AN ANALYSIS OF STORY MAPPING TECHNIQUE TO IMPROVE STUDENTS’ READING COMPREHENSION OF NARRATIVE
TEXTS AT A SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL PLUS IN RIAU
BY:
FUJIHAN PRATIWI SIN. 11714202604
FACULTY OF EDUCATION AND TEACHER TRAINING STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY OF SULTAN SYARIF KASIM RIAU
PEKANBARU 1444 H/ 2022 M
AN ANALYSIS OF STORY MAPPING TECHNIQUE TO IMPROVE STUDENTS’ READING COMPREHENSION OF NARRATIVE
TEXTS AT A SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL PLUS IN RIAU
BY:
FUJIHAN PRATIWI SIN. 11714202604
A Skripsi
Submitted as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for Bachelor Degree in English Education
(S. Pd.)
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF EDUCATION AND TEACHER TRAINING
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY OF SULTAN SYARIF KASIM RIAU
PEKANBARU
In the name of Allah SWT, the most Gracious and Merciful, praises belongs to Allah Almighty. By his guidance and blessing, the researcher has completed a thesis as a requirement to achieve of Bachelor degree (S.Pd) at Department of English Education Faculty of Education and Teacher Training, State Islamic University of Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau. Peace and solution be upon to Prophet Muhammad SAW, his family, his companion, and his adherence.
Appreciation and sincere thanks to my beloved parents, Mr. Afrizal and Mrs. Mesra Yenti, for their support, attention, motivation, help, love, and care. No words can describe how much I love them.
In conducting the research and finishing this project paper, the researcher got suggestion, encouragement, motivation, and support from many people.
Therefore, in this opportunity, the researcher would like to express huge gratitude to those who given a lot of things what researcher is able to finalize and publish this research:
1. Prof. Dr. Hairunas, M. Ag., the Rector of State Islamic University of Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau. Prof. Dr. Hj. Helmiati, M. Ag., as Vice Rector I, Dr. H.
Mas‟ud Zein, M.Pd., as Vice Rector II, Prof. Edi Erwan, S. Pt, M. Sc., Ph. D, as Vice Rector III, and staff. Thanks for the kindness and the encouragement.
2. Dr. H. Kadar, M.Ag., the Dean of Faculty of Education and Teacher Training, State Islamic University of Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau. Dr. H. Zarkasih, M.Ag., as Vice Dean I, Dr. Zubaidah Amir, MZ, M. Pd., as the Vice Dean II, Dr.
Amirah Diniaty, M. Pd. Kons., as Vice Dean III, and all staff.
iv
3. Dr. Faurina Anastasia, SS., M. Hum., the Head of Department of English Education, who has given me correction, suggestion support, advice, and guidance in completing the thesis.
4. Dr. Nur Aisyah Zulkifli, M.Pd., the Secretary of Department of English Education. Thank you very much for the guidance and kindness.
5. Dr. Riza Amelia, M.Pd., the researchers‟ beloved thesis supervisor who had given guidance, advice, encouragement, and motivation to the researcher from the beginning of writing the thesis until the final stages.
6. Dedy Wahyudi, M.Pd., as the researcher‟s academic supervisor and all lectures of English Education Department who have given suggestion and motivations.
7. The headmaster of SMAN Plus of Riau Province, Andri Karmidi, M.Pd., the English teacher of SMAN Plus of Riau Province, Tengku Emadesti, M.Pd., who helped and provided the necessary data to the researcher while conducting the research and as a sample of this research.
8. The writer‟s brother Febian Pratama S.T, his wife Noffa Febrina S.E , and Writer‟s nephew Nahda Bahira Alfatunisa, who have given the researcher a massive support in carrying out and finishing this thesis.
9. The researcher‟s special best friends, Lani Dwi Kurnia S.Pd, Ariqah Lindi Aisyah, Nurul Mahfuza S.Pd, Uchi Mukho Adrianty S.Pd, Wulan Rahma fanni S.Pd, Helen Futriasa S.E, Suci Nadilla S.Km, Riri Fikriah S.Pd, Shabrina, Gina Agustin and all my friend in English Department 17 who could not be mentioned one by one, and you know exactly who you are.
10. Last but not least, for the researcher herself. Thank you for doing hard work, for always moving forward, for battling every barrier, and thank you for not giving up during the process.
thesis. Therefore, constructive critiques and suggestion are needed in order to improve this thesis. May Allah almighty, the lord of universe bless you All.
Pekanbaru, Dzulhijjah 4, 1444 H July, 1th 2022 The Researcher
Fujihan Pratiwi SIN. 11714202604
vi ABSTRACT
Fujihan Pratiwi (2022): An Analysis of Story Mapping Technique to Improve Students’ Reading Comprehension of Narrative Texts at a Senior High School Plus in Riau
One of the problems which are still faced by students in teaching reading is in understanding of narrative text. The lack of vocabulary and knowledge of structure makes the students cannot read well. Based on those facts, the researcher used a technique in teaching narrative text which could help the students comprehend the text and be able to recognize the main element of the text, it was story mapping. This research aimed to investigate how story mapping technique improves students‟ reading comprehension in narrative text. This research used qualitative research with case study design was employed. This research was held from February until March 2022 at Senior High School Plus in Riau. The subjects of the research were Social class in the tenth grade of Senior high school plus in Riau and one English teacher. The data were gathered from observation, interview, and questionnaire. The findings showed that story mapping technique helped the students to comprehend the elements of narrative text easily. Story mapping could improve the students‟ reading comprehension in narrative text. The students could understand the text and helped the students in identifying the structure of narrative text.
Fujihan Pratiwi (2022): Analisa teknik pemetaan cerita dalam meningkatkan pemahaman membaca pada teks naratif pada Sekolah Menengah atas Plus Riau
Salah satu masalah yang sering dihadapi siswa dalam pembelajaran membaca adalah pemahaman pada teks naratif. Kurangnya kosakata dan pengetahuan tentang struktur membuat siswa tidak dapat membaca dengan baik. Berdasarkan fakta-fakta tersebut, peneliti menggunakan teknik pemetaan cerita dalam pengajaran teks naratif yang dapat membantu siswa memahami teks dan mampu mengenali unsur utama teks.
Penelitian ini dilakukan untuk mengetahui bagaimana teknik pemetaan cerita dapat meningkatkan pemahaman membaca pada teks naratif. Untuk mencapai tujuan tersebut digunakan penelitian kualitatif dengan rancangan studi kasus. Penelitian ini dilakukan pada bulan Februari sampai Maret pada tahun 2022. Subjek penelitian ini adalah kelas kelas X IPS pada SMA Plus Riau dan seorang guru Bahasa Inggris. Data dikumpulkan dari observasi, wawancara, dan angket. Temuan menunjukkan bahwa teknik story mapping membantu siswa dalam memahami unsur-unsur teks naratif dengan mudah.
Pemetaan cerita dapat meniingkatkan pemahaman membaca siswa dalam teks naratif.
Siswa dapat memahami teks dan membantu siswa dalam mengidentifikasi struktur teks naratif.
viii
LIST OF CONTENT
SUPERVISOR APPROVAL ... i
EXAMINES APPROVAL ... ii
ACKNOWLEDGMENT ... iii
ABSTRACK ... vi
ABSTRAK... vii
صخلم ... viii
LIST OF CONTENT ... ix
LIST OF TABLES ... xi
LIST OF FIGURES ... xii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xiii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Problem... 1
B. Problem of the Research ... 3
1. Identification of the Problem... 3
2. Limitation of the Problem ... 3
3. Formulation of the Problem ... 4
C. Objectives of the Research ... 4
D. Significance of the Research ... 5
E. Definition of the Terms ... 5
CHAPTER II REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Theoretical Framework ... 7
1. Reading Comprehension ... 7
x
2. Narrative Text ... 14
3. Perception ... 17
4. Story Mapping ... 19
B. Relevant Research ... 25
C. Conceptual Framework ... 27
CHAPTER III METHOD OF THE RESEARCH A. Research Design ... 29
B. Time and Location of the Research... 30
C. Participants of the Research ... 30
D. Sample of the Research ... 31
E. Subject and Object of the Research... 31
F. The technique of Data Collection... 31
G. The Technique of Data Analysis ... 34
CHAPTER IV FINDING AND DISCUSSION A. Finding ... 36
B. Discussion ... 48
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIO A. Conclusion ... 51
B. Suggestion ... 52 REFERENCES
APPENDICES
CURRICULUM VITAE
LIST OF TABLES
Table II.1 Character perspective chart ... 20 Table III.1 The schedule of classroom observation ... 29 Table IV.1 The result of Questionnaire ... 42
xii
LIST OF FIGURES
Figures II.1 The graphic of story map ... 20
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1 Syllabus and Lessons Plane Appendix 2 Instrument
Appendix 3 Supervisor Letters
Appendix 4 Thesis Supervision Activity Report Appendix 5 Recommendation Letters
1 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Study
Pang, Muaka, Bernhardt, & Kamil (2003) state that learning to read is an important educational goal. The ability to read the text in any form will bring great advantages to the readers (Dine Larsoen, 2000). Reading ability opens up new world and opportunities for students. It enables them to gain new knowledge, enjoys literature, and we do everything that is inseparable of modern life, such as: reading newspaper, job listing, textbook, maps, and so on.
Grabe in Richard and Renandya (2002) point out the primary purpose of reading is comprehension. Mc Shane (2005) defines reading comprehension as a process to get an understanding of meaning out in a text that being read.
Understanding in reading comprehension is very important for the students (Farichah, 2017). However, in reality reading comprehension in a second language is more challenging than in the first language (Nguyen, 2013).
According to Siriphanich (2010), L2 cannot comprehend the text because they do not understand how to locate the key terms in the text. They also have difficulty in drawing conclusion. Zugel (2009) argues that L2 students with a limited vocabulary have a lower score in reading comprehension.
Using appropriate reading techniques is one of the solutions that can be used to solve student problems in reading comprehension. One of them is the story mapping technique. Based on Sholicah (2017) story mapping is a good way to help students improve their reading comprehension. Students are able
to recognize the main element of the text during teaching-learning process (Kukuh, 2015). Through using story mapping, students adequate to understand the basic components of a story and can help students in answering the question from the text (Minha, 2017). Story mapping is based on the schema theory of reading comprehension that proper understanding is based on the reader‟s capacity to combine the prior knowledge structure (schemata with textual information (Anderson, Spiro, & Anderson; Singer & Donlan in Rathvon 2008).
Based on the reasons above, it seems that story mapping is probably the best solution to help students understanding the narrative text more effortlessly. The students could be equipped how to recognize the basic framework of narrative stories in order to improve their comprehension of the text throughly (Wright 2003). Fink in Amini (2020) states that knowing the elements of a story helps the students in understanding what is taking place in the story. For example they are taught how to find out the core elements of a story such as characters, setting, problems, events, and solution.
Based on the preliminary interview with one of the English teachers in Senior high school Plus in Riau, although reading is an important skill, it is also the most difficult skill to learn and teach in the classroom. The students don‟t understand the purpose of narrative text itself and finding information from the text. They need more time to process and comprehend the text based on the reading materials that teachers gives and they have to read the text in their second language.
3
In addition the students get difficulties to recognize the specific information from the text and they cannot combine the information that they have already read with their background knowledge. It is because the students were not practicing their English out of the class or in their home. They only learn English when they are studying English in the classroom.
In the previous study, the use of story mapping technique in narrative text has been investigated at the junior high school level (e.g Kukuh, 2015; Minha, 2017; sriyana, 2018; riza, 2013; Nurmala, 2018; Dian 2019). So in this research, the researcher would conduct the research at Senior High School level. Furthermore, most of previous study using quantitative method and research of the topic is to analyses testing and reading approach. So, further study needed to discover about the result of this technique through the process and perception in improving students reading comprehension of narrative text in classroom activities.
Given the description above, therefore, the researcher is interested in carrying out a research entitled: “AN ANALYSIS OF STORY MAPPING
TECHNIQUE TO IMPROVE STUDENT’S READING
COMPREHENSION OF NARRATIVE TEXTS AT A SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL PLUS IN RIAU”.
B. Problem of the Research
1. Identification of the Problem
a. They need more time to process and comprehend the text based on the reading materials that teachers gives
b. Some of students found difficulties to recognize the specific information in narrative text
2. Limitation of the Problem
The researcher will limit the problems on story mapping to improve student‟s reading comprehension in narrative text at a Senior High School in Riau. The writer limits the study only by applying story mapping technique in reading narrative text to the tenth grade students at Senior High School in Riau. The researcher does not involve directly in the classroom activity. The researcher observed about the process of reading through story mapping technique.
