A CORRELATION BETWEEN THE STU
DENTS’ SPEAKING
ANXIETY AND FLUENCY
(A Study of the Tenth Grade Students of SMA Negeri 1 Karanggede, Boyolali
in the Academic Year 2016/2017)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Broad of Examiners as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
for the Degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd)
in English Education Department
of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
Written By:
ANIS MAYA SURYA
NIM: 113-12-018
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN) SALATIGA
v
MOTTO
“
SCIENCE IS A LIFE FOR HEART FROM BLINDNESS, LIGHT
FOR SEEING FROM CRUEL THINGS AND POWER FOR BODY
FROM WEAKNESS”
(Imam Al Ghazali)
“BE SERIOUS WHEN
LEARNING THE SCEINCE, AVOID
LAZINESS AND BOREDOM CAUSE IF YOU DIDNOT DO
THAT YOU WILL BE IN
DANGER LOSE”
vi
DEDICATION
I dedicate this graduating paper to;
1. Allah SWT always gives me strength, thanks for listening to me, takes care of me, and gives me the best thing ever in my life
2. Rasulullah SAW the best guid and the best inspiration in this life
3. All of my family, especially for my mother (Mrs. Murmiyati) and my father (Mr. Sariyanto), thanks for your guidance, motivation, prayer, supports and everything till I finished this graduating paper, thanks for love that give to me
4. My Sapta Arja Sena, thanks for your prayers and attendance give me power to always move on
vii
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Firstly, In the name of Allah, the most gracious and merciful, the Lord of universe. Because of Him, the researcher can finish this graduating paper as one of the requirements for Sarjana Pendidikan at English Department of Teacher Training and Educational Faculty of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga in 2017.
Secondly, peace and mercy may always be given to our Prophet Muhammad SAW who has guided us from the darkness into the lightness. However, this success would not be achieved without those supports, guidance, advice, help, and encouragement from individual and institution, and the researcher somehow realizes that an appropriate moment for her to deepest gratitude for:
1. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M. Pd, the Rector of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
2. Suwardi, M. Pd, as the Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
3. Noor Malihah, Ph.D, as the Head of English Education Department
ix
ABSTRACT
Maya Surya, Anis. 2017. A CORRELATION BETWEEN THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ANXIETY AND FLUENCY (A Study of theTenth grade students of SMA Negeri 1 Karanggede, Boyolali 2016/2017) in Karanggede district, Boyolali regency. Graduating Paper. English Education Department. Teacher Training Program and Education Faculty. State Institutes of Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga. Consultant: Rr. Dewi Wahyu M, S.S., M.Pd.
Key words: Correlation, Speaking anxiety and fluency.
The research questions were: (1) To describe the students’speaking anxiety of the tenth gradestudents of SMA N 1 Karanggede, (2) To define
the students’speaking fluency of the tenth gradestudents of SMA N 1 Karanggede?, (3) To find the correlation between the students’ anxiety and
speaking fluency of the tenth grade students of SMA N 1 Karanggede?. The researcher conducted the research of the tenth grade students of SMA Negeri 1 Karanggede. In addition, this research used descriptive quantitative approach. The methods of collecting data were questionnaire, test and documentation. The results of the research showed that (1) most of the
students are at “Anxious” level, (2) the result of this result show that most of the students are in the middlespeaking fluency, (3) there are weak
significant relationship between students’ speaking anxiety and their
x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE ... i
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR’S NOTES ... iii
STATEMENT OF CERTIFICATION ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENT ... vii
ABSTRACT ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENT ... x
LIST OF TABLES ... xiv
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Research ... 1
B. Problems of the Research ... 4
C. Objectives of the Research ... 5
D. Limitation of the Research ... 5
E. Benefits of the Research... 5
F. Classification of the Key Terms ... 6
G. Hyphothesis of the Research... 7
H. Graduation Paper Organization ... 9
CHAPTER II:REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Previous Researches ... 10
xi
C. Kinds of Anxiety ... 13
D. Speaking ... 14
E. Aspects of Speaking ... 16
1. Speaking is face to face... 16
2. Speaking is interactive ... 16
3. Speaking happen in real time ... 16
F. Purpose of Speaking ... 17
1. Personal... 17
2. Explanatory... 17
3. Informative... 17
G. Elements of Speaking ... 18
1. Lack of hesitation ... 18
2. Lenght ... 18
3. Independence ... 18
H. Problems in Speaking Activity ... 19
1. Conflict between fluency and accuracy ... 19
xii
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH DISCUSSION
A. Students’ Speaking Anxiety ... 30
B. Students’ Speaking Fluency ... 34
C. Correlations between Students’ Speaking Anxiety and Fluency Scores 36 1. Normality Test ...37
2. Correlation result ...38
D. Discussion of the Data ...39
E. Hyphoteses Test ...40
CHAPTER V: CLOSURE A. Conclusions ... 41
B. Recomendatios ... 43
C. Direction for Future Research ...43
REFERENCES... 44
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Research
Based on 2004 curriculum, one of the aims of learning English is developing the ability to communicate in English in the form of spoken or written text. The ability involves four skills, and they are, listening, speaking, reading and writing.In additition, according to curriculum 2013, the purpose of learning English is increasing students’ ability to communicate in English in the spoken and written form. Moreover, Baker (2001:6) states that there are four language skills that must be mastered by the students, those are speaking, reading, writing and listening. The students can master the language if they can express their ideas and opinions. It means that there are 4 skills that have to be mastered in learning English, and the researcher focuses to discuss speaking in this research.
2
understand the language is by speaking because it is the first way for the students make communication to the listener.
