In an effort to overcome the unequal education of the past, a policy of Basic Education and Training for Adults has been established within South Africa. To increase quality in education and training and to redress past discrimination (Land et al 1999, pg 3).
The role of English Level 4 in ABET
Aim and Rationale
It is often wrongly assumed that passing a Level 4 English exam is a direct link to opportunities in the workplace. English Level 4 has benefits in the workplace, but students and management often fail to see these because their expectations were so unrealistic.
Introduction to Methodology
Classification of Research
Qualitative versus Quantitative Research
Qualitative Research Methods
Grounded theory is also developing theory, and Merriam and Simpson (1995, p. 112) assert that "as a qualitative, exploratory methodology, grounded theory is particularly suited to investigating problems for which little theory has been developed. In a study of grounded theory, one is constantly comparing groups to identify similarities and differences and to categorize the data.
Methods of Data Collection
Observation
Again, this is not ideal because the setting is not natural and the ethics are questionable (Merriam and Simpson 1995, p. 105). Interviewees are all asked the same questions, which are open-ended, and the interviews are semi-structured, as opposed to rigidly structured interviews.
Research Methods Used In This Study
The learners' interview questions and all the individual answers to the questions were consolidated by tabulating them on a spreadsheet. The percentages, which emerged within the learners' categories, were compared with the percentages within the managers' answers in order to compare the perceptions of learners and those of managers.
Literature Review
A Brief History of Adult Basic Education and Training in South Africa During the apartheid era, adult education in South Africa was very limited. In
Accreditation of providers to ensure consistency in quality and content of education/training courses. The Government of National Unity's White Paper on Education and Training (March 1995) gave the impression that ABET was a top priority and would be prioritized with the Department of Education, but it was not until 1996 that a Director of ABET was appointed and unfortunately, for due to lack of funds and staff, among other problems, there has been very little progress in the ABET arena.
The Laws
- The Skills Development Act (Act No.97 of 1998)
- The Skills Development Levies Act (Act No. 9 of 1999)
The purpose of the South African Qualifications Authority Act (SAQA Act) is to ensure that the quality of education and training in South Africa is of a high standard and this act has established a single system of education and training qualifications in place. While the SAQA Act is concerned with the quality of all education and training within South Africa, the main purpose of the Skills Development Act is to improve the skills of the workforce in order to grow the economy. Employees do this in the hope that by completing the courses they will benefit within the workplace.
I believe that students often unnecessarily start English level 4 because this is encouraged by employers. You have to wonder how teaching people to read and write will lead to all of the above. I also believe that ABET's expectations are often unrealistic. Wagner (1993, pg. 23) states this.
According to human capital theory, it is important that people are developed if they want to make a contribution to economic growth and share in the wealth of the country.
Research Findings
Background To Companies within the Study
- Commercial Sector Interviewees
- Shipping Sector Interviewees
- Manufacturing Sector Interviewees
- Hospitality Sector Interviewees
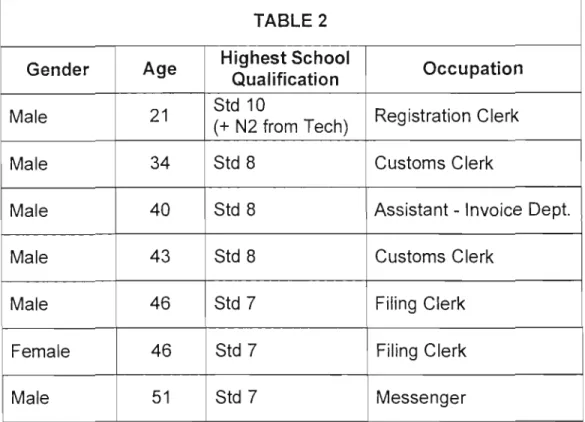
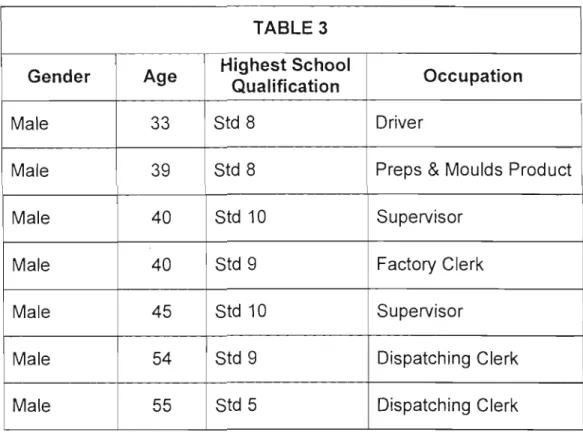
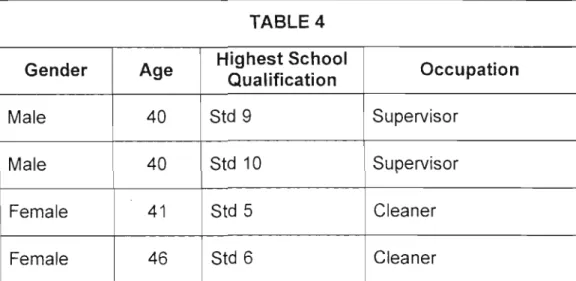
The following graph shows a comparison of the level of education of the respondents in the four sectors:-. It is interesting to note that despite the fact that English Level 4 is equivalent to Std 7 school level, respondents in all sectors had students who completed Std 7, 8, 9 or 10. Interestingly, those over 50 years, who have the lowest school education.
It is interesting to note that he attended the Technikon and qualified to apply for the course based on that. The general school-leaving standards, which are standards seven and eight, are lower in this sector than in the commercial sector, where respondents passed standard nine or ten. The minimum school qualification in the maritime sector is Std 7, which is higher than in the commercial sector where it is Std 5. It is not usual for a historically disadvantaged person who is 54 years old to have completed Std 9.
In general, it is young people who have high qualifications and when I asked the respondent, he stated that he attended night school at the age of 50.
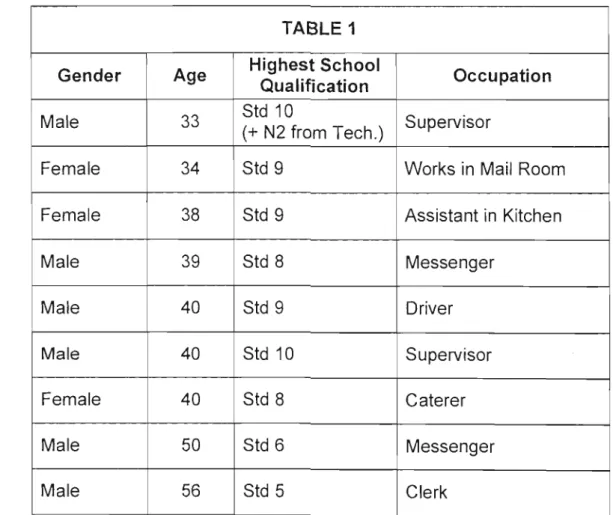
Background to Managerial Interviewees
Results
- Learner responses to where English Level 4 fits into ABET
- Manager responses to where English Level 4 fits into ABET
- Learners' motives for embarking upon English Level 4
- Managers' motives for implementing English Level 4
- Learner expectations in terms of (a) the course content and (b) benefits within the workplace
He believes that Level 4 English has improved his communication in English, which is also the aim of the course. This suspicion is supported by the fact that 52% of students expected a promotion, and 32% stated that they expected some improvement in the workplace (see Table 10). Students were asked what their expectations were regarding (a) course content and (b) workplace benefits.
Managers were asked what their expectations were in terms of (a) course content and (b) benefits within the workplace. 52% of managers expected production to increase and yet, they had little idea of the nature of the course. Students were asked whether their expectations regarding (a) course content and (b) benefits within the workplace were met.
