Urgensi standardisasi tanaman obat sebagai
bahan baku produk herbal
Bincang Riset PRBBOOT BRIN 27 September 2022
• Tropical Biopharmaca Research Center
• Department of Chemistry
• AR-Lab
Mohamad Rafi dan Rudi Heryanto
Biosketch
http://mra.staff.ipb.ac.id/
Education
• B.Sc - IPB University, Indonesia
• M.Sc – IPB University, Indonesia
• Ph.D – Gifu University, Japan
Dosen dan peneliti di Departemen Kimia FMIPA dan Pusat Studi Biofarmaka Tropika LPPM IPB. Saat ini diberi amanah sebagai Kaprodi S2/S3 Kimia, PIC Lab Metabolomik AR-Lab, dan Ketua editor Jurnal Jamu Indonesia, IPB. Selain itu juga sebagai Ketua Senior Himpunan Kimia Indonesia (2022), dan MD Kawasan INA I4 (2022-2024)
Penelitian yang dilakukan banyak di bidang metabolomik dan kemometrik untuk pengembangan metode kendali mutu, identifikasi senyawa penciri dan standardisasi tumbuhan untuk bahan baku obat herbal/pangan. Email: mra@apps.ipb.ac.id
Himpunan profesi yang diikuti:
• Himpunan Kimia Indonesia/Indonesian Chemical Society
• Metabolomics Society
• The Society of Chromatographic Science, Japan
• HPTLC Association
• Perhimpunan Peneliti Bahan Obat Alami/The Indonesian Association of Natural Drugs Researcher
Isi Presentasi
Karakteristik tanaman
obat
Standardisasi dan kendali mutu bahan baku produk herbal
Contoh
kendali mutu
bahan baku
dan produk
herbal
Karakteristik tanaman obat
Komponen kimia
Panen dan
pasca panen Waktu panen Lingkungan
tumbuh
Kultivasi/
tumbuh liar
Komposisi yang kompleks dengan variasi kosentrasi
dan belum diketahui total senyawa yang terkandung
di dalamnya
Karakteristik tanaman obat
mg/g
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
CUR DMC BDMC
M. Rafi et al. 2015. Food Analytical Methods. 8: 2185-2193.
Kadar kurkuminoid pada kunyit (CL) dan temulawak (CX)
Karakteristik tanaman obat
MS AS MA AA
Bogor 7.62 7.71 2.8 2.6
Sleman 2.39 2.47 1.28 1.51
Boyolali 0.56 1.6 0.65 0.93
Kuningan 1.87 2.59 0.52 0.59
CA-1 4.22 2.99 2.1 0.69
CA-2 1.29 1.1 2.86 2.24
CA-3A1 8.09 8.23 2.09 1.52
CA-3A2 7.55 7.51 2.43 2.06
CA-3A3 6.02 6.03 1.98 1.49
CA-3A4 5.73 5.85 1.98 1.33
CA-3A5 6.18 6.25 1.8 1.32
CA-3A6 8.04 7.52 1.73 1.48
CA-3A7 5.55 5.96 2.3 2.44
CA-4A1 2.59 2.45 6.39 4.76
CA-4A2 8.44 8 5.22 3.68
CA-4A3 6.81 6.6 5.48 4.46
CA-4A4 9.92 9.77 4.14 3.1
CA-4A5 15.12 13.55 1.27 1.16
CA-4A6 7.45 7.82 4.1 3.36
CA-4A7 7.1 6.59 4.49 3.18
CA-5A1 8.22 8.21 1.25 1.11
CA-5A2 7.52 7.45 0.9 0.43
CA-5A3 7.56 7.16 0.66 0.08
CA-5A4 8.93 9.05 0.8 0.31
CA-5A5 6.78 6.85 0.61 0.04
CA-5A6 7.53 7.41 0.6 0.11
CA-5A7 7.61 7.14 0.65 0.04
Analyte content (mg/g), n = 3
CA samples Kadar madekasosida, asiatikosida,
asam madekasat dan asam asiatat pada pegagan dengan waktu panen berbeda
M. Rafi et al. Industrial Crops & Products 122 (2018) 93–97
Karakteristik tanaman/produk obat herbal
Multikomponen Dapat lebih dari satu bahan -- Multikompnen
Karakteristik tanaman/produk obat herbal
Ma et al. Phytomedicine 45 (2018) 105–119
Problem dalam Obat Tradisional/Obat Herbal
