(Empirical Study at Public Accountant Firm in South Jakarta)
THESIS
Submitted to Faculty of Economics and Business as Partial Requirement for Acquiring the Bachelor Degree of Economics
By:
Mohamed Mohamud Warsame 109082100028
DEPARTMENT OF ACCOUNTING INTERNATIONAL CLASS PROGRAM FACULTY OF ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY JAKARTA
2015
vi ABSTRACT
Audit quality can be affected by several factors, both internal factors and external factors. The factors which have very important role in determining the quality of audit are competence and independence.
This study aims to analyze and prove the empirical evidence of the influence of auditors’ competence including experience and knowledge and auditors’ independence including long association with client, the pressure from client, peer review and non-audit services provided by Certified Public Accountant Firm towards audit quality. The samples are 52 respondents taken from auditors of Certified Accountant Firm in South Jakarta. As for answering the research hypothesis, the author used multiple regression analysis after testing its classical assumptions
Based on the T-test that has been calculated by the researcher, it shows that the value of auditor competence = 7.921 > 2.405 while the value of auditor independence = 6.006 > 2.405. It means that both the competence and independence of auditors partially affect towards audit quality. Moreover, the F- test result shows that F count > F table (169.589 > 3,190). It means that both the competence and independence of auditors simultaneously affect towards audit quality. Therefore, both the auditor and Certified Public Accounting Firm are expected to improve their competence and independence. The more competence and independence do the auditors have, the more quality of audit will be resulted.
Keywords: Auditor, Competence, Independence, Quality Audit.
vii
Figure 4.3 Chart Heteroscedasticity ... 47
viii Brief of Table
Table 3.1 Names of Certified Public Accountant Firm ... 29
Table 3.2 Scores in each Statements in the Research Instruments ... 31
Table 3.3 Number of each kind of Statements ... 31
Table 4.1 Descriptive Statistic ... 45
Table 4.2 Data Normality Test ... 46
Table 4.4 Multicollinearity Test ... 47
Table 4.5 Autocorrelation Test ... 48
Table 4.6 Correlation Test ... 48
Table 4.7 Reliability Test ... 49
Table 4.8 Model Summary ... 50
Table 4.9 ANOVA ... 50
Table 4.10 Coefficient Multiple Regression ... 50
Table 4.11 Coefficient Partial Regression ... 52
Table 4.12 Simultaneous Test ... 52
ix
Preface ... iii
Abstract ... vi
Brief of Figure ... vii
Brief of Table ... viii
Brief Contents ... ix
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background ... 1
B. Problem Formulation ... 5
C. Purposes of Research ... 5
D. Benefits of Research ... 6
CHAPTER II THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK A. Basic Theory ... 8
1. Auditing ... 8
2. Audit Quality ... 10
3. Competence ... 15
4. Independence ... 17
B. Conceptual Framework ... 22
C. Hypothesis ... 26
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. Research Design ... 27
B. Determination Sample Method ... 28
C. Data Collection Method ... 30
D. Research Instrument ... 30
E. Types and Sources of Data ... 32
F. Models and Techniques of Analysis Data ... 33
x
CHAPTER IV ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
A. Research Object Description ... 42
B. Result of Descriptive Text ... 45
C. Classical Assumption Test Result ... 45
D. Validity Test Result ... 48
E. Reliability Test Result ... 49
F. Regression Test Result ... 49
G. Hypothesis Test Result ... 51
H. Discussion ... 53
CHAPTER V CLOSING A. Conclusion ... 55
B. Limitation ... 56
C. Suggestion ... 56
REFERENCES ... 57
ATTACHMENTS ... 59
1 A. Background
The business world is currently experiencing very rapid growth. Many small businesses become large and even large enterprises become more advanced. It is tight enough oversight needed to manage enterprises and to the running of a business activity, so that the company can achieve its intended purpose. But with strict supervision sometimes not even able to detect and prevent potential fraud – dishonesty that occurs in the business world particularly in the financial statement fraud, and will therefore need a service that can detect and assess the reliability of the report dishonesty. In the service of this problem is audit services, especially public accountant services in audit assignment needed to evaluate and determine the reasonableness of a company’s financial report.
The audit report users expect that the report has been audited by independent public accountants of material misstatements, trustworthy authorization to serve as the basis of decision and in accordance with accounting principles applicable in Indonesia. Thus it needs an independent professional services and objective (ie public accountant) to evaluate the appropriateness of financial reports presented by management.
Many cases enterprises “fell” because business failures associated with the failure of auditors; this threatens the credibility of financial reporting.
2
This threat of further influence public perception, financial reports on wearer especially Audit quality is important because a high quality audit will produce a credible financial reporting as a basis for decision making.
De Angelo (1981) in Kusharyanti (2003:25) defines audit quality as the probability that the auditor will discover and report a breach of the client’s accounting system. Breach of audit findings related to measuring the quality of knowledge and expertise auditors. While the reporting of violations of hanging on to urge auditors to disclose violations. This impulse will depend on the auditor’s independence held.
Terms auditing on Auditing Standards, covering three General Standard: (SA Section 150, 2011)
1. Audit should be conducted by one or more persons who have the expertise and technical training enough.
2. In all matters relating to the alliance, independence in mental attitude should be maintained by the auditor.
3. In the implementation of the audit and compilation of the report, the auditor must use professional skills carefully.
Matters set forth in this General Standard which will later be used as a benchmark or parameters of the independent auditors, competent, and prudent or not in this study.
The use of professional support as the public accountant auditor in performing the audit work should be guided by the auditing standards established by the Indonesian Institute of Certified Public Accountants
(IAPI), which is a general standard, standard of field work and reporting standards, where the general standard is a reflection of personal qualities that should be possessed by an auditor who require auditors to have expertise and sufficient technical training in performing audit procedures. While the standard field work and reporting standards in the case of auditors organize data collection and other activities undertaken for conducting the audit and the auditor requires compiling a report on the audits of financial reports as a whole.
Great trust of the financial statement audit owner and other services provided by a public accountant produces. As for questions from the public on the quality of audits produced by the greater public accountant after an accountant’s many scandals involving public good in the country or outside the country, phenomena that occur in the state spotlight from the community that is such cases that hit the initial KAP (Certified Public Accountant Firm) partner “HTM”, a fine approximately 100 million rupiah. Offenses committed by partners KAP “HTM” is that it does not turn the audit risk in inflation detect any gains made PT Kimia Farma, although it has carried out the audit in accordance with EMS. One of the cases of PT Kimia Farma impact is through the secretary of the treasury to issue the ruling circle of number 423/KMK.06/2002 Service Public Accountant, also joined the issue Bapepam (Capital Market Executive Agency) rule number VIII.A.2 about independence accountants providing audit services on capital markets.
4
Based on Bapepam investigation, stated that the KAP that audited the financial statements of PT Kimia Farma has followed applicable audit standards, but failed to detect the fraud. In addition, the KAP is also not proven to help the management to commit fraud. In the context of the cheating scandal, if that happens is the auditor was unable to detect financial manipulation tricks, the core problem is that the KAP has not applying ethical principles, namely the competence of the accounting profession and the professional prudence that is, in terms of experience and knowledge, because there is nothing left in the inspection and audit results which lead to less quality, therefore it resulted in the presentation of false information to the users of the financial information of PT Kimia Farma (Bapepam Report Release : 2002).
The ability to discover fraud from the financial statements is determined by the competence of auditors. KAP party shall be liable to a fine of 100 million ie, fines it is necessary and intended that no KAP is doing or a material misstatement that could make the users of financial information over the loss of material information. It is expected that something like this does not happen again and the independent auditor can more carefully and more closely in the conduct of the examination and auditing firm while maintaining the principles and codes of professional conduct independent accountant.
The cases like these make the competence and independence of auditor in CPA firm spotlight in recent years. Public accountant profession as an independent party, known by the public must be able to produce a quality
audit services, in this case namely the audit report. In connection with that position, then the auditors are required to maintain the confidence that they get from the client, the decision makers and the public.
Based on the above description, writer is interested in further research on the influence of competence and independence of auditor in relation to audit quality. Therefore, the author does research with the title “the influence of competence and independence of auditor in certified public accountant firm towards audit quality.”
B. Problem Formulation
As for the problems in this study will be examined based on the background of the above can be formulated in the form of several research questions:
1. Does the competence of auditor influence audit quality?
2. Does the independence of auditor influence audit quality?
3. Do the competence and independence of auditor influence audit quality?
C. Purposes of Research
The purpose of the research is to get a number of relevant data and information about the influence of competence and independence of auditor towards audit quality in Certified Public Accountant Office. From the
6
problems that have been identified above, the purpose of this research is conducted as follows:
1. To find out how large the influence of competence towards audit quality.
2. To find out how large the influence of independence towards audit quality.
3. To find out how large the influence of competence and independence towards audit quality.
D. Benefits of Research 1. Practical Use
a. For Writer
As a means for researcher to develop and apply the knowledge acquired from the lecture halls in the work world.
b. For Public Accountant Profession
This can be used as input material for leader of Certified Public Accountant Firm in order to maintain or improve the competence and independence of auditors so that it can improve its audit quality.
This research can provide input material for auditors the in the course of their work so that they can audit as well as possible. This also can be an evaluation tool for them to improve their audit quality.
c. For Costumers
This can be a reference and guidance for costumers in order to assess the consistency of CPA Firm in maintaining audit quality that it provides.
2. Theoretical Use
a. This research is expected to give conceptual contribution to the similar researcher as well as other academic community in order to develop the science to the development and advancement of education.
b. This research will be useful as a source of information and references for parties interested in the kind of topic.
8 CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Basic Theory 1. Auditing
Definition of auditing mostly taken from ASOBAC (A Statement Basic of Auditing Concepts) :
“Auditing is broadly defined as a systematic process of objectively obtaining and evaluating evidence in respect of certain assertions about economic actions and events, to ascertain the degree of correspondence between those assertions and established criteria and reporting the results to interested parties”.
According to Arens, et al (2010:4) defined:
“Auditing is defined as an accumulation and evaluation of evidence about information to determine and report on the degree of correspondence between the information and established criteria”.
From above definition it can be concluded that auditing is an Inspection process that carried out systematically toward audit evidence objectively regarding assertions about economic actions and events in a corporate by a competent and independent, in order to be able to give an opinion in the auditor's report that is produced at the end of the examination.
According to those conclusions, then at least in auditing contains the following elements:
a. An audit is a systematic approach: the audit follows a structured, documented plan (audit plan).
b. An audit is objectively conducted: an audit is an independent, objective and expert examination and evaluation of evidence.
c. The auditor obtains and evaluates evidence. The auditor assesses the reliability and sufficiency of the information contained in the underlying accounting records and other source data.
d. The evidence obtained and evaluated by the auditor regards assertions about economic actions and events. The bases of evidence gathering objectives, the thing that the evidence must “prove” are the assertions of management.
e. The auditor ascertains the degree of correspondence between assertions and established criteria. The audit program tests most assertions by examining the physical evidence of documents, confirmation, inquiry and observation.
f. The goal, or objective, of the audit is communicating the results to interested users. The audit is conducted with a view of expressing an informed and credible opinion, in a written report.
An audit of the financial statements becomes something that is very important for each company. In addition to an opinion whether the report financial statements have been presented fairly in accordance with GAAP, there are several reasons are needed for the audit of the financial statements, are as follows:
a. If not audited, it is likely that the financial statements contain errors both intentional and unintentional. Therefore unaudited financial
10
statements less reliable reasonableness by those interested parties on the consolidated financial statements.
b. If the financial statements have been audited and received unqualified audit (reasonable without exceptions) of KAP, it is mean users can be confident that the financial statements are free of material misstatement and presenter in accordance with accounting principles which is generally accepted in Indonesia.
c. In the beginning of 2001 the company whose total assets of Rp 25 billion or more must get their Audited Financial Statements into Department of Trade and Industry.
d. Companies that already have existed in public must include their Financial Statement Audit to Bapepam no later than ninety days after the fiscal year.
The financial statements audited by a public accountant will be used by the parties to make decision, this means that the audit should be done by an ethical, experienced, and have expertise in this regard is by Certified Public Accountants.
Thus profession of public accounting is a public confidence.
Therefore Public Accountant is required to perform their duties professionally.
2. Audit Quality
Audit is a process to reduce disharmony information, contained between managers and shareholders using outsiders to give effect to the
financial statements. The users of financial statements, especially the shareholders will take a decision based on the report made by the auditors on the financial statements of a company endorsement.
This means that the auditor has an important role in the drafting of the financial statements of the company letter. Therefore, audit quality is an important thing must be maintained by the auditor in the audit process.
Goldman and Barlev (1974) in Meutia (2004) states that the auditor's report contains the interests of three groups, namely: (1) manager of the company that is being audited, (2) the shareholders of the company, (3) a third party or external parties such as potential investors, creditors and suppliers. Each of these interests is the source of interference that would put pressure on auditors to generate reports that may not be in accordance with professional standards. Furthermore, this will interfere with the quality of the audit.
