Human resource composition of ZINWA 16
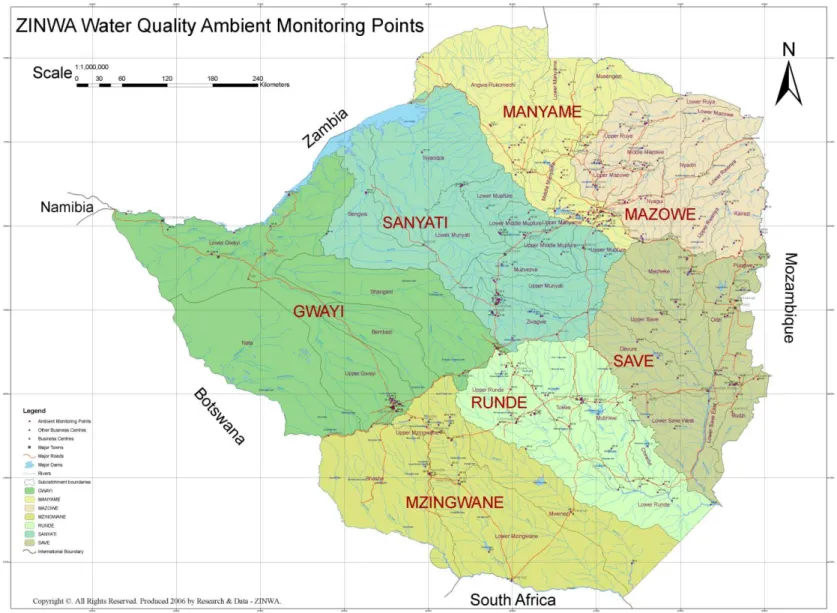
The seven catchments of Zimbabwe and ambient water quality
MinWRMD Minister of Water Resources Management and Development MZHRB Ministry of Water Resources Development and Management. Valuable, rare, inimitable and irreplaceable VRIN Valuable, rare, inimitable VRIO and Organization World Health Organization WHO.
INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND
Introduction
- Resource Based View (RBV) of the firm theory direction
Studies on the RBV theory of the firm have been done in other parts of the world such as the National Health Service of the United Kingdom (Bryson, Ackermann & Eden, 2007); However, there are no studies evaluating the use of RBV theory conducted in the Zimbabwean public sector and in particular the Zimbabwe National Water Authority (ZINWA).
Background
- Business Macro-environment in Zimbabwe
- Public Sector Analysis
There has been an increase in the number of players in data and voice services with coverage that has denied the rest of the country. Zimbabwe's natural environment is characterized by a late onset of rainy seasons, punctuated by dry periods in between.
Problem Statement
Floods in the lowest parts of the country such as Muzarabani, Kanyemba, Tsholosho, Malipati, Sanyati, Middle Save and Chikwalakwala destroy canals, dams and water supply infrastructure. Despite the benefits of RBV cited above and in section 1.1, ZINWA is struggling to maintain its operations.
