154
TRANSLATION ERRORS IN ENGLISH-INDONESIAN HUMOR
TEXT PRODUCED BY STUDENTS OF BASIC TRANSLATION
CLASS
Gunawan, F. 1, Rini, J. E. 2
1,2 English Department, Faculty of Letters, Petra Christian University Siwalankerto 121-131, Surabaya 60236, East Java, Indonesia e-mail: felicia_gunawan91@yahoo.com; jerini@peter.petra.ac.id
Abstract
This research aims to help people understand about errors in transferring message in humor text based
on Newmark’s Communicative Translation theory. The data is taken from eighty translation texts made by twenty students of Basic Translation Class period 2010/2011 batch 2009. The writer analyzes the translation data and classifies the errors based on the accuracy in transferring the message. The writer wants to find out the kinds of the error and the frequency. The findings are Errors in transferring the message and Possible Variations in Translation.
Keyword: Translation Error, Communicative Translation, Message
INTRODUCTION
Translation is a communication activity that involves language. People who do not have the same language can be connected by translation. Through translation they can understand any text that they read. Therefore, translation is important because it is a type of communication.
Translation has been part of human life since long ago. However, there are often cases where translation contains errorsand if there are errors in translation, the real message of the text is not communicated well. There could be misunderstanding because of error in translation. According to Simatupang (2000), “Translation is transferring the meaning of source language into the target language and expressing it in the target language with the form which is proper based on valid rules in the target language” (p. 2). So, in translation, the aim is to transfer the meaning of source language in the form which is proper in the target language. The errors in translation could happen because the translator does not get the meaning of source language.
The writer found that translation was quite complicated. In translation, people did not simply render the meaning of the text word-per-word, people also need to consider the context of the text. They need to use the right word for the right context and also have to be careful in choosing the word so that it will be appropriate with the sentence.
Based on personal experience, the writer interested in analyzing errors in English-Indonesian text translation produced by Basic Translation students to find out what kinds of error are usually produced by students. The writer has taken this class before and often she found the student made error in translation. The subjects of in this study were twenty students of Basic Translation class period 2010/2011 batch 2009. Basic Translation class purpose is to enable the students to understand the principles of translation and to translate different kinds of general easy short texts of intermediate level of difficulty from English into Indonesian. Humor text was mostly used in this class, so the writer chose to analyze the humor text.
155
Since the text that is used in this study is humor text, the writer used Newmark’s theory of
communicative translation as the underlying theory of this study because humor used more communicative translation.
The attempt of Communicative translation is to produce an effect to the reader as close as
possible with the reader of the original text. “This theory addresses itself solely to the second
reader, who does not anticipate difficulties or obscurities, and would expect a generous transfer of foreign elements into his own culture as well as his language where necessary” (Newmark, 1981, p.39). This theory wants to create an intimacy on the reader so that the reader can understand the message of the text. For example if there is difference of culture in the text, the translator could
adapt the culture on to the reader’s culture so that the reader can understand it.
Since communicative translation intended to achieve a certain effect on its readers’ mind, sometimes the translator has the right to correct or improve the logic in translating a text. It also has
to be remembered that Communicative translation must emphasize the ‘force’ rather than the
content of the message. For instance Bissiger Hund, the literal translation is ‘dog that bites’
however, in communicative translation, it should become “Beware of the dog!”.
According to Newmark: “Communicative translation is concerned mainly with the receptors,
usually in the context of a language and cultural variety.”(Newmark, 1981, p. 43.) Usually in communicative translation it is assumed that the readers of the translation identify with those of the original. However, this is unlikely when elements of the source language culture or of the source
language itself are discussed in the text. Nevertheless, ‘communication’ is as important as in a text
where the subject matter is of general interest. (Newmark, 1981, p.46)
In case of ‘pun’ for example, where not every languagehas the same ‘pun’, translator should
‘make’ the pun as well as explain it. It means that translator should be able to deliver the author’s
message communicatively and also address himself independently to the TL reader. Translator should understand the level of his reader’s knowledge and interest related with the aspect of the
source language or culture and also the text’s level of purpose by explaining the appropriate new
SL terms which is not familiar to his reader and adding their approximate cultural equivalents. However, if the text is specialized, the translator may give the reader all possible information including transcription, the cultural equivalent, the encyclopaedic definition within the source culture and the literal translation or any new term on the first occasion of its use. (Newmark, 1981, p.46)
According to Newmark: “In communicative translation, the ‘message’ is important and the
essential thing is to make the reader think, feel and/or act. There should be no loss in meaning and the aim, which is often realized, is to make the translation more effective as well as more elegant
that the original.”(Newmark, 1981, p. 48) It means in communicative translation, a good translation
is translation which is attractive, able to make the readers feel like they are part of the story which they read. However, the translator should be able to choose the word which would not make the readers confuse with the translation.