AAA Financial Accounting Standards Committee (2000) in Christiawan (2003) states that: "Audit quality is determined by two things, namely competence (skills) and independence, both of these directly affect the quality and potentially affect each other. Furthermore, the user perception of the quality of the audit of financial statements is a function of their perceptions of auditor independence and expertise ".
De Angelo (1981) in Watkins (2004) defines audit quality as the likelihood that the auditor will find and report violations of the accounting system with the knowledge and expertise of the auditor. While reporting
12
violations depend on the auditor urge to reveal violations. This impulse will depend on the independence possessed by the auditor.
From the definition of audit quality above that the auditors are required by interested parties with the company to provide a fairness opinion on the financial report presented by the management company in order to be able to perform their duties. There are three components that must be owned by the auditor such as competence (expertise), independence, and professional care. But in carrying out its functions, auditors often have conflicts of interest with the company's management.
Management may want the results of operations or performance looks successful depicted with higher data with the intent to get an award (eg bonuses). To achieve these goals often exert pressure on company management auidtor that audited financial statements were produced in accordance with the wishes of the client.
Based on the description above, the auditor has a strategic position in the eyes of management as well as in the eyes of users of financial statements. In addition, users of financial statements put much faith in the work of auditors in the audit of financial statements.
Great confidence of users of audited financial statements and auditor services rendered requires the auditor to the quality of its audits.
To be able to meet the good quality of the audit, the auditor in their profession as the examiner should be guided by the code of ethics
accountants, professional standards and applicable financial accounting standards in Indonesia.
Each audit should maintain integrity and objectivity in the performance of their duties to act honestly, decisively, without pretension so he can act fairly, without being influenced or request certain parties to meet their personal interests (Darmawanti, Deni, Khomsiyah and Rika, 2005).
In addition, a public accountant should also be guided by Generally Accepted Accounting Standards (SPAP) established by the Indonesian Institute of Accountants (IAI), in which case it is generally accepted auditing standards. Auditing standards consist of general standards, standards of field work and reporting standards (SPAP, 2011):
a. General Standard.
1). Audits should be conducted by one or more who have expertise and sufficient technical training as an auditor.
2). In all matters relating to the engagement, independence in mental attitude must be maintained by the auditor.
3). In the conduct of the audit and the preparation of its report, the auditor shall use professional skills carefully and thoroughly.
b. Field Work Standards.
1). The work should be planned well and if used assistants to be supervised properly.
14
2). Adequate understanding on the internal control structure must be obtained to plan the audit and determine the nature, timing, and extent of tests to be performed.
3). Sufficient competent audit evidence should be obtained through inspection, observation, submissions, questions and confirmation as a reasonable basis for an opinion regarding the financial statements audited.
c. Reporting Standards.
1). The auditor's report must state whether the financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in Indonesia.
2). The auditor's report should indicate or declare if there are inconsistencies in the application of accounting principles in the preparation of the financial statements of the current period compared to the application of accounting principles in the previous period.
3). Informative disclosures in the financial statements should be deemed sufficient, unless otherwise stated in the auditor's report 4). The auditor's report should contain a statement of opinion on the
financial statements as a whole on an assertion.
So based on the above description, the audit has a function as a process to reduce disharmony information, contained between managers and shareholders using external parties to give effect to the financial
statements. The users of financial statements, especially the shareholders will take a decision based on a report drawn up by the auditor.
This means that the auditor has an important role in the ratification of a company's financial statements. Therefore, the auditor must produce a quality audit so as to reduce the dissonance that occurs between management and owners. Indonesian Institute of Accountants (IAI) states that the audit quality is if it meets the standards of auditing and quality control standards.
Furthermore, according to De Angelo (1981) in Kusharyanti (2003:
25) defines audit quality as the possibility (probability) that the auditor will find and report violations that exist in the client's accounting system.
The ability to find a material misstatement in the financial statements of the company depends on the competence of the auditor's willingness to report the findings while the misstatement depends on its independence.
3. Competence
The first general standard (SA 210 section in SPAP, 2011) states that the audit should be conducted by one or more who have the adequate expertise and technical training as auditors, while the third general standard (SA 230 section in SPAP, 2011) mentions that in the audit and preparation of the report, the auditor must use finesse with careful and thorough professionalism (due professional care).
Lee and Stone (1995) in Elfarini (2007), defines competence as the considerable expertise that can be explicitly used to conduct audits
16
objectively. Another opinion is from Dreyfus (1986), defines competence as a skill a person who acts in a sustainable manner in which its movement through the learning process, of "knowing something" to "know how".
As for Bedard (1986) in Sri lastanti (2005: 88) defines the skill or competence as someone who has the knowledge and procedural skills demonstrated in extensive audit experience. Meanwhile, in the same article, Shanteau (1987) define expertise as the people who have the skills and ability at a high degree.
Based on the above it can be concluded that the competence of auditors is that auditors with sufficient knowledge and experience and can explicitly perform the audit objective, careful and thorough.
a. Knowledge
SPAP 2011 on General Standards explains that in conducting the audit, the auditor should have expertise and sufficient knowledge structure.
Knowledge is measured by how much education as such an auditor because the auditor will have more knowledge (views) of the field that they do in order to know the various issues in more depth, in addition to the auditor will be easier to follow the development of increasingly complex (Meinhard et.al , 1987 in Harhinto, 2004: 35).
b. Experience
Audit requires high expertise and professionalism. Expertise is not only influenced by formal education but many other factors
affecting among other is experience. According to Tubbs (1992) in Barry (2003) experienced auditor has advantages in terms of: (1) Detecting errors, (2) Understand errors accurately, (3) Finding the cause of the error.
Libby and Frederick (1990) in Kusharyanti (2002: 5) found that experienced auditors have a better understanding. They are also better able to provide a plausible explanation of the errors in the financial statements and can classify faults based on the audit objectives and the structure from the underlying accounting system (Libby et al., 1985) in Mayangsari (2003: 4). While Harhinto (2004) produced findings that auditors experience is positively related to audit quality.
4. Independence
Independence means public accountant is not easily influenced.
Public accountant is not justified biased towards anyone. Public accountants are obliged to be honest not only to the management and owners of the company, but also to creditors and other parties who put confidence in the work of public accountants (Christiawan, 2002).
