해양잔사유로부터 연료첨가제의 반응 메커니즘 연구 본 연구에서 살펴본 결과를 종합하여 해양유용 연료첨가제의 메커니즘을 부분적으로 규명할 수 있었다.
Marine fuel
The effects of fuel additives on emissions and engine efficiency were investigated using an on-road engine (Valentine J. et al., 2000). Unlike the fields of automobiles, boilers and bioenergy, the research or study of additives in heavy fuel has been very limited in the marine sector (Joanna G. et al., 2013).
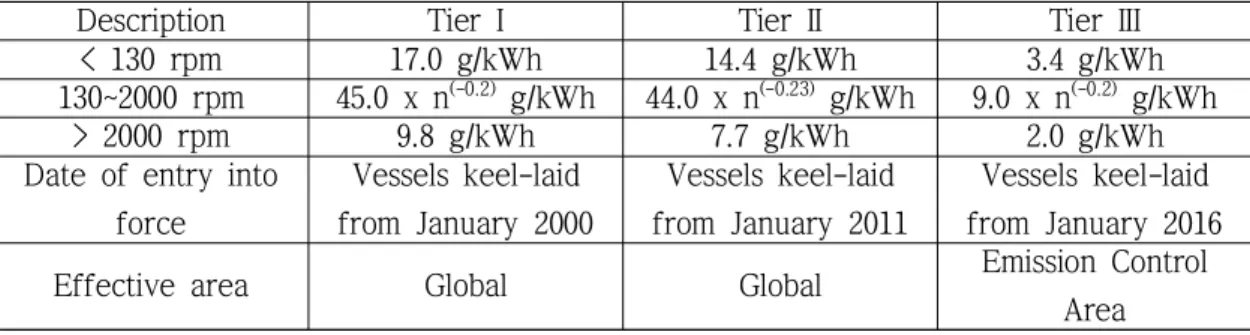
Basic properties of marine residual fuel oil
- Viscosity
- Density
- Flash point
- Pour point
- Sulfur
- Carbon residue
- Water
- Ash
- Vanadium, magnesium and sodium
- Aluminium and silicon
The pour point indicates the lowest temperature at which the fuel should be pumped and stored. Catalytic fines cause abrasive wear of moving parts, so the catfin content should be minimized by centrifuging the fuel oil before it is used in the engine.
Additives
History of additives
Increasing use of diesel additives means increasing demand for diesel fuel and changing diesel engine technology. Additive packages in the 1980s reflected the growth of the diesel fuel market and, in particular, the greater needs and expectations of passenger car users.
Information and technical achievements of diesel additives
Kim, "Fuel Properties and Exhaust Emission Characteristics by Type of Oxygenated Fuel Additives," Proceedings of the Korean Society of Automotive Engineers, pp. Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers, p.
Understanding additives and review of relevant literatures
Chemistry of combustion
Lawrence, “Reduction of nitrogen oxides NO and N2O to molecular nitrogen in the presence of iron, its oxides and carbon monoxide in a hot fluidized bed”, Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, Vol.41, No.9, pp. Choi, “Effect of EGR and Fuel Additive on Diesel Emissions,” Proceedings of the Korean Society of Automotive Engineers 1998, Spring, p.
Additive effects on ignition delay
Additive effects on emissions
- Reduction of NO to N 2 by reaction with particles of Fe
- Additive effects to the emission reduction
- Effects of an ignition-enhancing, diesel-fuel additive on
The primary effect of the 2-ethylhexyl nitrate additive is to accelerate the formation of the pre-ignition radical pool and thus shorten the auto-ignition period. The effects of 2-ethylhexyl nitrate are more significant at low temperature and low density conditions than the cetane number indicates. The flame lift results indicate that the primary effect of the additive is through the initial autoignition chemistry.
The results show that the primary effect of the additive is to increase radical formation very early in the autoignition period, leading to a shorter overall autoignition period for the diesel spray.
Experimental setup and analyzers
- Fuel dispersability analysis
- Fuel Ignition/Combustion Analysis (FIA/FCA)
- Thermo Gravimetirc Analysis
- Engine and auxiliary system
- Low engine load test setup
- Full engine load test setup
Sample C was the most effective in improving the ignition and combustion characteristics of the fuel oil. Fig.4-16 Comparison of specific fuel oil consumption at low engine load with different fuel oil additives. Cohen, "The Application of PIXE to the Mapping of Contaminants Deposited on a Monolithic Automotive Catalytic Converter", Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, Vol.109, pp.
