penentuan ulang citra referensi. Metode ini bekerja dengan cara menangkap ulang citra referensi yang akan digunakan dan menghapus semua citra refernsi yang telah ada. Citra referensi akan berubah berdasarkan hasil pengujian koordinat objek yang terdeteksi. Sistem akan menentukan ulang citra referensi jika mendeteksi pergerakan di koordinat yang sama. Kesamaan titik koordinat diuji terhadap dua frame citra yang dinyatakan mendeteksi pergerakan secara berurutan.
Metode ketiga digunakan untuk menanggulangi permasalahan yang muncul ketika menggunakan metode static template matching. Hasil pengujian dengan menggunakan metode DATM dapat dilihat pada gambar 6.
Gbr 6. Hasil Pengujian Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching
Gambar 6 merupakan urutan frame citra yang ditangkap pada saat pengujian Dynamic And Adaptive Template Matching (DATM). Urutan citra yang ditangkap diurutkan berdasarkan angka yang terdapat di pojok kanan atas masing-masing citra. Pada gambar 6, citra 1, 4, 7, 10, dan 13 merupakan citra referensi yang secara adaptif berubah sesuai dengan kondisi area yang ditangkap. Pada gambar terlihat jelas adanya objek statis yang dalam waktu tertentu berada di area tangkapan kamera tanpa melakukan pergerakan (diam). Sehingga citra dengan objek tersebut dianggap sebagai referensi oleh sistem. Penerapan metode DTM t-1 terlihat ketika terdeteksi gerak pada citra 2, 5, 8, dan 1, dimana citra referensi (1, 4, 7, 10 dan 13) yang digunakan merupakan citra yang ditangkap sebelum citra tersebut ditangkap. Sedangkan penerapan citra referensi t-n terlihat pada citra 3, 6, 9 dan 12. Citra tersebut menggunakan citra referensi pada saat t-2.
B. Perbandingan Metode DTM t-1 dengan Metode DATM
Pengujian pada bagian ini dilakukan untuk menguji tingkat akurasi dari metode pendeteksian yang dijelaskan pada bagian sebelumnya. Metode yang akan dibandingkan adalah metode DTM t-1 dan DATM. Metode static template matching tidak dibandingkan karena metode ini tidak adaptif dengan perubahan lingkungan. Oleh karena itu, pengujian ini hanya dilakukan untuk metode dynamic template matching.
Pengujian dan pengumpulan data dilakukan selama tiga hari. Setiap hari dilakukan pendeteksian selama 2 jam pada saat jam kantor. Pengujian dilakukan dengan menggunakan sebuah IP Camera berjenis PTZ (Pan Tilt Zoom) dengan merk Vivotek. Kamera ditempatkan di lobi gedung jurusan Teknik Elektro dan Teknologi Informasi FT UGM. Pengumpulan data dilakukan dengan menjalankan algoritma deteksi gerak DTM t-1 dan DATM secara bersamaan. Pengaturan fungsi frame differences sistem untuk kedua algoritma disamakan. Dimana, nilai threshold yang digunakan adalah 45, rentang nilai persentase terdeteksi (D) adalah dari 0,5% - 40%, resolusi citra yang digunakan adalah 256 × 192 piksel. Terkait dengan jenis citra, citra yang digunakan adalah citra RGB, dan metode frame differences yang digunakan adalah perbandingan rata-rata piksel komponen warna RGB.
Hasil pendeteksian sistem diklasifikasikan menjadi dua kondisi, yaitu: True Positive dan False Positive. True Positive berarti sistem menangkap citra dan menandai objek yang teridentifikasi bergerak. Sedangan False Positive merupakan kondisi dimana sistem menangkap citra tetapi menandai objek kosong, atau tidak ada objek yang teridentifikasi bergerak.
Hasil pengujian ini menghasilkan 1643 citra yang mendeteksi pergerakan untuk metode DTM t-1. Sedangkan metode DATM menghasilkan 1278 citra yang mendeteksi pergerakan. Hasil analisis dan perbandingan dari kedua metode ini dapat dilihat pada tabel 1. Perbandingan pada tabel 1 menjadi tabel acuan untuk tingkat akurasi pendeteksian yang dilakukan oleh kedua metode pendeteksian gerak ini.
