Appendix: Details on Soil Health Management Components of National Mission 65-75 for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA). To this end, the National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) was created to increase agricultural productivity, especially in rainfed areas, with emphasis on integrated farming, water use efficiency, soil health management and synergizing resource conservation. The Strategies and Programs of Action (POA) outlined in the mission document, approved 'in principle' by the Prime Minister's Council on Climate Change (PMCCC), aim to promote sustainable agriculture through a set of adaptation measures focusing on ten key dimensions. which covers Indian agriculture namely; 'Improved Crop Seeds, Livestock and Fish Culture', 'Water Use Efficiency', 'Pest Control', 'Improved Agricultural Practices'.
The NMSA architecture is designed by bringing together, consolidating and accommodating all ongoing and newly proposed activities/programs related to sustainable agriculture, with a special emphasis on soil and water conservation, water use efficiency, soil health management and rain-fed area development. National Mission for Agricultural Extension and Technology, National Food Security Mission, National Initiative for Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA) etc., in the field of climate change adaptation and mitigation measures;
Mission Interventions
Assistance will be provided for various improved packages of practices based on land use and soil characteristics, generated through Geographical Information System (GIS) based thematic maps and database on land and soil characteristics through extensive field level scientific surveys. This component will be implemented by State Govt., National Center of Organic Farming (NCOF), Central Fertilizer Quality Control. Comprehensive pilot blocks will be supported to illustrate functional mechanism for dissemination of rainfed technologies, planning, convergence and coordination with flagship schemes/missions like MGNREGS, IWMP, Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Program (AIBP), RKVY, NFSM, MIDH, NMAET etc.
A consortium approach will be developed with various stakeholders including knowledge partners such as State Agricultural Universities (SAUs), Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs), Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) institutes, etc. Climate change related monitoring, feedback, knowledge networks and skill development will also be supported under this component by State Agricultural Universities, ICAR Institutes National/International Institutes, KVKs, Public/Private R&D Organizations, etc.
Mission Structure
The PSC will be served by DAC's Natural Resource Management (NRM) and Food Farming System (RFS) Divisions. The duties/responsibilities, qualification and remuneration for the engagement of the Consultants/Chief Consultants will be as per the specifications given in Annexure-V and V(A). The Director (Agriculture) will be the Member Secretary and the Director (Horticulture) will be the Joint Member Secretary of the Committee.
The duties/responsibilities, qualification and remuneration for the engagement of the State Consultants will be as per the specifications given in Annexure-V and V(A). The duties/responsibilities, qualification and remuneration for the engagement of these Consultants will be as per the specifications given in Annexure-V and V(A).
Planning & Implementation
Component Specific Planning (CSP)
Himalayan States for the purpose of calculating financial assistance. iii) Location and crop specific technologically appropriate irrigation systems will be propagated to ensure minimum cost burden on the farmers/. iv). It can be ensured that at least 25% of the micro irrigation fund allocated to the state is used for the crop sector. v) Support to each farm family under the OFWM component will be limited to a farm size of 5 Ha. However, beneficiaries who have already availed the benefits of central subsidy for micro-irrigation cannot get additional assistance for the same land for the next 10 years. vi) Support to create secondary storage at the end of the canal system to store water when it is available in abundance (rainy season) or from perennial sources such as streams for use during dry periods through efficient on-farm water management. Provisional provisions for each component will be provided to facilitate States in preparing component-specific ones.
During the next five years, the effort for direct transfer of subsidy to the farmers/beneficiary will be done based on ADHAR no. The amount will be transferred only after securing the proof of purchase of equipment/inputs made by the farmer as per provisions and norms prescribed in the guidelines.
Monitoring and Evaluation
In cases where farmers do not have access to the Internet, they can use online kiosks, shared service centers, etc., which are already available in rural areas and are being used by farmers for various other activities. Such internet and online service providers should be allowed to charge a fixed fee from the farmer for submitting their application online and for further follow up. Apart from this, the names of the beneficiaries and the assistance given to them will also be placed on the website of the department in the public domain.
Selection and transfer of benefits should be time bound and can be done online so that the farmer does not need to visit the departmental office again and again for such things. APR) must be sent to the Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperation of the Ministry of Agriculture within three months after the end of the fiscal year.
Coverage
At the district level, monitoring will be done by the Joint Director/Deputy Director of Agriculture in collaboration with the respective Zilla Panchayati Raj Institutions.
Fund Flow Mechanism
Additional 16% and 8% of the total allocation or in proportion to SC/ST population in the district will be used for Special Component Plan (SCP) and Tribal Sub Plan (TSP) respectively.
Impact Assessment, Periodic Evaluation and Reporting
Expected Outcome
Rainfed Area Development (RAD)
50% of input cost of breeding system including cost of animals with one year concentrated feed limited to Rs. 50% of input cost of crop/vegetables. system including cost of fish farming limited to Rs. 100% assistance for silage making unit consisting of silo pit chaff cutters and weighing balance limited to Rs.