Research Objectives
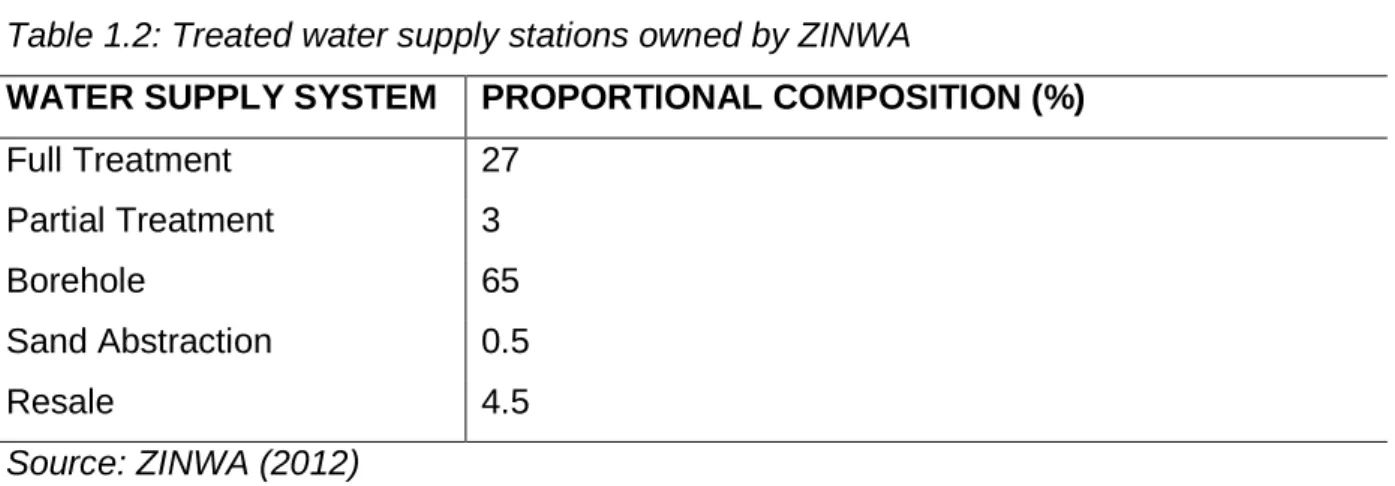
ZINWA survives on income from clear water supplies and to a lesser extent raw water supplies. To come up with recommendations on how resources owned by ZINWA can be used to gain value, increase viability and profitability.
Research Questions
To find out if ZINWA has used its resources and core competencies to increase its viability; And.
Scope of Research
Justification
From this study, the researcher will be able to produce the best RBV model that will be applicable in the Zimbabwean environment. This has enabled the researcher to become an effective business manager who will be able to lead any organization.
Research Proposition
The researcher will benefit from the research by broadening his knowledge of RBV theory and strategic business management in particular. This unique study of RBV in the public sector of Zimbabwe and ZINWA in particular has yielded results that will be applied even elsewhere for both research and strategic management.
Structure of the Study
The academic fraternity will use the findings of this research to guide them in their future research activities.
Chapter Conclusion
LITERATURE REVIEW
Introduction
Resource Based View Theory of the Firm
The later author's definition was that a firm's resources can be either tangible or intangible assets that are linked to the firm and can be used to develop a firm's competitive advantage. He further argues that resources and capabilities that are both valuable and scarce will lead to competitive advantage.
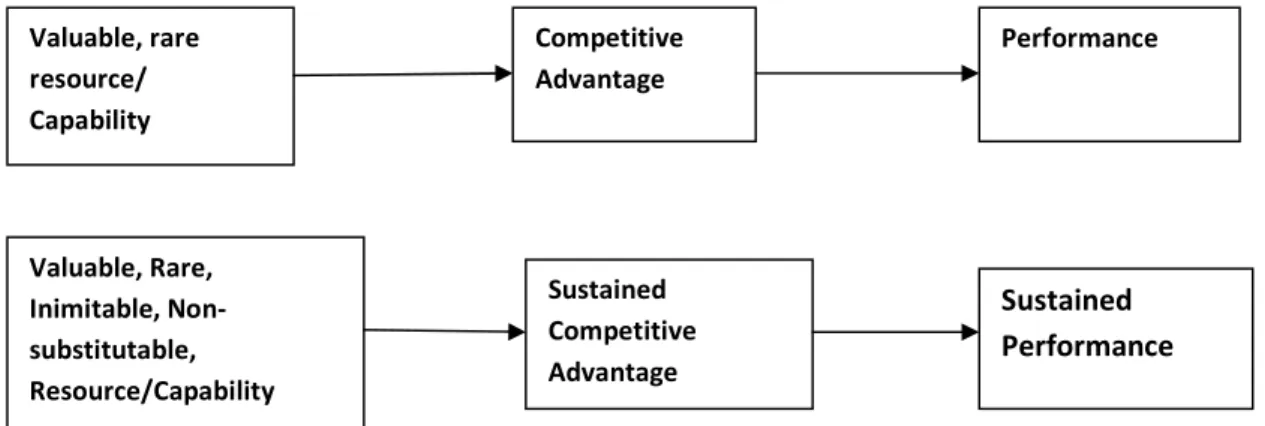
Resource Value
Kraaijenbrink (2012, p4) defines resource suitability as "the degree to which a resource contributes to the achievement of a particular goal". Resource combination is defined by Kraaijenbrink (2012, p4) as "the extent to which a resource can be effectively combined with other resources to which a firm has access".
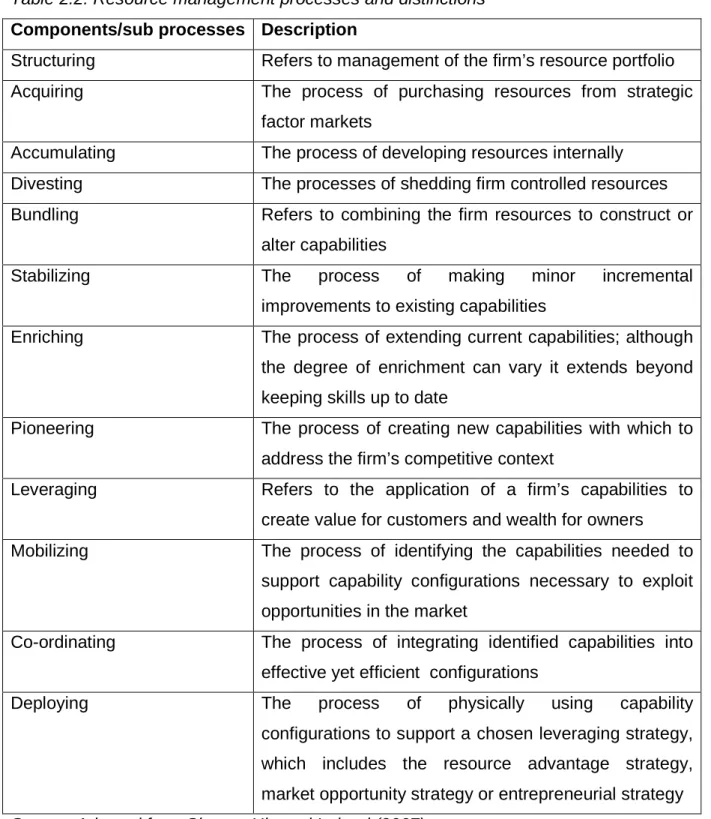
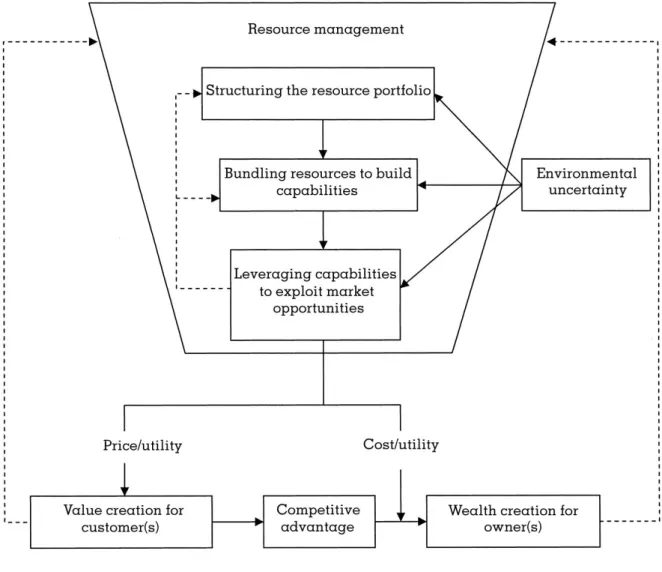
Resource Management
Structuring Refers to the management of the firm's portfolio of resources Acquisition The process of purchasing resources from the strategy. Accumulation The process of developing resources from within Allocation Processes of shedding resources controlled by the firm Combination refers to the combination of the firm's resources to build or. Pioneering The process of creating new capabilities to address the firm's competitive context.
