SELF-
DIRECTED
LEARNING OF SENIOR
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS IN LEARNING
ENGLISH AT HOME SCHOOL PENA
THESIS
Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S. Pd.) In Teaching English
By:
Hanifatul Ummah D05212037
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHER TRAINING
SUNAN AMPEL STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Sebagaisivitasakademika UINSunanAmpel Surabaya, yang bertandatangan di bawahini, saya:
Nama : Hanifatul Ummah
NIM : D05212037
Fakultas/Jurusan : FTK/Pendidikan Guru Bahasa Inggris
E-mail address : ummah.hani@gmail.com
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, menyetujuiu ntuk memberikan kepadaPerpustakaanUIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, Hak Bebas Royalti Non-Eksklusifatas karya ilmiah :
SkSekripsi Tesis Disertasi Lain-lain (………)
yang berjudul :
SELF DIRECTED LEARNING OF SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS IN LEARNING ENGLISH AT HOME SCHOOL PENA
Berseta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan Hak Bebas Royalti Non Ekslusifini Perpustakaan UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya berhak menyimpan, mengalih-media/format-kan, menelolanya dalam bentuk pangklan data (data base), mendistribusikannya, dan menampilkan/mempablikasikannya di Internet atau media lain secara fulltext untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta izin dari say selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis/pencipta atau penerbit yang bersangkutan.
Saya bersedia untuk menanggung pribadi tanpa melibatkan pihak Perpustakaan UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, segala bentuk tuntutan hokum yang timbul atas pelanggaran Hak Cipta dalam karya ilmiah saya ini.
Demikian pernyataan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya.
Surabaya, 28 Agustus 2016
Penulis
( Hanifatul Ummah)
KEMENTERIAN AGAMA
UNIVERSITAS ISLAM NEGERI SUNAN AMPEL SURABAYA
PERPUSTAKAAN
ABSTRACT
Ummah, Hanifatul. (2016). Self-Directed Learning of Senior High School Students in Learning English at Home School Pena.A Thesis. English Teacher Education Department, Faculty of Education and Teacher Training, State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel, Surabaya. Advisor: Dra. Hj. Arba’iyah YS., MA
Key Words: self-directed learning, independency in learning, SDL skill, SDL activities and SDL barrier.
Self-directed Learning, as a key component for 21st century learning skill, is important to be studied, developed and adopted. Self-directed learning is a
process during the learner takes the initiative and the responsibility for the whole
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
COVER ... i
ADVISOR APPROVAL SHEET ... ii
APPROVAL SHEET ... iii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xiv
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Research Question ... 7
C. Objective of the Study ... 7
D. Significance of the Study ... 8
E. Scope and Limitation of the Study ... 9
F. Definition of Key Term ... 10
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Review of Related Literature... 12
1. Self-Directed Learning... 12
2. Self-Directed Learning Model... 15
3. Self-Directed Learning Skill... 19
4. Self-Directed Learning Barrier... 21
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHOD
A. Research Design ... 32
B. Research Setting ... 33
C. Subject of the Study ... 34
D. Research Instrument ... 34
E. Data Collection Technique ... 36
F. Data Analysis Technique ... 37
CHAPTER IV: RESULT AND DISCUSSION A. Research Finding ... 39
1. Self-Directed Learning Activities in Learning English ... 39
2. Self-Directed Learning Skill ... 48
3. Self-Directed Learning Barrier in Learning English ... 52
B. Discussion ... 59
1. Self-Directed Learning Activitiesin Learning English ... 59
2. Students’ Self-Directed Learning Skill ... 66
3. Self-Directed Learning Barrier in Learning English ... 67
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion ... 70
B. Suggestion ... 71
LIST OF TABLE
Table 2. 1 Scoring Range of Self Rating Scale in Self Directed Learning ... 24
Table 2. 2 Locus of Control ... 30
Table 3. 3. Scoring range of Self Rating Scale in Self Directed Learning ... 37
Table 4. 4 The result of Students’ Self Rating Scale of SDL ... 40
LIST OF DIAGRAM
Diagram 4. 1 Distribution of Students’ Self-Directed Learning Skill ... 41
LIST OF ABBREVIATION
1. SDL
SDL stands for Self Directed Learning
2.ESP
1
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
This chapter gives an overview of the the background of study the
problems of study, objectives of study, significance of study, scope and limitation
and definitions of key terms used in this thesis.
A. Background of The Study
Because language is too complex1 and varied for students to learn, learning
language needs persistence and practice. The language classroom with limited
time cannot improve the students’ skill maximally. How good a teacher may be,
students will never learn language well unless they learn it outside the class.2
Therefore, independent learning of a foreign language is needed for learners.
As learning language, English in this case, is too complex3 so that students
cannot count only on face-to-face meetings with teacher. However, what occurs
on home school Pena is that students have limited face to face meeting to study
English. The home school has concept or approach different from formal schools
which allow them to participate in limited face-to-face meeting. Therefore, the
research which studied the students’ self-directed learning in learning English in
home school is important to conduct.
As a learner has a center role of learning, self-directed learning is part of
educational process but it does not depend on the process of institutionalized
1
Janice Yalden, The Principle of Course Design for Language Teaching. (England: Cambridge University Press, 2000), 149
2
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice Of English Language Teaching(England: Pearson Education, 2001), 335
3
2
education.4 Hence, self-directed learning practice is not limited on the certain
educational place such as formal school and university. Many of self-directed
learners are those taking online course5 and those conducting their own learning
project. Therefore, it is needed to know students’ preference in choosing
self-directed learning activities which they do outside the class to pursue the learning
goal while they have lack of classroom meetings.
Self directed learning is a learning process in which learner takes the
initiative to pursue a learning experience and responsibility for completing their
learning.6 In other words, self directed learning can be defined as self study which
is done by learners with full consideration and goal-oriented learning process.
Not only as a process, can self-directed learning be viewed as a skill. The
degree to which the learner maintains active control of the learning process is
called as directedness or directed learning skill. This ability to do
directed learning can be measured and analyzed through rating scale for
self-directed learning. Therefore, this study is also aimed to investigate the students’
level of self directed learning skill so that students can know how far they have
ability to control and maintain the learning process on their own.
