In this study, a series of chalcones and their Mannich base derivatives were synthesized and their antioxidant activity was evaluated. The results showed that the chalcone-derived Mannich bases exhibited better antioxidant activity than their corresponding chalcone parent compounds. A final year project report entitled “SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF CALCONE DERIVATIVES AND THEIR ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY” was prepared by CHANG LING YING and submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Bachelor of Chemistry (Hons) at Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman.
It is hereby acknowledged that CHANG LING YING (ID No: 19ADB01683) has completed this final year project report entitled "SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF CHALCONE DERIVATIVES AND THEIR ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY" under the supervision of ge.
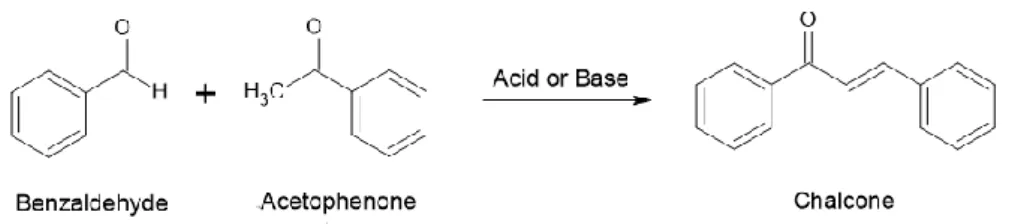
Chalcone
In basic catalysis, the chalcone is formed from the aldol product via the dehydration of the enolate mechanism. Common base reagents used include NaOH, KOH, and NaH, while Bronsted acids and Lewis acids such as HCl and BF3-Et2O have been used in the acid-catalyzed Claisen-Schmidt condensation. The base-catalyzed Claisen-Schmidt condensation reaction begins with removal of the proton of alpha acetophenone by a strong base, yielding a resonance-stabilized enolate ion.
Finally, dehydration of the aldol compound occurs spontaneously, giving an α, β conjugated unsaturated ketone, which is also known as a chalcone (Susanti and Setyowati, 2019).
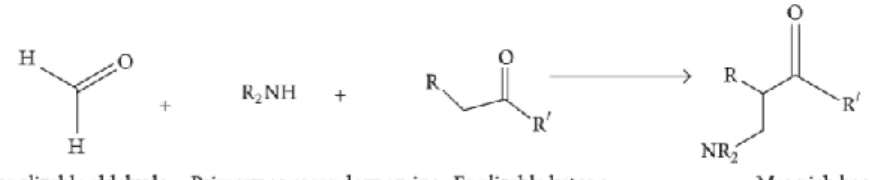
Mannich Base
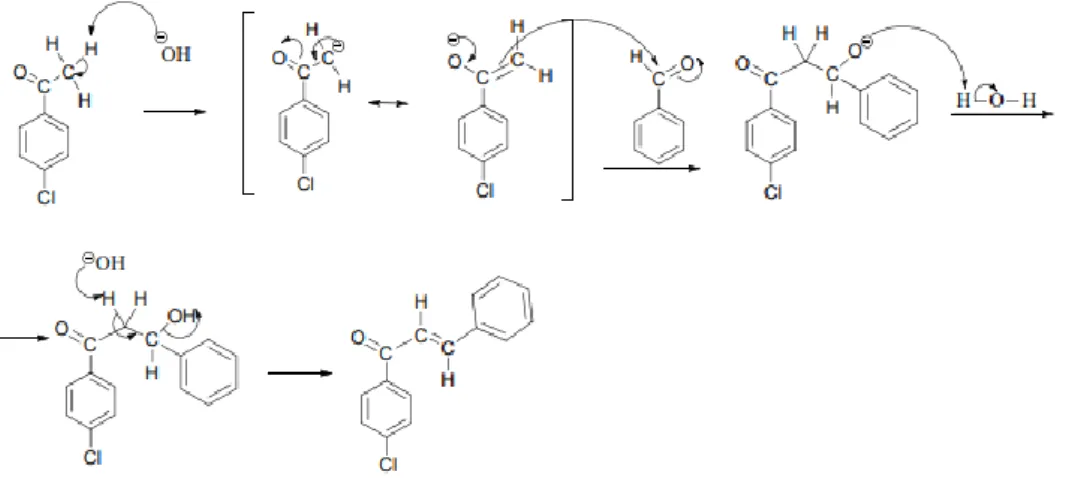
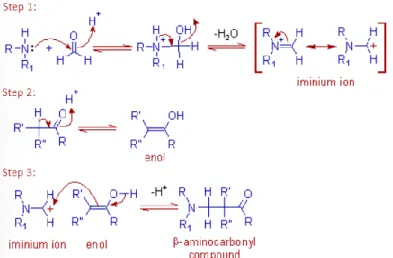
3 initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon belonging to benzaldehyde, leading to the formation of an alkoxide ion with an excess electronic charge on the oxygen atom. The Mannich reaction is initiated by the formation of an iminium ion by the nucleophilic addition of an amine to formaldehyde, which also results in the loss of a water molecule. The enolizable ketone is then converted to the enol form, and the enol then attacks the iminium ion on the positively charged carbon adjacent to the nitrogen atom.
5 The chalcone-derived Mannich bases also exhibit many useful medicinal properties, such as antimicrobial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-malarial, anti-HIV, anti-Alzheimer's, anthelmintic, analgesic, and so on (Marinescu, et al. , 2020).
Antioxidant Activity of Phenolic Compounds
6, on the other hand, is influenced by multiple factors, including their molecular structures, especially the number and position of the hydroxyl group present in the structure, and the nature of substituents on the aromatic rings (Minatel, et al., 2017). Chalcones, which consist of two phenyl rings in their general structure, are polyphenols when attached to one or more hydroxyl groups. In addition, the antioxidant properties of chalcones are also hypothesized to be contributed by the conjugated α-,β-unsaturated bond and the delocalized π-electrons across the aromatic rings.
It has been reported that chalcones with hydroxyl groups substituted at ortho or para positions show particularly high antioxidant activity compared to that of meta position due to the enhanced stability of the semiquinone radicals they form.
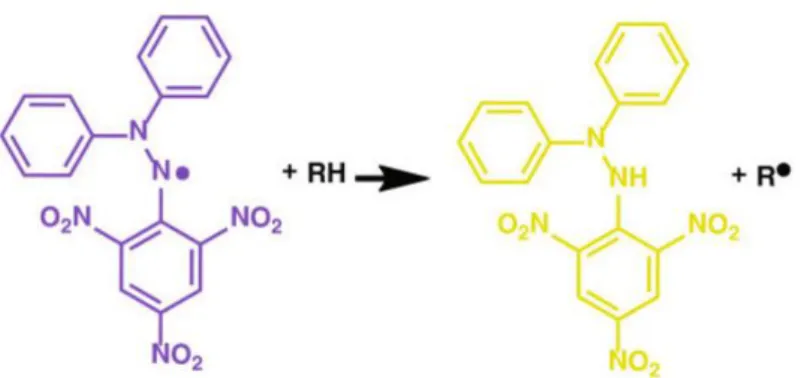
DPPH Radical Scavenging Capacity Assay
7, an antioxidant or reducing agent can provide an additional electron or hydrogen to the DPPH free radical. The radical scavenging capacity of a compound can be evaluated by determining the IC50 (half maximal inhibitory concentration) value of the compound, which is the concentration of the sample required to inhibit 50% of the DPPH free radical. A lower IC50 value means that a lower concentration is required to reduce the DPPH radical by 50% and thus a higher antioxidant capacity of the compound.
This project studies the antioxidant activity of various chalcones and their derivatives and how the antioxidant activity is affected by the substituents on the chalcones.
Objectives
In particular, they can act as antioxidants that help in the treatment of various diseases such as cancer, heart disease and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
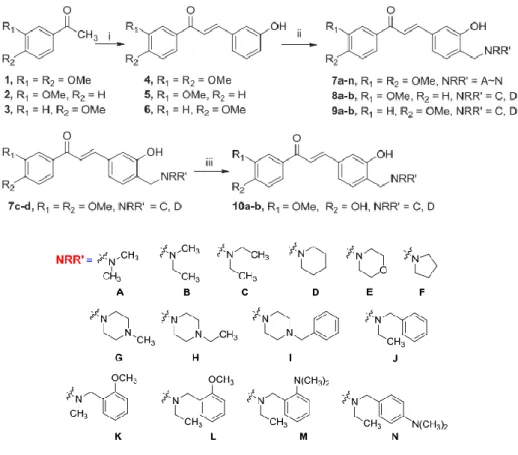
Synthesis of Chalcone Derivatives
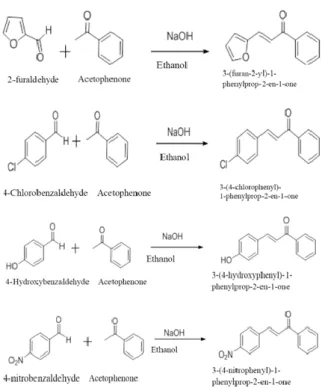
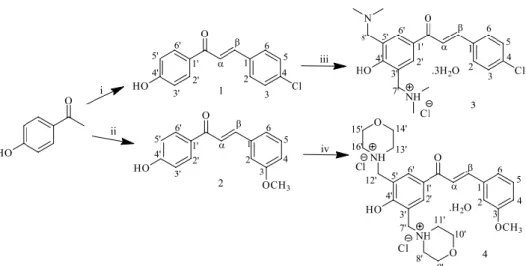
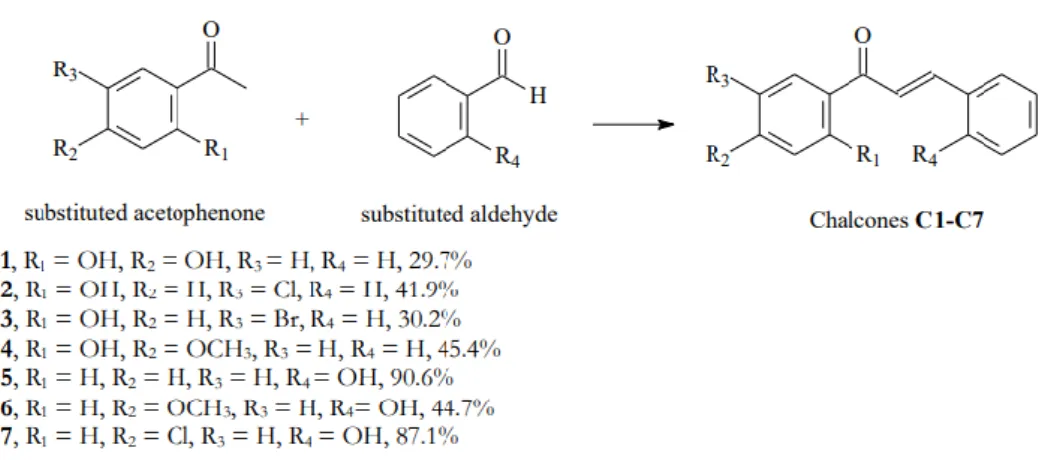
They have synthesized three 2-hydroxychalcone derivatives, namely -3-(4'-methyphenyl)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, 3-(4'-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2) -hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one and 3-(2'-chlorophenyl)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, through the base-catalyzed Claisen-Schmidt condensation of 2 - hydroxyacetophenone with 4'-methyl-, 4'-methoxyl- and 2'-chlorobenzaldehyde, respectively. 50% NaOH was used as base catalyst and absolute ethanol was used as solvent in this study. Eight chalcones, as listed in Table 2.1, were synthesized through the Claisen–Schmidt condensation of 2'-hydroxyacetophenone and various benzaldehyde derivatives in ethanol using 40% NaOH as catalyst.
The reaction mixture was stirred at below 10℃ for one hour before being allowed to stir overnight for the reaction to occur.
Synthesis of Chalcone Derived Mannich Bases
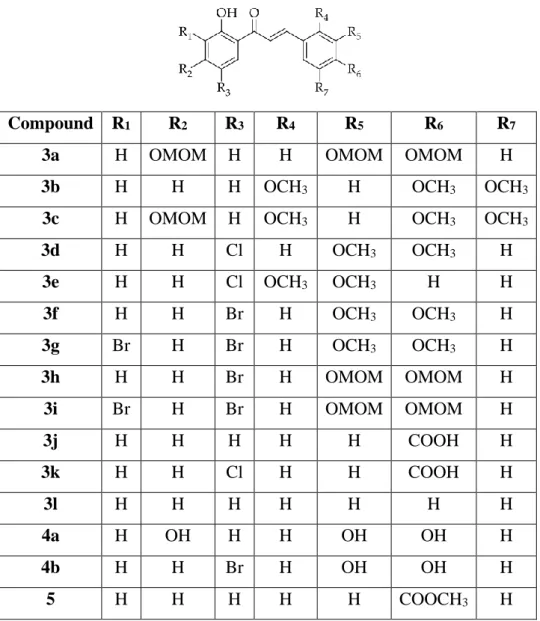
14 2.3 Antioxidant Activity of the Chalcone and Mannich Base Derivatives In the study conducted by Kostopoulou, et al. 2021), the antioxidant activity of a series of 2'-hydroxychalcone derivatives, as listed in Table 2.2, was studied. All studied compounds possessed a phenolic hydroxyl group (OH) that could contribute to the antioxidant activity of the compounds. On the other hand, the antioxidant activity of the chalcones 4a and 4b was greatly enhanced by other OH groups and the Br group in 4b substituted at different positions of the compounds.
The antioxidant activity of various substituted chalcones has also been studied by Rashdan, et al.
Materials
Instrumentation
Synthesis of Chalcones
To synthesize CA, equimolar portions of 4′-hydroxyacetophenone (20 mmol) and 4-chlorobenzaldehyde (20 mmol) were first dissolved in 6 mL of ethanol. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 24 h, until completion of the reaction was indicated by TLC. After the completion of the reaction, 50 mL of cold distilled water was added to the mixture solution, followed by the dropwise addition of 10% w/v HCl with continuous stirring.
The product was dissolved in hot absolute ethanol and then allowed to cool to room temperature for recrystallization process to take place.
Synthesis of Chalcone Mannich Base Derivatives
When the completion of the reaction was indicated by TLC, the reaction was stopped and the mixture was subjected to rotary evaporation to remove all the solvent. The mixture solution was then poured into a test vial and allowed to dry under air. The mass of the formed Mannich base derivative was measured and recorded after it was completely dry, and the percentage yield was calculated.
Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) Analysis
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
- Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectroscopy (LCMS)
- Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
To prepare the sample for NMR analysis, 15 mg of the solid product was dissolved in a small amount of the appropriate solvent in a sample vial. The sample for LCMS analysis was prepared by dissolving 1 mg of the solid product in 1 mL of HPLC grade methanol to create a concentration of 1000 ppm. Then, 200 μL of sample (in duplicate), positive control and blank (methanol) were introduced into the first row of the plate.
Serial dilutions were performed by transferring 100 μL of solution from the first row to the second row, then the second row to the third row, and so on.
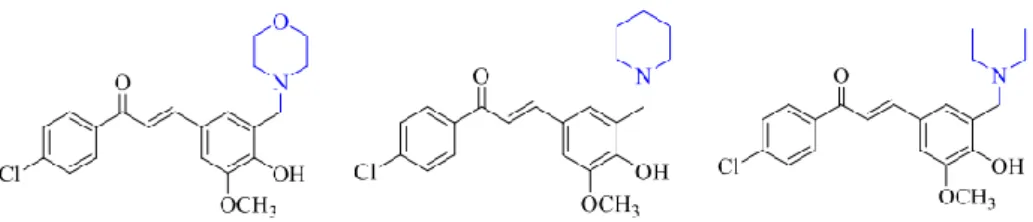
Molecular Structure of Compounds
Physical Properties of Compounds
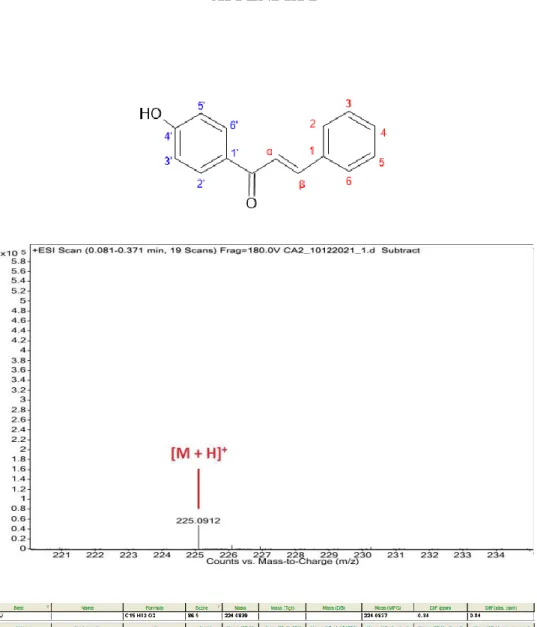
Structural Elucidation of 4-Chloro-4’-hydroxychalcone
A pair of doublet peaks observed at 7.87 and 7.61 ppm were attributed to the protons of the unsaturated double bond, Hβ and Hα, respectively. The doublets of the aromatic protons H2' and H6' appeared in the downfield region as they were shielded by the electronegative oxygen atom of the carbonyl group. In the HMBC spectrum of CA (Figure 4.15), one of the characteristic correlations observed was between the carbonyl carbon with Hα, Hβ, H2' and H6', indicating the correlations between the α,β-unsaturated carbonyl system and ring A.