3. Formulation of the Problem
The researcher specifies the problem discussed in the following formulated questions as follows:
a. How is the implementation of story mapping technique in improving students‟ reading comprehension of narrative text?
b. What are the students‟ and teacher‟s perception of the effectiveness story mapping technique in improving students‟ reading comprehension of narrative text?
C. Objective of the Research
The objectives of the research are:
a. To describe the implementation of story mapping technique in improving students‟ reading comprehension of narrative text
b. To explain the students‟ and teacher‟s perceptions of the effectiveness of story mapping technique in improving students‟ reading comprehension of narrative texts.
5
D. Significance of the Research
Theoretically, this research can be a reference for other future researchers. In practically both teacher and students can get understand narrative better through story mapping technique. The teacher by doing this research is expected to increase the knowledge on how motivate students to be interested in learning, The students is expected become more active and enjoyable in learning process.
E. Definition of the Terms
The researcher feels necessary to define the used terms in this research as follows:
1. Reading Comprehension
In this study, reading comprehension refers to the processes of deriving the meaning of one word to another in a text. Readers usually make use of background knowledge, vocabulary, grammatical knowledge and experience with text to help them understand written text (Pang, 2003). In this research, reading comprehension refers to the ability of students to understand element of narrative texts.
2. Story Mapping
In general, story mapping refers to an activity of deconstructing a story‟s elements into some graphical points. According to Pamela (2004), “story mapping is used to represent some story component in the form of graphic visualization, which has the purpose of giving the readers or writers a picture to provide an overview of a story.”
3. Narrative Text
In this study, Narrative text refers to a genre of text which delivers a story which may be fictional or based on fact. The primary purpose of narrative text is to entertain the readers. Smalley (2012) states that narrative text is telling a story or the experience of someone in chronological of an order. In this research, narrative texts refers to the narrative texts used by the students at the tenth grade, such as elements, structure and language features.
7 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Theoretical Framework
1. Reading Comprehension
a. Definition of Reading Comprehension
The discussion of reading cannot be separated from the definition of reading itself. According to Nunan (2000) reading is the result of a conceptual interaction between the writer and the reader. It is the reader‟s ability to clarify the writer‟s message or purpose of the text.
During this process, the reader tries to identify the writer‟s communicative intention. Reading is possible to expand one‟s perspective and gain a good knowledge of the foreign culture (Putranti, 2015). So, the main goal of reading is to gain the correct message form a text that the writer intended for the reader to receive.
Tankersley (2003) states that comprehension is the center of reading. She also says that comprehension is the heart of reading process and we bring our life experiences to the act of reading. The student should have good comprehension because comprehension is a process in which reader make meaning by interacting with the text through the combination of prior knowledge and previous experience (Duke, 2003). Gilakjani & Sabouri (2016) defines that reading comprehension is the process of making sense of a text. The purpose is to get an understanding of the written text rather than to acquire
meaning from individual words or sentences (Snow, 2002). As same as Pamela (2004) also points out that reading comprehension is the process of understanding the message that the writer is trying to convey. To put it another way, it is making meaning from the text at hand.
b. Problem in Reading Comprehension
Problem in reading comprehension have been issue in EFL teaching-learning setting for a long time. 52% of students with L2 reading comprehension problems had difficulties in learning a foreign language (Chen and Chen, 2015). Numerous studies have shown that most of EFL students often have difficulties in comprehending English text. First, students are probably not keen on reading L2 literature because they have to work hard to comprehend it. Second, studies mention several common problems in the EFL reading classroom such as insufficient vocabulary, problems understanding linguistic complexity including lexical and syntactic knowledge, language inaccessibility, poor reading skills and lack of schemata (Grabe, 1991;
Birch, 2002; alyousef, 2006; Rahman, 2004). The cause of students‟
problem in reading comprehension divided into external and internal factors (Fajar, 2009). He says that internal factor includes physics, intellectual, and psychological. While external factors include family and school environments.
9
Some internal factors are understanding long sentence and text problem in using reading strategies and problem in concentration (Fajar, 2009). First is understanding long sentences. It is supported by Barfield (1999) that shows almost L2 percent of students had problem in understanding long sentences in graded story and 20 percent in academic text. Second is using reading strategies. Duarte & Barner (2005) argues that the students who are not familiar with reading strategies will feel down and frustrated because the students lack of tool necessary to succeed in reading comprehension test. Third is Problem in concentration during reading. Problem in concentration is another reason for students‟ poor reading because concentration is an important factor for a good and affective reading and comprehension of a text results from reading with concentration (Shaw, 1959).
In external factors is reader environment. Home and school are two kinds of learners‟ environment that can influence their learning reading achievement (Peter, 2001). Freemsn & long says that every students needs attention from their parents to reach learning achievement. Students can feel better if their family can give a support.
They also argues that the school environment also can be a cause of student learning problem. The lack of learning media such as English books, magazines or newspapers make learning process become not effective and difficult in understanding the material.
c. Strategies of Reading Comprehension
To make reading comprehension successful, there are some strategies which can be practically applied. According Brown (2000), there are some strategies in reading comprehension in the classroom.
First is identifying the purpose of reading. By identifying the purpose of reading, the students can choose what information they need in reading. Second, use graphic rules and patterns to aid in bottom up decoding (especially for beginning level). In learning process in classroom, the teacher also explain for the student to read the sound words with sort vowel sounds such as (bat, leg, wish) and the sound words with final silent “e”, example (late, time, bite,). The third is using efficient silent reading techniques for relatively rapid comprehension. It is mean that the students do not need to produce their voice to pronounce every word but the comprehension of the text that they read is more important part. The fourth is skimming the text for the main idea. Through skimming can gives the students the advantage of being able to guess the purpose basic components that students read such as passage, main topic, message, and some supporting details. Next is scanning the text for specific information.
In scanning the students can quickly searching for some particular pieces of information that the students need when reading.
Adler in Nikmah (2007) argues, there are seven strategies to teach students reading comprehension. First is Monitoring Comprehension.
11
Students who are good at monitoring their comprehension, know when they understand what they read and when they do not. They have strategies to solve their problem as they occur in their understanding.
Second is metacognition. Good readers using their metacognitive strategies to think about have control over their reading. Before reading, they might clarify their purpose for reading and preview the text. During reading activities they can monitor their understanding, adjusting their reading speed to fit the difficulty form the text and solve any comprehension problem that they find.