Certified public accountants ethics code states that independence is the attitude expected of a certified public accountant for not having a personal interest in carrying out their duties, which is contrary to the principles of integrity and objectivity.
Research on independence has pretty much conducted both domestically and abroad. Lavin (1976) examined three factors that affect
18
the independence of public accountants, namely: (1) Association of financial and business relationship with the client, (2) furnishing of services other than audit services to clients, and (3) the duration of the relationship between public accountants with clients.
Shockley (1981) examined four factors that affect the independence, namely (1) Competition among public accountants, (2) Provision of consultancy services management to clients, (3) Firm Size, and (4) The duration of the relationship audit
a. Older Relationship With Clients (Audit Tenure)
In Indonesia, the problem of audit tenure is set up in the Ministry of Finance Decree 423 / KMK.06 / 2002 on public accounting services. The minister's decision to limit the auditor's work a maximum of 3 years for the same client, while for Public Accounting Firm (KAP) may be up to 5 years.
This restriction intended auditor not to be so close to the clients so as to prevent the occurrence of accounting scandals. As for the explanation of differences in some of the research results of previous studies stated as follows: "Assignment of audit that is too long is likely to encourage public accountant loses its independence as a public accountant is satisfied, less innovation, and less strict in performing audit procedures. Instead the old audits may also increase the possibility of independence for public accountants are familiar; the
work can be implemented efficiently and are more resistant to pressure the client "(Supriyono, 2006).
b. Pressure from clients
In performing its duties, the auditors often have conflicts of interest with the company's management. Management might want the operation or performance looks successful company, which is reflected through higher earnings with a view to creating an award.
To achieve these objectives it is not uncommon to pressure the company's management to the auditor that audited financial statements were produced in accordance with the wishes of the client. In this situation, the auditor is in a dilemma. On the one hand, if the auditor to follow the client's wishes, it violates professional standards. But if the auditor does not follow the client then the client may terminate the assignment or change the auditors KAP.
In addition, competition among accounting firms (KAP) is greater. KAP increased, while the growth of the company is not comparable to the growth of the firm. Moreover, many companies conduct mergers or acquisitions and due to the economic crisis in Indonesia, many companies that went bankrupt. So therefore the firm will be more difficult to get new clients that the firm was reluctant to remove the existing clients.
The client's financial condition also affects the auditor's ability to cope with pressure of clients (Knapp, 1985) in (Harhinto, 2004: 44).
20
Clients who have a strong financial condition could provide a sizeable audit fee and also can provide good facilities for auditor.Selain the probability of occurrence of bankruptcy clients who have a good financial condition is relatively small. In this situation the auditor become complacent resulting in less rigorous in auditing.
Based on the above, the auditor has a strategic position not only in the eyes of management but also in the eyes of the users of financial statements. In addition, users of financial statements put much faith in the work of auditors in the audit of financial statements.
To be able to meet the good quality of the audit the auditor in their profession as examiner should be guided by the code of ethics, professional standards and applicable financial accounting standards in Indonesia. Each auditor must maintain the integrity and objectivity in carrying out their duties to act honestly, decisively, without pretension so that he can act fairly, without pressures or demand is affected by certain parties to meet their personal interests.
c. Peer Review
The demands on the accounting profession to provide quality services demanded transparency of information about jobs and operating public accounting firm. Clarity of information about the quality control system in accordance with professional standards is one form of accountability to clients and the general public will be rendered.
Therefore, the work of public accountants and public accounting firm operations need to be monitored and audited to assess the feasibility of the design and quality control system for compliance with quality standards which hinted that the resulting output can reach high quality standards. Peer review as prepared by the auditor monitoring mechanism could improve the quality of accounting and auditing services.
Peer reviews perceived to provide good benefits for clients, public accounting firm that reviewed and auditors involved in the peer review team. The benefits derived from peer review, among others, to reduce the risk of litigation, providing a positive experience, enhance employee morale, and provide a competitive edge and more convincing clients of the quality of services rendered.
d. Non-Audit Services
Services provided by the CPA Firm not only attestation services but also non-attest services in the form of management consulting services, tax services and accounting services such as financial statements (Kusharyanti, 2002: 29).
The existence of two types of services provided by the firm makes auditor independence against his client in question which will affect the quality of the audit. The provision of services other than auditing is a potential threat to auditor independence, because
22
management can increase the pressure on auditors to be willing to issue a report required by the management is an unqualified.
B. Conceptual Framework
One of the functions of public accounting is to produce information that is accurate and reliable for decision-making. However, the conflict of interest between the internal and external company, demanding a public accountant to produce qualified audited report which can be used by these parties.
In addition, there are proliferation of financial scandals both domestic and foreign, largely departed from financial statements that have been published by the company. This has raised the question of how the quality of the resulting audit by a public accountant in the audit client's financial statements.
Various studies on the quality of audits that have been done resulted in different findings regarding the determining factors of the quality of audit.
But in general concluded that to produce quality audit, a certified public accountant who works in divulging the audit team is required to have sufficient competence and independence.
Based on the logical thinking of those explanations, the framework is developed for this study, namely:
1. Effect of Auditor Competence towards Audit Quality
Competence of auditors is that auditors with sufficient knowledge and experience and can explicitly perform the audit objective, careful and thorough.
Audit quality is every possibility that the auditor at the time of audit client's financial statements can be found violations that occur in the client's accounting system and reported in the audited financial statements, which the auditors in carrying out their duties guided by generally accepted auditing standards and codes of conduct relevant public accountant.
Therefore, it can be understood that an auditor who has sufficient knowledge and experience has better understanding about the various issues in more depth and easier to follow developments in an increasingly complex environment audit clients.
Thus, it can be concluded that the higher competency of auditors, the higher quality of the resulting audit.
2. Effect of Auditor Independence towards Audit Quality.
Independence is an attitude that is expected of a certified public accountant for not having a personal interest in carrying out their duties, which is contrary to the principles of integrity and objectivity.
Therefore it argued that to produce a quality audit requires independence of auditor because if the auditor loses its independence, the
24
audit report that is generated does not match with the reality that it cannot be used as a basis for decision making.
3. Effect of Competence and Independence of Auditor towards Audit Quality.
In performing the audit process, the auditor requires a good knowledge and experience because with those two things, auditors become better able to understand the financial condition and financial statements of their clients.
Then with its independence, the auditor can report the violation of the client's financial statements. Therefore, based on the logical explanation above, the competence and independence influence the good quality of audit process and its output.