In addition to study self-directed learning activities and students’ level of
self directed learning skill, the students’ self directed learning barrier is also
important to investigate. It will ease the learners to diagnose the factors resisting
them to do self-directed learning activities. Through knowing this barrier, the
4
Peter Jarvis, Adult Education And Lifelong Learning. (England : Rouledge Falmer, 2004), 184
5
Liyan Song, “A Conceptual Model for Understanding Self-Directed Learning in Online Environments”. Journal of Interactive Online Learning. Vol 6 No.1, 2007
6
3
students can elevate their level of self directed learning skill. Therefore, this
research tried to find out the students’ self directed learning activities, students’
level of self directed learning skill and their self directed learning barrier in
learning English.
In addition, self-directed learning nowadays is listed as a key component of
the 21st Century skills. Self-directed Learning is also often linked to lifelong
learning, which has been listed as a necessity for modern society by international
organizations such as UNESCO. Thus, many current frameworks on 21st century
learning use and adopt the concept of self-directed learning because it has often
been regarded as critical part of individualizing learning experiences.7 In short,
self‐direction is now recognized as an important 21st Century skill for learners in
which it needs to be studied and developed further.
Many researchers studied self-directed learning. The focus of those
researches is to investigate the influence and impact of implementing self-directed
learning. The results of the studies show that it can improve the learners’ critical
thinking skill8, reading skill,9 self efficacy,10 and intrapersonal skill11. As its
simplest, self-directed learning is now well-known with the good impact because
those researches point that self-directed learning can improve other skills. It
7
Caffarella, R. Self-Directed Learning. New Directions For Adult And Continuing Education, 1993, 57
8
Fahim Mansoor. “The Relationship between Self-Directed Learning and Critical Thinking Ability of Iranian Efl Learners”. International Journal of English Language, Literrature and Humanities. Vol 1 No.5. 2014
9
Morteza Khodabandehlou, “The Impact of Self-directed Learning Strategies on Reading Comprehension.” International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Vol. 3. No.7. 2012
10
Basereh Najmieh. “Self-Directed Learning and Self-Efficacy Belief among Iranian EFL Learners at the advanced Level of Language Proficiency.” Journal of Applied Linguistics and Language Research. Vol. 3 No.1. 2016
11
4
shows the importance of doing self-directed learning. However, because it is one
of the key components in 21st century learning, it still needs to be studied further.
Besides self-directed learning is implemented in home school, research on
home school also needs attention as the formal school because of its importance
and its equality. Based on National education system, home school has the
equality on some certain things from traditional school as stated in UU
No.20/2003 pasal 26:
“Pendidikan nonformal diselenggarakan bagi masyarakat yang
memerlukan layanan pendidikan yang berfungsi sebagai pengganti,
penambah, dan/ atau pelengkap pendidikan formal dalam rangka
mendukung pendidikan sepanjang hayat”
The law rule above stated that non-formal education is held for society who
need education service which functions as substitution, addition, or supplementary
of formal education in order to support long-life education. Hence, it infers that
non-formal education has the same significant function for social education need
so that the improvement of quality in non-formal education also needs to be
5
Another law related to non formal education, in verse 6 stated below.
“Hasil pendidikan nonformal dapat dihargai setara dengan
hasil program pendidikan formal setelah melalui proses penilaian
penyetaraan oleh lembaga yang ditunjuk oleh pemerintah atau
pemerintah daerah dengan mengacu pada standar pendidikan
nasional”.
The law above tells about the equality of non-formal and formal education
in the matter of assessment result. The rule says, “Result of non-formal education
can be appreciated as the result of formal education result after facing the equal
assessment held by government or local government based on national education
standard.”
The term equality refers to social effect, measure, impact, function and
standard comparing to traditional or formal school. What make them different are
the context, methodology, and approach to pursue that standard of competence.
Because home school has the same position as the formal school, educational
research on home school is also needed to improve its quality as formal school.
This research is conducted in Home School Pena. Home School Pena is a
home school located in Jl. Ketintang Baru III No. 03 Surabaya - Indonesia. This
home school provides education programs which equal with elementary school,
junior high school and senior high school.
The school policy sets three programs in the educational system. They are
private program, home school community and distance learning program. Private
program allows students to learn at a certain place. Home school community or
6
students to study together with a professional teacher. While distance learning is a
program in which students study independently.
This research is conducted based on students’ problem to pursue their
learning goal while they have limited class meeting. Therefore, the researcher uses
students in community learning program. Besides, this research is only conducted
on students of senior high school because of the life span age which is considered
to be adequate to have independency in learning based on the adult learner theory.
These programs have limited time in classroom allow students to apply
self-directed learning and according to the head of curriculum in this school,
despite students are required to learn more outside the class. But, they do not
know how far students have ability to study independently. Therefore, it is
suitable to be subject of study.
Based on the explanation above, it is important to know their sorts of self
directed learning activities, students’ self directed learning skill and its barrier in
self-directed learning practice at home school Pena. Therefore, this research is
entitled self-directed learning of senior high school students in learning English at
7
B. Research Question
Based on the background above, researcher formulates the problem:
1. What are sorts of self directed learning activities in learning English at
senior high school students of home school Pena?
2. What is the level of senior high school students’ self directed learning skill
in learning English at home school Pena?
3. What are sorts of self directed learning barrier in learning English at senior
high school students of home school Pena?
C. Objective of the Study
Based on the research question above, researcher formulates the objective
of study:
1. To know sorts of self directed learning activities in learning English at
senior high school students at home school Pena.
2. To know the level of senior high school students’ self directed learning
skill in learning English of home school Pena.
3. To know sorts of self directed learning barrier in learning English at senior
8
D. Significance of the Study
For learners: Students need to know the self-directed learning activities
they do outside the class because as self-directed learners or autonomous learner,
they must learn not only what to learn but also how to learn.12 They also need to
know their level of self directed learning and their barriers so that they can elevate
their level of self directed learning through fixing their self directed learning
barriers.
For English teachers: This study is useful because this research will help
teacher to diagnose students’ need in learning English independently so that it can
become teacher’s consideration to have a better role and design proper teaching
strategy in supporting their self-directed learning practice. Besides, this study can
be a suggestion related to the implementation of self directed learning practice
because teachers also need to do self-directed learning to improve their teaching
skill.
For course developer: This study will help to elaborate what students’
need to support their self-directed learning by describing students’ self-directed
learning skill, their sorts of activities and their barrier to do self-directed learning.
Thus, it is useful as reference and consideration for course developer to develop
the course better and to provide better self-access center or any other supporting
resources for students.
12
9
For education: This research will cover the gap in the whole previous
researches focusing on self-directed learning so that this research can be a part of
contribution to the 21st century learning framework and better education in future.
E. Scope and Limitation of the Study
Despite the aim of this research is to investigate the phenomenon of
self-directed learning practice, this research is only focused on the self-self-directed
learning practice in learning English of senior high school students at home school
PENA. This study is limited to describe the students’ self-directed learning skill,
sorts of activities in self directed learning practice and its barriers which only
faced by certain students of senior high school at home school Pena.
This research does not cover the study to how sorts of learning activities
held by students can support and improve students’ self-directed learning skill.
Besides, this research also will not study students’ self-directed learning skill
before and after they hold sorts of learning activities outside the classroom.
Despite this research tried to study students’ level of self-directed learning
skill and what self-directed learning activities they take, this research do not
illustrate the relationship between those variables quantitatively. However, the
researcher only describes self-directed learning activities that students take based
10
Self-directed learning studied in this research will not elaborate the
teacher’s role, classroom interaction or learning activities conducted inside the
classroom. Self-directed learning practice in this research will only focus on the
students’ self-directed learning and neglect the self-regulated learning practice
supported by teachers.
F. Definition of Key Term
1. Self directed learning is a learning process in which learner takes the
initiative to pursue a learning experience and responsibility for completing
their learning.13 In essence, Self-directed learning is an informal learning
process that primarily takes place outside the classroom. Therefore, this
research only focused on the students.
2. Self-directed learning skill is ability to do the process of self-directed
learning. As Knowles (1975) stated, self-directed learning is basic human
competence-the ability to learn on one's own (As cited in Jarvis 2003).14 In
this research, self directed learning skill is measured through self rating
scale of self directed learning.
3. Self-directed learning activity is sorts of learning activities used in
directed learning practice. Learning activity is a synonym for a
self-contained pedagogical scenario or a learning unit that is part of a larger
unit.15 Thus, in this research, self-directed learning activity refers to
students’ effort to learn outside the classroom in self-directed learning
context.
13
http://www.selfdirectedlearning.org/what-is-self-directed-learning[accessed on August 1st 2016]
14
Peter Jarvis, et.al., The Theory and Practice of Learning. (England: Routledge, 2003), 95
15
11
4. Self-directed learning barrier refers to learner’s factors which resist the
development of students’ self-directed learning. According to Knowles,
there are many factors that individuals weigh in choosing whether to
behave in a self-directed way at a particular point. These factors can be a
barrier to develop self-directed learning depending on the learners’
circumstance.
5. Home School Pena is a home school located in Jl. Ketintang Baru III No.
03 Surabaya - Indonesia. The school policy sets three programs in the
educational system. They are private program, home school community
and distance learning program. Private program allows students to learn at
a certain place. Home school community is a program in which each
classroom consists of 5 students to study together with a professional
teacher. In addition, distance learning is a program in which students study
independently. But, this research is limited for community learning
12
CHAPTER 2
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter consists of review of the previous study and theoretical
background. The theoretical background discusses some issues related to
self-directed learning, self-self-directed learning skill, self-self-directed learning model and
self-directed learning barrier.
A. Review of Related Literature
1. Self-Directed Learning
Self directed learning is a learning process in which learner takes the
initiative to pursue a learning experience and responsibility for completing their
learning.16 According to Knowles’ theory (1975), self directed learning is defined
as a process in which individuals determine their learning needs, set their learning
goals, identify available resources for learning, choose and implement appropriate
learning strategies, and evaluate learning outcomes (as cited in Spector, 2013).17
In other words, self directed learning is the learning activity which is controlled
and managed by the learners themselves.
Based on its development, self-directed learning has existed even from
classical antiquity. The proof is that self-study played an important part in the
lives of such Greek philosophers as Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle.18 Other
historical examples of self-directed learners included Alexander the Great, Caesar,
16
http://www.selfdirectedlearning.org/what-is-self-directed-learning[accessed on August 1st2016]
17
Michael J Spector, et, al., Handbook of Research on Educational Communications and Technology. (New York: Springer, 2013), 364
18
13
Erasmus, and Descartes. The fact that the development of knowledge occurs
without any formal education can be an example that people learn on their-own.
Early scholarly efforts to understand self-directed learning took place
some 150 years ago in the United States. Craik documented and celebrated the
self-education efforts of several people. About this same time in Great Britain,
Smiles published a book entitled Self-Help that applauded the value of personal
development. However, it is during the last three decades that self-directed
learning has become a major research area.19
Self directed learners are classified into three categories based on reasons
or participation in learning:
(a) goal-oriented, who participate mainly to achieve some end goal;
(b) activity-oriented, who participate for social or fellowship reasons;
(c) learning-oriented, who perceive of learning as an end in itself. It is this
latter group that resembles the self-directed learner identified in subsequent
research.
Then, Knowles popularized the term of Andragogy. He described two
opposite poles of a continuum of learning, with teacher- or other-directed
(pedagogical) learning at one end and self-directed (andragogical) at the other.
The pedagogical learner is dependent on the teacher to identify learning needs,
formulate objectives, plan and implement learning activities and evaluate learning.
Conversely, the andragogical learner prefers to take responsibility for meeting his
19
14
or her own learning needs. Therefore, self directed learning is the part of
andragogical learning.
On the other hands, Long developed the concept of self directed learning20
and identified three dimensions of the self directed learning; sociological,
pedagogical, and psychological.21 These three dimensions which have role in self
directed learning are explained below.
First, sociological dimension of self-directed learning in which the learner
is seen to be socially independent, though independent learning has sometimes
been viewed as learning in isolation. Sociological dimension include the
independency on task management.
Second, pedagogical dimension of self-directed learning refers to
pedagogical methods utilized by the learner. The learner is free to set his or her
own learning goals, choose the needed resources, decide the amount of time
required, and plan the appropriate evaluation. Pedagogical aspect also includes the
application in educational context and educational issues.
Third, psychological dimension of self-directed learning where the
emphasis is on the learner’s cognitive ability, include the capacity for critical
thought and reflection. Long believed that this psychological power of the learner
to maintain active control of the learning process is paramount in achieving
self-directed learning. He stated, "Psychological self-self-directedness, or psychological
control is the necessary and sufficient cause for self-directed learning.
20
Dr. Garrison. “Self Directed Learning: Toward A Comprehensive Model.” Research Gate Vol 48, No.1, 1997
21
15
2. Self-Directed Learning Model
Malcolm Knowles’ skill was then to put the idea of self direction into
packaged forms of activity that could be taken by learners. Self-directed learning
experience has a number of models of the process.