Maintenance must be ensured by the beneficiary. 100% of cost limited to Rs. 20 lakh / unit in general areas, Rs. 25 lakh/unit in hilly areas) for 10 ha command area or if applicable. 50% of the cost of installation and transmission system from the nearest source limited to Rs.
Soil Health Management (SHM) Details of SHM are in Chapter-2 C. On Farm Water Management (OFWM)
However, assistance to farmers will be subject to the norms for different sizes of land given in Annexure I. The maximum assistance allowed will be based on the length of pipe and limited to 5 ha per beneficiary/group. Construction of secondary storage structures with guardrail, canal/perennial source connectivity, distribution/discharge, intake and retention structures at feasible locations.
Upper limit of assistance will be limited to the amount according to the eligible pattern of assistance of the normative cost of installation. State will be supported to illustrate functional mechanism for dissemination of rainfed technologies, planning, convergence and coordination in pilot blocks. Research/model/pilot projects for different agro-climatic conditions on climate change adaptation and mitigation.
Quality Control and After Sales Services 1. Registration of Micro Irrigation Manufacturers
After Sales Service
Manufacturers should provide detailed operation and maintenance manuals in the local language at the time of installation of the system and provide proper orientation for operation and maintenance of drip/sprinkler irrigation systems. The manufacturer is responsible for any dispute/s arising in connection with the supply of the MI system or its components directly or through their distributors/dealers. In the event that the system supplier/manufacturer fails to provide satisfactory after-sales service, should be excluded (at SLC level) from renewal of registration.
Quality Control
Cost of installation of Drip Irrigation System for different spacing and land size
Wide Spaced crops
Mission Implementation Plan (MIP) (Suggestive List of Contents)
Preparation of Annual Action Plan A. Rainfed Area Development (RAD)
- Integrated Farming System
- Soil Health Management (SHM)
- On Farm Water Management (OFWM) I. Horticultural Crops
- Climate Change and Sustainable Agriculture: Modeling & Networking (CCSAMN)
- Rainfed Area Development
- Climate Change and Sustainable Agriculture: Modeling & Networking (CCSAMN)
IFS and/or value addition activity/activities, water management, resource conservation technologies, vermicompost/organic farming, post-harvest/NDFP, problematic soil reclamation etc. GH: Greenhouse/Polyhouse; WHS: Farm Pond, Check Dams, Common Reservoir, Reservoir Renovation etc.; WM: application, distribution, cladding, pipeline, last mile connectivity, etc.; RCT: in situ moisture conservation, contour/graded filling, vegetate. Establishment of a mobile soil testing laboratory. Promotion of INM, organic farming, micronutrients, etc.
Drip Irrigation System S & M (Wide Spacing Crop) Other Drip Irrigation System S & M (Close Spacing Crop) Other Micro Sprinkler Irrigation S & M. Semi Permanent Sprinkler S & M Irrigation System Other Large Volume Sprinkler S & M Irrigation System Other (Rain Gun). Portable Sprinkler S & M Irrigation System Other Semi-permanent Sprinkler S & M Irrigation System Other Large Volume Sprinkler S & M Irrigation System (Rain-. gun) Other.
Progress reporting format for TSP and SCSP component under NMSA
Physical achievement
Financial Target
Duties of Consultants under NMSA at National, State & District Level
State Level
National Level
Guidelines for implementation of Soil Health Management (SHM) component under National
Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA)
- Implementation of Mission Intervention on Soil Health Management (SHM)
- The details of specific components in this Intervention are given below:-
- Project Sanctioning System
- Monitoring and Evaluation
- SOIL HEALTH MANAGEMENT
- Strengthening Of Soil Testing Laboratories
- Strengthening of Existing Soil Testing Laboratories
- Creation of Data Bank for site specific Balanced Use of Fertilizer
- Adoption of village by STLs (maximum 10 Villages per STL) through Frontline Field Demonstration (FFD)
- Preparation of Digital District Soil Maps and Global Positioning System (GPS) based Soil Fertility Monitoring
- Portable Soil Testing Kits for Balanced Use of Fertilizers
- Promotion and Distribution of Micronutrient
- Strengthening Of Fertilizer Quality Control system
- Support to CFQC&TI
- INM & ORGANIC FARMING
- Support to NCOF
- Components to be implemented by NABARD
- Components to be implemented by State Govts./ICAR/SAUs etc
Funds will be released based on progress report, submission of utilization certificates for previously sanctioned projects, specific new needs etc. At the state level, the implementation process will be monitored by the State Standing Technical Committee (SSTC) and the State Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (SMSA) /. Web-based monitoring, video conferencing, desk reviews, field visits and evaluation of program implementation will be followed for effective monitoring.
At the district level, monitoring will be undertaken by the Joint Director/Deputy Director of Agriculture in collaboration with the concerned ZillaPanchayat Raj institutions. The number of programs will be decided by the INM division based on the proposal received from the states and UTs. These 800 STLs will be selected by the State Government, a list will be sent to GOI along with the proposal.
