IPO underpricing is a recurring phenomenon as it has been found to be widespread across various exchanges, including the Singapore Exchange (SGX) and Bursa Malaysia (KLSE). The results of IPO underpricing and their impact on long-term performance are relevant, especially for local and foreign investors, as these may influence their buy-hold-sell decisions.
INTRODUCTION
Background of the Study
There is various empirical evidence to support the existence of underpricing in IPOs across different markets, including the Singapore Stock Exchange and Bursa Malaysia. The changes in the level of underpricing have been said to cause IPOs to underperform in the long run.
Statement of the Research Problem
Does the level of IPO underpricing affect its long-term performance on the Singapore Stock Exchange and Bursa Malaysia. What are the differences in the degree of underpricing and long-term performance of initial public offerings on the Singapore Stock Exchange and the Malaysian Stock Exchange.
Objectives of the Study
What determinants of initial public offering underpricing are evident in Singapore Exchange and Bursa Malaysia. To examine the differences in the level of underpricing of IPOs and long-term performance in Singapore Exchange and Bursa Malaysia.
Statement of Hypotheses .1 Singapore Exchange
- Ownership Structure and Underpricing
- Firm Size and Underpricing
- Firm Age and Underpricing
- Offering Price and Underpricing
- Offering Size and Underpricing
- Financial Leverage and Underpricing
- Return on Equity (ROE) and Underpricing
- Firm Industry and Underpricing
- Long-run Performance and Underpricing
- Bursa Malaysia .1 Underpricing
- Ownership Structure and Underpricing
- Firm Size and Underpricing
- Firm Age and Underpricing
- Offering Price and Underpricing
- Offering Size and Underpricing
- Financial Leverage and Underpricing
- Return on Equity (ROE) and Underpricing
- Firm Industry and Underpricing
- Long-run Performance and Underpricing
To study the effect of initial public offering underpricing on long-run performance in Singapore Exchange and Bursa Malaysia. The offering size of a firm's IPO has no significant effect on IPO underpricing in the.
Significance of the Study
- Firms
- Individual Investors
- Philippine Investors
- Regulators
- Academe
- Researchers
This research is very comprehensive given that there is limited research comparing the level of underpricing and long-term performance of IPOs listed on the Singapore Stock Exchange and Bursa Malaysia. Furthermore, additional data on the level of IPO underpricing and long-term performance on the Singapore Stock Exchange and Bursa Malaysia can be obtained in this research.
Scope and Limitations of the Study
Also, only companies that have complete data will be included in the data for uniformity. Therefore, the researchers will examine the level of underpricing that exists in the Singapore Exchange and Bursa Malaysia.
Initial Public Offerings (IPO)
- Reasons for IPO
- Listing Process
- Singapore Exchange
- Bursa Malaysia
- Key IPO parties
- Issuing firm
- Underwriter
- Auditor
- Investor
As stated on the Singapore Exchange website (n.d.), the process of listing IPOs on SGX is as follows: (1) Evaluation and Planning Phase, (2) Preparation Phase, (3) Execution Phase and (4) Realization phase. According to the Bursa Malaysia Listing Practical Guide available on the Bursa Malaysia website (n.d.b), the general listing process is as follows: (1) Submission Process, (2) Approval Process, (3) Process of after approval and (4) Admission process.
IPO Underpricing
- IPO Underpricing Phenomenon
Evidence of IPO Underpricing and Underpricing Determinants
In addition, the study found that family governance and the degree of underpricing have a significant relationship with each other. Similarly, Mahatidana and Yunita (2017) analyzed the determinants of the level of underpricing of IPOs on the Indonesian stock market.
Long-run Performance of IPO
The researchers looked at two main anomalies found in IPOs, which are underpricing and long-term underperformance. The results of IPO underpricing and performance indicate that Italy, France and Germany are considered efficient markets.
Research Gap
Theoretical Framework .1 Underpricing
- Information Asymmetry Theory
- Signaling Theory
- Long-run Performance of IPOs
- Heterogeneous Expectations Hypothesis
- Fads Hypothesis
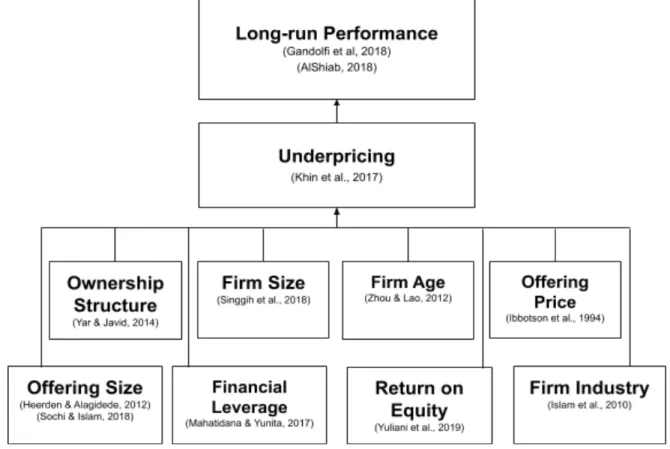
Considering the prevalence of the IPO underpricing phenomenon, it is clear that this phenomenon also affects the long-term performance of IPOs. In return, the overvaluation of the IPO stock leads to its underperformance in the long run.