Linear models; Knowles model was linear. His five step model involved:
1. diagnosing learning needs. 2. Formulating learning needs. 3. Identifying human
material resources for learning. 4. Choosing and implementing appropriate
learning strategies. 5. Evaluating learning outcomes.22
Interactive model; in the late 1980s and early 1990s, the researchers of
self-directed learning began to focus not only on the learners but also on the
context and nature of their learning. It is not as organized as the linier model, but
it depends on the personality characteristics of the learners, the environment and
the learning context. In Danis’s model, for example, learning strategies, phases of
the learning process, the content, the learner, and the environmental factors in the
context must all be taken into account in mapping the process of self-directed
learning.23
PRO models: This model is proposed by Brocket and Hiemstra. PRO
model was based upon the idea of personal responsibility. People are considered
to have control over how they respond to a given situation. Within the context of
learning, individuals have ability and willingness to take control of their own
learning that determines their potential to be self-directed learners.
22
http://infed.org/mobi/malcolm-knowles-informal-adult-education-self-direction-and-andragogy/[accessed on August 1st 2016]
23
16
Grow Model; the best known of self-directed learning model is Grow’s
Staged Self-Directed Learning (SSDL) model. Grow presents a matrix whereby
learners can locate themselves in terms of their readiness for and comfort with
being self-directed, and instructors can match the learners’ stage with appropriate
instructional strategies. For example, whereas a dependent learner needs more
introductory material and appreciates lecture, drill, and immediate correction, a
self-directed learner can engage in independent projects, student-directed
discussions, and discovery learning.24
Garrison’s model; Garrison proposed a comprehensive model of
self-directed learning based on three core components25:
a. Self- Management (control)
The self-management involves how the learner determines their own goal,
manages their learning process, and assesses their own ability. Therefore,
self-management becomes one essential part of self-directed learning model.
b. Motivation (entering and task)
Motivation plays a principal role in the psychological conceptualization of
self-directed learning. Long describes motivation as “energy, drive, or desire that
encourages, impels, stimulates, or sustains an individual to accomplish a goal or
task”.26 Two constructs of motivation are commonly referred to in the literature:
24
Ibid. Pp. 10
25
Malcolm Knowles, The Adult Learner. (London,: Elsevier, 2005), 137
26
H. B. Long. “Understanding Self-Direction in Learning.” In H.B. Long And Associates (Eds.),
17
intrinsic motivation that is generated within the learner, and extrinsic motivation
which is provided externally.
c. Self-Monitoring (responsibility)
His third component, self-monitoring, is the cognitive learning processes
as well as meta-cognitive skills a person needs to engage in self-directed learning.
According to Garrison, Adult Education traditionally focused on the first
component, the control of learning, and paid less attention to the learning
processes. He suggests that equal attention should be focused on motivation
issues, including the motivation to engage in self-directed learning and to
complete self-directed learning tasks. Learners need to pay attention to all three
18
The other self-directed learning model is found in Tough's list of 13 steps
in beginning a self-directed learning project:27
a. Deciding what detailed knowledge and skill to learn;
b. Deciding the specific activities, methods, resources, or equipment
for learning;
c. Deciding where to learn;
d. Setting specific deadlines or intermediate targets;
e. Deciding when to begin a learning episode;
f. Deciding the pace at which to proceed during a learning episode;
g. Estimating the current level of knowledge and skill and progress in
gaining the desired knowledge and skill;
h. Detecting any factor that has been backing or hindering learning;
i. Obtaining the desired resources or equipment;
j. Preparing or adapting a room;
k. Saving or obtain the money necessary for the use of certain human
or nonhuman resources;
l. Finding time for the learning; and
m. Taking certain steps to increase the motivation for learning
It is interesting to note that although this list includes many practical issues
regarding self-directed learning, Tough did not ignore motivation, which is
especially important for self-directed learning.
3. Self-Directed Learning Skill
27
19
Self-directed learning is not only a process of one’s learning but also one’s
ability to do the process of self-directed learning itself. As Knowles (1975) stated,
self-directed learning is basic human competence-the ability to learn on one's own
(As cited in Jarvis 2003).28 It means that self-directedness can be measured. The
degree of its development can be varied depend on the individual’s capability.29
It is important for both educators and learners to know the learners’
self-directedness to help them in pursuing better learning for future. Students will have
the opportunity to develop an insight into self-directed learning and a better
understanding of the concept, which is crucial for developing of self-directed,
independent and lifelong learning. On the other hand, teachers will be better able
to guide students from their positions of learning dependence to independence,
considering each student's individual learning needs.
One of the measuring instruments for learners’ directedness is
self-rating scale of self-directed learning (SRSSDL). It consists of 60-items
categorized under five broad areas of self-directed learning30 which includes
awareness, learning strategies, learning activities, evaluation, and interpersonal
skills. Students ‘response toward the rating scale is able to rate the level of
self-directed learning indicator.
To know the result of their self-directedness, it needs the analysis of those
five broad areas. The point scale “always” is counted as 5 and the weakest point is
on the scale “never” with only 1. The number of scale is sum up to find the total
28
Peter, Jarvis, et, al.,, The Theory and Practice of Learning(England: Routledge, 2003), 95
29
Williamson. “The Development of A Self-Rating Scale of Self-Directed Learning (Srssdl).”
Nurse Researcher Vol. 14, 2007, 68
30
20
number of scale. Then, the level of self-directed learning can be analyzed using
the table below.
Table 2. 1
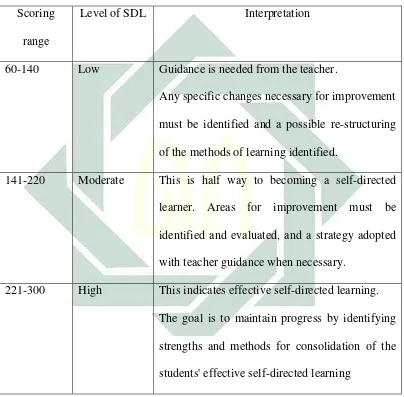
Scoring Range of Self Rating Scale in Self Directed Learning
Scoring
range
Level of SDL Interpretation
60-140 Low Guidance is needed from the teacher.
Any specific changes necessary for improvement
must be identified and a possible re-structuring
of the methods of learning identified.
141-220 Moderate This is half way to becoming a self-directed
learner. Areas for improvement must be
identified and evaluated, and a strategy adopted
with teacher guidance when necessary.
221-300 High This indicates effective self-directed learning.
The goal is to maintain progress by identifying
strengths and methods for consolidation of the
students' effective self-directed learning
Basically, all individuals are capable to have self-directed learning. But,
degree of the development are varied depends on the learner.31 Students with low
self-directed learning have lack of ability to set their own goal, manage their
31
Williamson. “The Development of A Self-Rating Scale of Self-Directed Learning (Srssdl).”