Figure 2.1
CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
KNOWLEDGE EXPERIENCE COMPETENCE (X1)
LONG- RELATIONSHIP
WITH CLIENT PRESSURE FROM
CLIENTS PEER REVIEW
NON-AUDIT SERVICES INDEPENDENCE (X2)
AUDIT QUALITY (Y)
26
C. Hypothesis
Based on the description that has been stated above, the research hypothesis that is used by the author in this study are:
H01 : there is no partial influence of auditor’s competence towards audit quality.
Ha1 : there is partial influence of auditor’s competence towards audit quality.
H02 : there is no partial influence of auditor’s independence towards audit quality.
Ha2 : there is partial influence of auditor’s independence towards audit quality.
H03 : there is no simultaneous influence of auditor’s competence and independence towards audit quality.
Ha3 : there is simultaneous influence of auditor’s competence and independence towards audit quality.
27 CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. Research Design
This study was a survey research in the form of research explanation and testing hypotheses which uses descriptive and exploratory methods because the core of the discussion are auditor’s competence and independence which are related to the audit quality of public accounting.
Thus, the researchers used a survey questionnaire because it is considered the most appropriate technique to answer their questions.
This study uses two independent variables, namely the competence of auditors (X1) and the independence of auditors (X2) while the dependent variable is quality of audit (Y).
Auditor’s competence (XI) is the auditor with sufficient knowledge and experience and can explicitly perform the audit objectively, carefully and thoroughly. Auditor’s independence (X2) is the expected behavior of a public accountant for not having a personal interest in carrying out their duties, which is contrary to the principles of integrity and objectivity.
While the quality of the audit (Y) is any possibility when auditing client's financial statements, auditor can find violations that occur in the client's accounting system and reported in the audited financial statements, which in carrying out these duties; the auditor is guided by auditing standards and relevant code of ethics public accountants.
28
B. Determination Sample Method 1. Population
The population of this study is public accountants who worked at a public accounting firm located in South Jakarta. This study takes the object to the behavior of the external auditor who worked on the public accounting firm located in South Jakarta.
Population is the generalization which consists of object and subject of a certain quantity and characteristics applied by researchers to learn and then drawn the conclusion. Population is subject or objects which have certain qualities and characteristics are determined by researcher.
Thus, the population is not only people but also objects or other natural objects. Population is also not only quantity but includes all of the characteristics’ subject or object (Sugiyono, 2008:57).
2. Sample
Samples are selected using convenience sampling. It means that sample units can be reached easily, anywhere and anytime. It is not troublesome to measure and cooperative (Abdul Hamid, 2007: 30).
Sample is a subgroup of the elements of the population selected for participation in the study (Maholtra, 2006:373).
Thus, the respondents that will be used as sample in this study are selected senior auditors, supervisors and junior auditors who work at public accounting firms in South Jakarta.
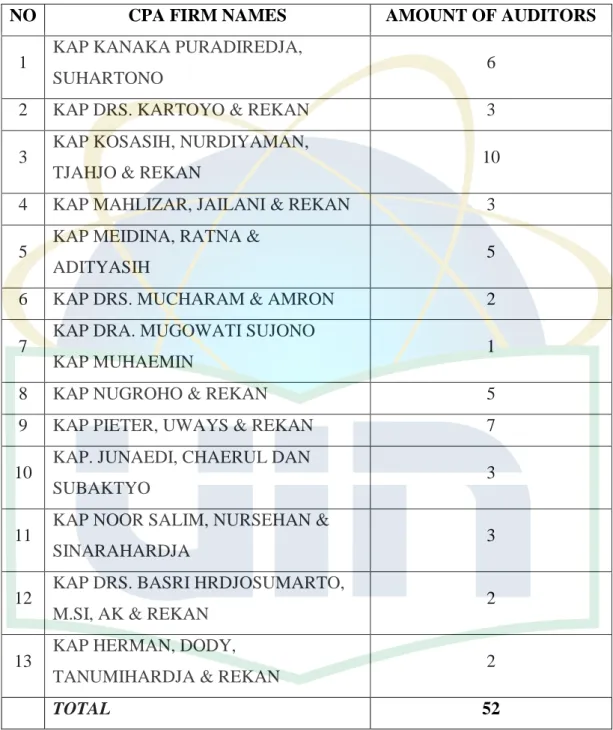
Table 3.1 Names of Certified Public Accountant Firm and the Amount of its Auditors
NO CPA FIRM NAMES AMOUNT OF AUDITORS
1 KAP KANAKA PURADIREDJA,
SUHARTONO 6
2 KAP DRS. KARTOYO & REKAN 3 3 KAP KOSASIH, NURDIYAMAN,
TJAHJO & REKAN 10
4 KAP MAHLIZAR, JAILANI & REKAN 3 5 KAP MEIDINA, RATNA &
ADITYASIH 5
6 KAP DRS. MUCHARAM & AMRON 2 7 KAP DRA. MUGOWATI SUJONO
KAP MUHAEMIN 1
8 KAP NUGROHO & REKAN 5
9 KAP PIETER, UWAYS & REKAN 7 10 KAP. JUNAEDI, CHAERUL DAN
SUBAKTYO 3
11 KAP NOOR SALIM, NURSEHAN &
SINARAHARDJA 3
12 KAP DRS. BASRI HRDJOSUMARTO,
M.SI, AK & REKAN 2
13 KAP HERMAN, DODY,
TANUMIHARDJA & REKAN 2
TOTAL 52
30
C. Data Collection Method
Data collection methods used in the study as follows:
1. Literature Review
The research is conducted by collecting, reading, and studying literature and reference books as well as relevant to the issues to be studied in an effort to get clarity of concept formulation of the basic theory that is useful in the discussion.
2. Field Research
Field research is research that is conducted by obtaining data directly in the field via questionnaires.
D. Research Instrument
The concept in this study includes the concept of competence and independence as an independent variable in which competence is projected into 2 sub-variables: knowledge and experience while independence is projected into 4 sub variables: pressure from clients, long-standing relationships with clients, colleagues study of audit and non-audit services.
As the dependent variable is the quality of the audit.