Conceptual Framework
Operational Framework
Another objective of this research is to examine whether the degree of underpricing will affect the long-term performance of IPO stocks. The dependent variable in the second model, long-term performance, will be measured using firms' weekly cumulative average adjusted returns (CAR) up to the third year after the offer date.
A priori Expectations
- Model 1 A priori Expectations
- Model 2 A priori Expectation
They concluded that among the variables they tested, they found that supply size plays a significant role in the level of underpricing. Moreover, they claimed that financial leverage is insignificant but positively correlated with the level of underpricing.
Research Design
A comparative research design will be used to compare and contrast the level of underpricing and long-term performance of both exchanges. Quantitative data will be composed of several variables such as underpricing, ownership structure, firm size, firm age, offer price, offer size, financial leverage, long-term performance and return on equity (ROE).
Method of Data Collection
First, the researchers will identify and compare the level of underpricing, measured by the market-adjusted abnormal returns (MAAR), and long-term performance, measured by cumulative abnormal returns (CAR), of IPOs in SGX and KLSE for 2007-2016. This method was chosen by the researchers as it can represent the performance of the company and its progress in the stock exchange up to its third year of listing. Furthermore, the researchers believe that this method of sampling can represent both extremes of the population.
Additionally, the level of underpricing is adjusted based on the market index using the market-adjusted abnormal return (MAAR) model. Information technology industry (qv) Companies belonging to the information technology industry based on the Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS). qv) Companies belonging to the communications services industry based on the Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS). Real Estate Industry (qv) Companies belonging to the real estate industry based on Global Industry.
Method of Data Analysis
- Level of Underpricing and Long-run Performance
The initial objective of this research focuses on determining the level of underprices and the long-term performance of the companies on the Singapore Exchange and Bursa Malaysia. This is done to monitor how the long-term performance of the IPOs changes on a weekly basis. Therefore, in the first phase, an analysis of the descriptive statistics will be performed to determine the average level of underprice found in the resulting average of the descriptive statistics, and the long-term performance for both SGX and KLSE.
Given that this analysis can generate mean, minimum, median, standard deviation and maximum, etc. of each variable, this can be used as a basis for quantitative data analysis. reflect the difference between the IPO market of SGX and KLSE in the variables mentioned above. A stepwise regression analysis is performed to test the significance of the relationship between the given variables and the degree of undercutting. The final stage is focused on determining whether the level of underpricing significantly affects the long-term performance of IPO stocks using a simple linear regression of underpricing (average MAAR) and long-term performance (average CAR) of IPOs. stocks in the first and third year.
Methodological Limitations
- Descriptive Statistics
- Regression Analysis
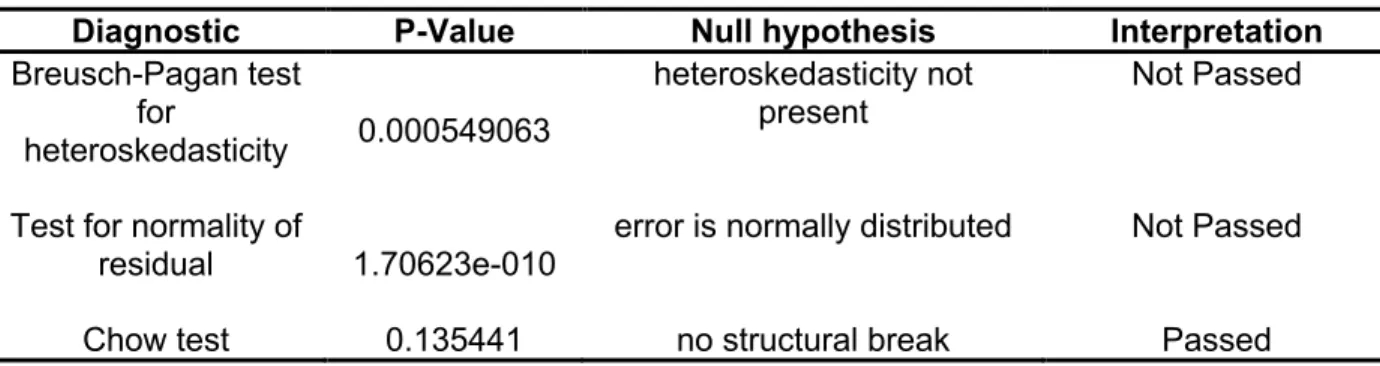
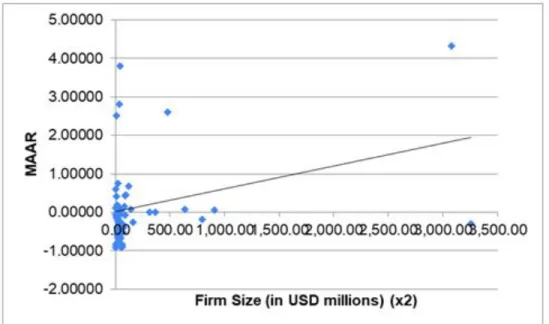
This reflects the variables taken into account in determining the determinants of underpricing in the two stock exchanges. With that, since the level of underpricing in IPOs is evident in SGX during the period from 2007 to 2016, we reject 01. The minimum level of underpricing was the case when NWP Holdings' share price fell by 7.6% on the first day of trading has. .
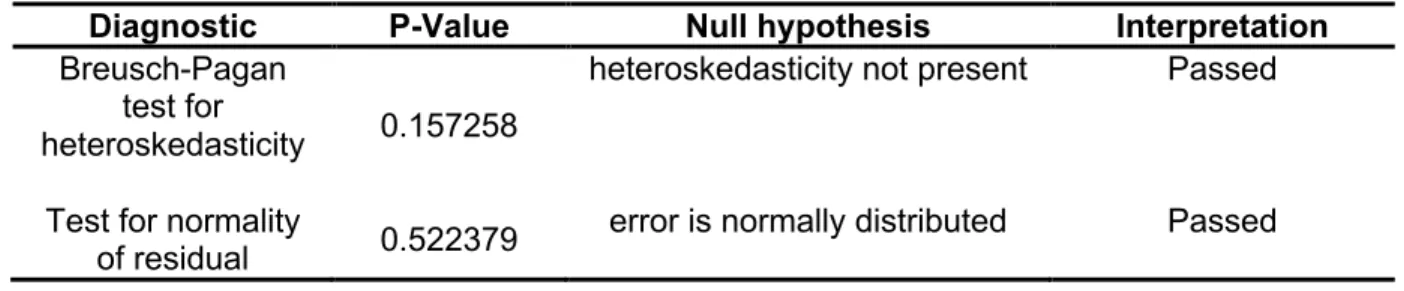
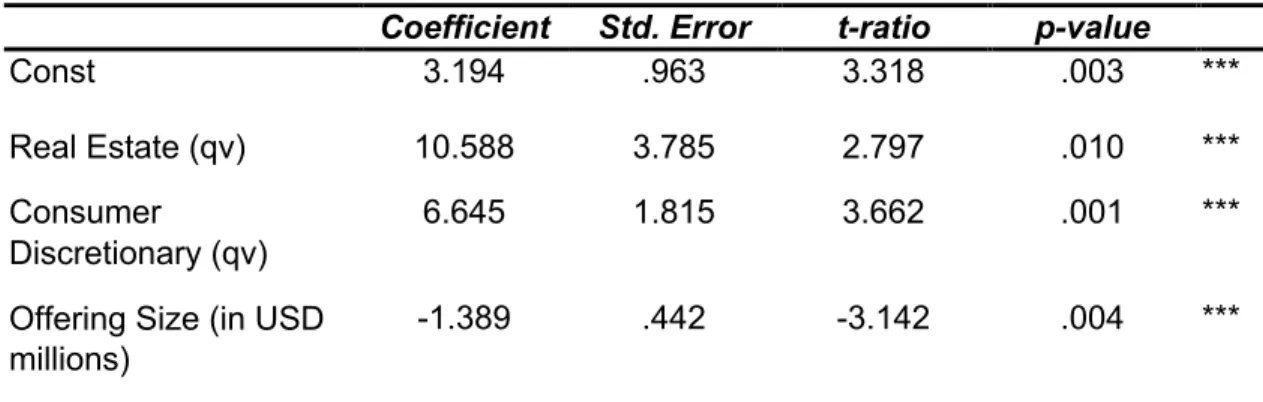
Using the regression analysis, the fixed industry in terms of consumer discretionary (< 0.05) is a significant predictor of the level of underpricing in the Singapore Exchange. A regression model for the level of underpricing for SGX was derived from the statistical results using the stepwise regression analysis. Based on the regression analysis, only firm size is a significant predictor of the level of underpricing in Bursa Malaysia.