Managers were asked whether their expectations regarding (a) course content and (b) workplace benefits were met.
General Comparisons of Learners and Managers Responses
The man who answered that he had not added any value to the company was one of the people who expected productivity to improve but had no idea about the content of the course. In comparing the responses of students and managers, it is interesting to note that after buying into the program and investing a lot of money, half of the managers think it was a waste of time and without any benefit for the company. Of course the students are the people who have wasted their time, and yet most would sign up if given the chance again, even if they were aware of the true nature of the course.
52% of students expected promotion within the workplace, while 52% of managers interviewed expected production to increase. Despite their expectations not being met, 80% of students realized that there were other benefits, not related to the workplace, but to their personal lives and therefore, they had benefited from Level 4 English and they would. course again. One of the managers stated that "a more confident and positive attitude from students can ultimately be beneficial to the company." This position is consistent with Human Resource Development, which was discussed in the literature review.
It is noteworthy that even these students, who were informed about the nature of the course, expected a connection between the content of the course and the workplace.
Analysis of Marketing Interview
The comprehension sections are very long and, in my opinion, there are only three, which are relevant to the everyday social and work life of the learners. The language taught includes puns, figurative language, irony and sarcasm and there is absolutely no connection to the workplace. However, it is possible to adapt the course content to make it more meaningful and relevant to the workplace.
The writing exercises in Lessons 21 - 24 are much more useful for students than comprehension and language, as the writing skills that are learned can be transferred to the workplace as well as being useful within a wider context. social. These students had taken the general skills they had been taught in the classroom and transferred these skills to the workplace. Looking at the course content, it is clear that there is nothing within the course that is directly job related.
Unrealistic expectations of students and managers arise from a number of sources and Chapter 5 briefly summarizes the conclusions that can be drawn about expectations.
Conclusions and Recommendations
Conclusions
The people attending the presentations should be informed about the structure of the NQF. When students are made aware of the course content, they will realize that these English skills are an important part of becoming more competent in the workplace and that they should be combined with on-the-job training to be more beneficial. This will ensure that students' expectations are not unrealistic and that they realize that English Level 4 is a small, albeit very important, part of a whole.
Course developers also have a role to play, and course content needs to be reviewed and updated to make it applicable in the workplace. The moderator should make an effort to become familiar with the nature of all students' jobs in order to tailor the lessons effectively. It is their duty to be fully aware of the content of the course, to be aware of the benefits of the training for the company as well as for the participants.
If students receive on-the-job training and begin English Level 4, many of the expectations of managers and students will be met.
Commissioned by the New South Wales Key Competences Pilot Project - Department of Education and Training Co-ordination, New South Wales. National Center for Research in Vocational Education and Center for the Study of Writing and Literacy, Berkeley, CA, University of California.
National Qualifications Framework
Proposed Unit Standards-Based GETC ABET Level 4
Unit Standards-Based GETC
Interview Questions for the HR Managers, Training Managers and Supervisors
Basis for Compilation of Workplace Skills Plan
Mokgadi Pela - Sunday Tribune, 13 October 2002
Implement job equity
Lesson Example
Then she noticed her pained expression, "Judging from the look on your face, I assume you don't approve." 34;I just want to tell you that there is no room for others on four legs, although what you can do about the young lady who comes to dinner with you on Tuesdays and Fridays is entirely your own business.” 34; But to put your mind at rest, she's not exactly young anymore, and I have no intention of adding to the number of mouths to feed."
34;In that case, - said my cat as she closed her eyes dreamily, - I will expect an immediate improvement in the variety and choice of gastronomic foods, with special emphasis on lobster and chicken. 34;It has a whole list of phone numbers that offer the services of gentleman cats from Abyssinia, Burma, Devon, Persia and Siam, and says that they reserve the right to refuse services to any queen they deem unsuitable, so to eliminate you." But from the sound of things you should take advantage of those single ladies phone numbers".
34; Now you're catty - if you'll excuse the pun I You must put out two saucers full of milk next time - one creature for you.".