Standardisasi obat herbal
Pemalsuan dengan bahan kimia obat
atau tumbuhan lainnya yang mirip
Menggunakan tumbuhan obat
yang salah
Dosis yang tidak tepat
Produk dengan kualitas rendah
Toksisitas
Interaksi dengan obat herbal/kimia
lainnya
Problem
Kesalahpahaman bahwa obat herbal pasti aman
Penggunaan obat herbal untuk indikasi yang
berbeda
Standardisasi obat herbal
MV Shinde, K Dhalwal, K Potdar, K Mahadik. 2009. International Journal of Phytomedicine 1: 4
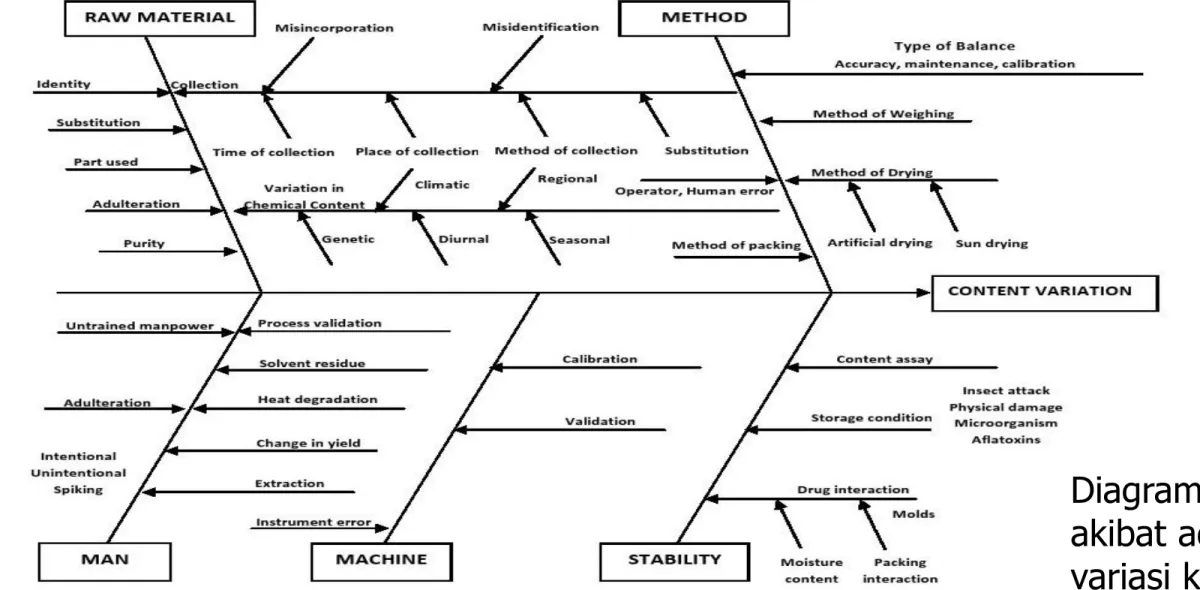
Diagram sebab
akibat adanya
variasi khasiat
obat herbal
Standardisasi obat herbal
Jadi singkatnya, standardisasi (kendali mutu) tumbuhan obat dan produknya sangat diperlukan
1. Apakah suatu produk obat herbal mengandung komponen seperti yang tertera pada klaim label? --- IDENTIFIKASI
2. Apakah memang obat herbal yang saya beli benar-benar yang tepat? --- ADULTERASI
3. Apakah harga obat herbal yang dibeli sesuai khasiatnya atau tampilan luar saja?
--- KUALITAS
4. Apakah komposisi komponen penyusun obat herbal sesuai dengan yang tertera pada label klaim? --- KUANTITAS
5. Apakah akan ada perubahan komposisi dengan berjalannya waktu? ---
STABILITAS
Standardisasi obat herbal
• Standardization is a system to ensure that every packet of medicine that is being sold has the correct amount and will induced its therapeutic effect (Chaudury 1992)
• Standardization refers to the body of information and controls
necessary to produce material of reasonable consistency. This is
achieved through minimizing the inherent variation of natural
product composition through quality assurance practices applied
to agricultural and manufacturing processes (American Herbal
Product Association)
Standardisasi obat herbal
Main issue
kualitas
khasiat
keamanan
Standardisasi
Tiga isu utama (kualitas, keamanan, dan khasiat) dalam pengembangan obat herbal dapat tercapai jika dilakukan proses standardisasi sejak menanam hingga produksinya
→ standardisasi --- kendali mutu
Proses
Standardisasi obat herbal
The complex factors affecting quality of herbal medicine products
Liu et al. Phytomedicine 44: 247-257
Standardisasi obat herbal
Standardisasi obat herbal
Standardisasi obat herbal
Standardisasi obat herbal
Metode analitik untuk
mengetahui komposisi fitokimia (kualitatif dan kuantitatif) dalam
rangka menstandarkan bahan baku/produk obat herbal aktivitas farmakologi yang konsisten akan dihasilkan dari profil kimia yang konsisten pula
Obat herbal terstandar
Aktivitas biologis konsisten
Fitokimia
Standardisasi obat herbal
Wei et al. Chin Med (2020) 15:56
Standardisasi obat herbal
Wei et al. Chin Med (2020) 15:56
Kendali mutu tumbuhan obat
Simmler, C., Graham, J.G., Chen, S.-N., Pauli, G.F. 2018. Fitoterapia, 129, pp. 401-414
Parameters affecting the determination of botanical authenticity
Kendali mutu tumbuhan obat
Simmler, C., Graham, J.G., Chen, S.-N., Pauli, G.F. 2018. Fitoterapia, 129, pp. 401-414
A three-step process for the assessment of authenticity
(step 1) documentation of traceability, which encourages supply chain transparency and helps identify risks pertaining to possible contaminations/adulterations
(step 2) validation of botanical identity and integrity of the plant material or extract together with
(step 3) the implementation of a variety of complementary phytochemical analyses to confirm the chemical identity and
composition of the botanical, utilizing
techniques that are also capable of detecting potential chemical adulterations
Metode kendali mutu TO/OH
QC method with metabolomics
approach
Fingerprint analysis
Holistic Profiling
analysis Targeted
analysis
Commonly used
Identification, discrimination and
authentication (IDA) of medicinal plants
Metode kendali mutu TO/OH
APPROACH TARGETED ANALYSIS METABOLITE PROFILING
METABOLITE FINGERPRINTING STRENGHT • Quantitative
• Low detection limit
• High troughput
Global image of the samples
• Global image of the samples
• Directly applicable to pattern recognition
• Highest throughput PITFALL • Limited number of targeted
compounds
• No detection of untargeted compounds
• Need for the pure targeted compounds for the
calibration
• Expensive
• Semi-quantitative
• Difficulties in informatics
• Medium throughput
No compound identification
TECHNIQUES Chromatography and spectroscopy
5 P Vernocchi et al. 2012. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 2: Article 156
Different approaches and respective techniques: pitfalls and strengths5
Targeted analysis
curcumin
demethoxycurcumin
bisdemethoxycurcumin
xanthorrhizol
Temulawak
E Erpina et al. Journal of Liquid Chromatography and Related Techniques 40(12): 635-639.
Metabolite profiling/fingerprinting
Kunyit (C. longa) Temulawak (C.
xanthorrhiza)
Temu mangga (C.
mangga) Temu hitam (C.
aeruginosa)
IDENTIFIKASI DAN
AUTENTIKASI
Metabolite profiling/fingerprinting
Spektrum UV-Vis representatif dari 4
spesies Curcuma
M Rafi et al. 2018. International Food Research Journal 25(2): 643-648.
Metabolite profiling/fingerprinting
• Instrumentasi: Spektrofotometer UV-Vis
• Prapemrosesan sinyal: standar normal variate
• Metode kemometrik: a. principal component analysis (PCA) dan b. canonical variate
analysis (CVA)
a
b
M Rafi et al. 2018. International Food Research Journal 25(2): 643-648.
Contoh metode kendali mutu
bahan baku dan produk obat
herbal
Diskriminasi minyak atsiri serai wangi
Spektrum NIRs daun sereh wangi (a) dan daun sereh dapur (b)
a
b
http://cybex.pertanian.go.id/mobile/artikel/92607 /Perbedaan-Sereh-Wangi-Dan-Sereh-Dapur/
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104277
Diskriminasi minyak atsiri serai wangi
Plot score PCA
(variable: absorbance data 4000-6500 cm-1) C. nardus
C. citratus
Diskriminasi minyak atsiri serai wangi
Plot score OPLS-DA minyak atsiri
daun ( ▲ ) C. citratus , ( ) C. nardus
, ( ■ ) campuran 25% C. citratus , dan
(●) campuran 10% C. citratus dalam
C. nardus
Manakah yang merupakan meniran hijau (Phyllanthus niruri)?