Table 1. Perbandingan Akurasi DTM -1 dan DATM
Perbandingan Metode
DTM t-1 DATM
True Positive 1474 89,8% 1221 95,5% False Positive 169 10,2 % 57 4,5%
Berdasarkan tabel 1 dapat disimpulkan bahwa metode pendeteksian gerak dengan menggunakan teknik DATM memiliki tingkat akurasi pendeteksian yang lebih tinggi (95,5 %) jika dibandingan dengan metode DTM t-1 (89,8 %). Metode DATM juga behasil menekan jumlah citra hasil pendeteksian yang berpengaruh terhadap penggunaan harddisk untuk pendeteksian.
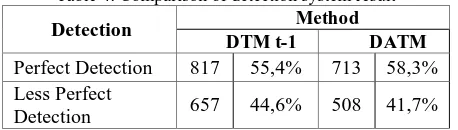
Table 2 Perbandingan Hasil Pendeteksian Sistem
Hasil Deteksi Metode DTM t-1 DATM
Terdeteksi Sempurna 817 55,4% 713 58,3% Terdeteksi Kurang
Sempurna 657 44,6% 508 41,7%
Pada tabel 2 hasil pendeteksian dikelompokkan menjadi 2 bagian yang dibedakan berdasarkan hasil penandaan. Kedua bagian tersebut antara lain: Terdeteksi Sempurna dan
Terdeteksi Kurang Sempurna. Terdeteksi sempurna berarti
sistem mampu menandai objek dengan sempurna berdasarkan pada koordinat objek tersebut. Sedangkan terdeteksi kurang sempurna terjadi ketika sistem menandai objek tetapi penandaan mengalami pelebaran. Sehingga tidak fokus menandai objek yang diidentifikasi bergerak. Dari tabel 2 terlihat bahwa metode DTM t-1 menghasilkan 55,4% untuk keadaan Terdeteksi Sempurna dan 58,3 % untuk metode DTAM.
V. KESIMPULAN DAN SARAN
Metode pendeteksian gerak Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching (DATM) secara dinamis dan adapatif menjadi solusi terhadap kelemahan yang terjadi ketika menggunakan metode penentuan citra referensi pada saat t-1 (DTM t-1) dan static template matching. Pengujian pendeteksian gerak yang dilakukan menghasilkan suatu metode pendeteksian gerak dengan menggunakan teknik frame differences. Dimana metode penentuan citra referensi yang digunakan dikenal dengan Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching (DATM). Berdasarkan perbandingan metode DTM t-1 dengan DATM, metode DTAM memiliki tingkat akurasi pendeteksian 95,5 %, sedangan metode DTM t-1 hanya memiliki akurasi 89,8 %.
Penelitian lanjutan yang akan dilakukan adalah segmentasi objek. Sehingga setiap objek yang terdeteksi bisa dikelompokkan berdasarkan kedekatan titik piksel yang terdeteksi. Dengan demikian sistem dapat mengenali jumlah objek yang terdeteksi.
DAFTAR PUSTAKA
[1] Sumita Mishra, Prabhat Mishra, Naresh K Chaudhary, and Pallavi Asthana, "A Novel Comprehensive Method for Real Time Video Motion Detection Surveillance," International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 2, Issue 4, 2011.
[2] P. Spagnolo, T. D'Orazio, M.Leo, and A.Distante, "Moving Object Segmentation by Background Subtraction and Temporal Analysis," Image and Vision Computing, vol. 24, pp. 411-423, May 2006.
[3] Zhen Tang and Zhenjiang Miao, "Fast Background Subtraction Using Improved GMM and Graph Cut," in Congress on Image and Signal Processing, 2008. CISP '08. , 2008, pp. 181 - 185. [4] Hongyan Li and Hongyan Cao, "Detection and Segmentation of
Moving Objects Based on Support Vector Machine," in 2010 Third International Symposium on Information Processing, Shandong China, 2010, pp. 193-197.
[5] M. Allili, M.-F. Auclair-Fortier, P. Poulin, and D. Ziou, "A Computational Algebraic Topology Approach for Optical Flow," in ICPR '02 Proceedings of the 16 th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR'02) Volume 1 - Volume 1 , Washington DC, USA, 2002.
Tracking of Static and Moving Objects in Video Surveillance Scenarios," in ICIP 2008. 15th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, 2008, pp. 2716 - 2719.
[7] Ho Gi Jung, Jae Kyu Suhr, Kwanghyuk Bae, and Jaihie Kim, "Free Parking Space Detection Using Optical Flow-based Euclidean 3D Reconstruction," in Proceedings of the IAPR Conference on Machine Vision Applications (IAPR MVA 2007), Tokyo, Japan, 2007, pp. 16-18.
[8] Jens Klappstein, Tobi Vaudrey, Clemens Rabe, Andreas Wedel, and Reinhard Klette, "Moving Object Segmentation using Optical Flow and Depth Information," Advances in Image and Video Technology, 2009.
[9] H H Kenchannavar, Gaurang S Patkar, U P Kulkarni, and M M Math, "Simulink Model for Frame Difference and Background Subtraction comparision in Visual Sensor Network," in 2010 The 3rd International Conference on Machine Vision (ICMV 2010), Hongkong China, 2010.
[10] Yee Ching Yong, Rubita Sudirman, and Kim Mey Chew, "Motion Detection and Analysis with Four Different Detectors," in 2011 Third International Conference on Computational Intelligence, Modelling and Simulation, Langkawi, 2011, pp. 46-50.
[11] Xiaoshi Zheng, Yanling Zhao, Na Li, and Huimin Wu, "An Automatic Moving Object Detection Algorithm for Video Surveillance Applications," in 2009 International Conference on Embedded Software and Systems, Hangzhou China, 2009, pp. 541-543.
[12] S Murali and R Girisha, "Segmentation of Motion Objects from Surveillance Video Sequences using Temporal Differencing Combined with Multiple Correlation," in 2009 Sixth IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance, Genova, Italy , 2009, pp. 472-477.
[13] li Fang, Zhang Meng, Claire Chen, and Qian Hui, "Smart Motion Detection Surveillance System," in 2009 International Conference on Education Technology and Computer, Singapore, 2009, pp. 171-175.
[14] Takanori Yokoyama, Toshiki Iwasaki, and Toshinori Watanabe, "Motion Vector Based Moving Object Detection and Tracking in the MPEG Compressed Domain," in 2009 Seventh International Workshop on Content-Based Multimedia Indexing, Chania, Crete, 2009, pp. 201-206.
[15] Y Kameda and M Minoh, "A Human Motion Estimation Method Using 3-Successive Viedo Frames," in International Conference on Virtual Systems and Multimedia, 1996, pp. 135– 140.
I. INTRODUCTION
The camera is device is used to monitor an area or object. There are various types of cameras used for monitoring that aim for security system. One of the camera monitors are commonly used in monitoring is the IP Camera. Application of a monitoring system has features motion detection based on the detected image. Motion detection is done by analyzing the images captured.
Motion detection mechanism starts from the determination of the reference image by image comparison. The image contrast is considered as the normal condition of a room. The image is compared with the imagery condition after the arrest. Image capture process carried out at regular intervals in accordance with the requirements of the system.
According to a study conducted by Mishra et al. [1], there are three methods that commonly is used to detect a motion. They are background subtraction, optical flow and temporal differences. Background subtraction is done by comparing a specific image with the image used as a reference. Background subtraction makes motion detection by using the technique of determining the reference image statically [2, 3, 4].
Study [5, 6, 7, 8] use optical flow in research on motion detection performed. The study is quite difficult to implement for real time video surveillance. The application of optical flow requires additional hardware to support the performance and monitoring systems. Method of temporal differences is also known by the name of the frame differences. This method is performed by comparing image frames are captured. Another study conducted by Kenchannavar et al. [9] describes the algorithm implemented in the method of background subtraction and frame differences. Research carried out by applying the concept of SAD. SAD stands for Sum of Absolute Difference. SAD is used to declare whether or not the movement of an image pair.
Frame differences using the method specified in the reference image to detect motion. The method applied in using of a reference image is known as template matching. There are two methods of determination of the template uses; static template matching (background subtraction) and dynamic template matching
This study uses a dynamic template matching method in determining the reference image. Dynamic template matching method is developed and modified to be adaptive to environmental changes. This method is here in after referred to as the dynamic and adaptive template matching. Motion detection using this method was developed and implemented for web-based applications, so the programming language used is a web programming language.
II. RELATED WORKS
Research conducted by Yong et al. [10] using four methods of motion detection. These methods include methods of frame differences, background subtraction, pixellate filter and blobcounter. Frame differences method uses an image to t-1 as the reference image. This study uses the C# to do the
detection. Support Vector Machine (SVM) is also applied in the motion detection [4]. This study is not only performing motion detection, but also the segmentation of the objects. This detection is designed by using the C++ and OpenCV.
Research related to motion detection is also performed by Zheng et al. [11]. This study uses frame differences are coupled with an adaptive threshold setting (adaptive threshold). Motion detection is also realized by using the method of statistical correlation method [12]. This method is used after the process of analysing the temporal differences in some of the image frame. The detection of motion by combining the frame differences technique with optical flow. This method is followed by a morphological filter technique [13].
Research conducted by Yokoyama et al. [14] also applying the concept of vectors to movement detection. This method is performed by comparing multiple frames and marks the points of difference between the frames. This method also yields information about the direction of movement of the object. Zheng et al. [11] explains that there are other methods used to detect motion. This method is known as the Statistical Learning Algorithm. Research by applying a similar method is also performed by Murali and Girisha [12]. Just like optical flow, this method requires large computational time. It occurs because these algorithms require complex steps
Regarding with the technique of determining the reference image, one of the methods of motion detection was done by using double differences technique. Image comparison technique was developed by Kameda and Minoh [15]. Double differences done by comparing the image with time t to image 1, then performed a second comparison between the image t-1 with the image of t-2. In contrast to the method developed by Collins et al. [16], the comparisons were made between the image t with the image of t-1, and the image t with the image of t-2.
Based on such review, it was concluded that there are a lot of research done in the motion detection by using the image. The research that proposed in this paper have differences in the methods, determination techniques of the reference image and programming language used in the motion detection.
III. PROPOSED MOTION DETECTION ALGORITHM
A. Frame Differences
This study uses frame differences method by comparing the average RGB components of each pixel. Equation 1 and equation 2 are used for the calibration step.
colour components. T is the threshold or thresholds RGB value and then performed counting the percentage of pixels detected object. The detection is done using equation 3.
B. Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching
Regarding with the determination reference image, this study proposed a method of determining the reference image with different techniques. Reference method that used is a combination of reference at the time t-1, t-n and the establishment of a new reference image if the environment (captured area of the camera) undergoing significant change.
Significant changes are intended to be: (1) changes in the brightness of the object; in this case it can occur if the room lights turned off, or the sun-lit room; (2) changes in captured area of the camera, this condition occurs when the camera position is changed; (3) changes in environmental conditions if there are objects come and statically bases in a particular position on an ongoing. The algorithm to determining the reference image is referred to as the Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching. Dynamic algorithms and adaptive template matching works based on the diagram in figure 1.
START
Capture Image
Already have reference image? Set image as
reference
Motion Detection
Save as Reference Image And Save the Detection
Coordinates (XY)
0,1% < D < 40%
Latest (XY) != Existing (XY)
Delete All the References
Image
Mark the object and then
Save as detected image END Yes
No
Yes No
Yes No
Figure 7. Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching (DATM) Method Flow Chart
IV. MOTION DETECTION ANALYSIS
A. DTM t-1, Static Template Matching and DATM Methods
Dynamic Template Matching t-1
Figure 2 and figure 3 is the result of the moving objects captured that identified by using the DTM method t-1. Both images are captured sequentially by using the IP Camera.
Figure 8. Motion Detection t-1 Reference Image
In Figure 2, figure 2 (b) and 2 (c) motion detection has been detected in the image 2 (a) and 2 (b). This situation is a
weakness of the method of DTM t-1. When examined further, the weakness can be seen in figure 3.
Figure 9. Motion detection with reference t-1 is characterized by the Red Box
Figure 3 is motion detection with DTM t-1 method is equipped with a red box marker. Figure 3 (c) marks the empty object that an object previously contained in figure 3(b). This test further confirms the weakness of DTM t-1 methods in detecting movement.
Static Template Matching
Testing is
then performed using a reference image that
has been set by the system. This method can be called by the name of the static template matching. Testing that using this method can be seen in Figure 4.Figure 10. Static Template Matching Method
In figure 4, the system managed to overcome weaknesses that occur when applying
the DTM t-1 method. Each image
contained in Figure 4 successfully detects moving objects and mark exactly on the object area.Figure 11. Error on motion detection with Static Template Matching Method
area. This can be shown in figure 5. There are objects (mouse) are entered in figure 5 (b). The object is detected as moving by the result of the captured on the next image (figure 5 (c), (d), (e)). It can be seen that the system is not adaptive to changes in catchment area. This will certainly be a problem if the brightness changes because of the light.
Based on tests performed on two methods of determining the reference image before, there are drawbacks regarding with the method of determining the reference image. The design of new algorithm in determining the reference image is shown on Figure 1. This algorithm is a modification of the method of dynamic template matching. This method was introduced by the name of Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching (DATM). This method works by adjusting the reference image based on the condition of the captured area.
Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching
In general, this system works by using three methods of determining the reference image. The method is dynamically changing and adaptive. The first method is the reference at the time t-1. This method is used for conditions when the system first captures the movement, then the reference t-1 will have a role as a comparison to the detected image. If the next frame the system still detects movement, the references used are the images at t-2. If the next frame and detect the movement continues, then the reference image is used as t-3, and so on. This method is called with the technique of determining the reference image when t-n. T-n method is the second method that used by the system. The value of n is adapted to the result of the detection the sequence of frames.
The third method is used by determining the new of the reference image. This method works by capturing a reference image to be re-used and remove all existing reference image. Reference image is changed based on results of testing the coordinates of detected objects. The system will redefine the reference image if it detects movement in the same coordinate. The similarities of the point coordinates are tested on two image frames are declared movement detection in a sequence. The third method used to overcome the problems that arise when using the static template matching method. The test results using the DATM method can be seen in figure 6.
Figure 6 is a sequence of image frames are captured at the time of testing Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching image before the image is captured. While the applying of the reference image t-n, it can be seen in 3, 6, 9 and 12 images. Based on these tests, a DATM method capable of resolving a problem encountered when using the DTM t-1 and Static Template Matching.
Figure 12. Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching Testing Results
B. The Comparison of DTM t-1 Method with DATM Method Testing in this section was conducted to examine the Every day it takes 2 hours to do detection during office hours. Experiments were done by using a type IP Camera PTZ (Pan Tilt Zoom) with Vivotek brands. The camera is placed in the lobby of the building department of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology UGM. The data was collected by running the motion detection algorithm DTM t-1 and DATM simultaneously. The Setting function of frame differences system for both algorithms comparable. That is, the threshold value used is 45, the range of percentage values was detected (D) is from 0.5% - 40%, the image resolution used is 256 ×192 pixels. Regarding with this type of image, the image used is RGB image, and the methods used frame differences is the comparison of the average pixel RGB colour components.
The results of the detection system are classified into two conditions, namely: True Positive and False Positive. True Positive means the system captures the image and mark the identified moving objects. Whereas, False Positive is a condition in which the system captures the image, but mark the empty object or no identifiable objects moving.
There are 1643 images that detects the movement when used t-1 DTM method. While this method produces 1278 images movement for DATM method. The analysis and comparison of these two methods can be seen in table 1.
Table 3. Comparison of DTM -1 And DATM Accuracy
Comparison Method
DTM t-1 DATM
True Positive 1474 89,8% 1221 95,5% False Positive 169 10,2 % 57 4,5%
storage usage. The storage usage case will be concern to the motion detection system for future research.
Table 4. Comparison of detection system result
Detection Method include: Detected Less Perfect and Perfect. Perfect detected means the system is able to perfectly detected objects based on the coordinates of the object. While detected Less Perfect occur when the system mark object but the tagging system is experiencing widening. So it is not the focus of identified moving object mark. Based on table 2 show that the DTM t-1 method produced 55.4% for the state and 58.3% detected Perfect for DTAM method.
V. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORKS
Method of motion detection Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching (DATM) dynamically and adaptive be a solution to the weakness that occurs when using the method of determining the reference image at time t-1 (DTM t-1) and the static template matching. Motion detection test is performed to produce a method of motion detection by using frame differences. Where the reference image determination method used is known as Dynamic and Adaptive Template Matching (DATM). Based on the comparison of both methods, DATM method has detection accuracy rate 95.5%, Whereas, DTM t-1 method only has an accuracy of 89.8%.
However, further research will be done is the object
segmentation. So that each detected object can be grouped
by the proximity of the detected pixel point. Thus the system can identify the number of detected objects.REFERENCES
[1] Sumita Mishra, Prabhat Mishra, Naresh K Chaudhary, and Pallavi Asthana, "A Novel Comprehensive Method for Real Time Video Motion Detection Surveillance," International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 2, Issue 4, 2011.
[2] P. Spagnolo, T. D'Orazio, M.Leo, and A.Distante, "Moving Object Segmentation by Background Subtraction and Temporal Analysis," Image and Vision Computing, vol. 24, pp. 411-423, May 2006.
[3] Zhen Tang and Zhenjiang Miao, "Fast Background Subtraction Using Improved GMM and Graph Cut," in Congress on Image and Signal Processing, 2008. CISP '08. , 2008, pp. 181 - 185. [4] Hongyan Li and Hongyan Cao, "Detection and Segmentation of
Moving Objects Based on Support Vector Machine," in 2010 Third International Symposium on Information Processing, Shandong China, 2010, pp. 193-197.
[5] M. Allili, M.-F. Auclair-Fortier, P. Poulin, and D. Ziou, "A
Computational Algebraic Topology Approach for Optical Flow," in ICPR '02 Proceedings of the 16 th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR'02) Volume 1 - Volume 1 , Washington DC, USA, 2002.
[6] J Gallego, M. Pardas, and J.-L. Landabaso, "Segmentation and Tracking of Static and Moving Objects in Video Surveillance Scenarios," in ICIP 2008. 15th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, 2008, pp. 2716 - 2719.
[7] Ho Gi Jung, Jae Kyu Suhr, Kwanghyuk Bae, and Jaihie Kim, "Free Parking Space Detection Using Optical Flow-based Euclidean 3D Reconstruction," in Proceedings of the IAPR Conference on Machine Vision Applications (IAPR MVA 2007), Tokyo, Japan, 2007, pp. 16-18.
[8] Jens Klappstein, Tobi Vaudrey, Clemens Rabe, Andreas Wedel, and Reinhard Klette, "Moving Object Segmentation using Optical Flow and Depth Information," Advances in Image and Video Technology, 2009.
[9] H H Kenchannavar, Gaurang S Patkar, U P Kulkarni, and M M Math, "Simulink Model for Frame Difference and Background Subtraction comparision in Visual Sensor Network," in 2010 The 3rd International Conference on Machine Vision (ICMV 2010), Hongkong China, 2010.
[10] Yee Ching Yong, Rubita Sudirman, and Kim Mey Chew, "Motion Detection and Analysis with Four Different Detectors," in 2011 Third International Conference on Computational Intelligence, Modelling and Simulation, Langkawi, 2011, pp. 46-50.
[11] Xiaoshi Zheng, Yanling Zhao, Na Li, and Huimin Wu, "An Automatic Moving Object Detection Algorithm for Video Surveillance Applications," in 2009 International Conference on Embedded Software and Systems, Hangzhou China, 2009, pp. 541-543.
[12] S Murali and R Girisha, "Segmentation of Motion Objects from Surveillance Video Sequences using Temporal Differencing Combined with Multiple Correlation," in 2009 Sixth IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance, Genova, Italy , 2009, pp. 472-477.
[13] Li Fang, Zhang Meng, Claire Chen, and Qian Hui, "Smart Motion Detection Surveillance System," in 2009 International Conference on Education Technology and Computer, Singapore, 2009, pp. 171-175.
[14] Takanori Yokoyama, Toshiki Iwasaki, and Toshinori Watanabe, "Motion Vector Based Moving Object Detection and Tracking in the MPEG Compressed Domain," in 2009 Seventh International Workshop on Content-Based Multimedia Indexing, Chania, Crete, 2009, pp. 201-206.
[15] Y Kameda and M Minoh, "A Human Motion Estimation Method Using 3-Successive Viedo Frames," in International Conference on Virtual Systems and Multimedia, 1996, pp. 135– 140.