There are also some problems in using communicative translation. The first problem is to decide to what extent one should simplify and emphasize the basic message. The second is to decide on the highest common factor of intelligence, knowledge and sensitivity possessed by the total readership. The third is not to insult the intelligence of the readership. However, the most important problem is the intuitive nature of communicative translation, which its success can be measured only by investigating the reaction of the readers to whom it is addressed. (Newmark, 1981, p.53)
From the table of comparison between Newmark’s Semantic and Communicative translation (Munday, 2008), the writer found that the criterion of evaluation of communicative translation is
the ‘accuracy of communication of ST (Source Text)message in TT (Target Text)’, therefore it can
be assumed that error in communicative translation happened if the communication of ST message it not delivered well in TT. Thus the writer will use this as the criteria of evaluating the data.
156
METHODSIn conducting this research, the writer used qualitative method. In doing this research, the writer did not deal with the reasons why the errors occured. The instrument of the study was the writer herself. The source of the data were eighty texts translation made by students of Basic Translation class.
In collecting the datas, the writer cooperated with the lecturer of the basic translation class by asking for some materials of the translation text made by the student. From all of the materials given by the lecturer, there were eight texts of humor translation, so writer chose four texts and analyzed them.
The writer read the translated text per sentence and compared it with the original. She focused on the errors found in the text translation, especially errors in message. Then, the writer divided the results become text translation which contained errors in message and text translation which did not contain errors in message, which then called possible variation.
For the numbering system, there are two digits number. The first number indicates the
student, while the second number indicates the student’s error. For example, 1.1 means first
student, first error made by the student or 1.2 means first student, second error made by the student.
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
After analyzing the data, the writer found two findings which are Errors in transferring the message and Possible Variations, which can be seen in the table below. After counting the number of error and the possible variation, the writer put the number on the table.
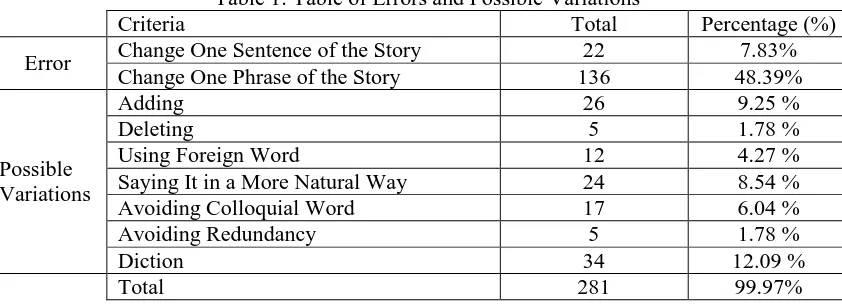
Table 1: Table of Errors and Possible Variations
Criteria Total Percentage (%)
Error Change One Sentence of the Story 22 7.83%
Change One Phrase of the Story 136 48.39%
Possible Variations
Adding 26 9.25 %
Deleting 5 1.78 %
Using Foreign Word 12 4.27 %
Saying It in a More Natural Way 24 8.54 %
Avoiding Colloquial Word 17 6.04 %
Avoiding Redundancy 5 1.78 %
Diction 34 12.09 %
Total 281 99.97%
There should be four kinds of error in transferring the message, however the writer did not include the other two, which are Errors which Change the Whole Story and Errors which Change Half of the Story. Since the unit used is per sentence, she did not include them in the table because they cannot be counted per sentence. If they were counted as per sentence, then the errors could not be seen. The writer used the formula in the chapter 3 to find out the percentage of each result. From the results above, it can be seen that the error which occurs the most is Errors which Change One Phrase of the Story.
For the discussion, the writer classifies the analysis into two parts, the first part is the one which contains error in transferring the message and the second part is the one which does not contain error in transferring the message which is called Possible Variation in Translation.
1. Errors in Transferring the Message
In this part, the writer puts the translated text with error in message, which means that it did not have the same message with the original. Here the writer will divide discussion into four categories: Errors which change the whole story, Errors which Change half of the Story, Errors which Change One Sentence, and Errors which Change One Phrases.
157
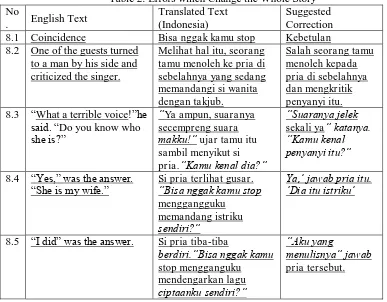
This category shows the errors in transferring the message which change the whole story. The example is taken from data translation of Text 1.
Table 2: Errors which Change the Whole Story No 8.1 Coincidence Bisa nggak kamu stop Kebetulan 8.2 One of the guests turned
to a man by his side and criticized the singer.
Melihat hal itu, seorang tamu menoleh ke pria di sebelahnya yang sedang
“She is my wife.” Si pria terlihat gusar. “Bisa nggak kamu stop menggangguku
became ‘Bisa Nggak Kamu Stop (Can You Stop)’. The data 8.1 is not written here since the student
did not make error in translating it. However, for the rest of the story, the student changed it. In data 8.2 the translated text stated that the guest who looked at the singer turned to a man by his side who stared the singer in amazement. However, the original text stated that one of the guests who looks at the singer turned to a man by his side and criticized her. The student omitted the word
‘criticized’ which is the important point of the story. Then, on the example 8.3 the student using
idiom ‘secempreng suara makku (as shrill as my mother’s voice)’ to translate the ‘terrible voice’.
Communicative translation is reader oriented, therefore the used of idiom in communicative translation is permitted as long as the reader understand the idiom. However, the idiom used in the
translated text is uncommonly used. The readers do not know how shrill the voice of the guest’s
mother is, therefore that idiom could not be used, so it is considered as an error. In example 8.4, the student changed the tone in the text. The original text only stated the husband said that the singer is his wife. While in the translation, the husband is angry and told the guest to stop bothering him staring his wife. Stating the husband was angry give different tone to the reader, the reader would imagine the husband is a quick-tempered person, while in the original, the husband just answer without any emotion displayed. Besides, in the translated text, the husband told the guest to stop bothering him, as if the guest has bothered him continuously. In example 8.6, the original just
stated that the husband answers the guest’s question. While in the translation, the husband angrily
tells the guest to stop bothering him listening to his own created song. Again, the student changed the feeling in the text.
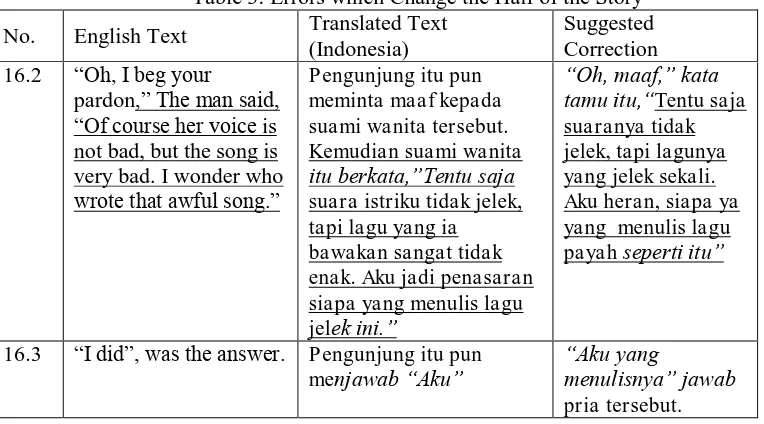
1.2 Errors which Change the Half of the Story
158
Table 3: Errors which Change the Half of the Story
No. English Text Translated Text (Indonesia)
16.3 “I did”, was the answer. Pengunjung itu pun
menjawab “Aku”
“Aku yang
menulisnya” jawab pria tersebut.
The data in table 2 is taken from data student 16. The student has translated the half of the story correctly, however, for the rest of the story the student made errors in transferring the message. In those two examples, the message is different with the original text. The problem here is the speaker which is different between the original and translated text. In the example 16.2, it should be the guest who said the sentence instead of the husband. The guest who apologized to the
husband said that it was not the wife’s voice which was bad but the song was. However, in the
translated text, it is the husband who said the sentence, stated that it is not the voice of his wife which is bad. Then in the example 16.3, it should be the husband who answered stating that he is the one who wrote the song. However in the translated text, it is the guest who answered stating that he is the one who wrote the song. By changing the speaker, the message of the sentence could be different.
1.3 Errors which Change One Sentence of the Story
This category shows the errors in transferring the message which change one sentence. The data is taken from data translation of Text 2.
