MOTIVATION OF ACADEMIC STAFF AT UNIVERSITIES OF TECHNOLOGY IN MYANMAR. was submitted to Mahidol University College of Management for the Master of Management degree. PRATTANA PUNNAKITIKASHEM, DR., SIMON ZABY, DR. The purpose of this research is to find out the motivation levels and factors affecting the motivation and job satisfaction of academic staff working in universities of technology throughout Myanmar. The research topic of this thematic paper is to analyze the level of motivation among teachers working in universities of technology in Myanmar based on Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory.
Most teachers working at these Technological Universities are unhappy, demotivated, incompetent and unqualified because they do not get enough support and feedback. The first aim of this paper is to analyze the level of motivation among teachers working at Technological Universities in Myanmar. Second is to describe the work motivation factors based on Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory.
The final purpose is to share useful information and recommendations with these universities and others interested in this research. The scope of this study is limited to collecting data from teachers working in universities of technology in Myanmar.

LITERATURE REVIEW
- Academic Staff in Myanmar
- Motivation in higher education
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory
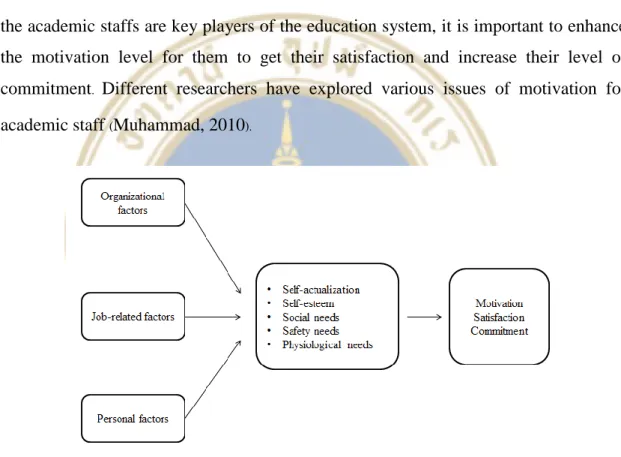
- Proposed Framework
In addition, inadequate housing and an unsafe living environment also affect the motivation and job satisfaction of the academic staff. Academic staff have the most important place in any society because they are the sources of transformation of knowledge (Imrab, Mushtaq, Qudsia, 2013). Ololube (2004) makes the same point that the education system can be boosted by increasing the motivation of academic staff to increase their productivity.
The motivation and satisfaction of academic staff can influence teaching and also student learning. Motivation can encourage the academic staff to be productive in their work and it can increase the glory of the universities and also the satisfaction of the academic staff. The incompetent supervision, characterized by selective justice and witch-hunting (Bennell, 2004), is one of the problems that can affect the motivation and satisfaction of academic staff.