Scott, “Use of a constant volume combustor analyzer to predict the derived cetane number of aviation turbine fuels”, 11th International Conference on Stability, Handling and Use of Liquid Fuels, 2009.
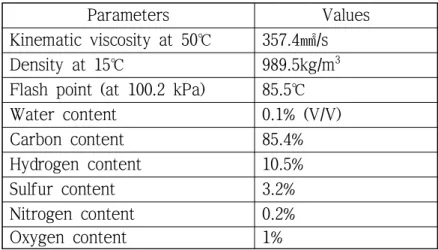
Results and Discussion
Investigation of fuel dispersant mechanism
- Basic properties
- Dispersants
- Deposit control by dispersants
- Dispersant structure
Fig. 4-2 shows surface characteristics of solid particles such as fuel molecule, pigment, extender, etc. against flocculation tendencies (www.afcona.com.my/DispersingTechnology.pdf). As shown in Fig.4-3, the best separation distance between two particles is at best at the critical distance or even better where the combination of both forces is zero (www.afcona.com.my/DispersingTechnology.pdf). Fig.4-7 Fuel surface adsorption of low molecular weight dispersant (Mw) Low molecular weight dispersant cannot effectively respond to steric hindrance in the range of 800~2,000 g/mol, but it is able to create synergy when cooperating with dispersant with high molecular weight.
A dispersant molecule consists of three distinct structural features: a hydrocarbon group, a polar group, and a linking group or bond as shown in Fig.4-10 below.
Fuel oil combustion characteristics by FIA/FCA
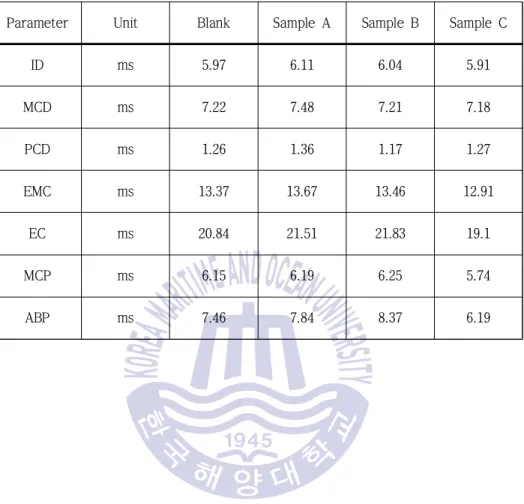
-11 Comparison of pressure trace analysis parameters obtained via FIA/FCA Different combustion characteristics were found from the FCA. Based on the IP541/06 analysis, sample C shows superior combustion enhancing properties. 2007) studied the combustion properties using simple analyzers. It also means that only FIA/FCA verified combustion properties can be generated under CVCC conditions.
This study investigates a simple method to evaluate combustion characteristics during the entire combustion period centered around P.ROHR.
Thermogravimetric analysis
Fig.4-14 TGA analysis of fuel mass reduction with respect to temperature Fig.4-14 indicates arc-shaped loss in mass from the beginning up to 500℃. On the other hand, Blank maintains an arcuate mass loss from the beginning to the end of the analysis, i.e. up to 900 ℃. Fig. 4-15 TGA Analysis of Fuel Mass Conservation Ratio vs. Temperature Similarly, as observed in Fig. 4-14, the mass conservation ratio of samples A, B, C decreases to 10% up to 500℃ with a curved shape.
If the effects of the iron-based fuel additives were to be discussed based on the results of Fig.4-14 and Fig.4-15, it can be said that regardless of the different kinds of additives, there is still a positive and clear effect on the faster reduction of fuel mass compared to the empty fuel oil.
Fuel oil consumption
- Fuel oil consumption at low engine load
- Fuel oil consumption at fuel engine load
The reference fuel oil is fuel oil without additives and has the highest fuel consumption. Fig.4-20 shows that water can increase with higher engine load and it should also be noted that the gap creates higher water than other additives. According to the investigations of the previous chapters, the empty sample consumed much more diesel and could be emitted as an increased part of PM in the exhaust with the help of SO2, water and unburned hydrocarbons.
Figure 4-17 Comparison of specific fuel oil consumption at full engine load with different fuel oil additives.
Investigation of fuel combustion improver effect to engine
An understanding of the characteristics of the alkali metal 1A is necessary for the 2A series, which is the subject of the study. An alkali metal has a low density and melting point, and these tendencies become regular as the atomic number increases. These properties mean that an alkali metal has good reactivity and easily loses an electron to become an ion containing a 1+ charge.