Table 4: Errors which Change One Sentence of the Story
The data in table 3 is taken from data 15.3 from Text 2. The original text stated that Tom is angry because the price of the bicycle is not included with the lamp in the advertisement. But, the translation stated that Tom is angry because of the price is not put in the advertisement. In this case, Tom is angry because of two completely different reasons. Although it does not change the plot of the story, it still change message in the sentence thus it is considered as an error
No. English Text Translated Text
159
1.4 Errors which Change One Phrase of the Story
This category shows the errors in transferring the message which change one phrase. The example is taken from data translation of Text 4.
Table 5: Errors which Change One Phrase of the Story
The data in the table 4 is taken from data 1.4 Text 4. In data 1.4, the student made error in
translating ‘visiting from America’ as ‘mengunjungi Amerika (visiting America)’ which both
clearly have different meaning.
2. Possible Variations in Translation 2.1 Adding
This section discussed about translated text which does not contain errors, however there are some adding description in the text.
Table 6: Adding 2.2 A woman was singing. Di sebuah pub, seorang
penyanyi pendatang baru
In those examples above, the students adding some description such as location (bar, pub), or another information to make the translation sounds more natural.
2.2 Deleting
This section discussed about translated text which does not contain error but there are some part of the text which does not translated.
Table 7: Deleting
No. English Text Translated Text (Indonesia)
Suggested Correction
11.1 “Oh, I beg your
pardon,” The man said,
“Of course her voice is
not bad, but the song is
This example is taken from data 11.1 of Text 1, the student omits the phrase ‘the man said’, but
since it does not change the message of the story, so it is not considered as error. No. English Text Translated Text
(Indonesia) Suggested Correction 1.4 The couple, visiting from
160
2.3 Using Foreign WordBasic translation class taught about translating English Text into Indonesian. However, there are some students who use foreign word which does not belong to Indonesian in the translated text.
Table 8: Using Foreign Word
No. English Text Translated Text (Indonesia)
Suggested Correction 18.1 “Oh, I beg your
pardon,” The man said,
“Of course her voice is
not bad, but the song is
The examples of using foreign word is taken from data 18.1 of Text 1.The students are asked to translate the original text which is in English into Indonesian. However, there are some words which are translated using another language, such as English. In the data 18.1, the student using
‘sorry’ instead of ‘maaf’ in translating ‘I beg your pardon’.
2.4 Saying It in a More Natural Way
This section discusses about the naturalness of the sentence in the Indonesian and the using of word appropriately with the connotation. Although the message is correct, sometimes the sentence seems unnatural in Indonesian.
Table 9: Saying it in a more natural way
No 1.2 Howard had also planned
to lie around the hotel pool, soak up the sun, read a good book, and look at pretty women in their bathing suits.
The data in Table 9 is taken from data translation of Text 3. The student in data 1.2 literary
translated ‘soak up the sun’ as ‘menyerap sinar matahari’ which is odd as the correct term in
Indonesian is ‘berjemur’.
2.5 Avoiding Colloquial Word
This section discusses about the using of too informal language in translating the text.
Table 10: Colloquial
161
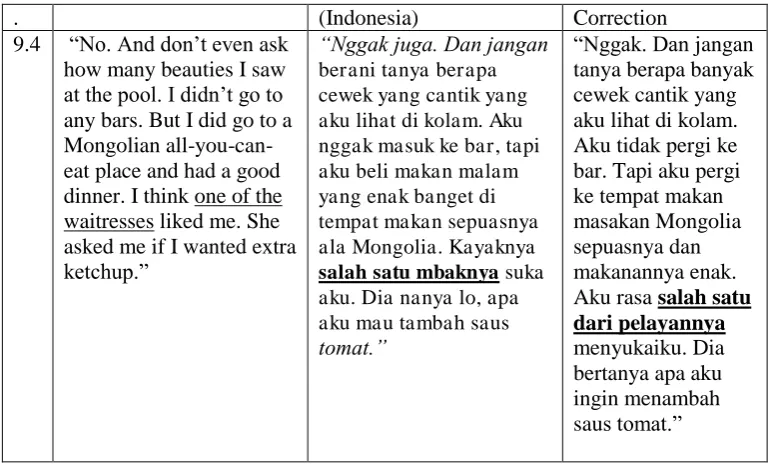
. (Indonesia) Correction
9.4 “No. And don’t even ask how many beauties I saw
at the pool. I didn’t go to asked me if I wanted extra
ketchup.”