Therefore, these factors can be used as motivational factors for academic staff commitment and satisfaction. Therefore, since the academic staff is a key player in the education system, it is important to increase the level of motivation for them so that they are satisfied and increase their level of commitment.

METHODOLOGY
Population
Sample size
Questionnaire Designs and Data analysis
After the data is collected, Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) is used to analyze the data. The data will be analyzed by frequency distribution tables with percentages and figures, as well as other descriptive statistics.
RESRARCH FINDINGS
- Demographic Information
- Levels of needs
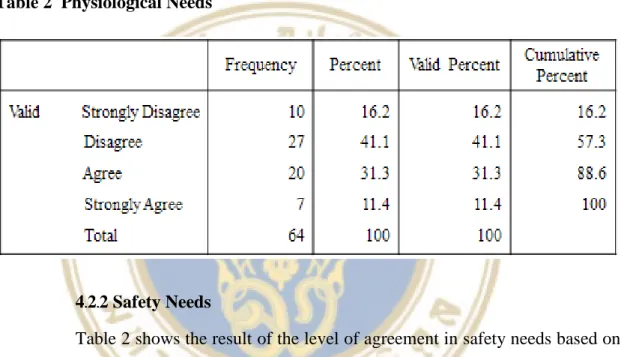
- Physiological Needs
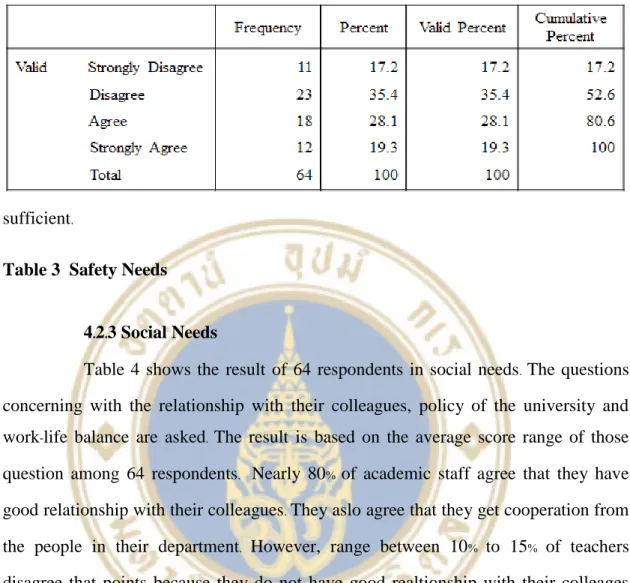
- Safety Needs
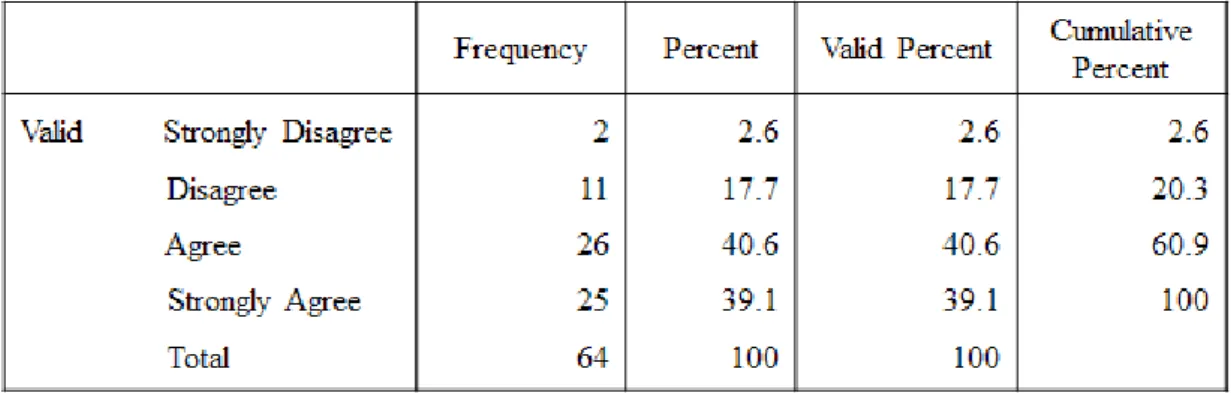
- Social Needs
- Esteem Needs
- Self-Actualizatoin
- Satisfaction
- Motivation
- Commitment
- Main Findings
In addition, the salaries of academic staff are lower than those of other professions with the same level of education. But most academic staff do not get enough support for their physiological needs because top management does not focus on motivating staff by meeting their needs. But more than 50% of academic staff do not get any care for their health at the university, while other universities take care of the health of the rest.
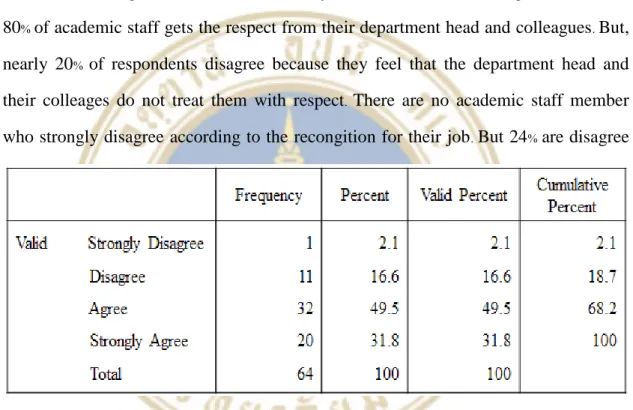
Most academic staff feel that the universities do not take responsibility for their health and for the safety of the working environment. But most of the scientific staff have a good relationship with their colleagues, and they can work well with people in their department. There are no scientific employees who disagree strongly according to the recognition of their job.
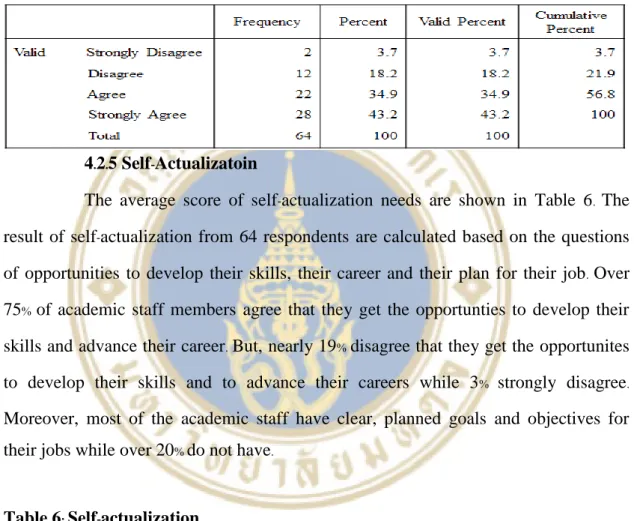
But nearly 17% of academic staff disagree that they have sufficient assessment needs, while 2% strongly disagree. Over 75% of academic staff members agree that they have opportunities to develop their skills and advance their careers. Furthermore, the majority of academic staff have clear, planned goals and objectives for their work, while over 20% do not.