The third is graphic and Semantic Organizers. Graphic organizers illustrate concepts and relationship between concepts in a text or using diagrams. Regardless of label, graphic organizers can help readers focus on concepts and how they are related to other concepts. Not only that, graphic organizers help students read and understand textbooks and picture books.
The fourth is Answering Questions. It will be effective through answering question, because they give students a purpose for reading, students‟ attention, help students to think actively as they read, encourage students to monitor their comprehension and help students to review content and relate they have learned to what they already know.
Fifth is generating Questions. By generating questions, students become aware of whether they can answer the questions and
understand what they are reading. Students can combine information from different part of the text through ask the question to themselves.
The sixth is recognizing Story Structure. Students learn to identify the categories of content (characters, setting, events, problem and resolution). Students learn to recognize story structure through the use of story maps. Instruction in story structure improves students‟
comprehension.
The last is Summarizing. Summarizing can help students to determine important part after reading and put it into their own word.
It can help students to identify or generate main ideas to connect the main or central ideas, to eliminate unnecessary information to remember what they read.
d. Teaching Reading
In teaching reading, the role of teacher is important because they determine whether the reading lessons are successful or not. The teacher has responsibility to encourage students to set their own learning goals, and it is also the teacher‟s responsibility to encourage students not to be afraid to fail and figure out exactly what they have learned.
William in Hidayati (2017) argues that for effective teaching of reading in the classroom, there are three activities involved in the reading activity, they are pre-reading, while reading, and after reading activities. First is Pre-reading. In pre-reading stage, teacher should
13
carefully design the activities that prepare the students mentally to accept what they are going to teach in the next stage. Pre reading is the phase that teachers do in class before students begin to read the selection and can affect comprehension. The function of pre-reading is to introduce and arouse interest in the topic, to motivate learners by giving a reason for reading and to provide some language preparation for the text.
Second is While-reading. In this phase also called during-reading activity, this is draws the students on text and involves them in the thinking process. The activities here will help the learners understand the writer‟s purpose, the text structure, and the context (Jansen, 2008).
In while-reading, student should be involved in activities which enable them to respond cognitively, emotionally and imaginatively. The teacher should create some useful activities in this phase for the better output from the students in the next stage. The activities in this stage should be designed according to the level and standard of the students.
The last phase is post-reading. The function of this stage is to evaluate what the teacher has taught in the while reading stage. The teacher may ask the students to know their reaction to the text. This stage is also important since this stage is supposed to evaluate and examine the output of and feedback from the students.
2. Narrative Text
a. Definition of Narrative Text
According to McQuillan in Millah (2013) narrative text that is told in language. Narrative text is found in stories and has structural organization that is include beginning, middle, and the end (Carrasquillo, 2004).
Farris (2004) reading a narrative text in a historical period or related to a scientific finding usually necessitates having some related knowledge in that specific area. It is mean that the readers who reads narrative text needs to become familiar with the previously reviewed elements of narrative text such as character, setting, problem and solution.
Moreover Chatman (1978) has classified narrative text into four basic elements. First is Setting, this is important component is usually found in the beginning of the story and provides clues regarding some of the background information the reader needs to understand the story. In this part also explains to the reader where and when the story is take place, the setting or location of the story and the period or the time of the story. If the setting sufficiently foreign to the student, the teacher will need to build background information to enhance comprehension.
Second is plot, the plot includes a series of episode or events that written by the author for the reader‟s attention and create a particular
15
fun moment of the story take place. Very simple stories can usually be explained using the beginning, middle and end story structure. In the beginning we usually find out: Who the story is about, where the story take place and what the problem is. In the middle, we usually find three attempts at solving the problem. In the end, we usually find solution to the problem. The last is conclusion. The author ends the story with summarize and tell the solution based on the problem in the story.
b. Purpose of Narrative Text
When someone tells another person about something that happened or occurred, they are reading a story or a plot. A narrative is a story that can amuse or entertain the readers. As well as Basith (2010) stated that the purpose of narrative text to tell a story about something or someone, to amuse or entertain the readers or the listeners, and get the moral lesson from the story.
c. Organization or the Generic Structure of Narrative Text
A more detailed generic structure of a narrative text has been proposed by Anderson and Anderson (2003) who argue that a narrative text includes Orientation, complication, sequences of events and resolution.
In Orientation, the readers are introduced to the main characters and possibly some minor characters. Some indicators are generally given of where the action is located when it is taking place. The next is
complication. Complication tells the beginning of the problem which lead to the crisis of the main participants. The complications is published along by a series of events, during we usually expect some of sort complications or problem to arise. It just would not be so interesting if something unexpected did not happen. This complication will involve the main characters and often serves toward them from reaching their goal. This is where the narrator tells how the character reacts to the complication in Sequence of events/climax. It includes their feeling and what they do. It includes their feeling and what they do. The event can be told in chronological order (the order in which they happen) or with flashback. The audience is given the narrator‟s point of view. In resolution, the implication may be resolved for better or worse, but it is rarely left completely unresolved. In resolution, provide solution to the problem either in a happy or in a sad ending. In some narrative texts, some narrator includes the part which is called by
„coda‟ if there is a moral or message to be learned from the story. That is only the optional part of a story.
d. Language Features of Narrative Text
Mark and Aderson (2003) said that each text type has each characteristic includes its language features. By knowing and understanding the language features, it is expected to help students learn easier. There are some language features that usually found as follow: Specific character. (e.g Cinderella, Snow White, Alibaba),
17
using simple past tense (e.g killed, drunk, went), using adverb of time (Once upon a time, one day), using cction verb, a verb that shows an action (e.g killed, dug, walked), and using direct speech, it is to make the story lively (e.g Snow White said “ My name is Snow White).
3. Perception
a. Definition of perception
Perception is the process to input or message or information to human‟s brain. This process that concerns about the entry or message or information through five senses, namely sense of sight, sense of hearing, sense of smell, sense of taste, and sense of touch (Slameto, 2003). According to Bimo (2003) perception is the process that take place within the individual that e\begins with the receipt of excitatory until is realized and understood by the individual, so that the individual can recognize himself and his surroundings.
Perception can be influenced by an individual‟s mental awareness, past experience, knowledge, motivation, and social interaction (Chee, 200). Robbin (2003) said that perception taken by individual to send and interpret perception of sensory to give significance in environment. Perception can be defined as our recognition and interpretation of sensory information. Perception also includes how we respond for the information.