“Nggak juga. Dan jangan berani tanya berapa cewek yang cantik yang aku lihat di kolam. Aku nggak masuk ke bar, tapi aku beli makan malam yang enak banget di tempat makan sepuasnya ala Mongolia. Kayaknya salah satu mbaknya suka aku. Dia nanya lo, apa
The writer found that colloquial is found most in the text 3, and nothing in the text 4. The writer assumed that it is not found in the text 4 because the context of the text is conversation between manager of the hotel and the guest which is required to use more formal language. In the text 3, the conversation is between friends, therefore students tend to use informal language to make it more natural, because it will be peculiar using formal language in conversation between friends. The problem in using too informal language is that there might be some reader who does
not understand the sentence. For instance, data 9.4 from text 3, the student translated ‘one of the waitresses’ as ‘salah satu mbaknya’. Some people might understand that ‘mbak’ in here is the
waitress, however, there could be people who do not understand ‘mbak’ as the waitress. It is better
to use more general word such as ‘pelayan’.
2.6 Avoiding Redundancy
This section discusses about the repetition of words which have the same meaning.
Table 11: Redundancy
No. English Text Translated Text (Indonesia)
the price of the bicycle.
It’s an extra.”
This example is taken from Text 2 data 11.2. Here the student use two words which have the same meaning tambahan and ekstra.
2.7 Diction
This section discusses about the choice of word which sometimes have different meaning, however it does not change the message of the text.
162
1.1 One of the guests turnedto a man by his side and criticized the singer.
Salah satu tamu ngomong ke pria yang di
sebelahnya dan kasih kritik sama yang nyanyi.
Salah seorang tamu menoleh kepada pria di sebelahnya dan mengkritik penyanyi itu.
Data 1.1 is from Text 1. The underlined word on the translation data is actually has its own English word. However, since they did not change the message of the original text, they were not considered as error.
3. Title
This section discusses about the some of the translated title which the writer think is interesting. Some of this title might be incorrect in meaning, however, this title reveal the message of the story and might has effect on the reader.
Table 12: Title
No. English Text Translated Text (Indonesia)
Suggested Correction 5.1 Fishing for Girls Menggaet Wanita Berburu Cewek 11.1 Goodbye to Clean
Couple
Selamat Tinggal Pasangan Nyentrik
Selamat Tinggal Pasangan Cinta Bersih
Those data in Table 12 are title of two texts. ‘Fishing for Girls’ is the Title of Text 3, and
‘Goodbye to Clean Couple’ is the title of Text 4. If we use Communicative translation, those title is
not incorrect even though they did not have the same meaning with the original Text. Moreover, in the case of Title which should be attractive so that it will trigger the reader to read the text, those translated Title are considered as correct. For example, the data 5.1, if the title is literary translated, it will be ‘Memancing Cewek’ but, student in data 5.1 translated it as ‘Menggaet Cewek’ which
have closer meaning to Indonesian reader. Another example is the title of Text 4, ‘Goodbye to
Clean Couple’ is translated as ‘Selamat Tinggal Pasangan Nyentrik’ in data 11.1. It is considered as
correct, since it related with the content of the story which is about a couple of clean freak.
CONCLUSION
After analyzing the data translation of humor texts produced by the student of Basic Translation class period 2010/2011, the writer found many errors in transferring the message of the text. As the finding, the writer found four kinds of error in transferring the message, and eight kinds of Possible Variation in Translation in the data translation which the writer has analyzed. The errors in transferring the message are Errors which change the whole story, Errors which change half of the story, Errors which change one sentence of the story, and Errors which change one phrase of the story. The Possible Variation in Translation are Adding, Deletion, Using Foreign Word, Naturalness, Inconsistency, Colloquial, Redundancy, and Diction. Besides, the writer also found some exception about the translation of the Title.
Then, answering the second question which is about the frequency of the error, the writer found that Errors which change one phrase has the biggest number of frequency, meant that there were many phrases which have different message with the original text.
Then, the error which had the least number is the Errors which changed the whole story. It had the least number, but it was the most significant error since the student change the whole message of the story.
Concerning the translation of the Title, there are some students who creatively translated the Title so that it became more interesting and trigger the reader to read the text. So, they have used
the communicative translation, which aim to create a certain effect on reader’s mind, in translating
the title.
163
One Phrase of the Story, but this error did not ruin the whole text, at least the reader might still be able to understand what the author’s meant.
The writer hopes this research about error in transferring message, can help others who are planning to write similar topic with her. She also suggests other topic which is interesting to be analyzed such as errors related with discourse and register analysis, or cultural and ideological turns. By considering that, studies on translation could be more comprehensive.