21
learning activity outside classroom and assess their learning progress. These
students need guidance to improve their learning ability. Students with high
self-directed learning having high quality on independency of learning should also be
supported in order to help maintain and further develop their abilities in becoming
independent life-long learners. This scale is used by many researches to describe
students self directedness.
4. Self-Directed Learning Barrier
According to Knowles, there are many factors that individuals weigh in
choosing whether to behave in a self-directed way at a particular point. These
factors can either support or become barrier to develop self-directed learning
depending on the learners’ circumstance.
This factor depends on the locus of control32 in the learning process. Locus
of control is a circumstance in which people attribute the cause or control of
events to themselves or to an external environment. Each type of learning has
different locus of control.33 The table below is the table of locus of control based
on type of learning.
32
Malcolm Knowles, The Adult Learner.( London,: Elsevier, 2005), 139
33
22
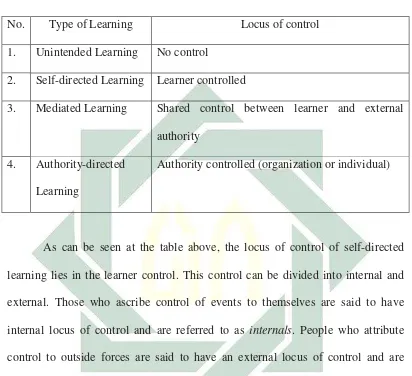
Table 2. 2
Locus of Control
No. Type of Learning Locus of control
1. Unintended Learning No control
2. Self-directed Learning Learner controlled
3. Mediated Learning Shared control between learner and external
authority
4. Authority-directed
Learning
Authority controlled (organization or individual)
As can be seen at the table above, the locus of control of self-directed
learning lies in the learner control. This control can be divided into internal and
external. Those who ascribe control of events to themselves are said to have
internal locus of control and are referred to as internals. People who attribute
control to outside forces are said to have an external locus of control and are
termed externals. Therefore, the barrier of self-directed learning can be viewed
from two perspectives ─internal and external factor.
The internal factor which can be supporting factor or barrier to
Self-directed learning includes a readiness to learn.34 Having high readiness to learn
can support the self-directed learning practice. On the other hands, it can be
barrier when the learner has low readiness to learn. Some other barriers in
34
23
implementation of self-directed learning strategies include student confusion,
frustration and dissatisfaction.35
The other research found that the most frequent obstacles to conducting
self-directed learning projects are finding the time for the learning activity, home
responsibilities; difficulty deciding what knowledge or skill to learn; difficulty
remembering new material or information; and poor health.36
The external factor is factor which comes from outside of the learners such
as socio-economic factor, the role of teacher, curriculum barrier and facility to
study. For instance, a research found that one of self-directed learning barrier
which occur on older adults is the cost of the learning activity.37
2.1. Review of the Previous Study
A lot of researches have similar topic which studied self-directed learning.
Some of them studied it quantitatively and the others studied it qualitatively. The
first research is entitled After the Final Bell: The Self-Directed Learning Practices
of Elementary Teachers which is authored by Susan Renee Wagner. This study is
submitted as the fulfillment of Doctoral Dissertations in University of Tennessee,
Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange.
The purpose of this study was to examine the level of elementary teachers’
self-directed learning skill and activities in their classrooms. It used a mixed
method design. The quantitative Phase I of this study involved using a survey
35
S. Shelley. Payne, Joan Rocks, Barbara Schaffner. “Self-Direction in Learning and Academic Motivation Development in Undergraduate Health Profession Students.” International Journal of Self-Directed Learning . Vol. 11, No. 1, 2014
36
Sears, Emma Jo Benson, Dissertation: “Self-Directed Learning Projects of Older Adults”. Doctor of Philosophy (College and University Teaching), 1989
37
24
instrument in order to identify self-directed learners and identify categories of
teacher learners. This score fell within the “above average” range which indicated
high self-directedness. In Phase II, nine teachers scoring “high” and “above
average” were interviewed. Result describes that the participants planned and got
additional knowledge on their own.38
Despite the dissertation and this research studied on the analysis of self
directed learning practice, there are some differences between this dissertation and
this research. The respondents of the dissertation research are the elementary
teachers while the research studies the home school students. From the
methodology perspective, both this dissertation research and this study use mixed
method. However, this dissertation uses SDLRS (Self Directed Learning
Readiness Scale) as the instrument to measure the participants’ self directedness
while this research uses self-rating scale of self-directed learning (SRSSDL).
The second research is entitled Self-Directed Learning and Academic
Achievement in Secondary Online Students which is authored by Elaine
Hendricks Carson submitted to the Faculty of the University of Tennessee in
Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements of the Degree of Doctor of Education.
This dissertation research is conducted on August 2012. This study examined
attributes of self-directed learning (SDL) in students taking online courses through
a state-wide online program in the Southeastern United States and investigated the
relationship between the students’ self-directedness and their academic
achievement. Results of inferential statistics support the premise that statistically
38
25
different level of self-directed learning exists in the population and show that
there is a correlation between self-directed learning and academic achievement.39
The third research is entitled The Relationship between Self-Directed
Learning and Learning Styles. This research is studied by James Boyd Canipe
from University of Tennessee – Knoxville. The results of this study indicate that
there are significant correlations between self-directed learning readiness and two
of the modes of learning.40
The second and third researches above are different from this study
because they use correlation study using quantitative research design. Besides, no
one of them studied the self-directed learning practice applied by the students of
senior high school in home school. Therefore, this thesis has different scope with
the second and third research above.
The fourth research is entitled Self-Directed Learning Projects of Older
Adults authored by Emma Jo Benson Sears, R.N., B.S.N., M.S.N. in 1989 in
Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements For the Degree of Doctor Of Philosophy
in University of North Texas Denton.