Speaking is one way to communicate ideas orinformationof a message orally. O’Malley & Pearce (1996:59) state that speaking involves two or more people in negotiating meanings, and it always related to the context in which it occurs. Moreover, Gert and Hans (2008:207) say that speaking is speech or utterances with the purpose of having intention to be recognized by speaker and the receiver processes the statements in order to recognize their intention. It means that speaking is speech process which aspeaker needs a partner or listener to speak, and purpose of speaking process is to convey message.
In the speaking activity, there are some processes that have to be through. According to Brown (2001:9), “Speaking is not a single skill rather speaking is an interactive process of constructing meaning that
involves producing, receiving and processing information.” In addition,
Aliya (2007:1) claims that speaking is complicated soul process and productive skill. It could be concluded that speaking is productive process of building, transferring, receiving and processing information. Purpose to convey information that involving speaker and the receiver both verbal and non-verbal interaction.
3
being able to speak is one of indicators of mastering language.Moreover, according to Ur (1996:120), “Speaking seems intuitively the most
important: people who know a language are referred to as ‘speaker’ of that
language, and many if not most foreign language learners are primarily interest in the learning to speak.” In addition, Abousenna (1995:15) claims that in this globalism we live nowadays, the relationship of nations and
countries make a need for global language and no language qualifies for
this better than English.It could be concluded that the important part of
mastering the language is speaking because through speaking the students can express their idea and being able to speak. Moreover, live in this globalism time, it is very principal for the students to master speaking
English because through English they can study abroad, and do many other positive acts.
4
Furthermore, Cui (2011:875) states that anxiety has been believed influencing students in learning new language. In addition,MacIntyre &Gardner (1991:86) claim that anxiety cause potential problem for language learners.It can be concluded that anxiety in learning new language can cause potential problem of doing mistake.
Based on the description above, the students get difficulties to speak English because of the anxiety. That is serious problem that make them speak slowly or even make them lost the words that they want to say.
Based on the reasons stated above, the researcher is interestedto
conduct a research entitled: “A CORRELATION BETWEEN THE
STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ANXIETY AND THE FLUENCY (A Study of
the Tenth Grade Students of SMA N 1 Karanggede in Academic Year 2016/2017)”. The researcher hopes that this research can provide benefit for many people.
B. Problems of the Research
The researcher formulates the problem as follow:
1. How is the students’ speaking anxiety of the tenth grade students of SMA N 1 Karanggede?
2. How is the students’ speaking fluency of the tenth grade students of SMA N 1 Karanggede?
5
C. Objectives of the Research
The objective of the research is:
1. To describe the students’ speaking anxiety of the tenth grade students of SMA N 1 Karanggede
2. To define the students’ speaking fluency of the tenth grade students of SMA N 1 Karanggede?
3. To find the correlation between the students’ anxiety and speaking fluency of the tenth grade students of SMA N 1 Karanggede?
D. Limitation of the Research
The limitation of this research only focuses on the students’ speaking
anxiety which predicted to be correlated to the students’ speaking anxiety. Other factors which arises in the production of speaking are not discussed.
E. Benefits of the Research
By conducting this research, the researcher hopes that her research could give benefit to anybody who reads this research paper. The researcher also hopes that the teachers would give more attention toward
students’ anxiety and the best way on how to overcome students’ anxiety
6
1. Practically
a. For the Teacher
Generally, it enables the students to enrich their knowledge about language skills, especially in speaking skills.
b. For the Students
The findings of this study can be used as a reference in their knowledge about language skills, especially in speaking skills. c. For other researcher
The findings of this study can be used as a reference in conducting an analysis of speaking subject.
2. Theoretically
7
F. Classification of the Key Terms
To avoid any misinterpretations toward the title, the researcher needs to explain the terms in the title as follows:
1. Anxiety
According to Lejla (2011:15), “Anxiety is a fear of expressing oneself orally”. It can be assumed that anxiety gives influence to the students’ speaking ability.
2. Speaking
According to Brown (1994:22),“Speaking is an interactive process of constructing meaning that involves producing, receiving and also
processing information.”It can be said that there are three processes in
speaking those are producing, receiving and processing information. 3. Speaking anxiety
8
G. Hyphothesis of the Research
To know weather there is any significant relation or not between X and Y variables, the researcher formulate Ho (Null Hyphotesis) and Ha (Alternative Hyphotesis) as follows:
1) Null Hyphotesis (Ho) : There is no significant relationship between
X (students’ speaking anxiety) and Y (students’ speaking fluency)
variable.
2) Alternative Hyphotesis (Ha) : There is significant relationship
between X (students’ speaking anxiety) and Y (students’ speaking
fluency) variable.
The significance hyphotesis was formulated as follow:
Ho : r = 0
Ha : r ≠ 0
If rxy>rtable means There is significant relationship between X and Y
variable. Ha is accepted and Ho is rejected.
If rxy<rtable means There is no significant relationship between X and
9
H. Graduation Paper Organization
This graduating paper consists of five chapters. Each chapter is going to discuss such terms:
Chapter I is introduction.It is explains of the background of the research, problemsof the research,objectives of the research, limitation of the research, benefitsof the research, classificationof the key terms, hyphotesis of the researchand graduating paper organization.
Chapter II is review of related literature.It is explains about the previous study, the theories of keyword based on the experts.
Chapter III is research methodology. It is consists of general description of SMA N 1 Karanggede, method of the research, population and sample, time allocation of the research, subjects of the research, technique of instrument and data collection.
Chapter IV is research discussions. It is present the data analysis.
10
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF LITERATURES
A. Previous Researches
There are some related researches have been done previously. Those previous researches are discussed in the following paragraphs.
Firstly,Thorky (2006) who had done the research of the effectiveness of a task-based instruction program in developing the English language speaking skills of secondary stage students. In this research, the researcher usedtest instrument that was adapted from Horwitz. In the conclusion, there were significant correlations in the students’ speaking skill and anxiety.