REFERENCES
Munday, J. (2008). Introducing translation studies. New York, NY: Routledge Newmark, P. (1981). Approach to Translation. Oxford: Pergamon Press
Simatupang, M. (2000). Pengantar Teori Terjemahan. Jakarta: Direktorat Jenderal Pendidikan Tinggi Departemen Pendidikan Nasional
164
Appendix Text 1
Coincidence
A woman was singing. One of the guests turned to a man by his side and criticized the singer.
“What a terrible voice!” he said. “Do you know who she is?” “Yes,” was the answer. “She is my wife.”
“Oh, I beg your pardon,” The man said, “Of course her voice is not bad, but the song is very bad. I wonder who wrote that awful song.”
“I did.” was the answer.
Text 2
A Girl Not Included
Tom saw an advertisement in a newspaper for a beautiful, modern bicycle which cost £54. 99, so he went to the shop which had put the advertisement in and asked to see one of their beautiful bicycles.
The shopkeeper was very happy to show one to Tom, who examined carefully and turned into the shop, saying: "There is not a lamp on the bicycle, but there was one on the bicycle in your
advertisement.”
"Yes, Sir.” answered the shopkeeper, "but the lamp isn't included in the price of the bicycle. It is
an extra. "
"Not included in the price of the bicycle!" Tom said angrily. "But that's not honest. If the lamp is in the advertisement, it should have been included in the price you gave there. "
"Well, Sir.” answered the shopkeeper calmly. "There is a girl on the bicycle in our advertisement, but we don't supply one of them with the bicycle either.”
Text 3
Fishing for Girls
Wednesday night, Howard asked Glenn if he wanted to go fishing and girl-watching that weekend
at Santa Fe Lake. “We’ll leave Friday morning and return late Sunday night,” he said. Glenn said
he had to clean out his garage, so Howard went by himself.
Howard had also planned to lie around the hotel pool, soak up the sun, read a good book, and look at pretty women in their bathing suits. His own apartment didn't have a pool, so whenever he traveled, he always liked to stay at a place with a pool. But when he arrived at the hotel about noon, he saw that there were no pretty girls at the pool. There were no girls at all. There was nobody at the pool, because the pool was empty. It was being repaired all that week. The staff had
“forgotten” to tell Howard this little detail. Howard called Glenn late Friday night.
“How was the fishing?” Glenn asked.
“Didn’t see any, didn’t catch any,” replied Howard. “Well, did you catch any women?”
“No. And don’t even ask how many beauties I saw at the pool. I didn’t go to any bars. But I did go to a Mongolian all-you-can-eat place and had a good dinner. I think one of the waitresses liked me.
She asked me if I wanted extra ketchup.”
“Well, I hope you said yes. Any time a woman asks you if you want extra anything, that’s female
code. It means they like you.”
“I said no. There was a whole bottle right in front of me.”
“Well, you blew it. I don’t know when you’re going to learn to pick up on those signals. Next time I’ll go with you and show you all the tricks.”
“If you knew all the tricks, you wouldn’t be divorced three times.”
Text 4
165
Wijaya, the manager of the Paradise Hotel, told a middle-aged couple that they would have to leave the hotel after just one night. The couple, visiting from America, had booked a room for eight nights.
“They wanted a sterile environment,” Wijaya said. “They should have rented a room in a hospital, maybe an operating room. This hotel is clean, but it isn’t that clean.”
Wijaya said that, on the very first day, the couple brought all the sheets, pillowcases, and bedspreads down to the main lobby and just dropped them next to the front desk. They stood there next to this pile of bedding while other guests looked, pointed, and murmured. The hotel got three cancellations within the hour from people who witnessed this strange event.
When Wijaya asked the couple what the problem was, they said that their bedding was filthy and
they wanted it replaced. The couple could not identify any specific “filth” on the bedding. The
wife just said, “We’re paying good money to stay here. How dare you doubt us? We know the filth
is there. That’s all the proof you need.” Theodore called room service, and the bedding was
replaced immediately.
Early the next evening, however, the couple marched to the front desk again and demanded seven
cans of spray disinfectant. “We need a can for each night. We have to spray the phone, the TV, all
the door handles, the toilet handle, the shower stall, the faucet, the sink, and any hotel staff
entering our room.”
Worried about what their demands might be in the following days, Wijaya politely suggested that
a hotel more suitable for them was just around the corner. He then called ahead to reserve a “very clean” room, and gave them free transportation in the hotel limousine.