First, it is useful for business people who want to learn more about the commercial impact of HIV/AIDS worldwide and the role that business plays in the epidemic. Furthermore, AIDS and Business could be of interest to the public health or social activist, as well as to the general reader seeking insight into one of the most important social phenomena of our time: the HIV/AIDS pandemic. Improving manager's understanding of the economic, political and socio-cultural factors contributing to the spread of HIV/AIDS (Case Studies 1 and 2).
Initiatives such as the Global Business Coalition on HIV/AIDS have been key in raising international awareness of the responsibility of business in the fight against AIDS.
Acknowledgments
Prevention in Brazil and the so-called ABC model 18 1.3 Spotlight on discrimination: The case of people with. Availability of funds to pay for antiretroviral treatments 67 2.5 A view from the field: the complementarity between. Government and business in the HIV/AIDS battle in Brazil 69 2.6 A view from the field: WHO's Ted Karpf on the.
1 A Medical Anthropologist in Morocco
Unfortunately, due to alarm about the spread of HIV/AIDS in Africa, much of the focus of HIV and sex-related research has been on the. Cultural differences in the perception of time may affect the success of HIV/AIDS medical regimens. Fatalism may play a role in the transmission, voluntary testing and treatment of HIV/AIDS.
Men who had sex with men as a group already faced stigma in most countries before the advent of HIV/AIDS. In the United States, HIV among MSM declined over the first two decades after the first explosion of HIV/AIDS cases. Postscript: HIV/AIDS—How bad does it have to be before we believe it is bad.
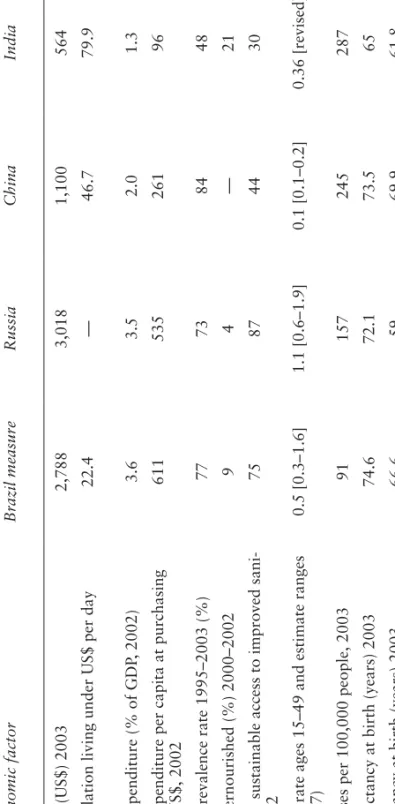
2 Addressing a Global Cause in Local Contexts
Other factors may be at play that make tracking HIV/AIDS cases unreliable, as discussed in the next section. Oster (2005)105 and Barnett and Whiteside (2002), among others, argue that HIV/AIDS data provide conservative estimates of the true size of the epidemic. Patients receive ARV medications in the AIDS Drug Dispensing Units, usually the pharmacies of the HIV/AIDS outpatient clinics.
The role played by international organizations in the fight against HIV/AIDS At the beginning of the epidemic, it was assumed that the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations (UN) would be able to slow the spread of HIV. There are a large number of non-governmental organizations (NGOs) dedicated to or involved in HIV/AIDS. Their commitment to people with HIV/AIDS is just one of many projects run by the organization.