Technical suitability of the kit will be decided in consultation with ICAR institutes like IARI, New Delhi. Assistance will be provided only to those State laboratories which are functional and functioning well and there will be no duplicate responsibility on the part of the Central Government. States- During the 12th plan a two week duration will be organized with 20 participants in each course.
Innovative Components for SHM - Any innovative project submitted by a State Government to further the objectives of this scheme will be eligible for funding under the scheme, within the overall expenditure and budget limits. The course is open to rural youth with a degree/diploma in Agriculture/Science with Biology. SAUs/educational institutions can also sponsor their students for such courses. 100% assistance will be provided to State Governments/Government Agencies up to a maximum limit of Rs 190 lakh/unit and to individuals/private bodies in the form of Capital Investment Subsidy @ 33% of Total Financial Expenditure (TFO), limited to Rs.63 lakh as credit-linked subsidies through NABARD have been terminated.
Component wise Pattern of assistance (under centrally sponsored scheme)
Soil Health components of SHM under NMSA Sl. No
Organic& INM components of SHM under NMSA Component
Activities to be implemented by GOI Institutes /Centres Component
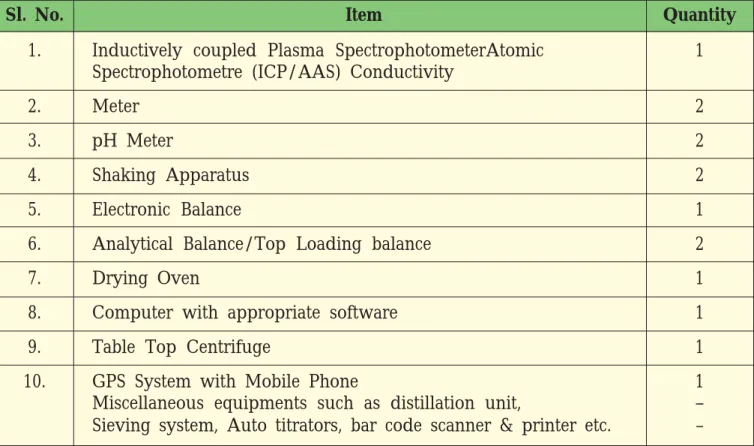
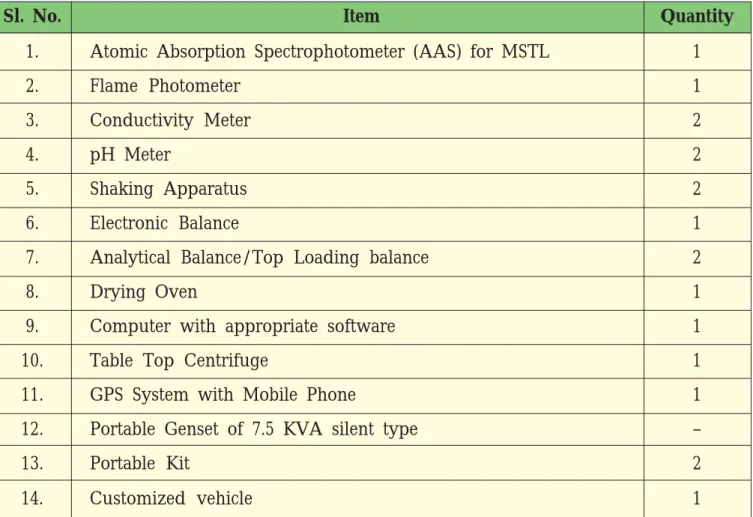
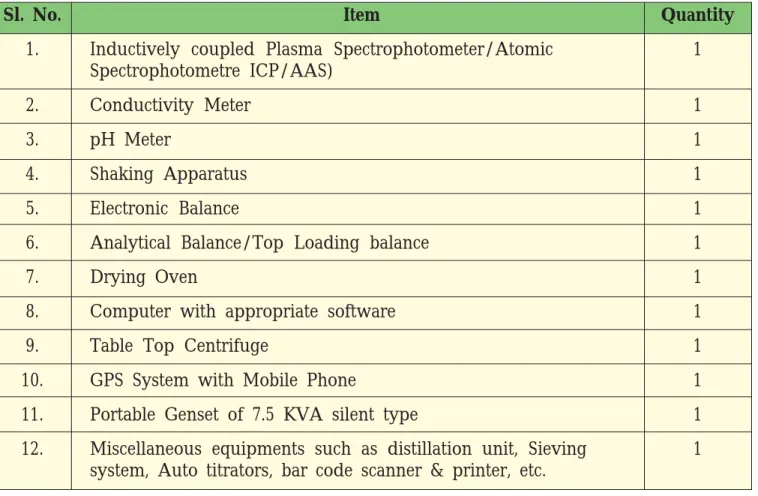
List of Suggestive Equipments for MSTL
Fermentation and biomass up-scaling equipments and machines