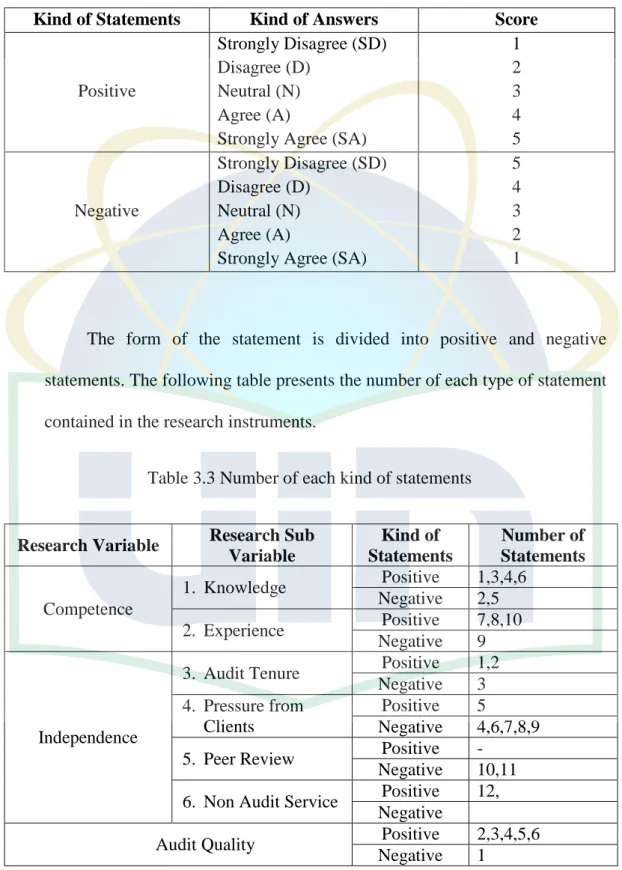
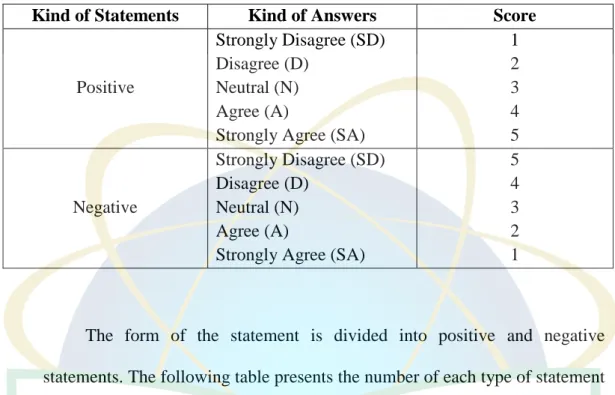
This concept is measured by giving a score for each respondent's answer. As each answer of the statement has been determined the score
Table 3.2 Scores in each statements in the research instruments
Kind of Statements Kind of Answers Score
Positive
Strongly Disagree (SD) Disagree (D)
Neutral (N) Agree (A)
Strongly Agree (SA)
1 2 3 4 5
Negative
Strongly Disagree (SD) Disagree (D)
Neutral (N) Agree (A)
Strongly Agree (SA)
5 4 3 2 1
The form of the statement is divided into positive and negative statements. The following table presents the number of each type of statement contained in the research instruments.
Table 3.3 Number of each kind of statements
Research Variable Research Sub Variable
Kind of Statements
Number of Statements Competence
1. Knowledge Positive 1,3,4,6 Negative 2,5 2. Experience Positive 7,8,10
Negative 9
Independence
3. Audit Tenure Positive 1,2 Negative 3 4. Pressure from
Clients
Positive 5
Negative 4,6,7,8,9 5. Peer Review Positive -
Negative 10,11 6. Non Audit Service Positive 12,
Negative
Audit Quality Positive 2,3,4,5,6
Negative 1
32
The questionnaire in this study is the question of competence, independence and audit quality. Type of statement is closed, where respondents only give tick mark (√) in the answer choices.
E. Types and Sources of Data 1. Data type
The type of data used in this study is the quantitative data in the form of grades or scores on the answers given by the respondents to the questions in the questionnaire.
2. Source of Data
Sources of data used in this study are:
a) Primary data
Primary data were obtained directly from the data source or a place where research is conducted directly (Indriantoro and Bambang Supomo, 2009: 65). The primary data in this study was obtained through a questionnaire distributed to respondents.
b) Secondary Data
Secondary data sources of the study were obtained indirectly through an intermediary medium (Indriantoro and Bambang Supomo, 2009: 65). As an empirical study, the secondary data in this research is obtained from articles, journals, and previous studies.
F. Models and Techniques of Analysis Data 1. Model of Analysis Data
Model of analysis data used in this study is Multiple Linear Regression Analysis. Purbayu (2005) suggested that the multiple correlations are the relationship of several independent variables with the dependent variable.
If a dependent variable depends on more than one independent variable, the relationship between the two variables is called multiple regression analysis (Wahid Sulaiman, 2004: 80).
Multiple linear regression equation is as follows:
Y =α + β1X1 + β2X2 + e Description:
Y : Audit Quality.
X1 : Auditor Competence.
X2 : Auditor Independence.
α : Constant.
β : Coefficient Regression.
e : Error.
34
2. Techniques of Analysis Data a) Data Quality Testing
The Commitment of measuring and testing of a questionnaire or hypothesis depends heavily on the quality of the data used in testing. The research data will not be useful if the instrument which is used to collect research data does not have reliability (level of reliability) and validity (the degree of truth / validity high).
Testing the measurement of each show consistency and accuracy of data collected. Testing the validity and reliability of the questionnaire in this study is using SPSS (Statistical Product and Service Solutions).
1) Validity Test
Validity is a measurement that indicates the extent to which the measuring instrument is able to measure what you want to measure (Purbayu, 2005: 247). Validity testing is intended to measure how real a test or instrument. Measurement is valid if it truly measures the objectives.
Testing the validity of data in this research is conducted statistically by calculating the correlation between each of these questions with a total score using Pearson Product Moment Correlation. Data declared valid if the score r-count which is the value
of Corrected Item-Total Correlation > r-table on significance 0.05 (5%).
2) Reliability Test
Reliability is a measure which shows consistency of the measuring instrument in measuring the same phenomenon in other occasions (Purbayu, 2005: 251). Reliability of a variable which is formed from the list of questionnaire is good if it has Cronbach’s Alpha value > 0,60.
3. Classical Assumptions Test
To obtain unbiased result atau Best Linear Unbiased Estimator / BLUE, then the regression model must fulfill several assumptions which is called classical assumptions. The classical assumptions, namely:
a) Normality test
Normality test aims to test whether the regression model, both dependent and independent variables have a normal distribution or not (Ghozali 2005: 110). Good regression model must have a normal data distribution.
Data Normality test in this study uses SPSS for Windows application for testing the sample data for each variable. In detecting the normality of the data through the normal output curve graph pp plot, a variable is called normal if the distribution picture in which the data points are spread around the diagonal line and the spread of the
36
data points follow the direction of the diagonal line (Nugroho, 2005:
24 in Jimmy, 2007).
In addition to using the graph p-plot, testing normality of the data was also performed using the histogram curve. Normality of data when viewed by means of the curve can be determined based on the histogram picture curve, i.e. when the shape of the curve has a slope that tends to balance on either the left or right side and a bell-shaped curve that is almost perfect.
b) Multicollinearity
This test is intended to detect symptoms of correlation between the independent variable with the other independent variables.
Multicollinearity assumption states that the independent variable must be free of symptoms of multicollinearity. Multicollinearity symptom is a symptom correlation, between variables independent.
This phenomenon is demonstrated with significant correlations between independent variables.
In the event of symptoms of multicollinearity, one of the steps to improve the model is to eliminate variables from the regression model, so it can be selected the best models (Purbayu, 2005: 238).
Wahid Sulaiman (2004: 89), multicollinearity means that there is a perfect linear relationship among some or all of the independent variables from the regression model.
Multicollinearity test can be conducted in two ways, namely by looking at the VIF (Variance Inflation Factors) and the value of tolerance. If VIF < 10 and tolerance values > 0.10 then no symptoms of Multicollinearity (Ghozali, 2005: 92).
c) Heteroscedasticity
Heteroscedasticity test aims to test whether the regression model occur unequal variance from one observation to other observation residuals which remain, or called Homoscedasticity (Ghozali, 2005: 105).
A good regression model is homoscedasticity, no heteroscedasticity (Ghozali, 2005: 105). Heterocedastity assumption is the assumption in regression where variance from residuals is not equal for one observation to other observations.
In regression, one of the assumptions that must be met is that the variance of the residuals from an observation to other observations is not similar between the variance of the residuals. Symptoms of unequal variances is called heterocedastity symptoms, whereas the presence of residual symptoms similar to observations from divulging other observations called homoscedasticity, one of the way to test this is by seeing heteroscedasticity spread of residual variance (Purbayu, 2005: 242).
38
d) Autocorrelation Test
Autocorrelation is used for the sole purpose of knowing whether there is a correlation between members of a set of observed data and analyzed according to a (cross section). This test aims to see whether there is a residual in an observation with other observation on the model. In these research, researcher uses Durbin Watson test. A model that can be expressed is not the case if probability value autocorrelation symptoms Durbin Watson > 0.05 (Wibowo 2012:106).
4. Hypothesis Test
Hypothesis test in this research will be tested by using linear regression analysis, the analysis used to determine the extent of the influence of the competence and independence of auditors as independent variables on audit quality as the dependent variable. To test hypotheses about the competence and independence of the auditor simultaneously and partially effect significantly on audit quality, hypothesis simultaneously effect with the F test, and partially by t test.
a) Partial Test (t test)
T-test is used to determine the effect of each independent variable on the dependent variable. T test is carried out by comparing t-count with t-table. Determining the value of t-table is determined by the significance level of 5% with degrees of freedom df = (n-k- 1) where n is the number of respondents and k is the number of variables.
Testing criteria used are:
If t-count> t-table (n-k-1) then Ho is rejected If t-count <t-table (n-k-1) then Ho is accepted
In addition, the t-test can also be seen from the probability value (p value) compared with 0.05 (Level of significance α = 5%).
The test criterion used is
If the p value <0.05, then Ho is rejected If the p value> 0.05 then Ho is accepted
To find out how much percentage contribution of the independent variables X1, X2 partially on audit quality as the dependent variable can be seen from the magnitude of the coefficient of determination (r2). Where r2 explain how much the independent variables used in this study could explain the dependent variable.
b) Simultaneous Test (F Test)
The F test is used to determine whether there is influence simultaneously the independent variables to the dependent variable.
Proof is conducted by comparing the value of F with F table at the 95% confidence level and degrees of freedom (degree of freedom) df
= (nk-1) where n is the number of respondents and k is the number of variables.
40
Testing criteria used are:
If F-count > F-table (n-k-1) then Ho is rejected
Meaning of statistical data that is used proves that all the independent variables (X1 and X2) effect on the value of the variable (Y).
If F-count < F-table (n-k-1) then Ho is accepted
Meaning of statistical data that is used proves that all the independent variables (X1 and X2) do not affect the value of the variable (Y).
In addition, the F test can also be seen from the probability value (p value) compared with 0.05 (Level of significance α = 5%). The test criteria used are:
If the p value <0.05, then Ho is rejected If the p value> 0.05 then Ho is accepted
With a level of significance in this study using the alpha 5% or 0.05 F test results can then be calculated with SPSS ANOVA table.
Furthermore, to determine how large a percentage of the contribution of the independent variables X1, X2 together on audit quality as the dependent variable can be seen from the magnitude of the coefficient of determination (r2). Where r2 explain how large independent variables used in this study could explain the dependent variable.
41 A. Research Object Description
Research object used in this study was Certified Public Accounting Firm (KAP), a business entity that has received permission from the finance minister or other authorized officials as a place for public accountants in providing services. Meanwhile, an independent public accountant or auditor is an accountant who has received clearance from the finance minister or the competent authority to provide services.
Certified Public Accounting Firm main duty is to provide some services named audit services. Explanations of these services are:
1. Audit Services
In his capacity as an independent auditor, public accounting firm perform a general audit of the financial statements to give a statement about the fairness of the financial statements.
2. Special Audit
Special audit can be a particular statement of audit performed using a mutually agreed procedures, the audit of financial statements prepared on a comprehensive basis and audit of financial information for a particular purpose.
42
3. Attestation Services
Services related to the issuance of a report containing conclusions about divulging state assertions (statements) written, is the responsibility of the other party, held from inspection, review and mutually agreed procedures.
4. Financial Statements Review
Financial Statements Review is a service that provides limited confidence that there are no material modifications that should be implemented for the financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles on other comprehensive basis of accounting.
5. Services Compilation of Financial Statements
Services to prepare financial statements based on financial records and other information provided by management of a particular entity.
6. Consulting Services
These services include a variety of shapes and areas of competence in accordance with a public accountant. For example, a general consulting services to management, systems planning and implementation of accounting systems, education and training, implementation of selection and recruitment of personnel to provide other consulting services.
7. Tax Services
Services provided include general tax advisory services, tax planning, review types of taxes, tax return filling and settlement of tax matters.