Secondly, Praditha (2014) who had done the research ofthe relationship between students’ anxiety and their English reading comprehension. In this research she used survey employing correlation study. In her conclusion, there were no significant correlation between
students’ anxiety and their English reading comprehension.
11
research, the researcher usedan application and questionnaire.In the conclusion, there were significant correlation between students’ guided individual activities and their speaking skill.
Those previous researches are used as comparisons and foundations of
this research. This research is a correlation between the students’ speaking
anxiety and fluency. The difference between this research and Praditha (2014) are the objective of this research isgrammar, whereas the objective
of Pradhita’s research is reading comprehension.
Then, the difference between thisresearch with Thorky (2006) is the first variable of this research is speaking anxiety whereas the first variable
of Thorky’s research is grammar. In addition the objective of this research
is speaking fluency whereas Thorky’s research is speaking skill.
The last, the difference between this research and Kamiskiene and Kavaliauskiene (2014) is the first variable. The first variable of this research is speaking anxiety whereas the first variable of Kavaliauskiene is attitudes.It can be concludedthat this research contains different variables and object with those three previous researches above, namelyanxiety and speaking fluency.
B. Anxiety
12
addition,according to Lanerferdt (1992:53-54), “Anxiety is something that has a great impact on students self-confidence since it often made students experience failure when not being able to speak out and show what the students knows.”It means that anxiety is feeling of worry that make the students cannot speak well or even fail in the speaking process.
According to Lightbown and Spada (2003:60-61), “Anxiety is something that is more likely depend on special situation that can make the students feel uncomfortably for example, an oral presentation in front of a
large group people.” Further, MacIntern (1999:27) states that anxiety is
worry and negative emotional reaction appears when learning or using the second language. It could be concluded that anxiety is a feeling of fear and negative reaction that can happen in the common or certain situation in the learning process.
13
C. Kinds of Anxiety
Macintyre and Gardner (1991:85-177) divide anxiety into two types, trait anxietyand state anxiety. Trait anxiety is a sense of uneasiness that may be experienced at a particular moment in time, as a responds to a certain situation. Another definition of trait anxiety according toHuberty (2009:13), “Anxiety refers to anxiety that occurs in specific situations and usually has a clear trigger.”Itmeans that state anxiety is felling of worry that happen in the certain situation.
Otherwise, state anxiety according toMacIntyre and Gardner (1991:85-117), “Anxiety is people with high level of trait anxiety (i.e. people who are anxious in general) are usually likely to get an increase state anxiety.” Another definition of state anxiety according to Spielberg (1966:3-20), “Trait anxiety is refers to student’s possibility of becoming anxious in any situation.”It could be concluded that trait anxiety is an anxious feeling that may happen whenever it is.
14
D. Speaking
Speaking is one of basic skills when the students learning English. In order to make sure that the researcher knows exactly what speaking is, the researcher writes some definitions of speaking because one definition is not enough to define the term of speaking. Thus, here are some definitions of speaking according to some experts in the following paragraphs.
Brown (1994:22) states thatspeaking is an interactive process of constructing meaning that involves producing, receiving and also processing information. In addition, according to Carter & Canthy (1997:124), “Speaking is one of the types composing in language, the type that is swift, complicated, frequent and primary, because the language itself is a symbolic to use by communicators to construct and convey
information.” It means that speaking is a complex process of constructing
meaning to convey a message.
15
According to Richard and Renandya (2002:204), “Effective oral communication requires the ability to use the language appropriately in social interaction that involves not only verbal communication but also paralinguistic element of speech such as pitch, stress and intonation. Furthermore, nonlinguistic elements such as gesture, body language and expression are needed in conveying message directly without any accompanying speech. Moreover, Stack (1996:83) claims that speaking is sound production including training in correct positioning of the vocal organs and formation of linguistic habit through intensive practice. It means in speaking it is not only about conveying an utterance, but also involves another thing such stress or intonation that can make it clearer.
Speaking ability is indeed an important aspect in learning a certain language. Huebner (1960:4) states that Language is very important speech, and speech is basically communication by sounds. To sum up, from the definition above speaking is an interactive process of sound producing by their speech organ that involves complex skill to convey message. Therefore, the goal of speaking is the students can express their feeling.
16
E. Aspects of Speaking
1. Speaking is face to face
According to Cornbleet & Carter (2001:16), “Most conversation takes face to face which allows speakers to get immediate feedback.” In addition, Fayoumy (1997:10) says that speaking has many assets, such as facial expression, gestures and even body language. Speaking also occurs, most of the time, in situation where the participants are present. It means that in the speaking process usuallythe studentstake face to face position because it involvessome elements such us facial expression and body language.
2. Speaking is interactive
Miller (2001:27) state that in the speaking process usually it turns smoothly and involves participant contribution that should not be there is a gap between them. Moreover, Hughest (2002:76) claims that the use of the formulations such as; expression, self-correction, and repetition can help speaker become more fluent in speaking English. Then it can make the conversation run well. It can be concluded that speaking process itself need an interaction between the speaker and listener. The speaker cannot speak fluently if there is not good team work between the speaker and listener.
3. Speaking happen in real time
17
speaker often starts to say something and change in the mid-way. The
speakers’ sentence cannot be as long or as complex writing. It means
that the speaking process happen in the real time. It makes the speaker can convey their message freely, although sometimes they may change their topic or even forget about the thing that they want to say.
F. Purpose of Speaking
According to Kingen (2000:281) there are several purposes of speaking those are;
1. Personal
Trough speaking students can expresstheir personal feelings, opinions, believe and idea about the picture that they were described.
2. Explanatory
The students explaining, supporting ideas and opinions about the subject that they were described.
3. Informative
18
G. Element of Speaking
The element of speaking in this research only focuses on speaking
fluency. Fluency is also used as a criterion to measure one’s speaking
competence. Speaking fluently means being able to communicate one’s
ideas without having to stop and think too much about what one is saying. Richard (1992:141) defines fluency as the features which give speech the qualities of being natural and normal. More specifically, Burry (2005) points out the criteria for assessing fluency. They are as follow:
1. Lack of hesitation: students speak smoothly, at a natural speech. They do not hesitate long and it is easy to follow what they are saying.
2. Length: the students can put ideas together to form a message or an argument. They can make not only the simplest of sentence pattern but also complex ones to complete the task.
19
H. Problem in Speaking Activity
In this research the researcher only focueses on the speaking anxiety problem. Even if they are not inhibited, the researcher is often heard the students complain that they cannot think if nothing to say or feel anxious; they have not motive to express themselves beyond the guilty feeling that they should be speaking.
According to Scarcella and Oxford (1994:165) sum several problem faced by the students while speaking English those are:
1. The conflict between fluency and accuracy: though the students may gain confidence in using new language by being let uncorrected, the sudents language will continue to be inaccurate/incorrect.
20
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METODOLOGY
A. General Description of State SMA Negeri 1 Karanggede
The researcher conducted at SMA N 1 Karanggede. SMA Negeri 1 Karanggede is located at Jl. Sawungrono KM 2 Karanggede district, Boyolali regency 35383. SMA Negeri 1 Karanggede was built above 20.605m2. SMA Negeri 1 Karanggede has a headmaster, fifty four teachers and eleven staffs. Totalof thestudents of SMA N 1 Karanggede on 715 January 2016.
B. Method of the Research
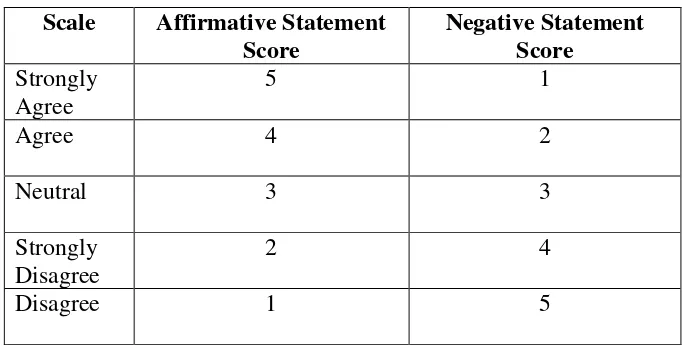
The research method in this study was quantitative research. According to Kasmiran (2010:172) states that,
Quantitative research is a process to get knowledge that applies the nominal data as a tool to analyze the information what we want to know. The descriptive research is a research which is purposed to give the fact. Indication and phenomenon systematicly and accurately about the characteristic of the population in certain area, thus the purpose of this research is to describe systematically the facts and the characteristics of a given population or area of interest, factually and accurately. Descriptive method is not only limited to collect and arrange the data, but also to analyze and interpret the meaning of the data.
21
Karanggede because they were still in the process of adapting with new condition in the high school and they were also have adapting with the new member of the class.
The researcher used correlation study. The correlation research design was chosen to find out whether or not relationship that exist between two variables of the research. The independent variable of the research is the students’ speaking anxiety as X variable, and the
dependent variable of the research is students’ speaking fluency as Y
variable.
C. Population and Sample
According to Gay (1992:125), “Population is the group of interest
to the researcher, the group to which they would like the result of the study to be generalizes”. In this research, the populations were the students in tenth grade students of SMA N 1 Karanggede in the academic year 2016/2017of science students’ classes(125 students) and they were social students’ class (134 students).The totals of tenth grade students were 254 students that divided into 8 classes. Arikunto (2010:174) states thatsample is part of the representative of population that is observed.Moreover, Arikunto (2002:112) also states if the subject less than 100, it is better taken all so it is research constitutes population. Then if the total subject outgrow, therefore get among been taken 10-25% or
22
In taking sample, the researcher used random sampling because it is more practical to use in large number of population. Based onthe approach that is used by the researcher in taking the sample,the researcher randomly took 16% students from 254 students that were 40 students.
D. Time Allocation of the Research
The research was conducted from January 25th until February 08th, 2017. The detail time is provided in the following table:
Table.3.1
Time Allocation of the Research
Num. Date Activities
1. November 14th,2016 Researcher submitted the proposal 2. January 23th, 2017 Researcher gave the letter in relation to
asking permission to conduct research. 3. January 25th, 2017 Researcher gave the letter to meet the
teacher in relation to make schedules. 4. January 31th Researcher distributed the
questionnaire. 5. February 1th- February
7th, 2017
Researcher conducted speaking test.
23
E. Subjects of the Research
The subjects of the research were studentsat two classes those are, science and social classesof SMA N1 Karanggede. The students were taken from grade tenth grade students at science and social classes. They were taken from different classes. The researcher took 15% from total 254 students those were 40 students.
F. Technique of Instrument and Data Collection
To collect the data, the researcher used two instruments. They were questionnaire for assessing the students’ anxiety level and descriptive speaking test to measure the students’ speaking comprehension.
1. Questionnaire
24
The questionnaire translated into Bahasa Indonesiaenclosed. Thisaims to avoid the possibility of different perception in understanding the statement. Therefore, using Bahasa Indonesia in the statement wasuseful for the students to understand and answer the question.
2. Test
The test instrument played an important role in collecting the data. According to Arikunto (1992:115), “Test is a set of stimulus that is given to the students that aims at getting answer as the basic of scoring.”To get the data the researcher used test to know the students comprehension.