Leveraging Refers to the application of a firm's capabilities to create value for customers and wealth for owners Mobilization The process of identifying the capabilities needed for it.
Firm Capabilities (Core Competencies) and Resource Based View Theory
Therefore, internal capabilities cannot be bought but must be built by the firm (Makadok, 2001, cited in Ahn, Gray & Collier, 2012) and combined with external partnerships they are seen as a flexible innovation system (Su, 2009) . Liu, Baskaran and Li (2009), describe firm capability as consisting of process type, evolution, context dependence and path dependence in a firm's processes. They elaborate that capabilities are embedded in a firm and its structure and they must have a strategic fit with the firm's strategy.
Dynamic ability is defined by Teece, Pisano, and Shuen (1997) in Won (2010 p6) as “the firm's ability to integrate, build, and reconfigure internal and external competencies to address rapidly changing environments ”.
Benefits of RBV
- RBV and Innovation
Powell (2001); Priem and Butler (2001) and Rouse and Daellenbach (2002) cited in Karthikeyan, Bhagat and Kannan (2011) report that RBV theory hinges around the concept of outsourcing a firm's non-core functions. Firm resources and capabilities are the determinants of a firm's capacity for innovation (Kostopoulos, Spanos & Pratacos, 2012). Sensing and responding capabilities refer to the firm's ability to quickly anticipate trends in the business environment and come up with the corresponding ideal changes using the available resources (Kostopoulos, Spanos & Pratacos, 2012).
D which results in appropriate innovation. explained by Teece et al. 1997) cited in Kostopoulos, Spanos and Pratacos (2012), as the firm's ability to integrate, build and reconfigure internal and external competencies to address rapidly changing business environment.
Public Sector Management and RBV
Selzinick (1957) believed that an organization should identify, invest and protect its special competencies. In a study by Massukado-Nakatani and Teixeira (2009) entitled “The resource-based view as a perspective for public tourism management research: Evidence from two Brazilian tourism destinations”, showed that resource ownership is key to the success of public tourism. in Brazil. They found that investing in tourism infrastructure and training people working in tourism is an important factor for the success of public tourism.
Critique of Resource Based View Theory
No single paper or collection of related papers measures the benefits defined by RBV theory; adjust resource costs; provides evidence that resources meet RBV criteria;. Bowman and Toms (2008) point out that according to Miller and Shamisie (1996) and Makadok and Coff (2002); RBV theory cannot be fully explained without talking about value theory. While the RBV theory recognizes the presence of resource heterogeneity that is unique among firms, it does not provide a model of the firm that has resources that fit the VRIN model (Bowman and Toms, 2008).
Toms (2010) reported that the elements of value and accountability are the two missing elements in RBV theory.