- Firm Industry Analysis
- Comparison Between Time Periods
- Impact of Level of Underpricing on Long-run Performance .1 Descriptive Statistics
- Regression Analysis
- Recommendations
The findings for SGX are similar to those of Sochi and Islam (2018) as they pointed out that the size of the company does not significantly influence the level of underpricing on the Dhaka Stock Exchange. On the other hand, this relationship is consistent with the findings of Islam and Ahmad's (2010) study when they examined the underprice of IPOs on the Chittagong Stock Exchange. While Malaysia only has firm size (+) as an important determinant of underprices, similar to the findings in the period 2007 to 2016.
In addition, the results are against the a priori expectations established in this research as the study by AlShiab (2018) found that in the MENA region for the period of underpricing has a significant and negative effect on the long-term performance of the IPO stock. Exploiting Seasonality in the Singapore Straits Times Index (Bachelor of Business Administration Thesis, Jönköping University, Jönköping, Sweden). An Empirical Study of the Underpricing of IPOs in the Chittagong Stock Exchange.
KLSE
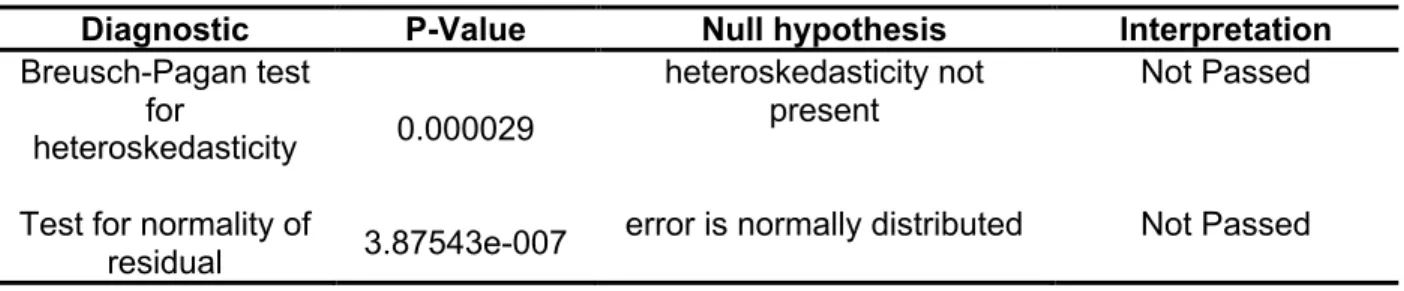
Diagnostic Test for the Stepwise Regression Analysis of KLSE Diagnostic P-value Null Hypothesis Interpretation Breusch-Heiden test.
Regression
Case statistics used are based on cases with no missing values for any variable used. For models with dependent variable MAAR, the following variables are either constant or have missing correlations: x8, x13, x15, x16. For models with dependent variable MAAR, the following variables are either constant or have missing correlations: x14.
For models with dependent variable MAAR, the following variables are constant or have missing correlations: x13, x17, x18. For models with dependent variable MAAR, the following variables are constant or have missing correlations: x14, x17, x18. For models with dependent variable MAAR, the following variables are constant or have missing correlations: x17, x18.
That the data used and presented in the study have not been manipulated by the proponent (either through falsification or fabrication of sources or materials, omission or alteration of data sources/results and/or other means that could make the study or results materially good or acceptable). We hereby certify that we understand and are aware of the University's policy regarding plagiarism and accept the consequences of any plagiarized work submitted by us.
DE LA SALLE UNIVERSITY General Research Ethics Checklist
This checklist must be completed AFTER the De La Salle University Code of Ethics has been read. Does your research involve human participants (this includes new data collected or use of pre-existing data). I have no conflict of interest of any kind (personal, financial, proprietary or professional) with the sponsoring/granting organization, the study, co-.
I have a personal/family or professional interest in the results of the study (family members who are co-proposers or personnel in the study, membership in relevant professionals. I have a proper interest in this study (with the intention of applying for a patent, trademark , copyright or license).I have substantial financial interest vested in this study (remuneration exceeding P250,000.00 annually or equity interest in the form of shares, stock options or other ownership interests) .
Declaration