Series 2A is called an alkaline earth metal and is stronger, higher density, and higher melting point than alkali metal.
Emission characteristics
- Emission characteristics at low engine load
- Emission characteristics at full engine load
If the interaction were reflected in this study, NOx emissions should be higher for sample B and sample C. Figure 4-27 shows the emission characteristics of PM, which normally decrease as engine speed increases, except in the blank sample during the test. In other cases, the PM emission for the blank fuel oil increased as the engine speed increased.
Blank fuel emitted the minimum NOx among sample fuels and the NOx emission increases as engine load increases.
Optical analysis
- Raman spectroscopy
- Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy
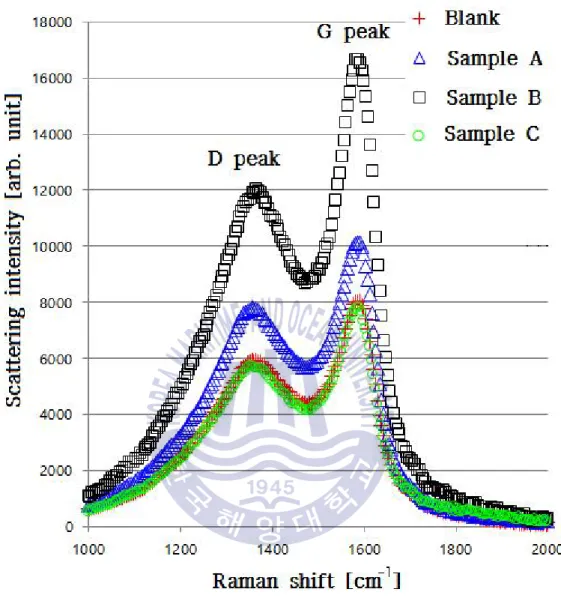
Different peak locations and peak shapes from raman spectroscopy can help find small changes in material. In this study, particles at the end of the exhaust pipe were sampled and analyzed using Raman spectroscopy. Similar to Figure 4-32, sample B has fine particles that are well dispersed over the surface.
Because, sample A shows low fraction of carbon black and blank, sample B and C show graphite in Raman analysis.
Conclusions
Dispersant mechanism
The dispersion mechanism consists of three basic properties and the mechanism is cited from other research. Wetting means a compound added to a liquid in small amounts to promote the spreading of the liquid on a surface or the penetration of the liquid into the solid particles in the liquid and/and the solid substrate in contact with the liquid to improve. the liquid.
Fuel oil combustion characteristics by FIA/FCA
The maximum heat release rate was 0.216 MPa/ms in sample C, and the position of maximum heat release rate was 8.16 ms, which is the fastest position among the samples. But this expectation is based solely on the test at CVCC, and the result may be different if the fuel combustion takes place inside a real piston engine. The trend of these values implies that M.ROHR can be varied with different fuel oils, and P.ROHR, which is the index of burning rate, can also be varied accordingly.
This simple method is derived from the concept that the ROHR and the position of ROHR should be considered simultaneously.
Thermogravimetric Analysis
Fuel oil consumption evaluation
- Fuel oil consumption at low engine load
- Fuel oil consumption at full engine load
Samples C and A had a break point at 750rpm, above which more or less fuel was consumed. Samples B and A recorded the lowest SFOC, but sample B recorded more higher SFOC at 25% engine load.
Investigation of fuel combustion improver effect to engine
Oxidation of Fe can result in fuel with oxygen content capable of leading to fuel lean combustion and will also help to get closer to complete combustion. The afterburning can be described as ash, unburnt metal and carbon contained in the exhaust gas. When the exhaust gas has sufficient heat energy to overcome the activation energy, the remaining metal can carry out further catalyst reaction.
But after exhaust gas has lost heat energy, the metal can be stuck on the surface of carbon or ash and water.
Emission characteristics
- Emission characteristics at low engine load
- Emission characteristics at full engine load
Costa, “Simultaneous Reduction of NOx and Particulate Emissions from Heavy Fuel Oil Furnaces,” Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, Vol.29, No. 2, pp. Chemical Properties with Refining Treatment and Additive Mixture for Marine Fuel Oil”, Journal of the Korean Society of Marine Environment & Safety, Vol.13, No.1, pp. Rajasekhar, “Investigation of particulate emission characteristics of a diesel engine powered by higher alcohol/biodiesel blends”, Applied Energy, Vol.163, pp.
McNesby, "Additive Influence on the Formation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons", Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, Vol.29, p.
Optical analysis
- Raman spectroscopy
- Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy