Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more. Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more.
Financial Objectives and Shareholder Wealth
In a world of geopolitical, social and economic uncertainty, strategic economic management is in a process of change, which requires a reassessment of the basic assumptions that go beyond the traditional boundaries of the discipline. The overall, normative goal of strategic financial management should be the maximization of the shareholders' wealth represented by their ownership stake in the company, for which the company's current market price per share is a disciplined, universal measure.
Wealth Creation and Value Added
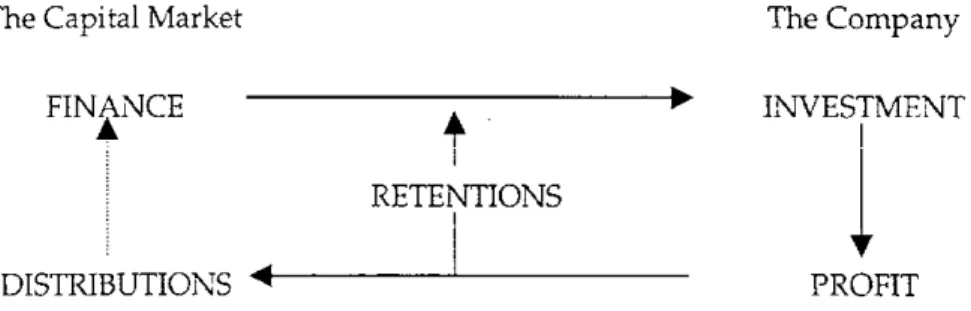
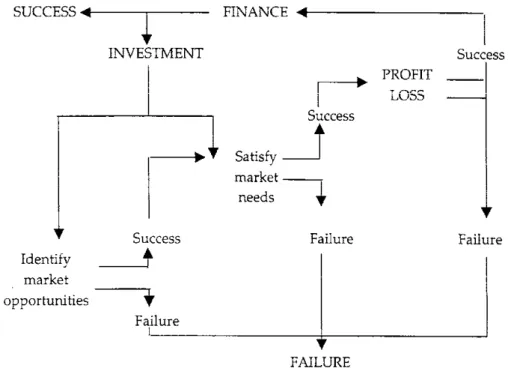
Finance – an overview Figure 1.2 separates the "winners" from the "losers" in their quest to add value by summarizing in financial terms why some businesses fail.
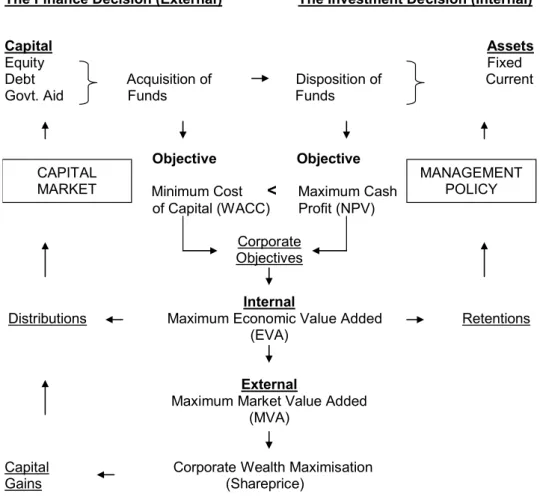
The Investment and Finance Decision
Strategic financial management Finance – an overview Strategic management investments and finance functions are therefore interconnected via a company's weighted average cost of capital (WACC).
STUDY AT A TOP RANKED
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS SCHOOL
- Decision Structures and Corporate Governance
- The Developing Finance Function
- The Principles of Investment
- Perfect Markets and the Separation Theorem
For an international overview of the theoretical and empirical research on the subject see the Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis 38 (2003). However, a broader picture of the role of modern financial management can be drawn through an appreciation of its historical development.
CLICK HERE
Summary and Conclusions
From a financial management point of view, dividend payout policies are irrelevant (what academics call a passive residue) in determining a company's value and assets. Now that we have separated the individual's consumption decision from the firm's investment decision, let's explore in more detail today's financial world, the different functions of strategic financial management, and their analytical models.
Selected References
Part Two
The Role of Capital Budgeting
To simplify matters, academics and practitioners categorize investment and financing decisions into long-term (strategic), medium-term (tactical), and short-term (operational). Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click the ad to read more Click the ad to read more Click the ad to read more Click the ad to read more.
Liquidity, Profitability and Present Value
The value of money has simply changed because of what we can do with it. Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click the ad to read more Click the ad to read more Click the ad to read more Click the ad to read more Click the ad to read more Click the ad to read more.
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
So the project's rate of return exceeds 8 percent (ie NPV is positive by 8 percent), of which more later. Remember that NPV corresponds to today's cash surplus at the end of a project's life.