This study determined the number of self-directed learning projects
undertaken by older adults and examined the motivational factors, anticipated
benefits related to the learning activities, and obstacles in conducting self-directed
learning. The majority of the learning projects were self-planned for the purpose
of self-enjoyment and self-fulfillment. The results of this study shows that older
39
Elaine Hendricks Carson, Dissertation: “Self-Directed Learning And Academic Achievement In Secondary Online Students” (University Of Tennessee., 2012)
40
26
adults value self-directed learning as a major source of self-fulfillment in their
lives and are motivated to develop new knowledge and skills through
self-planned, self-directed learning projects.41
The fifth research is entitled The Relationship of Self-Directed Learning
Readiness To Knowledge-Based and Performance-Based Measures of Success in
Third-Year Medical Students authored by Brian W. Findley in 2009. This research
is his dissertation submitted to The Faculty of The College of Education in Florida
Atlantic University. This study was aimed to investigate the self-directed learning
(SDL) readiness of third-year medical students; the relationship between
self-directed learning readiness and knowledge-based and performance-based
measures of success in a medical school using an integrated medical curriculum;
and to determine if knowledge-based and performance-based measures of success
are significant in predicting Self-Directed Learning Readiness Survey/Learner
Preference Assessment (SDLRS/LPA) and National Board of Medical Examiners
FamilyMedicine Shelf Examination (NBME-FM) scores.42
The sixth research is conducted by Patricia Lynne Linder entitled An
Analysis of Self-Directed Learning of First-Year, First-Generation College
Students. This is her dissertation in University of South Florida on January, 2013.
Study findings highlighted the importance of a support system that includes
coursework designed to facilitate understanding of individual learner
41
Sears, Emma Jo Benson, Dissertation: “Self-Directed Learning Projects of Older Adults”. Doctor of Philosophy (College and University Teaching), 1989
42
Brian Findley, Dissertation: “The Relationship of Self-Directed Learning Readiness To Knowledge-Based and Performance-Based Measures of Success in Third-Year Medical Students.”
27
characteristics, emphasize strategies to maximize learner efforts that lead to
successful outcomes, and empower students to become more self-directed. This
study also expands the field of adult education by providing evidence that learner
control is a key component of self-direction and is positively correlated to
academic success.43
The seventh research is in Indonesian language, entitled Perbedaan Self
Directed Learning Siswa Sekolah Menengah Atas Dan Sekolah Menengah
Kejuruan Di Yayasan Dharma Bakti Medan which means Comparative Study on
Self-directed Learning in Senior High School and Vocational High School in
Dharma Bakti Foundation Medan. It is written by Gladys Ema Sarlina Bangun to
her Fulfillment in Thesis in Psychology Faculty in Sumatera Utara University.
The research was done in 2010/2011. The result illustrates that there is significant
difference between those variables.44
The eighth research is entitled Perbedaan Self Directed Learning ditinjau
dari Pola pembelajaran E-Learning pada Mahasiswa Universitas Sumatera Utara.
This research is conducted by Maulidini Nazlely as his thesis on psychology
faculty in Sumatera Utara University in 2011/2012. The result of this research is
that there is a difference of self directed learning based on e-learning model in
students of Sumatera Utara University.45
43
Patricia Lynne Linder, Dissertation: “An Analysis of Self-Directed Learning of Year, First-Generation College Students.” (Florida: University of South Florida, 2003)
44
Gladys Sarlina, Thesis: “Perbedaan Self Directed Learning Siswa Sekolah Menengah Atas Dan Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Di Yayasan Dharma Bakti” ( Medan :Sumatera Utara University. 2011)
45
28
The similarity of the seventh and eighth research with this study is that the
researches conduct in Indonesia. But, they also have different population. They
studies students in Sumatera Utara. Mean while this study uses home school
students in Pena, Surabaya as the subject. Moreover, they have difference scope
with this study. They try to investigate self directed learning in psychological area
while this study is in the area of learning English.
The ninth research is entitled The Impact of Self-directed Learning
Strategies on Reading Comprehension autored by Morteza Khodabandehlou,
Shahrokh Jahandar, Gohar Seyedi, Reza Mousavi Dolat Abadi. This study is
published in International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume
3, Issue 7, in June-2012. There is 92 out of 150 upper-intermediate and advanced
EFL female high school students studying in IELTS & TOEFL Center of Arian in
Gorgan, Iran selected randomly and divided into two groups: control and
experimental. The control group trained in teacher-directed strategies and the
experimental group trained and practiced self-directed learning reading strategies
in an 8-week course of English reading texts.
The results reveal that there is a significant difference between mean score
of TDL (Teacher-Directed Learning) and self-directed learning, and after
treatment students perform better that proves superiority of self-directed over
teacher-directed readers. 46
The tenth research is entitled Self-Directed Learning and Self-Efficacy
Belief among Iranian EFL Learners at the advanced Level of Language
46
29
Proficiency authored by Najmieh Basereh M.A. in TEFL from Islamic azad
university, Bandar Abbas Branch Kian Pishkar from Faculty Member of Islamic
Azad University, Jieroft Branch. This research is published in Journal of Applied
Linguistics and Language Research Volume 3, Issue 1 in 2016. The subject of this
study is Iranian EFL students who were studying English at the advanced level in
Language Institute in Bandar Abbas. The findings of the present study revealed
that there was a significant relationship between Self-Efficacy Belief and
self-directed learning of Iranian EFL learners at the advanced level of Language
Proficiency.47
The eleventh study is entitled The Perception of Adult Learners
Concerning their Satisfaction of Their Educational Experiences in a Midwestern
Community College Constance The purpose of this study was to determine
whether selected immutable and conditional variables influenced the perception of
adult learners concerning the educational experience they pursued in a
Midwestern Community College. Findings in this study indicated that when
viewing the adult learner through the characteristics and experiences of selected
immutable and conditional variables, significant differences within the adult
learner population appeared. These findings suggest that there is a need for
institutions of higher learning to understand the unique learning requirements of
47
30
the adult learner in order to organize and deliver an educational experience
specifically for each individual.48
The twelfth research is conducted by Pfeiffer, Jim entitled Self-Directed
Learning in the Middle School Classroom. This research was conducted in 2006
as an Action Research Projects in University of Nebraska The purpose of this
action research project is to create an opportunity to allow the students in
classroom implement the learning strategy to improve their self-directedness.
The scope of self-directed learning in the twelfth research above is limited
in the classroom. Vice versa, this study studies the self-directed learning practice
outside the classroom. From the methodology, the twelfth research is different
from this research because it uses classroom action research. The subjects are also
different. This research uses non-formal school while the twelfth research above
uses formal school.49
The thirteenth research is conducted in Iowa State University by Adenuga,
Babatunde O. with his dissertation entitled Self-directed learning readiness and
learning style preferences of adult learners. This study was conducted on 1989.