25
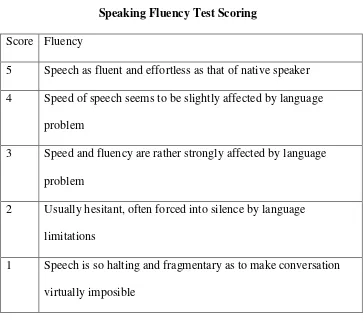
orally.According to Haris (1969:84-85) all good speaking fluency must be rated by the following criteria;
Table 3.3
Speaking Fluency Test Scoring
Score Fluency
5 Speech as fluent and effortless as that of native speaker 4 Speed of speech seems to be slightly affected by language
problem
3 Speed and fluency are rather strongly affected by language problem
2 Usually hesitant, often forced into silence by language limitations
1 Speech is so halting and fragmentary as to make conversation virtually imposible
3. Documentation
26
Theresearcher also recorded the test using recordingthen transcribing it. The researcher form used to support and help the recording data in case the recoding data lost or did not clear. Bigklen (1992:121) cited in Cresswel (2001:182) that recording is a tool to divide or separate descriptive notes from reflective notes. This can be meant that recording is
an activity to get data and it is used to support the researcher’s analysis.
The researcher took recording during asking the students to describe the picture that already prepared.
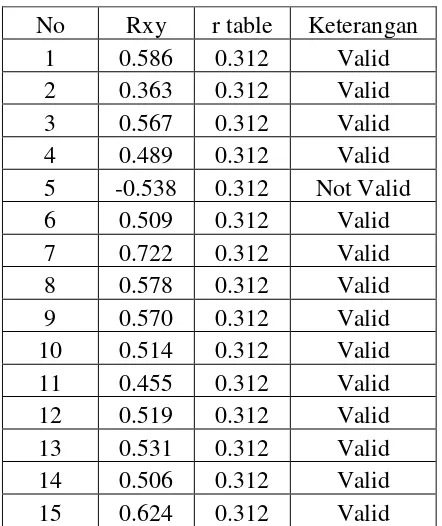
4. Validity of the Instrument
27
a. Validity of questionnaire
Table 3.5
Questionnaire Validity
From the result it can be seen that from 15 questionnaire there were 14 valid and 1 questionnaire that were in valid. It can be said that the researcher only could gave 14 questions to the students.
b. Reliability of Instrument
The researcher used SPSS 16 in order to know the reliability of questionnaire. The result can be seen as below:
28
Table 3.5
The Reliability of Questionnaire
Reliability Statistics
Reliability Statistics
Cronbach's Alpha N of Items .821 14
From the result it can be seen that rresult=0.821. Then the researcher compared to rtable with N=40 and 5% as significance level, that is rtable =0.312. It can be concluded that the instrument is reliable because rresult>rtable=0.821>0.312. Those the researcher can conclude that the instrument is reliable.
5. Data Analysis
After getting the data from questionnaire and speaking test, the researcher analyzed the data by using comparative technique. The researcher compared the data from questionnaire and speaking test.
29
moment test to find out the correlation score of students’ speaking anxiety and their speaking fluency. The formula as follows:
𝑟𝑥𝑦 = N(∑ XY) − (∑ X). (∑ Y)
√[N ∑ X2− (∑ X2)]. [N ∑ Y2− (∑ Y2)]
𝑟𝑥𝑦 : The number of index correlation ‘r’ product moment
𝑁 : Number of Cases
∑ 𝑋𝑌 : The sum of multiplication between deviation of variable
X : scores and deviation of variable Y scores
∑ 𝑋 : The sum of X scores
∑ 𝑌 : The sum of Y scores
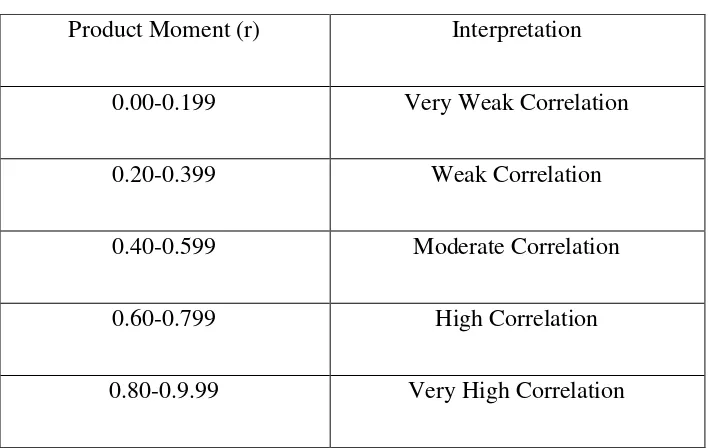
After r was found, then the researcher interprets based on following level of correlation by Arikunto (1999:15) as followed;
Table 3.6
The Level of Correlation
Product Moment (r) Interpretation
0.00-0.199 Very Weak Correlation
0.20-0.399 Weak Correlation
0.40-0.599 Moderate Correlation
0.60-0.799 High Correlation
30
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDING AND DISCUSSION
A. Students’ Speaking Anxiety
In this chapter the researcher shows the result of data that the researcher got from the test, whereas the participants of the test was tenth grade students os SMA N 1 Karanggede. There were two kinds of test; they were speaking anxiety test and speaking fluency test.
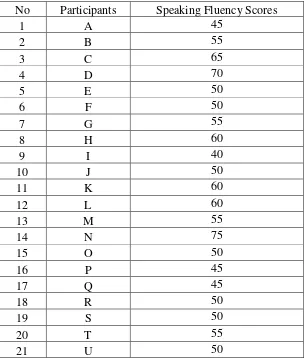
The statistical calculation of 40 the students’ anxiety score and their
speaking fluency were calculated. The total students’ anxiety score were 1842 and the students’ speaking fluency got the total score 2310. The result of anxiety score and speaking fluency score can be seen as follow:
Table 4.1
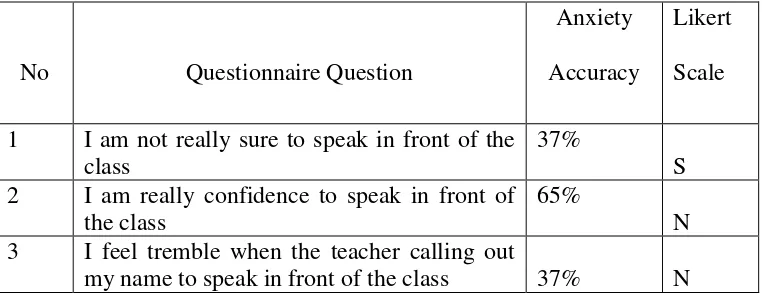
Table 4.1 Scores of Anxiety Occurances of the students
31
4 I am always think that my friends can speak
better than me 45% N
9 I am usually cannot concentrate well when I
feel anxious 57% S
speaking than writing, reading and listening 45% S 13 When I am in the speaking class I feel calm
and confidence 52% N
14 I am afraid if my friends will laugh at me if I
fail to pronounce well 35% TS
This table was table appearance of anxiety of the students’ that looked
from the homogeneity of the data. Number one was dominated by “S” with
score resist 37,5%. Number two was dominated by “N” with score resist
65%. Number three was dominated by “N” with score resist 37,5%.
Number four was dominated by “N” with score resist 45%. Number five
was dominated by “S” with score resist 40%. Number six was dominated
by “S” with score resist 40%. Number seven was dominated by “S” with
score resist 67,5%. Number eight was dominated by “S” with score resist
45%. Number nine was dominated by “S” with score resist 57,5%.
Number ten was dominated by “N” with score resist 47,5%. Number
32
dominated by “S” with score resist 45%. Number thirteen was dominated
by “N” with score resist 52,5%. Number fourteen was dominated by “TS”
with score resist 35%. It could be concluded that students anxiety score were high it showed from there are 7 questionnaire that showed students
answered dominated by “S”.
Furthermore, the researcher will show another data about students
speaking anxiety score. This is to gain the students the most students’
fluency in speaking. It present in the following table:
Table 4.2
Students’ Speaking Anxiety Score
34
41 Total 1842
B. Students’ Speaking Fluency
The result of this test, then will be analyzed in the next section to see if
there is any correlation between students’ speaking anxiety and speaking
fluency. The researcher shows in the table below:
TABLE 4.3
Speaking Fluency Scores
No Participants Speaking Fluency Scores
35
C. Correlations between Students’ Anxiety and their Speaking
FluencyScores
To see how significance is the relationship between students’ anxiety and their speaking fluency, it is calculated through Pearson Product moment formula. Before calculating the data, here are the results of X and Y scores:
N = 40
36 ∑ 𝑌 = 2310
∑ 𝑋𝑌 = 106465
∑ 𝑋2 = 86344
∑ 𝑌2 = 136900
After the calculation of whole data from X and Y variables, the next step is to insert the data from the table into the Pearson Product moment formula to find the correlation between X and Y variables as follow:
r = 𝑁 ∑ 𝑋𝑌−(∑ 𝑋)(∑ 𝑌)
√[(𝑁 ∑ 𝑋2−(∑ 𝑋)2)][(𝑁 ∑ 𝑌2−(∑ 𝑌)2)]
r = 40𝑋106465−(1842)(2310)
√[(61796)−(139900)][(5476000−(5336100)]
r = 3580 √8645260400
r = 3580 92979,89 r = 0,038
37
1. Normality Test
The researcher used SPSS 16 to count the normality of each instrument. The instrument would be normal distribution if the result of calculation from SPSS 16 showed less than the result from Shapiro-Wilk table with the number of sample (n) is 40.
These tests are valued using SPSS 16. The normality Using One-Sample Shapiro-Wilk test result can be seen as bellow:
Table 4.4
Normality Data of Variable X and Y
Tests of Normality
Kolmogorov-Smirnova Shapiro-Wilk
Statistic Df Sig. Statistic Df Sig. ANXIETY .105 40 .200* .956 40 .118
SPEAKING .143 40 .037 .959 40 .152 a. Lilliefors Significance Correction
*. This is a lower bound of the true significance.
38
Hypothesis:
Ho : Population are normally distributed
Ha : Population is not normally distributed (randomly distributed)
Criteria of normality test are:
Ho is rejected if probability of significant value < 0.05
Ha is accepted if probability of significant value > 0.05
2. Correlation result
Table 4.5
The Result of Correlation Calculation
From the table, the researcher describes that r coefficient is 0.039 and the sig; (2-tailed) is 0.812. Theresearcher looked to r table as mentioned in chapter III.
From the table rresultisincluded in the first category (0.00-0.20) that
describes that there isveryweak correlation between X variable and Y
Correlations
ANXIETY SPEAKING ANXIETY Pearson Correlation 1 .039
Sig. (2-tailed) .812 N 40 40 SPEAKING Pearson Correlation .039 1
Sig. (2-tailed) .812
39
variable. It is can be conclude that there is very weak correlation between X and Y variable. The result showed rxy<rtable=0.039< 0.312. it means that
Ho is accepted and Ha is rejected. Itcan be concluded that the higher
students’ anxiety does not guarantee the lower students’ speaking fluency
or else it can be stated that there is very weak significant relationship
between students’ speaking anxiety and their speaking fluency.
D. Discussion of the Data
Based on the analysis above, there was very weak relationship between the students’ speaking anxiety and their fluency. In the data analysis, the result of the normality test both questionnaire and speaking fluency test showed that the data were normally distributed. After that Pearson Product Moment formula was conducted to know the result of hypotheses. Then the result showed if rtable>rresult, it means that Ho is accepted. Therefore it can be stated that there were very weak significant
relationship between students’ speaking anxiety and their speaking
fluency.
Moreover in the data analysis of the students’ speaking anxiety and
their speaking fluency showed rxy<rtable =0.03<0.312. Thus, it means that
there was very weak correlation as compared with the level of correlation.
Hence the highest students’ anxiety does not guarantee the lower students’
40
E. Hypotheses Test
As describe in previous chapter that, if rxy>rtablemeans there isvery
weak relationship between X and Y variable, Ha is accepted and Ho is rejected. Then if rxy<rtablemeans there is no significant relationship
41
CHAPTER V
CLOSURE
A. Conclusion
This research aimed to investigate the students’ speaking
anxiety and their speaking fluency. Based on the research findings, the researcher conclude that:
1. The result of this result shows that most of the students are at
“Anxious” level. There are 7 questionnaire who experience “Anxious”
level, those are number 1,5,6,7,8,9, and 12. There are 6 questionnaire
who experience “Mildly Anxious” level, those are number
2,3,4,10,11, and 13.There are 1 questionnaire who experience
“Relaxed” level, that is number14.
2. The result of this result shows that most of the students are in the fair speaking fluency.
42
meanwhile the result from rtable in 5% significance level is 0.312. Thus
rxy is lower than rtable or it can be stated that rxy< rtable: 0.039<0.0312.
The result means that there is no significant relationship between
students’ speaking anxiety and their speaking fluency at the tenth
grade students’ of SMA N 1Karanggede, Boyolali in the academic
year 2016/2017. The conclusion shows that the higher students’
anxiety does not guarantee the lower students’ speaking anxiety.
B. Recommendations
The result of research says that the students’ speaking anxiety
and their speaking fluency is good enough. Dealing with this result, many factors were seen as the cause of the problem. Therefore, it would be wise to convoy recommendations to improve the students’ speaking fluency especially into Report text teaching and learning process in SMA N 1 Karanggede. Here are some recommendations towards this research.
1. Enriching teachers’ knowledge of speaking anxiety.
43
3. Developing the relationship between teachers and students to
cooperate in succeeding overcoming the students’ speaking
anxiety.
C. Direction for Future Research
This research focused on the students’ perspective on the
47
REFERENCES
Abousenna, M. (1994). “Opening Speech. Global Age: Issues in English Language
Education". Proceedings of 13th National Symposium on English Language
Teaching. March 30-April 1, 1993. CEDELT, Ain Shams University.
Atta, A.M. S. S.,& Mosaad A.A.D. (2014). The Relationship between Speaking Anxiety and
Oral Fluency of Special Education Arab Learners of English.Canadian Center of
Science and Education. 10(12).
Arikunto, S. (2002). Prosedur Penelitian, suatu Pendekatan Praktik. Jakarta: PT Intan Putra
Arikunto, S. (2010). Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan Praktik. Jakarta : Rineka Cipta.
Bailey, K.M. (2003). Speaking in Nunan, David (Editor), Practical English Language
Teaching. Singapore:McGraw-Hill. p. 47-66.
Baker, J., and Westrup H (2001). Essensial Speaking Skill. A Handbook for English
Language Teachers, London:Continuum
Brown, G., Yule., &George. (1994). Teaching the spoken Language. Cambridge University Press
Brown, H.D. (1994). Teaching by Principles: An Interactive approach to Language
Pedadgogy. New Jersey: Prentice Hall
Brown, H.D. (2001). Teaching by Principles: An Interactive approach to Language
Pedadgogy. New York: Logman
48
Charter, R. & Michael, M. (1997). Exploring Spoken English, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press,
Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, Kurikulum 2004, Standar Kompetensi Bahasa Inggris,
Sekolah Menengah Atas dan Madrasah Aliyah, (Jakarta:2003), p.14
Efrizal, D. (2012). Improving Students’ Speaking through Communicative Language Teaching Method at Mts Ja-alhaq, Sentot Ali Basa Islamic Boarding School of Bengkulu, Indonesia. 2(20).
Fauzan, U. (2014). The Use of Improvisation technique to improve the Speaking ability of EFL students. DINAMIKA ILMU. 14(2).
Gay, L. R & Airasian, P. (1992). Educational Research: Competences for Analysis and application. USA:Prentice Hall
Horwitz, E. K., Horwitz, B., & Cope, J. (1986). Foreign Language Classroom anxiety. The
modern Language Journal, 70, p. 125-132.
Cui, J.(2011). Research on High School Students’ English Learning Anxiety; Journal
Language Teaching and Research, 2, p.875
Kasiram, M. (2010). Metodologi Penelitian Kualitatif-Kuantitatif. Malang:UIN Maliki Press.
Kamiskiene, L.&Kavaliauskien, G. (2014). Attitudes to improving speaking skills by guided individual activities. SANTALKA: Filologija, Edukologija/Coactivity:Philology, Educology, 22(1), p.39-48.
Lanerfeldt, M. T. A part of: Rudberg, L. (1992), (Red.), Barns tal- och språksvårigheter.
Lund: Studentlitteratur.
49
Lightbown, P.,& Spada, N. (2003).How languages are learned. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
MacIntyre, P.D., & Gardner,R.C.(1991a). ‘Language Anxiety: Its Relationship to Other
Anxieties and to Processing in Native and Second Languages’, Language
Learning 41, p. 85-117.
McCarthy, M. (1998). Spoken Language and Applied Linguistics. Cambridge: Cambridge
University Press.
Melouah, A. (2013). Foreign Language Anxiety in EFL speaking classrooms: A case study of first-year LMD students of English at Saad Dahlab University of Blida, Algeria.