The Inadequacies of IRR and the Case for NPV
The implication is that the cost of capital and reinvestment rates are equal to the IRR, which remains constant over the life of the project to produce a zero NPV. Using the data from Activity 6 with its 8 percent churn rate and Equations 10–11, confirm that the project's NPV is £7,050 and acceptable to management because the residual life equals an NTV of £8,881.
Summary and Conclusions
Furthermore, when considering a project in isolation, IRR produces the same accept-reject decision as an NPV by using a firm's cost of capital or rate of return as a discount rate (r). Combining the NPV and IRR equations from Chapter Two, projects are acceptable if they generate a lifetime cash surplus, i.e.
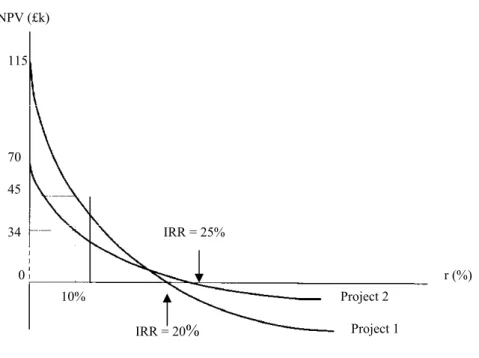
Ranking and Acceptance Under IRR and NPV
Also consider the effects of other discount rates on the NPV for each project shown in the graph below. Between the two extremes, different discount rates determine the slope of each NPV curve based on the size and timing of the project's cash flows.
The Incremental IRR
Capital Rationing, Project Divisibility and NPV
The following table confirms that the ranking of projects by NPV per The £ method, rather than their individual NPV, maximizes the total NPV and hence total firm wealth.
Relevant Cash Flows and Working Capital
The net effect of these working capital adjustments is to charge the project with lost interest (the opportunity cost of capital) on funds that have been invested throughout its life. Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Get help now.
Capital Budgeting and Taxation
Capital budgeting and the case for NPV Of course, we still haven't taken into account the timing discrepancy associated with deferred tax payments. Once we include working capital (if any) in the schedule, all that is needed is to discount the net cash flows at the project's opportunity cost of capital adjusted for inflation.
NPV and Purchasing Power Risk
Even today, SKF's innovative know-how is crucial for running a large proportion of the world's wind turbines. Obviously, if fixed costs are truly "fixed" (accurred regardless of project acceptance), they should be ignored.
Summary and Conclusions
Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more.
Dysfunctional Risk Methodologies
The financial risk associated with project financing and how the profit distributed to investors determines the company's cost of capital (discount rate). Also, the cost of capital is better left until we discuss securities prices in Part Three.
Decision Trees, Sensitivity and Computers
Computer simulation can be used in conjunction with decision trees, sensitivity analysis, or any technique to quickly calculate countless permutations of likely cash flows. As tools, however, decision trees, sensitivity analyzes and computer simulation are only as sound as the data on which they are based.
Mean-Variance Methodology
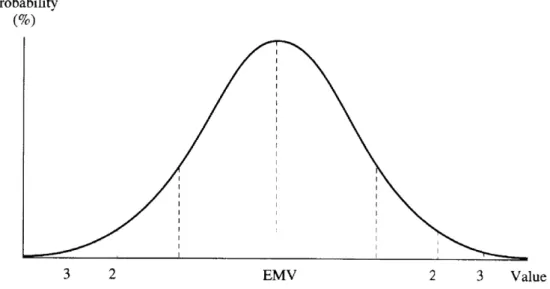
To solve the dilemma, the standard deviation is used to measure the average spread of cash flows of their EMV. Management then compares the standard deviation to the expected return to assess a project's risk-return profile; the interpretation is that for a given rate of return, the lower the standard deviation, the lower the risk and vice versa.
EXPERIENCE THE POWER OF FULL ENGAGEMENT…
Mean-Variance Analyses
Since a normal distribution is symmetric, the probability that a variable deviates above and below the mean is given by 2z. To determine the probability of contributions deviating above or below the average as specified, we must.
The Mean-Variance Paradox
Over the years, research has revealed that probabilistic analysis has gained ground (see Arnold and Hatzopoulus, 2000). One reason is that the risk-return profile for any normal distribution is fit within predetermined confidence limits. Add zeros to the data from the previous project and note that the coefficients remain the same.
SETASIGNThis e-book
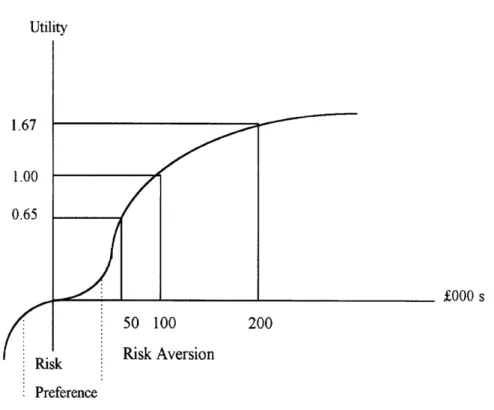
Certainty Equivalence and Investor Utility
If the procedure is repeated in full, the investor's utility function will emerge in accordance with his risk attitude, such as the profile drawn in Figure 4.2 to the right. Returning to our example, applying Equation (8) using the investor's utility curve shows that despite a positive ENPV, the project should be rejected.