Chapter Conclusion
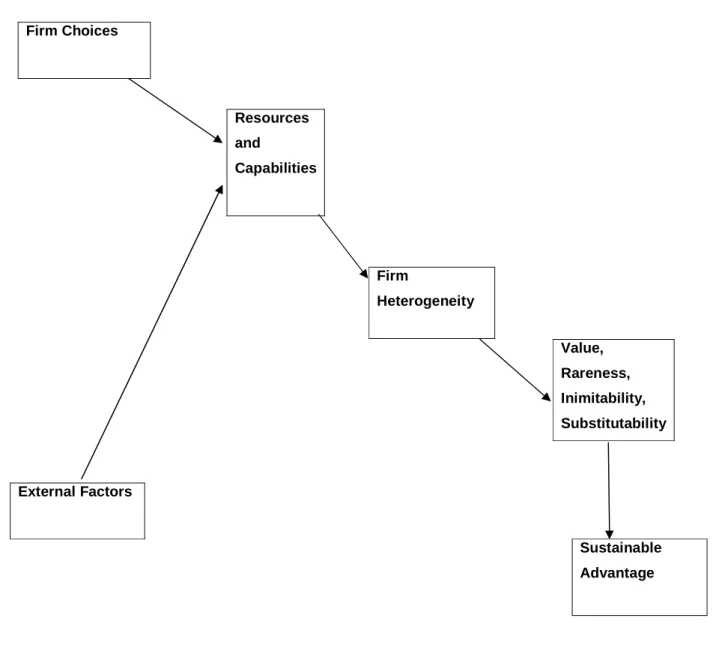
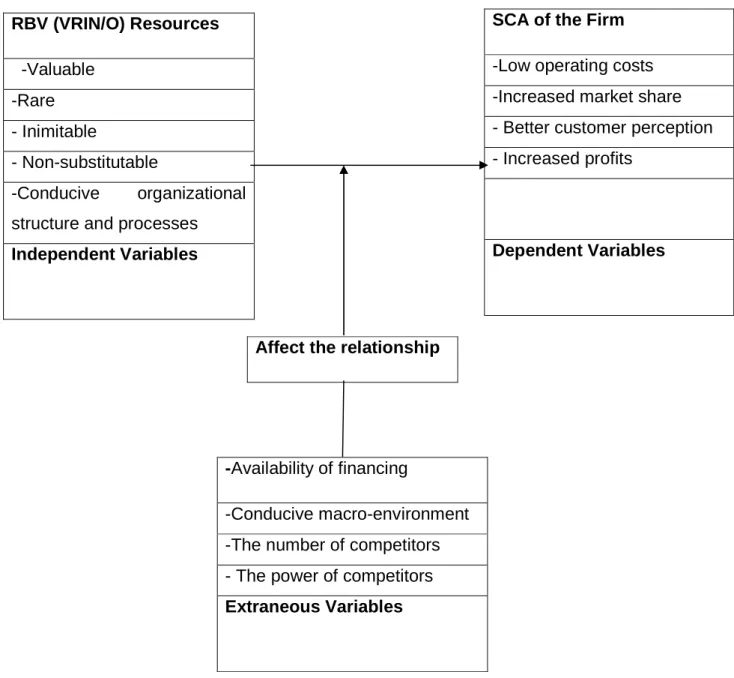
Therefore, a study to evaluate the use of RBV theory in the public sector in Zimbabwe concentrating on ZINWA as a case and basing the research on the conceptual framework explained below and the methodology in Chapter 3 is necessary. The conceptual framework discussed below shows how the researcher will evaluate the use of the RBV theory in the public sector in Zimbabwe using ZINWA as a case study. The conceptual framework helps in the illustration of the research study using the independent variables, dependent variables and the exogenous factors that influence this interaction.