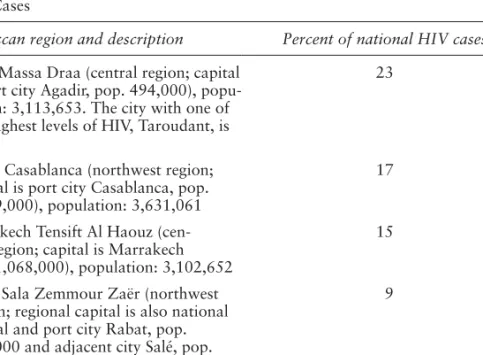
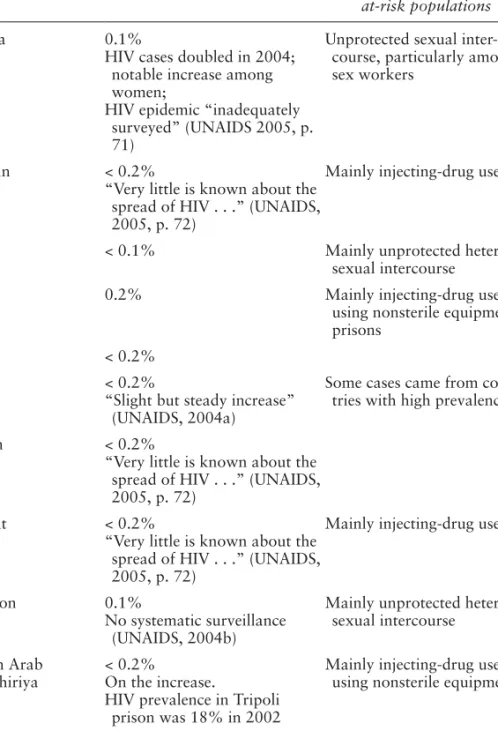
The prevalence of AIDS remains extremely high in this part of the world: South Africa is home to one third of all people with HIV/AIDS worldwide.159. Such behavior should also be seen in the light of a certain acceptance of HIV/AIDS in the media discourse and in a different social environment. Is cultural resistance (or cultural facilitation) the main issue in the fight against HIV/AIDS?
Compare successful countries with unsuccessful countries in the fight against HIV/AIDS and in selling this cause to their citizens. What are (can be?) the objectives of social marketing campaigns regarding HIV/AIDS.
3 Mexicom Designs a National Public Health HIV/AIDS Campaign
The list of "needs" to be met by the country's HIV/AIDS program is presented in Table 3.2. Migrants often return to rural areas where there is little or no HIV/AIDS public health communication. 26. Everything known about mass communication and behavior change suggests that marketing communications for HIV/AIDS campaigns must be properly designed, targeting specific audiences in terms of age, gender, socio-economic status and ethnicity.
A wide range of theories and models coexist in HIV/AIDS activism, communication and relevant social science research. How Brazil Keeps Its HIV/AIDS Message Fresh and Appealing and Avoids "Safe-Sex Fatigue." Commonly used in the development of national public health programs, such as HIV/AIDS prevention.
Smoking cessation literature has been used by communication planners to model HIV/AIDS prevention programs. Social cognitive theory has been considered particularly useful in supporting HIV/AIDS communication efforts because of its recognition of the importance of individuals' social interaction. Sexual behavior is one area where rational thinking about HIV/AIDS may be less applicable than emotion.
To have the greatest impact, the key target groups of the Mexican-designed HIV/AIDS campaign must be considered. The campaign consists of a series of short animated, hand-drawn films that focus on the life of someone living with HIV/AIDS.

4 Ross IVD
Worse, Weiss opined, there are a handful of HIV/AIDS activists who would jump at the chance to publicize differential pricing for their fellow activists here in the US. In the United States, about 30 to 40 percent of test takers do not return their results,20 a figure that is likely to be higher in resource-poor regions. If the test is positive, post-test counseling can be provided, as well as a list of medical facilities in the client's region. 22.
As the WHO document on post-test counseling states, “counseling is a relationship” and counselors must be sensitive to the client's context, culture, and emotions. A third series may be necessary, especially if the results in the first and second series were inconsistent (discordant). HIV tests detect antibodies to HIV in the blood; therefore, the body must produce a significant number of them in order for them to be detectable.
What are the arguments for and against their mandatory testing in the case of target populations considered "at risk". As with any health service, social marketing may be necessary to raise awareness and interest in HIV testing. There is a high level of mistrust of health care services among African Americans, so trust is an issue that must be actively addressed in the testing campaign.
There can be high levels of fear in the group due to the strong influence of the Catholic Church and its conservative attitude about sex. Discuss buying behavior in the case of organizations (large international organizations such as World Health Organization, ministries of health, hospitals, health care systems, faith-based organizations or non-governmental organizations fighting HIV/AIDS).