Arab world English Journal, 4(1), p. 64-76.
O’maley, J.M.,& Pierce, L.V. (1996). Authenthic Assessment For English Language
Learners. Practical Approach For Teachers. Addison-Wesley Publishing
Company.
Praditha, S.N. (2014). The Relationship between Students’ Anxiety and their English
Reading Comprehension. Syarief Hidayatullah State Islamic University.
Rebecca, H. (2006). SpokenEnglish, TESOL, and Applied Linguistics: Challange for Theory
and Practice. Great Britain: CPI Antony Rowe
Richards, J. C., & Renandya, W. A. (2002). Methodology in Language Teaching:
An Anthology of Current Practice.Cambridge University Press:New York.
Rickheit, Gert, Stronher., &Hans. (2008). Hanbook of Communication Competence. Germany
Saito, Y.E.K. Horwitz., & Thomas, J. G. (1999). Foreign Language Reading Anxiety, The
50
Spielberger, C. S. (1966). Theory and research on anxiety. In C. S. Spielberger (Ed.), Anxiety and Behaviour, Academic Press, New York, p. 3-20.
Thorky, A. S. E. F. (2006). The Effectiveness of a Task- Based Instruction program
inDevelopingthe English Language Speaking Skillsof Secondary Stage Students.
Ain Shams University
Ur, P. (1996) A course in language teaching: practice and theory. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Young, D. J. (1990). An investigation of students’ perspectives on anxiety and speaking.
Foreign Language Annals, 23(6), p. 539–553.
51
APPENDIX 1
The Correlation Score of X and Y Variable
52
1. Jawablah pertanyaan ini dengan jujur.
2. Berilah tanda checklist (V) pada jawaban anda B. Biodata responden (penjawab pertanyaan)
1. Nama :
53
2 Saya sangat percaya diri ketika berbicara (speaking) di depan kelas
3 Saya gemetaran ketika dipanggil untuk berbicara (speaking) di depan kelas
4 Saya selalu berpikir bahwa teman-teman saya lebih baik dalam berbicara (speaking) dari saya 5 Saya merasa tenang ketika berbicara (speaking) di
depan kelas
6 Saya biasanya mulai panik ketika harus berbicara (speaking) tanpa persiapan
7 Saya khawatir gagal dikelas berbicara (speaking) 8 Ketika gerogi berada di kelas berbicara (speaking)
biasanya saya lupa kosa kata yang sudah saya tahu 9 Walaupun saya sudah mempersiapkan dengan
baik sebelum berbicara (speaking) di depan kelas saya tetap merasa khawatir
10 Saya biasanya tidak bisa berkonsentrasi dengan baik ketika merasa gugup
11 Saya merasa saya juga bisa berbicara (speaking) dengan baik
12 Saya sangat merasa khawatir berbicara (speaking) di depan kelas
13 Saya merasa lebih tertekan dan grogi ketika berbicara (speaking) di bandingkan dengan menulis (writing), membaca (reading) maupun mendengarkan (listening)
14 Ketika saya berada di kelas berbicara (speaking) saya merasa tenang dan percaya diri
15 Saya takut kalau teman-teman saya akan menertawakan saya ketika saya melakukan kesalahan pengucapan (pronounciation) di kelas berbicara (speaking)
APPENDIX 3
57
APPENDIX 4
The Answer of Students’ Anxiety Test
No Nama 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Total
1 A 2 2 4 3 4 4 4 4 4 3 3 2 3 2 3 72
2 B 3 3 4 3 2 3 4 4 4 3 4 4 3 4 2 75
3 C 1 2 3 3 4 3 4 3 4 4 2 4 4 2 4 72
4 D 2 3 2 3 3 3 2 4 3 3 2 2 3 3 3 66
5 E 3 3 3 3 2 4 3 3 3 4 4 3 3 4 3 73
6 F 2 3 2 4 3 4 2 4 3 4 2 2 2 3 1 66
7 G 2 3 3 3 3 3 2 4 3 3 2 2 2 3 2 65
8 H 2 2 2 4 4 5 4 4 4 4 3 2 4 2 2 73
9 I 3 2 4 4 2 5 2 4 4 4 2 3 4 3 3 74
10 J 3 4 3 4 2 5 4 4 4 4 3 3 4 4 3 79
11 K 4 3 4 4 2 4 4 4 3 4 3 4 4 4 4 80
12 L 4 3 4 3 2 5 4 5 4 3 3 4 4 4 4 81
13 M 3 2 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 2 4 2 2 2 74
14 N 3 3 4 4 3 5 4 4 3 3 2 4 3 3 3 76
15 O 3 2 4 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 3 2 70
59
APPENDIX 5
The Students’ Speaking Fluency Test
62
Appendic 8
CURICULUM VITAE
Nama : Anis Maya Surya Tempat, Tanggal Lahir : Boyolali, 13 Juli 1995 Jenis Kelamin : Perempuan
Agama : Islam
Alamat : Ds. Guwo RT 09 RW 02,
Kecamatan Kemusu, Kabupaten Boyolali Pendidian Terakhir : S1 Pendidikan
IPK : 3.51
Status : Belum Kawin
Telp/Hp : 085211563570
RIWAYAT PENDIDIKAN
1. SD N GUWO 2 (LULUS TH 2006)
67
DECLARATION AND PERMISSION FOR PUBLICATION
I have been marked below:
Name : Anis Maya Surya NIM : 113-12-018
Faculty : Teacher Training and Education Faculty Department : English Education Department
Declares that this graduation paper is written by the researcher and it does not copy from other researchers. Theories and citations are used codes of ethrics of writing for graduating paper. I give permission to publish this graduating paper on
IAIN Salatiga’s e-repository.
Salatiga, September 20th 2017 The researcher,