Demographic variables exert both direct and indirect (through learning style)
influences on readiness for self-directed learning The degree of readiness of
individuals with similar levels of formal education differ significantly, depending
48
L. McCallum Dissertations: "The Perception of Adult Learners Concerning their Satisfaction of Their Educational Experiences in a Midwestern Community College". (Western Michigan University 2012)
49
31
on whether one is from a developed nation or a developing nation learning style
becomes the next best predictor of readiness for self-directed learning.50
From the previous studies above, many of them studied self-directed
learning from the psychological perspective. However, the scope of this research
is limited to education. Therefore, it can be concluded that there is no research
which studied the same scope as this study which investigate the self-directed
learning practice in learning English of senior high school students in home
school Pena.
50
32
CHAPTER 3
RESEARCH METHOD
This research is aimed to know students’ directed learning skill,
self-directed learning activities and self-self-directed learning barriers. This chapter
presents the method used to collect data of the study. The research methods
include the research design, setting of the study, subject of the study, data
collection technique, research instrument, and data analysis technique.
A. Research Design
This study used descriptive method. According to Danim, descriptive
method is a method aimed to describe situation or phenomena or characteristic of
individual or group accurately. In other words, descriptive method is describing
the condition of existence and classifying the information.51
This method suits with this study because it describes the self-directed
learning of the senior high school students in home school Pena. Self-directed
learning which is studied in this research will focus on describing students’
self-directed learning activities, their level of self self-directed learning and self self-directed
learning barrier.
B. Research Setting
This research will be conducted at Home School Pena. Home School Pena
is one of the home schools in Surabaya. It is located on Ketintang III Surabaya.
Concerning the legality status of home school in Indonesia, home school
has the same equality with regular school. Based on Surat Edaran Menteri
51
33
Pendidikan Nasional Republik Indonesia No. 107/MPN/MS/2006, it says that
each person who passes equality test in A, B, or C packet, he or she has the same
and equal of equality right with they who gets certificate from formal school to
continue his or her study in the higher level.
Homeschooling Pena is a learning center for society as a legal alternative
educational system for elementary school, junior high school and senior high
school with the permission of local government in Surabaya No :
188/7736/436.6.4/2014, in which the existence is legal and considered as the same
position as formal school based on the law (Permendikbud No. 29 Tahun 2014
tentang Sekolah Rumah, Undang-undang Sistem Pendidikan Nasional : UU No
20/2003 pasal 1 dan 2, dan Surat Edaran Menteri Pendidikan Nasional Republik
Indonesia No. 107/MPN/MS/2006)52
Home School Pena is chosen as the field of study because of the following
reasons. Home school Pena drives their students to implement self-directed
learning. The students have only two-three meetings in a week. This circumstance
allows them to have more portions to study on their own rather than inside the
classroom. Besides, the head of curriculum stated that they are motivated to learn
by themselves independently. Therefore, it indicates that the students in this
school implements self-directed learning.
C. Subject of The Study
The subject of the study is senior high school students in Home School
Pena. In Learning Community Program, there are two streams in the Home
52
34
school; Science and Social streams. Science Class has two meetings for English
subject while Social Class has three meetings for English Subject in the whole
semester.
The subject of this research is chosen based on the age of the students.
According to Levinson’s Life-Span Theories, students’ age which reaches
approximately 17 years old is considered to have ability in independency of
learning.53 This ability is important to explore self-directed learning. Therefore,
the researcher conducts the study on the students who reach 17 years old.
D. Research Instrument
Research instrument is important to find out the data which is
investigated in this study. The instruments used in this research are questionnaire
and interview guideline.
53
35
1. Questionnaire
Questionnaires are written sets of some questions used to gain responses
in non-face-to-face situations; questions are usually focused on specific
information.54 The questionnaire used in this research is Self-rating scale of
self-directed learning.
Self-rating scale of self-directed learning is a scale to measure someone’s
self-directedness. This scale uses rating response which each item are rated by
using a five-point scale: 5 = always: 4 = often: 3 = sometimes: 2 = seldom: 1 =
never. The participants are required to answer the rate of each indicator based on
their learning experience.
Self-rating scale of self-directed learning (SRSSDL) consists of 60-items
categorized under five broad areas of self-directed learning55:
a. Awareness: 12 items relating to learners' understanding of the factors
contributing to be self-directed learners.
b. Learning strategies: 12 items explaining the various strategies of
directed learners which should adopt in order to become
self-directed in their learning processes.
c. Learning activities: 12 items specifying the requisite learning activities
learners should actively engage in order to become self-directed in their
learning processes.
54
Margono, Metodologi Penelitian Pendidikan (Jakarta: Rineka Cipta. 2007), 168
55
36
d. Evaluation: 12 items revealing learners' specific attributes in order to
help monitor their learning activities.
e. Interpersonal skills: 12 Items relating to learners' skills in inter-personal
relationships, which are pre-requisite to their becoming self-directed
learners.
The SRSSDL, originally developed by Williamson and then validated in
the Italian context was adopted. The Italian version of the SRSSDL has
demonstrated good internal consistency56
2. Interview Guideline
The interview guideline in this research is open ended questions designed
to obtain the data. The interview will be focused on how learners implement
self-directed learning, how they determine their own goal, to what extend and what
sorts of activities they learn by themselves. Also, the interview will be about their
barrier in implementing self-directed learning.
E. Data Collection Technique
Data collection techniques is a sequence of ways that researcher takes to
collect data empirically and objectively. To obtain valid data, some techniques of
data collection were applied. In this case, researcher used some techniques such as
distributing questionnaire and conducting interview.
56
37
1. Questionnaire
Researcher gave the questionnaire to the respondents. Then, the
respondents are required to answer the questionnaire sheets by choosing one of
five point scales to rate the indicators of self-directed learning.
2. Interview
Interview is a data collection technique with communication between two
people or more to get information.57 Researcher conducts the interview to the
respondents using the interview guideline.
F. Data Analysis Technique
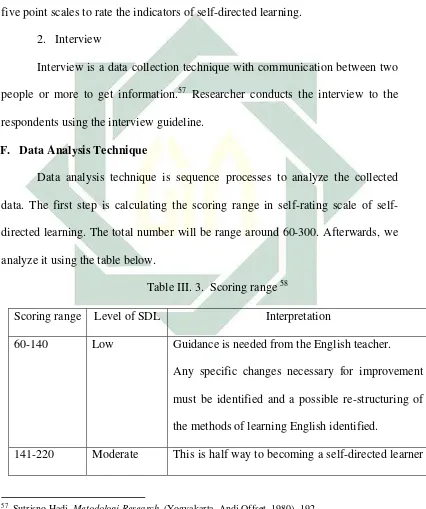
Data analysis technique is sequence processes to analyze the collected
data. The first step is calculating the scoring range in rating scale of
self-directed learning. The total number will be range around 60-300. Afterwards, we
analyze it using the table below.