Summary and Conclusions
Part Three
The Capitalisation Concept
In the second chapter we defined the present value of an investment (PV) as its corresponding periodic cash flows (Ct) discounted at a constant cost of capital (r) over time (n). The term r is called the capitalization rate because the transformation of a series of cash flows into value (ie equity) is called "capitalization."
Single-Period Dividend Valuation
Finite Dividend Valuation
The prospective shareholder expects a dividend per share of 10p and 11p in the first and second years respectively, after which the shares are expected to be sold ex div for £3.00 each. If the equity capitalization rate is 20 per cent per annum, confirm that the highest current ex-div price at which the shares should be bought is £2.24.
General Dividend Valuation
Constant Dividend Valuation
The Dividend Yield and Corporate Cost of Equity
Dividend Growth and the Cost of Equity
Capital Growth and the Cost of Equity
Strategic Financial Management Equity Valuation and Cost of Capital Since the same stock cannot be sold at different prices, it follows from equation (16) that the dividend growth rate (g) must be equal to (G) the annual growth rate of the stock price (capital gains). If a company currently trading at £4.00 per share with a forecast dividend of 20 pence is expected to grow at five per cent per annum, confirm that the equity capitalization rate is 10 per cent using the appropriate dividend and capital gain models.
Earnings Valuation and the Cut-Off Rate
Equity valuation and cost of capital Of course, proponents of earnings (such as dividends) who are confident in their forecasts need not limit themselves to one period or zero growth. Strategic Finance Management Equity Valuation and Cost of Capital Because the same stock cannot trade at two prices, equity returns (Ke) must differ in the corresponding dividend and earnings equations for P0 to remain the same.
Summary and Conclusions
Selected References
For example, the marginal cost of retained earnings for new investments is measured by the current return lost to shareholders, while debt is purchased at an explicit market rate. Explicit or not, to establish the total cost of capital as a project discount rate, management must first identify the current (marginal) cost of each type of invested capital (both debt and equity). The component costs must then be combined to form the marginal weighted average cost of capital (WACC).
Capital Gearing (Leverage): An Introduction
The Value of Debt Capital and Capital Cost
Strategic Financial Management Debt Valuation and the Cost of Capital If ten-year callable debt was issued at the same price with the same coupon rate, we must derive the current yield by solving for the IRR using Equation (5). In a tax-free economy (more on this later), this rate of interest demanded by investors represents the firm's marginal cost of capital for this source of funds.
The Tax-Deductibility of Debt
Strategic Financial Management Debt valuation and the cost of capital where: P0 = the current market price of debt,. To calculate the after-tax cost of capital, it is necessary to derive an IRR.
The Impact of Issue Costs
This is, by definition, higher than the cost of retained earnings, since the latter do not cause issuance costs. Returning to the inventory cost of the loan, issuance costs also increase the marginal cost of capital.
Summary and Conclusions
In this newly created situation, the company's overall cost of capital (rather than its cost of capital) measured by a weighted average cost of capital (WACC) would appear to be a more appropriate investment criterion. Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more Click on the ad to read more.
The Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC)
Strategic financial management Capital acceleration and capital costs The individual costs of equity and debt are weighted according to their share in the total market value of the company. Thus, the WACC used as the company's discount rate for assessing new projects is 10.4 percent.
WACC Assumptions
Thus, the cost of capital employed for any particular project is not the cost of a particular source of funds, but the total cost of the association of the firm: namely, the WACC. Strategic Financial Management Capital equipment and the cost of capital Even when funds are raised specifically from a single source to finance an incremental investment, there are good reasons to use the WACC as a discount rate, especially if the change in capital structure represents a short-term deviation from the desired capital mix.
The Real-World Problems of WACC Estimation
The equity implications of the appropriate acceptance-rejection decision using WACC as the discount rate can be confirmed by analyzing the investment's impact on equity returns. Finally, let's rephrase this cash return as a return on the common stock issue associated with the investment.
Summary and Conclusions
Selected Reference
Part Four
- The Concept of Economic Value Added (EVA)
- The Concept of Market Value Added (MVA)
- Profit and Cash Flow
- EVA and Periodic MVA
- NPV Maximisation, Value Added and Wealth
- Summary and Conclusions
- Selected References
The second part focused on the managerial investment decision with only oblique reference to deriving its breakeven rate. Therefore, added value represents an external check on the consequences of managerial action that companies ignore at their peril.