Organizational structure within the firm as follows:
a. Colleague or partner, the co-chairman who has the highest positions in the firm. His job overall charge of the work handled by the firm.
b. Manager, the examiner supervisor, coordinator of senior auditors. His job reviewing the audit program, reviewing working papers, audit reports and management letter.
c. Senior auditor or coordinator of junior auditor, accountant planner who is responsible for the implementation of inspection. His job is directing and reviewing the work of junior accountants.
d. Junior auditor or auditor staff, those who implement the procedures detailed inspection in accordance with the guidance of a senior accountant. His job is to make the paper work.
This study was conducted on a public accountant by the number of respondents was 52. It is revealed that competence factors include knowledge and experience, independence factors that include long-standing relationships with clients, the pressure of a client, peer review of auditors and non-audit services and audit quality. The data were taken using a questionnaire instrument that has been tested for validity and reliability.
50
From table 4.10 above, it can be obtained a multiple regression equation as follows:
Y = (-4,924) + 0,412 X1 + 0,332 X2
Here are the explanations of the multiple regression equation which are formed:
1. Auditor competence have t value of 7.921, the value of the coefficient B is 0.412 and significant level of 0.000. This indicates that the coefficient of the variable auditor competence (X1) has a positive effect (unidirectional) to audit quality (Y), with a significant level of 0.000. This means that the higher auditor competence, the higher quality of audit
2. Independence of auditors has t value of 6.006, with a coefficient B 0.332, and a significant level of 0.000. This indicates that the coefficient of the variable auditor independence (X2) has a positive effect (unidirectional) to audit quality (Y) with a significant level of 0.000. This means that the higher the auditor's independence, the higher quality of audit.
3. Constants of (-4.924) means that an auditor should have the competence and independence if he/she wants to have a good quality of audit.
G. Hypothesis Test Result 1. t Test Results (Partial)
T-test is used to determine the effect of each independent variable on the dependent variable, between the competence and independence on audit
The variable of independent is projected through the long-standing relationships with clients, pressure from clients, peer review, audit and non-audit services provided, having a significant impact on audit quality, namely with the value of the regression coefficient of 0.332, which means that every unit increase in the independent variable it will improve the quality of audits produced by the auditor of 0,332 units.
From the research, it is known simultaneously that audit quality of auditors in certified public accounting firm in South Jakarta can be determined by competency and independency in the coefficient of determination R2 0.874 or 87.4% and the remaining 12.6% is determined by other factors beyond of this research model.
These results can be concluded that in order to improve audit quality, it is affected by two variables, namely competence and independence. This can be understood as if the auditors have the competence; the result of audit will be maximized, as supported by knowledge and experience even when the auditor has independence it will not be affected by the client. Auditors will be free to perform audit tasks. But if it does not have the competence and independence, especially if it gets pressure from the client then audit quality is not optimal.
54 CHAPTER V
CLOSING
A. Conclusion
Based on the research that has been conducted which aims to find empirical evidence about the relationship between competence and independence of auditors towards audit quality in CPA Firm in South Jakarta. It can be concluded that:
1. There is partial influence between the variables of auditor’s competence towards audit quality. It can be seen from the T-test that has been calculated by the researcher, it shows that the value of T-count > T-table (7.921 > 2.405) then H0 is rejected.
2. There is partial influence between the variables of auditor’s independence towards audit quality. It can be seen from the T-test that has been calculated by the researcher, it shows that the value of T-count > T-table (6.006 > 2.405) then H0 is rejected.
3. There is simultaneous influence between auditor’s competence and auditor’s independence towards audit quality. It is shown by the results of the F test hypothesis (simultaneous) which showed that there is effect on audit quality from both of them because F count > F table (169.589 > 3,190) then Ho is rejected, it means that auditor competence and independence jointly affect the quality of the audit.
B. Limitation
This study is limited to the research object auditors who work in Certified Public Accounting Firm (CPA Firm) in South Jakarta. Thus are allowing the differences in the results, discussion or conclusions for different research objects.
Measurement of audit quality will be better if other studies objects are added such as leadership of the CPA Firm.
C. Suggestion
Based on the research that has been conducted, and then suggestions are submitted, among others:
1. To improve the quality of audit, it is necessary to increase the competence of auditors by giving training and opportunity to follow courses or an increase in professional education.
2. Auditors are expected to increase their independence because independence factors can affect the quality of audit. The auditors which are in charge of their client are sought a truly independent, not under pressure of clients, do not have embarrassment in performing audit tasks completely objective and can produce a quality audit.
3. Respondents in further research should be expanded, not only from the scope of the auditor's executives, but can also be from the head of the Public Accounting Firm.
4. For further research, we should be able to consider adding other variables that can affect the quality of audit.
56 REFERENCES
AAA Financial Accounting Standar Committee. 2000. Commentary SEC Auditor Independce Requirements. Accounting Horizons Vol.15 No.4 December 2001, Hal 373-386.
Arens Alvin, et. All. “Auditing and Assurance Services”. 12th edition, Prentice Hall Inc, New Jersey, 2010.
Christiawan, Yulius Jogi. 2003. Kompetensi dan Independensi Akuntan Publik:
Refleksi Hasil Penelitian Empiris. Akuntansi dan Keuangan Vol.4 No. 2 (Nov) Page. 79-92
Elfarini, Eunike Christina. 2007. Pengaruh Kompetensi Dan Independensi Auditor Terhadap Kualitas Audit (Studi Empiris Pada Kantor Akuntan Publik di Jawa Tengah, Thesis of Faculty of Economy in Semarang State University.
Ghozali, Imam.2005. Aplikasi Analisis Multivariat Dengan Program SPSS.
Semarang : BP Undip.
Hamid, Abdul, 2007. “Panduan Penulisan Skripsi”, FEIS: Jakarta.
Harhinto, Teguh . 2004. Pengaruh Keahlian dan Independensi Terhadap Kualitas Audit. Studi Empiris Pada KAP di Jawa Timur. Semarang. Tesis Maksi :UniversitasDiponegoro.(Tidak dipublikasikan).
Ikatan Akuntan Publik Indonesia. 2011. Standar Profesional Akuntan Publik Per 31 Maret 2011. Salemba Empat: Jakarta.
Indriantoro, Nur dan Bambang Supomo. 2009. Metode Penelitian Bisnis. First Edition Yogyakarta: BPFE
Maholtra, Naers K, Mark Peterson, 2007. “Basic Marketing Research”, 2 edition.
Prentice Hall.
Masran, Jimmy. 2007. Pengaruh Kemampuan Kerja dan Motivasi terhadap Kinerja Karyawan, Thesis of Faculty of Economy in Hasanuddin University.