Table III. 3. Scoring range 58
Scoring range Level of SDL Interpretation
60-140 Low Guidance is needed from the English teacher.
Any specific changes necessary for improvement
must be identified and a possible re-structuring of
the methods of learning English identified.
141-220 Moderate This is half way to becoming a self-directed learner
57
Sutrisno Hadi, Metodologi Research, (Yogyakarta, Andi Offset, 1980), 192.
58
Williamson. “The Development of A Self-Rating Scale of Self-Directed Learning (Srssdl).”
38
in learning English.
Areas for improvement must be identified and
evaluated, and a strategy adopted with teacher
guidance when necessary.
221-300 High This indicates effective self-directed learning.
The goal is to maintain progress by identifying
strengths and methods for consolidation of the
students' effective self-directed learning
After analyzing the instrument, we can know the level of the students’
self-directedness by counting the score of the students’ result. Then, the students
are interviewed by the researcher. The data of interview is analyzed as these steps.
First, the interviews were transcribed or converted in to written form.
Second, the transcribed were given back to the respondents to check whether it
has reflected what they meant to provide data for analysis. Third, the transcripts
were condensed into briefer statements in which the main sense of what is said is
rephrased in a few words. Finally, the data would be categorized by using data
39 CHAPTER 4
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
This research is aimed to know students’ directed learning skill,
self-directed learning activities and self-self-directed learning barriers. This chapter deals
with the findings of the study as well as the discussions of the findings. These
findings and discussions are arranged and presented in such a way in which the
research question became the basis or reference for the arrangement and
presentation.
A. Research Finding
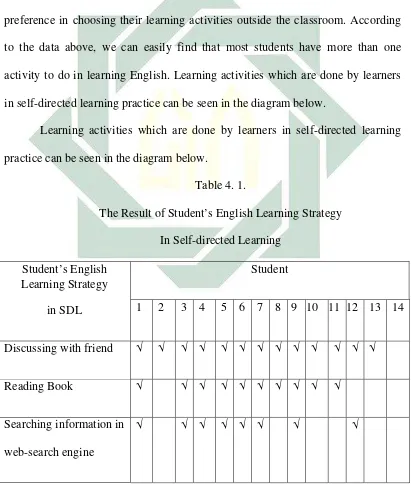
1. Self-Directed Learning Activities in Learning English
Self-directed learning is a learning process with full of initiative in taking
the whole learning progress. To accomplish the learning goal, learners select their
English learning strategies. To know students’ self-directed learning activities in
learning English, a researcher conducts interview. The result of interview show
that the self-directed learning activities in analyzing qualitative data are like
follows.
a. Student 1
Age : 17 years old
Program : Community Learning Program
To perceive his learning goal, Student 1 does some activities such as
searching information in the internet, discussing with friend, reading book, joining
40
and doing exercise. The book that he learns is an English book given from the
school. In addition to those activities, he sets his social media in English to learn
English.
He diagnoses his learning progress through practice. He is good in
listening but weak in speaking. His learning goal is that he wants to improve his
speaking skill which he thinks it is his weakness. The second goal is to master the
whole English skill so that he becomes international musician.
b. Student 2
Program : Community Learning Program
In learning English, student 2 does some activities such as discussing with
friend, joining learning community, using social media to learn English, doing
homework, joining online group/ forum discussion, doing Exercise, watching
English tutorial on YouTube, joining English course or additional course, and
watching TV program/news. . Besides, she sets his social media in English to
learn English.
She can diagnose her lack and strength in English. She is good in all
English skill. His learning goal is that she got improvement more than she gets
right now.
c. Student 3
Age : 18 years old
Program : Community Learning Program
Student 3 is interested in informatics. She believes that English can
41
high self-directed learner. She spends her time to do some learning activities such
as discussing with friend, reading book, searching information in web-search
engine, joining learning community, using social media to learn English, Doing
homework, joining online group, forum discussion, doing exercise, watching
English tutorial on YouTube, joining English course or additional course, reading
e-book, watching TV program/news, and making dream board to identify her
learning goal.
She can diagnose her own learning progress, her weakness and strength in
learning English. She stated that she is not good in learning theory but she find
easy in practicing English. So her learning objective is mastering the theory.
d. Student 4
Age : 18 years old
Program : Community Learning Program
In the middle of his busyness as entrepreneur, he spends his time to do
some learning activities such as discussing with friend, reading book, searching
information in web-search engine, joining learning community, using social
media to learn English, doing homework, joining online group, forum discussion,
doing exercise, watching English tutorial on YouTube, reading e-book , reading
English article and news.
Above all, learning from social media is fun because it is effortless.
However, it results in positive impact in his learning progress. He can diagnose
her lack and strength in English. His learning goal is that he got improvement
42
e. Student 5
Age : 18 years old
Program : Community Learning Program
Student 5 does some learning strategies to improve his English such as
discussing with friend, reading book, searching information in web-search engine,
joining learning community, using social media to learn English, doing
homework, joining online group/ forum discussion, doing exercise, watching
English tutorial on YouTube, and reading e-book
Similar to student 1, he used book from school as a resource. He is also
able to evaluate himself. Based on his self-assessment, he is smart in all English
skill but perfect in listening. His learning goal is that he got improvement more in
English
f. Student 6
Age : 17 years old
Program : Community Learning Program
Student 6 tries to do some learning activities such as discussing with
friend, reading book, searching information in web-search engine, joining
learning community, using social media to learn English, doing homework,
joining online group/ forum discussion, doing exercise, watching English tutorial
on YouTube, and reading e-book. She is difficult to assess her own skill. Her
43
g. Student 7
Age : 17 years old
Program : Community Learning Program
Student 7 is interested in automotive. He believes that English can support
his career. He also uses dream board to strengthen his dreams. He is moderate
self-directed learner. He spends her time to do some learning activities such as
discussing with friend, reading book, searching information in web-search engine,
joining learning community, using social media to learn English, Doing
homework, and joining online group/ forum discussion.
He also can diagnose his learning English. He stated that he is good in
speaking. He can know it through assessing his understanding of the materials. He
is interested in English for specific purpose. His learning goal is to understand the
vocabularies and terms in automotive, his interest.
h. Student 8
Age : 17 years old
Program : Community Learning Program
Student 8 learns English outside the classroom through doing some
learning activities such as discussing with friend, reading book, doing homework,
watching English tutorial on YouTube, joining English course or additional