I declare that this report entitled “PRONUNCIATION MODELING OF PENANG HOKKIEN DIALECT FOR TEXT-TO-WORD SYSTEM” is my own work, except as mentioned in the references. This is an academic research about Penang Hokkien pronunciation modeling for Text-to-Speech System which is under the field of study, Speech Synthesis. The Penang Hokkien language, an unwritten language spoken in the north of the southern peninsula of Malaysia is selected as the case study of this research where its linguistic sources are partially documented.
As this project is part of the efforts to revive the Penang Hokkien language, the traditional Chinese character has been chosen as the standard for the writing system and the Penang Hokkien spelling system created by the Hokkien Association of Penang has been selected as the standard for the spelling of the pronunciation. A list of phonemes with categorization of them into initials and finals is taken as Penang Hokkien is a tonal language. In addition, nine tones are marked with the use of diacritics based on the Penang Hokkien spelling system under tone marking rules.
LIST OF TABLES
Introduction
- Introduction
- Problem Statement
- Motivation
- Research Objectives
- Research Background
- Speech Synthesis Techniques
- Min Languages Origin
- Penang Hokkien Language
- Penang Hokkien Facing Extinction
- Project Scope
- Contributions
- Report Organization
In this research, a potential unwritten language in Malaysia, Penang Hokkien is taken as a case study for this research. Therefore, this research will standardize the spelling and pronunciation of Penang Hokkien by gathering sources from above. Timothy Tye suggests a fully Romanized grapheme-like writing system for Penang Hokkien, which is called the Taiji System [11].
The title of this project is Pronunciation Modeling of Penang Hokkien Dialect for Text-To-Speech System. The project will collect a large amount of lexical resources of the Penang Hokkien language, including: 1. The rest of the collected resources will be needed for future research on the Penang Hokkien TTS system.
This research is more relevant to the revitalization efforts of the Penang Hokkien language. With this project acting as a first step to contribute to the efforts to develop a synthetic Penang Hokkien system within the revitalization of the Penang Hokkien language.
Literature Reviews
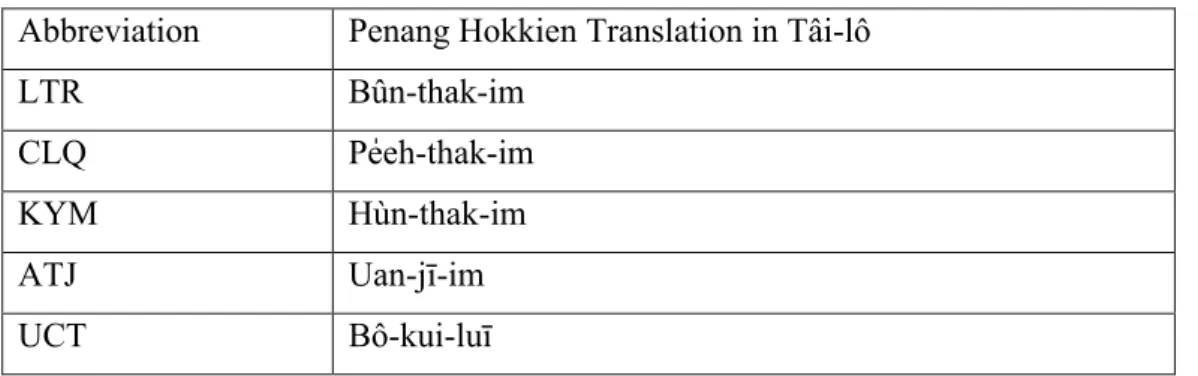
- Penang Hokkien Language Writing and Pronunciation System .1 Traditional Chinese Characters with 9 Tones
- Taiji System with 4 Tones
- Comparison of Both Systems
- Non-Similar Language Corpus Construction Review .1 Cantonese Corpora Construction
- Czech Corpora Construction
- Similar Language Corpus Construction Review .1 Singapore Hokkien Corpus Construction
- Minnan Child Speech Corpus Construction
Therefore, romanization of the text of the language should be avoided in order to preserve the culture of Chinese elements. But the romanization should be used as a transliteration, not as the main writing system of the language. Furthermore, the implementation of tone system of the language increased the accurate tempo of each phrase during the recording process.
The involvement of expertise in the corpora verification processes ensured the quality of the corpora. During the recording phase, the management of the recording session assumed a very important responsibility to control the quality of the recording. In addition, two annotation methods were used during corpora construction to maintain the quality and accuracy of the recordings.
Combining the ASCII phone string symbols with the romanized spelling for each occurrence in the syllable might give better results in romanizing the language. Audio files were transcribed into text files using orthographic transcription and phonetic transcription in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) [26].
System Model
- Research Flow Chart
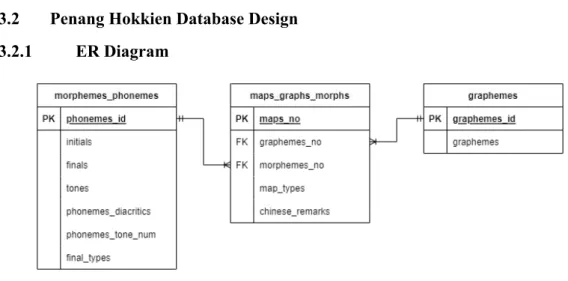
- Penang Hokkien Database Design .1 ER Diagram
- Data Dictionary morphemes_phonemes
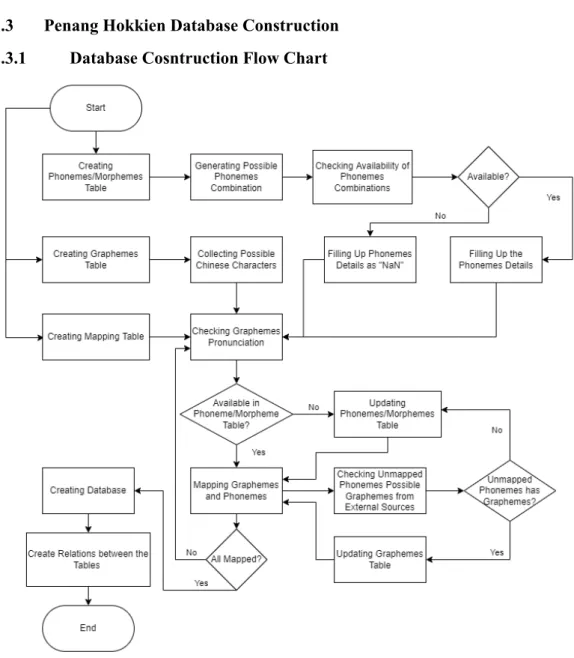
- Penang Hokkien Database Construction .1 Database Cosntruction Flow Chart
- Software and Dictionaries Used
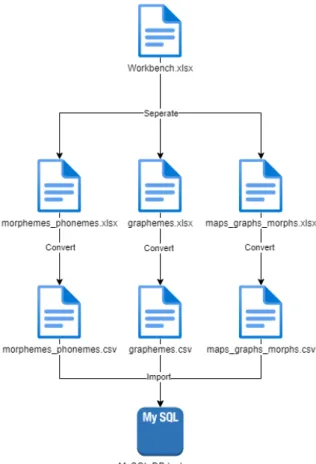
The maps_graphs_morphs is the table that resolves many-to-many relationships between morpheme_phonemes and grapheme tables, and it also serves as the mapping table for both tables. Foreign key "graphemes_no" in maps_graphs_morphs table refers to graphemes_id in graphemes table and morphemes_no table refers to morphemes _id in morphemes table. In Figure 3.3.1-1, the database construction process for this research began by creating several tables that store different types of data.
The first table is the Phonemes/Morphhemes Table, where after this table is created, possible phoneme combinations will be generated. The phoneme details were filled in the table if the phoneme combinations are available, otherwise all the details were filled. From the second table created - Graphemes, literally stores graphemes of Penang Hokkien which are Chinese characters.
After Mapping Table was created, the pronunciations of graphemes from the Graphemes Table were checked manually using dictionaries. If the pronunciations of the graphemes were available in the phoneme/morphement table, the graphemes and phonemes were mapped by filling the necessary information into the mapping table; otherwise the Phonemes/Morphement Table was updated by adding the phonemes that were marked unavailable. During the mapping process, if there were phonemes that were not mapped, the phonemes were checked against dictionaries to investigate the missed graphemes during data collection and were updated in the Graphemes table when the graphemes were available, otherwise the phonemes that were checked has no graphemes have been updated in the phonemes/morphement table with all details filled in.
The mapping processes were stopped until all the graphemes and phonemes were all mapped, then a database was created. The progress of the database construction ended with the created relationships between the 3 tables mentioned in Figure 3.3.1-1.
EXPERIMENT
- Phonemes of Penang Hokkien
- Initials
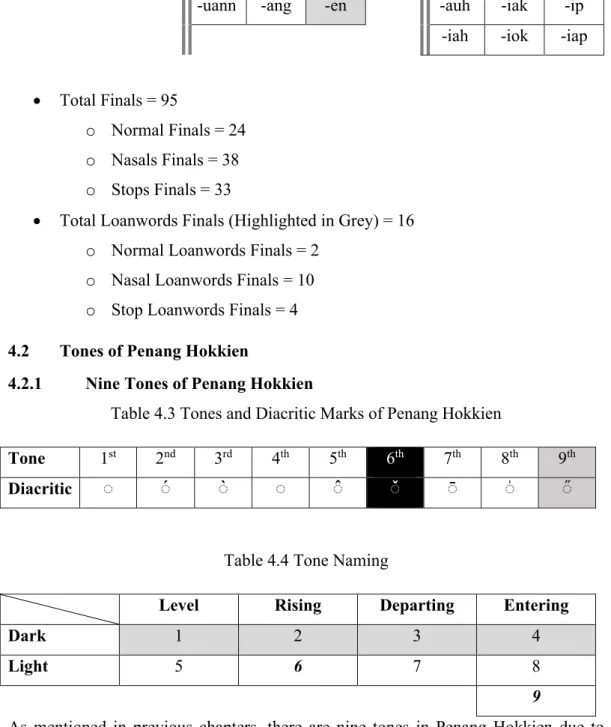
- Nine Tones of Penang Hokkien
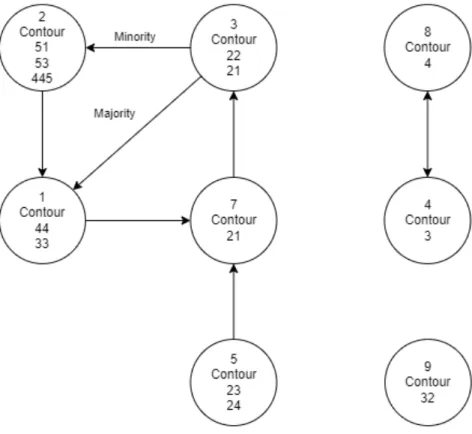
- Tones Letter and Tones Contour
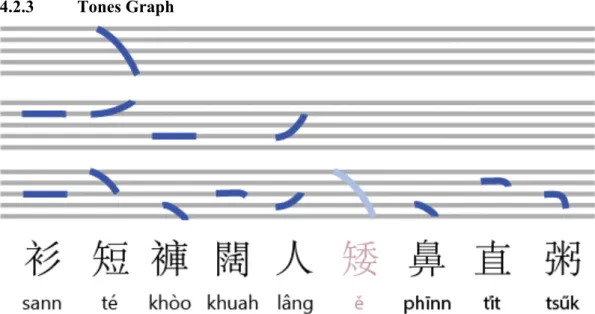
- Tones Graph
- Tones Marking Rules
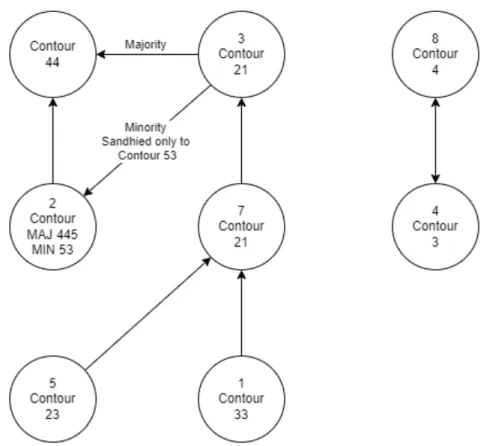
- Tone Sandhi
- Tone Table Creation as Guidelines for Future Research
- Database Construction for Penang Hokkien Morphemes and Phonemes .1 Morphemes_Phonemes Table Creation
- Graphemes Table Creation
- Mapping Table Creation
- Implementation of Tables into the Database
- Database Implementation Issues
- Articles and Sentences Collection .1 Taiwanese Hokkien Articles
- Penang Hokkien Sentences
- Audio Guidelines Collection
- Concluding Remarks
Referring to Figure 4.6, the Online Taiwanese Hokkien Dictionary provides indexing by initials, finals, and tones. Referring to Figure 4.8, the tables should be separated into the different files.
SYSTEM EVALUATION AND DISCUSSION
- Data Refining on Pre-Implementation Database Tables .1 Tables of Pre-refining Process
- Results
- Simple Data Analysis Towards Pre-Implementation Database Tables .1 Morphemes_Phonemes Table
- Mapping Table
- ER Diagram Redesign with Data Dictionaries
- Reimplementation of Tables in Database
- Project Challenges
- Concluding Remarks
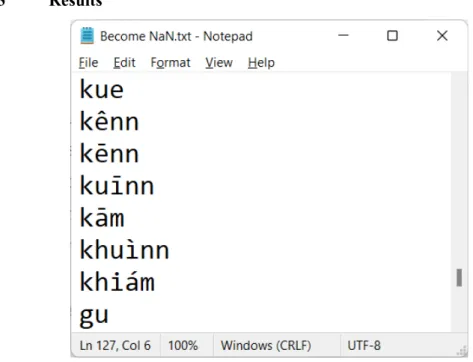
This mapping process tracked missing graphemes and phonemes and additional phonemes that were added to the corresponding tables. From Figure 5.3, 127 additional phonemes that were not available in Penang Hokkien were added and removed from the Morpheme_Phonemes Table. The refined Morpheme_Phonemes table has its records increased from 2102 to 2110 as shown in Figure 5.1 and 5.6.