The NMR spectral data of the compound CA are listed in Table 4.6 and 4.7, which were consistent with the literature values reported by Anwar, et al. The protons of the amine substituent occurred in the upfield region, whereby the single peak was attributed to H7'. The compound 4'-hydroxy-3'-dimethylaminomethylchalcone (DA2) showed similar spectral properties to DA as they possess identical structural backbones with only difference of the substituent at position 4 of ring B.
The compound 4'-hydroxy-3'-pyrrolidinomethylchalcone (PY2) exhibited similar spectral properties to PY as they possess identical structural skeletons with only the difference in the substituent at position 4 of ring B. Proton peaks attributed to the amine substituent include the singlet at 3.75 ppm, which was assigned to H7', triplets at 1.98 ppm corresponded to H9' and H13', triplets at 1.24 ppm which represented H10' and H12' and multiplets at 1.66 ppm which were assigned to H11'. The compound 4'-hydroxy-3'-piperidinomethylchalcone (PI2) showed similar spectral properties to PI as they possess identical structural backbones with only the difference in the substituent at position 4 of ring B.
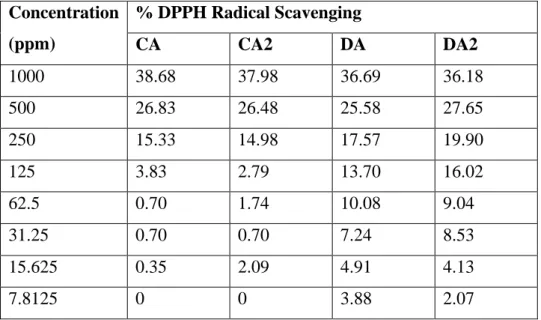
83 A plot of percent DPPH radical scavenging versus compound concentration, as shown in Figure 4.31, is plotted to obtain the IC50. At the lowest concentration, both chalcone derivatives showed zero antioxidant activity, while all Mannich base derivatives showed antioxidant activity despite low DPPH radical scavenging rates. Moreover, the results had also revealed that the chloro-substituent at the 4-position of the B-ring had improved the antioxidant activity of the compounds.
This indicates that the antioxidant activity of the chalcone and Mannich base derivatives is relatively much weaker than ascorbic acid.
Conclusion
88 In addition, the antioxidant activity of the synthesized compounds was also investigated using the DPPH antioxidant assay test. Nevertheless, remarkable antioxidant activity was shown only by the Mannich bases substituted with pyrrolidine (PY and PY2). The IC50 values of compound PY and PY2 were recorded at 550 and 700 ppm, respectively.
This indicates that the antioxidant activity of chalcone derivatives can be improved through structure modification.
Further Studies
Synthesis of chalcone derivatives and their in vitro anticancer assay against breast (T47D) and colon (WiDr) cancer cell line. Study of reactions of two Mannich bases derived from 4'- hydroxychalcones with glutathione by RP-TLC, RP-HPLC and RP-HPLC- ESI-MS analysis. Synthesis, characterization and biological studies of chalcone derivatives containing Schiff bases: Synthetic derivatives for the treatment of epilepsy and Alzheimer's disease.
Exploring the 2'-hydroxy-chalcone framework for the development of dual antioxidant and soybean lipoxygenase inhibitory agents. Synthesis, density functional theory study and in vitro antimicrobial evaluation of new benzimidazole Mannich bases. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of Mannich bases of heterocyclic chalcone analogues as cytotoxic agents.
Study of interaction of 4'-hydroxychalcones and their Mannich derivatives with calf thymus DNA by TLC and spectroscopic methods, study of DNA cleavage. Design, synthesis and evaluation of chalcone Mannich base derivatives as multifunctional agents for potential treatment of Alzheimer's disease.