Therefore, most academic staff members have enough self-actualization needs because they get enough support for their skills and career development, while more than 20% do not. The correlation values of these variables show a highly significant relationship with academic staff job satisfaction. Nevertheless, most academic staff do not get enough motivation to work.
But while almost 50% of academic staff do not agree that they should always be loyal to their department or university, another 50% agree to be loyal. Moreover, 50% of academic staff agree that they would feel guilty if they left their university now, while another 50% disagree. For greater commitment to work, the five levels of needs are necessary to fulfill for the academic staff.
But most of the academic staff members have enough needs for esteem and self-actualization that the commitment level is higher than the satisfaction. Almost 60% of academic staff agree that they do not get enough support for this level because they do not get adequate housing and accommodation, and the lack of fairness from the administrators.
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
Conclusion
In addition, all factors need to be developed to increase motivation and satisfaction, as each factor is important for academic staff. Teachers will be more satisfied and committed to their work if they get enough support and motivation for their needs. The findings of this study also justify that academic staff satisfaction depends on motivational factors such as work environment and promotion.
This result focuses only on demonstrators, supervisors and teaching assistants, who suffer from the lack of motivation to commit to their jobs more than other academic staff. After collecting data and analysis with many factors, the research shows that most of the number of academic staff are satisfied with their career without getting sufficient fulfillment of basic needs such as physiological needs and safety needs. The author believed that if they do not meet their needs at lower levels, they will not be engaged in their jobs and they will not be satisfied.
But Maslow's theory may not hold for the academic staff of the Technological Universiteis because most of the staff have enough needs for esteem fulfillment, including satisfying to be a teacher and getting respect from their department head and colleagues, even if they don't get enough need for it basic levels. Moreover, they also have enough actualization needs, including having clear, planned goals and objectives for their jobs and getting opportunities to develop their skills and advance their careers. From the research findings, it shows that encouragement and support for a career development plan is the most motivating aspect.
The least motivating factors for respondents are salary and delays in promotion because they can reduce staff motivation to contribute to high performance. The findings also show that respondents are less satisfied with their university's research and development support and administration policies, and more satisfied with supervision by the head of department.
Recommendations
The principle must create a good relationship among employees in order to get cooperation in the workplace with their manager and colleagues and give them the opportunity to participate in decision-making regarding professional matters. Every university should have the assessment for each position to track their improvement and improve their performance. The clear, planned and framework for training for all levels of staff should be designed to be the professional.
The principle and head of department must know the needs of each staff to support individual training needs. The involvement of the government and the principles in research will help to improve the performance of staff. They should invest more in research to encourage and motivate the staff to create innovative technologies.
It is hoped that the outcome of this study will increase awareness and understanding of the effect of motivational factors on job satisfaction and engagement. The problems found in this study can make a major contribution to improving the job satisfaction of academic staff as well as the level of training.
Limitations and Suggestions for Further Research
So, if the future research can focus on all levels of scientific staff, gender and age, and also can analyze and find more factors that are important for the motivation and satisfaction of the scientific staff, it can help to get more accurate and representative results .
The relationship between teachers' job satisfaction and teachers' teaching performance in three basic secondary schools in Myitkyina, Kachin State, Myanmar. Factors Affecting Motivation and Job Satisfaction of Academic Staff in Universities in the South-South Geopolitical Zone of Nigeria. Factors affecting the motivation of academic staff (A case study of University College Kotli, UAJ&K).
Impact of HR Practices on Performance of Teachers in Colleges of Azad Kashmir Author Details. Motivation and Effective Performance of Academic Staff in Higher Education (Case Study of Adekunle Ajasin University, Ondo State, Nigeria).
APPENDICES
There are no right or wrong answers to the questions, and the answers to all questions are important to the successful performance of the study. Your answers to the questions will be anonymous and will not be used for purposes other than this research study. The questions below use a 4-point Likert rating scale, meaning (1) Very dissatisfied/disagree at all/significantly reduces work motivation.
The University takes reasonable steps to provide a safe and secure working environment for all members of staff. The consistency and fairness of my department head with employees at all levels motivates me.