2 1
3
Identifikasi dan autentikasi Phyllanthus niruri
Pn9 Pd1 Ll1 Ll2 Ll3 Pn1 Pn7 Pn5 Pu1 Pu2 1. Filantin
2. Hipofilantin 1
2
Identifikasi dan autentikasi Phyllanthus niruri
Pn: Phyllanthus niruri Pd: Phyllanthus debilis Pu: Phyllanthus urinaria Ll: Leucaena leucocephala
http://biofarmaka.ipb.ac.id/
news/2334-download-atlas- kromatografi-lapis-tipis- tumbuhan-obat-indonesia- volume-1-2019
1
Identifikasi dan autentikasi Phyllanthus niruri
1
2.5 5.0 7.5 10.0 12.5 15.0 17.5 20.0 22.5 25.0 27.5 30.0 32.5 35.0 37.5 min
0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0
uV(x100,000)
1
2
3 4 5
6
7 8 9 10
12 13
11 14 a
b c d e f g h i
(a) PN-5 100 %
(b) PN-5:PU-5 (75:25 %) (c) PN-5:PU-5 (50:50 %) (d) PN-5:PU-5 (25:75 %)
(h) PU-5 100 % (i) PD-5 100 %) (e) PN-5:PD-5 (75:25 %)
(f) PN-5:PD-5 (50:50 %) (g) PN-5:PD-5 (25:75 %)
3 4
a b c d e f g h i
Identifikasi dan autentikasi Phyllanthus niruri
1
Plot analisis diskriminan
PN PU
PD
Identifikasi dan autentikasi Phyllanthus niruri
Investigation of α-glucosidase inhibitory activity in Yacon leaves extracts
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11130-021-00926-3
IC 50 inhibition of α-glucosidase
In vitro ɑ-glucosidase inhibitor activity profile of Yacon leaf
extracts, expressed in IC50 value (J = Yacon leaves from Wonosobo- Central Java, B = Yacon leaves from Lembang-West Java, 50 and 95
reflecting ethanol 50 and 95% as extraction solvent, W = water
extract, ACA = Acarbose). The values
were the mean from 5 replications
LC-MS/MS analysis
Representative Chromatogram of LC-MS/MS water extract (JW), 95% ethanol extract (J95) and 50% ethanol extract (J50) from Yacon J leaves
OPLS analysis--- LC-MS/MS
OPLS analysis of LC–MS data A: Score scatter plot, showing samples grouping based on their ɑ-glucosidase inhibitor activity B: S-plot to identify LC-retention time responsible for the sample separation based on the IC50 in the score scatter plot. Retention times located in the left side of the plot are the dominant peaks in the chromatogram of the sample with higherɑ-glucosidase inhibitor activity
More active
Less active
OPLS analysis--- LC-MS/MS
In silico
Framework for quality control of Ayurvedic drugs by the Ministry of AYUSH (India)
Katoch et al. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 197 (2017) 25–31
Standardisasi produk obat herbal, TCM
Yang et al. 2017. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 7 (4): 439-446
Q-marker in TCM
• The Q-marker of TCM refers to the intrinsic or processing/ preparation-resultant chemical substances closely associated with the functional properties that exist in the raw materials and products of TCM (involving the decoction pieces, decoctions, extractives, and Chinese patent medicines), which can be used as the indicators for quality control of TCM to embody the safety and effectiveness.
• Q-marker was proposed by considering the complex factors from the basic theory of TCM, the formulation, preparation technology, dosage form, and usage of formula preparations, to standardize TCM quality research and quality standards elaboration, to enhance the quality consistency, controllability, and traceability.
• The establishment of Q-marker integrates multi- disciplinary technologies like natural products chemistry, analytical chemistry, bionics, chemometrics, pharmacology, systems biology, and pharmacodynamics, etc
Yang et al. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B (2017) 7(4):439–446
Q-marker in TCM
Yang et al. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B (2017) 7(4):439–446
The basic properties of Q-marker can be outlined in four aspects:
1) They are the intrinsic chemical components in TCM materials and products, or processing/ preparation-resultant;
2) They are functional properties-associated, with definite chemical structures;
3) They can be qualitatively characterized and quantitatively determined; and
4) For the formulae, there presentative substances of the Monarchare firstly considered, and those from the Minister, Assistant, and Guide, should be considered as well, following the compatibility theory. The factors, involving 1)cell and tissue specificity, 2) organ specificity, 3) developmental specificity for biosynthesis, 4) the extrinsic factors of growing process (drugmaterials), and 5) the preparation factors (formula preparations), can affect Q-markers.
In establishment of Q-markers, special attention should be paid to the components that ensure the authenticity (identity marker), differentiate the quality difference (superiority/inferiority marker), and identify the geo-authenticity (geo-authentic marker).
Q-marker in TCM
Xie et al. RSC Adv., 2018, 8, 812
Q-marker in TCM
Strategy of Q- biomarkers screening and validation
Xin et al. Phytomedicine 44: 103-108
Q-marker in TCM
Identification of the quality markers for quality and
process control of herbal
medicinal products
Liu et al. Phytomedicine 44: 247-257
Q-marker in TCM
The network
database for the traceability
platform of
herbal medicinal products
Liu et al. Phytomedicine 44: 247-257
Q-marker in TCM
Identify quality markers based on integration
methodology to
establish the quality markers for
production process system from raw materials to
products
Liu et al. Phytomedicine 44: 247-257