In morphemes_phonemes.xlsx, the solution was to remove the phoneme_diacritics column since the special diacritics were the main problems of importing the table into the database. In maps_graphs_morphs.xlsx, the solution was to delete the chinese_remarks column, since the Chinese characters were the main problems of importing the table into the database. The steps for entering the tables into the database were the same as in the previous subchapter 4.3.4.
After the tables were successfully imported into the database where their successful import logs were similar as shown in Figure 5.11, the next step was to set up the primary keys and foreign keys in the tables using the redesigned ER Diagram and Data Dictionaries in the previous follow chapter 5.3.4 as shown in Figure and 5.14. Next, the foreign keys are configured in maps_graphs_morphs as shown in Figure 5.15 with successful configuration result in Figure 5.16 below. Reverse Engineer Function in MySQL was used to visualize the Entity Relationship of the Tables as shown in Figure 5.17 below which is the same as the Redesigned ER Diagram in subchapter 5.3.4.
I had contacted the Speak Hokkien Campaign authority to request the data needed in the research; however, no response was received. Re-implementing the tables in the database was successful and using the MySQL Re-engineering feature to generate ER diagram of the tables in the database is the same with the redesigned ER diagram.
Conclusion and Recommendation
- Conclusion
- Recommendations
The research ended with successful re-implementation of tables in database corresponding to the redesigned ERD and Data Dictionaries. Due to limited time and scarcity of human resources, many early planned research objectives were stopped and abandoned. The high complexity of Penang Hokkien dialects under categorization of Southern Min Language was one of the obstacles in this research project.
As a first recommendation for future research on related research, it is necessary to gain knowledge about the various romanizations of the Southern Min languages, because the current non-standardized methods of romanization have been invented. In addition, experts in Old and Middle Chinese phonology and graphemes should be included in the research to trace the forbidden graphemes. Due to the inappropriate graphemes used by Taiwan's Ministry of Education to replace banned graphemes in their online dictionaries, there is a lot of controversy towards the Ministry, the graphemes taken from them should be compared with other Southern Min linguists who do not work under Taiwan's Ministry of Education.
Hou, "Minyu [Min Languages]," in Xiandai Hanyufangyan gai lun, Shanghai: Shanghai Educational Publishing House, 2002, p. Mok, "George Town exhibit shows decline of Hokkien language in bid to save it," Malaymail.com, 2020.
Ching, “Development of Cantonese spoken language corpora for speech applications,” in International Symposium on Chinese Spoken Language Processing, 1998, p. Romportl, “Construction of a speech corpus optimized for unit choice synthesis,” in Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, LREC p. Lim, “Towards an interactive voice agent for Singapore Hokkien,” in HAI 2016 - Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Human Agent Interaction, 2016, p.
Tsay, “Construction and automation of a corpus of Minnan child speech with some research findings,” International Journal of Computational Linguistics & Chinese Language Processing , vol. Douglas, Chinese-English dictionary of the vernacular or colloquial language of Amoy: with the principal variations of the Chang-Chew and Chin-Chew dialects. 33] Ministry of Education R.O.C, "Jiaoyubu Taiwan Minnanyu Changyongci Cidian - Bianji Shuoming [Ministry of Education Taiwan Mini South Dictionary of Frequently Used Phrases - Editing Guidelines - Phonetic Guidelines]." https://twblg.dict.edu.tw/holodict_new/compile1_3_9_3.jsp (accessed 08 September 2022).
A-1elor of Information Systems (Honours) Information Systems Engineeringlity of Information and Communication Technology (Kampar Campus), UTAR P END IX A Pe n an g H ok kie n S p elli n g Syste m.
APPENDIX B EVUALATION LOGS
APPENDIX C FYP 2 Poster
APPENDIX D
FINAL YEAR PROJECT WEEKLY REPORT
WORK DONE
SELF EVALUATION OF THE PROGRESS 3 out of 5
PROBLEMS ENCOUNTERED No
WORK TO BE DONE
PROBLEMS ENCOUNTERED
PLAGIARISM CHECK RESULT
CHECKLIST
UNIVERSITI TUNKU ABDUL RAHMAN FACULTY OF INFORMATION & COMMUNICATION
TECHNOLOGY (KAMPAR CAMPUS)