Company SCA - Low operating costs - Higher market share - Better customer perception - Higher profit.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- Introduction
- Research Design
- Research Philosophy
- Quantitative versus Qualitative Research Philosophy
- Rationale for Qualitative Philosophy
- Research Strategy
- Design of Case Study Strategy
- ZINWA as a Typical Single Case
- Data Collection and Analysis
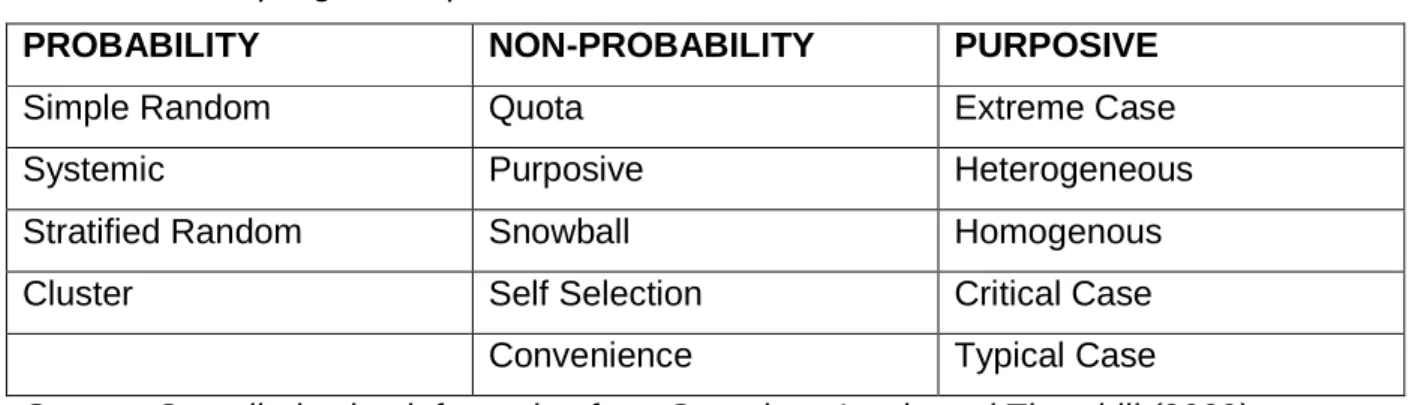
- Data Sampling
The researcher could also gain a detailed understanding of the application of the RBV theory in the case at hand from. Action research - the researcher is an integral part of the population within which the research takes place. A third reason for using a single case study is the typical or representative population being studied.
Differences between groups can be difficult to analyze due to the qualitative nature of the data.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Introduction
Key Respondents: Category 1
- Demographics
- General Issues
- Objective One: ZINWA Resources
- Objective Two: ZINWA Resources and VRIN Model
- Objective Three: ZINWA Core Competencies
- Objective Four: Use of ZINWA Resources and Core Competencies
Limited financial resources emerged as the major challenge hampering the full implementation of ZINWA's strategic plan. Thus, it is clear that human capital and water infrastructure were ZINWA's resources which were scarce. It is clear from the results above that human capital and water infrastructure were ZINWA's resources that follow the VRIN model, which would provide sustained competitive advantage.
What huddles have you experienced in using your resources and core competencies to increase ZINWA's profitability.
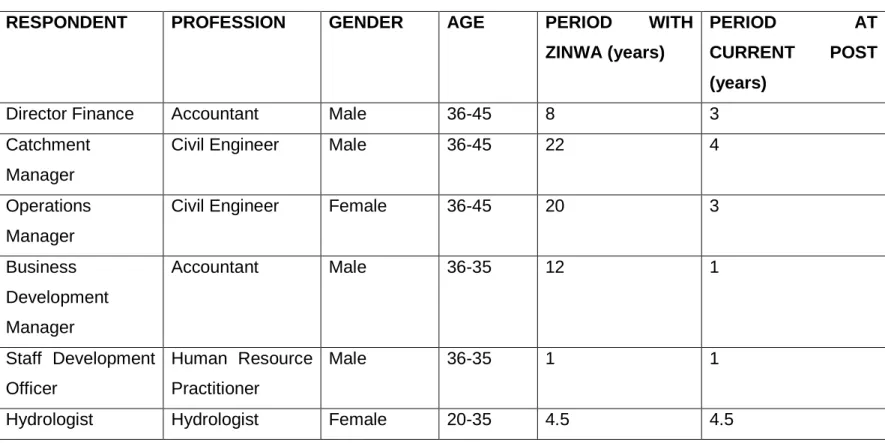
Key Respondents: Category 2
- ZINWA’s Business Strategy
- ZINWA’s Resources
- ZINWA’s Core Competencies
- ZINWA’s Resources and Core Competencies Use for Survival
Moreover, the organogram as discussed in the Sections above could not provide for the proper implementation of the business strategy. Resource management is "the comprehensive process of structuring the firm's resource portfolio, bundling the resource to create capabilities and utilizing these capabilities with the goal of creating value for customers and owners" (Sirmon, Hitt & Ireland, 2007, p273) . It was reported that the existing organogram does not allow the full implementation of the stated business strategies.