In addition, perception is also described as the interpretation of an object, event or information that is grounded by the life experience of a
person who performs that interpretation. The experiences will be interpreted by their brain to certain impressions which are maybe different from one to another. This is similarity from Jalaludin (2003), he said that perception is the result of one‟s mind form a particular situation.
b. Types of Perception
There are three type of perception based on Robbins (2003), these types as follow:
1. Person Perception
Person perception refers two those process which come to know and think about other. Include characteristic, qualities and inner state. We construct imagine of others in ways that serve to stabilize, make predictable and render their manageable view of social world extend to attribute stable straits and enduring disposition to other people. It is feel better to understand their behavior and predict their future actions and use these nations to guide interactions.
2. Social Perception
Social perception means that trying to understand people whether they are professional athletes, political, leaders, criminal, defendants, entertainer, or loved one closer to home is not easy task. Social life dictates that we do something more than creatures of the moment.
Sustained patterns of interactions or social relationship require us to retain the information, as the situation require.
19
3. Perception of Situation
Social psycholinguistic views a situation as all the social factors that influence a person‟s experience or behavior at a given time and give a place. It is an interaction of time and space within which we act in specific ways. The situation contest in which stimuli occur has consequences for their interpretation.
4. Story Mapping
a. Definition of Story Mapping
Firstly, the origin of this technique from Farris in Abdul (2014). She says that:
“The origin of story maps lies within story grammar research. The term story grammar refers to the hierarchical rules or psychological structures that people use to create and remember stories,, the skeleton underlying a story to speak. These psychological models of comprehension and memory are used by both adults and children to encode and store in information in their long-term memories.”
Farris (2004) argues that Story mapping is a procedure which trains students to recognize the basic framework of narrative stories in order to enhance their comprehension of text. Story mapping help readers to understand content of the text and other useful information such as characters, setting, events, and resolution.
Similarly, Sorrel in Riza (2017) points out that story mapping is a schema construction technique that shows the relationships of different parts of a story with each other to the reader and give them the basic elements of the story schema in order to draw the attention of the reader. It is also stated by Reutzel in Richard T. Boon (2015),
that a story mapping is a visual framework typically presented in the from of a graphic organizer to facilitate the acquisition of story structure and story elements.
Sholichah (2017) argues that story mapping is effective in improving the students‟ reading comprehension achievement, clarify some reasons. Firstly, the students may discover the main concept, conclusion, and enhance their vocabulary through story mapping technique while reading the texts. Story mapping after reading the texts can easily recall the message of the text when it comes to comprehension exercises and the students can look at the story mapping containing the keywords of the texts and its description.
Each keyword in the story mapping represents certain information in the reading text. It is supported by the description of the keywords.
Secondly, the students taught the story mapping technique have higher motivation in reading texts. Thirdly, the story mapping technique can avoid the students‟ boredom while reading the texts.
In addition, according to Antonnaci and O‟ Callaghan (2012), story mapping technique provides a visual display of story element that will assist the students in remembering, comprehending and retelling the story that they listen and read. Story maps are visual representations of parts of a story that assist learners in guiding their way through it, from the beginning to the end of the text. Kurniawan (2007) said that story mapping technique is the way of teaching where students are
21
taught to organize the story into specific parts, including setting, problem, goal, action and outcome. It means that that story mapping technique is the way to encourage students‟ understanding in finding information details of the story.
Actually this technique not only can be used for helping students‟
reading comprehension, but also for another skill and ability, such as grammar, vocabulary, or even speaking or writing. As stated by Harida (2015), story mapping technique also used for students to improve vocabulary. Vocabulary teaching can be easily taught by using this technique. The students will be easier to understand and develop their vocabularies if the teachers of the students themselves use it as a way or process of vocabulary learning. So, it is stated that mind mapping or story is good using for teaching or learning English in every kinds of level or skills.
b. Kinds of Story Mapping
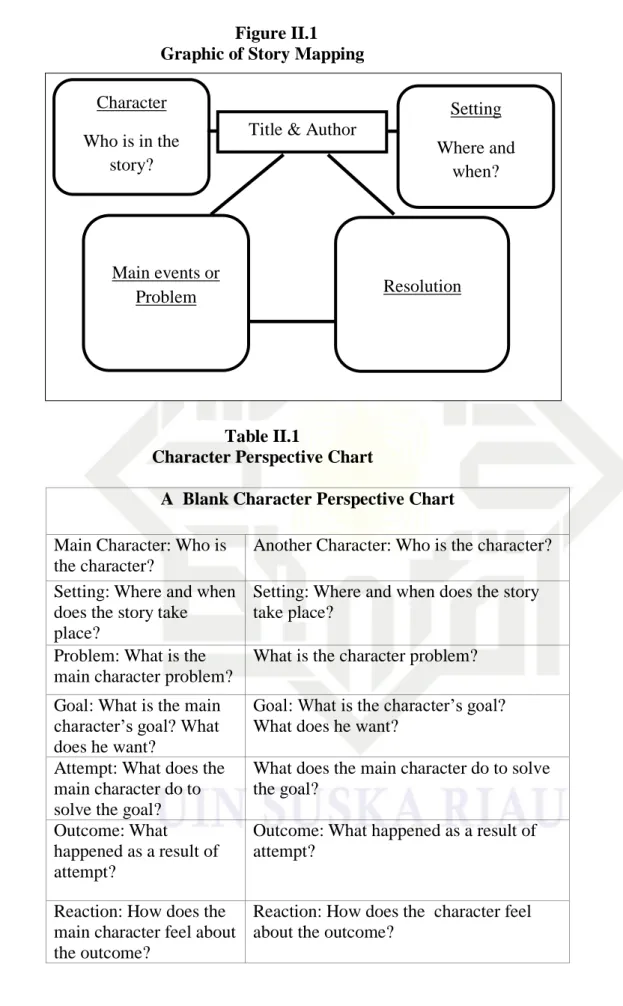
A story map is a strategy that uses a graphic organizer to help students learn the element of story. By identifying story characters, plot, setting, problem and solution, students read carefully to learn the details (Farris, 2004). She divides kinds of story mapping into two types; graphic story map or bubble and character perspective chart or CPC, but in this research the researcher only using graphic story map to make it simpler and easier to understand.
Figure II.1 Graphic of Story Mapping
Table II.1
Character Perspective Chart
A Blank Character Perspective Chart Main Character: Who is
the character?
Another Character: Who is the character?
Setting: Where and when does the story take place?
Setting: Where and when does the story take place?
Problem: What is the main character problem?
What is the character problem?
Goal: What is the main character‟s goal? What does he want?
Goal: What is the character‟s goal?
What does he want?
Attempt: What does the main character do to solve the goal?
What does the main character do to solve the goal?
Outcome: What
happened as a result of attempt?
Outcome: What happened as a result of attempt?
Reaction: How does the main character feel about the outcome?
Reaction: How does the character feel about the outcome?
Title & Author
Setting Where and
when?
Character Who is in the
story?
Main events or
Problem Resolution
23
Theme: What point did the author want to make?
Theme: What point did the author want to make?
c. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Story Mapping By implementing this technique, the students get many benefits through story mapping Sholichah (2017). Using story mapping technique in narrative text can help students effectively arrange the information from the reading materials. It will teach the students how to locate the keywords in each paragraph and write done the information linked with the keywords, as well as providing opportunities for students to recall specific detail from reading materials. In teaching and learning process using story mapping helps keep the students from becoming bored. It turns out that it could be an effective way to improve students‟ reading comprehension achievement.
According to Farris in Prawulandari (2014), some advantages of story mapping allows the students to store the information in their minds and in the learning process, so the students can see how the story parts connect together more quickly. When students predict what will happen next in one story after another, their knowledge is constantly applied. With story mapping can improve students‟
understanding by arranging and organizing main story elements to resolve problems of narrative text comprehension, so it can increase students‟ awareness that story characters and events are interrelated.
However, story mapping also had its own limitation. Farris in Prawulandari (2014) point out using story mapping technique can be used only in certain kinds of narrative text and it will take a quite long time for the students in understanding the steps of the story map. So, the teacher should help students to manage the time.
Indeed, the selection is only used for narrative text because it discusses the literally of story.
d. The procedure of Using Story Mapping
Before applying this method, the teacher is supposed to know well how to apply and use it. There are some steps of using story mapping to teach narrative text (Farris in Prawulandari (2014)).
First introducing the concept of a story mapping together with the benefits for the students. The teacher give explanation about benefits and tell the students how important story mapping in the learning process. Second, the teacher explain the main elements of story mapping such as title, the theme of the story, characters and personality, setting, main events or problem and resolution. In this part, the teacher give the students an interactive instruction for each elements through questioning before and after reading. It can motivate and check their comprehension. Third is helpful the students if there is something difficult with guidance question and ordered them to reread the text. Fourth have students read independently. Guide the students to find out the key words and
25
using them to fill the story map. The teacher can give some direction and asking the story mapping elements. Fifth, ask the students through selected stories and complete the story map worksheet after the students using story mapping. The last is evaluation. The teacher give a feedback and check their understanding with orally or distributed the printed test.
B. Relevant Research
Some researchers have conducted the research about story mapping. The first was the journal article from Kukuh Prakusumasari (2015) entitled “The Use Story Mapping Technique in Teaching Reading Skill at the Second Year of SMP Muhammadiyah 6 Surakarta‟‟. In her research she used descriptive research. The data was taken from event, informant, and document.
In collecting data, the researcher used observation and interview.
There result of this research showed that the used of story mapping technique as a technique in teaching reading can help the students understand the narrative text easily. The improvement of students during teaching-learning process was they were able to identify the generic structure of narrative text, they were able to use story mapping technique in reading narrative text, and the students‟
understanding increases every meeting.
The second is an article from Minha (2017) entitled “Using story mapping technique in comprehension of narrative text”. The
method used in this research was descriptive qualitative. Data collection instrument was the observation sheet and list of question of interview. The results of this study indicate that the story mapping technique can improve students‟ reading comprehension.
The students were able to understand the basic components of a story. It can help students in answering the question from the text.
The third is a research by Sriyana (2018) entitled “Using Story Mapping Technique to Improve Students‟ Participation in Reading Comprehension of Narrative text”. This research used a classroom action research. The tools of data collection were observation checklist and field notes. The result showed that Story Mapping Technique was able to improve students; participations in term of paying attention, answering question, and joining the discussion.
Through story mapping technique can increase the students‟
participation in reading comprehension.
In conclusion, this research is similar with previous research about using story mapping in reading comprehension. But it was conducted in different places and times with different samples and populations. In the current research, the researcher focused on using the story mapping technique in Junior High School with the qualitative method. In this research the researcher will apply the story mapping technique on Senior High School with qualitative method. Furthermore, most of previous study using quantitative
27
method and research of the topic is to analyses testing and reading approach. So, in this research, the researcher want to know the result of this technique through the process and perception in improving students reading comprehension of narrative text in the classroom activities.
C. Conceptual Framework
To avoid misunderstanding and misinterpreting, the conceptual Framework will be used in this research. The conceptual frameworks are to generate an understanding of the students‟ comprehension in reading narrative text by using story mapping technique. Therefore,
Reading comprehens
ion
Process
Perception Story
Mapping Technique
Students activity
Teachers performance
Classroom atmosphere
Students’
responses after using story mapping technique
Response of the teacher after using story mapping technique
researcher assumed that it is important to know whether story mapping technique will help students to understand narrative text.
29 CHAPTER III
METHOD OF THE RESEARCH
This chapter presents and elaborates how this research was conducted in order to discover the answer of preceding research questions. It offers research design, site and participants, data collection technique and data analysis.
A. Research Design
This study applied the qualitative research. According to Cresswell (2012) qualitative research is to explore the phenomenon of the problems from the perspective of different education students. In a qualitative research, source of primary data are the actions, words, and the source of additional data such as written, pictures, or statistical data (Moleong, 2005). The reason of researcher chose qualitative research is to get clear description of teaching and learning process by using story mapping technique at the eleventh grade of senior high school plus in Riau.
In this research, the researcher used a case study design. The case study design is a process of collecting data and information depth, intensive, holistic, and systematic detail about people, social events, settings, or groups, using various methods and techniques as well as many sources of information to understand effectively how people, events, natural settings operate or function in their context (Yusuf, 2019). In a case study, the researcher tries to examine individual or group in depth. The researchers attempts to discover all the variable that are important in the history or development of the subject (Ary, 2006).
The data of this research are all information about the students‟ activities that the researcher gathered from field notes of the observation, interview, and questionnaire. The observation in collecting the data, the source the data is the movable thing or the process which is observed. Interview and questionnaire in collecting the data, someone who answer and response the researcher‟s question is the source of data.
B. Time and Location of the Research
This research was conducted from February until March 2022 at a Senior High School Plus in Riau. This is one of Favorite School in Riau especially in Pekanbaru. It is located at Jl. Kubang Raya, Kubang Jaya, Kec. Siak Hulu, Kabupaten Kampar, Riau.
C. Participants and Sample of the Research 1. Participant of the Research
The study was conducted in Senior High School Plus in Riau. It involved one class of the tenth grade students and English teacher.
Moreover, there were five classes which consisted of 150 students, they were Mathematic Sciences Major and Social Sciences Major. Actually, in the school there were 4 English teachers. The explanation above can be seen from the following table.
Table III.1
Total of the Students
Class Number of Students
X Ms 1 30
X Ms 2 30
X Ms 3 30
X Ms 4 30
31
X Ss 1 30
Total 150 students
Table III.1I
Total of English Teachers Population of English
Teachers
Number of English Teacher English teachers 4
Total 4 English Teachers
2. Sample of this research
Researcher used a purposive sampling. According to Marguerite (2006), a purposive sampling technique is a common procedure in qualitative research that identifies key informants or people who have specific knowledge about the topic being studied. The process of selecting sample by taking subject that is not based on the level or area, but it is taken based on the specific purpose. In a purposive sampling technique, the researcher chose the participants of this research who were the students of the tenth grade of Social Major which consisted of 30 students and one English teacher. The researcher chose the teacher who became the sample of this research was the teacher who has applied the story mapping technique.
D. Subject and Object of the Research 1. Subject of the Research
The subject of this research were the tenth grade students and one English teacher at Senior High School Plus in Riau
2. Object of the Research
The object of this research was story mapping technique in students‟
reading comprehension at Senior High School Plus in Riau.
E. The Technique of Data Collection
In collecting the data, the researcher used triangulation technique.
According to Setiyadi (2006), triangulation is the use of two more ways to collect the data about the subject of the survey‟s attitude. Because human attitudes are complicated, using a single way to obtain qualitative data is usually underexplored. In this research, there are some steps used to collect the data needed, namely:
1. Observation
Creswell (2005) said that observation is the process of gathering opened, firsthand information by observing people and place at a research site. In this research, the researcher observed about process, students‟
activities and description of classroom atmosphere by using story mapping technique to get the data. The researcher did not involve directly in the classroom activity because the researcher as passive participants.
Some procedures that the researcher did in the observation made the field note about what happens during the activity in the classroom, how the technique works, how the students‟ respond, participants, and everything which are found during learning process. The observation was conducted in 2 meetings. Each meeting ran for sixty minutes. In addition, the schedule of observation is presented in table below
33
Table III.1
The schedule of classroom observation
Meeting Date Activities
1st meeting February 15th 2022 Learning Schematic of Narrative text 2st meeting February, 22th 2022 Learning Schematic of
Narrative text 2. Interview
After observing the teaching and learning process, the researcher interviewed the English teacher. According to Lodico (2010), there are five types of interviews, they are one to one, group interview, structured interview, semi-structured interview, unstructured interview. The researcher used semi-structure interview because the researcher prepare the list of question to the interviewee, although the researcher prepare the list, it did not limit the researcher to ask questions only based on the list.
The researcher prepared a list of questions to ask the teacher during the interview to get the information about teacher‟s opinion in using story mapping technique and about the strength and weaknesses of the technique. The interview was adapted from Abdul (2014). The questions of interview can be seen in the Appendix 2. The interview was conducted after the observation was finished. It was delivered in Bahasa Indonesia to make the respondent easier to answer and avoid misunderstanding.
3. Questionnaire
The researcher gave the questionnaire after the process of teaching and learning reading by using the story mapping technique. The researcher
gave the questionnaire to the students in order to know the further opinions and to know the aspect about the student‟s perceptions and to confirm the data from observation and interview. To measure attitudes, opinions, perceptions and satisfaction of a person or group of people about a problem, it used on a Likert scale (Sugiyono, 2013).
The questionnaire procedure used by the researcher was to send a list of questionnaires via Google forms that are easily accessible to the students and give the time to answer after using story mapping in the classroom activity. The questionnaire also adapted from Abdul (2014) see appendix 3.
F. The Technique of Data Analysis
The analysis of qualitative data is used in this research is based on the Miles and Huberman (1994) theory. The steps of analyzing the data are as follows:
1. Data reduction
Data reduction refers to the process of selecting, focusing, simplifying, abstracting, and transforming the data that appear in written-up field notes or transcriptions. In this case, the researcher selects the data derived from observation on teaching and learning process, interview to the teacher and students and questionnaire to the students as the supporting data to the result of interview of the students.
35
2. Data Display
Data display is a second component or level in Miles and Huberman model of qualitative data analysis. Generally, a display is an organized, compressed set of information that permits conclusion drawing and action. The displays included many types text or a diagram, graph, chart, table or matrix.
3. Conclusion Drawing and Verification
The last step of analyzing the data is conclusion drawing and verification. Conclusion drawing involves stepping back to consider what the analyzed data mean and to assess their implication for the questions at hand. Verification refers to process which is able to explain the answer of research question and research objectives.
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion
` Based on the results to gain the data from observation, interview and questionnaire, it is possible to conclude that the process of reading comprehension by using story mapping technique is well-run but not maximal. Over all it is an effective way, it seems the classroom atmosphere looked active, enthusiasm, and got positive interaction between the teacher and the students. But there are some of students who look less receptive to interaction. The problem faced by the teacher and students that influence each other, the teacher has difficulty to manage the time because it was took a long time, and the students find difficulties to finding the key words and develop their ideas.
Beside that, based on the data that researcher got from the research, using of story mapping technique in teaching reading comprehension has successfully. The students can understand the text and help the students in identifying the structure of the text easily. Teaching and learning process by using story mapping technique has improved the students‟ reading comprehension in understanding narrative text. It is also supported by the result of the questionnaire after using story mapping technique. The last, the teacher‟s perception about this technique, is that it would be a good way in teaching reading in narrative. Therefore, story mapping can
52
improve the students‟ reading comprehension in narrative because they get good result and easier to answer their task.
B. Suggestion
From the conclusion above, the researcher would like to offer some suggestion especially for English teacher to practice this technique and improve students‟ reading comprehension and follow the procedure well and should manage the time in using this technique.
The students should expand their vocabulary, so it would be easy to comprehending narrative story by using story mapping technique and during learning process the students should focus and pay attention. For further research who have the same problem and interested in conducting research in other fields such as speaking and writing.
REFERENCES
Alturki, N. (2017). The Effectiveness of Using Group Story Mapping Strategy to Improve Reading Comprehension of Students with Learning Disabilities.
Academic Journal, 12(18), 915-926. http://doi.org/10.5897/ERR2017.3320 Anderson, J. Neil. (2003). Active Skill For Reading :Student Book 4. New York
:Heinle &Heinle Thomas Learning Inc.
Annisa, I., & Oktavia, W. (2020). Using Story Mapping in Teaching Reading of Narrative Text for Junior High School Student. Journal of English Language Teaching, 9(1), 20-24. http://ejournal.unp.ac.id
Basith, AU. (2010). The Common Vocabulary Book. Pare, KRC publishing.
Brown, D. (2000). Principles of Language Learning and Teaching. San Fransisco:
Longman.http://angol.uni-miskolc.hu/wp-
content/media/2016/10/Principles_of_language_learning.pdf Creswell, Jhon. (2005). Educational Research. New Jersey: Prentice Hall
Dewi, N. (2018). The Effect of Story Mapping Technique to improve the Students' Reading and Writing Achievement. Journal Pendidikan, 19(2), 104-116.
https://jurnal.unej.ac.id/index.php/pancaran/article/download/705/523/
Farris, P. J., & et.al. (2004). Teaching Reading: A Balanced Approach for Today's Classroom. McGraw-Hill.
Firmansyah, H., IStikomah, & Sri, H. (2019). Using Story Strategy and Reading Motivation to Improve Reading Narrative Comprehension Achievement.
Linguists, 5(2), 44-53.
https://ejournal.iainbengkulu.ac.id/index.php/linguists/article /index.php/linguists/article/view/2378
Grabe, William & Fredrika L. Stoller (2002). Teaching and Researching Reading.
England: Pearson Education.
Hidayanti, N. (2017). Teaching Reading Comprehension by Using Story Mapping Technique on Narrative Text. Lampung: English Education of State University of Lampung.
http://repository.radenintan.ac.id/3043/1/TEHSIS.pdf
54
Idol, L. (1987). Group Story Mapping: A Comprehension Strategy for Both Skilled and Unskilled Readers. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 20, 196- 205.
https://www.ideals.illinois.edu/bitstream/handle/2142/17922/ctrstreadtechr epv01985i00363_opt.pdf?sequence=1
Kisfinata, R., Arianii, M., & Putu, S. (2013). The Effect of Using Story Mapping Technique on Reading Comprehension Achievement of the Eight Year Students as MTS Negeri Bangsalsari. Pancaran, 97-104.
https://jurnal.unej.ac.id/index.php/pancaran/article/view/705/523
Latifah, N., & Rahmawati, N. (2019). Teaching and Learning Narrative Text Writing Through Story Mapping. English Education: Jurnal Tadris Bahasa Inggris, 12(1), 78-96. https://doi.org/10.24042/ee-jtbi.v12i1.4428 Li, K., & Wen, P. N. (2017). The use of Story MAp in Improving Year Four
Pupils' Ability in Reading Comprehension. JEE, 2, 56-67.
https://doi.org/10.31327/jee.v2i1.239
Nunan, C. (2000). Teaching Reading Skills in a Foreign Language. Oxford:
Macmillan.
McShane, S. (2005). Applying Research in Reading Instruction for Adults: First Steps for Teachers. Washington D.C: The National Center Family Literacy.
Octaviana, V. (2021). Students‟ Perceptions on the Use of Story Maps in Reading.
Jounal of Eglish teaching Adi Buana, 6(2), 135-142.
Pang, E. S., Muaka, A., Bernhardt, E. B., & Kamil, M, L. (2003). Teaching reading. Brussel: The International Academy of Education (IAE).
Kurniawan, A., Rufinus, A., & Suhartono, L. (2013). Improving students‟ reading comprehension on narrative text through story mapping strategy. Journal
Pendidikan dan Pembelajaran, 2 (5)
http://download.portalgaruda.org/article.php?article=111880&val=2338 Prakusumasari, K. (2015). The Use Story Mapping Technique in Teaching
Reading Skill at the Year of SMP Muhammadiyah 6 Surakarta.
Publication Article. 1(1). http://eprints.ums.ac.id/32938/
Renandya, W.A.,& Richards, J.C. (2002). Methodology in Language Teaching.
New York : Cambridge University Press.
Roihatul, M. (2018). Utilizing Story Mapping Strategy to Improve Students' Reading Comprehension in Finding Main Idea. NOBEL: Journal of Literature and Language Teaching, 9, 57-72.
Sartika, D., Eka, H., & Zainuddin. (2019). Story Mapping Technique and Comprehending Narrative Text. TAZKIR: Jurnal Penelitian Ilmu-ilmu Sosial dan Keislaman, 222-233. https://doi.org/10.24952/tazkir.v5i2.2292 Setiadi, B. (2006). Metode Penelitian Untuk Bahasa Asing. Yogyakarta: Graha
Ilmu.
Sholichah, & Ita, N. (2017). The Effect of Story Mapping on Reading Comprehension. Jurnal Penelitian Ilmiah Intaj, 1(1), 29-48.
https://doi.org/10.35897/intaj.v1i1.43
Snow, C. (2002). Reading for Understanding: Toward an R&D Program in Reading Comprehension. Santa Monica: RAND
Sriyana. (2018). Using Story Mapping Technique to Improve Students' Participants in Reading Comprehension of Narrative Text. 1-10.
Susan, S., & Salehi, H. (2014). The Role of Teachung Reading Strategies in Enchancing Reading Comprehension. Iran: Islamci azad University, 4(1), 10922-10928.
Tankersley, Karen. (2003). The Threads Of Reading. Alexandria: ASCD. P 90 Thornbury, S. (2005). How to Teach Speaking. London: Longman.
Zulaikah, S., & Andriani, D. (2019). Story Mapping Strategy to Teach Reading Comprehension Achievement. Channing: English Language Education and Literature, 4(2), 50-55. https://doi.org/10.30599/channing.v4i2.747