5 Protectom
Fabre had pushed Protectom beyond the obvious and into a larger market than that of the aging gay men who had experienced the AIDS scare in the 1980s. As if having sex without a condom is as crazy as playing hockey naked!”1 Protectom even worked closely with the Stop AIDS campaign on a number of issues for the Swiss market, the Condoms Essential Wear2 campaign in Britain, and the Michael Stich Foundation3 in Germany. In the sense of business marketing, condoms are a product like any other commercially available medical device.
The advent of vulcanization of rubber in the mid-1800s made condoms a widely available, mass-produced product. Since then, the biggest change came from the use of latex manufacturing in the 1930s, and later the use of polyurethane, which enabled the development of the female condom. In 2008, condoms were still condemned by the Vatican and a number of church leaders, but there are many dissenting voices in the Catholic Church, such as Catholics for Choice23 and others, who refer to a "lesser evil" in using condoms to avoid death from AIDS.
Due to the advent of birth control pills in the 1960s, the primary demand for condoms declined and the number of users declined, while pregnancy responsibility shifted from men to women. AIDS In the 1980s there was growing concern about the use of condoms as a means of preventing sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV/AIDS. This is not done on the basis of sampling part of the production, which is common elsewhere.
It's a tough retail business with about six hundred vending machines across Switzerland and small operators who do most of the work at home (filling the packages with the condoms they buy) and then servicing the vending machines. It is not in Doetsch Grether's general policy to undertake social marketing of condoms on a global scale;50 however, the company donates sets of condoms to NGOs or governments in Africa that are off-market but still usable.

6 Global Pricing and Ethics of Marketing HIV/AIDS Drugs
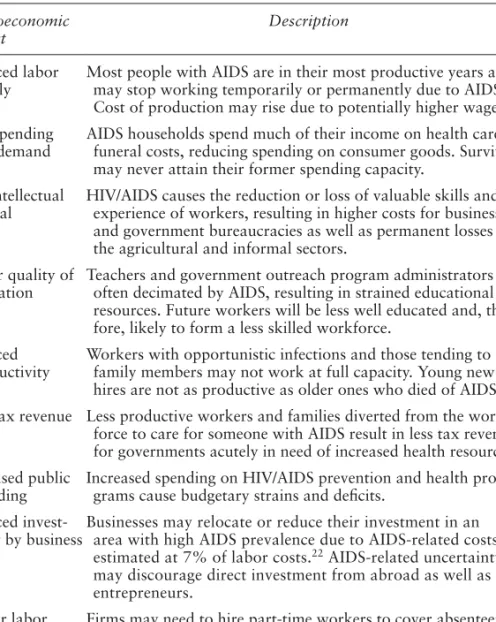
The main impacts of HIV/AIDS have consequences in the economic, political and sociocultural spheres of the affected countries. In Africa, the report notes that military personnel and peacekeepers have HIV/AIDS infection rates two to three times that of the general population. Many activists believe that treatment should be offered to everyone with HIV/AIDS because of the moral equality of all people - an idea developed in the writings of Hobbes, Kant and Rousseau.
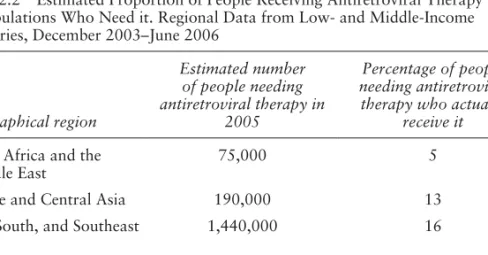
Probably the human right that is most directly relevant to HIV/AIDS in the rights literature is the right to health. It is well documented that antiretrovirals improve the quality of life and survival of people with HIV/AIDS in high-income countries. Should high-income countries such as the United States send HIV/AIDS funds abroad if some people at home cannot afford to be treated?
Box 6.1 Is business involvement in the fight against the HIV/AIDS pandemic just 'enlightened self-interest'. Some companies contribute to the broader efforts made to increase HIV/AIDS awareness and education. Pharmaceutical companies in the United States and around the world argue that drug patents should remain intact, in the face of many poorer nations seeking patent exemptions for HIV/AIDS drugs.
Collaborative programs include building technical capacity for clinical management of people living with HIV/AIDS. Treatment is under the supervision of doctors, often specialists in HIV/AIDS, according to the latest guidelines.