It was also reported that the development of irrigation systems to ensure the supply of water to the farmer's peripheral field was a new project that could be undertaken to take advantage of the water and irrigation development capabilities available to ZINWA.
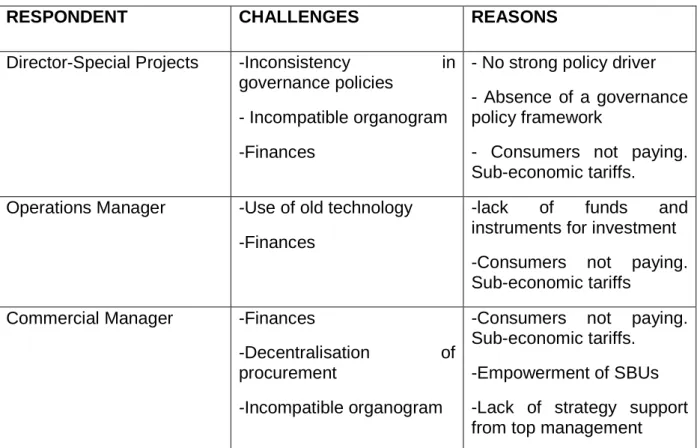
Summary of Findings
Human capital and water supply infrastructure therefore follow the VRIN model of RBV theory proposed by Barney (1991). Bottled water could be made using groundwater from boreholes, water kiosks, hydroelectric power stations, and the development of irrigation systems right up to the edge of the farmers. These are some of the projects that can be implemented to leverage ZINWA's resources and core competencies. The research is largely consistent with the statement as there was very limited application of the company's RBV theory at ZINWA due to limited support from top management to leverage their resources and core competencies.
Although the current business strategies were designed to make use of the resources and core competencies of ZINWA, it is not clear whether they were really based on the RBV theory.
Conclusion
The study also found that the resources and core competencies of ZINWA can be used to generate new businesses in the form of fishing, boating and lodges at various dams. The results also showed various projects such as irrigation development, hydropower generation, fisheries, boating and water bottling that could be undertaken by ZINWA using its resources and core competencies to improve its profitability. The following Chapter 5 focuses on the conclusions of the study, limitations and challenges faced by the study, recommendations and areas for further research.
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
- Introduction
- Conclusions
- Objective One: To establish the resources that are owned by ZINWA
- Objective Two: To determine if resources possessed by ZINWA are valuable,
- Objective Three: To establish the core competences of ZINWA
- Objective Four: To find out if ZINWA has been using its resources and core
- Test of the Research Proposition
- Recommendations
- Strategic Management
- Valuation of ZINWA Resources
- Use of VRIN Resources and Core Competencies (Capabilities)
- Study Limitations and Areas for Further Research
Thus the situation at ZINWA did not follow the VRIO model a modification of the VRIN model which is key to the application of the RBV theory of the firm. Some of the respondents could not provide attitudes about the organizational chart that were responsible for ZINWA's poor performance. Accounting for competitive advantage: The resource-based view of the firm and the labor theory of value.
Empirical research on resource-based view of the firm: An assessment and suggestions for future research.
AN ASSESSMENT OF THE APPLICATION OF THE RESOURCE VIEW (RBV) THEORY IN THE ZIMBABWE PUBLIC SECTOR: THE CASE OF ZINWA. This study is being conducted by Graham Mugati, a student at the University of Zimbabwe who is partially fulfilling the requirements for a Masters in Business Administration. What are the substitutes for the mentioned funds and what are the substitutes for?
What challenges have you encountered in using your resources and core competencies to increase ZINWA's profitability?